Research Advances of d-allulose: An Overview of Physiological Functions, Enzymatic Biotransformation Technologies, and Production Processes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
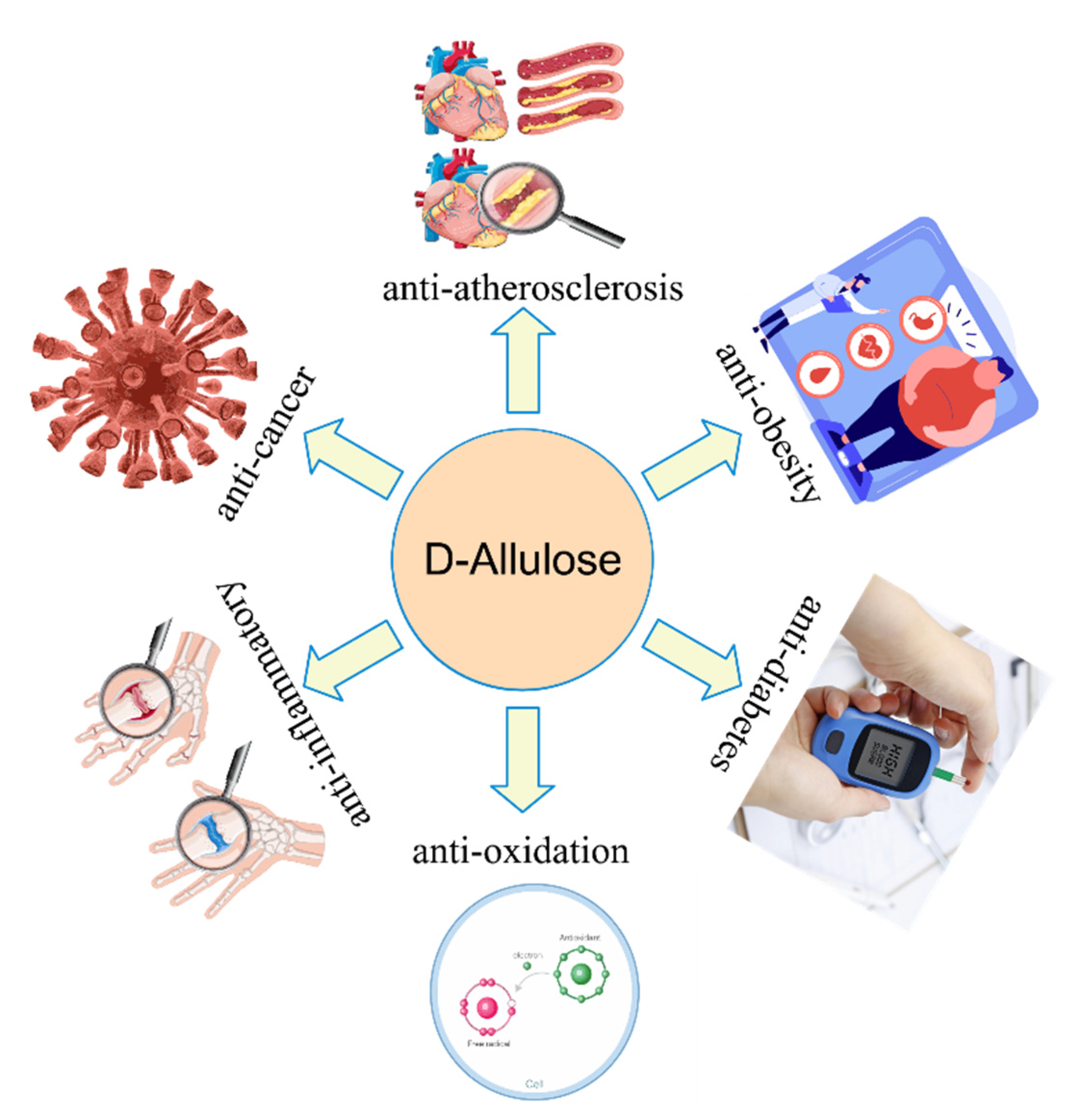
2. Physiological Functions of d-allulose
2.1. Anti-Obesity
2.2. Anti-Diabetes
2.3. Anti-Oxidation
2.4. Application of d-allulose in Food Industries
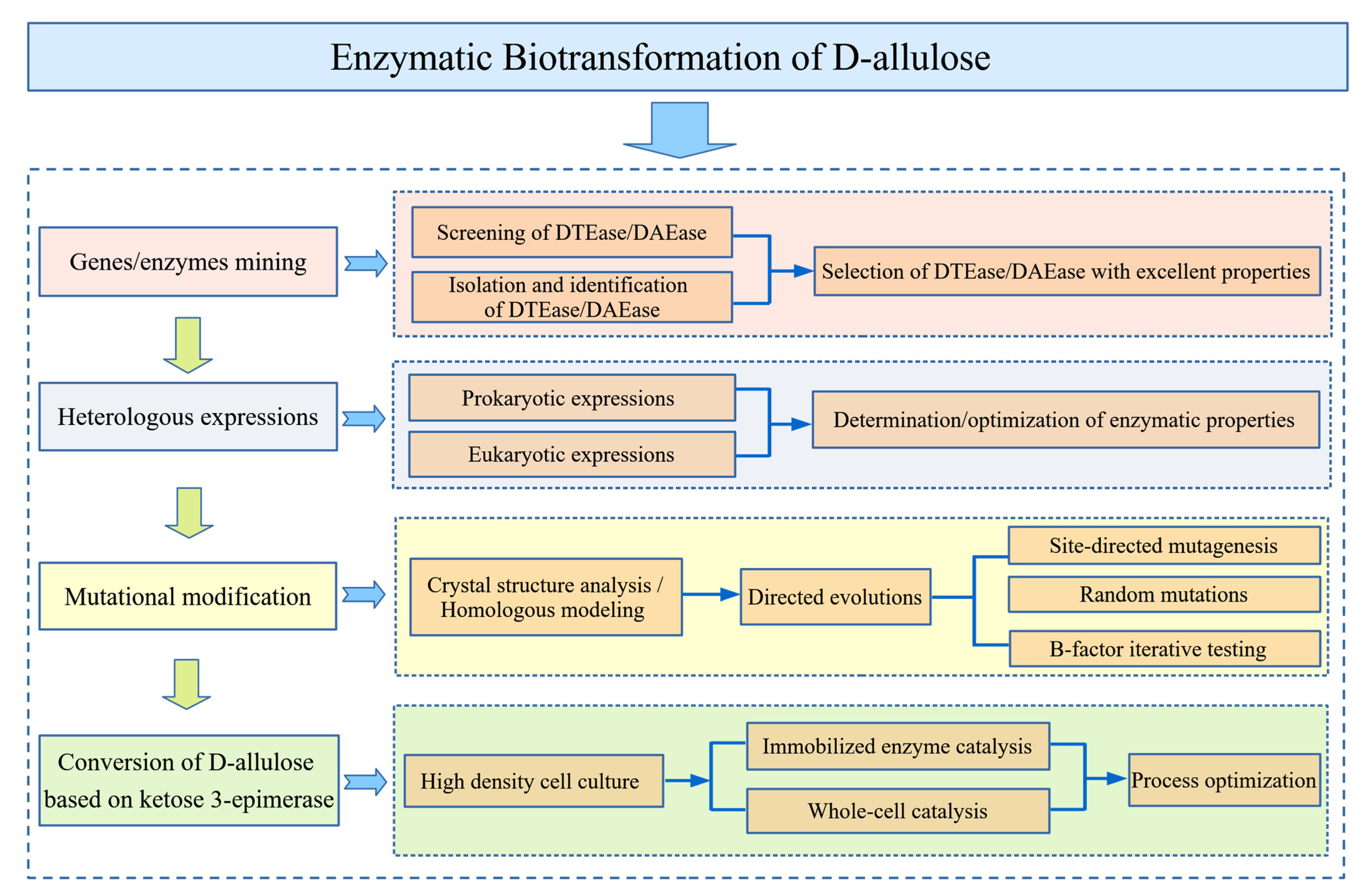
3. Enzymatic Biotransformation of d-allulose
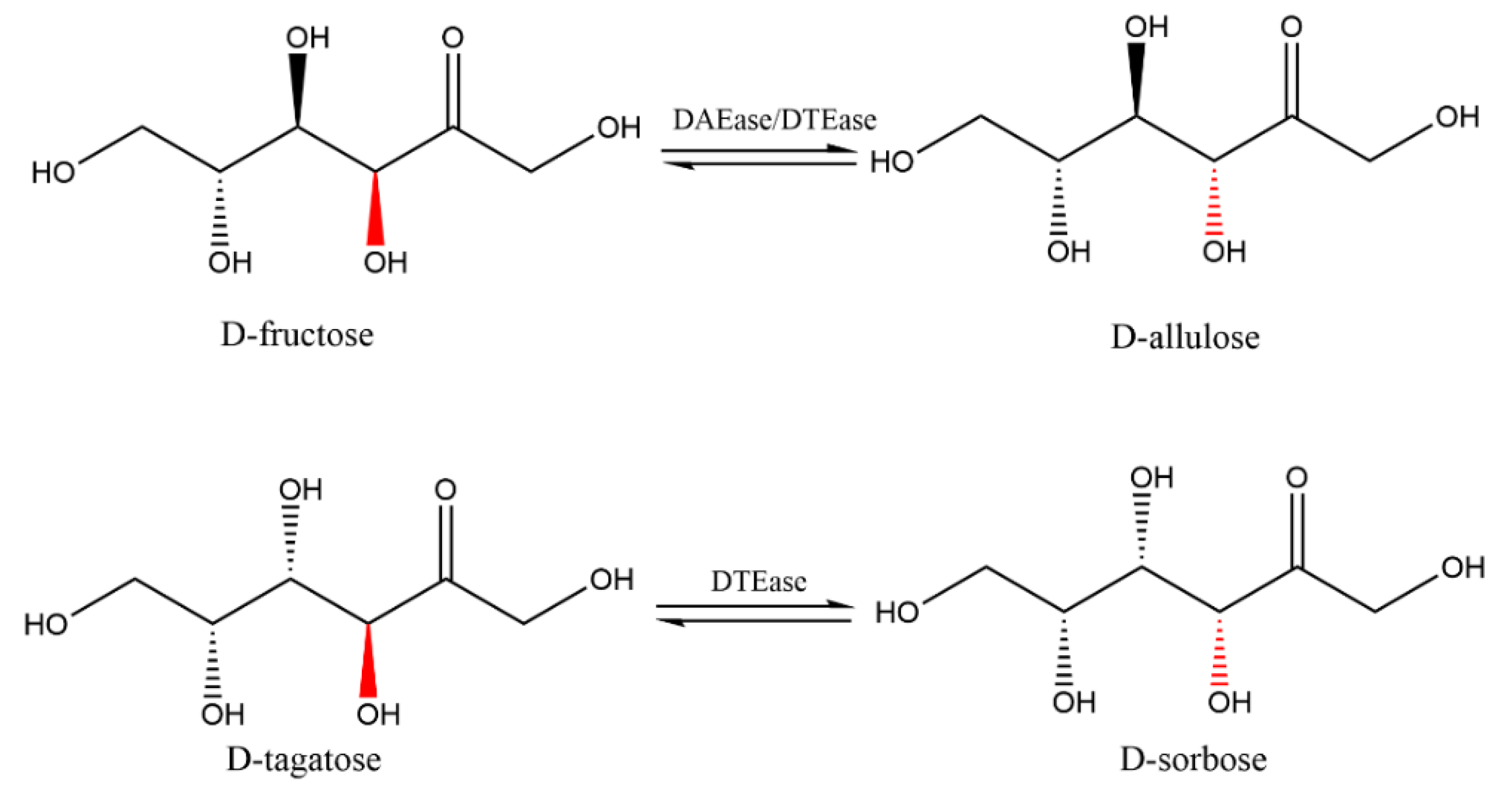
3.1. Source of Enzymes
3.2. Structural Features of the Enzymes
3.3. Mutational Modification Studies of Enzymes
3.3.1. Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.3.2. B-Factor Iterative Testing
3.4. Other Enzymes
3.5. Enzyme Expression Systems
3.5.1. Enzyme Expression in Prokaryotic Systems
3.5.2. Enzyme Expression in Eukaryotic Systems
3.6. Double Enzyme Coupling and Construction of the Gene Expression Cassette
3.7. Biotransformation of d-allulose Based on DAEase/DTEase
3.7.1. Biotransformation Using Immobilized Enzymes
3.7.2. Biotransformation Using Whole-Cells
4. Production of d-allulose
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowry, A.D.K.; Lewey, J.; Dugani, S.B.; Choudhry, N.K. The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Epidemiology and Management. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015, 31, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, H.E.K.; Koskinen, T.T.; Voutilainen, S.; Mursu, J.; Tuomainen, T.P.; Kokko, P.; Virtanen, J.K. Intake of different dietary proteins and risk of type 2 diabetes in men: The Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hossain, A.; Yamaguchi, F.; Matsuo, T.; Tsukamoto, I.; Toyoda, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Nagata, Y.; Tokuda, M. Rare sugar D-allulose: Potential role and therapeutic monitoring in maintaining obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 155, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Tanaka, T.; Hashiguchi, M.; Izumori, K.; Suzuki, H. Metabolic effects of D-psicose in rats: Studies on faecal and urinary excretion and caecal fermentation. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 12, 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Fukada, K.; Ishii, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yamaji, M.; Yamaoka, Y.; Kobashi, K.-I.; Izumori, K. Crystal Structure, Solubility, and Mutarotation of the Rare Monosaccharide D-Psicose. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 83, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.S.; Swain, T. Chromatographic analyses of the free amino-acids, organic acids and sugars in wheat plant extracts. J. Sci. Food 1960, 11, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cree, G.M.; Perlin, A.S. O-isopropylidene derivatives of D-allulose (D-psicose) and D-erythro-hexopyranos-2,3-diulose. Can. J. Biochem. 1968, 46, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, B.J.; Hollinshead, J.; Saville, A.W.; Nakagawa, S.; Adachi, I.; Kato, A.; Izumori, K.; Bartholomew, B.; Fleet, G.W.; Nash, R.J. Iteamine, the first alkaloid isolated from Itea virginica L. inflorescence. Phytochemistry 2014, 100, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishii, N.; Takashima, S.; Kobatake, Y.; Tokuda, M.; Kitagawa, H. The long-term safety of D-allulose administration in healthy dogs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanasaki, A.; Niibo, M.; Iida, T. Effect of D-allulose feeding on the hepatic metabolomics profile in male Wistar rats. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3931–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, Y.; Kanasaki, A.; Tamaru, S.; Tanaka, K. D-psicose, an epimer of D-fructose, favorably alters lipid metabolism in Sprague-Dawley rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3168–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, M.K.; Yamaguchi, F.; Nakanose, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Hatano, N.; Tsukamoto, I.; Nagata, M.; Izumori, K.; Tokuda, M. Neuroprotective effect of D-psicose on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Han, Y.; Kwon, E.Y.; Choi, M.S. D-allulose Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction in C57BL/KsJ-db/db Mice. Molecules 2020, 25, 3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.G. D-psicose, a sweet monosaccharide, ameliorate hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia in C57BL/6J db/db mice. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, H49–H53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Charoen, S.; Hayakawa, S.; Ogawa, M. Food properties of egg white protein modified by rare ketohexoses through Maillard reaction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilik, V.; Tihlarik, K. Reaction of saccharides catalyzed by molybdate ions. IX. Epimerization of ketohexoses. Chem. Pap. 1973, 28, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- McDonald, E.J. A new synthesis of D-psicose (D-ribo-hexulose). Carbohydr. Res. 1967, 5, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doner, L.W. Isomerization of D-fructose by base: Liquid-chromatographic evaluation and the isolation of D-psicose. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 70, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Hyun, E.