Impact of Feeding Probiotics on Blood Parameters, Tail Fat Metabolites, and Volatile Flavor Components of Sunit Sheep
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments and Feeding Methods
2.2. Sample Collection at Slaughter
2.3. Determination of Blood Lipid Parameters in Sunit Sheep
2.4. Lipid Metabolism Genes in the Sunit Sheep Crude Tail Fat
2.4.1. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR
2.4.2. Quantitative PCR
2.5. Determination of Sunit Sheep Crude Tail Fat Metabolites
2.5.1. LC-MS Analysis of Tail Fat Metabolites
2.5.2. Tail Fat Metabolite Analysis
2.5.3. Functional Predictive Analysis of Tail Fat Metabolites
2.6. Determination of Volatile Flavor Compounds in Tail Fat
2.7. Statistical Analysis of Experimental Data
3. Results
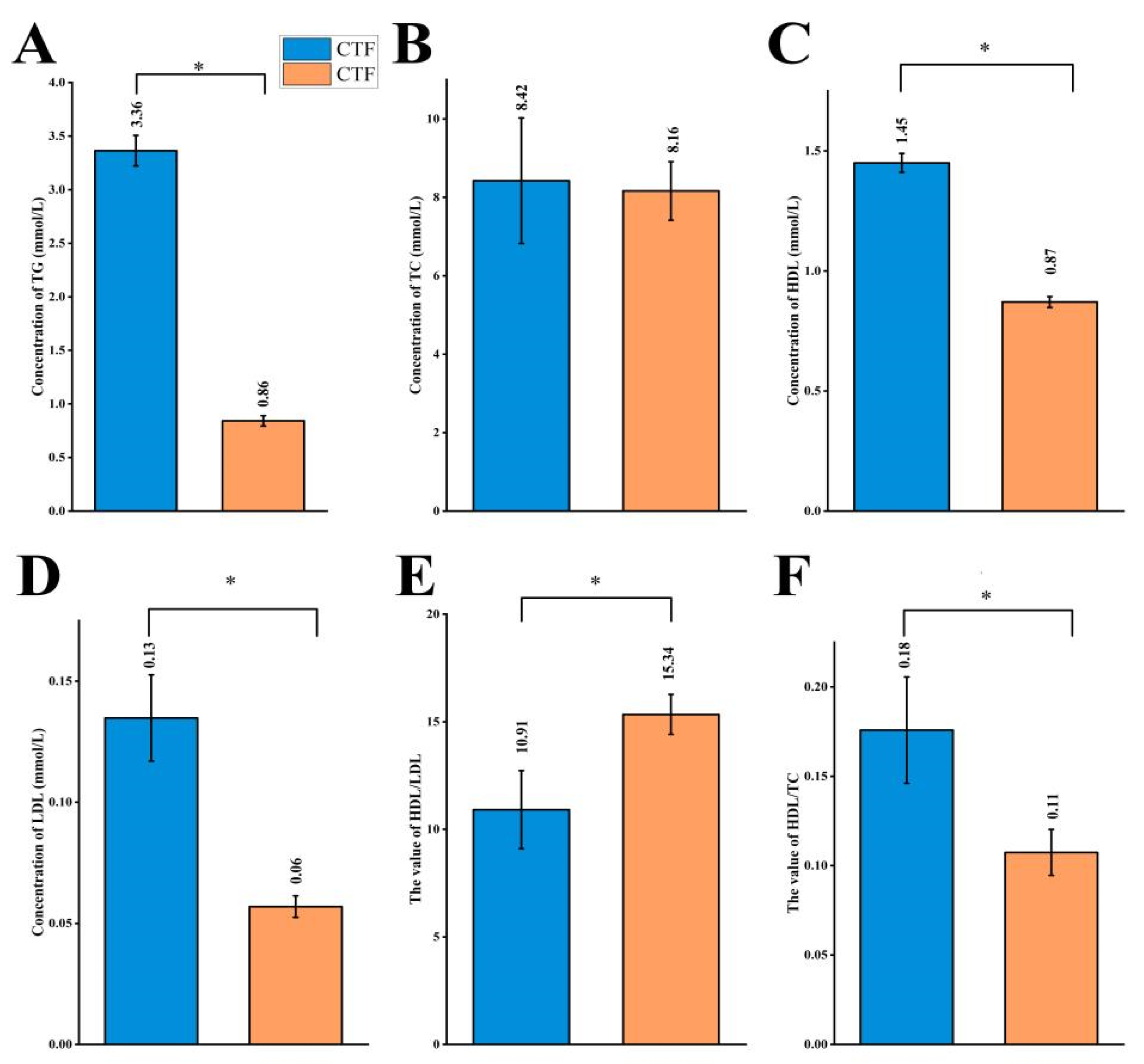
3.1. Effects of Probiotics on Plasma Lipid Profiles
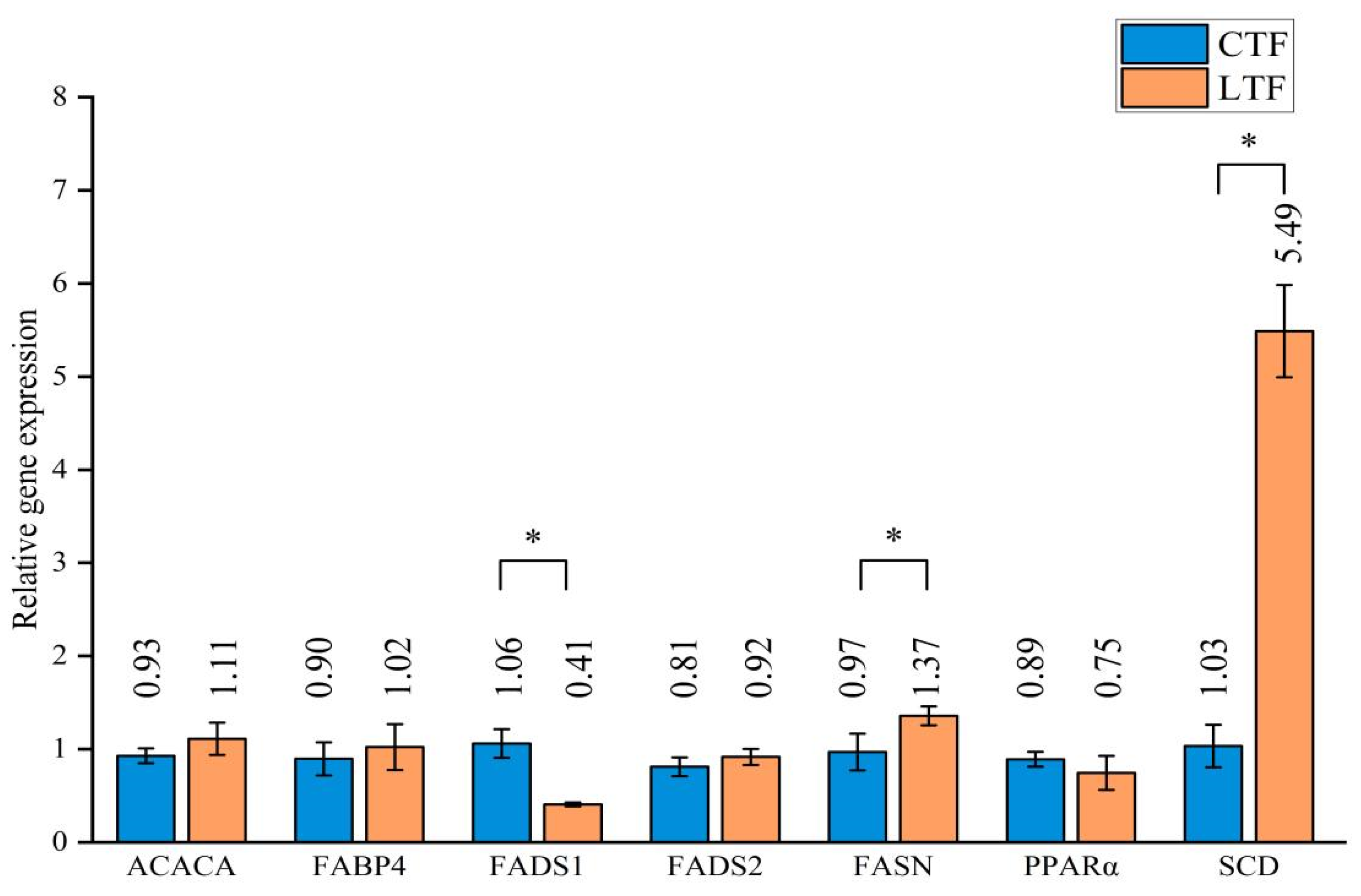
3.2. Effects of Probiotics on Lipid Metabolism Genes in Tail Fat
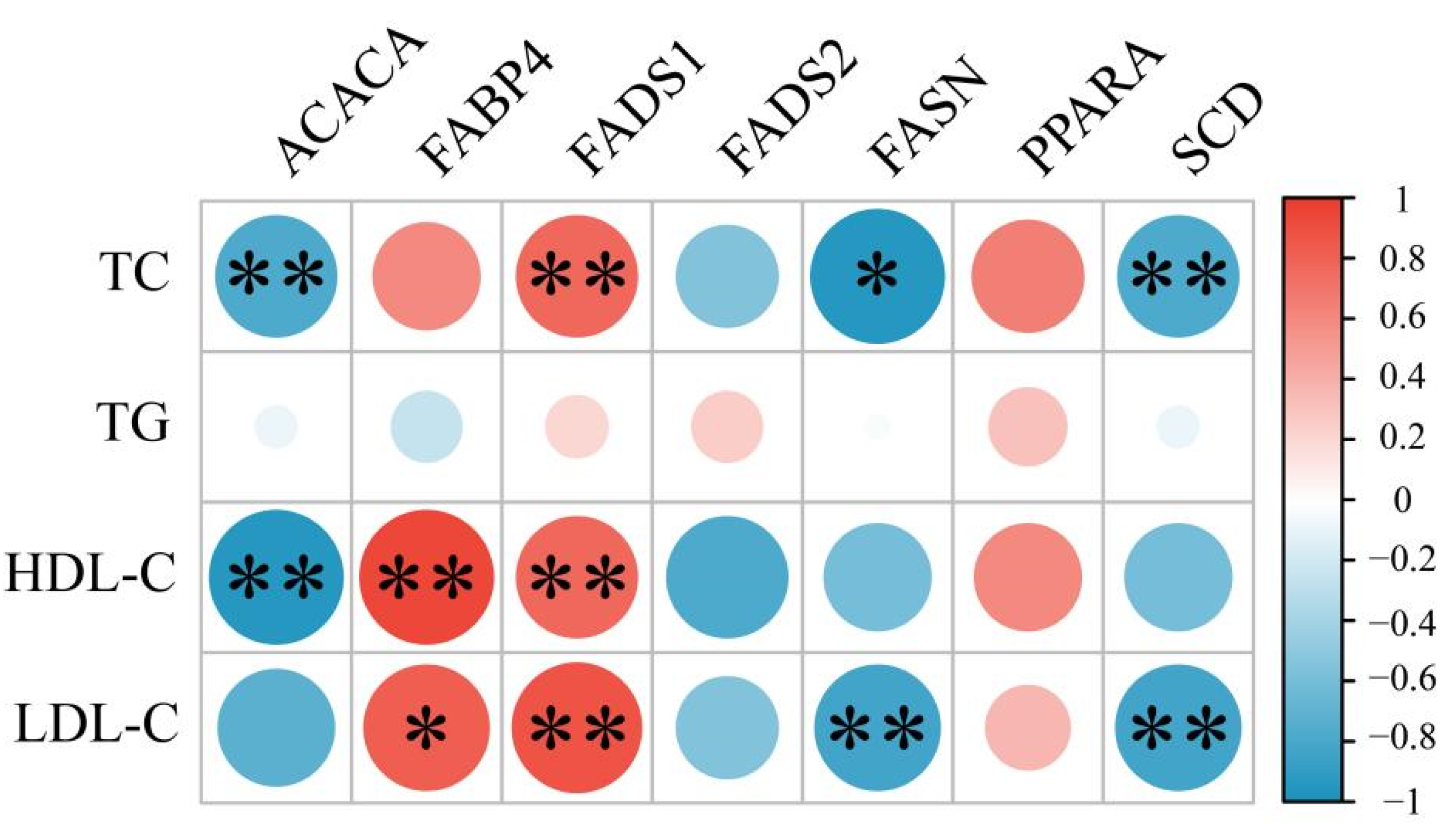
3.3. Correlations between Blood lipid Parameters and Lipid Metabolism Genes
3.4. Effects of Probiotics on Sheep Crude Tail Fat Metabolites
3.4.1. Screening for Differential Metabolites
3.4.2. Lipid Metabolite Correlation Analysis
3.4.3. KEGG Annotation and Metabolic Pathway Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.5. Volatile Flavor Compounds in Tail Fat
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Luo, Y.; Su, R.; Su, L.; Zhao, L.; Jin, Y. Effects of feeding regimens on meat quality, fatty acid composition and metabolism as related to gene expression in Chinese Sunit sheep. Small Rumin. Res. 2018, 169, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdarian, M.; Zamiri, M.J.; Hashemi, M.; Noorolahi, H. Relationships of fat-tail dimensions with fat-tail weight and carcass characteristics at different slaughter weights of Torki-Ghashghaii sheep. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Liu, E.; Liu, Z.; Kijas, J.W.; Zhu, C.; Hu, S.; Ma, X.; Zhang, L.; Du, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Selection signature analysis reveals genes associated with tail type in Chinese indigenous sheep. Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Pu, D.D.; Hao, Z.L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.Y. The Effect of Prickly Ash (Zanthoxylum Bungeanum Maxim) on the Taste Perception of Stewed Sheep Tail Fat by LC-QTOF-MS/MS and a Chemometrics Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, J.; Kang, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of dietary nutrition on tail fat deposition and evaluation of tail-related genes in fat-tailed sheep. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 46, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arowolo, M.A.; He, J. Use of probiotics and botanical extracts to improve ruminant production in the tropics: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Song, L.; Huang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Zhu, S.; Lu, S.; Hou, L.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Effect of Lactobacillus Plantarum HT121 on Serum Lipid Profile, Gut Microbiota, and Liver Transcriptome and Metabolomics in a Highcholesterol Diet-Induced Hypercholesterolemia Rat Model. Nutrition 2020, 79–80, 110966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Nie, S.-P.; Zhu, K.-X.; Ding, Q.; Li, C.; Xiong, T.; Xie, M.-Y. Lactobacillus plantarum NCU116 improves liver function, oxidative stress and lipid metabolism in rats with high fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Su, F.; Yao, G.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum P-8 on lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic rat model. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2012, 114, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottram, D.S. Flavour formation in meat and meat a review products. Food Chem. 1998, 62, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, C.; Su, R.; Hou, Y.; Yao, D.; Zhao, L.; Su, L.; Jin, Y. Meat quality, fatty acids, volatile compounds, and antioxidant properties of lambs fed pasture versus mixed diet. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2796–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherratt, S.C.R.; Juliano, R.A.; Mason, R.P. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) has optimal chain length and degree of unsaturation to inhibit oxidation of small dense LDL and membrane cholesterol domains as compared to related fatty acids in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, G.; Adegoke, O.A.J. Effects of ketoisocaproic acid and inflammation on glucose transport in muscle cells. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Jiao, N.; Qiu, K.; Yin, J. Surplus dietary isoleucine intake enhanced monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis and fat accumulation in skeletal muscle of finishing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminlari, L.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Nazifi, S.; Sajedianfard, J.; Eskandari, M.H. Effect of Probiotics Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus plantarum on Lipid Profile and Feces Bacteria of Rats Fed Cholesterol-Enriched Diet. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.T.; Kang, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Characterization of Lactobacillus plantarum PH04, a potential probiotic bacterium with cholesterol-lowering effects. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 113, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratna Sudha, M.; Chauhan, A.; Dixit, K.; Babu, S.; Jamil, K. Probiotics as complementary therapy for hypercholesterolemia. Biol. Med. 2009, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Anno, M.; Callegari, M.L.; Reggi, S.; Caprarulo, V.; Giromini, C.; Spalletta, A.; Coranelli, S.; Sgoifo Rossi, C.A.; Rossi, L. Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus reuteri as Functional Feed Additives to Prevent Diarrhoea in Weaned Piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, A.; Buttarazzi, I.; Kolida, S.; Quercia, S.; Baldini, J.; Swann, J.R.; Brigidi, P.; Gibson, G.R. An in vivo assessment of the cholesterol-lowering efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum ECGC 13110402 in normal to mildly hypercholesterolaemic adults. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guan, W.; Piao, C.; Wang, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum LP104 ameliorates hyperlipidemia induced by AMPK pathways in C57BL/6N mice fed high-fat diet. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, P.S.; Loke, C.F.; Ho, Y.W.; Tan, H.Y. Cholesterol homeostasis associated with probiotic supplementationin vivo. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1374–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Costa Alvarenga, T.I.; Chen, Y.; Lewandowski, P.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Sadiq, S.; Clayton, E.H.; van de Ven, R.J.; Olalquiaga Perez, J.R.; Hopkins, D.L. The expression of genes encoding enzymes regulating fat metabolism is affected by maternal nutrition when lambs are fed algae high in omega-3. Livest. Sci. 2016, 187, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Ballantyne, C.M. Dietary and Pharmacological Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Health. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 1030–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, A.; Yamane, M.; Yamada, H.; Sugawara, I. The omega-hydroxy palmitic acid induced apoptosis in human lung carcinoma cell lines H596 and A549. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys. JBMBB Off. J. Fed. Asian Ocean. Biochem. Mol. Biol. (FAOBMB) 2002, 6, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.-J.; Cao, H.-X.; Yang, R.-X.; Zhang, R.-N.; Pan, Q. PNPLA3 rs139051 is associated with phospholipid metabolite profile and hepatic inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Clin. Cases 2018, 6, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazueta, C.; Buelna-Chontal, M.; Macias-Lopez, A.; Roman-Anguiano, N.G.; Gonzalez-Pacheco, H.; Pavon, N.; Springall, R.; Aranda-Frausto, A.; Bojalil, R.; Silva-Palacios, A.; et al. Cytidine-5 ’-Diphosphocholine Protects the Liver From Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Preserving Mitochondrial Function and Reducing Oxidative Stress. Liver Transplant. 2018, 24, 1070–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata-Perez, R.; Wanders, R.J.A.; van Karnebeek, C.D.M.; Houtkooper, R.H. NAD(+) homeostasis in human health and disease. Embo Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, S.; Zerrouk, N.; Aussel, C.; Moinard, C.; Crenn, P.; Curis, E.; Chaumeil, J.