A Comprehensive Review of Moringa oleifera Bioactive Compounds—Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Their Encapsulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bioactive Components of Moringa oleifera
2.1. Impact on the Human Health
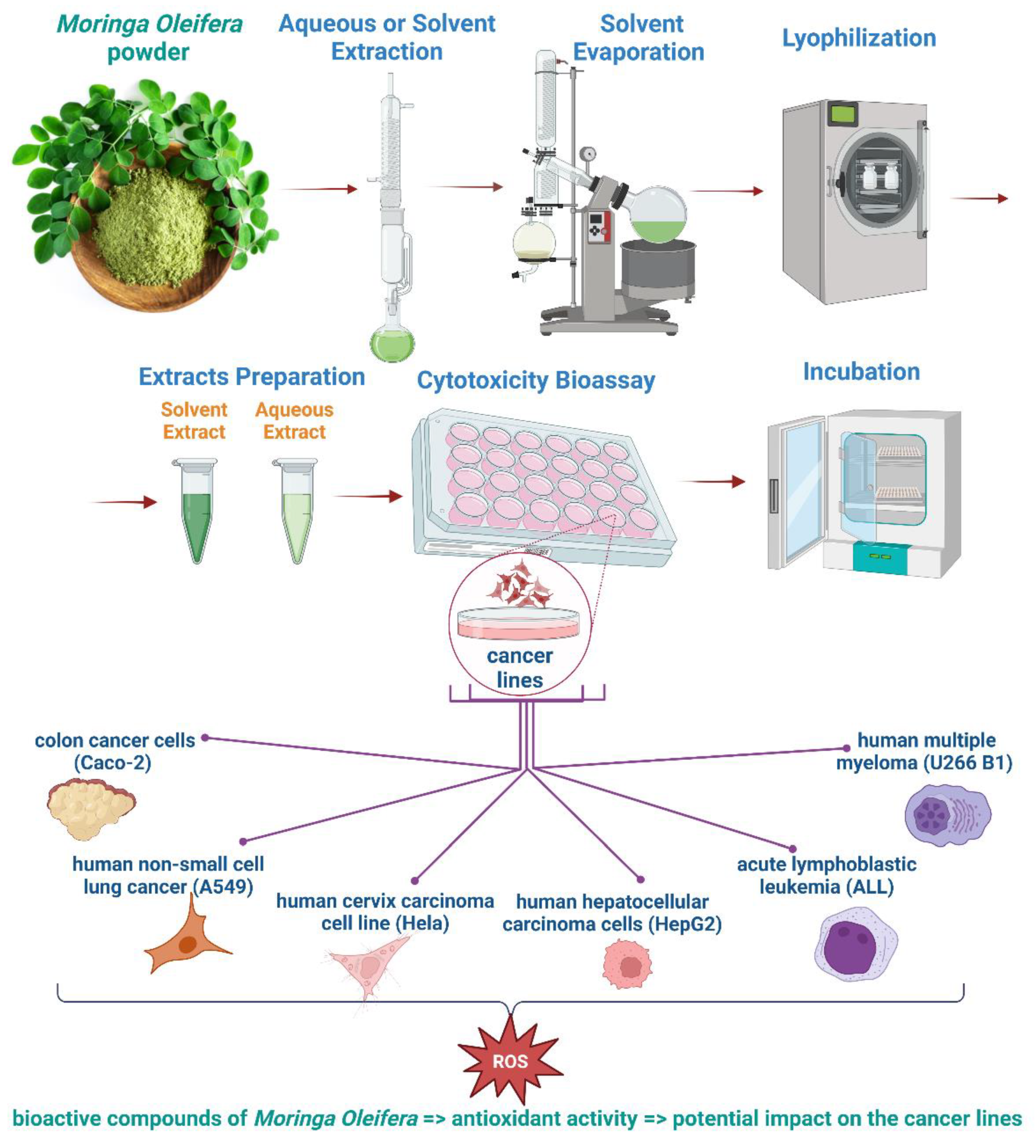
2.2. Cytotoxicity of Moringa oleifera
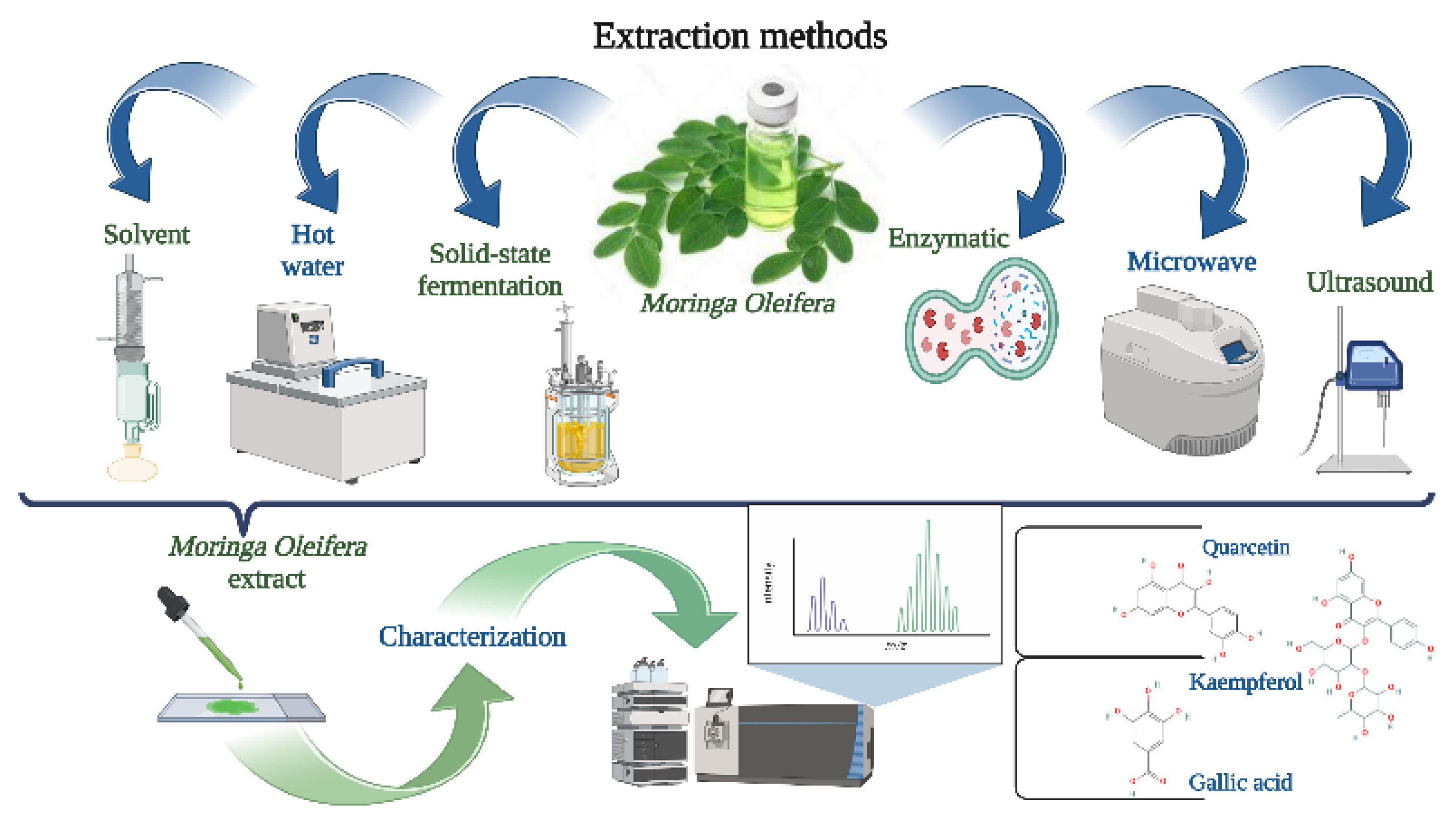
3. Extraction Techniques Prior to Encapsulation
3.1. Traditional Extraction Techniques
3.1.1. Solvent Extraction
3.1.2. Hot Water
3.1.3. Solid-State Fermentation
3.2. Nontraditional Extraction Techniques
3.2.1. Ultrasound
3.2.2. Microwave
3.2.3. Enzymatic
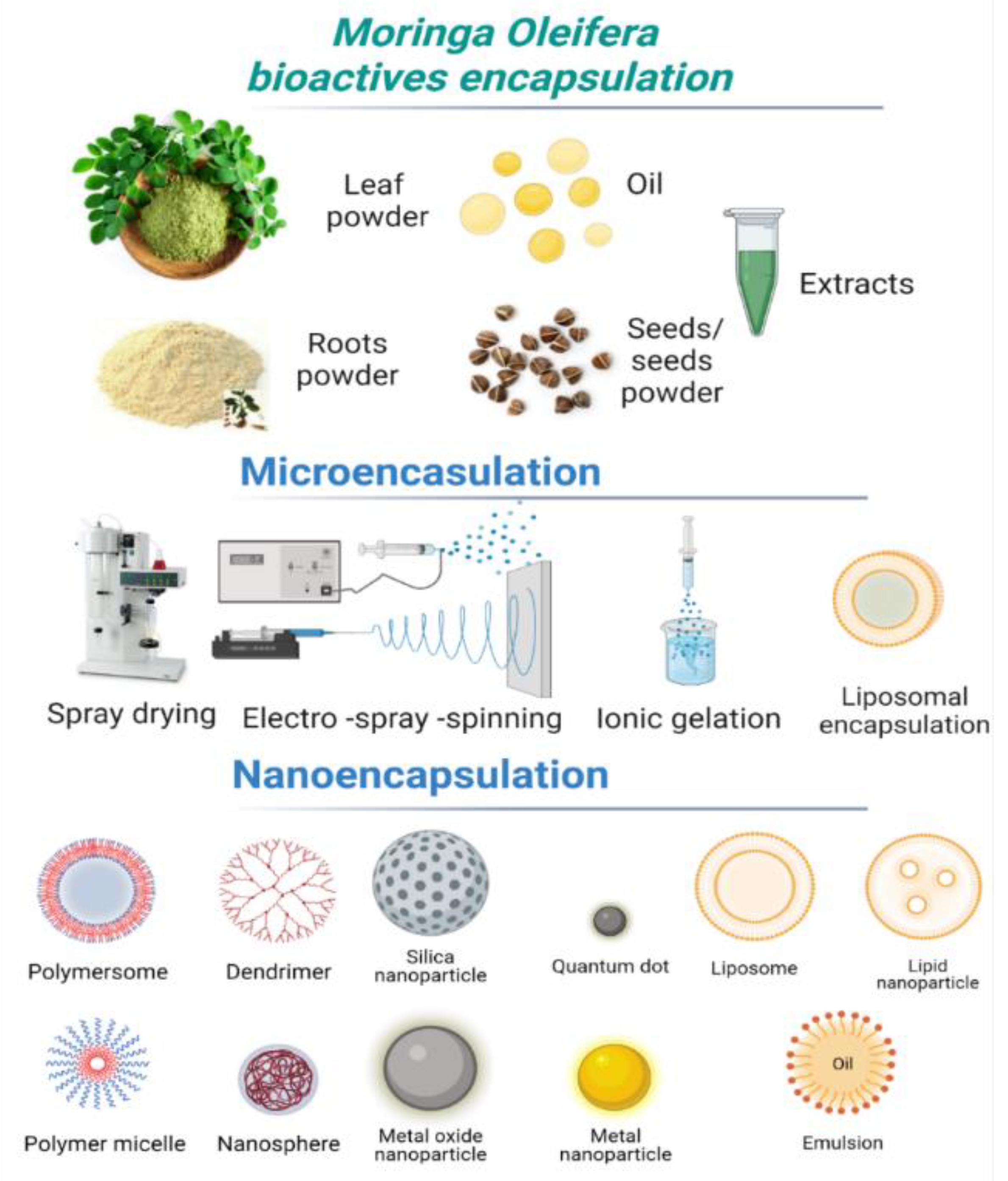
4. Encapsulation Methods of Bioactive Compounds from Moringa oleifera
4.1. Microencapsulation of Moringa oleifera and Their Food Applications
4.2. Nanoencapsulation
4.3. Electrospinning Method
4.4. Electrospraying Method
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kashyap, P.; Kumar, S.; Riar, C.S.; Jindal, N.; Baniwal, P.; Guine, R.P.F.; Correia, P.M.R.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, H. Recent Advances in Drumstick (Moringa oleifera) Leaves Bioactive Compounds: Composition, Health Benefits, Bioaccessibility, and Dietary Applications. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saucedo-Pompa, S.; Torres-Castillo, J.A.; Castro-Lopez, C.; Rojas, R.; Sanchez-Alejo, E.J.; Ngangyo-Heya, M.; Martinez-Avila, G.C.G. Moringa plants: Bioactive compounds and promising applications in food products. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.A. Development of Fiber Enriched Herbal Biscuits: A Preliminary Study on Sensory Evaluation and chemical Composition. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 3, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, G.; Nitride, C.; Ferranti, P. Moringa oleifera Lam. Proteins: Properties and Food Applications. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuberti, G.; Rocchetti, G.; Montesano, D.; Lucini, L. The potential of Moringa oleifera in food formulation: A promising source of functional compounds with health-promoting properties. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 42, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.-y.; Wei, X.-m.; Gao, Z.-t.; Han, J.-p. Values, properties and utility of different parts of Moringa oleifera: An overview. Chin. Herb. Med. 2018, 10, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, R.; Demak, I.P.K.; Radhiah, S.; Rusydi, M.; Mantao, E.; Larasati, R.D. The effect of moringa leaf extracton increasing hemoglobin and bodyweight in post-disaster pregnant women. Enfermería Clínica 2020, 30, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, Z.; Islam, S.M.R.; Hossen, F.; Mahtab-Ul-Islam, K.; Hasan, M.R.; Karim, R. Moringa oleifera is a Prominent Source of Nutrients with Potential Health Benefits. Int. J. Food Sci. 2021, 2021, 6627265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, L.; Doriya, K.; Kumar, D.S. Moringa oleifera: A review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2016, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Wadhwa, S.S.; Waterhouse, G.I.N. Spray-Drying Microencapsulation of Polyphenol Bioactives: A Comparative Study Using Different Natural Fibre Polymers as Encapsulants. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 6, 2376–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzuvor, C.K.O.; Pan, S.; Amanze, C.; Amuzu, P.; Asakiya, C.; Kubi, F. Bioactive components from Moringa oleifera seeds: Production, functionalities and applications—A critical review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premi, M.; Sharma, H.K. Effect of extraction conditions on the bioactive compounds from Moringa oleifera (PKM 1) seeds and their identification using LC–MS. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2017, 11, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osamede Airouyuwa, J.; Kaewmanee, T. Microencapsulation of Moringa oleifera leaf extracts with vegetable protein as wall materials. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2019, 25, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, Q.; Fu, X.; Liu, R.H. Microwave-assisted extraction of polysaccharides from Moringa oleifera Lam. leaves: Characterization and hypoglycemic activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulat, M.; Khan, F.; Muluneh, G.; Pandita, A. Phytochemical Profile and Antimicrobial Effects of Different Medicinal Plant: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Curr. Tradit. Med. 2020, 6, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Sivanesan, I.; Keum, Y.S. Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: A review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance. 3 Biotech 2016, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouman, W.; Anwar, F.; Gull, T.; Newton, A.; Rosa, E.; Domínguez-Perles, R. Profiling of polyphenolics, nutrients and antioxidant potential of germplasm’s leaves from seven cultivars of Moringa oleifera Lam. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 83, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Deng, J.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Lan, T.; Wu, D.; Gong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z. Optimization of Phenolic Compound Extraction from Chinese Moringa oleifera Leaves and Antioxidant Activities. J. Food Qual. 2019, 2019, 5346279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.K.; Shetty, N.P.; Giridhar, P. Carotenoid content in vegetative and reproductive parts of commercially grown Moringa oleifera Lam. cultivars from India by LC–APCI–MS. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 238, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, K.L. Chapter 40—Glucosinolates. In Nutraceuticals; Gupta, R.C.., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, M.; Hara, M.; Fukino, N.; Kakizaki, T.; Morimitsu, Y. Glucosinolate metabolism, functionality and breeding for the improvement of Brassicaceae vegetables. Breed. Sci. 2014, 64, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Nutritional, phytochemical, antioxidant, α-glucosidase and α-amylase inhibitory properties of Moringa oleifera seeds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 133, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.-L.; Cai, S.-Y.; Gao, M.; Chu, X.-M.; Pan, X.-Y.; Gong, K.-K.; Xiao, C.-W.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Wang, B.; et al. Purification of antioxidant peptides of Moringa oleifera seeds and their protective effects on H2O2 oxidative damaged Chang liver cells. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Selvasekaran, P.; Kapoor, S.; Barbhai, M.D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Saurabh, V.; Potkule, J.; Changan, S.; ElKelish, A.; Selim, S.; et al. Moringa oleifera Lam. seed proteins: Extraction, preparation of protein hydrolysates, bioactivities, functional food properties, and industrial application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.Q.; Ghazali, S.B. Dataset on physicochemical properties of particle-sized Moringa oleifera seed cake and its application as bio-coagulants in water treatment application. Chem. Data Collect. 