The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling, and Sous Vide Cooking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Squid Sample Preparation
2.2. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis
2.3. Determination of Cooking Loss
2.4. Color Measurements
2.5. Texture Profile Analysis
2.6. Sodium Dodecyl-Sulfate Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis Analysis
2.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.9. GC-IMS Analysis of Squid Volatiles
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydration Characteristics during ST, BO, and SV Assessed by LF-NMR
3.2. Cooking Loss
3.3. Color Analysis
3.4. Texture Profile Analysis
3.5. SDS-PAGE Analysis
3.6. Fourier Transform-Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Analysis
3.7. Microstructure of SMM Treated with Different Cooking Methods
3.8. GC-IMS Analysis Results on Squid Volatiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.N.; Zeng, S.K.; Qiu, Y.; Lin, H.S.; Zhang, C.H. Effects of heating temperature and time on the surface microstructure of Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis. Fish. Mod. 2020, 47, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, H.J.; Yang, S.L.; Yang, X.Q.; Hao, S.X.; Zhang, P.; Lin, W.L. Nutritional component analysis and quality evaluation of Ryukyu squid in South China sea. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2014, 35, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonrat, T.; Soottawat, B.; Wonnop, V. Chemical composition and thermal property of cuttlefish (Sepia pharaonis) muscle. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 127–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M.M.; Muela, E.; Olleta, J.L.; Moreno, L.A.; Santaliestra-Pasías, A.M.; Mesana, M.I.; Sañudoa, C. Influence of cooking method on the nutrient composition of Spanish light lamb. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 31, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, A.F.; Alfaia, C.M.M.; Partidário, A.M.C.P.C.; Lemos, J.P.C.; Prates, J.A.M. Influence of household cooking methods on amino acids and minerals of Barrosã-PDO veal. Meat Sci. 2015, 99, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyotis, D.; Skandamis, P.N.; Juneja, V.K. Thermal inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp. in sous-vide processed marinated chicken breast. