Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Jinhua ham Using Three Extraction Methods Combined with Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Instruments and Equipment
2.3. Extraction of Volatile Compounds
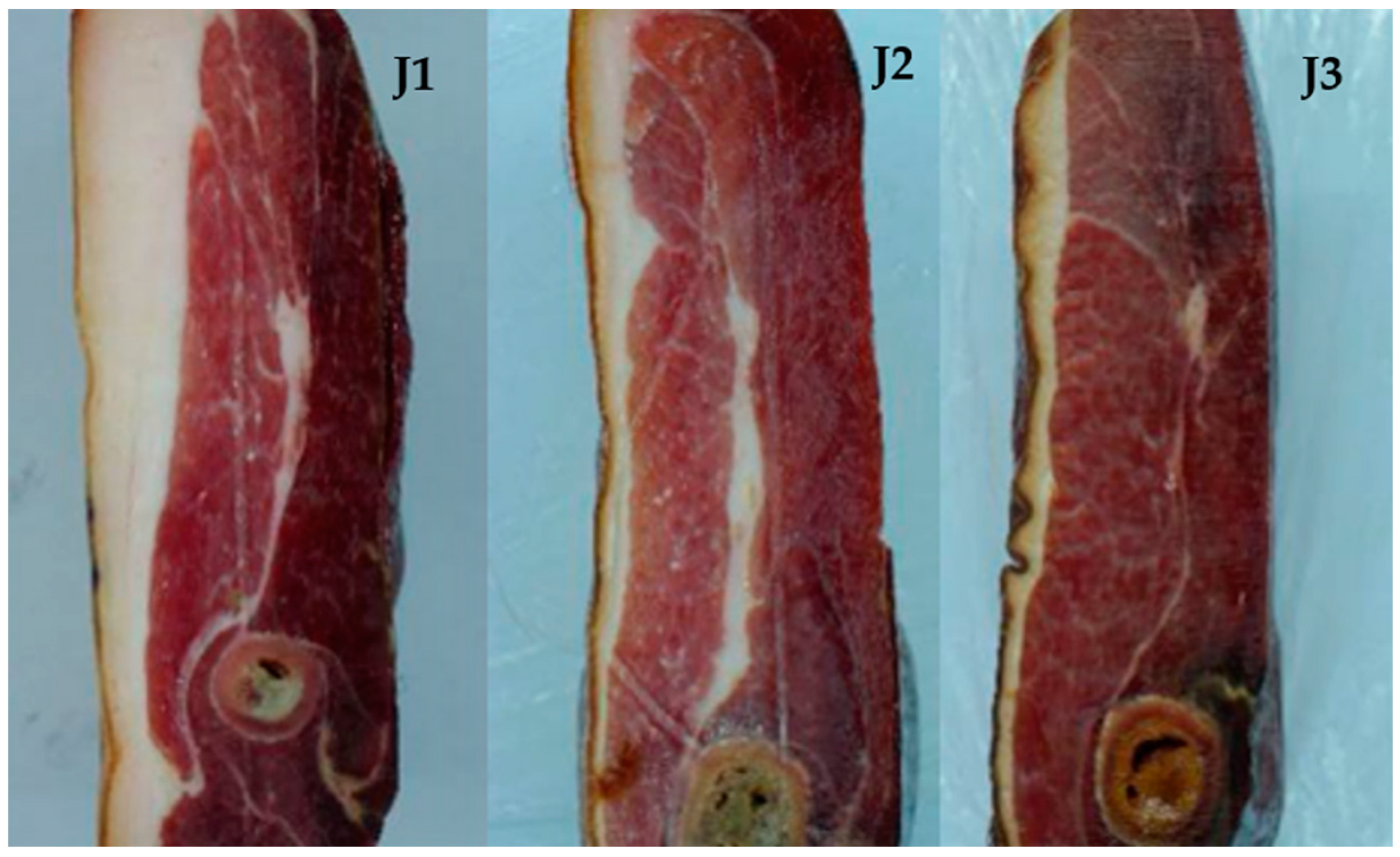
2.3.1. Sample Preparation
2.3.2. The Extraction of Aroma Compounds Using SAFE
2.3.3. The Extraction of Aroma Compounds Using SPME
2.3.4. The Extraction of Aroma Compounds Using NT
2.4. GC–TOF/MS Analysis
2.5. Identification of Volatile Compounds
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Volatile Compounds of Jinhua ham Extracted by SAFE, SPME, and NT
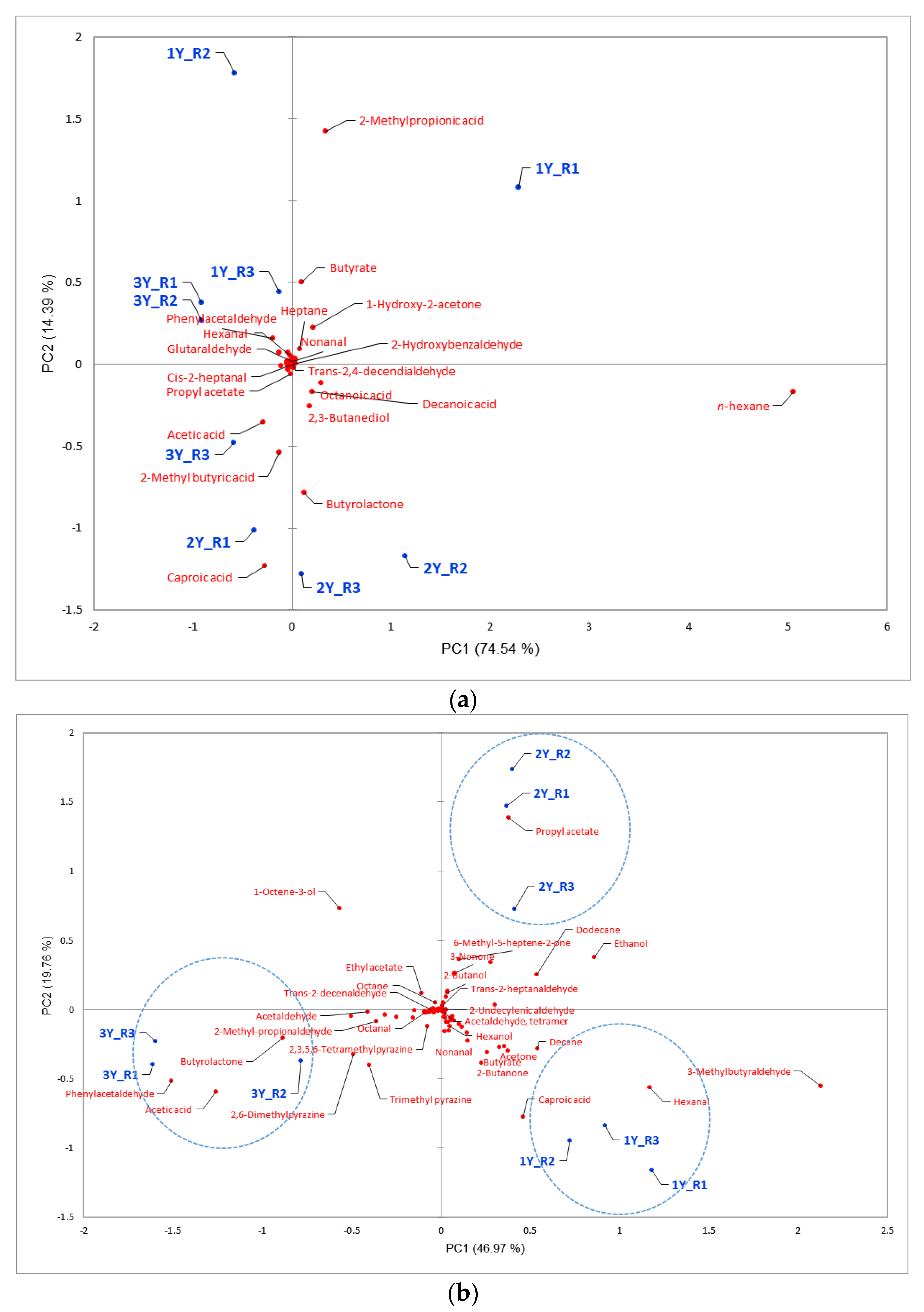
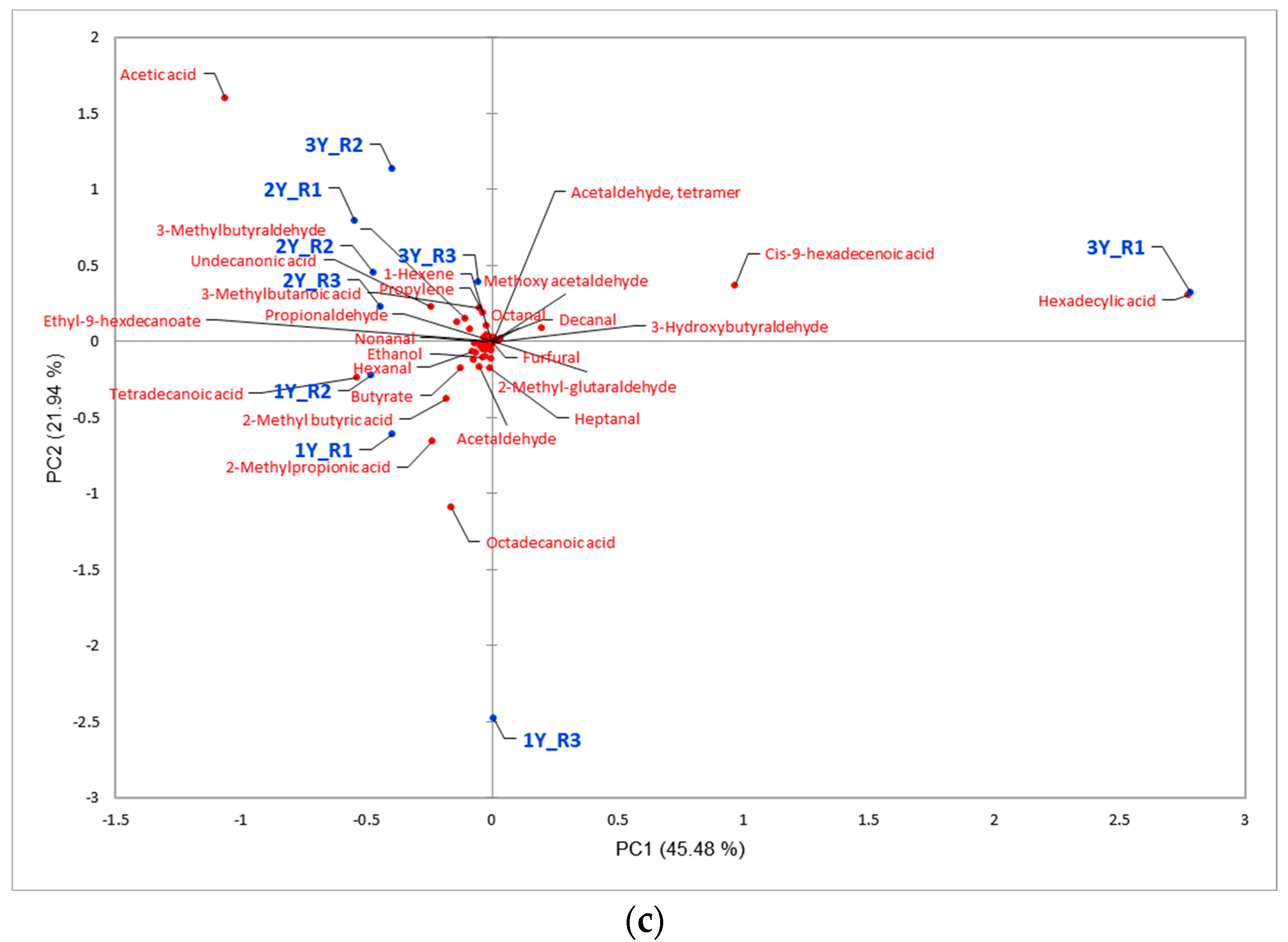
3.2. Comparison Analysis of Three Pretreatment Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, G.; Zhao, G. Biochemical changes during processing of traditional Jinhua ham. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Bai, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, D.; Yao, W.; Zhang, H.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Jinhua ham aroma profiles in specific to aging time by gas chromatography-ion mobility spectrometry (GC-IMS). Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majcher, M.A.; Jeleń, H.H. Comparison of suitability of SPME, SAFE and SDE methods for isolation of flavor compounds from extruded potato snacks. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- And, P.M.C.-S.; Peterson, D.G. Inhibition of Key Aroma Compound Generated during Ultrahigh-Temperature Processing of Bovine Milk via Epicatechin Addition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 53, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, W.; Bahr, W.; Schieberle, P. Solvent assisted flavour evaporation—A new and versatile technique for the careful and direct isolation of aroma compounds from complex food matrices. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 1999, 209, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Lord, H.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Applications of solid-phase microextraction in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 880, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkaew, M.; Sangta, J.; Chansakaow, S.; Jantanasakulwong, K.; Rachtanapun, P.; Sommano, S.R. Volatile profiles from over-ripe purée of Thai mango varieties and their physiochemical properties during heat processing. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Esteban, M.; Ansorena, D.; Astiasaran, I.; Martin, D.; Ruiz, J. Comparison of simultaneous distillation extraction(SDE) and solid-phase microextraction(SPME) for the analysis of volatile compounds in dry-cured ham. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kędziora, K.; Wasiak, W. Extraction media used in needle trap devices—Progress in development and application. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1505, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, H.L.; Zhan, W.; Pawliszyn, J. Fundamentals and applications of needle trap devices: A critical review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 677, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mieth, M.; Schubert, J.K.; Gröger, T.; Sabel, B.; Kischkel, S.; Fuchs, P.; Hein, D.; Zimmermann, R.; Miekisch, W. Automated Needle Trap Heart-Cut GC/MS and Needle Trap Comprehensive Two-Dimensional GC/TOF-MS for Breath Gas Analysis in the Clinical Environment. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, M.; Castellanos, M.; Besalú, E.; Sanchez, J.M. A headspace needle-trap method for the analysis of volatile organic compounds in whole blood. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1252, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koziel, J.A.; Odziemkowski, M.; Pawliszyn, J. Sampling and Analysis of Airborne Particulate Matter and Aerosols Using In-Needle Trap and SPME Fiber Devices. Anal. Chem. 2000, 73, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Feng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, B.; Sun, B.; Tian, H.; Liu, Y. Analysis of volatile compounds in Chinese dry-cured hams by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Meat Sci. 2018, 140, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Capone, D.L.; Jeffery, D.W. Identification and Quantitative Analysis of 2-Methyl-4-propyl-1,3-oxathiane in Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10808–10815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xu, H.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, B. Correlation of characteristic flavor and microbial community in Jinhua ham during the post-ripening stage. LWT 2022, 171, 114067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, G.; Xu, X.; Peng, Z. Changes in flavor compounds of dry-cured Chinese Jinhua ham during processing. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Shen, Q.; Pan, T.; Hui, T.; Ma, J. Characterization of Key Aroma Compounds in Beijing Roasted Duck by Gas Chromatography–Olfactometry–Mass Spectrometry, Odor-Activity Values, and Aroma-Recombination Experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5847–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhan, G.; Pan, D.