2019, 24, 100284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, S.; Zaku, S. Moringa oleifera seed-cake, alternative biodegradable and biocompatibility organic fertilizer for modern farming. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am. 2011, 2, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, H.M.; Asmawi, M.Z.; Khan, N.A.K.; Sadikun, A. Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Leaves on Body Weight and Hyperglycemia of Diabetic Rats. Pak. J. Nutr. 2016, 15, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandave, M.; Ojha, S.K.; Joshi, S.; Kumari, S.; Arya, D.S. Moringa oleifera leaf extract prevents isoproterenol-induced myocardial damage in rats: Evidence for an antioxidant, antiperoxidative, and cardioprotective intervention. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontual, E.V.; Pires-Neto, D.F.; Fraige, K.; Higino, T.M.M.; Carvalho, B.E.A.; Alves, N.M.P.; Lima, T.A.; Zingali, R.B.; Coelho, L.C.B.B.; Bolzani, V.S.; et al. A trypsin inhibitor from Moringa oleifera flower extract is cytotoxic to Trypanosoma cruzi with high selectivity over mammalian cells. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 2940–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujah, O.; Ujah, I.; Johnson, J.T.; Ekam, V.; Udenze, E. Hepatoprotective property of ethanolic leaf extract of Moringa oleifera oncarbon tetrachloride (CCl4) induced hepatotoxicity. J. Nat. Prod. Plant Resour. 2013, 3, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Prabakaran, M.; Kim, S.-H.; Sasireka, A.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Chung, I.-M. Polyphenol composition and antimicrobial activity of various solvent extracts from different plant parts of Moringa oleifera. Food Biosci. 2018, 26, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momoh, M.A.; Chime, S.A.; Kenechukwu, F.C. Novel drug delivery system of plant extract for the management of diabetes: An antidiabetic study. J. Diet. Suppl. 2013, 10, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakre, A.G.; Aderibigbe, A.O.; Ademowo, O.G. Studies on neuropharmacological profile of ethanol extract of Moringa oleifera leaves in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 149, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aekthammarat, D.; Pannangpetch, P.; Tangsucharit, P. Moringa oleifera leaf extract lowers high blood pressure by alleviating vascular dysfunction and decreasing oxidative stress in L-NAME hypertensive rats. Phytomedicine 2019, 54, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, F.; Latif, S.; Ashraf, M.; Gilani, A.H. Moringa oleifera: A food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytother. Res. PTR 2007, 21, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.Y.; Jalil, J.; Ng, P.Y.; Ng, S.F. Development and formulation of Moringa oleifera standardised leaf extract film dressing for wound healing application. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Invally, M.; Sanzagiri, R.; Buttar, H.S. Evaluation of the antidepressant activity of Moringa oleifera alone and in combination with fluoxetine. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 2015, 6, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhye, K.; Rangari, V.; Mathur, V. Antimigraine activity study of Moringa oleifera leaf juice. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2012, 6, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, P.; Kar, A. Role of Moringa oleifera leaf extract in the regulation of thyroid hormone status in adult male and female rats. Pharm. Res. 2000, 41, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasolo, J.N.; Bimenya, G.S.; Ojok, L.; Ochieng, J.; Ogwal-Okeng, J.W. Phytochemicals and uses of Moringa oleifera leaves in Ugandan rural communities. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 753–757. [Google Scholar]
