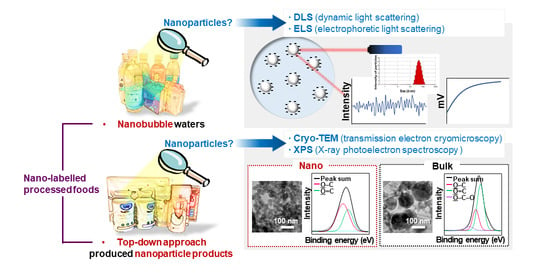
Characterization and Determination of Nanoparticles in Commercial Processed Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering and Electrophoretic Light Scattering Analysis
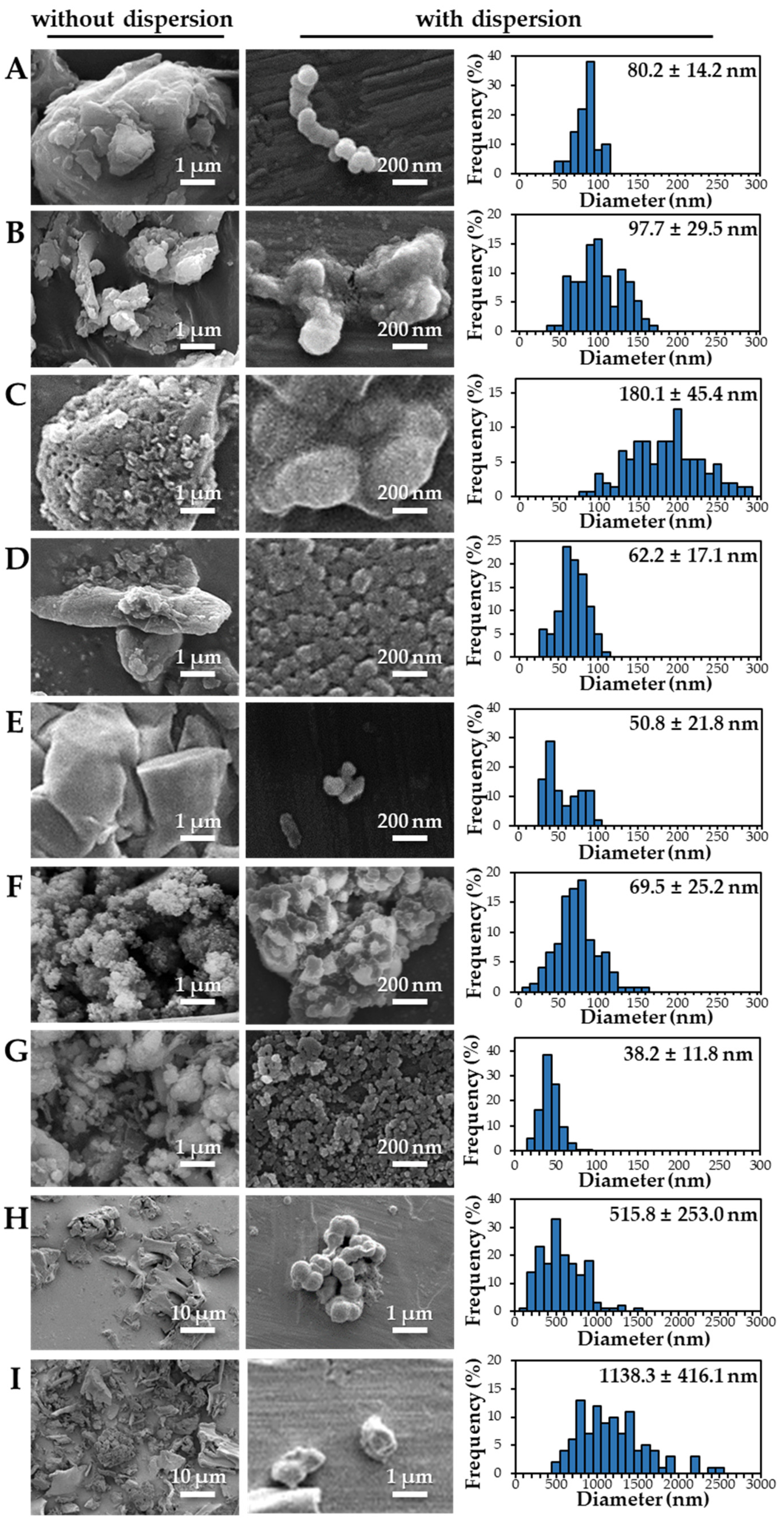
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopic Analysis
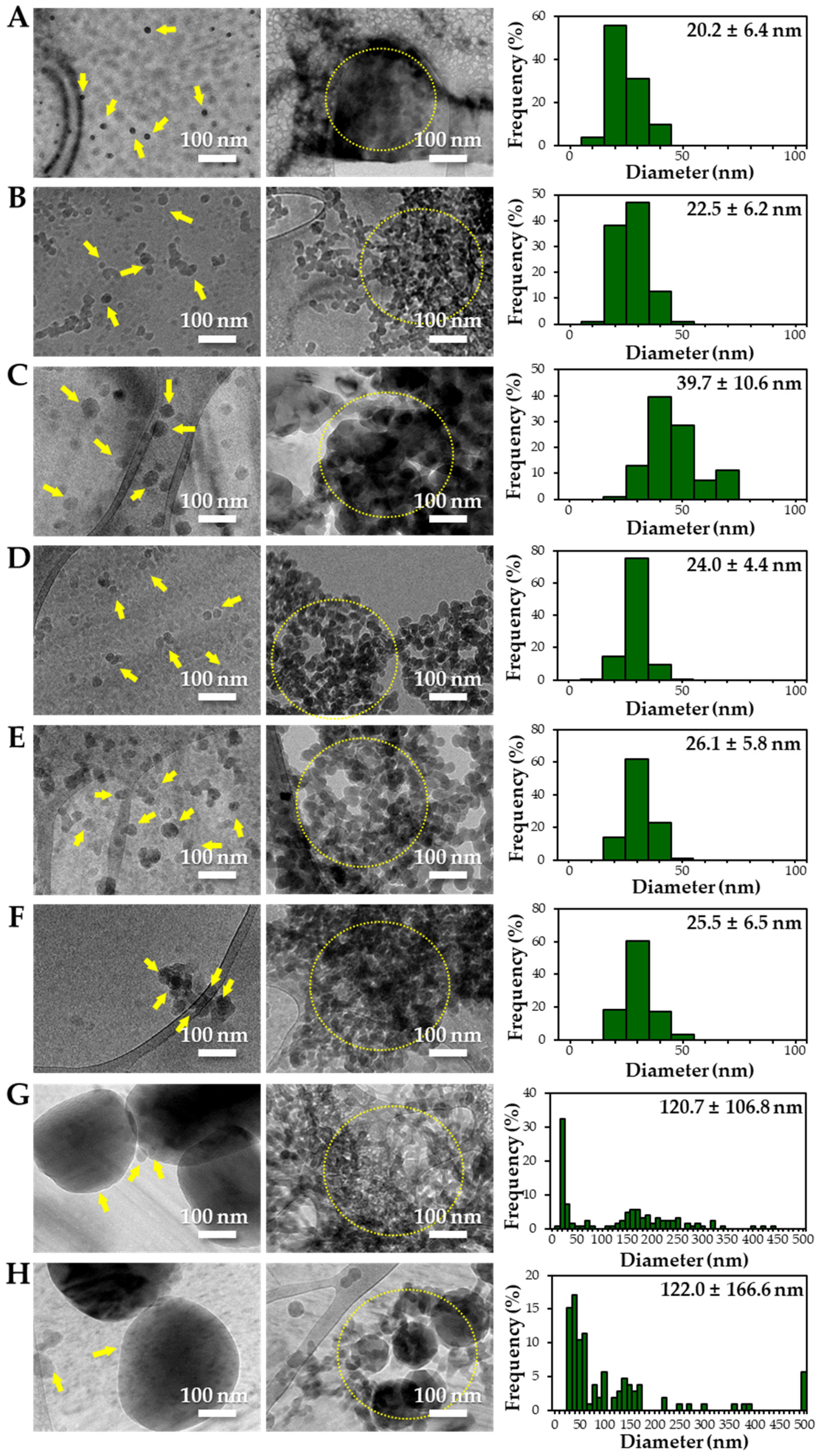
2.5. Cryogenic Transmission Electron Microscopic Analysis
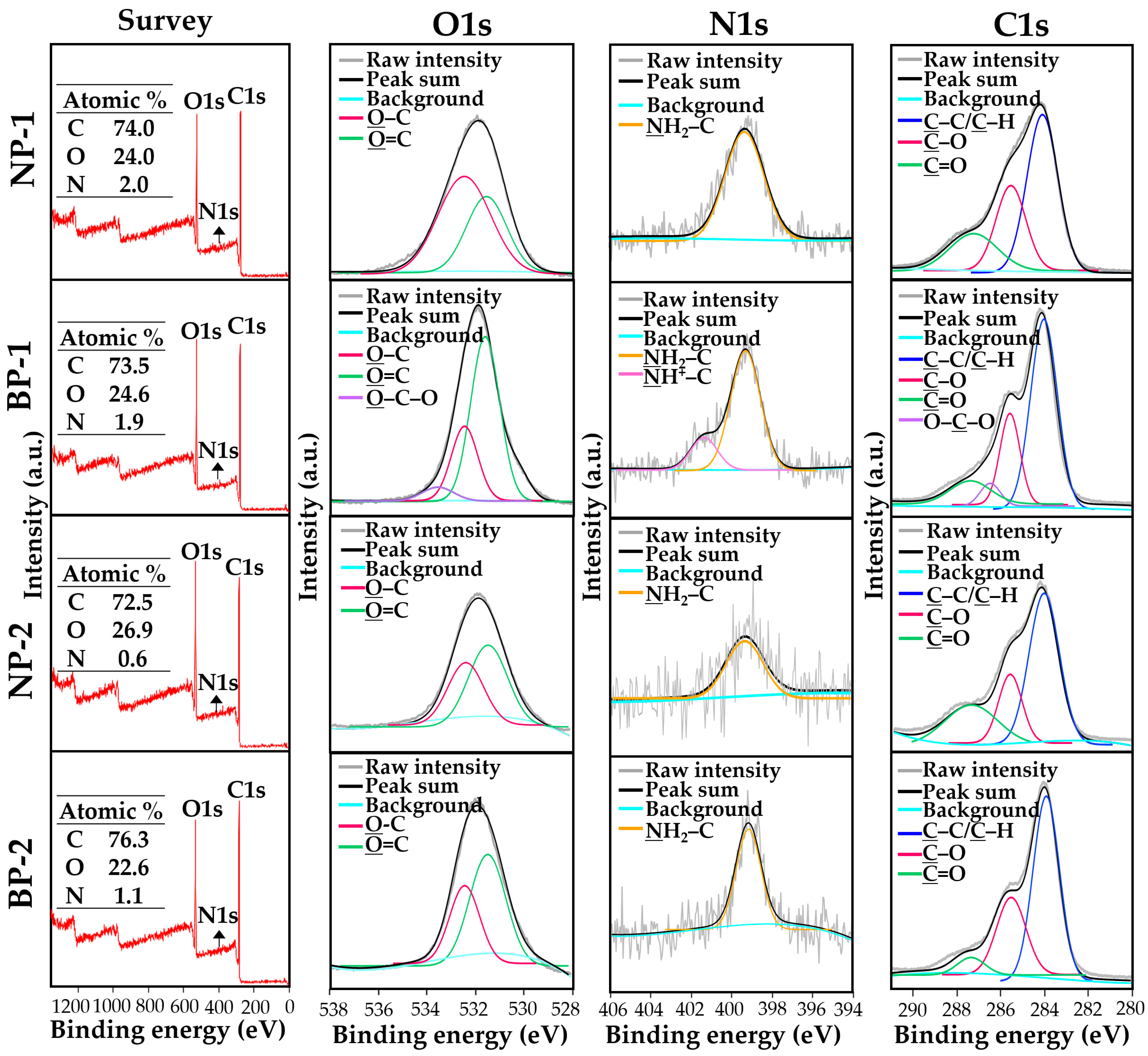
2.6. Surface Chemical Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nanobubbles in NBWs
3.2. Characterization of Powdered TD-NP Foods
3.3. Constituent Particle Sizes of Powdered TD-NP Foods
3.4. Surface Chemical Characterization of Powdered TD-NP Foods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Deng, H.; Hwang, H.M. The current application of nanotechnology in food and agriculture. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClements, D.J.; Xiao, H. Is nano safe in foods? Establishing the factors impacting the gastrointestinal fate and toxicity of organic and inorganic food-grade nanoparticles. NPJ Sci. Food 2017, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, B.S. Food nanotechnology—An overview. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2010, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, E. Bioavailability of nanoparticles in nutrient and nutraceutical delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, I.C.; Ishola, O.S. Appropriation of nanoparticle as food additive: A possibility. EJARBLS 2020, 8, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission recommendation of 18 October 2011 on the definition of nanomaterial (2011/696/EU). Off. J. Eur. Union 2011, L375, 38–40. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, H.; Yeo, S.K.; Wirz, C.D.; Scheufele, D.A.; Brossard, D.; Xenos, M.A.; Corley, E.A. Are attitudes toward labeling nano products linked to attitudes toward GMO? Exploring a potential ‘spillover’ effect for attitudes toward controversial technologies. J. Responsible Innov. 2019, 6, 50–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenta, V.; Aschberger, K.; Arena, M.; Bouwmeester, H.; Moniz, F.B.; Brandhoff, P.; Gottardo, S.