The Role of the Emotional Sequence in the Communication of the Territorial Cheeses: A Neuromarketing Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Hypotheses
2.2. Instrumentation
2.3. Study Population and Experimental Protocol
- ;
- ;
- Total sample size = 40;
- Number of groups = 2;
- Correlation among the repeated measures = 0.5;
- Nonsphericity correction = 1.
2.4. Video Segmentation
2.5. EEG Processing
2.6. SC and PPG Processing
2.7. Baseline Normalisation
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. EEG-Related Indices
3.2. SC- and BVP-Related Indices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Video Description
Appendix A.1. Rewind
Appendix A.2. The Myth
References
- Russo, V.; Milani Marin, L.E.; Fici, A.; Bilucaglia, M.; Circi, R.; Rivetti, F.; Bellati, M.; Zito, M. Strategic communication and neuromarketing in the fisheries sector: Generating ideas from the territory. Front. Commun. 2021, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Zito, M.; Bilucaglia, M.; Circi, R.; Bellati, M.; Milani Marin, L.E.; Catania, E.; Licitra, G. Dairy Products with Certification Marks: The Role of Territoriality and Safety Perception on Intention to Buy. Foods 2021, 10, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Valentine, G. Consuming Geographies: We Are Where We Eat; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cacciolatti, L.A.; Garcia, C.C.; Kalantzakis, M. Traditional food products: The effect of consumers’ characteristics, product knowledge, and perceived value on actual purchase. J. Int. Food Agribus. Mark. 2015, 27, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaleix-Treguer, S.; Emlinger, C.; Gaigné, C.; Latouche, K. On the competitiveness effects of quality labels: Evidence from French cheese industry. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conférence of Agricultural Economists, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 28 July–2 August 2018; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wägeli, S.; Janssen, M.; Hamm, U. Organic consumers’ preferences and willingness-to-pay for locally produced animal products. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2016, 40, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryła, P. The role of appeals to tradition in origin food marketing. A survey among Polish consumers. Appetite 2015, 91, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilone, V.; De Lucia, C.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Contò, F. Policy developments of consumer’s acceptance of traditional products innovation: The case of environmental sustainability and shelf life extension of a PGI Italian cheese. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loo, E.J.; Grebitus, C.; Roosen, J. Explaining attention and choice for origin labeled cheese by means of consumer ethnocentrism. Food Qual. Prefer. 2019, 78, 103716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C. Culture, Intellectual Property and Territorial Rural Development. Sociol. Rural. 1998, 38, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R.P.; Gopinath, M.; Nyer, P.U. The role of emotions in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1999, 27, 184–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poels, K.; Dewitte, S. How to capture the heart? Reviewing 20 years of emotion measurement in advertising. J. Advert. Res. 2006, 46, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinski, P.; Fransen, M.L.; Tan, E.S. Predicting advertising effectiveness by facial expressions in response to amusing persuasive stimuli. J. Neurosci. Psychol. Econ. 2014, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, Z.; Verges, M. Freeze or flee? Negative stimuli elicit selective responding. Cognition 2008, 108, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeBlanc, V.R.; McConnell, M.M.; Monteiro, S.D. Predictable chaos: A review of the effects of emotions on attention, memory and decision making. Adv. Health Sci. Educ. 2015, 20, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otamendi, F.J.; Sutil Martín, D.L. The emotional effectiveness of advertisement. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labroo, A.A.; Ramanathan, S. The influence of experience and sequence of conflicting emotions on ad attitudes. J. Consum. Res. 2007, 33, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M. The effect of sequential structure in charity advertising on message elaboration and donation intention: The mediating role of empathy. J. Promot. Manag. 2021, 27, 177–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, P.; Oceja, L. Drawing mixed emotions: Sequential or simultaneous experiences? Cogn. Emot. 2007, 21, 422–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R. Individual characteristics and the arousal of mixed emotions: Consequences for the effectiveness of charity fundraising advertisements. Int. J. Nonprofit Volunt. Sect. Mark. 2015, 20, 188–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.; Ford, J.B.; Sargeant, A. Charitable organizations’ storytelling influence on donors’ emotions and intentions. J. Bus. Res. 2010, 63, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.; Hinrichs, C. Buying into ‘buy local’: Engagements of United States local food initiatives. In Alternative Food Geographies: Representation and Practice; Emerald: Bingley, UK, 2007; pp. 255–272. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.S. Local food campaign in a globalization context: A systematic review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ittersum, K.; Meulenberg, M.T.; Van Trijp, H.C.; Candel, M.J. Consumers’ appreciation of regional certification labels: A Pan-European study. J. Agric. Econ. 2007, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimbo, F.; Roselli, L.; Carlucci, D.; de Gennaro, B.C. Consumer Misuse of Country-of-Origin Label: Insights from the Italian Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Market. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, R.G.; Harrison, G.W.; Rutström, E.E. Homegrown values and hypothetical surveys: Is the dichotomous choice approach incentive-compatible? Am. Econ. Rev. 1995, 85, 260–266. [Google Scholar]
- Nisbett, R.E.; Wilson, T.D. Telling more than we can know: Verbal reports on mental processes. Psychol. Rev. 1977, 84, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, P.; Hall, L.; Sikström, S.; Tärning, B.; Lind, A. How something can be said about telling more than we can know: On choice blindness and introspection. Conscious. Cogn. 2006, 15, 673–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeley, S.M.; Cronley, M.L. When Research Participants Don’t Tell It like It Is: Pinpointing the Effects of Social Desirability Bias Using Self vs. Indirect-Questioning; ACR North American Advances: Duluth, MN, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Smithson, J. Using and analysing focus groups: Limitations and possibilities. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2000, 3, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- List, J.A.; Gallet, C.A. What Experimental Protocol Influence Disparities Between Actual and Hypothetical Stated Values? Environ. Resour. Econ. 2001, 20, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellion, G.; Markham, S.K. Perspective: New Product Failure Rates: Influence of Argumentum ad Populum and Self-Interest. J. Prod. Innov. Manag. 2012, 30, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.M. Marketing Research and the New Product Failure Rate. J. Mark. 1977, 41, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, A.; Levy, D.J. A gateway to consumers’ minds: Achievements, caveats, and prospects of electroencephalography-based prediction in neuromarketing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2019, 10, e1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Broderick, A.J.; Chamberlain, L. What is ‘neuromarketing’? A discussion and agenda for future research. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2007, 63, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsøy, T.Z. Building a foundation for neuromarketing and consumer neuroscience research: How researchers can apply academic rigor to the neuroscientific study of advertising effects. J. Advert. Res. 2019, 59, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.C.; Reimann, M. Data Triangulation in Consumer Neuroscience: Integrating Functional Neuroimaging With Meta-Analyses, Psychometrics, and Behavioral Data. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 550204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plassmann, H.; Weber, B. Individual differences in marketing placebo effects: Evidence from brain imaging and behavioral experiments. J. Mark. Res. 2015, 52, 493–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, M.Y.T. RETRACTED: Cognitive systems research for neuromarketing assessment on evaluating consumer learning theory with fMRI: Comparing how two Word-Of-Mouth strategies affect the human brain differently after a product harm crisis. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2018, 49, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmarkar, U.R.; Plassmann, H. Consumer neuroscience: Past, present, and future. Organ. Res. Methods 2019, 22, 174–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmarkar, U.R.; Yoon, C. Consumer neuroscience: Advances in understanding consumer psychology. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2016, 10, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plassmann, H.; Venkatraman, V.; Huettel, S.; Yoon, C. Consumer Neuroscience: Applications, Challenges, and Possible Solutions. J. Mark. Res. 2015, 52, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Bernheim, B.D.; Camerer, C.F.; Rangel, A. Neural Activity Reveals Preferences without Choices. Am. Econ. J. Microecon. 2014, 6, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciceri, A.; Russo, V.; Songa, G.; Gabrielli, G.; Clement, J. A Neuroscientific Method for Assessing Effectiveness of Digital vs. Print Ads: Using Biometric Techniques to Measure Cross-Media Ad Experience and Recall. J. Advert. Res. 2020, 60, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Valesi, R.; Gallo, A.; Laureanti, R.; Zito, M. “The Theater of the Mind”: The Effect of Radio Exposure on TV Advertising. Soc. Sci. 2020, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, D.; Tur-Viñes, V.; Mengual, A. Neuromarketing Applied to Educational Toy Packaging. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missaglia, A.L.; Oppo, A.; Mauri, M.; Ghiringhelli, B.; Ciceri, A.; Russo, V. The impact of emotions on recall: An empirical study on social ads. J. Consum. Behav. 2017, 16, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, E.; Rossi, D.; Cartocci, G.; Perrotta, D.; Feo, P.D.; Mancini, M.; Aricò, P.; Inguscio, B.M.S.; Babiloni, F. Neurophysiological Profile of Antismoking Campaigns. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stasi, A.; Songa, G.; Mauri, M.; Ciceri, A.; Diotallevi, F.; Nardone, G.; Russo, V. Neuromarketing empirical approaches and food choice: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagan, N.M.; Pagan, K.M.; Teixeira, A.A.; de Moura Engracia Giraldi, J.; Stefanelli, N.O.; de Oliveira, J.H.C. Application of Neuroscience in the Area of Sustainability: Mapping the Territory. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2020, 21, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurier, P.; Fort, F.; Sirieix, L. Exploring terroir product meanings for the consumer. Anthropol. Food 2005, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biasi, R.; Brunori, E.; Smiraglia, D.; Salvati, L. Linking traditional tree-crop landscapes and agro-biodiversity in central Italy using a database of typical and traditional products: A multiple risk assessment through a data mining analysis. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 3009–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherubino, P.; Martinez-Levy, A.C.; Caratù, M.; Cartocci, G.; Flumeri, G.D.; Modica, E.; Rossi, D.; Mancini, M.; Trettel, A. Consumer Behaviour through the Eyes of Neurophysiological Measures: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2019, 2019, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilucaglia, M.; Laureanti, R.; Zito, M.; Circi, R.; Fici, A.; Russo, V.; Mainardi, L. It’s a Question of Methods: Computational Factors Influencing the Frontal Asymmetry in Measuring the Emotional Valence. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Mexico City, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 575–578. [Google Scholar]
- Eddie Harmon-Jones, E.; Gable, P.A.; Peterson, C. The role of asymmetric frontal cortical activity in emotion-related phenomena: A review and update. Biol. Psychol. 2010, 84, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, C.; Mangels, J.A. Coherent theta-band EEG activity predicts item-context binding during encoding. NeuroImage 2005, 24, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiato, G.; Babiloni, F.; Astolfi, L.; Toppi, J.; Vecchiato, G.; Astolfi, L.; Cherubino, P.; Dai, J.; Kong, W.; Wei, D. Enhance of theta EEG spectral activity related to the memorization of commercial advertisings in Chinese and Italian subjects. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI), Shanghai, China, 15–17 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mauss, I.B.; Robinson, M.D. Measures of emotion: A review. Cogn. Emot. 2009, 23, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchiato, G.; Maglione, A.G.; Cherubino, P.; Wasikowska, B.; Wawrzyniak, A.; Latuszynska, A.; Latuszynska, M.; Nermend, K.; Graziani, I.; Leucci, M.R.; et al. Neurophysiological tools to investigate consumer’s gender differences during the observation of TV commercials. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2014, 2014, 912981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuwer, M.R. 10-10 electrode system for EEG recording. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilucaglia, M.; Masi, R.; Stanislao, G.D.; Laureanti, R.; Fici, A.; Circi, R.; Zito, M.; Russo, V. ESB: A low-cost EEG Synchronization Box. HardwareX 2020, 8, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.R.; Sullivan, L.; Sabau, D.; San-Juan, D.; Dombrowski, K.E.; Halford, J.J.; Hani, A.J.; Drislane, F.W.; Stecker, M.M. American Clinical Neurophysiology Society Guideline 1. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 33, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friard, O.; Gamba, M. BORIS: A free, versatile open-source event-logging software for video/audio coding and live observations. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Medica 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laureanti, R.; Bilucaglia, M.; Zito, M.; Circi, R.; Fici, A.; Rivetti, F.; Valesi, R.; Wahl, S.; Mainardi, L.T.; Russo, V. Yellow (Lens) Better: Bioelectrical and Biometrical Measures to Assess Arousing and Focusing Effects. In Proceedings of the 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Mexico City, Mexico, 1–5 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.Y.; Hsu, S.H.; Pion-Tonachini, L.; Jung, T.P. Evaluation of Artifact Subspace Reconstruction for Automatic Artifact Components Removal in Multi-Channel EEG Recordings. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 67, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urigüen, J.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B. EEG artifact removal—State-of-the-art and guidelines. J. Neural Eng. 2015, 12, 031001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pion-Tonachini, L.; Kreutz-Delgado, K.; Makeig, S. ICLabel: An automated electroencephalographic independent component classifier, dataset, and website. NeuroImage 2019, 198, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayser, J.; Tenke, C.E. On the benefits of using surface Laplacian (current source density) methodology in electrophysiology. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2015, 97, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Flumeri, G.D.; Sciaraffa, N.; Babiloni, F. Correlation and Similarity between Cerebral and Non-Cerebral Electrical Activity for User’s States Assessment. Sensors 2019, 19, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, J.J.; Cohen, M.X. Deconstructing the “resting” state: Exploring the temporal dynamics of frontal alpha asymmetry as an endophenotype for depression. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2010, 4, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilucaglia, M.; Laureanti, R.; Zito, M.; Circi, R.; Fici, A.; Rivetti, F.; Valesi, R.; Wahl, S.; Russo, V. Looking through blue glasses: Bioelectrical measures to assess the awakening after a calm situation. In Proceedings of the 2019 41st Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 July 2019; pp. 526–529. [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner, I.R.; Jones, R.M.; Wilder-Smith, O.; Wormwood, J.B.; Akcakaya, M.; Quigley, K.S.; Lord, C.; Goodwin, M.S. Simple, Transparent, and Flexible Automated Quality Assessment Procedures for Ambulatory Electrodermal Activity Data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 65, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.; Valenza, G.; Lanata, A.; Scilingo, E.P.; Citi, L. CvxEDA: A convex optimization approach to electrodermal activity processing. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, BME-32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zito, M.; Fici, A.; Bilucaglia, M.; Ambrogetti, F.S.; Russo, V. Assessing the emotional response in social communication: The role of neuromarketing. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 625570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zito, M.; Bilucaglia, M.; Fici, A.; Gabrielli, G.; Russo, V. Job Assessment Through Bioelectrical Measures: A Neuromanagement Perspective. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 673012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, J.; Selker, R.; Marsman, M.; Jamil, T.; Dropmann, D.; Verhagen, J.; Ly, A.; Gronau, Q.F.; Šmíra, M.; Epskamp, S.; et al. JASP: Graphical statistical software for common statistical designs. J. Stat. Softw. 2019, 88, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verma, J.P. Repeated Measures Design for Empirical Researchers; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Valenza, G.; Greco, A.; Gentili, C.; Lanata, A.; Sebastiani, L.; Menicucci, D.; Gemignani, A.; Scilingo, E. Combining electroencephalographic activity and instantaneous heart rate for assessing brain–heart dynamics during visual emotional elicitation in healthy subjects. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winkler, I.; Jager, M.; Mihajlović, V.; Tsoneva, T. Frontal EEG Asymmetry Based Classification of Emotional Valence using Common Spatial Patterns. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. Int. J. Med. Health Biomed. Bioeng. Pharm. Eng. 2010, 4, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Harmon-Jones, E.; Allen, J.J.B. Anger and frontal brain activity: EEG asymmetry consistent with approach motivation despite negative affective valence. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1998, 74, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Ciorciari, J.; van Laer, T. Using EEG to examine the role of attention, working memory, emotion, and imagination in narrative transportation. Eur. J. Mark. 2018, 52, 92–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slater, M.D.; Rouner, D. Entertainment—Education and elaboration likelihood: Understanding the processing of narrative persuasion. Commun. Theory 2002, 12, 173–191. [Google Scholar]