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100 Pt 1, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveena, B.M.; Khansole, P.S.; Shashi Kumar, M.; Krishnaiah, N.; Kulkarni, V.V.; Deepak, S. Effect of sous-vide processing on physicochemical, ultrastructural, microbial and sensory changes in vacuum packaged chicken sausages. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2017, 23, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldan, M.; Antequera, T.; Martin, A.; Mayoral, A.I.; Ruiz, J. Effect of different temperature-time combinations on physicochemical, microbiological, textural and structural features of sous-vide cooked lamb loins. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigioni, G.; Langman, L.; Szerman, N.; Iruruet, M.; Vaudagna, S.R. Effect of whey protein concentrate and sodium chloride concentrations on the odour profle of sous vide cooked whole-muscle beef from Argentina. Meat Sci. 2008, 79, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, P.; Nieto, G.; Garrido, M.D.; Banon, S. Microbial, physical-chemical and sensory spoilage during the refrigerated storage of cooked pork loin processed by the sous vide method. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pulgar, J.S.; Gazquez, A.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Physico-chemical, textural and structural characteristics of sous-vide cooked pork cheeks as affected by vacuum, cooking temperature, and cooking time. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głuchowski, A.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Wasiak-Zys, G.; Nowak, D. Effect of Various Cooking Methods on Technological and Sensory Quality of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Foods 2019, 8, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasinska, E.; Rutkowska, J.; Czarniecka-Skubina, E.; Tambor, K. Effects of cooking methods on changes in fatty acids contents, lipid oxidation and volatile compounds of rabbit meat. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 110, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropotovaa, J.; Mozuraityteb, R.; Standalb, I.B.; Rustad, T. Assessment of lipid oxidation in Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) subjected to different antioxidant and sous-vide cooking treatments by conventional and fluorescence microscopy methods. Food Control 2019, 104, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuño, J.; Mateo, L.; Rodríguez-Estrada, M.T.; Bañón, S. Effects of sous vide vs grilling methods on lamb meat colour and lipid stability during cooking and heated display. Meat Sci. 2020, 171, 108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.T.; Pereira, J.; Zhou, L.