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Cao, J. Charactering the spoilage mechanism of “three sticks” of Jinhua ham. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2022, 11, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, M.; Ingram, D.A.; Bett, K.L.; Toldrá, F.; Spanier, A.M. Sensory Characteristics of Spanish "Serrano" Dry-Cured Ham. J. Sens. Stud. 1997, 12, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, J.S.; Mottram, D.S.; Enser, M.; Wood, J.D. Effect of the Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Composition of Beef Muscle on the Profile of Aroma Volatiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-González, D.L.; Aparicio, R.; Ruiz, R.A. Volatile and Amino Acid Profiling of Dry Cured Hams from Different Swine Breeds and Processing Methods. Molecules 2013, 18, 3927–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabio, E.; Vidal-Aragón, M.; Bernalte, M.; Gata, J. Volatile compounds present in six types of dry-cured ham from south European countries. Food Chem. 1998, 61, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Careri, M.; Mangia, A.; Barbieri, G.; Bouoni, L.; Virgili, R.; Parolari, G. Sensory property relationships to chemical data of Italian-type dry-cured ham. J. Food Sci. 1993, 58, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, G. Changes in the volatile flavour components of Jinhua ham during the traditional ageing process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 41, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Carballo, J.; Franco, D. Effect of the Inclusion of Chestnut in the Finishing Diet on Volatile Compounds of Dry-Cured Ham from Celta Pig Breed. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, R.; Franco, D.; Carballo, J.; Lorenzo, J.M. Influence of type of muscle on volatile compounds throughout the manufacture of Celta dry-cured ham. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2015, 21, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, J.; Yu, X.; Long, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Influence of partial replacement of NaCl with KCl on profiles of volatile compounds in dry-cured bacon during processing. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, G.; Magni, S.; Rossi, R.; Pagliarini, E.; Baldini, P.; Dirinck, P.; Van Opstaele, F.; Corino, C. Influence of dietary fat, on fatty acid composition and sensory properties of dry-cured Parma ham. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, C.; Berdagué, J.; Antequera, T.; López-Bote, C.; Córdoba, J.; Ventanas, J. Volatile components of dry cured Iberian ham. Food Chem. 1991, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, T.; Zhou, G. Effect of intensifying high-temperature ripening on proteolysis, lipolysis and flavor of Jinhua ham. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Palacios, T.; Ruiz, J.; Martín, D.; Grau, R.; Antequera, T. Influence of pre-cure freezing on the profile of volatile compounds during the processing of Iberian hams. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, A. A metabolomics-based approach investigates volatile flavor formation and characteristic compounds of the Dahe black pig dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2019, 158, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muriel, E.; Antequera, T.; Petrón, M.J.; Andrés, A.I.; Ruiz-Carrascal, J. Volatile compounds in Iberian dry-cured loin. Meat Sci. 2004, 68, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandemer, G. Lipids in muscles and adipose tissues, changes during processing and sensory properties of meat products. Meat Sci. 2002, 62, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, D.L.; Tena, N.; Aparicio-Ruiz, R.; Morales, M.T. Relationship between sensory attributes and volatile compounds qualifying dry-cured hams. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Carballo, J. Changes in physico-chemical properties and volatile compounds throughout the manufacturing process of dry-cured foal loin. Meat Sci. 2015, 99, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugliese, C.; Sirtori, F.; Škrlep, M.; Piasentier, E.; Calamai, L.; Franci, O.; Čandek-Potokar, M. The effect of ripening time on the chemical, textural, volatile and sensorial traits of Bicep femoris and Semimembranosus muscles of the Slovenian dry-cured ham Kraški pršut. Meat Sci. 2015, 100, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Feng, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, Y. Physical properties, compositions and volatile profiles of Chinese dry-cured hams from different regions. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 14, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Domínguez, R.; Munekata, P.E.; Cittadini, A. Effect of the partial NaCl substitution by other chloride salts on the volatile profile during the ripening of dry-cured lacón. Grasas Y Aceites 2016, 67, e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-S.; Liu, J.-B.; Yang, Z.-M.; Song, H.-L.; Liu, Y.; Zou, T.-T. Aroma-Active Compounds in Jinhua Ham Produced With Different Fermentation Periods. Molecules 2014, 19, 19097–19113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Mercier, F.; Tournayre, P.; Martin, J.