- Mbikay, M. Therapeutic Potential of Moringa oleifera Leaves in Chronic Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia: A Review. Front. Pharm. 2012, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalafalla, M.M.; Abdellatef, E.; Dafalla, H.M.; Nassrallah, A.A.; Aboul-Enein, K.M.; Lightfoot, D.A.; El-Deeb, F.E.; El-Shemy, H.A. Active principle from Moringa oleifera Lam leaves effective against two leukemias and a hepatocarcinoma. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 8467–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshney, R.I. Cytotoxicity. In Culture of Animal Cells: A Manual of Basic Technique; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlachetka, K.; Kut, P.; Stępień, A. Cytotoxic and anticancer activity of Moringa oleifera. Eur. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 18, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guevara, A.P.; Vargas, C.; Sakurai, H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Maoka, T.; Kozuka, M.; Ito, Y.; Tokuda, H.; Nishino, H. An antitumor promoter from Moringa oleifera Lam. Mutat. Res. 1999, 440, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, M.V.S.; Umamaheshwari, A. Cytotoxic Effect of Moringa Oleifera Leaf Extracts On Human Multiple Myeloma Cell Lines. Trends Med. Res. 2007, 2, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, I.L.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.C. A potential oral anticancer drug candidate, Moringa oleifera leaf extract, induces the apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarain, A.; Asghari, G.; Ghassami, E. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of Moringa oleifera Lam. callus and leaf extracts on Hela cells. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohaib, M.; Al-Barakah, F.N.I.; Migdadi, H.M.; Husain, F.M. Comparative study among Avicennia marina, Phragmites australis, and Moringa oleifera based ethanolic-extracts for their antimicrobial, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour, H.; Sadrameli, S.M.; Eslami, F.; Asoodeh, A. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of Moringa peregrina oil with response surface methodology and comparison with Soxhlet method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 131, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuapia, Y.; Al-Hamimi, S.; Matshediso, P.G.; Cukrowska, E.; Tutu, H.; Turner, C.; Chimuka, L. Selective pressurized hot water extraction of nutritious macro-nutrients vs. micro-nutrients in Moringa oleifera leaves-a chemometric approach. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2495–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuapia, Y.; Cukrowska, E.; Tutu, H.; Chimuka, L. Statistical comparison of two modeling methods on pressurized hot water extraction of vitamin C and phenolic compounds from Moringa oleifera leaves. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, L.; Tringaniello, C.; Ianni, F.; Blasi, F.; Manes, J.; Cossignani, L. Impact of Ultrasound Extraction Parameters on the Antioxidant Properties of Moringa Oleifera Leaves. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Pérez, C.; Mendiola, J.A.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Ibáñez, E.; Segura-Carretero, A. Green downstream processing using supercritical carbon dioxide, CO2-expanded ethanol and pressurized hot water extractions for recovering bioactive compounds from Moringa oleifera leaves. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 116, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Perez, C.; Gilbert-Lopez, B.; Mendiola, J.A.; Quirantes-Pine, R.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Ibanez, E. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction and pressurized liquid extraction of phenolic compounds from Moringa oleifera leaves by multiresponse surface methodology. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerena-Prieto, B.J.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, M.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González-de-Peredo, A.V.; García-Alvarado, M.Á.; Palma, M.; Rodríguez-Jimenes, G.d.C.; Barbero, G.F. Optimization of an Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction Method Applied to the Extraction of Flavonoids from Moringa Leaves (Moringa oleífera Lam.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Qin, X. The application of ultrasound and microwave to increase oil extraction from Moringa oleifera seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 120, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matshediso, P.G.; Cukrowska, E.; Chimuka, L. Development of pressurised hot water extraction (PHWE) for essential compounds from Moringa oleifera leaf extracts. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feitosa, P.R.B.; Santos, T.R.J.; Gualberto, N.C.; Narain, N.; de Aquino Santana, L.C.L. Solid-state fermentation with Aspergillus niger for the bio-enrichment of bioactive compounds in Moringa oleifera (moringa) leaves. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 27, 101709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, T.; Xie, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Sheng, J. Solid-state fermentation of Moringa oleifera leaf meal using Bacillus pumilus CICC 10440. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Shu, G.; Chen, L.; Dai, C.; Wan, H.; Chen, H.; Dong, X. Ultrasound-microwave assisted extraction of proteins from Moringa oleifera leaves: Comparative optimization study and LC-MS analysis of the protein concentrate. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Porto, C.; Decorti, D.; Natolino, A. Microwave pretreatment of Moringa oleifera seed: Effect on oil obtained by pilot-scale supercritical carbon dioxide extraction and Soxhlet apparatus. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, S.; Anwar, F.; Hussain, A.I.; Shahid, M. Aqueous enzymatic process for oil and protein extraction from Moringa oleifera seed. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2011, 113, 1012–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Yusoff, M.; Gordon, M.H.; Ezeh, O.; Niranjan, K. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of Moringa oleifera oil. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutada, P.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Nemade, P.R.; Jain, R.D. Solvent assisted extraction of oil from Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 82, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobosse, P.; Fombang, E.N.; Mbofung, C.M.F. Effects of age and extraction solvent on phytochemical content and antioxidant activity of fresh Moringa oleifera L. leaves. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivapat, S.; Sincharoenpokai, P.; Suppajariyawat, P.; Rungsipipat, A.; Phattarapornchaiwat, S.; Chantarateptawan, V. Safety Evaluations of Ethanolic Extract of Moringa oleifera Lam. Seed in Experimental Animals. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2012, 42, 343–352. [Google Scholar]