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Tian, X.N.; Zhang, W.W. Insight into the Effects of Sous Vide on Cathepsin B and L Activities, Protein Degradation and the Ultrastructure of Beef. Foods 2020, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.; Ertbjerg, P.; Løje, H.; Risbo, J.; van den Berg, F.W.J.; Christensen, M. Relationship between meat toughness and properties of connective tissue from cows and young bulls heat treated at low temperatures for prolonged times. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, M.C.; Díaz, P.; Linares, M.B.; Teruel, M.R.; Garrido, M.D. Quality characteristics of sous vide ready to eat seabream processed by high pressure. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Alvarez, O.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Gómez-Guillén, M.D.C.; Montero, P. The effect of several cooking treatments on subsequent chilled storage of thawed deep water pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris) treated with different melanosis-inhibiting formulas. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.B.; Kumari, N.; Senapati, S.R.; Lekshmi, M.; Nagalakshmi, K.; Balange, A.K.; Chouksey, M.K.; Venkateshwarlu, G.; Xavier, K.M. Sous vide processed ready-to-cook seerfish steaks: Process optimization by response surface methodology and its quality evaluation. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongiorno, T.; Tulli, F.; Comi, G.; Sensidoni, A.; Andyanto, D.; Iacumin, L. Sous vide cook-chill mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis): Evaluation of chemical, microbiological and sensory quality during chilled storage (3 °C). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 91, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, K.; Kubota, K.; Aishima, T. Investigating Influence of pH and Parts on Sensory Characteristics and Volatile Components in Boiled Squid Using Experimental Designs. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.K.; Yan, H.; Manoli, T.; Mo, H.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, H. Changes in the volatile components of squid (illex argentinus) for different cooking methods via headspace–gas chromatography–ion mobility spectrometry. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratini, G.; Lois, S.; Pazos, M.; Parisi, G.; Medina, I. Volatile profile of Atlantic shellfish species by HS-SPME GC/MS. Food Res. Int. 2012, 48, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Xue, Y.; Xue, C.H. Effects of konjac glucomannan on heat-induced changes of physicochemical and structural properties of surimi gels. Food Res. Int. 2016, 83, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, S.Q.; Lin, R.; Cheng, S.S.; Yuan, B.; Wang, Z.X.; Tan, M.Q. Effect of Different Cooking Methods on Proton Dynamics and Physicochemical Attributes in Spanish Mackerel Assessed by Low-Field NMR. Foods. 2020, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nyaisaba, B.M.; Miao, W.; Hatab, S.; Siloam, A.; Chen, M.; Deng, S. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on squid proteases and gel properties of protein concentrate from squid (Argentinus ilex) mantle. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.H.; Cao, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Yao, H. The mechanistic effect of bromelain and papain on tenderization in jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) muscle. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 108991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.D.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Xue, C.H. Effects of Microwave Radiation and Water Bath Heating on the Physicochemical Properties of Actomyosin from Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) during Setting. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.S.; Wang, X.H.; Yang, H.M.; Lin, R.; Wang, H.T.; Tan, M.Q. Characterization of moisture migration of beef during refrigeration storage by low-field NMR and its relationship to beef quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, C.K.; Allen, P.; Duggan, E.; Arimi, J.M.; Casey, E.; Duane, G.; Lyng, J.G. The effect of salt and fibre direction on water dynamics, distribution and mobility in pork muscle: A low field NMR study. Meat Sci. 2013, 95, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.B.; Liu, D.Y.; Zhou, G.H.; Xu, X.L.; Qi, J.; Shi, P.L.; Xia, T.L. Meat quality and cooking attributes of thawed pork with different low field NMR T 21. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.K.; Zang, X.; Kamal, T.; Bi, J.R.; Cong, S.; Zhu, B.W.; Tan, M.Q. Real-time detection of water dynamics in abalone (Haliotis discus hannai Ino) during drying and rehydration processes assessed by LF-NMR and MRI. Dry Technol. 