SLE Single-Step Purification and HPLC Isolation Method for Sterols and Triterpenic Dialcohols Analysis from Olive Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Solutions
2.2. Samples
2.3. Instrumentation
2.3.1. HPLC Isolation
2.3.2. Gas Chromatography-Flame Ionization Detector (GC-FID) Analysis
2.3.3. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
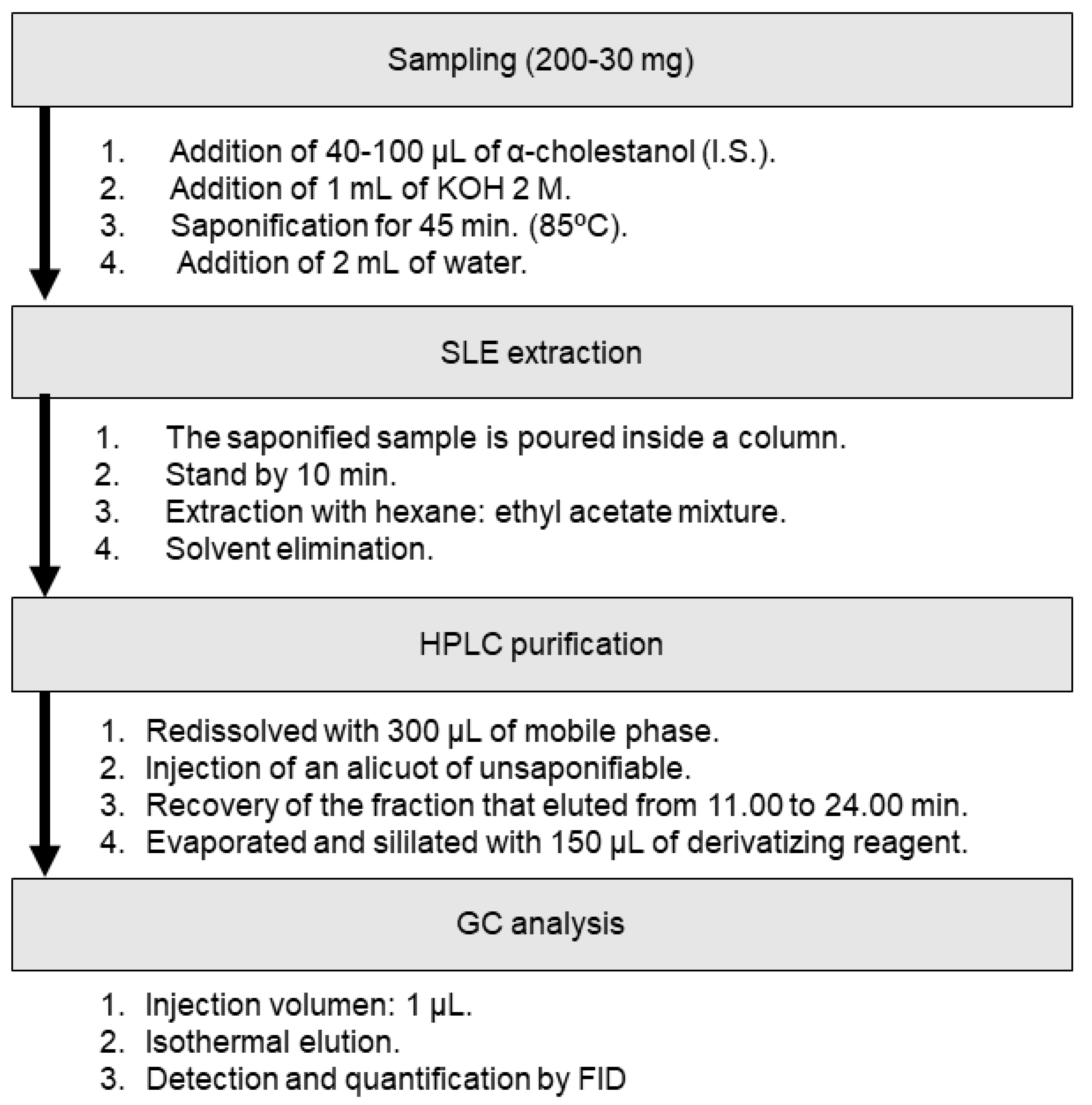
2.4. Sample Treatment
2.4.1. IOC and EU Methods (Liquid–Liquid Extraction Method)
2.4.2. Proposed Method (Supported Liquid Extraction Method)
2.5. GC-Data Analysis
2.6. ATR-FTIR Spectra
2.7. Recovery and Precision
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Saponification, SLE and HPLC Isolation
3.2. Gas Chromatography Determination of Sterols and Dialcoholic Triterpenes
3.3. Validation of the Method
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- León-Camacho, M.; Morales, M.T. Chapter 7: Gas and Liquid Chromatography: Methodology Applied to Olive Oil. In Handbook of Olive Oil, Analysis and Properties, 1st ed.; Aparicio, R., Harwood, J., Eds.; Aspen Publishers: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2001; pp. 163–217. [Google Scholar]
- Azadmard-Damirchi, S. Review of the use of phytosterols as a detection tool for adulteration of olive oil with hazelnut oil. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, W.; Dionisi, F.; Hischenhuber, C.; Engel, K. Authenticity assessment of fats and oils. Food Rev. Int. 2001, 17, 249–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieffenbacher, A.; Pocklington, W.D. (Eds.) IUPAC. 2.401: Determination of the Unsaponifiable Matter in Standard Methods for the Analysis of Oil, Fats and Derivatives, 7th ed; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- International Olive Council. Determination of the Sterol Composition and Content and Alcoholic Compounds by Capillary Gas Chromatography; COI/T.20/ Doc. No 26/Rev.; International Olive Council: Madrid, Spain, 5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EEC) No 2568. Of 11 July 2011. On the Characteristics of Olive Oil and Olive-Residue Oil and on the Relevant Methods of Analysis (Consolidated Text). Off. J. Eur. 1991, L 248, 35–46.
- Regulation (EU) No 1604. Of 27 September 2019. Amending Regulation (EEC) No 2568/91 on the characteristics of olive oil and olive-residue oil and on the relevant methods of analysis. Off. J. Eur. 2019, L 250, 36–48.
