Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Simulation System Preparation
2.2. Equilibrium Simulations
2.3. Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.4. Trajectory Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
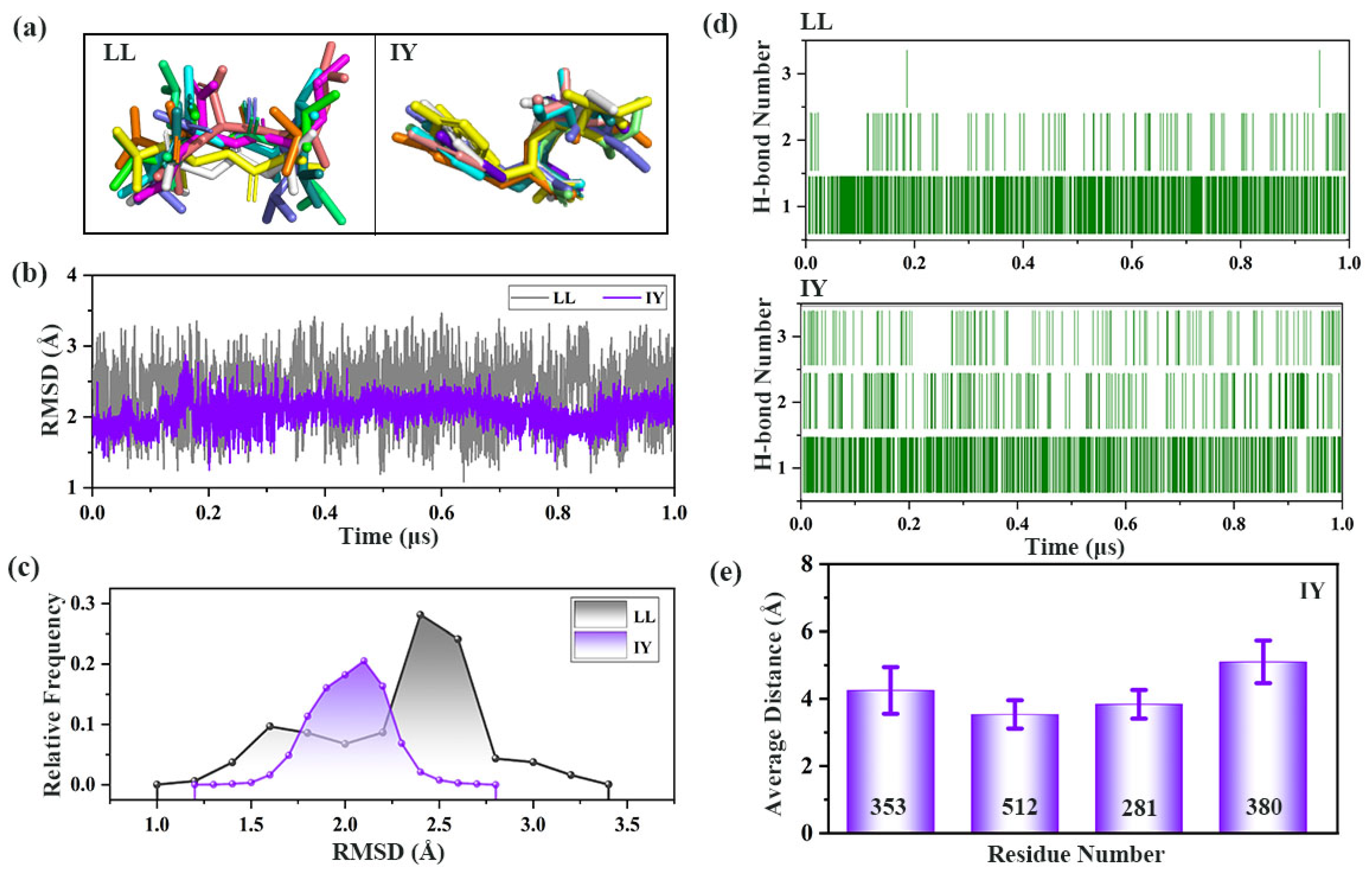
3.1. Structural Stability and Flexibility of the ACE–Inhibitor Complex
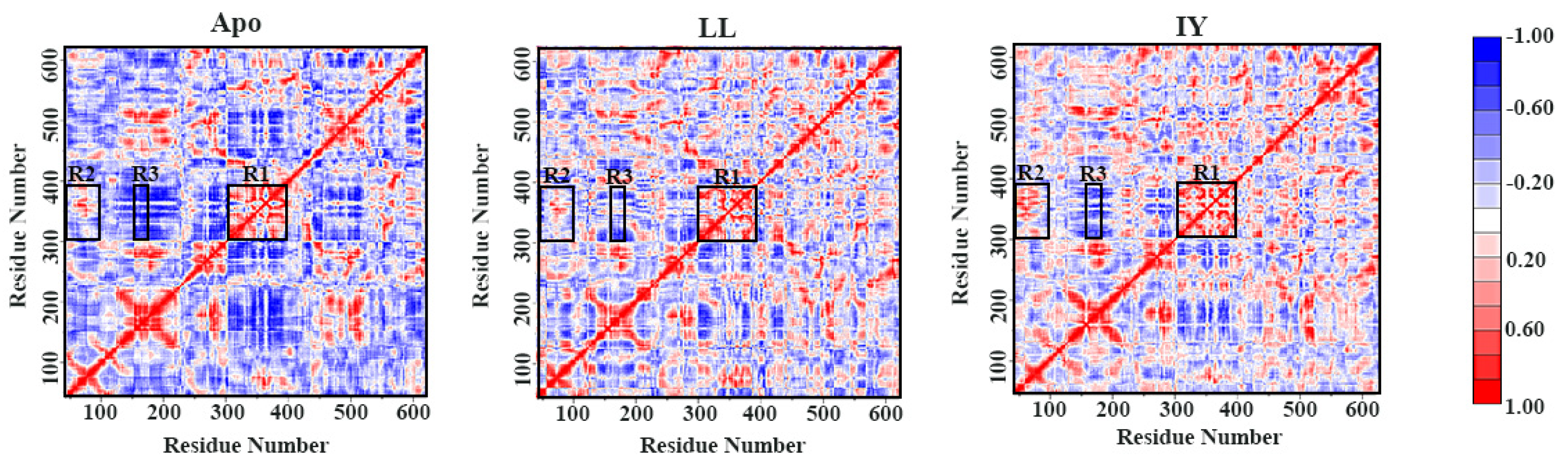