-C.; Cynober, L.; Sfar, S. Citrulline: From metabolism to therapeutic use. Nutrition 2013, 29, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.E.; Weiser, J.N. Microbial Modulation of Host Immunity with the Small Molecule Phosphorylcholine. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, J.; Ai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X. Theoretical Studies on the Photophysics and Photochemistry of 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine: The Oxidative Products of Epigenetic Modification of Cytosine in DNA. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2704–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Tu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Deng, K.; El-Samahy, M.A.; You, P.; Fan, Y.; Wang, F. gamma-Linolenic Acid Prevents Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Palmitic Acid-Treated Alpha Mouse Liver-12 Cells by Balancing Autophagy and Apoptosis via the LKB1-AMPK-mTOR Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8257–8267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.-M.; Chao, L.K.; Wu, C.-S.; Ye, Z.-S.; Chen, H.-C. Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction Analysis of Volatile Components in Peanut Oil. Molecules 2021, 26, 3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, S.; Setyabrata, D.; Bonham, C.C.; Kim, Y.H.B. Evaluation of functional and chemical properties of crust from dry-aged beef loins as a novel food ingredient. Meat Sci. 2021, 173, 108403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Sowndhararajan, K.; Choi, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Kim, S. Olfactory Stimulation Effect of Aldehydes, Nonanal, and Decanal on the Human Electroencephalographic Activity, According to Nostril Variation. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.-B.; Xiang, X.-F.; Yang, W.-X.; Zhu, B.-Q.; Pu, H.-T.; Duan, C.-Q. Characterization of Free and Glycosidically Bound Volatile Compounds, Fatty Acids, and Amino Acids InVitis DavidiiFoex Grape Species Native to China. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.M.; van Gorkom, L.C.; Watts, A. Partitioning Behaviour of 1-Hexanol into Lipid Membranes as Studied by Deuterium NMR Spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1069, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, I.S.; Jones, P.R. Photosynthesis-Dependent Biosynthesis of Medium Chain-Length Fatty Acids and Alcohols. Metab. Eng. 2018, 49, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phi, N.T.L.; Nishiyama, C.; Choi, H.S.; Sawamura, M. Evaluation of Characteristic Aroma Compounds of Citrus Natsudaidai Hayata (Natsudaidai) Cold-Pressed Peel Oil. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1832–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, L.; Brown, P.D. Effects of octane derivatives on activity of the volume-regulated anion channel in rat pancreatic beta-cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 1317–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altinoz, M.A.; Ozpinar, A.; Seyfried, T.N. Caprylic (Octanoic) Acid as a Potential Fatty Acid Chemotherapeutic for Glioblastoma. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2020, 159, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebiere, L.; Clark, A.C.; Schmidtke, L.M.; Prenzler, P.D.; Scollary, G.R. A robust method for quantification of volatile compounds within and between vintages using headspace-solid-phase micro-extraction coupled with GC-MS—Application on Semillon wines. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 660, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

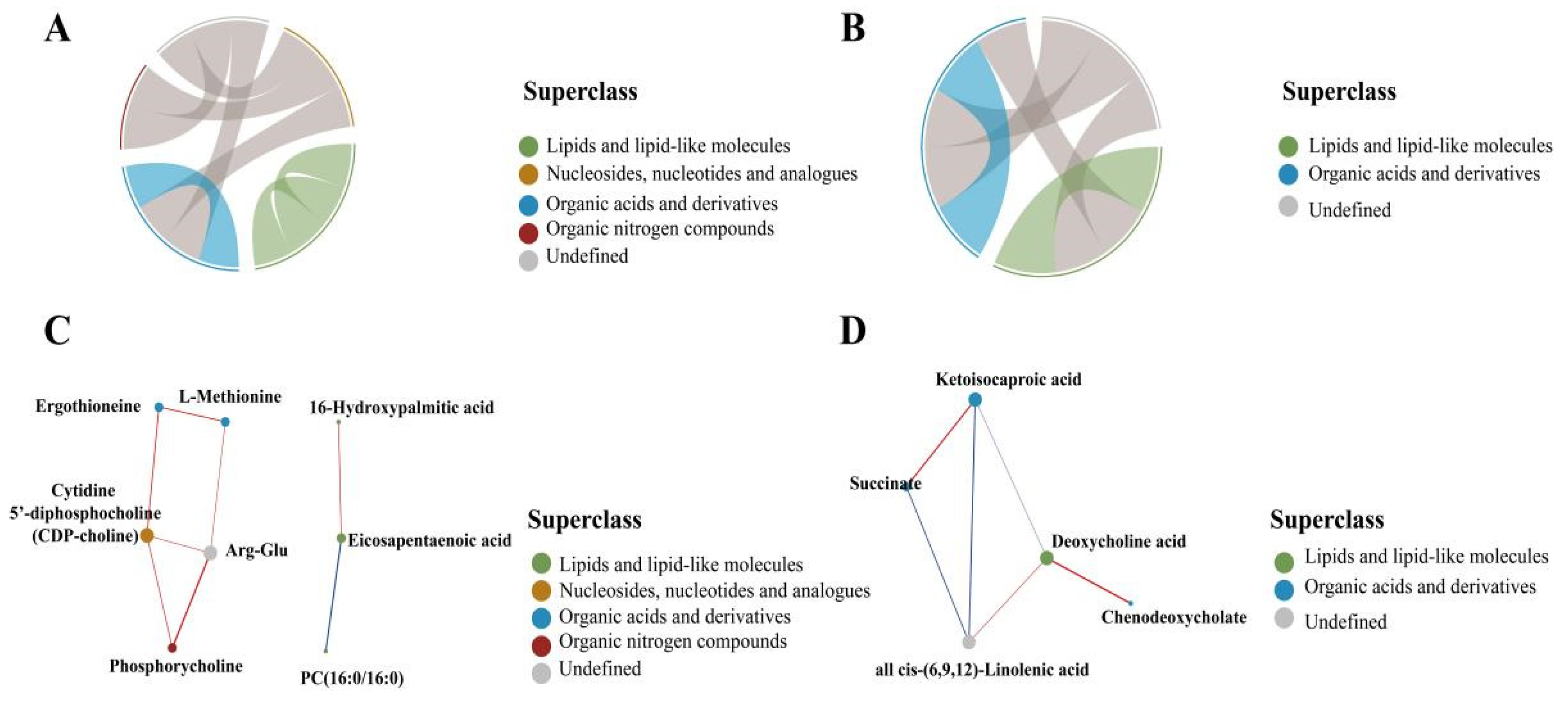
| No | RT (min) | Metabolites | VIP | m/z | Adduct Ion | L/C Group | Pathways |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 1.241 | Undecanoic acid | 2.954 | 185.154 | (M−H)− | ↓ * | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
| F2 | 4.624 | Deoxycholic acid | 1.700 | 391.2842 | (M−H)− | ↓ * | |
| F3 | 1.776 | Heptadecanoic acid | 2.496 | 269.2478 | (M−H)− | ↓ * | |
| F4 | 4.349 | Chenodeoxycholate | 2.568 | 391.2839 | (M−H)− | ↓ * | |
| F5 | 1.588 | Pelargonic acid | 1.555 | 157.1229 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | |
| F6 | 1.243 | Eicosapentaenoic acid | 1.855 | 303.2317 | (M+H)+ | ↑ ** | |