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Mech, A.; Pesudo, L.Q.; et al. Regulatory aspects of nanotechnology in the agri/feed/food sector in EU and non-EU countries. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2015, 73, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuah, A.S.F.; Leong, A.D.; Cummings, C.L.; Ho, S.S. Label it or ban it? Public perceptions of nano-food labels and propositions for banning nano-food applications. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameta, S.K.; Rai, A.K.; Hiran, D.; Ameta, R.; Ameta, S.C. Use of nanomaterials in food science. In Biogenic Nano-Particles and their Use in Agro-Ecosystems, 1st ed.; Ghorbanpour, M., Bhargava, P., Varma, A., Choudhary, D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 457–488. [Google Scholar]
- Rashidi, L.; Khosravi-Darani, K. The applications of nanotechnology in food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2011, 51, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aillon, K.L.; Xie, Y.; El-Gendy, N.; Berkland, C.J.; Forrest, M.L. Effects of nanomaterial physicochemical properties on in vivo toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2009, 61, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Choi, S.J. Particle size and biological fate of ZnO do not cause acute toxicity, but affect toxicokinetics and gene expression profiles in the rat livers after oral administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, M.R.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Yu, J.; Choi, S.J. Interactions between food additive silica nanoparticles and food matrices. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, M.R.; Yu, J.; Bae, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, S.J. Effects of interactions between ZnO nanoparticles and saccharides on biological responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardy, A.; Benford, D.; Halldorsson, T.; Jeger, M.J.; Knutsen, H.K.; More, S.; Naegeli, H.; Noteborn, H.; Ockleford, C.; Ricci, A.; et al. Guidance on risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain: Part 1, human and animal health. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Athinarayanan, J.