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, D.K. Characterization of an Agrobacterium tumefaciens D-psicose 3-epimerase that converts D-fructose to D-psicose. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mu, W.M.; Chu, F.F.; Jiang, B. Characterization of a Novel D-tagatose 3-Epimerase from Clostridium scindens ATCC 35704. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, S536–S537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, C.; Mao, S.; Lu, F.; Qin, H.-M. Improving the enzyme property of D-allulose 3-epimerase from a thermophilic organism of Halanaerobium congolense through rational design. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 149, 109850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W.M. Biochemical characterization of a D-psicose 3-epimerase from Treponema primitia ZAS-1 and its application on enzymatic production of D-psicose. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W.; Zhang, T. Bioproduction of D-psicose using permeabilized cells of newly isolated Rhodobacter sphaeroides SK011. Front. Chem. Eng. China 2009, 3, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Huang, J.W.; Chen, Z.W.; Zhang, T.; Guang, C.; Mu, W.M. Thermostability Improvement of the D-Allulose 3-Epimerase from Dorea sp. CAG317 by Site-Directed Mutagenesis at the Interface Regions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5593–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ravikumar, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Parvez, A.; Qi, X.; Sun, W. Biocatalytic Synthesis of D-Allulose Using Novel D-Tagatose 3-Epimerase From Christensenella minuta. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 622325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, T.; Han, P.; You, C. Thermodynamics-Driven Production of Value-Added d-Allulose from Inexpensive Starch by an In Vitro Enzymatic Synthetic Biosystem. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 5088–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekeberg, D.; Morgenlie, S.; Stenstrøm, Y. Aldose–ketose interconversion in pyridine in the presence of aluminium oxide. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, D.I.; Jeong, K.W.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, Y.; Oh, D.K. Conversion shift of D-fructose to D-psicose for enzyme-catalyzed epimerization by addition of borate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3008–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.D.; Le, T.H.; Kim, J.I.; Lee, J.W.; Koo, Y.M. Separation of D-psicose and D-fructose using simulated moving bed chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1987–1995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.; Bosshart, A.; Failmezger, J.; Bechtold, M.; Panke, S. A separation-integrated cascade reaction to overcome thermodynamic limitations in rare-sugar synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 4182–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Lu, F.; Qin, H.M. Engineering a thermostable version of D-allulose 3-epimerase from Rhodopirellula baltica via site-directed mutagenesis based on B-factors analysis. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 132, 109441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zeng, G.; Tang, L.; Pang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Lei, X.; Wu, M.; Ren, P.; et al. Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of phenolic compounds. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 115, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wen, Q.; Chen, S.; Le, X.; Zhou, X.; Huang, L. Synthesis of amine-functionalized Fe3O4@C nanoparticles for laccase immobilization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, T.; Hayashi, N.; Yamada, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Miyazato, S.; Kishimoto, Y.; Okuma, K.; Tokuda, M.; Izumori, K. Failure of d-psicose absorbed in the small intestine to metabolize into energy and its low large intestinal fermentability in humans. Metabolism 2010, 59, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, I.; Hossain, A.; Yamaguchi, F.; Hirata, Y.; Dong, Y.; Kamitori, K.; Sui, L.; Nonaka, M.; Ueno, M.; Nishimoto, K.; et al. Intestinal absorption, organ distribution, and urinary excretion of the rare sugar D-psicose. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2014, 8, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, N.; Iida, T.; Yamada, T.; Okuma, K.; Takehara, I.; Yamamoto, T.; Yamada, K.; Tokuda, M. Study on the postprandial blood glucose suppression effect of D-psicose in borderline diabetes and the safety of long-term ingestion by normal human subjects. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iida, T.; Kishimoto, Y.; Yoshukawa, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Okuma, K.; Tohi, M.; Yagi, K.; Matsuo, T.; Izumori, K. Acute D-Psicose Administration Decreases the Glycemic Responses to an Oral Maltodextrin Tolerance Test in Normal Adults. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2008, 54, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, M.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.C.; Park, C.; Kim, H.J. 90-Day repeated oral toxicity test of D-allulose produced from Microbacterium foliorum. Regul. Toxicol. Pharm. 2019, 109, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Han, H.J.; Kim, A.