2018, 36, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aursand, I.G.; Veliyulin, E.; Böcker, U.; Ofstad, R.; Rustad, T.; Erikson, U. Water and salt distribution in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) studied by low-field 1H NMR, 1H and 23Na MRI and light microscopy: Effects of raw material quality and brine salting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 57, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Xu, W.; Huang, L.; Song, Y.; Zhu, B.W.; Tan, M.Q. Water dynamics of turbot flesh during frying, boiling, and stewing processes and its relationship with color and texture properties: Low-field NMR and MRI studies. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pathare, P.B.; Roskilly, A.P. Quality and energy evaluation in meat cooking. Food Eng. Rev. 2016, 8, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sikes, A.L.; Warner, R. Application of high hydrostatic pressure for meat tenderization. Innov. Food Process. Technol. 2016, 259–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modzelewska-Kapituła, M.; Pietrzak-Fiećko, R.; Tkacz, K.; Draszanowska, A.; Więk, A. Influence of sous vide and steam cooking on mineral contents, fatty acid composition and tenderness of semimembranosus muscle from Holstein Friesian bulls. Meat Sci. 2019, 157, 107877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroeira, C.N.; de Almeida Torres Filho, R.; Fontes, P.R.; de Lemos Souza Ramos, A.; de Miranda Gomide, L.A.; Ladeira, M.M.; Ramos, E.M. Effect of freezing prior to aging on myoglobin redox forms and CIE color of beef from Nellore and Aberdeen Angus cattle. Meat Sci. 2017, 125, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zhong, K.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effects of different freezing treatments on physicochemical responses and microbial characteristics of Japanese sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicas) fillets during refrigerated storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Zhu, Y.P.; Han, M.Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, R.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Classification of chicken muscle with different freeze–thaw cycles using impedance and physicochemical properties. J. Food Eng. 2017, 196, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, F.