Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods
Abstract
:1. Basic Introduction to Organic Acids
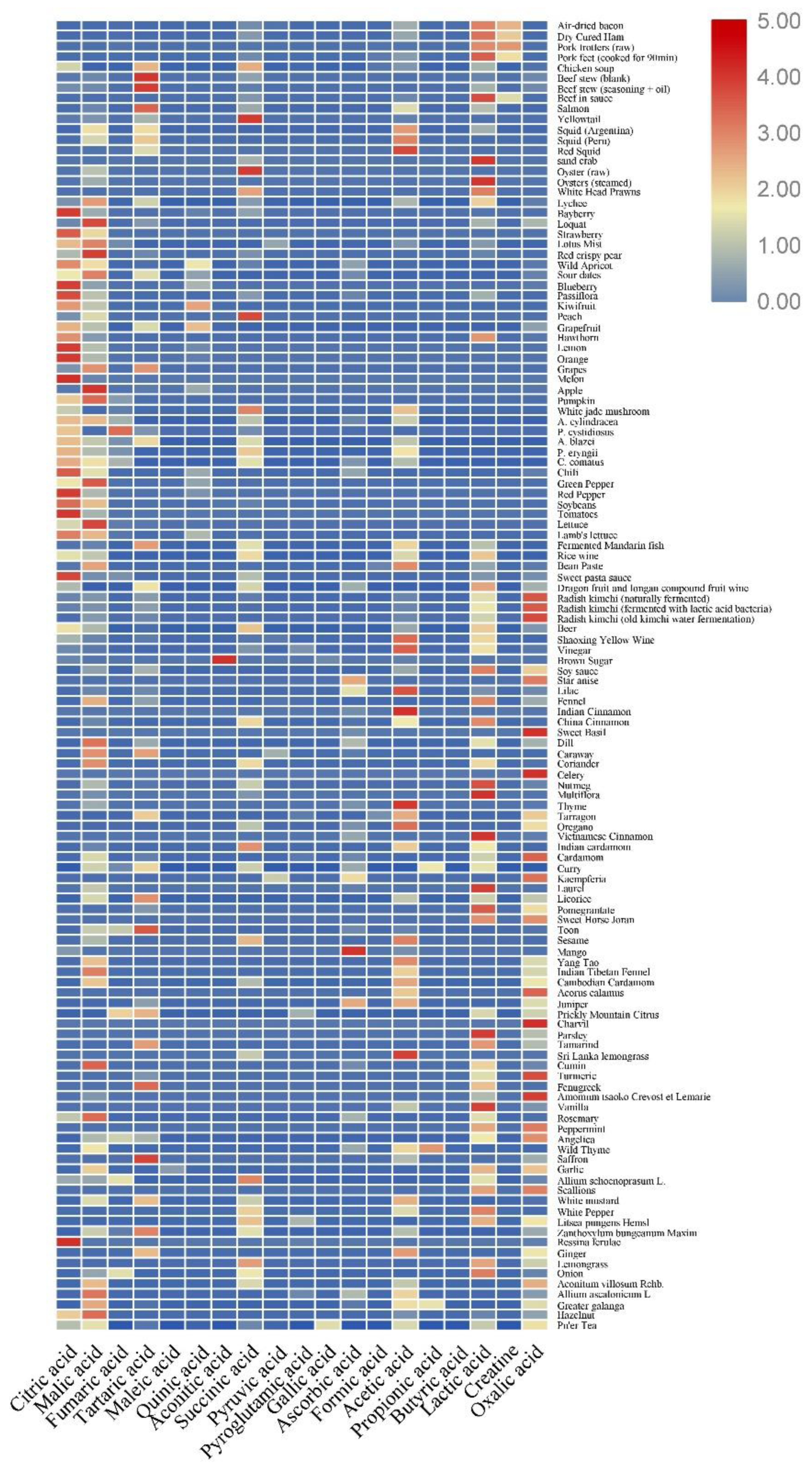
2. Content of Organic Acids in Food and Their Detection Methods
| Number | Separation Method | Detectors | Characteristic | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GC | Hydrogen flame ion detector | Its sensitivity is high and the optimized response varies very little with factors such as detector temperature, flow rates of hydrogen and new carrier gas, and other | [54] |
| Mass Spectrometry Detectors | High performance, high selectivity, high sensitivity, fast analysis speed, application range, can be used in conjunction with analysis | [55] | ||
| 2 | LC | Conductivity detector | It is sensitive and selective, and can be performed quickly and easily. | [56] |
| Chemiluminescent detectors | The wavelength is used to identify substances with high selectivity and detection limits in the range of low micrograms to low picograms. | [57] | ||
| Volt-ampere detector | Reproducibility with the simple and rapid procedure without derivatization of analytes. | [58] | ||
| Mass Spectrometry Detectors | It is more sensitive, selective, and specific, and can determine trace amounts of substances. | [59] | ||
| Fourier infrared detector | The coupling of LC and IR systems can be performed offline or in-line. On-line analysis offers the advantages of the high chromatographic resolution, real-time measurements, instrument simplicity, low cost, and the ability to use non-volatile buffers | [60] | ||
| evaporative light scattering detector | It is more affordable than mass spectrometry detection methods and is also compatible with a wide range of solvents and gradient elutions. | [10] | ||
| Refractive index detector | Simplicity of operation, cost, energy consumption, and availability in most QC labs are better than mass spectrometry detectors | [61,62] | ||
| Diode array detector | The technique allows an easy quantification | [11,63,64] | ||
| 3 | Thin-layer chromatography | UV detector | Fast, sensitive (small amount), highly selective, simple, easy color development | [12] |
| 4 | Ion exchange chromatography | Conductivity detector | High precision and accuracy with good reproducibility | [13] |
| 5 | Capillary zone electrophoresis method | UV detector | High resolution, high automation, simple operation, fast speed, low chemical consumption, low sample preparation volume | [8] |
| 6 | NMR | Ultra-low temperature probe | Non-destructive, non-selective analysis, can directly analyze and detect a large number of compounds at once, but it is more difficult to detect complex mixtures | [13,18] |
| Inverse detection probe | ||||
| 7 | UV spectrophotometer method | Photomultiplier tube | Reaction of organic acids with other substances and measurement of complexes at specific wavelengths | [6] |
2.1. Content of Organic Acids in Fruits
2.2. Content of Organic Acids in Vegetables
2.3. Organic Acid Content in Livestock and Poultry Meat
2.4. Organic Acid Content in Aquatic and Seafood Products
2.5. Content of Organic Acids in Fermented Foods
2.6. Content of Organic Acids in Seasonings
2.7. Summary
3. Flavoring Properties of Organic Acids
3.1. Taste Mechanism of Acidity
3.2. Binary Taste Interactions
3.3. Interaction of Organic Acids with Saltness
3.4. Interaction of Organic Acids with Umami
3.5. Interaction of Organic Acids with Sweetness
3.6. Interaction of Organic Acids with Bitterness
4. Physiological Properties of Organic Acids
4.1. Provide Energy
4.2. Regulation of Metabolism
4.3. Bacterial Inhibition
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.H.; Feng, X.S. Progress in pretreatment and analysis of organic Acids: An update since 2010. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, W.J. Salt intake, stroke, and cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. Yearb. Cardiol. 2010, 339, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.D.; Shan, Y.M.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.G.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, Y.Y. Recent trends in aroma release and perception during food oral processing: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Zhang, L.Y. Enhancing effects of organic acids on saltiness of low-sodium salt. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2012, 33, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.D.; Wei, W.; Tao, H.Y.; Mu, X.T.; Li, D.; Xia, R.; Lu, F. Organic acids in traditional vinegar and human health. China Brew. 2021, 40, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Vereda Alonso, E.; García de Torres, A.; Rivero Molina, A.; Cano Pavón, J.M. Determination of organic acids in wines. A review. Quim. Anal. Bellaterra 1998, 17, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Mato, I.; Suárez-Luque, S.; Huidobro, J.F. A review of the analytical methods to determine organic acids in grape juices and wines. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, I.; Suárez-Luque, S.; Huidobro, J.F. Simple determination of main organic acids in grape juice and wine by using capillary zone electrophoresis with direct UV detection. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, C.F. Thin-layer chromatography: Challenges and opportunities. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1000, 963–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spizzirri, U.G.; Restuccia, D.; Curcio, M.; Parisi, O.I.; Iemma, F.; Picci, N. Determination of biogenic amines in different cheese samples by LC with evaporative light scattering detector. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2013, 29, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B.; Areias, F.; Ferreres, F.; Seabra, R.M. Analysis of vervain flavonoids by HPLC/diode array detector method. Its application to quality control. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 4579–4582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, R.L.; Fang, J.B.; Guo, L.L.; Xie, H.Z. Extraction Conditions Optimization of Mai n Organic Acids from Fruits. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2014, 47, 2625–2633. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Pan, D.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Cao, J. 1H NMR-based metabolomics profiling and taste of stewed pork-hock in soy sauce. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, M.V.; Carcouet, E.; Pailly, O.; Gambotti, C.; Luro, F.; Berti, L. Changes in organic acids and sugars during early stages of development of acidic and acidless citrus fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8335–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, I.; Fukuda, T.; Shimohashi, A.; Oota, T. Sugar and organic acid composition in the fruit juice of different Actinidia varieties. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, L.T.; Ardö, Y.; Bredie, W.L. Study of taste-active compounds in the water-soluble extract of mature Cheddar cheese. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, C.H.; Ji, H.W.; Xie, W.C.; Feng, X.M.; Fu, G.Z. Analysis of Taste-active Components of Autolysate of Penaeus vannamei Shrimp Head. Food Sci. 2010, 31, 184–187. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, J.; Erny, G.; Barros, A.; Esteves, V.; Brandão, T.; Ferreira, A.; Cabrita, E.; Gil, A. Quantification of organic acids in beer by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-based methods. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 674, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Huang, L.L.; Fang, C.F.; Gu, Y.P.; Zhang, S.F. Comparison of Taste-Related Compounds and Analysis Using Electronic Tongue of Feizixiao and Huaizhi Lychee Fruits from Different Planting Area. J. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 31, 984–990. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Gu, Z. Evaluation of sugar, free amino acid, and organic acid compositions of different varieties of vegetable soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr). Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 50, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.L.; Wu, J.J.; Li, C.P.; Xu, K.H.; Dai, Z.Y. Analysis and Comparison on Characterization of Taste Components in Muscle ofThree Species Squids. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 14, 244–250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Gu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Non-volatile taste components of several cultivated mushrooms. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Li, C.P.; Wu, J.J.; Zhao, Q.L.; Ling, D.Z. Identification and Analysis of the Tasty Compounds in Stinky Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) during Fermentation. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 15, 222–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.; Tang, J.; Pei, F.; Wang, S.; Chen, G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, L. The influence of four drying methods on nonvolatile taste components of White Hypsizygus marmoreus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, L.P.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.D.; Xu, K.H. Study on the taste compounds and the contributions to taste of cultured large yellow croaker. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2015, 36, 82–85+90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.F.; Li, L.P.; Gao, L.; Wang, M.; Ying, D.S.; Zhang, R.L. Analysis of Organic Acids in Passion Fruit by Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2015, 36, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Quan, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xi, W. Determination of sugars, organic acids, aroma components, and carotenoids in grapefruit pulps. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Chen, H.T. Determination of the free amino acid, organic acid, and nucleotide in commercial vinegars. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.N.; Su, Y.T.; Zhao, S.M.; Du, H.Y. Analyses of nutritional composition in four kinds of fermented sweet rice wines and sensory evaluation with electronic tongue. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2018, 37, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Sun, Y.; Pan, D.; Ou, C.; Dang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, D. 1H NMR and multivariate data analysis of the differences of metabolites in five types of dry-cured hams. Food Res. Int. 2018, 113, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.T.; Liang, Z.Y.; Fan, S.H.; Xia, N.; Chen, D.W. Analysis of Characteristic Taste Components of Soldier Crab (Mictyris brevidactylus). Food Sci. 2018, 39, 236–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Tang, X. Analysis and Evaluation of the Characteristic Taste Components in Portobello Mushroom. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Tian, H. Taste characteristics of Chinese bayberry juice characterized by sensory evaluation. chromatography analysis, and an electronic tongue. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Qiao, K.N.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Chen, H.T. Effects of two cooking methods on the taste components of Sanhuang chicken and Black-bone silky fowl meat. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, 13772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H.T. Evaluation of non-volatile taste components in commercial soy sauces. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S. Influence of ripening stage and cultivar on physicochemical properties, sugar and organic acid profiles, and antioxidant compositions of strawberries. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 1659–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Sun, Q.; Deng, W.Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.S.; Fan, Z.Y.; You, J.G.; Li, H. A HPLC Method for Determination of Seven Kinds of Organic Acids in Broad Bean Paste with Different Fermentation Year. Food Ferment. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 128–131+141. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.L.; Yang, Z.G.; Wang, H.R.; Li, M.P. Determination of Six Organic Acids Contents in Red Fragrant Pear by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 2103–2106+2138. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, W.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparison of nonvolatile taste components in 18 strong fragrance spices. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.C.; Cai, J.H.; Gu, S.Q.; Qian, B.; Wang, L.; Lü, F.; Ding, Y.T. Analysis of Characteristic Flavor Substances of Traditional Shaoxing Rice Wines of Different Ages. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Qiao, K.; Duan, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Huang, Y. Comparison of taste components in stewed beef broth under different conditions by means of chemical analyzed. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zou, S.; Wu, J.; Shahid, M.Q.; He, Y.; Lin, S.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X. Identification of key taste components in loquat using widely targeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, D.; Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Xia, Q.; Cao, J. The application of 1H NMR to explore the taste difference caused by taste active metabolites of different Chinese sauce–stewed beef. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 4868–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Duan, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Pu, D.D.; Tang, Y.; Liu, C. Sensory taste properties of chicken (Hy-Line brown) soup as prepared with five different parts of the chicken. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1804–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.F.; Wu, G.B.; Ye, H.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F.H. Simultaneous Determination of Seven Organic Acids in Wax Apple (Syzygium samarangenese [Blume] Merrill & L.M. Perry) Fruit during Postharvest Storage by High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 175–180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.Z.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, H.X.; Wang, G.H.; Li, J.W.; Yu, G.B. Determination of Organic Acids Content in Brown Sugar by Solid-phase Extraction-High Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Res. Dev. 2020, 41, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Xing, L. Effects of ultrasound on the taste components from aqueous extract of unsmoked bacon. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ji, W.; Jiang, H.; Shi, Y.; He, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhu, S. Comparison of biochemical composition and non-volatile taste active compounds in raw, high hydrostatic pressure-treated and steamed oysters Crassostrea hongkongensis. Food Chem. 2021, 344, 128632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.D.; Li, N.; Wei, B.H.; Du, W.H. Analysis of the Changes of Organic Acids in Pickled Radish with Different Fermentation Methods. China Condiment 2021, 46, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.M.; He, Y.; Chen, D.H.; Zhuang, P.L.; Chen, G.C.; Xu, S.Y. Study on the Production Technology of Longan-Pitaya Wine and its Organic Acids. Liquor.-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 24–28+35. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.G.; Ke, F.; Liang, Z.R.; Zhang, L.; Dai, Z.R.; Shi, S.Y.; Luo, D.; Li, G.L. Determination of 18 Organic Acids in Rice Flavored Liquor Fermentation Broth by High Pressure Liquid Chromatography. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Beauvoit, B.; Belouah, I.; Bertin, N.; Cakpo, C.B.; Colombie, S.; Dai, Z.; Gautier, H.; Genard, M.; Moing, A.; Roch, L.; et al. Putting primary metabolism into perspective to obtain better fruits. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.H.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, T. Aspects of the mechanism of the flame ionization detector. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 842, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.G. Analysis of Non-Volatile Organic Acids in Sweet Sauce. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Talamond, P.; Gallon, G.; Treche, S. Rapid and sensitive liquid chromatographic method using a conductivity detector for the determination of phytic acid in food. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 805, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birks, J.W.; Kuge, M.C. Chemiluminescent aerosol spray detector for liquid chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1980, 52, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, A.; Miyaguchi, Y.; Tomita, E.; Takamura, K.; Kusu, F. Determination of organic acids by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection during wine brewing. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Duan, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.F.; Pan, Q.H.; Li, J.M.; Huang, W.D. Determination of Organic Acids in Red Wine and Must on Only One RP-LC-Column Directly After Sample Dilution and Filtration. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, J.; Quintás, G.; Garrigues, S.; Lendl, B.; de la Guardia, M. Recent advances in on-line liquid chromatography-infrared spectrometry (LC-IR). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.D.; Dong, M.S.; Huang, K.H. Determination of water-soluble organic acids and vitamins in juicy peach using HPLC-DAD. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2009, 32, 151–154. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sanea, M.M.; Gamal, M. Critical analytical review: Rare and recent applications of refractive index detector in HPLC chromatographic drug analysis. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortera, P.; Zuljan, F.A.; Magni, C.; Bortolato, S.A.; Alarcon, S.H. Multivariate analysis of organic acids in fermented food from reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography data. Talanta 2018, 178, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lawless, H.T.; Rapacki, F.; Horne, J.; Hayes, A. The taste of calcium and magnesium salts and anionic modifications. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.X.; Liu, X.H.; Chen, L.S. Advances in research on organic acid metabolism in fruits. J. Fruit Sci. 2005, 05, 526–531. [Google Scholar]
- Millar, A.H.; Hoefnagel, M.H.; Day, D.A.; Wiskich, J.T. Wiskich. Specificity of the Organic Acid Activation of Alternative Oxidase in Plant Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1996, 111, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Ma, W.; Deng, J.; Peng, Y.; Tian, R.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Ma, F.; Li, M.; Ma, B. A MdMa13 gene encoding tonoplast P3B-type ATPase regulates organic acid accumulation in apple. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 296, 110916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil, I.M.; Siddiqui, M.W. Postharvest Quality of Fruits and Vegetables: An Overview. In Preharvest Modulation of Postharvest Fruit and Vegetable Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zampini, M.; Wantling, E.; Phillips, N.; Spence, C. Multisensory flavor perception: Assessing the influence of fruit acids and color cues on the perception of fruit-flavored beverages. Food Qual. Prefer. 2008, 19, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.S.; Xiao, G.S.; Xu, Y.J.; Wu, J.J.; Fu, M.Q.; Wen, J. Slight fermentation with Lactobacillus fermentium improves the taste (sugar: Acid ratio) of citrus (Citrus reticulata cv. chachiensis) juice. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 2543–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, P.; Hellín, P.; Fenoll, J. Determination of organic acids in fruits and vegetables by liquid chromatography with tandem-mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamljen, T.; Medic, A.; Veberic, R.; Hudina, M.; Jakopic, J.; Slatnar, A. Metabolic Variation among Fruits of Different Chili Cultivars (Capsicum spp.) Using HPLC/MS. Plants 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Galdon, B.; Tascon Rodriguez, C.; Rodríguez Rodríguez, E.; Diaz Romero, C. Organic acid contents in onion cultivars (Allium cepa L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 6512–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, S.I.; van Boekel, M.A. A kinetic model for the glucose/glycine Maillard reaction pathways. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; Sentandreu, M.A.; Toldra, F. Effect of Cooking Conditions on Creatinine Formation in Cooked Ham. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 11279–11284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyss, M.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R. Creatine and creatinine metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 1107–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodin, N.; Amiel, A.; Fouche, E.; Sardenne, F.; Chassot, E.; Debrauwer, L.; Guillou, H.; Tremblay-Franco, M.; Canlet, C. NMR-based metabolic profiling and discrimination of wild tropical tunas by species, size category, geographic origin, and on-board storage condition. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, Y.L.; Choi, S.D.; Seo, K.I.; Joo, O.S. Changes in Organic Acid Contents on Heating Conditions of Fishes. J. Korean Soc. Food Nutr. 1994, 23, 939. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.Z.; Fang, F. Synthesis ability and pathways of isoamyl alcohol in yeasts from fermented grains. Microbiol. China 2022, 49, 3740–3752. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y. Microbiology of Modern Liquor Brewing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 280–329. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Peng, Z.; Hardie, W.J.; Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, M.; Xiong, T. Exploring the typical flavours formation by combined with metatranscriptomics and metabolomics during Chinese Sichuan paocai fermentation. LWT 2022, 153, 112474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Luo, L.; Lin, W. Bacterial dynamics and metabolite changes in solid-state acetic acid fermentation of Shanxi aged vinegar. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4395–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Tian, Z.Q.; Ma, Y.Q.; Shao, F.L.; Huang, J.L.; Wu, H.; Tian, L. Origin identification of the sauce-flavor Chinese Baijiu by organic acids, trace elements, and the stable carbon isotope ratio. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 7525201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chidi, B.S.; Bauer, F.F.; Rossouw, D. Organic acid metabolism and the impact of fermentation practices on wine acidity: A review. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2018, 39, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, W.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tang, Y. Determination of free amino acids, organic acids, and nucleotides in 29 elegant spices. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3777–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Duan, W.; Xiao, J.F.; Liu, H.; Zhou, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Tang, Y.; Sun, B.G.; Li, Z. Characterization of the taste compounds in 20 pungent spices by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 1680–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.W. The Relation of the Taste of Acids to their Degree of Dissociation, II. J. Phys. Chem. 2002, 4, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, M.; Noble, A.; Pangborn, R. Human saliva and taste responses to acids varying in anions, titratable acidity, and pH. Physiol. Behav. 1984, 32, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CoSeteng, M.Y.; McLellan, M.R.; Downing, D.L. Influence of titratable acidity and pH on intensity of sourness of citric, malic, tartaric, lactic and acetic acids solutions and on the overall acceptability of imitation apple juice. Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 1989, 22, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neta, E.R.; Johanningsmeier, S.D.; Drake, M.A.; McFeeters, R.F. Effects of pH adjustment and sodium ions on sour taste intensity of organic acids. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.L.; Chen, X.; Hoon, M.A.; Chandrashekar, J.; Guo, W.; Tränkner, D.; Ryba, N.J.; Zuker, C.S. The cells and logic for mammalian sour taste detection. Nature 2006, 442, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishimaru, Y.; Inada, H.; Kubota, M.; Zhuang, H.; Tominaga, M.; Matsunami, H. Transient receptor potential family members PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 form a candidate sour taste receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12569–12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horio, N.; Yoshida, R.; Yasumatsu, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Ishimaru, Y.; Matsunami, H.; Ninomiya, Y. Sour taste responses in mice lacking PKD channels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, B.; Wilson, C.E.; Tu, Y.H.; Joshi, N.R.; Kinnamon, S.C.; Liman, E.R. Cellular and neural responses to sour stimuli require the proton channel Otop1. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 3647–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, H.; Zhang, W.; Ding, C.; O’Keeffe, S.; Ye, M.; Zuker, C.S. Sour sensing from the tongue to the brain. Cell 2019, 179, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Chang, R.B.; Bushman, J.D.; Tu, Y.H.; Mulhall, E.M.; Wilson, C.E.; Cooper, A.J.; Chick, W.S.; Hill-Eubanks, D.C.; Nelson, M.T. The K+ channel KIR2. 1 functions in tandem with proton influx to mediate sour taste transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, N.; Lu, M.; Echeverri, F.; Laita, B.; Kalabat, D.; Williams, M.E.; Hevezi, P.; Zlotnik, A.; Moyer, B.D. Voltage-gated sodium channels in taste bud cells. BMC Neurosci. 2009, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, B. Receptors and transduction in taste. Nature 2001, 413, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbeuch, A.; Zorec, R.; Kinnamon, S.C. Capacitance measurements of regulated exocytosis in mouse taste cells. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 14695–14701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, H.E.; Amato, K.; Trautwein, M.; Maia, P.; Liman, E.R.; Nichols, L.M.; Schwenk, K.; Breslin, P.A.; Dunn, R.R. The evolution of sour taste. Proc. R. Soc. B 2022, 289, 20211918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetz, W.; Thomas, G.H.; Joy, J.B.; Hartmann, K.; Mooers, A.O. The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature 2012, 491, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marui, T.; Caprio, J. Teleost gustation. In Fish Chemoreception; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 6, pp. 171–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, A.; Chandel, A.; Turner, H.; Wang, S.; Liman, E.R.; Montell, C. Requirement for an Otopetrin-like protei D.n for acid taste in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 2110641118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.D.; Shan, Y.M.; Zhang, L.L.; Sun, B.G.; Zhang, Y.Y. Identification and Inhibition of the Key Off-Odorants in Duck Broth by Means of the Sensomics Approach and Binary Odor Mixture. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13367–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.N.; Yu, P.; Sun, J.Y.; Jia, Y.M.; Wan, C.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, F.H. Investigation of volatile thiol contributions to rapeseed oil by odor active value measurement and perceptual interactions. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Duan, W.; Zhang, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G. Characterization and molecular docking study of taste peptides from chicken soup by sensory analysis combined with nano-LC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2022, 383, 132455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Zhou, C.C.; Zhang, J.C.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sun, B.G.; Zhang, Y.Y. Characteristics of Umami Peptides Identified from Porcine Bone Soup and Molecular Docking to the Taste Receptor T1R1/T1R3. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, J.H.; Bartoshuk, L.M. Bitterness suppression as revealed by split-tongue taste stimulation in humans. Physiol. Behav. 1985, 35, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, P.M.; Breslin, P.A. Relationships among taste qualities assessed with response-context effects. Chem. Senses 2011, 36, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslin, P.A. Interactions among salty, sour and bitter compounds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Danguin, T.; Guichard, E.; Salles, C. Cross-modal interactions as a strategy to enhance salty taste and to maintain liking of low-salt food: A review. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5269–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatae, K.; Takeutchi, F.; Sakamoto, M.; Ogasawara, Y.; Akano, H. Saltiness and acidity: Detection and recognition thresholds and their interaction near the threshold. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellemann, U. Perceived taste of NaCl and acid mixtures in water and bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1992, 27, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, B.G.; Ren, F.; Zhang, H.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Tang, Y. Characterization of the key taste compounds during bread oral processing by instrumental analysis and dynamic sensory evaluation. LWT 2021, 138, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.Y.; Tsai, M.L.; Liu, T. Enhancing saltiness perception using chitin nanofibers when curing tilapia fillets. LWT 2017, 86, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.M.; Cruz-Romero, M.C.; Duffy, G.; Kerry, J.P. The application of response surface methodology for the development of sensory accepted low-salt cooked ham using high pressure processing and a mix of organic acids. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keast, R.S.; Breslin, P.A. An overview of binary taste—Taste interactions. Food Qual. Prefer. 2003, 14, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindemann, B. Taste reception. Physiol. Rev. 1996, 76, 719–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.; DeSimone, J.; Hill, D. New perspectives in a gustatory physiology: Transduction, development, and plasticity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1997, 272, C1–C26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowski, B.C.; Sukumaran, S.K.; Margolskee, R.F.; Bachmanov, A.A. Amiloride-insensitive salt taste is mediated by two populations of type III taste cells with distinct transduction mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chikazoe, J.; Lee, D.H.; Kriegeskorte, N.; Anderson, A.K. Distinct representations of basic taste qualities in human gustatory cortex. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miranda, A.M.; Ingram, M.; Nuessle, T.M.; Santorico, S.A.; Garneau, N.L. Factors affecting detection of a bimodal sour-savory mixture and inter-individual umami taste perception. Food Qual. Prefer. 2021, 89, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffman, S.S.; Sennewald, K.; Gagnon, J. Comparison of taste qualities and thresholds of D-and L-amino acids. Physiol. Behav. 1981, 27, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, H.; Sekizaki, Y.; Hirota, M.; Sekine-Hayakawa, Y.; Nonaka, M. Analysis of binary taste-taste interactions of MSG, lactic acid, and NaCl by temporal dominance of sensations. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 52, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, F.W.; Blum, H. Relative taste-potency of some basic food constituents and their competitive and compensatory action. Food Res. 1943, 8, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangborn, R.M. Taste interrelationships. II. Suprathreshold solutions of sucrose and citric acid. J. Food Sci. 1961, 26, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.; Ripandelli, N.; Wakeling, I. Binary taste mixture interactions in prop non-tasters, medium-tasters and super-tasters. Chem. Senses 2001, 26, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.J.; Maruyama, Y.; Dvoryanchikov, G.; Pereira, E.; Chaudhari, N.; Roper, S.D. The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell–cell communication in mouse taste buds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6436–6441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomchik, S.M.; Berg, S.; Kim, J.W.; Chaudhari, N.; Roper, S.D. Breadth of tuning and taste coding in mammalian taste buds. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 10840–10848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junge, J.Y.; Bertelsen, A.S.; Mielby, L.A.; Zeng, Y.; Sun, Y.X.; Byrne, D.V.; Kidmose, U. Taste interactions between sweetness of sucrose and sourness of citric and tartaric acid among Chinese and Danish consumers. Foods 2020, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J. The misuse of taste names by untrained observers. Br. J. Psychol. 1970, 61, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerhof, W.; Batram, C.; Kuhn, C.; Brockhoff, A.; Chudoba, E.; Bufe, B.; Appendino, G.; Behrens, M. The molecular receptive ranges of human TAS2R bitter taste receptors. Chem. Senses 2010, 35, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoyama, M.; Uchida, S.; Tanaka, S.; Hakamata, A.; Odagiri, K.; Inui, N.; Watanabe, H.; Namiki, N. Citric acid suppresses the bitter taste of olopatadine hydrochloride orally disintegrating tablets. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Liu, R.; Weng, Y. The Discovery and Revelation of Tricarboxylie Acid Cycle. Med. Philos. 2012, 33, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Mailloux, R.J.; Beriault, R.; Lemire, J.; Singh, R.; Chenier, D.R.; Hamel, R.D.; Appanna, V.D. The tricarboxylic acid cycle, an ancient metabolic network with a novel twist. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krebs, H.A. The history of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1970, 14, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.L.; Wu, Q.P.; Huang, J.M.; Chen, R.; Cai, M.; Tan, J.B. Effects of L-malate on physical stamina and activities of enzymes related to the malate-aspartate shuttle in liver of mice. Physiol. Res. 2007, 56, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Wu, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M. Research Progress of Physiological Functions of L-malate. Food Sci. 2008, 29, 692–695. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, N.K.; Bohannon, J.K.; Hernandez, A.; Patil, T.K.; Sherwood, E.R. Regulation of leukocyte function by citric acid cycle intermediates. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallimann, T.; Tokarska-Schlattner, M.; Schlattner, U. The creatine kinase system and pleiotropic effects of creatine. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1271–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ydfors, M.; Hughes, M.C.; Laham, R.; Schlattner, U.; Norrbom, J.; Perry, C.G. Modelling in vivo creatine/phosphocreatine in vitro reveals divergent adaptations in human muscle mitochondrial respiratory control by ADP after acute and chronic exercise. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3127–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Östman, E.M.; Nilsson, M.; Elmståhl, H.L.; Molin, G.; Björck, I. On the effect of lactic acid on blood glucose and insulin responses to cereal products: Mechanistic studies in healthy subjects and in vitro. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.L.; Wu, Q.P.; Yang, X.F.; Wei, M.K.; Zhang, J.M.; Huang, Q.; Zhou, X.Y. L-malate reverses oxidative stress and antioxidative defenses in liver and heart of aged rats. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sakamoto, K. Citric acid promoted melanin synthesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells, but inhibited it in human epidermal melanocytes and HMV-II melanoma cells via the GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, M.; Tang, A.; Wakaki, Y.; Koyama, W. Glycemic index of single and mixed meal foods among common Japanese foods with white rice as a reference food. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fried, M.; Abramson, S.; Meyer, J. Passage of salivary amylase through the stomach in humans. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1987, 32, 1097–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Kishi, M.; Fushimi, T.; Ugajin, S.; Kaga, T. Vinegar intake reduces body weight, body fat mass, and serum triglyceride levels in obese Japanese subjects. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Da Silva, R.P.; Leonard, K.A.; Jacobs, R.L. Dietary creatine supplementation lowers hepatic triacylglycerol by increasing lipoprotein secretion in rats fed high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, D.; de Moraes, R.; Tibirica, E. Effects of dietary supplementation with creatine on homocysteinemia and systemic microvascular endothelial function in individuals adhering to vegan diets. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Hayashi, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Tsuchiya, H. Caffeine citrate enhanced cisplatin antitumor effects in osteosarcoma and fibrosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshfield, I.N.; Terzulli, S.; O’Byrne, C. Weak organic acids: A panoply of effects on bacteria. Sci. Prog. 2003, 86, 245–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, L.M.; Yohannes, E.; Bondurant, S.S.; Radmacher, M.; Slonczewski, J.L. pH regulates genes for flagellar motility, catabolism, and oxidative stress in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricke, S. Perspectives on the use of organic acids and short chain fatty acids as antimicrobials. Poult. Sci. 2003, 82, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, P.M.; Taylor, T.M.; Schmidt, S.E. Chemical preservatives and natural antimicrobial compounds. In Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 765–801. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Pu, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213408
Shi Y, Pu D, Zhou X, Zhang Y. Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods. Foods. 2022; 11(21):3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213408
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yige, Dandan Pu, Xuewei Zhou, and Yuyu Zhang. 2022. "Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods" Foods 11, no. 21: 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213408
APA StyleShi, Y., Pu, D., Zhou, X., & Zhang, Y. (2022). Recent Progress in the Study of Taste Characteristics and the Nutrition and Health Properties of Organic Acids in Foods. Foods, 11(21), 3408. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11213408