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Periasamy, V.S.; Al-Warthan, A.A. Identification of nanoscale ingredients in commercial food products and their induction of mitochondrially mediated cytotoxic effects on human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, N459–N464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.X.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Y.X.; Cao, A.; Liu, J.H.; Du, L.J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. Characterization and preliminary toxicity assay of nano-titanium dioxide additive in sugar-coated chewing gum. Small 2013, 9, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.S.; Yu, J.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, J.M.; Choi, S.J. Food additive titanium dioxide and its fate in commercial foods. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.M.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, Y.R.; Choi, S.J. Determination of the fate and biological responses of food additive silica particles in commercial foods. Food Chem. 2020, 331, 127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Meng, Q. Recent advances in processing food powders by using superfine grinding techniques: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2222–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Zhong, Q. Organic nanoparticles in foods: Fabrication, characterization, and utilization. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, I.S.; O’Fallon, K.S.; Gaines, P.; Demokritou, P.; Bello, D. Ingested engineered nanomaterials: State of science in nanotoxicity testing and future research needs. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, Q.; Watkins, R.; Castle, L. (Eds.) Nanotechnologies in food: What, why and how? In Nanotechnologies in Food, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Erfanian, A.; Mirhosseini, H.; Rasti, B.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Mustafa, S.B.; Manap, M.Y.A. Absorption and bioavailability of nano-size reduced calcium citrate fortified milk powder in ovariectomized and ovariectomized-osteoporosis rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5795–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Hu, B.; Lei, Z.; Kobayashi, M.; Adachi, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z. Effects of nanobubble water on the growth of Lactobacillus acidophilus 1028 and its lactic acid production. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 30760–30767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.K.A.; Shi, X.; Hua, L.; Manzueta, L.; Qing, W.; Marhaba, T.; Zhang, W. Influences of air, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide nanobubbles on seed germination and plant growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5117–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Oshita, S.; Makino, Y.; Wang, Q.; Kawagoe, Y.; Uchida, T. Oxidative capacity of nanobubbles and its effect on seed germination. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameshkumar, C.; Sankar, S.L.; Senthilkumar, G. Characterisation of seed germination using nanaobubbled water. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2019, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Hirao, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Kawato, Y.; Kaneshiro, S.; Morimoto, T.; Koizumi, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Oxygen and air nanobubble water solution promote the growth of plants, fishes, and mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rafeeq, S.; Shiroodi, S.; Schwarz, M.H.; Nitin, N.; Ovissipour, R. Inactivation of Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio parahaemolyticus by curcumin-mediated photosensitization and nanobubble-ultrasonication approaches. Foods 2020, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asada, R.; Kageyama, K.; Tanaka, H.; Matsui, H.; Kimura, M.; Saitoh, Y.; Miwa, N. Antitumor effects of nano-bubble hydrogen-dissolved water are enhanced by coexistent platinum colloid and the combined hyperthermia with apoptosis-like cell death. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, R.H.; Solorio, L.; Wu, H.; Gangolli, M.; Silverman, E.; Hernandez, C.; Peiris, P.M.; Broome, A.M.; Exner, A.A. Nanobubble ultrasound contrast agents for enhanced delivery of thermal sensitizer to tumors undergoing radiofrequency ablation. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mech, A.; Rauscher, H.; Babik, F.; Hodoroaba, V.D.; Ghanem, A.; Wohlleben, W.; Marvin, H.; Weigel, S.; Brungel, R.; Friedrich, C.M. The NanoDefine Methods Manual. Part 1: The NanoDefiner Framework and Tools; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2019; pp. 11–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tuz, A.A.; Simsek, A.K.; Kazanci, M. Production of organic nanoparticles by using nanoporous membranes. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1809, 020048-1–020048-7. [Google Scholar]