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, S.J.; Park, Y.B.; Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. d-Allulose supplementation normalized the body weight and fat-pad mass in diet-induced obese mice via the regulation of lipid metabolism under isocaloric fed condition. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1695–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.Y.; Oh, D.K.; Lee, K.W. Hypoglycemic health benefits of D-psicose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Kitagaki, S.; Nakano, D.; Nishiyama, A.; Funamoto, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Tsukamoto, I.; Yamaguchi, F.; Kamitori, K.; Dong, Y.; et al. Rare sugar D-psicose improves insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in type 2 diabetes Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishida, K.; Martinez, G.; Iida, T.; Yamada, T.; Ferraris, R.P.; Toyoda, Y. d-Allulose is a substrate of glucose transporter type 5 (GLUT5) in the small intestine. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murao, K.; Yu, X.; Cao, W.M.; Imachi, H.; Chen, K.; Muraoka, T.; Kitanaka, N.; Li, J.; Ahmed, R.A.; Matsumoto, K.; et al. D-Psicose inhibits the expression of MCP-1 induced by high-glucose stimulation in HUVECs. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yoon, J.; Choi, M.S. Tracing the Anti-Inflammatory Mechanism/Triggers of d-Allulose: A Profile Study of Microbiome Composition and mRNA Expression in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Kwon, E.Y.; Yu, M.K.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, M.S. A Preliminary Study for Evaluating the Dose-Dependent Effect of d-Allulose for Fat Mass Reduction in Adult Humans: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yagi, K.; Matsuo, T. The Study on Long-Term Toxicity of D-Psicose in Rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Choi, K. Inhibition of 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Differentiation by D-allulose. Biotechnol. Bioprocess. Eng. 2020, 25, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.M.; Hyun Lee, J.; Youl Kim, D.; Hwang, S.H.; Hong, Y.H.; Kim, S.B.; Jin Lee, S.; Hye Park, C. Dietary D-psicose reduced visceral fat mass in high-fat diet-induced obese rats. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, H53–H58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanasaki, A.; Jiang, Z.; Mizokami, T.; Shirouchi, B.; Iida, T.; Nagata, Y.; Sato, M. Dietary d-allulose alters cholesterol metabolism in Golden Syrian hamsters partly by reducing serum PCSK9 levels. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.R.; Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, M.S. Role of Synbiotics Containing d-Allulose in the Alteration of Body Fat and Hepatic Lipids in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, K.; Mizuno, S.; Hama, S.; Oshima, W.; Kawamata, M.; Hossain, A.; Ishihara, Y.; Tokuda, M. Beneficial Effects of Supplementation of the Rare Sugar “D-allulose” Against Hepatic Steatosis and Severe Obesity in Lep(ob)/Lep(ob) Mice. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, H1619–H1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, T.; Izumori, K. Effects of dietary D-psicose on diurnal variation in plasma glucose and insulin concentrations of rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2081–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, T.; Izumori, K. D-Psicose Inhibits Intestinal alpha-Glucosidase and Suppresses the Glycemic Response after Ingestion of Carbohydrates in Rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2009, 45, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hishiike, T.; Ogawa, M.; Hayakawa, S.; Nakajima, D.; O’Charoen, S.; Ooshima, H.; Sun, Y. Transepithelial transports of rare sugar D-psicose in human intestine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7381–7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, M.; Hira, T.; Nakamura, M.; Iida, T.; Kishimoto, Y.; Hara, H. Secretion of GLP-1 but not GIP is potently stimulated by luminal D-allulose (D-psicose) in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, Y.; Sendo, M.; Dezaki, K.; Hira, T.; Sato, T.; Nakata, M.; Goswami, C.; Aoki, R.; Arai, T.; Kumari, P.; et al. GLP-1 release and vagal afferent activation mediate the beneficial metabolic and chronotherapeutic effects of D-allulose. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, A.; Yamaguchi, F.; Hirose, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Sui, L.; Hirata, Y.; Noguchi, C.; Katagi, A.; Kamitori, K.; Dong, Y.; et al. Rare sugar D-psicose prevents progression and development of diabetes in T2DM model Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2015, 9, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanasaki, A.; Iida, T.; Murao, K.; Shirouchi, B.; Sato, M. D-Allulose enhances uptake of HDL-cholesterol into rat’s primary hepatocyte via SR-B1. Cytotechnology 2020, 72, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, A.; Sekiya, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamaguchi, F.; Hatano, N.; Izumori, K.; Tokuda, M. A novel inhibitory effect of D-allose on production of reactive oxygen species from neutrophils. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 96, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suna, S.; Yamaguchi, F.; Kimura, S.; Tokuda, M.; Jitsunari, F. Preventive effect of D-psicose, one of rare ketohexoses, on di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP)-induced testicular injury in rat. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 173, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tas, O.; Ertugrul, U.; Oztop, M.H.; Mazi, B.G. Glycation of soy protein isolate with two ketoses: D-allulose and fructose. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, E.G.; Ozvural, E.B.; Oztop, M.H. In vitro digestibility of rare sugar (D-allulose) added pectin-soy protein gels. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3421–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, E.G.; Ozvural, E.B.; Oztop, M.H. Understanding the role of D-allulose and soy protein addition in pectin gels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, M.; Inoue, M.; Hayakawa, S.; O’Charoen, S.; Ogawa, M. Effects of rare sugar d-allulose on heat-induced gelation of surimi prepared from marine fish. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5014–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, T.; Sakoguchi, H.; Yoshihara, A.; Izumori, K.; Sato, M. d-Allulose, a stereoisomer of d-fructose, extends Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan through a dietary restriction mechanism: A new candidate dietary restriction mimetic. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoto-Nira, H.; Moriya, N.; Hayakawa, S.; Kuramasu, K.; Ohmori, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Ogawa, M. Effects of rare sugar D-allulose on acid production and probiotic activities of dairy lactic acid bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 5936–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.P.; Mu, W.M.; Jiang, B. Characterization of ribose-5-phosphate isomerase converting D-psicose to D-allose from Thermotoga lettingae TMO. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.J.; Zhu, Y.M.; Men, Y.; Yang, J.G.; Liu, C.; Sun, Y.X. Production of allitol from D-psicose by a novel isolated strain of Klebsiella oxytoca G4A4. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izumori, K. Izumoring: A strategy for bioproduction of all hexoses. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 124, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Yoshihara, A.; Ishii, T.; Izumori, K.; Kamitori, S. X-ray structures of the Pseudomonas cichorii D-tagatose 3-epimerase mutant form C66S recognizing deoxy sugars as substrates. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10403–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Yamada, M.; Nishitani, T.; Takada, G.; Izumori, K.; Karnitori, S. Crystal structures of D-tagatose 3-epimerase from Pseudomonas cichorii and its complexes with D-tagatose and D-fructose. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 374, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.C.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ko, T.P.; Huang, C.H.; Ren, F.; Chen, C.C.; Ma, Y.; Guo, R.T.; Sun, Y. Crystal structures of D-psicose 3-epimerase from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10 and its complex with ketohexose sugars. Protein Cell 2012, 3, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Yang, J.G.; Sun, Y.X.; Li, Z.M.; You, C. Artificial ATP-Free in Vitro Synthetic Enzymatic Biosystems Facilitate Aldolase-Mediated C-C Bond Formation for Biomanufacturing. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Huang, K.; Wei, M.; Meisner, J.; Liu, Y.; Garner, K.; Zang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Fang, J.; et al. Facile Enzymatic Synthesis of Ketoses. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 12654–12658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishida, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Itoh, H.; Kimura, Y.; Izumori, K. Cloning and characterization of the D-tagatose 3-epimerase gene from Pseudomonas cichorii ST-24. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1997, 83, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mu, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Characterization of D-tagatose-3-epimerase from Rhodobacter sphaeroides that converts D-fructose into D-psicose. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.L.; Fang, D.; Xing, Q.C.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W.M. Characterization of a Novel Metal-Dependent D-Psicose 3-Epimerase from Clostridium scindens 35704. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guang, C.; Mu, W. Characterization of a D-tagatose 3-epimerase from Caballeronia fortuita and its application in rare sugar production. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, W.; Chu, F.; Xing, Q.; Yu, S.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, B. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a D-psicose 3-epimerase from Clostridium cellulolyticum H10. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7785–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Men, Y.; Bai, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y. Overexpression of D-psicose 3-epimerase from Ruminococcus sp. in Escherichia coli and its potential application in D-psicose production. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 1901–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Fang, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; Jiang, B.; Mu, W. Characterization of a metal-dependent D-psicose 3-epimerase from a novel strain, Desmospora sp. 8437. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 11468–11476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Kaushal, G.; Singh, S.P. D-Allulose 3-epimerase of Bacillus sp. origin manifests profuse heat-stability and noteworthy potential of D-fructose epimerization. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.N.; Kaushal, G.; Singha, S.P. A Novel D-Allulose 3-Epimerase Gene from the Metagenome of a Thermal Aquatic Habitat and D-Allulose Production by Bacillus subtilis Whole-Cell Catalysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02605–e02619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Kamiya, T.; Izumori, K. Production of D-tagatose 3-epimerase of Pseudomonas cichorii ST-24 using recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 1997, 84, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Ruan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Lv, P.; Wang, Z. Engineered Bacillus subtilis harbouring gene of D-tagatose 3-epimerase for the bioconversion of D-fructose into D-psicose through fermentation. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2020, 136, 109531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.K.; Kim, N.H.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.S.; Kim, S.W.; Ko, M.; Park, B.W.; Jung, M.H.; Yoon, K.H. D-Psicose production from D-fructose using an isolated strain, Sinorhizobium sp. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 23, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Mu, W.; Chu, F.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, L.L.; Zhang, T. A D-psicose 3-epimerase with neutral pH optimum from Clostridium bolteae for D-psicose production: Cloning, expression, purification, and characterization. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Hang, F.; Liu, J. Expression of d-psicose-3-epimerase from Clostridium bolteae and Dorea sp. and whole-cell production of D-psicose in Bacillus subtilis. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, C.; Du, K.; Lin, H.; Lin, J. D-psicose 3-epimerase secretory overexpression, immobilization, and d-psicose biotransformation, separation and crystallization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Chen, D.; Ke, M.Y.; Ye, S.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Mu, W.M. Characterization of a Recombinant d-Allulose 3-epimerase from Thermoclostridium caenicola with Potential Application in D-allulose Production. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, A.; Kozakai, T.; Shintani, T.; Matsutani, R.; Ohtani, K.; Iida, T.; Akimitsu, K.; Izumori, K.; Gullapalli, P.K. Purification and characterization of D-allulose 3-epimerase derived from Arthrobacter globiformis M30, a GRAS microorganism. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 123, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Mu, D.; Jiang, S.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Du, M. Cell regeneration and cyclic catalysis of engineered Kluyveromyces marxianus of a D-psicose-3-epimerase gene from Agrobacterium tumefaciens for D-allulose production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S.; Kim, T.; Hong, S.H.; Shin, K.C.; Kim, K.R.; Oh, D.K. D-Allulose Production from D-Fructose by Permeabilized Recombinant Cells of Corynebacterium glutamicum Cells Expressing D-Allulose 3-Epimerase Flavonifractor plautii. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Feng, Z.Y.; Guan, L.J.; Lu, F.P.; Qin, H.M. Two-step biosynthesis of D-allulose via a multienzyme cascade for the bioconversion of fruit juices. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.X.; Sun, C.Y.; Jin, Y.T.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zheng, Y.G.; Li, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, D.S. Properties of d-allulose 3-epimerase mined from Novibacillus thermophilus and its application to synthesis of d-allulose. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2021, 148, 109816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Yeom, S.J.; Kim, K.; Rhee, S.; Kim, D.; Oh, D.K. Mutational analysis of the active site residues of a D-psicose 3-epimerase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Gao, D.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Tanokura, M.; Qin, H.M.; Lu, F. Redesign of a novel D-allulose 3-epimerase from Staphylococcus aureus for thermostability and efficient biocatalytic production of D-allulose. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bosshart, A.; Hee, C.S.; Bechtold, M.; Schirmer, T.; Panke, S. Directed Divergent Evolution of a Thermostable D-Tagatose Epimerase towards Improved Activity for Two Hexose Substrates. Chembiochem 2015, 16, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Hu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X. Metabolic engineering pathways for rare sugars biosynthesis, physiological functionalities, and applications-a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.K.; Wang, X.Y.; Tanokura, M.; Qin, H.M.; Lu, F.P. Biochemical characterization and biocatalytic application of a novel d-tagatose 3-epimerase from Sinorhizobium sp. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, C.S.; Park, C.S.; Shin, K.C.; Oh, D.K. Production of D-psicose from d-fructose by whole recombinant cells with high-level expression of D-psicose 3-epimerase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosshart, A.; Panke, S.; Bechtold, M. Systematic optimization of interface interactions increases the thermostability of a multimeric enzyme. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 9673–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, H.; Yoneda, K.; Satomura, T.; Kawakami, R.; Ohshima, T. Structure of a D-tagatose 3-epimerase-related protein from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. Acta Crystallogr. F-Struct. Biol. Commun. 2009, 65, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T.; Carballeira, J.D.; Vogel, A. Iterative saturation mutagenesis on the basis of B factors as a strategy for increasing protein thermostability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 7745–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qu, G.; Feng, Y.; Reetz, M.T. Utility of B-Factors in Protein Science: Interpreting Rigidity, Flexibility, and Internal Motion and Engineering Thermostability. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 1626–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Griend, A.A.; Wigneron, J.P. The b-factor as a function of frequency and canopy type at h-polarization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, D.F.; Feng, Y. Engineering thermostable (R)-selective amine transaminase from Aspergillus terreus through in silico design employing B-factor and folding free energy calculations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, M.T.; Soni, P.; Fernandez, L. Knowledge-guided laboratory evolution of protein thermolability. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 102, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, H.; Campillo-Brocal, J.C.; Humble, M.S.; Berglund, P. B-factor Guided Proline Substitutions in Chromobacterium violaceum Amine Transaminase: Evaluation of the Proline Rule as a Method for Enzyme Stabilization. Chembiochem 2019, 20, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acevedo-Rocha, C.G.; Hoebenreich, S.; Reetz, M.T. Iterative saturation mutagenesis: A powerful approach to engineer proteins by systematically simulating Darwinian evolution. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1179, 103–128. [Google Scholar]
- Diao, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Lu, F.; Lu, Z. Enhanced Thermostability of Lipoxygenase from Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 by Site-Directed Mutagenesis Based on Computer-Aided Rational Design. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 178, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Yoshihara, A.; Kato, S.; Mochizuki, S.; Akimitsu, K.; Izumori, K.; Kamitori, S. Crystal structure of a novel homodimeric l-ribulose 3-epimerase from Methylomonus sp. FEBS Open Bio. 2021, 11, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Cai, L.; Qi, Q.; Wang, P.G. Enzymatic synthesis of D-sorbose and D-psicose with aldolase RhaD: Effect of acceptor configuration on enzyme stereoselectivity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 7081–7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Cai, L.; Duan, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, P.; Nakanishi, H.; Gao, X.D. Enzymatic synthesis of rare sugars with L-rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase from Thermotoga maritima MSB8. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3980–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R. Bacterial expression systems for recombinant protein production: E. coli and beyond. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1102–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Lee, S.Y. Secretory and extracellular production of recombinant proteins using Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, B.; Yin, H.; Gao, C.; Xu, P.; Yang, C. Efficient secretory expression of recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli with a novel actinomycete signal peptide. Protein Expr. Purif. 2017, 129, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Sun, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K.; Wu, J. Highly efficient production of Clostridium cellulolyticum H10 D-psicose 3-epimerase in Bacillus subtilis and use of these cells to produce D-psicose. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneja, A.; Zhang, G.; Jin, Y.S.; Singh, V. Bioprocessing and technoeconomic feasibility analysis of simultaneous production of d-psicose and ethanol using engineered yeast strain KAM-2GD. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limtong, S.; Sringiew, C.; Yongmanitchai, W. Production of fuel ethanol at high temperature from sugar cane juice by a newly isolated Kluyveromyces marxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 3367–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonklang, S.; Abdel-Banat, B.M.A.; Cha-Aim, K.; Moonjai, N.; Hoshida, H.; Limtong, S.; Yamada, M.; Akada, R. High-Temperature Ethanol Fermentation and Transformation with Linear DNA in the Thermotolerant Yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus DMKU3-1042. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7514–7521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gombert, A.K.; Madeira, J.V.; Cerdan, M.E.; Gonzalez-Siso, M.I. Kluyveromyces marxianus as a host for heterologous protein synthesis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6193–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Signori, L.; Passolunghi, S.; Ruohonen, L.; Porro, D.; Branduardi, P. Effect of oxygenation and temperature on glucose-xylose fermentation in Kluyveromyces marxianus CBS712 strain. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2014, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Men, Y.; Zhu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y. The development of low-calorie sugar and functional jujube food using biological transformation and fermentation coupling technology. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosshart, A.; Wagner, N.; Lei, L.; Panke, S.; Bechtold, M. Highly efficient production of rare sugars D-psicose and L-tagatose by two engineered D-tagatose epimerases. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mu, W.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X.; Zhang, T. Food-Grade Expression of d-Psicose 3-Epimerase with Tandem Repeat Genes in Bacillus subtilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5701–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Zhang, T.; Ren, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Men, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, Y. Development of food-grade expression system for D-allulose 3-epimerase preparation with tandem isoenzyme genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum and its application in conversion of cane molasses to D-allulose. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Niu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X. High Conversion of D-Fructose into D-Allulose by Enzymes Coupling with an ATP Regeneration System. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cetinus, S.A.; Oztop, H.N. Immobilization of catalase into chemically crosslinked chitosan beads. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atacan, K.; Cakiroglu, B.; Ozacar, M. Improvement of the stability and activity of immobilized trypsin on modified Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for hydrolysis of bovine serum albumin and its application in the bovine milk. Food Chem. 2016, 212, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedania, S.R.; Patel, M.J.; Patel, D.M.; Akhani, R.C.; Patel, D.H. Immobilization on graphene oxide improves the thermal stability and bioconversion efficiency of D-psicose 3-epimerase for rare sugar production. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2017, 107, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan Patel, S.; Singh, V.; Sharma, M.; Sangwan, R.S.; Singhal, N.K.; Singh, S.P. Development of a thermo-stable and recyclable magnetic nanobiocatalyst for bioprocessing of fruit processing residues and D-allulose synthesis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, B.; Chen, J. Improved Performance of D-Psicose 3-Epimerase by Immobilisation on Amino-Epoxide Support with Intense Multipoint Attachment. Foods 2021, 10, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, G.; Tan, D.; Zhao, J.; Fan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Fan, P.; Fang, X.; Lu, X. Functionalized polyhydroxyalkanoate nano-beads as a stable biocatalyst for cost-effective production of the rare sugar D-allulose. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mu, W.; Jiang, B.; Yan, X.; Zhang, T. Construction of a Food Grade Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Based on Replicative Plasmids with an Auxotrophic Marker for Biotransformation of D-Fructose to D-Allulose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 3243–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Li, Z.; Tachikawa, H.; Gao, X.D.; Nakanishi, H. Use of yeast spores for microencapsulation of enzymes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 4502–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Duan, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, P.; Nakanishi, H.; Gao, X.D. Bioconversion of D-glucose to D-psicose with immobilized D-xylose isomerase and D-psicose 3-epimerase on Saccharomyces cerevisiae spores. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 42, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Qi, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C. High production of D-psicose from D-fructose by immobilized whole recombinant Bacillus subtilis cells expressing D-psicose 3-epimerase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Lin, J.; Gao, L.; Lin, H.; Lin, J. Enzymatic fructose removal from D-psicose bioproduction model solution and the system modeling and simulation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lia, W.; Z, Y.; Jianga, X.; Zhanga, W.; Guanga, C.; Mu, W. One-pot production of D-allulose from inulin by a novel identified thermostable exoinulinase from Aspergillus piperis and Dorea sp. D-allulose 3-epimerase. Process Biochem. 2020, 99, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, P.; Men, Y.; Yang, J.; Yue, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y. A one-pot two-enzyme system on the production of high value-added D-allulose from Jerusalem artichoke tubers. Process Biochem. 2020, 88, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kand, D.; Bagus Raharjo, I.; Castro-Montoya, J.; Dickhoefer, U. The effects of rumen nitrogen balance on in vitro rumen fermentation and microbial protein synthesis vary with dietary carbohydrate and nitrogen sources. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 241, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Yamada, T.; Hayashi, N.; Okuma, K.; Izumori, K.; Ishii, R.; Matsuo, T. Reduction of abdominal fat accumulation in rats by 8-week ingestion of a newly developed sweetener made from high fructose corn syrup. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Chemical Properties | Description |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H12O6 |