- International Olive Council. Trade Standard Applying to Olive Oils and Olive Pomace Oils; COI/T.15/NC No 3/Rev.; International Olive Council: Madrid, Spain, 16 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dieffenbacher, A.; Pocklington, W.D. (Eds.) IUPAC. 2.403: Identification and Determination of Sterols by Gas Liquid Chromatography in Standard Methods for the Analysis of Oil, Fats and Derivatives, 7th ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Dieffenbacher, A.; Pocklington, W.D. (Eds.) IUPAC. 2.404: Determination of the Total Sterols Content in Standard Methods for the Analysis of Oil, Fats and Derivatives, 7th ed.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Toivo, J.; Piiroren, V.; Kalo, P.; Varo, P. Gas chromatographic determination of major sterols in edible oils and fats using solid-phase extraction in sample preparation. Chromatographia 1998, 48, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadmard-Damirchi, S.; Dutta, P.C. Novel solid-phase extraction method to separate 4-desmethyl-, 4-monomethyl-, and 4,4′-dimethylsterols in vegetable oils. J. Chrom. A 2006, 1108, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.C. Rapid isolation of the sterol fraction in edible oils using silica cartridge. J. AOAC Int. 1992, 75, 1120–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Señoráns, F.J.; Tabera, I.; Herraiz, M. Rapid separation of free sterols in edible oils by on-line coupled reversed phase liquid chromatography-gas chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 3189–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewington, C.R.; Caress, E.A.; Schwartz, D.P. Isolation and identification of new milk fat. J. Lipid Res. 1979, 11, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelio, M.; Rizzo, R.; Varazini, F. Determination of sterols, erythrodiol, uvaol and alkanols in olive oils using combined solid-phase extraction, high-performance liquid chromatographic and high-resolution gas chromatographic techniques. J. Chrom. A. 1992, 606, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapa, E.; Brusius, M.; Krepich, S.; Aqeel, Z.; Detsch, J. Determination of Sterols in Olive Oil Using Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE), Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) and GC-FID, (TN-1004). 2017. Available online: https://www.phenomenex.com/ViewDocument?id=determination+of+sterols+in+olive+oil&fsr=1 (accessed on 29 June 2018).