- Wuhrer, R.; Moran, K. Low voltage imaging and X-ray microanalysis in the SEM: Challenges and opportunities. IOP Conf. Ser-Mat. Sci. 2016, 109, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danino, D. Cryo-TEM of soft molecular assemblies. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Davarani, F.H.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Hewage, S.A.; Batagoda, J.H. Stability of nanobubbles. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Yoon, S.; Choi, Y.; Jang, J.; Park, S.; Choi, J. Stability of engineered micro or nanobubbles for biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Li, M.; Shin, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.S. Influence of organic acids and heat treatment on ginsenoside conversion. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Fraction (Number%) | Z-Average Diameter (nm) | PDI | DLS Histogram (Intensity%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 nm | 100–200 nm | >200 nm | ||||
| NBW-1 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 920 ± 504 ab | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 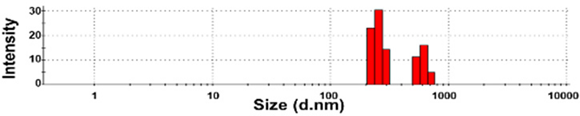 |
| NBW-2 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 513 ± 9 ab | 0.2 ± 0.0 |  |
| NBW-3 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 130 ± 43 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 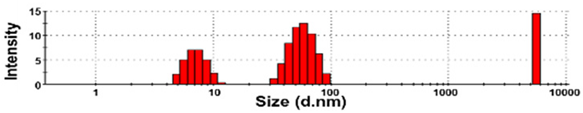 |
| NBW-4 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1181 ± 397 b | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 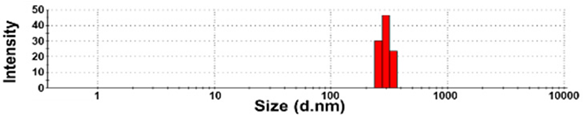 |
| NBW-5 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1244 ± 105 b | 0.9 ± 0.1 |  |
| NBW-6 | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. | N.D. |  |
| NBW-7 | 14 ± 19 | 10 ± 17 | 76 ± 21 | 763 ± 525 ab | 0.9 ± 0.1 |  |
| SW-1 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 74,967 ± 42,928 c | 0.9 ± 0.2 |  |