- Pedale, T.; Santangelo, V. Perceptual salience affects the contents of working memory during free-recollection of objects from natural scenes. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrican, R.; Moscovitch, M.; Schimmack, U. Cognitive resources, valence, and memory retrieval of emotional events in older adults. Psychol. Aging 2008, 23, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbruzzese, L.; Magnani, N.; Robertson, I.H.; Mancuso, M. Age and gender differences in emotion recognition. Front. Psychol. 2021, 10, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Graves, L.V.; Moreno, C.C.; Seewald, M.; Holden, H.M.; Van Etten, E.J.; Uttarwar, V.; McDonald, C.R.; Delano-Wood, L.; Bondi, M.W.; Woods, S.P.; et al. Effects of age and gender on recall and recognition discriminability. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2017, 32, 972–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Theme | Video | M | SD | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | M | 0.001 | 0.251 | 18 |
| R | −0.015 | 0.687 | 17 | |
| Pr | M | −0.028 | 0.307 | 18 |
| R | −0.310 | 0.365 | 17 | |
| Prd | M | 0.021 | 0.515 | 18 |
| R | −0.076 | 0.347 | 17 | |
| Tr | M | 0.230 | 0.481 | 18 |
| R | −0.420 | 0.480 | 17 |
| Theme | Video | M | SD | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | M | 0.087 | 0.735 | 16 |
| R | −1.090 | 0.906 | 16 | |
| Pr | M | −0.310 | 0.538 | 16 |
| R | −0.970 | 0.866 | 16 | |
| Prd | M | 0.316 | 0.513 | 16 |
| R | −1.081 | 0.803 | 16 | |
| Tr | M | 0.232 | 1.241 | 16 |
| R | −0.324 | 1.514 | 16 |
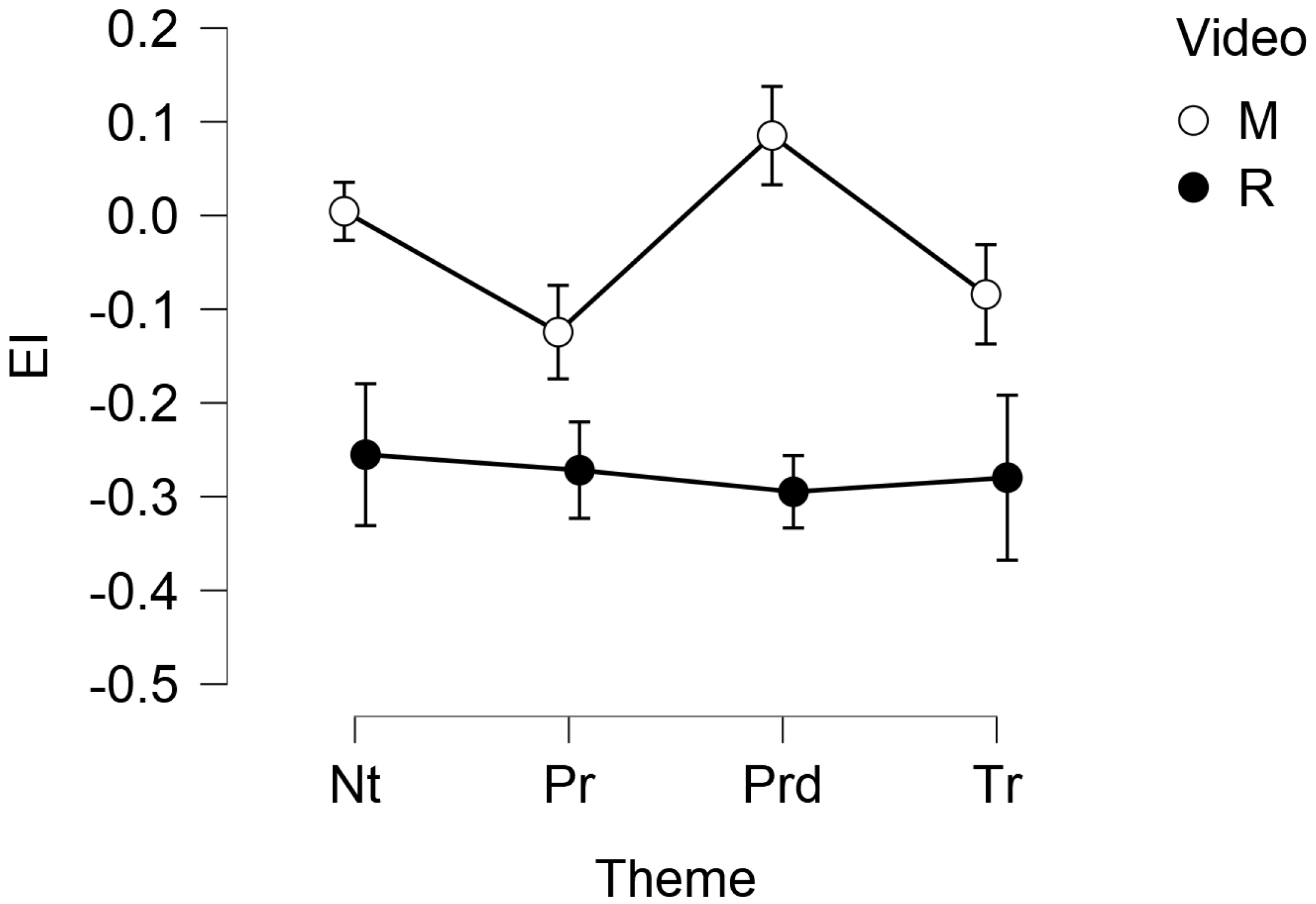
| Theme | Video | M | SD | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nt | M | 0.005 | 0.178 | 16 |
| R | −0.255 | 0.345 | 17 | |
| Pr | M | −0.124 | 0.129 | 16 |
| R | −0.272 | 0.352 | 17 | |
| Prd | M | 0.085 | 0.224 | 16 |
| R | −0.295 | 0.286 | 17 | |
| Tr | M | −0.084 | 0.273 | 16 |
| R | −0.280 | 0.581 | 17 |
| Research Hypothesis | Metric | Direction | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| H1 * | AWI | M > R | n.s. |
| HR | M > R | 0.045 | |
| EI | M > R | 0.009 | |
| H2 | AWI | Nt > Nt | n.s. |
| Prd > Prd | n.s. | ||
| Tr > Tr | n.s. | ||
| HR | Nt > Nt | n.s. | |
| Prd > Prd | n.s. | ||
| Tr > Tr | n.s. | ||
| EI | Nt > Nt | n.s. | |
| Prd > Prd | n.s. | ||
| Tr > Tr | n.s. | ||
| H3 | AWI | Pr > Pr | n.s. |
| HR | Pr > Pr | n.s. | |
| EI | Pr > Pr | n.s. | |
| H4 † | MI | M > R | 0.025 |
| H5 * | MI | Nt > Nt | n.s. |
| Prd > Prd | n.s. | ||
| Tr > Tr | 0.001 | ||
| H6 | MI | Pr > Pr | n.s. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, V.; Bilucaglia, M.; Circi, R.; Bellati, M.; Valesi, R.; Laureanti, R.; Licitra, G.; Zito, M. The Role of the Emotional Sequence in the Communication of the Territorial Cheeses: A Neuromarketing Approach. Foods 2022, 11, 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152349
Russo V, Bilucaglia M, Circi R, Bellati M, Valesi R, Laureanti R, Licitra G, Zito M. The Role of the Emotional Sequence in the Communication of the Territorial Cheeses: A Neuromarketing Approach. Foods. 2022; 11(15):2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152349
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Vincenzo, Marco Bilucaglia, Riccardo Circi, Mara Bellati, Riccardo Valesi, Rita Laureanti, Giuseppe Licitra, and Margherita Zito. 2022. "The Role of the Emotional Sequence in the Communication of the Territorial Cheeses: A Neuromarketing Approach" Foods 11, no. 15: 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152349
APA StyleRusso, V., Bilucaglia, M., Circi, R., Bellati, M., Valesi, R., Laureanti, R., Licitra, G., & Zito, M. (2022). The Role of the Emotional Sequence in the Communication of the Territorial Cheeses: A Neuromarketing Approach. Foods, 11(15), 2349. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11152349








