Pasting and Rheological Properties of Starch Paste/Gels in a Sugar-Acid System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Starch Isolation
2.3. Starch Composition
2.4. Food Model Systems
2.5. Molecular Weight Profile of Native Starches
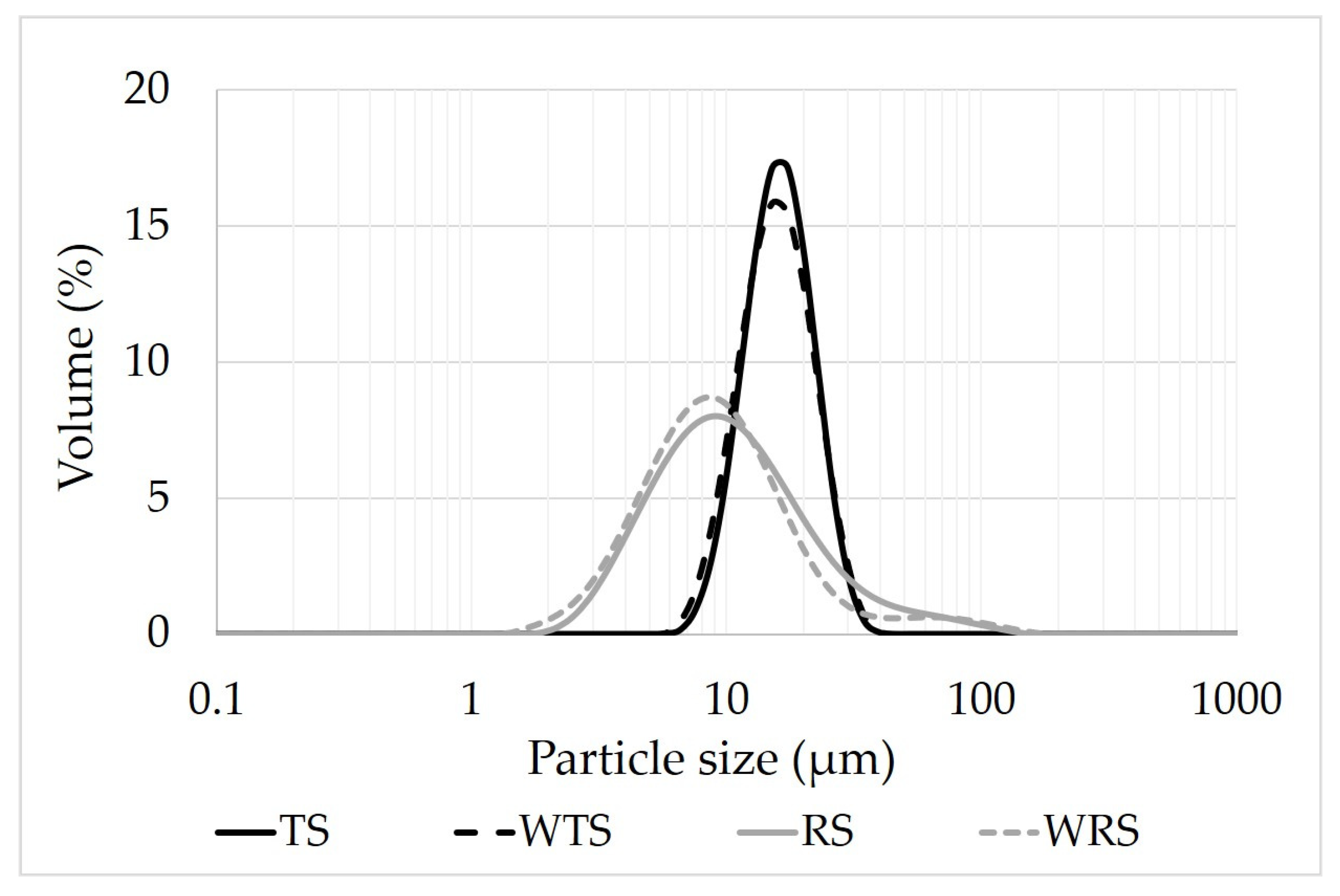
2.6. Starch Granule Size Distribution and Morphology
2.7. Measurements of Starch Physico-Chemical Properties
2.8. Pasting Properties
2.9. Rheological Properties of Starch Gels
2.9.1. Starch Gels Preparation
2.9.2. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (SAOS)
2.9.3. Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LAOS)
2.10. Starch Paste/Gel Microstructure
2.11. Statistical analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Granule Size and Morphology of Native Starches
3.2. Chemical Compositions and Molecular Characteristics of Native Starches
3.3. Effect of Granule and Starch Polymer Characteristics, on Physico-Chemical and Pasting Properties
3.3.1. Gelatinization Properties
3.3.2. Swelling Behavior and Paste Clarity
3.3.3. Pasting Properties of Native Starches
Pasting Temperature (PT) and Peak Viscosity (PV)
Breakdown (BD) and Trough Viscosity (T)
Setback (SB) and Final Viscosity (FV)
3.4. Effect of Granule and Starch Polymer Characteristics on Rheological Properties of Starch Gels
3.4.1. Small Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (SAOS)
3.4.2. Large Amplitude Oscillatory Shear (LAOS)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, J.C.; Garwood, D.L.; Boyer, C.D. Chapter 3-Genetics and Physiology of Starch Development. In Starch, 3rd ed.; BeMiller, J., Whistler, R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 23–82. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoft, E. Understanding Starch Structure: Recent Progress. Agronomy 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, Y.; Jane, J.-L. Chapter 3-Understanding Starch Structure and Functionality. In Starch in Food, 2nd ed.; Sjöö, M., Nilsson, L., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 151–178. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Yoo, B. Effect of tapioca starch addition on rheological, thermal, and gelling properties of rice starch. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortuna, T.; Januszewska, R.; Juszczak, L.; Kielski, A.; Pałasiński, M. The influence of starch pore characteristics on pasting behaviour. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhital, S.; Shrestha, A.K.; Hasjim, J.; Gidley, M.J. Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Maize and Potato Starches as a Function of Granule Size. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 10151–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo-Ramírez, Y.I.; Martínez-Cruz, O.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J. The structural characteristics of starches and their functional properties. CyTA J. Food 2018, 16, 1003–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterschoot, J.; Gomand, S.V.; Delcour, J.A. Impact of swelling power and granule size on pasting of blends of potato, waxy rice and maize starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Morrison, W.R. Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. I. Effects of amylopectin, amylose, and lipids. Cereal Chem. J. 1990, 67, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Biliaderis, C.G.; Juliano, B.O. Thermal and mechanical properties of concentrated rice starch gels of varying composition. Food Chem. 1993, 48, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kaur, S.; Isono, N.; Ichihashi, Y.; Noda, T.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Diversity in characteristics of starch amongst rice bean (Vigna umbellate) germplasm: Amylopectin structure, granules size distribution, thermal and rheology. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-Z.; Hamaker, B.R. Amylopectin Fine Structure and Rice Starch Paste Breakdown. J. Cereal Sci. 2001, 34, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chantaro, P.; Pongsawatmanit, R. Influence of sucrose on thermal and pasting properties of tapioca starch and xanthan gum mixtures. J. Food Eng. 2010, 98, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotelli, E.; Rolée, A.; Le Meste, M. Effect of Sucrose on the Thermomechanical Behavior of Concentrated Wheat and Waxy Corn Starch−Water Preparations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoover, R.; Senanayake, N. Effect of Sugars on the Thermal and Retrogradation Properties of Oat Starches. J. Food Biochem. 1996, 20, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; van den Hoek, I.A.F.; van der Sman, R.G.M. Mechanisms controlling wheat starch gelatinization and pasting behaviour in presence of sugars and sugar replacers: Role of hydrogen bonding and plasticizer molar volume. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, T.J.; Grush, E.; Allan, M.C.; Mauer, L.J. The effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the pasting and granular swelling of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongsawatmanit, R.; Temsiripong, T.; Suwonsichon, T. Thermal and rheological properties of tapioca starch and xyloglucan mixtures in the presence of sucrose. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.B.; Williams, P.A. Effect of sugars on the thermal and rheological properties of sago starch. Biopolymers 1999, 50, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Copeland, L. Effect of Acid Hydrolysis on Starch Structure and Functionality: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Xie, F.; Zhao, L.; Qiao, Q.; Liu, X. Effect of acid hydrolysis on the multi-scale structure change of starch with different amylose content. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Zhu, L.; Gu, Z. Effects of sugar, salt and acid on tapioca starch and tapioca starch-xanthan gum combinations. Starch Stärke 2014, 66, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Ferrero, C.; Redigonda, V.; Beleia, A.P.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; Zaritzky, N.E. Influence of pH and hydrocolloids addition on yam (Dioscorea alata) starch pastes stability. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirashima, M.; Takahashi, R.; Nishinari, K. Effects of adding acids before and after gelatinization on the viscoelasticity of cornstarch pastes. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumdubwong, N.; Seib, P.A. Rice Starch Isolation by Alkaline Protease Digestion of Wet-milled Rice Flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2000, 31, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC. Approved Methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, 10th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemist: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chrastil, J. Improved colorimetric determination of amylose in starches or flours. Carbohydr. Res. 1987, 159, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, A.; Varela, P.; Sanz, T.; Fiszman, S.M. Native tapioca starch as a potential thickener for fruit fillings. Evaluation of mixed models containing low-methoxyl pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Vu, H.P.; Lumdubwong, N. Starch behaviors and mechanical properties of starch blend films with different plasticizers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-F.; Liu, W.; Whaley, J.K.; Shi, Y.-C. Structure and functional properties of waxy starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, G.B. The relationship between starch swelling properties, paste viscosity and boiled noodle quality in wheat flours. J. Cereal Sci. 1991, 13, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S.A.S.; Maningat, C.C.; Seib, P.A.; Hoseney, R.C. Starch paste clarity. Cereal Chem. 1989, 66, 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Ewoldt, R.H.; Hosoi, A.E.; McKinley, G.H. New measures for characterizing nonlinear viscoelasticity in large amplitude oscillatory shear. J. Rheol. 2008, 52, 1427–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewoldt, R.H.; Winter, P.; Maxey, J.; McKinley, G.H. Large amplitude oscillatory shear of pseudoplastic and elastoviscoplastic materials. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 191–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatokun, O. Micrometrics and Morphological Properties of Starch. In Chemical Properties of Starch; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S. Morphology and physicochemical properties of mechanically activated rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomand, S.V.; Lamberts, L.; Derde, L.J.; Goesaert, H.; Vandeputte, G.E.; Goderis, B.; Visser, R.G.F.; Delcour, J.A. Structural properties and gelatinisation characteristics of potato and cassava starches and mutants thereof. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, K.; Denyer, K. Starch synthesis in cereal grains. Adv. Bot. Res. 2003, 40, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa Silva Clerici, M.T.; Sampaio, U.M.; Schmiele, M. Chapter 2-Identification and Analysis of Starch. In Starches for Food Application; Silva Clerici, M.T.P., Schmiele, M., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 23–69. [Google Scholar]
- Breuninger, W.F.; Piyachomkwan, K.; Sriroth, K. Chapter 12-Tapioca/Cassava Starch: Production and Use. In Starch, 3rd ed.; BeMiller, J., Whistler, R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 541–568. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte, G.E.; Vermeylen, R.; Geeroms, J.; Delcour, J.A. Rice starches. I. Structural aspects provide insight into crystallinity characteristics and gelatinisation behaviour of granular starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2003, 38, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland-Sabaté, A.; Sánchez, T.; Buléon, A.; Colonna, P.; Jaillais, B.; Ceballos, H.; Dufour, D. Structural characterization of novel cassava starches with low and high-amylose contents in comparison with other commercial sources. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jane, J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lee, L.F.; McPherson, A.E.; Wong, K.S.; Radosavljevic, M.; Kasemsuwan, T. Effects of Amylopectin Branch Chain Length and Amylose Content on the Gelatinization and Pasting Properties of Starch. Cereal Chem. 1999, 76, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Beparva, P.; Farahnaky, A.; Badii, F. Effects of malic acid and citric acid on the functional properties of native and cross-linked wheat starches. Starch Stärke 2014, 66, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohishi, K.; Kasai, M.; Shimada, A.; Hatae, K. Effects of acetic acid on the rice gelatinization and pasting properties of rice starch during cooking. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Yang, S.; Zeng, L.; Han, W.; Ran, X. Study on physicochemical properties of purple waxy wheat starch. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Bergman, C.J. Chapter 10-Rice Flour and Starch Functionality. In Starch in Food, 2nd ed.; Sjöö, M., Nilsson, L., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 373–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kowittaya, C.; Lumdubwong, N. Molecular weight, chain profile of rice amylopectin and starch pasting properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lim, W.-J.; Lim, S.-T. Characterization of nanoparticles prepared by acid hydrolysis of various starches. Starch Stärke 2012, 64, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Khatkar, B. Thermal, pasting and morphological properties of starch granules of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterschoot, J.; Gomand, S.V.; Willebrords, J.K.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Pasting properties of blends of potato, rice and maize starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, M.; Daler, J.M.; Flöter, E. Acid hydrolysis of corn starch genotypes. II. Impact on functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-H.; Sasaki, T.; Li, Y.-Y.; Yoshihashi, T.; Li, L.-T.; Kohyama, K. Effect of amylose content and rice type on dynamic viscoelasticity of a composite rice starch gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.G.