Effect of Xanthan Gum, Kappa–Carrageenan, and Guar Gum on the Functional Characteristics of Egg White Liquid and Intermolecular Interaction Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Foaming Properties
2.4. Foam Microstructure
2.5. Emulsifying Properties
2.6. Creaming Index
2.7. Interfacial Protein Adsorption
2.8. Viscosity Determination
2.9. Surface Hydrophobicity
2.10. Sulfhydryl Group Analysis
2.11. Confocal Microscopy
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Polysaccharides on the Foaming Properties of Egg White Liquid
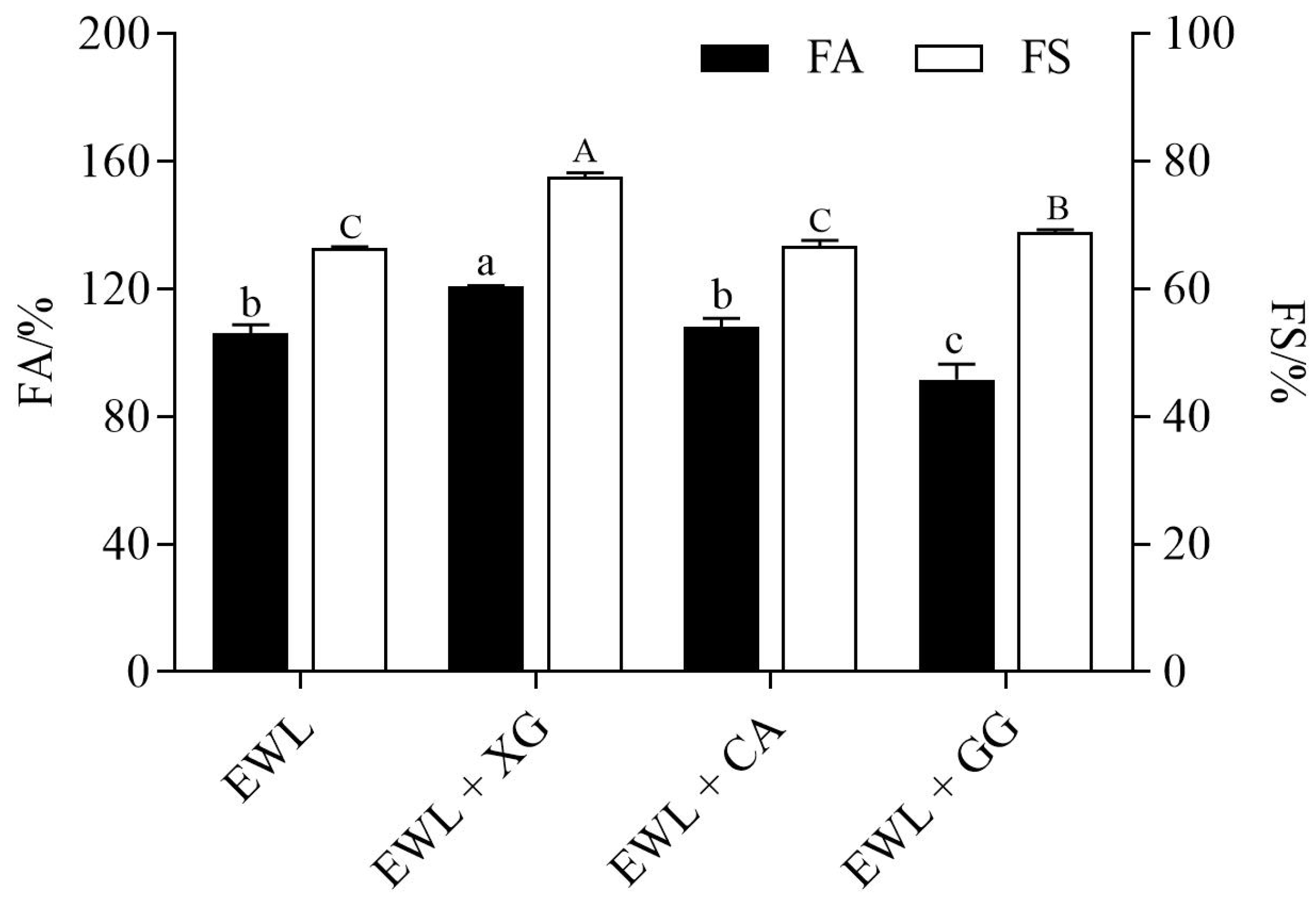
3.1.1. Effect of Polysaccharides on FA and FS of Egg White Liquid
3.1.2. Effect of Polysaccharides on Foam Structure of Egg White Liquid
3.2. Effect of Polysaccharides on the Emulsifying Property of Egg White Liquid
3.2.1. Effect of Polysaccharides on Emulsifying Activity and Stability Indexes of Egg White Liquid
3.2.2. Effect of Polysaccharides on Adsorption of Interfacial Proteins in Emulsion
3.2.3. Effect of Polysaccharides on the Creaming Index of Emulsions
3.3. Intermolecular Interaction of the Polysaccharide–Egg White Protein Complexes
3.3.1. Hydrogen Bonds and Electrostatic Interactions between Polysaccharides and Egg White Protein
3.3.2. Effects of Polysaccharides on the Hydrophobic Interactions between Egg White Proteins
3.3.3. Effects of Polysaccharides on the Sulfhydryl Content of Egg White Protein
3.4. Effect of Polysaccharides on the Microstructure of Egg White Protein
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grant, M.C.; Estelle, M. Creation and characterisation of aerated food products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Du, H.; Tang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, Y.; Hu, M.; Xu, M. Effects of incorporating different kinds of peptides on the foaming properties of egg white powder. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 72, 102742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.L.; Day, L.; Aguilar, M.I.; Wooster, T.J. Protein folding at emulsion oil/water interfaces. Curr. Opin. Colloid 2013, 18, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili–Firoozinezhad, S.; Filippi, M.; Mohabatpour, F.; Letourneur, D.; Scherberich, A. Chicken egg white: Hatching of a new old biomaterial. Mater. Today 2020, 40, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréa, A.S.; Márcia, C.T.R.V.; Valéria, P.R.M.; Luis, A.M. Ovalbumin and guar gum foam and its surface properties as influenced by sucrose and sorbitol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendorff, V.; Cuvelier, G.; Michon, C.; Launay, B.; Parker, A.; De–Kruif, C.G. Effects of carrageenan type on the behaviour of carrageenan/milk mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 4, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, D.; Samira, Y. Effect of Persian gum and Xanthan gum on foaming properties and stability of pasteurized fresh egg white foam. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, X.; McClements, D.J.; Shi, M.; Shang, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Physicochemical and functional properties of lactoferrin–hyaluronic acid complexes: Effect of non–covalent and covalent interactions. LWT 2021, 151, 112121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axel, B.; Abraham, A.; Rachel, L.; Nissim, G. Formation and characterization of amphiphilic conjugates of whey protein isolate (WPI)/xanthan to improve surface activity. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 21, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ding, L.; Xia, M.; Huang, X.; Isobe, K.; Handa, A.; Cai, Z. Role of lysozyme on liquid egg white foaming properties: Interface behavior, physicochemical characteristics and protein structure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Deng, L.; Wang, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Luo, S.; Liu, C. Impact of rutin on the foaming properties of soybean protein: Formation and characterization of flavonoid—protein complexes. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercelebi, E.A.; Ibanoglu, E. Characterization of phase separation behavior, emulsion stability, rheology, and microstructure of egg white–polysaccharide mixtures. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, C506–C512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, X.; Zheng, Q.; Pan, M.; Chiou, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Duan, S.; Wei, S.; et al. Liposomal vesicles-protein interaction: Influences of iron liposomes on emulsifying properties of whey protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Gao, Y.; Su, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Influence of chitosan on the emulsifying properties of egg yolk hydrolysates: Study on creaming, thermal and oxidative stability. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4691–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepika, K.; Jiyoung, J.; Samatha, H.; Louise, W. Sugar beet pectin fractionated using isopropanol differs in galacturonic acid, protein, ferulic acid and surface hydrophobicity. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazumasa, T.; Takayuki, T.; Keiichi, N.; Kazuhiko, T. Capillary electrophoresis with a chemiluminescence detector using the two reactions of luminol and peroxyoxalate. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahi, M.R.; Mohebbi, M. Development of soy milk in the form of wet foam in the presences of whey protein concentrate and polysaccharides at different whipping temperatures: Study of physical, rheological and microstructural properties. LWT 2020, 137, 110444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joice, N.M.; Suzana, C.; Da, S.L. Egg albumin and guar gum influence on foam thixotropy. J. Texture Stud. 2009, 40, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquelim, J.N.; Lannes, S.C.S.; Mezzenga, R. pH Influence on the stability of foams with protein–polysaccharide complexes at their interfaces. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Xiao, N.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Xu, M.; Du, H.; Wu, N.; Tu, Y. Effect of polysaccharides on the functional properties of egg white protein: A review. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.R.; Ettiarachchy, N.S.H. Effect of xanthan gum on enhancing the foaming properties of soy protein isolate. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1998, 75, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, C.L.; Hettiarachchy, N.S.; Qi, M. Effect of xanthan gum on enhancing the foaming properties of whey protein isolate. JAOCS J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.N.; Windhab, E.J. Influence of process parameters on microstructure of food foam whipped in a rotor–stator device within a wide static pressure range. Colloids Surf. A 2005, 263, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Dai, T.T.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, T.; Liu, C.M.; Mcclements, D.J. Protein-polyphenol functional ingredients: The foaming properties of lactoferrin are enhanced by forming complexes with procyanidin. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 128145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, W.F.; Wei, P.; Sun, L.; Jin, F.Y.; Wang, S. Experimental investigation of viscoelastic polymers for stabilizing foam. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 47, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, B.; Liu, Q.; Xia, X.; Chen, H. Improvement of the emulsifying and oxidative stability of myofibrillar protein prepared oil-in-water emulsions by addition of zein hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2016, 53, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, M.; Annekathrin, M.; Peter, F. Mechanical properties of protein adsorption layers at the air/water and oil/water interface: A comparison in light of the thermodynamical stability of proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaolu, T.J.; Zhao, G. Fabricating a Pickering Stabilizer from Okara Dietary Fibre Particulates by Conjugating with Soy Protein Isolate via Maillard Reaction. Foods 2020, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casas, J.A.; Mohedano, A.F.; García, O.F. Viscosity of guar gum and xanthan/guar gum mixture solutions. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2000, 80, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagorn, S.C.; Gueguen, J.; Lefebvre, J. Emulsifying Properties of Pea Globulins as Related to Their Adsorption Behaviors. J. Food Sci. 1987, 52, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Li, X.; Li, J.H.; Niu, F.; Zhang, M.Q.; Zhou, B.; Yang, Y.J. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis on characteristics and synergistic efficiency of pectin on emulsifying properties of egg white protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 65, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Khan, N.M.; Ali, F.; Khan, Z.U.; Ahmad, S.; Jan, A.K.; Rehman, N.; Muhammad, N. Effect of protein and oil volume concentrations on emulsifying properties of acorn protein isolate. Food Chem. 2020, 324, 126894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Luo, W.; Lin, D.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Qin, W. Molecular structure and functional properties of glycinin conjugated to kappa-carrageenan and guar gum: A comparative study. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruakpa, F.; Arntfield, S. Surface hydrophobicity of commercial canola proteins mixed with κ-carrageenan or guar gum. Food Chem. 2005, 95, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.; Chenlo, F.; Torres, D.M.; Glazer, J. Rheological properties of gelatinized chestnut starch dispersions: Effect of concentration and temperature. J. Food Eng. 2012, 112, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, K.D.; Baeza, R.I.; Millan, F.; Pilosof, A. Effect of limited hydrolysis of sunflower protein on the interactions with polysaccharides in foams. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 19, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ren, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Shen, M. Interactions between tapioca starch and Mesona chinensis polysaccharide: Effects of urea and NaCl. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Daniel, R. A Novel Carboxylesterase Derived from a Compost Metagenome Exhibiting High Stability and Activity towards High Salinity. Genes 2021, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Fang, Y.; Nishinari, K.; Phillips, G.O. Hydrogen bonding enhances the electrostatic complex coacervation between κ–carrageenan and gelatin. Colloids Surf. A 2015, 482, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zou, Y.; Cui, B.; Fang, Y.; Lu, L.; Xu, D. Influence of cyclodextrins on the gelation behavior of κ-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldursdottir, S.G.; Fullerton, M.S.; Nielsen, S.H.; Jorgensen, L. Adsorption of proteins at the oil/water interface--observation of protein adsorption by interfacial shear stress measurements. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 79, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H. Antioxidant activities and emulsifying properties of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates modified by oxidized tannic acid and oxidized chlorogenic acid. Process Biochem. 