- Grob, K. Development of the transfer techniques for on-line high-performance liquid chromatography-capillary gas chromatography. J. Chrom. A 1995, 703, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreuls, J.J.; de Jong, G.J.; Ghijsen, R.T.; Th Brinkman, U.A. Liquid chromatography coupled on-line with gas chromatography: State of the art. J. AOAC. Int. 1994, 77, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Señoráns, F.J.; Herraiz, M.; Tabera, J. On-line reversed-phase liquid chromatography-capillary gas chromatography using a programmed temperature vaporizer as interface. J. Sep. Sci. 1995, 18, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Señoráns, F.J.; Reglero, G.; Herraiz, M. Use of a Programmed Temperature Injector for On-Line Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography-Capillary Gas Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 1995, 33, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homberg, E. Vitamin D-Bestimmung in Lebertram. Fat Sci. Tech. 1993, 95, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hadorn, H.; Zürcher, K. Der Scheidetrichter, ein mangelhaftes Gerät im analytischen Labor. Gordian 1973, 73, 198–201. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, C.R.; Zhang, B.; Fantauzzi, P.; Hocker, M.; Yager, K.M. Libraries of N-alkylaminoheterocycles from nucleophilic aromatic substitution with purification by solid supported liquid extraction. Tetrahedron 1998, 54, 4097–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathison, B.; Holstege, D. A Rapid Method to Determine Sterol, Erthyrodiol, and Uvaol Concentrations in Olive Oil. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4506–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tena, N.; Aparicio, R.; García-González, D.L. Thermal Deterioration of Virgin Olive Oil Monitored by ATR-FTIR Analysis of Trans Content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9997–10003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Ellison, S.L.R.; Wood, R. Harmonized guidelines for singlelaboratory validation of methods of analysis. Pure Appl. Chem. 2002, 74, 835–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cert, A.; Moreda, W.; García-Morena, J. Determinación de esteroles y dialcoholes triterpénicos en aceite de oliva mediante separación de la fracción por cromatografía líquida de alta eficacia y análisis por cromatografía de gases. Estandarización del método analítico. Grasas Aceites 1997, 48, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- León-Camacho, M.; Cert Ventulá, A. Recomendaciones para la aplicación de algunos métodos analíticos incluidos en el reglamento CEE 2568/91 relativo a las características de los aceites de oliva y de orujo de oliva. Grasas Aceites 1994, 45, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena, N.; Aparicio-Ruiz, R.; García-González, D.L. Time Course Analysis of Fractionated Thermoxidized Virgin Olive Oil by FTIR Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 3212–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission Decision No 657. Of August 12, 2002, implementing Council Directive 96/23/EC concerning the performance of analytical methods and the interpretation of results. Off. J. Eur. 2002, L 221, 8–36.




| Steeps | L–L Method | SLE Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Official Methods | Commercial [17] | Proposed Method | |
| Sample amount | 5 g | 0.2–0.4 g | 0.3 g |
| Water addition | 100 mL | 13.5 mL | 2 mL |
| Extraction | 3 × 100 mL | 3 × 15 mL | 45 mL |
| Washed | 3 × 50 mL | no | no |
| Dryed | 30–50 g Na2SO4 | SPE Na2SO4 | no |
| FFAs removal | KOH in TLC Si | KOH in SPE Si | no |
| Purification | TLC or HPLC | no | HPLC |
| Steeps | L–L Method | SLE Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Official Methods | Commercial [17] | Proposed Method | |
| Sampling and Internal standard addition | 7:00 | 1:20 | 1:20 |
| KOH 2M training and addition | 3:11 | 1:00 | 1:00 |
| Saponification | 60:00 | 50:00 | 45:00 |