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, S.J. Large amplitude oscillatory shear behavior of complex fluids investigated by a network model: A guideline for classification. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2003, 112, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Sample | Chemical Compositions | Amylose Content (%) | Maximum Wavelength (nm) | % Light Transmittance (%T) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (%) | Fat (%) | Ash (%) | Colorimetric Method | HPSEC Method | Neutral System | Sugar–Acid System | ||
| TS | 0.23 ±0.03 b | 0.06 ±0.01 ab | 0.23±0.01 a | 25.92 ±0.78 b | 21.71 ±1.13 b | 581.0 ± 3.6 a | 56.2 ± 0.1 b | 72.2 ± 0.1 b |
| WTS | 0.22 ±0.01 b | 0.01 ±0.01 b | 0.18 ±0.01 a | 0.39 ±0.55 c | 0.00 ±0.00 c | 539.8 ± 2.9 b | 62.1 ± 1.0 a | 85.3 ± 0.1 a |
| RS | 0.47 ±0.03 a | 0.08 ±0.03 a | 0.21 ±0.03 a | 36.89 ±0.94 a | 30.91 ±0.26 a | 581.8 ± 3.0 a | 13.9 ± 0.1 d | 6.5 ± 0.1 d |
| WRS | 0.22 ±0.10 b | 0.13 ±0.03 a | 0.16 ±0.02 a | 0.28 ±0.39 c | 0.00 ±0.00 c | 524.0 ± 0.0 c | 18.6 ± 0.5 c | 54.5 ± 0.1 c |
| Sample | Fraction I (AP) | Fraction II (IM) | Fraction III (AM) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(107 g/mol) | (107 g/mol) | (105) | %Area | (106 g/mol) | (106 g/mol) | (104) | %Area | (105 g/mol) | (105 g/mol) | (103) | %Area | |
| TS | 6.75 a | 5.17 a | 4.17 a | 66.31 c | 6.81 b | 5.50 b | 4.20 b | 11.98 b | 19.40 a | 16.20 a | 12.00 a | 21.71 b |
| WTS | 6.52 a | 5.00 a | 4.02 a | 87.25 a | 13.90 a | 11.10 a | 8.60 a | 12.75 b | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| RS | 6.70 a | 5.14 a | 4.14 a | 52.76 d | 12.20 a | 9.76 a | 7.55 a | 16.54 b | 7.62 b | 6.48 b | 4.71 b | 30.91 a |
| WRS | 6.17 a | 4.74 a | 3.81 a | 75.55 b | 11.50 a | 9.19 a | 7.10 a | 24.46 a | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Sample | Peak I | Peak II | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tc − To (°C) | ∆H (J/g) | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tc − To (°C) | ∆H (J/g) | |
| Neutral system | ||||||||||
| TS | 64.00 ± 0.21 c | 70.75 ± 0.11 c | 82.25 ± 0.17 c | 18.26 ± 0.04 a | 10.62 ± 0.72 b | |||||
| WTS | 68.78 ± 0.09 b | 74.42 ± 0.12 b | 84.96 ± 0.30 b | 16.18 ± 0.21 b | 12.63 ± 0.41 a | |||||
| RS | 76.51 ± 0.06 a | 81.42 ± 0.12 a | 89.06 ± 0.09 a | 12.55 ± 0.03 c | 11.19 ± 0.31 b | 95.96 ± 0.00 | 107.83 ± 0.00 | 117.25 ± 0.30 | 21.29 ± 0.30 | 0.08 ± 0.04 |
| WRS | 63.88 ± 0.38 c | 70.92 ± 0.35 c | 82.30 ± 0.59 c | 18.42 ± 0.21 a | 10.69 ± 0.45 b | |||||
| Sugar-acid system | ||||||||||
| TS | 75.28 ±0.02 c | 82.59 ±0.12 d | 95.52 ±0.21 b | 20.25 ±0.23 a | 13.19 ±0.71 a | |||||
| WTS | 79.85 ±0.04 b | 85.50 ±0.00 b | 99.87 ±0.72 a | 20.02 ±0.76 a | 13.94 ±0.21 a | |||||
| RS | 88.46 ±0.08 a | 93.09 ± 0.12 a | 100.71 ±0.17 a | 12.25 ±0.08 b | 11.15 ±0.71 b | 108.64 ± 0.40 | 115.50 ± 0.24 | 121.04 ± 0.2 | 12.40 ± 0.18 | 0.39 ± 0.04 |
| WRS | 74.96 ±0.07 d | 82.92 ±0.12 c | 95.08 ±0.71 b | 20.12 ±0.64 a | 13.15 ±0.88 a | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boonkor, P.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Lumdubwong, N. Pasting and Rheological Properties of Starch Paste/Gels in a Sugar-Acid System. Foods 2022, 11, 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244060
Boonkor P, Sagis LMC, Lumdubwong N. Pasting and Rheological Properties of Starch Paste/Gels in a Sugar-Acid System. Foods. 2022; 11(24):4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244060
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoonkor, Ployfon, Leonard M. C. Sagis, and Namfone Lumdubwong. 2022. "Pasting and Rheological Properties of Starch Paste/Gels in a Sugar-Acid System" Foods 11, no. 24: 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244060
APA StyleBoonkor, P., Sagis, L. M. C., & Lumdubwong, N. (2022). Pasting and Rheological Properties of Starch Paste/Gels in a Sugar-Acid System. Foods, 11(24), 4060. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11244060