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Changes in meat quality of ovine longissimus dorsi muscle in response to repeated freeze and thaw. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palka, K. The influence of post-mortem ageing and roasting on the microstructure, texture and collagen solubility of bovine semitendinosus muscle. Meat Sci. 2003, 64, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.T.; Kaido, T.; Kasukawa, M.; Zhong, C.; Sun, L.C.; Okazaki, E.; Osako, K. Mechanism study of high browning degree of mantle muscle meat from Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus during air-drying. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas-Lopez, J.L.; Haard, N.F. Cysteine protease activity in Jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) hepatopancreas extracts. J. Food Biochem. 2005, 29, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas-Lopez, J.L.; Haard, N.F. Identification of a cysteine proteinase from Jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) hepatopancreas as cathepsin L. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Umezawa, E.; Rui, D.; Konno, K. Three types of proteinase in squid (Todarodes pacificus) hepatopancreas as studied by using carp myofibrils as substrate. Fish. Sci. 2010, 76, 356–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ertbjerg, P.; Mielche, M.M.; Larsen, L.M.; Miller, A.J. Relationship between proteolytic changes and tenderness in prerigor lactic acid marinated beef. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, J.L.; Zheng, J.Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.L. Effect of salt content on the denaturation of pike eel (Muraenesox cinereus Forsskal, 1775) actomyosin. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 767–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Mantsch, H.H. Halogenated alcohols as solvents for proteins: FTIR spectroscopic studies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1118, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.K.; Gill, T.A.; Paulson, A.T. The dynamics of thermal denaturation of fish myosins. Food Res. Int. 1992, 25, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Luo, Y.L.; Wang, Y.G.; Zhao, Y.Y. Effect of different drying methods on the myosin structure, amino acid composition, protein digestibility and volatile profile of squid fillets. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
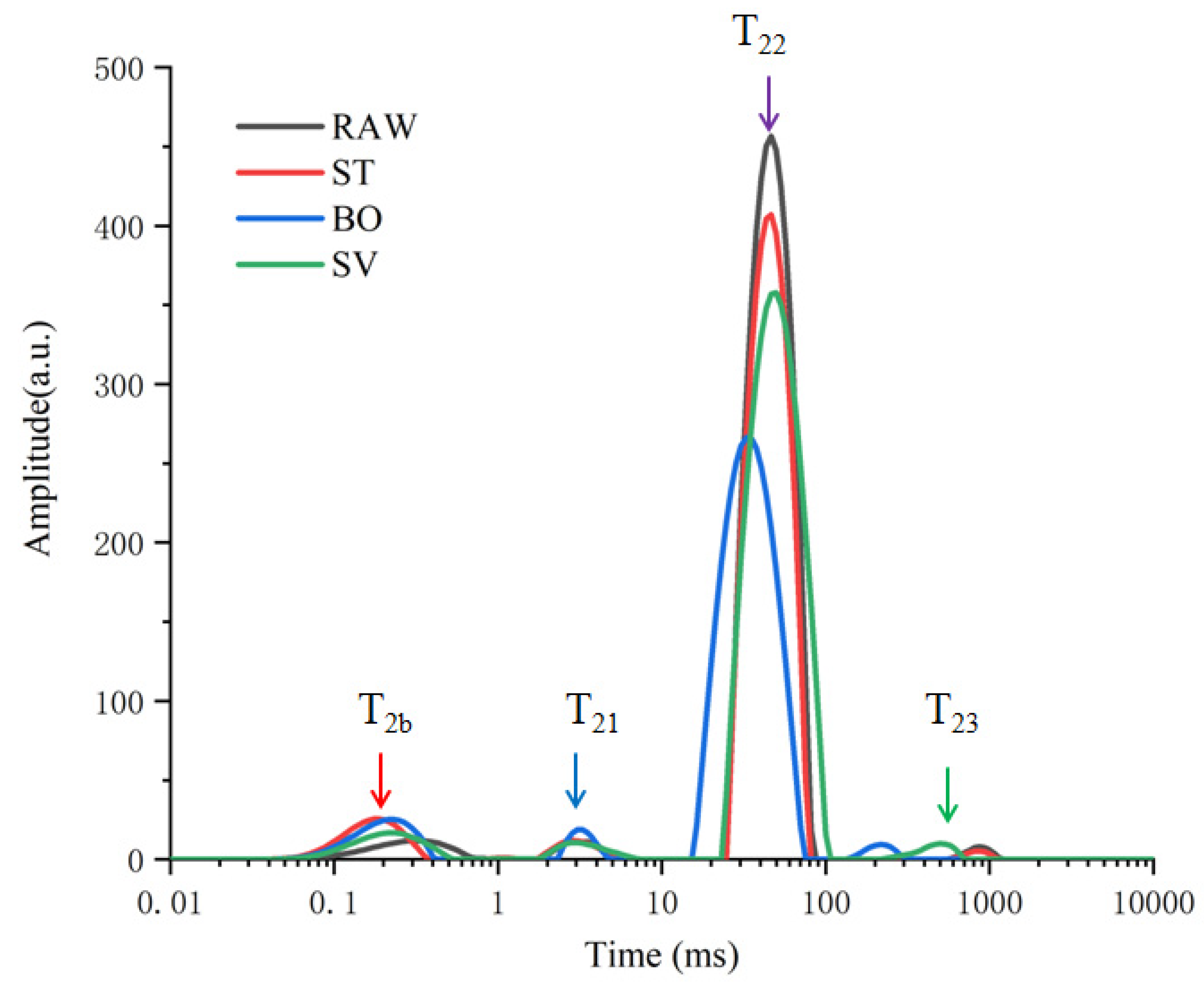