-L.; Berdagué, J.-L. Identification and origin of odorous sulfur compounds in cooked ham. Food Chem. 2014, 155, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Arellano, I.; Flores, M.; Toldrá, F. The ability of peptide extracts obtained at different dry cured ham ripening stages to bind aroma compounds. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söllner, K.; Schieberle, P. Decoding the Key Aroma Compounds of a Hungarian-Type Salami by Molecular Sensory Science Approaches. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4319–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Mercier, F.; Tournayre, P.; Martin, J.-L.; Berdagué, J.-L. Effect of added thiamine on the key odorant compounds and aroma of cooked ham. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Onandi, N.; Rivas-Cañedo, A.; Nuñez, M.; Picon, A. Effect of chemical composition and high pressure processing on the volatile fraction of Serrano dry-cured ham. Meat Sci. 2016, 111, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petričević, S.; Marusic Radovčić, N.; Lukić, K.; Listeš, E.; Medić, H. Differentiation of dry-cured hams from different processing methods by means of volatile compounds, physico-chemical and sensory analysis. Meat Sci. 2018, 137, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Yang, C.; Bai, L.; Feng, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Jinhua ham Using Three Extraction Methods Combined with Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 3897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233897
Liu D, Yang C, Bai L, Feng X, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y. Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Jinhua ham Using Three Extraction Methods Combined with Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Foods. 2022; 11(23):3897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233897
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dengyong, Cong Yang, Lu Bai, Xi Feng, Yanping Chen, Yin Zhang, and Yuan Liu. 2022. "Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Jinhua ham Using Three Extraction Methods Combined with Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry" Foods 11, no. 23: 3897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233897
APA StyleLiu, D., Yang, C., Bai, L., Feng, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2022). Analysis of Volatile Compounds in Jinhua ham Using Three Extraction Methods Combined with Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Foods, 11(23), 3897. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11233897