| SW-2 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 193,933 ± 69,743 d | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 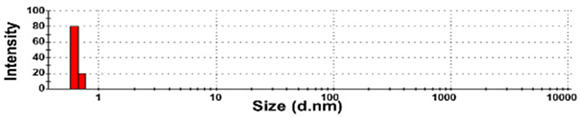 |
| Sample | Fraction (Number%) | Z-Average Diameter (nm) | PDI | DLS Histogram (Intensity%) | Zeta Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 nm | 100–200 nm | >200 nm | |||||
| NBW-1 | N.D. | 39 ± 31 | 61 ± 31 | 422 ± 29 c | 0.5 ± 0.2 |  | −20 ± 2 a |
| NBW-2 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 454 ± 33 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 | 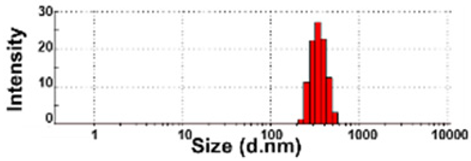 | −8 ± 0 cd |
| NBW-3 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 132 ± 53 a | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 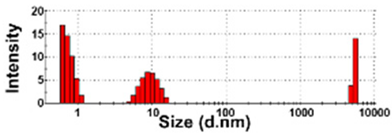 | −10 ± 2 c |
| NBW-4 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 732 ± 51 d | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 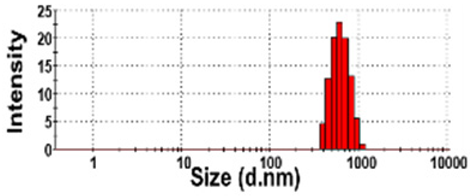 | −6 ± 2 cd |
| NBW-5 | N.D. | 13 ± 14 | 87 ± 14 | 386 ± 39 c | 0.3 ± 0.1 |  | −8 ± 2 cd |
| NBW-6 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 18 ± 6 b | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 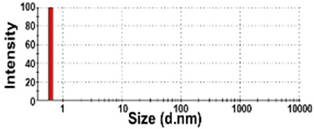 | −5 ± 1 d |
| NBW-7 | N.D. | 5 ± 5 | 95 ± 5 | 369 ± 30 c | 0.4 ± 0.2 |  | −15 ± 2 b |
| SW-1 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 35,820 ± 7653 e | 1.0 ± 0.0 | 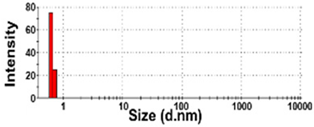 | −0 ± 0 e |
| SW-2 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 61,587 ± 33,772 e | 1.0 ± 0.0 |  | −0 ± 1 e |
| DW | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 219 ± 10 a | 1.0 ± 0.0 |  | N.D. |
| Sample | Fraction (Number%) | Z-Average Diameter (nm) | PDI | DLS Histogram (Intensity%) | Zeta Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 nm | 100–200 nm | >200 nm | |||||
| NBW-1 | N.D. | 4 ± 6 | 96 ± 6 | 601 ± 85 d | 0.7 ± 0.1 | 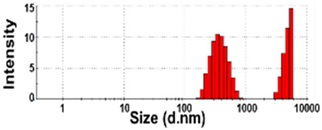 | −8 ± 1 c |
| NBW-2 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 402 ± 14 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 |  | −8 ± 2 c |
| NBW-3 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 193 ± 92 b | 0.9 ± 0.1 |  | −1 ± 1 a |
| NBW-4 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 907 ± 238 d | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 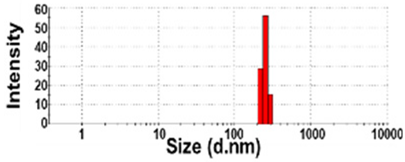 | −3 ± 1 b |