| Water addition and cooling | 30:00 | 15:00 | 10:00 |
| Extraction with organic solvent | 15:00 | 5:00 | 5:00 |
| Washed | 20:36 | no | no |
| Dryed | 20:36 | 15:00 SPE Na2SO4 | no |
| Free Fatty Acids removal | 17:25 | 15:00 SPE Si, KOH | no |
| Purified + derivatization | 50:00 | 30:00 | 30:00 |
| GC Analysis | 30:00 | 70:00 | 30:00 |
| TOTAL time | 253:48 | 202:20 | 122:20 |
| Commercial [17] | Proposed Method | |
|---|---|---|
| Volume (mL) | 75 | 25 |
| Stuffing amount (g) | 19.0 | 5.0 |
| Length (cm) | 14.0 | 8.5 |
| Sorbent | Unknown | diatomaceous earth |
| VOO | OPO | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | OM * | SLE | OM * | |||||||||
| Means ** N = 6 | SD | RSD (%) | Means ** N = 6 | SD | RSD (%) | Means ** N = 6 | SD | RSD (%) | Means ** N = 6 | SD | RSD (%) | |
| Cholesterol | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 0.20 | 0.03 | 15.00 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 20.36 |
| Campesterol | 2.83 | 0.07 | 2.47 | 2.81 | 0.04 | 1.42 | 2.63 | 0.03 | 1.07 | 2.56 | 0.01 | 0.50 |
| Stigmasterol | 0.74 | 0.07 | 9.46 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 7.35 | 0.89 | 0.06 | 7.01 | 0.95 | 0.02 | 1.61 |
| Δ5,23-stigmastadienol | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 0.55 | 0.02 | 3.93 | 0.51 | 0.00 | 0.88 |
| Clerosterol | 1.04 | 0.05 | 4.81 | 1.06 | 0.1 | 9.43 | 0.86 | 0.02 | 1.89 | 0.86 | 0.02 | 2.42 |
| β-sitosterol | 83.95 | 1.07 | 1.27 | 83.96 | 1.75 | 2.08 | 74.75 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 73.85 | 0.45 | 0.60 |
| Sitostanol | 0.69 | 0.03 | 4.35 | 0.78 | 0.04 | 5.13 | 1.45 | 0.11 | 7.38 | 1.44 | 0.06 | 4.23 |
| Δ5-avenasterol | 7.37 | 0.18 | 2.44 | 7.34 | 0.18 | 2.45 | 1.48 | 0.03 | 2.27 | 1.49 | 0.12 | 7.87 |
| Δ5,24-stigmastadienol | 0.70 | 0.04 | 5.71 | 0.61 | 0.07 | 11.48 | 1.31 | 0.04 | 2.81 | 1.46 | 0.02 | 1.71 |
| Δ7-stigmastenol | 0.42 | 0.04 | 9.52 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 10.53 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 8.57 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 12.90 |
| Δ7-avenasterol | 0.74 | 0.07 | 9.46 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 10.61 | 0.28 | 0.01 | 3.57 | 0.35 | 0.01 | 2.13 |
| Erythrodiol + Uvaol *** | 1.52 | 0.06 | 3.95 | 1.72 | 0.04 | 2.33 | 15.25 | 0.29 | 1.88 | 16.07 | 0.56 | 3.51 |
| Total sterols (ppm) | 1231.38 | 30.21 | 2.45 | 1224.19 | 30.73 | 2.51 | 5529.87 | 309.19 | 5.59 | 5183.04 | 57.45 | 1.11 |
| VOO | OPO | |
|---|---|---|
| Cholesterol | nd | 133.33 |
| Campesterol | 100.71 | 102.73 |
| Stigmasterol | 108.82 | 93.68 |
| Δ5,23-stigmastadienol | nd | 107.84 |
| Clerosterol | 98.11 | 100.00 |
| β-sitosterol | 99.99 | 101.22 |
| Sitostanol | 88.46 | 100.69 |
| Δ5-avenasterol | 100.41 | 99.33 |
| Δ5,24-stigmastadienol | 114.75 | 89.73 |
| Δ7-stigmastenol | 110.53 | 112.90 |
| Δ7-avenasterol | 112.12 | 80.00 |
| Erytrodiol + Uvaol | 88.37 | 94.90 |
| Total sterols (ppm) | 100.59 | 106.69 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
León-Camacho, M.; del Carmen Pérez-Camino, M. SLE Single-Step Purification and HPLC Isolation Method for Sterols and Triterpenic Dialcohols Analysis from Olive Oil. Foods 2021, 10, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092019
León-Camacho M, del Carmen Pérez-Camino M. SLE Single-Step Purification and HPLC Isolation Method for Sterols and Triterpenic Dialcohols Analysis from Olive Oil. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092019
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeón-Camacho, Manuel, and María del Carmen Pérez-Camino. 2021. "SLE Single-Step Purification and HPLC Isolation Method for Sterols and Triterpenic Dialcohols Analysis from Olive Oil" Foods 10, no. 9: 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092019
APA StyleLeón-Camacho, M., & del Carmen Pérez-Camino, M. (2021). SLE Single-Step Purification and HPLC Isolation Method for Sterols and Triterpenic Dialcohols Analysis from Olive Oil. Foods, 10(9), 2019. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092019