| CAS | 551-68-8 |
| Molar mass | 180.156 g/mol |
| PubChem CID | 90,008 |
| Physical state | White solid crystal |
| Crystallize | β-D-pyranose |
| Conformation | 1C (1C4 (d)) |
| Smell | / |
| Melting point | 96 °C |
| Optical rotation | ca. −85 degdm−1∙g−1∙cm3 |
| Solubility | Dissolve 291 g in 100 g water |
| Sweetness (relative to sucrose) | 70% |
| Energy | 0.007 kcal/g |
| Physiological Functions | Possible Mechanisms |
|---|---|
| Anti-obesity | Inhibition of the synthase activity for fatty acid production; increase of energy expenditure [45], and inhibition of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation [47]. |
| Anti-diabetes | Inhibition of intestinal α-glucosidase [53], suppression of the glycemic response upon carbohydrate ingestion [53], and reduction of postprandial glucose levels [56,57]. |
| Anti-atherosclerosis | Inhibition of the expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 [43], decrease of serum PCSK9 levels [49], and enhancement of hepatic HDL-cholesterol uptake via SR-B1 [58]. |
| Anti-inflammatory | Decrease of the expression levels of gene Gm12250 [44]. |
| Anti-oxidation | Effective scavenging of reactive oxygen radicals [59]. |
| Sources of Enzyme | GenBank | Expression Host | Expression Cassette | Molecular Weight of Native Protein | Optimal pH | Optimal Temperature (°C) | Metal Ions Required | Conversion Ratio | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTEase | P.cichorii ST24 | BAA24429 | E. coli.JM105 | pIK-01-DTE | 33 | 7.5–8.0 | 60 | Mn2+ | 20% | [84] |
| R.sphaeroides SK011 | ACO59490 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DTE | 128 (tetramer) | 9.0 | 40 | Mn2+ | 23% | [23] | |
| C.scindens | WP_004607502.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DTE | 31 | 7.5–8.0 | 60 | Mn2+ | 28% | [20] | |
| C. fortuita | WP_061137998.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DTE | 70 (dimer) | 7.5 | 65 | Co2+ | 29.4% | [78] | |
| R. baltica SH 1 | NC_005027 | B. subtilis WB800 | pP43NMK-DTE | 32 | 7 | 35 | NR | 25.86% | [85] | |
| C. minuta | NZ_CP029256.1 | E. coli Rosetta (DE3) | pANY1-DTE | 33 | 6 | 50 | Ni2+ | 30% | [25] | |
| Sinorhizobium sp | NZ_CP016452.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-28a (+)-DTE | 68 (dimer) | 8.0 | 50 | Mn2+ | 34% | [86] | |
| DAEase | Clostridium bolteae | CLOBOL_00069 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DAE | 139 (tetramer) | 7.0 | 55 | Co2+ | 28.8% | [87] |
| Dorea sp. CAG317 | FR892665.1 | B.subtilis WB800 | pSTOP1622-P43- DAE | 32.7 | 6.0 | 70 | NR | NR | [88] | |
| Ruminococcus sp. | ZP_04858451 | Bacillus pumilus | pNCMO2-DAE | 128 (tetramer) | 8.0 | 60 | Mn2+ | 26% | [89] | |
| Treponema primitia ZAS-1 | ZP_09717154.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DAE | 33.3 | 8.0 | 70 | Co2+ | 28% | [22] | |
| Thermoclostridium caenicola | SHI77623.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DAE | 33 | 7.5 | 65 | Co2+ | 28% | [90] | |
| A.globiformis M30 | BAW27657.1 | NR | NR | 128 (tetramer) | 7.0–8.0 | 70 | Mg2+ | 24% | [91] | |
| A. tumefaciens EHA 105 | KX098480.1 | K. marxianus | pRS42H-DAE | 33 | 8.0 | 55 | Mn2+ | 25.3% | [92] | |
| Flavonifractor plautii | EHM40452.1 | C. glutamicum ATCC 13032 | pEKEx2-DAE | 33 | 7.0 | 65 | Co2+ | 31% | [93] | |
| Pirellula sp. SH-Sr6A | WP_146677337.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DAE | 32 | 7.5 | 60 | Co2+ | 31.44% | [94] | |
| C.cellulolyticum H10 | NC_011898 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET-22b (+)-DAE | 33 | 8.0 | 55 | Co2+ | 32% | [79] | |
| Novibacillus thermophilus | WP_077721022.1 | E. coli BL21(DE3) | pET28b (+)-DAE | 130 (tetramer) | 7.0 | 70 | Co2+ | 29.7% | [95] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Mu, W.; Hu, X.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z. Research Advances of d-allulose: An Overview of Physiological Functions, Enzymatic Biotransformation Technologies, and Production Processes. Foods 2021, 10, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092186
Xia Y, Cheng Q, Mu W, Hu X, Sun Z, Qiu Y, Liu X, Wang Z. Research Advances of d-allulose: An Overview of Physiological Functions, Enzymatic Biotransformation Technologies, and Production Processes. Foods. 2021; 10(9):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092186
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Yu, Qianqian Cheng, Wanmeng Mu, Xiuyu Hu, Zhen Sun, Yangyu Qiu, Ximing Liu, and Zhouping Wang. 2021. "Research Advances of d-allulose: An Overview of Physiological Functions, Enzymatic Biotransformation Technologies, and Production Processes" Foods 10, no. 9: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092186
APA StyleXia, Y., Cheng, Q., Mu, W., Hu, X., Sun, Z., Qiu, Y., Liu, X., & Wang, Z. (2021). Research Advances of d-allulose: An Overview of Physiological Functions, Enzymatic Biotransformation Technologies, and Production Processes. Foods, 10(9), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10092186