| NBW-5 | N.D. | 6 ± 6 | 94 ± 5 | 358 ± 103 c | 0.3 ± 0.1 |  | −7 ± 1 c |
| NBW-6 | 100 ± 0 | N.D. | N.D. | 19 ± 5 a | 1.0 ± 0.1 |  | −1 ± 0 a |
| NBW-7 | 8 ± 14 | 46 ± 45 | 46 ± 48 | 414 ± 115 cd | 0.9 ± 0.2 |  | −6 ± 2 bc |
| Sample | Fraction (Number%) | Z-Average Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <100 nm | 100–200 nm | >200 nm | ||||
| NP-1 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1771 ± 17 cd | 0.7 ± 0.3 | −21 ± 1 d |
| NP-2 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 800 ± 30 b | 0.2 ± 0.1 | −35 ± 0 b |
| NP-3 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1756 ± 304 cd | 0.7 ± 0.1 | −27 ± 1 c |
| NP-4 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1198 ± 65 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 | −31 ± 1 bc |
| NP-5 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1403 ± 232 c | 0.2 ± 0.1 | −32 ± 1 b |
| NP-6 | 93 ± 11 | 6 ± 11 | 1 ± 0 | 327 ± 8 a | 0.5 ± 0.1 | −20 ± 0 d |
| NP-7 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 2148 ± 376 d | 0.3 ± 0.3 | −14 ± 3 e |
| BP-1 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1246 ± 126 c | 0.3 ± 0.2 | −27 ± 3 c |
| BP-2 | N.D. | N.D. | 100 ± 0 | 1788 ± 53 cd | 0.2 ± 0.0 | −47 ± 2 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Jeon, Y.-R.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, E.-B.; Choi, S.-J. Characterization and Determination of Nanoparticles in Commercial Processed Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092020
Yu J, Jeon Y-R, Kim Y-H, Jung E-B, Choi S-J. Characterization and Determination of Nanoparticles in Commercial Processed Foods. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092020
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jin, Ye-Rin Jeon, Ye-Hyun Kim, Eun-Been Jung, and Soo-Jin Choi. 2021. "Characterization and Determination of Nanoparticles in Commercial Processed Foods" Foods 10, no. 9: 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092020
APA StyleYu, J., Jeon, Y.-R., Kim, Y.-H., Jung, E.-B., & Choi, S.-J. (2021). Characterization and Determination of Nanoparticles in Commercial Processed Foods. Foods, 10(9), 2020. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092020