- Landazuri, A.C.; Gualle, A.; Castaneda, V.; Morales, E.; Caicedo, A.; Orejuela-Escobar, L.M. Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf powder antioxidant activity and cytotoxicity in human primary fibroblasts. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 6194–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Bakar, S.N.H.; Abu Hasan, H.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Kasan, N.A.; Muhamad, M.H.; Kurniawan, S.B. A review of the production process of bacteria-based polymeric flocculants. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayanan, B.U.R.; Sagum, R.S. Microwave and Ultrasound Pretreatment of Moringa oleifera Lam. Seeds: Effects on Oil Expression, Oil Quality, and Bioactive Component. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhammouche, T.; Melo, A.; Martins, Z.; Faria, M.A.; Pinho, S.C.M.; Ferreira, I.; Zaidi, F. Nutritional quality of protein concentrates from Moringa Oleifera leaves and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 128858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chang, X.; Yang, M.; He, J.; Tian, Y.; Sheng, J. Anti-photoaging effects of flexible nanoliposomes encapsulated Moringa oleifera Lam. isothiocyanate in UVB-induced cell damage in HaCaT cells. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militao, I.M.; Roddick, F.; Bergamasco, R.; Fan, L. Rapid adsorption of PFAS: Application of Moringa oleifera seed powder encapsulated in alginate beads. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-López, C.; Espinoza-González, C.; Ramos-González, R.; Boone-Villa, V.D.; Aguilar-González, M.A.; Martínez-Ávila, G.C.; Aguilar, C.N.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J.M. Spray-drying encapsulation of microwave-assisted extracted polyphenols from Moringa oleifera: Influence of tragacanth, locust bean, and carboxymethyl-cellulose formulations. Food Res. Int. 2021, 144, 110291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürbüz, E.; Keresteci, B.; Günneç, C.; Baysal, G. Encapsulation Applications and Production Techniques in the Food Industry. J. Nutr. Health Sci. 2020, 7, 106. [Google Scholar]
- Batra, G.; Gortzi, O.; Lalas, S.I.; Galidi, A.; Alibade, A.; Nanos, G.D. Enhanced antioxidant activity of Capsicum annuum L. and Moringa oleifera L. extracts after encapsulation in microemulsions. ChemEngineering 2017, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsa, O.; Alibade, A.; Batra, G.; Bozinou, E.; Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S.I. Fortification of chocolate using Moringa oleifera extract encapsulated in microemulsions. OCL 2021, 28, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsa, O.; Alibade, A.; Bozinou, E.; Makris, D.P.; Lalas, S.I. Encapsulation of Moringa oleifera extract in Ca-alginate chocolate beads: Physical and antioxidant properties. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 5549873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hani, N.; Azarian, M.H.; Torkamani, A.E.; Kamil Mahmood, W.A. Characterisation of gelatin nanoparticles encapsulated with Moringa oleifera bioactive extract. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 51, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop, O.L.; Vodnar, D.C.; Suharoschi, R.; Mudura, E.; Socaciu, C.L. plantarum ATCC 8014 Entrapment with Prebiotics and Lucerne Green Juice and Their Behavior in Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions. J. Food Process Eng. 2016, 39, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Sethuraman, L.; Panjanathan, R.; Natarajan, A.; Solaiappan, V.; Thilagaraj, W.R. Biosorption of heavy metals from actual electroplating wastewater using encapsulated Moringa oleifera beads in fixed bed column. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 3572–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Farooq, B.; Lamba, S.; Koul, B. Foliar spray of Moringa oleifera Lam. leaf extracts (MLE) enhances the stevioside, zeatin and mineral contents in Stevia rebaudiana Betoni. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 132, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milla, P.G.; Penalver, R.; Nieto, G. Health Benefits of Uses and Applications of Moringa oleifera in Bakery Products. Plants 2021, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyeyinka, A.T.; Oyeyinka, S.A. Moringa oleifera as a food fortificant: Recent trends and prospects. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 2018, 17, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollah, S.; Abdulkarim, S.M.; Ahmad, S.H.; Khoramnia, A.; Ghazali, H.M. Physicochemical properties and potential food applications of Moringa oleifera seed oil blended with other vegetable oils. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqurashi, R.M.; Aldossary, H.M. In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of Moringa oleifera leaf as a natural food preservative in chicken burgers. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2021, 33, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.G.; Abd-Rabou, H.S.; El-Sohaimy, S.A. Plant Extracts in Probiotic Encapsulation: Evaluation of their Effects on Strains Survivability in Juice and Drinkable Yogurt During Storage and an in-vitro Gastrointestinal Model. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 13, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.T.; Oyenihi, A.B.; Rautenbach, F.; Obilana, A.O. Characterization of Moringa oleifera Leaf Powder Extract Encapsulated in Maltodextrin and/or Gum Arabic Coatings. Foods 2021, 10, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premi, M.; Sharma, H.K. Effect of different combinations of maltodextrin, gum arabic and whey protein concentrate on the encapsulation behavior and oxidative stability of spray dried drumstick (Moringa oleifera) oil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 105, 1232–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-López, C.; Gonçalves, C.; Ventura-Sobrevilla, J.M.; Pastrana, L.M.; Aguilar-González, C.N.; Martínez-Ávila, G.C. Moringa oleifera—Storage Stability, In Vitro-Simulated Digestion and Cytotoxicity Assessment of Microencapsulated Extract. Processes 2020, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, N.M.; Hosny, N.S.; El-Desoky, N.I.; Shehata, M.G. Effect of Nanoencapsulated Alginate-Synbiotic on Gut Microflora Balance, Immunity, and Growth Performance of Growing Rabbits. Polymers 2021, 13, 4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gu, Y.; Cui, H. Moringa oil/chitosan nanoparticles embedded gelatin nanofibers for food packaging against Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus on cheese. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 19, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, M.; Sadasivam, R.; Packirisamy, G.; Pichiah, S. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile-Moringa Olifera based nanofibrous bio-sorbent for remediation of Congo red dye. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Cimpeanu, C.; Turcus, V.; Predoi, G.; Iordache, F. Nanoencapsulation techniques for compounds and products with antioxidant and antimicrobial activity—A critical view. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 1326–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Houssiny, A.S.; Fouad, E.A.; Hegazi, A.G. A Comparative Antimicrobial Activity Study of Moringa oleifera Extracts Encapsulated within ALg Nanoparticles. Nanosci. Nanotechnol.-Asia 2021, 11, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, E. Electrospinning of Essential Oils. Polymers 2020, 12, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afolabi-owolabi, O.T.; Abidin, S.Z.; Ariffin, F. Electrospun Polymer Nanofiber from Moringa Oleifera Kernel Oil with Coaxial Electrospinning Method. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 16, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Hamblin, M.R. Electrospraying as a novel method of particle engineering for drug delivery vehicles. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Encapsulation Technique | Encapsulated Material | Encapsulation Matrix | Encapsulation Formulation | Features | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-linking gelation | Moringa oleifera leaf extract | Alginate, whey protein, cacao powder | 0, 2, 4, and 6% extract concentration |
| food ingredient | [78] |
| Moringa oleifera seed powder (MSP) | Sodium alginate |
|
| pollutants removal | [73] | |
| Moringa oleifera seed powder (MSP) | Sodium alginate |
| pollutants removal | [81] | ||
| Freeze-drying | Moringa oleifera leaf powder ethanol extract | Maltodextrin, arabic gum | Malto-dextrin, arabic gum |
| food fortification | [88] |
| Micro-emulsion | Carotenoids Moringa oleifera L. leaves | Lecithin, sunflower oil, absolute ethanol, water |
| antioxidant | [76] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaves extract | Coconut/ soybean oil, tween80, span80 | 4%, 8% Moringa oleifera leaves extract |
| food fortification | [77] | |
| Spray drying | Drumstick oil (30%) | Maltodextrin (MD) Gum Arabic (GA) Whey Protein (WP) | MD: GA (25:75, 50:50, 75:25) MD: WPC (25:75, 50:50, 75:25) |
| food fortification | [89] |
| Polyphenols (M. oleifera) extracted by microwave- assisted extraction | Tragacanth gum (TG), locust bean gum (LBG), and carboxymethyl-cellulose (CMC) | TG 1%, LBG 1%, CMC 1%, LBG 0.5% + TG 0.5%, TG 0.5% + CMC 0.5%, CMC 0.5% + LBG 0.5% |
| antioxidant | [74] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaves extract (MLE) | Soy protein isolate (SPI), pea protein isolate (PPI) | 10% plant-based protein 11–22% (w/v) (MLE) |
| antioxidant | [13] | |
| Moringa oleifera leaves extract (MLE) | Tragacanth gum | 1% tragacanth gum |
| antioxidant | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pop, O.L.; Kerezsi, A.D.; Ciont, C. A Comprehensive Review of Moringa oleifera Bioactive Compounds—Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Their Encapsulation. Foods 2022, 11, 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233787
Pop OL, Kerezsi AD, Ciont C. A Comprehensive Review of Moringa oleifera Bioactive Compounds—Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Their Encapsulation. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233787
Chicago/Turabian StylePop, Oana Lelia, Andreea Diana Kerezsi, and Călina Ciont (Nagy). 2022. "A Comprehensive Review of Moringa oleifera Bioactive Compounds—Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Their Encapsulation" Foods 11, no. 23: 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233787
APA StylePop, O. L., Kerezsi, A. D., & Ciont, C. (2022). A Comprehensive Review of Moringa oleifera Bioactive Compounds—Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Their Encapsulation. Foods, 11(23), 3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233787







