Influence of Different Aggregation States on Volatile Organic Compounds Released by Dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains’ Origin
2.2. Cells Obtainment in MATS, Planktonic, and in Biofilm-Detached States
2.3. Volatile Organic Compounds Determination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
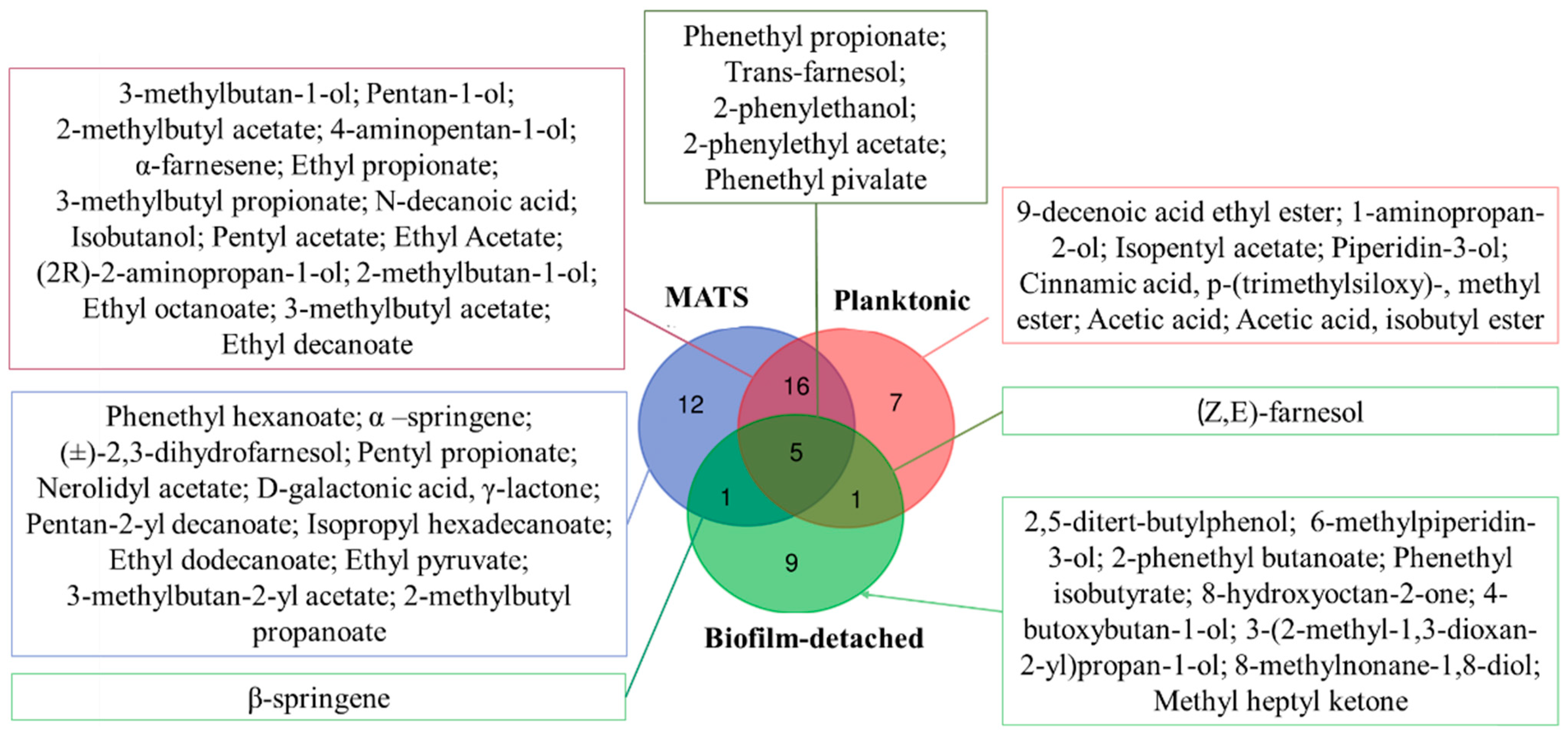
3.1. Complexity of K. marxianus Volatilome under Different Conditions
3.2. Klyveromyces Marxianus Strains’ Volatilome
3.3. PCA Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lukondeh, T.; Ashbolt, N.J.; Rogers, P.L. Evaluation of Kluyveromyces marxianus FII 510700 grown on a lactose-based medium as a source of a natural bioemulsifier. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spohner, S.C.; Schaum, V.; Quitmann, H.; Czermak, P. Kluyveromyces lactis: An emerging tool in biotechnology. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 222, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, A.; Gerliani, N.; Aïder, M. Kluyveromyces marxianus: An emerging yeast cell factory for applications in food and biotechnology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 333, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, J.A.; Gethins, L.; Stanton, C.; Ross, P.; Morrissey, J.P. Applications of Kluyveromyces marxianus in Biotechnology. In Yeast Diversity in Human Welfare; Satyanarayana, T., Kunze, G., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 439–453. [Google Scholar]
- Gardini, F.; Tofalo, R.; Belletti, N.; Iucci, L.; Suzzi, G.; Torriani, S.; Guerzoni, M.E.; Lanciotti, R. Characterization of yeasts involved in the ripening of Pecorino Crotonese cheese. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasoli, G.; Tofalo, R.; Lanciotti, R.; Schirone, M.; Patrignani, F.; Perpetuini, G.; Grazia, L.; Corsetti, A.; Suzzi, G. Chromosome arrangement, differentiation of growth kinetics and volatile molecule profiles in Kluyveromyces marxianus strains from Italian cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 214, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofalo, R.; Fasoli, G.; Schirone, M.; Perpetuini, G.; Pepe, A.; Corsetti, A.; Suzzi, G. The predominance, biodiversity and biotechnological properties of Kluyveromyces marxianus in the production of Pecorino di Farindola cheese. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 187, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, K.; Knudsen, P.B.; Nielsen, K.F.; Arneborg, N.; Jespersen, L. Alcohol-based quorum sensing plays a role in adhesion and sliding motility of the yeast Debaryomyces hansenii. FEMS Yeast Res. 2011, 11, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq-Perlat, M.N.; Corrieu, G.; Spinnler, H.E. Comparison of volatile compounds produced in model cheese medium deacidified by Debaryomyces hansenii or Kluyveromyces marxianus. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zara, G.; Budroni, M.; Mannazzu, I.; Fancello, F.; Zara, S. Yeast biofilm in food realms: Occurrence and control. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga, M.; Guerrero, R. Living together in biofilms: The microbial cell factory and its biotechnological implications. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppuluri, P.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Srinivasan, A.; Banerjee, M.; Ramasubramaniam, A.K.; Köhler, J.R.; Kadosh, D.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Dispersion as an important step in the Candida albicans biofilm developmental cycle. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 6, e1000828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollet, C.; Gal, L.; Guzzo, J. Biofilm-detached cells, a transition from a sessile to a planktonic phenotype: A comparative study of adhesion and physiological characteristics in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 290, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, C.; Gougeon, R.D.; Perepelkine, L.; Alexandre, H.; Guzzo, J.; Weidmann, S. Chemical transfers occurring through Oenococcus oeni biofilm in different enological conditions. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tofalo, R.; Battistelli, N.; Perpetuini, G.; Valbonetti, L.; Rossetti, A.P.; Perla, C.; Zulli, C.; Arfelli, G. Oenococcus oeni lifestyle modulates wine volatilome and malolactic fermentation outcome. Front. Food Microbiol. 