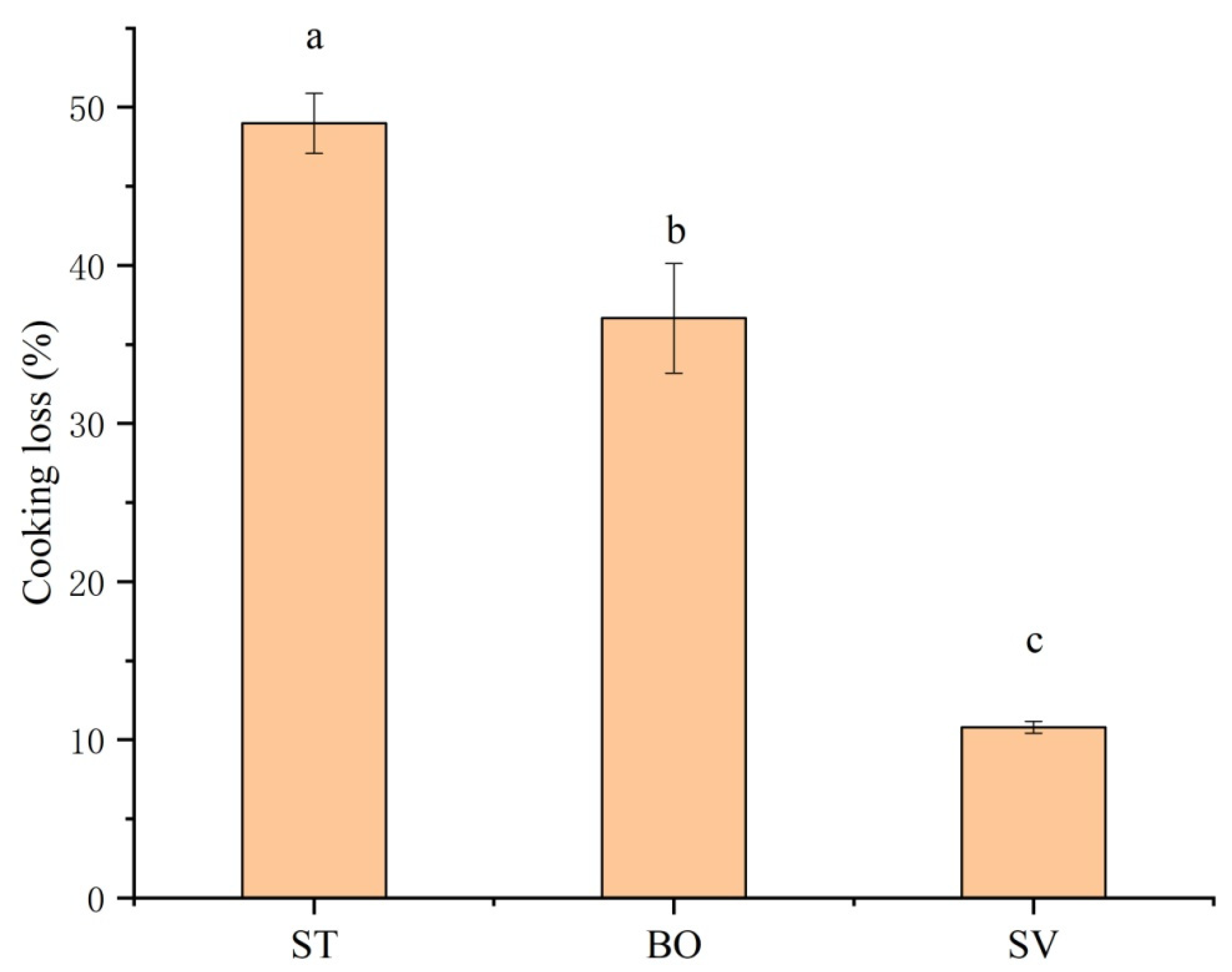
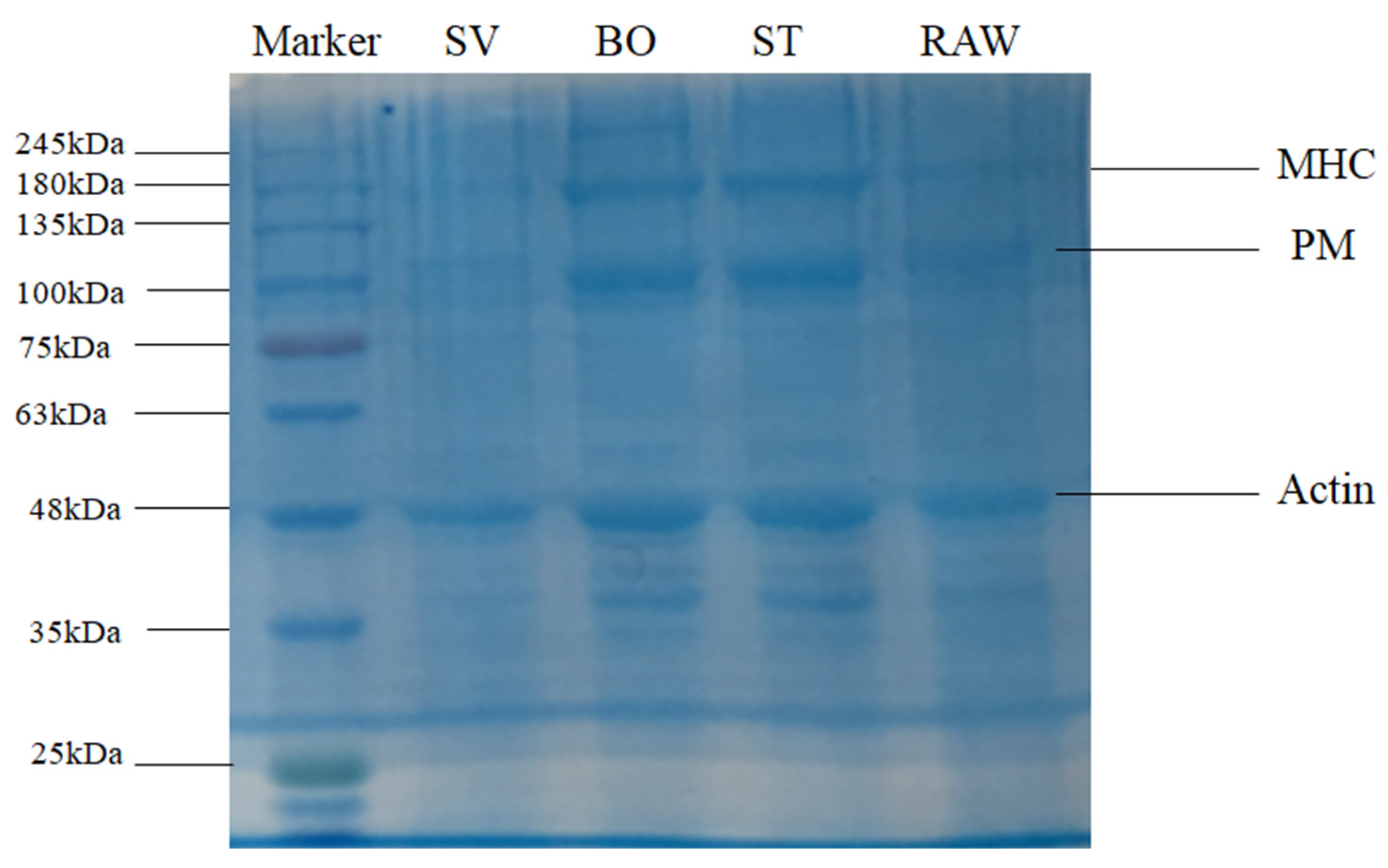



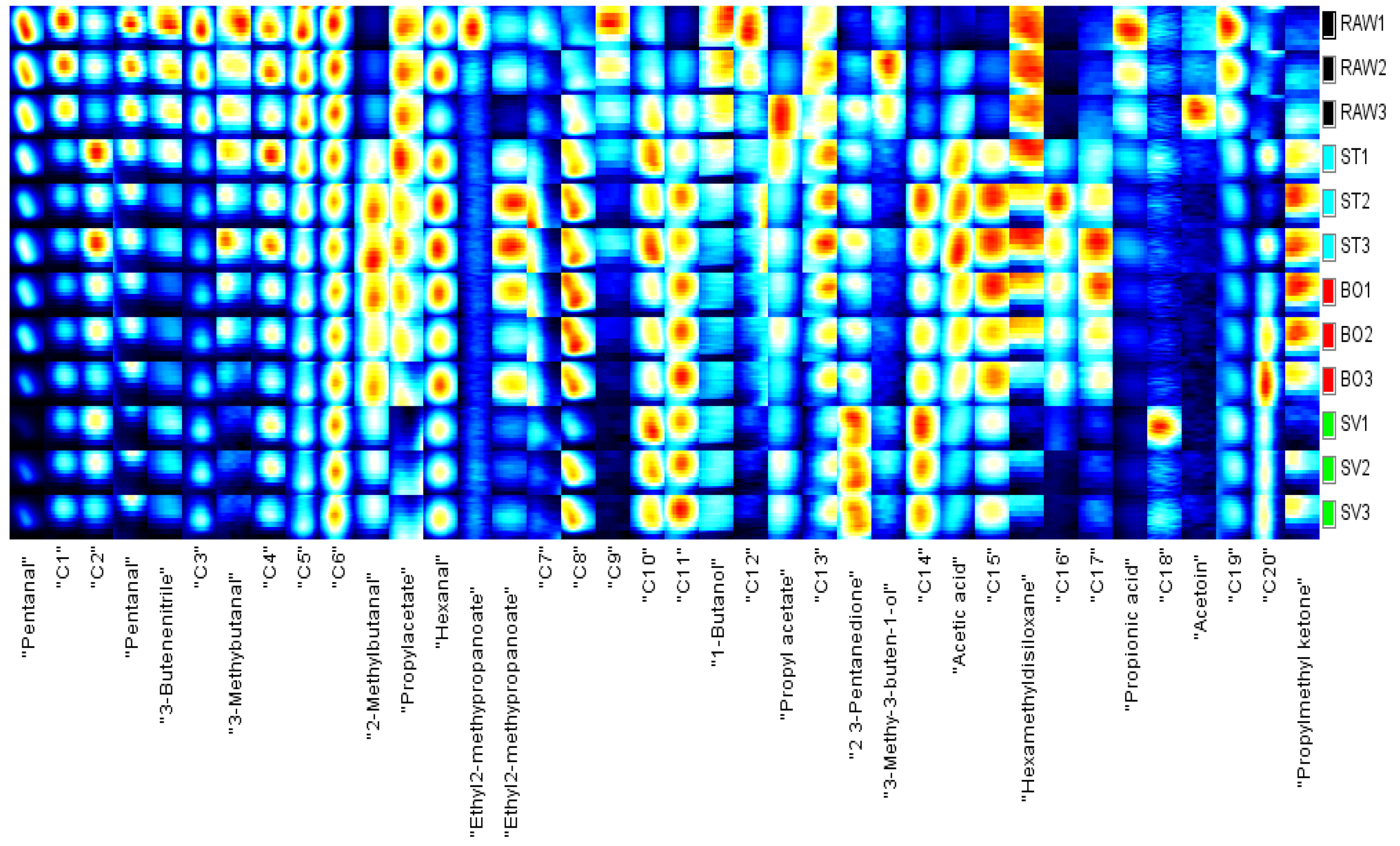

| Treatment | A2b | A21 | A22 | A23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | 279.36 ± 42.09 a | 11.34 ± 12.06 a | 4899.75 ± 158.87 a | 46.66 ± 3.51 a |
| ST | 362.41 ± 55.72 b | 139.25 ± 13.83 b | 4074.15 ± 333.28 b | 31. 35 ± 4.64 a |
| BO | 371.65 ± 14.19 b | 120.53 ± 1.33 a | 3697.65 ± 161.04 b | 52.69 ± 22.00 a |
| SV | 248.95 ± 40.67 a | 131.36 ± 24.36 a | 4507.95 ± 546.77 a | 47.95 ± 24.42 a |
| Treatment | L* | a* | b* | Whiteness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | 61.09 ± 1.09 a | 6.16 ± 2.19 b | 5.01 ± 0.99 c | 60.24 ± 1.50 a |
| ST | 68.22 ± 4.28 a | 7.95 ± 4.17 a | 14.64 ± 1.80 b | 63.86 ± 4.12 a |
| BO | 61.64 ± 5.27 a | 12.53 ± 2.91 a | 18.35 ± 1.79 a | 55.56 ± 5.36 a |
| SV | 61.61 ± 3.30 a | 3.23 ± 0.24 b | 4.10 ± 0.51 c | 61.26 ± 3.23 a |
| Treatment | Hardness (N) | Cohesiveness | Springiness | Gumminess | Chewiness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAW | 16.60 ± 1.07 b | 0.37 ± 0.04 b | 1.31 ± 0.20 b | 6.09 ± 0.87 c | 8.09 ± 2.21 c |
| ST | 19.15 ± 2.02 b | 0.63 ± 0.03 a | 2.09 ± 0.31 a | 12.13 ± 1.23 b | 25.62 ± 5.86 b |
| BO | 25.69 ± 1.45 a | 0.66 ± 0.02 a | 2.21 ± 0.07 a | 17.09 ± 1.32 a | 37.78 ± 2.84 a |
| SV | 10.81 ± 2.35 c | 0.33 ± 0.03 b | 1.11 ± 0.16 b | 3.35 ± 0.40 d | 3.97 ± 0.84 c |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, H.; Li, N.; Yan, L.; Xue, Y. The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling, and Sous Vide Cooking. Foods 2021, 10, 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071646
Xiao H, Li N, Yan L, Xue Y. The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling, and Sous Vide Cooking. Foods. 2021; 10(7):1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071646
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Hong, Nannan Li, Longtao Yan, and Yong Xue. 2021. "The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling, and Sous Vide Cooking" Foods 10, no. 7: 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071646
APA StyleXiao, H., Li, N., Yan, L., & Xue, Y. (2021). The Hydration Characteristics, Structural Properties and Volatile Profile of Squid (Symplectoteuthis oualaniensis) Mantle Muscle: Impacts of Steaming, Boiling, and Sous Vide Cooking. Foods, 10(7), 1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10071646