3.2. Dynamic Cross-Correlation Map
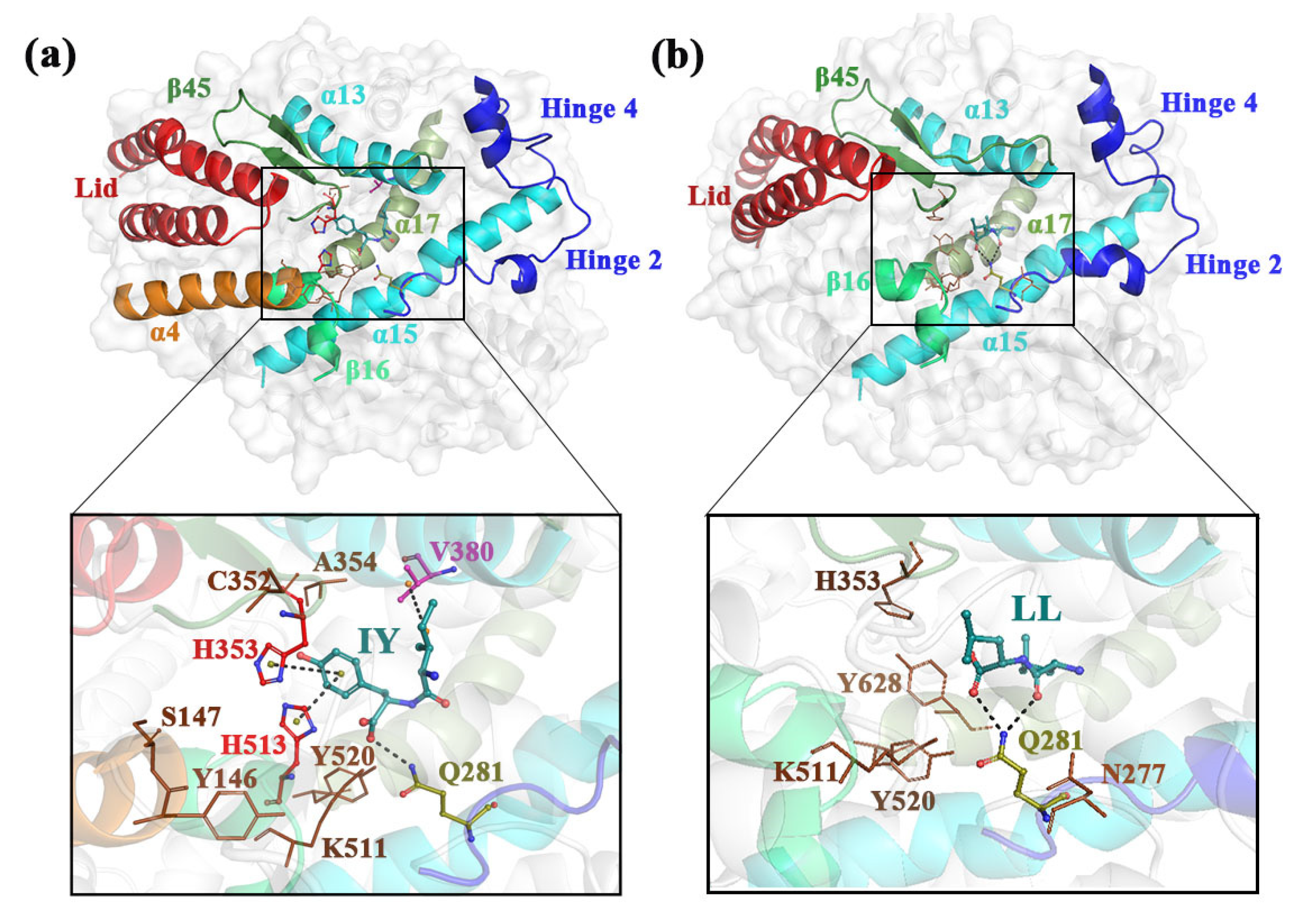
3.3. Analysis of the Interaction between ACE and Dipeptide Inhibitors
3.4. Structural Characterization of ACE upon Binding LL/IY