| F7 | 1.142 | 16-Hydroxypalmitic acid | 3.835 | 314.2689 | (M+CH3CN+H)+ | ↑ ** | |
| F8 | 5.177 | Hepatic phosphatidylcholine (PC) (16:0/16:0) | 2.661 | 756.553 | (M+Na)+ | ↓ ** | |
| F9 | 5.016 | Stearoylcarnitine | 3.836 | 428.373 | (M+H)+ | ↓ * | |
| F10 | 4.973 | (S)-(-)-Citronellic acid | 2.842 | 212.164 | (M+CH3CN+H)+ | ↑ * | |
| F11 | 7.779 | Guanosine | 2.038 | 282.084 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues |
| F12 | 14.752 | Cytidine 5’-diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) | 2.408 | 489.1145 | (M+H)+ | ↑ ** | |
| F13 | 15.236 | β-Nicotinamide D-ribonucleotide | 1.441 | 335.0636 | M+ | ↑ ** | |
| F14 | 12.195 | Succinate | 1.527 | 117.019 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | Organic acids and derivatives |
| F15 | 1.190 | Ketoisocaproic acid | 3.890 | 129.055 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | |
| F16 | 12.863 | L-Citrulline | 1.620 | 176.1026 | (M+H)+ | ↑ ** | |
| F17 | 10.823 | Ergothioneine | 1.271 | 230.096 | (M+H)+ | ↑ * | |
| F18 | 9.374 | L-Methionine | 1.097 | 150.058 | (M+H)+ | ↑ * | |
| F19 | 15.423 | Phosphorylcholine | 7.547 | 184.073 | (M+H)+ | ↑ ** | Organic nitrogen compounds |
| F20 | 9.199 | Choline | 2.583 | 104.106 | M+ | ↓ * | |
| F21 | 1.044 | 4-Pyridoxic acid | 2.435 | 182.045 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
| F22 | 6.880 | Cytosine | 1.274 | 112.050 | (M+H)+ | ↑ ** | |
| F23 | 70.79 | All cis-(6,9,12)-Linolenic acid | 9.573 | 277.217 | (M−H)− | ↓ ** | |
| F24 | 11.593 | D-gluconate | 1.517 | 195.051 | (M−H)− | ↑ * | Organic oxygen compounds |
| Compound (μg/1 kg) | CTF | LTF | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aldehydes | Hexanal | 25.23 ± 5.86 | 32.87 ± 14.97 | NS |
| Octanal | 46.91 ± 8.95 | 68.71 ± 11.69 | NS | |
| Nonanal | 151.72 ± 12.74 b | 241.19 ± 23.98 a | ** | |
| Decanal | 28.27 ± 2.55 b | 38.92 ± 3.70 a | * | |
| 2-Nonenal, (E)- | 19.33 ± 0.89 | 21.90 ± 1.67 | NS | |
| Alcohols | 1-Hexanol | 19.11 ± 2.06 b | 32.03 ± 4.43 a | * |
| 1-Octen-3-ol | 32.87 ± 5.57 | 40.27 ± 0.37 | NS | |
| 2-Octen-1-ol,(E)- | 22.92 ± 3.47 | 11.44 ± 4.79 | NS | |
| 1-Octanol | 18.42 ± 1.51 b | 31.89 ± 2.91 a | ** | |