2021, 12, 736789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perpetuini, G.; Rossetti, A.P.; Tittarelli, F.; Battistelli, N.; Arfelli, G.; Suzzi, G.; Tofalo, R. Promoting Candida zemplinina adhesion on oak chips: A strategy to enhance esters and glycerol content of Montepulciano d’Abruzzo organic wines. Food Res. Int. 2021, 150 Pt A, 110772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recht, J.; Martínez, A.; Torello, S.; Kolter, R. Genetic analysis of sliding motility in Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 4348–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.B.; Fink, G.R. Bakers’ Yeast, a Model for Fungal Biofilm Formation. Science 2001, 291, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, G.; Tittarelli, F.; Suzzi, G.; Tofalo, R. Cell wall surface properties of Kluyveromyces marxianus strains from dairy-products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoli, G.; Barrio, E.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G.; Belloch, C. Multilocus analysis reveals large genetic diversity in Kluyveromyces marxianus strains isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano and Pecorino di Farindola cheeses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 233, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittarelli, F.; Varela, J.A.; Gethins, L.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P.; Suzzi, G.; Grazia, L.; Tofalo, R.; Morrissey, J.P. Development and implementation of multilocus sequence typing to study the diversity of the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus in Italian cheeses. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofalo, R.; Patrignani, F.; Lanciotti, R.; Perpetuini, G.; Schirone, M.; Di Gianvito, P.; Pizzoni, D.; Arfelli, G.; Suzzi, G. Aroma profile of Montepulciano d’Abruzzo wine fermented by single and co-culture starters of autochthonous Saccharomyces and non-Saccharomyces yeasts. Front. Food Microbiol. 2016, 7, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjević, V.; Willaert, R.; Gibson, B.; Nedović, V. Immobilized yeast cells and secondary metabolites. In Fungal Metabolites; Mérillon, J.M., Ramawat, K., Eds.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Schrader, J. Microbial flavour production. In Flavours and Fragrances; Berger, R.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 507–574. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-García, J.; Mauricio, J.C.; Moreno, J.; García-Martínez, T. Differential proteome analysis of a flor yeast strain under biofilm formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-García, J.; Ogawa, M.; Joseph, C.L.; Mauricio, J.C.; Moreno, J.; García-Martínez, T. Comparative analysis of intracellular metabolites, proteins and their molecular functions in a flor yeast strain under two enological conditions. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannella, G.; Lombardi, S.J.; Coppola, F.; Vergalito, F.; Iorizzo, M.; Succi, M.; Tremonte, P.; Iannini, C.; Sorrentino, E.; Coppola, R. Effect of biofilm formation by Lactobacillus plantarum on the Malolactic Fermentation in Model Wine. Foods 2020, 9, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrechts, M.G.; Pretorius, I.S. Yeast and its importance to wine aroma-a review. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2000, 21, 97–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordente, A.G.; Schmidt, S.; Beltran, G.; Torija, M.J.; Curtin, C.D. Harnessing yeast metabolism of aromatic amino acids for fermented beverage bioflavouring and bioproduction. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4325–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomascolo, A.; Lesage-Meessen, L.; Haon, M.; Navarro, D.; Antona, C.; Faulds, C.; Marcel, A. Evaluation of the potential of Aspergillus niger species for the bioconversion of L-phenylalanine into 2-phenylethanol. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, S.; Mukherjee, V.; Lievens, B.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Thevelein, J.M. Bioflavoring by non-conventional yeasts in sequential beer fermentations. Food Microbiol. 2018, 72, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, E.J.; Teixeira, J.A.; Brányik, T.; Vicente, A.A. Yeast: The soul of beer’s aroma—A review of flavour-active esters and higher alcohols produced by the brewing yeast. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneşer, O.; Karagül-Yüceer, Y.; Wilkowska, A.; Kregiel, D. Volatile metabolites produced from agro-industrial wastes by Na-alginate entrapped Kluyveromyces marxianus. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2016, 47, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risner, D.; Tomasino, E.; Hughes, P.; Meunier-Goddik, L. Volatile aroma composition of distillates produced from fermented sweet and acid whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, A.; Hahn, V.; Bornscheuer, U.Y.; Schauer, F. Metabolism of alkenes and ketones by Candida maltosa and related yeasts. AMB Exp. 2014, 4, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotani, T.; Yurimoto, H.; Kato, N.; Sakai, Y. Novel acetone metabolism in a propane-utilizing bacterium, Gordonia sp. strain TY-5. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chia, J.Y.; Liu, S.Q. Impact of addition of aromatic amino acids on non-volatile and volatile compounds in lychee wine fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae MERIT. ferm. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 170, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Báez, L.; López-Molina, A.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.; Pineda-Muñoz, C.; Conde-Mejía, C. Economic projection of 2-phenylethanol production from whey. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 115, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Gao, H.; Qian, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, W.; Xin, F.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M. Biotechnological applications of the non-conventional yeast Meyerozyma guilliermondii. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 46, 107674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fink, G.R. Feedback control of morphogenesis in fungi by aromatic alcohols. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-García, J.; García-Martínez, T.; Millán, M.C.; Mauricio, J.C.; Moreno, J. Proteins involved in wine aroma compounds metabolism by a Saccharomyces cerevisiae flor-velum yeast strain grown in two conditions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Breda, V.; Jolly, N.; van Wyk, J. Characterisation of commercial and natural Torulaspora delbrueckii wine yeast strains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 163, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, T.B. The Opi1p transcription factor affects expression of FLO11, MAT formation, and invasive growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eukaryot. Cell 2006, 5, 1266–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpetuini, G.; Tittarelli, F.; Mattarelli, P.; Modesto, M.; Cilli, E.; Suzzi, G.; Tofalo, R. Intraspecies polymorphisms of Kluyveromyces marxianus strains from Yaghnob valley. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bódi, Z.; Farkas, Z.; Nevozhay, D.; Kalapis, D.; Lázár, V.; Csörgő, B.; Nyerges, A.; Szamecz, B.; Fekete, G.; Papp, B.; et al. Phenotypic heterogeneity promotes adaptive evolution. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perpetuini, G.; Tittarelli, F.; Perla, C.; Tofalo, R. Influence of Different Aggregation States on Volatile Organic Compounds Released by Dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains. Foods 2022, 11, 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182910
Perpetuini G, Tittarelli F, Perla C, Tofalo R. Influence of Different Aggregation States on Volatile Organic Compounds Released by Dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains. Foods. 2022; 11(18):2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182910
Chicago/Turabian StylePerpetuini, Giorgia, Fabrizia Tittarelli, Carlo Perla, and Rosanna Tofalo. 2022. "Influence of Different Aggregation States on Volatile Organic Compounds Released by Dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains" Foods 11, no. 18: 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182910
APA StylePerpetuini, G., Tittarelli, F., Perla, C., & Tofalo, R. (2022). Influence of Different Aggregation States on Volatile Organic Compounds Released by Dairy Kluyveromyces marxianus Strains. Foods, 11(18), 2910. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11182910