2019, 79, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Li, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, X. Effect of a multiple freeze-thaw process on structural and foaming properties of individual egg white proteins. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Du, Z.; Liang, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Adsorption and foaming properties of edible egg yolk peptide nanoparticles: Effect of particle aggregation. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Tang, W.J.; Xu, Z.; Wen, L.; Chen, M.L. Structure and functional properties of rice protein-dextran conjugates prepared by the Maillard reaction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on secondary structure and emulsifying behavior of sweet potato protein. High Press. Res. 2015, 35, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafarpour, R.; Koocheki, A.; Milani, E.; Varidi, M. Extruded soy protein as a novel emulsifier: Structure, interfacial activity and emulsifying property. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, T.; Yu, G.; Shao, M. Covalent Interaction between High Hydrostatic Pressure-Pretreated Rice Bran Protein Hydrolysates and Ferulic Acid: Focus on Antioxidant Activities and Emulsifying Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7777–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xue, S.; Xu, X. Effects of ultrasound frequency mode on myofibrillar protein structure and emulsifying properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koen, J.A.J.; Kristof, B.; Jan, A.D.; Martin, G.S. Amyloid-like aggregation of ovalbumin: Effect of disulfide reduction and other egg white proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Electrostatic complexation of beta–lactoglobulin aggregates with kappa–carrageenan and the resulting emulsifying and foaming properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 8709–8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.F.; Oey, I.; Bremer, P.; Carne, A.; Silcock, P. Effects of pH, temperature and pulsed electric fields on the turbidity and protein aggregation of ovomucin-depleted egg white. Food Res. Int. 2017, 91, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasahara, K.; Yagi, H.; Naiki, H.; Goto, Y. Heat-induced Conversion of β2-Microglobulin and Hen Egg-white Lysozyme into Amyloid Fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Items | EWL | EWL + XG | EWL + CA | EWL + GG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of foam | 22 | 57 | 49 | 169 |
| Average area of foam/mm2 | 0.127 ± 0.141 a | 0.052 ± 0.040 b | 0.120 ± 0.144 a | 0.022 ± 0.062 b |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, S.; Shi, X.; Zheng, J.; Dai, R.; Li, J.; Xu, G.; Li, X. Effect of Xanthan Gum, Kappa–Carrageenan, and Guar Gum on the Functional Characteristics of Egg White Liquid and Intermolecular Interaction Mechanism. Foods 2022, 11, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142119
Gong S, Shi X, Zheng J, Dai R, Li J, Xu G, Li X. Effect of Xanthan Gum, Kappa–Carrageenan, and Guar Gum on the Functional Characteristics of Egg White Liquid and Intermolecular Interaction Mechanism. Foods. 2022; 11(14):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142119
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Sijia, Xuefeng Shi, Jiangxia Zheng, Ruitong Dai, Junying Li, Guiyun Xu, and Xingmin Li. 2022. "Effect of Xanthan Gum, Kappa–Carrageenan, and Guar Gum on the Functional Characteristics of Egg White Liquid and Intermolecular Interaction Mechanism" Foods 11, no. 14: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142119
APA StyleGong, S., Shi, X., Zheng, J., Dai, R., Li, J., Xu, G., & Li, X. (2022). Effect of Xanthan Gum, Kappa–Carrageenan, and Guar Gum on the Functional Characteristics of Egg White Liquid and Intermolecular Interaction Mechanism. Foods, 11(14), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11142119