| Acids | Octanoic acid | 25.62 ± 5.55 b | 51.93 ± 9.83 a | * |
| Nonanoic acid | 51.23 ± 17.48 | 98.15 ± 20.59 | NS | |
| Undecanoic acid | 32.41 ± 5.47 | 158.36 ± 64.89 | NS | |
| Esters | Allyl 2-ethyl butyrate | 41.37 ± 2.99 | 39.10 ± 2.26 | NS |
| Acetic acid, nonyl ester | 13.86 ± 0.78 | 15.50 ± 0.59 | NS | |
| Nonanoic acid, ethyl ester | 17.52 ± 1.12b | 26.00 ± 2.13a | * | |
| Octanoic acid, ethyl ester | 17.78 ± 4.86 | 21.88 ± 7.94 | NS | |
| Hexanoic acid, ethyl ester | 11.20 ± 1.55 | 14.30 ± 0.49 | NS | |
| Amines | Ethanolamine | 36.67 ± 5.67 | 23.71 ± 6.63 | NS |
| Aromatic hydrocarbons | Ethylbenzene | 197.68 ± 8.78 | 178.35 ± 5.06 | NS |
| Hydrocarbons | Styrene | 21.79 ± 7.62 | 20.79 ± 4.43 | NS |
| Longifolene | 14.98 ± 3.29 | 31.96 ± 6.73 | NS | |
| Limonene | 62.62 ± 5.46 b | 157.43 ± 18.55 a | ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Duan, Y.; Su, L.; Tian, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, B.; Jin, Y. Impact of Feeding Probiotics on Blood Parameters, Tail Fat Metabolites, and Volatile Flavor Components of Sunit Sheep. Foods 2022, 11, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172644
Liu T, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Yang L, Duan Y, Su L, Tian J, Sun L, Wang B, Jin Y. Impact of Feeding Probiotics on Blood Parameters, Tail Fat Metabolites, and Volatile Flavor Components of Sunit Sheep. Foods. 2022; 11(17):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172644
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ting, Taiwu Zhang, Yanni Zhang, Le Yang, Yan Duan, Lin Su, Jianjun Tian, Lina Sun, Bohui Wang, and Ye Jin. 2022. "Impact of Feeding Probiotics on Blood Parameters, Tail Fat Metabolites, and Volatile Flavor Components of Sunit Sheep" Foods 11, no. 17: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172644
APA StyleLiu, T., Zhang, T., Zhang, Y., Yang, L., Duan, Y., Su, L., Tian, J., Sun, L., Wang, B., & Jin, Y. (2022). Impact of Feeding Probiotics on Blood Parameters, Tail Fat Metabolites, and Volatile Flavor Components of Sunit Sheep. Foods, 11(17), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11172644