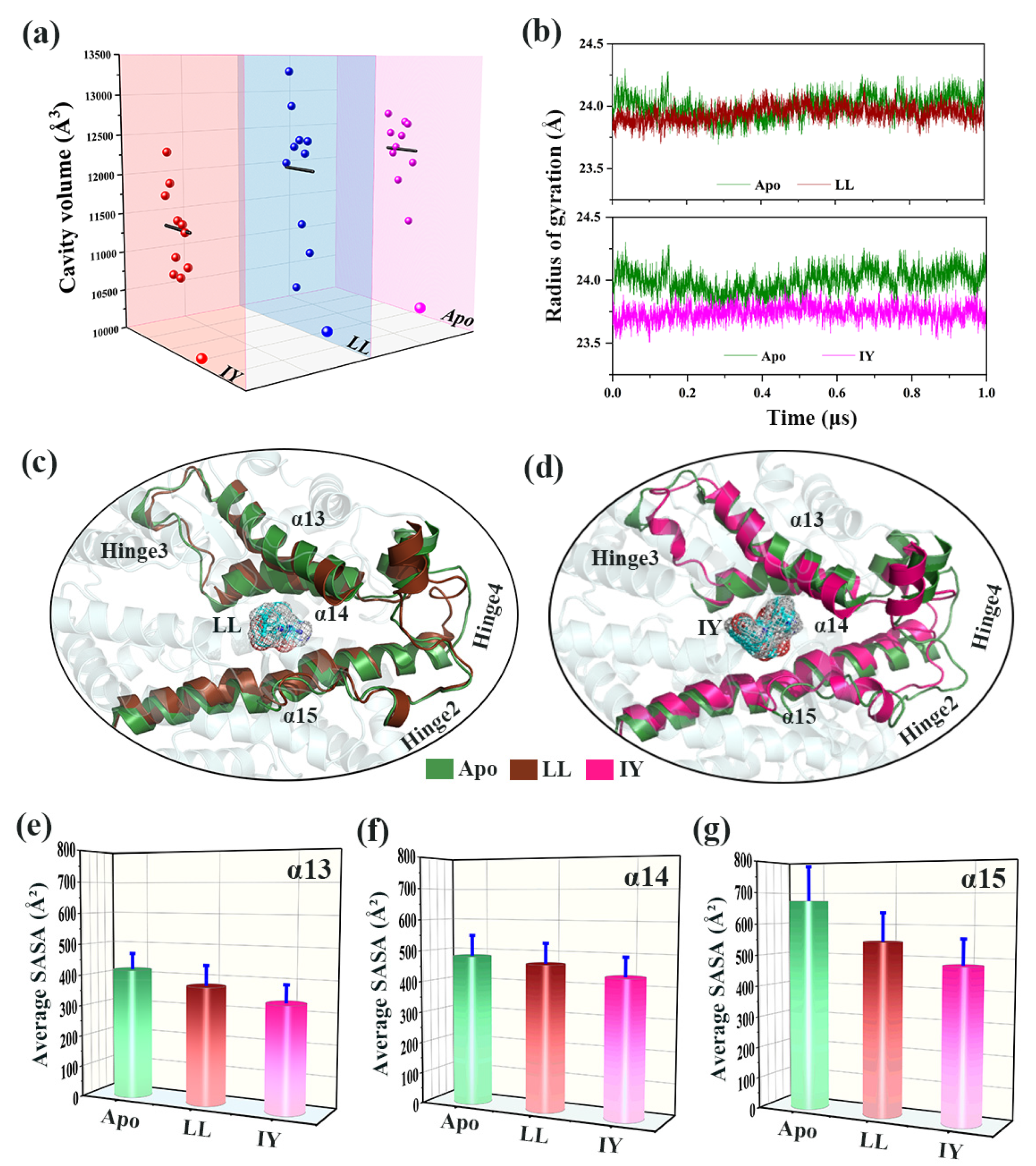
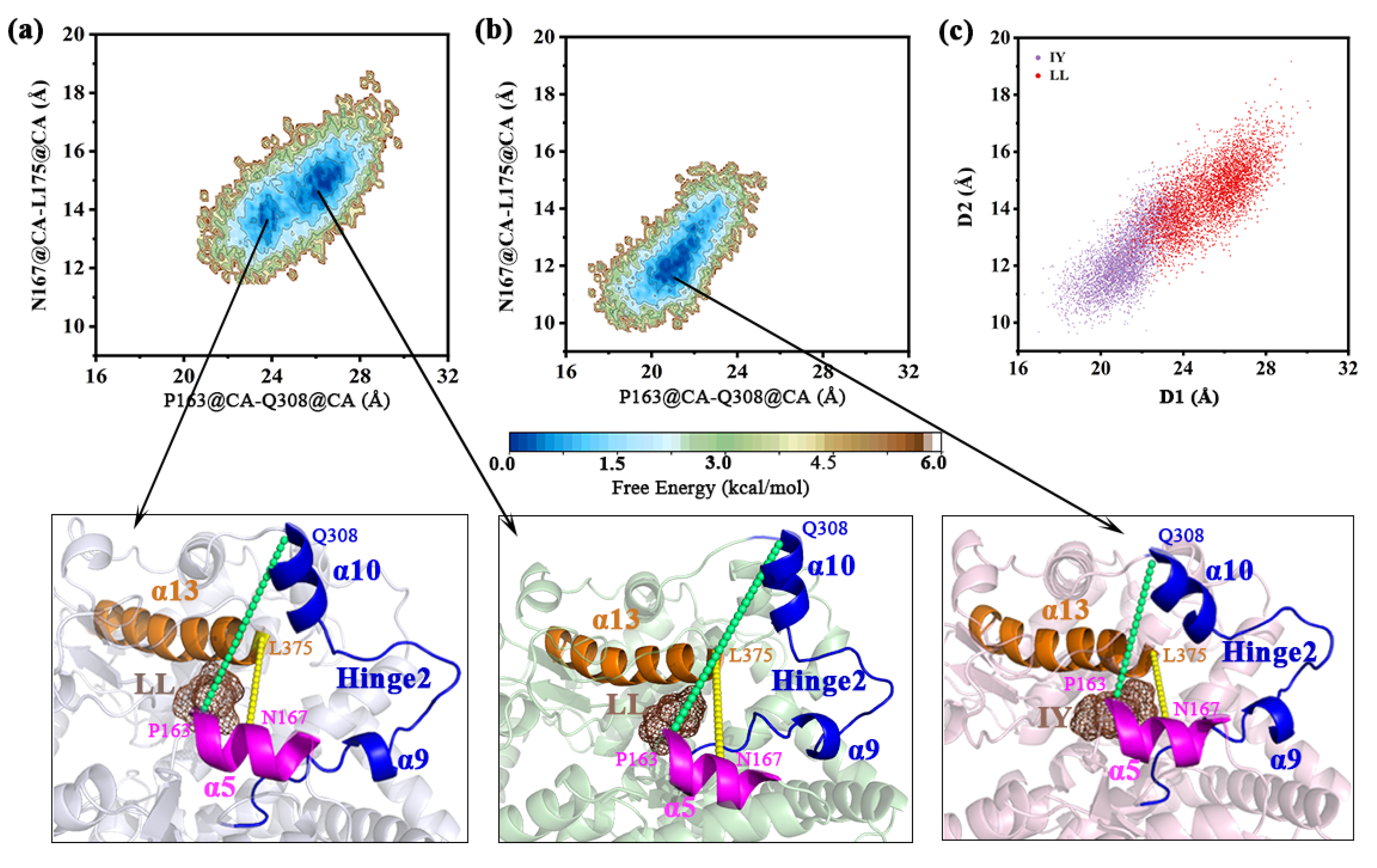
3.4.1. IY Inhibitor Binding Leads to ACE Active Site Contraction
3.4.2. Dynamic Analysis of Active Site
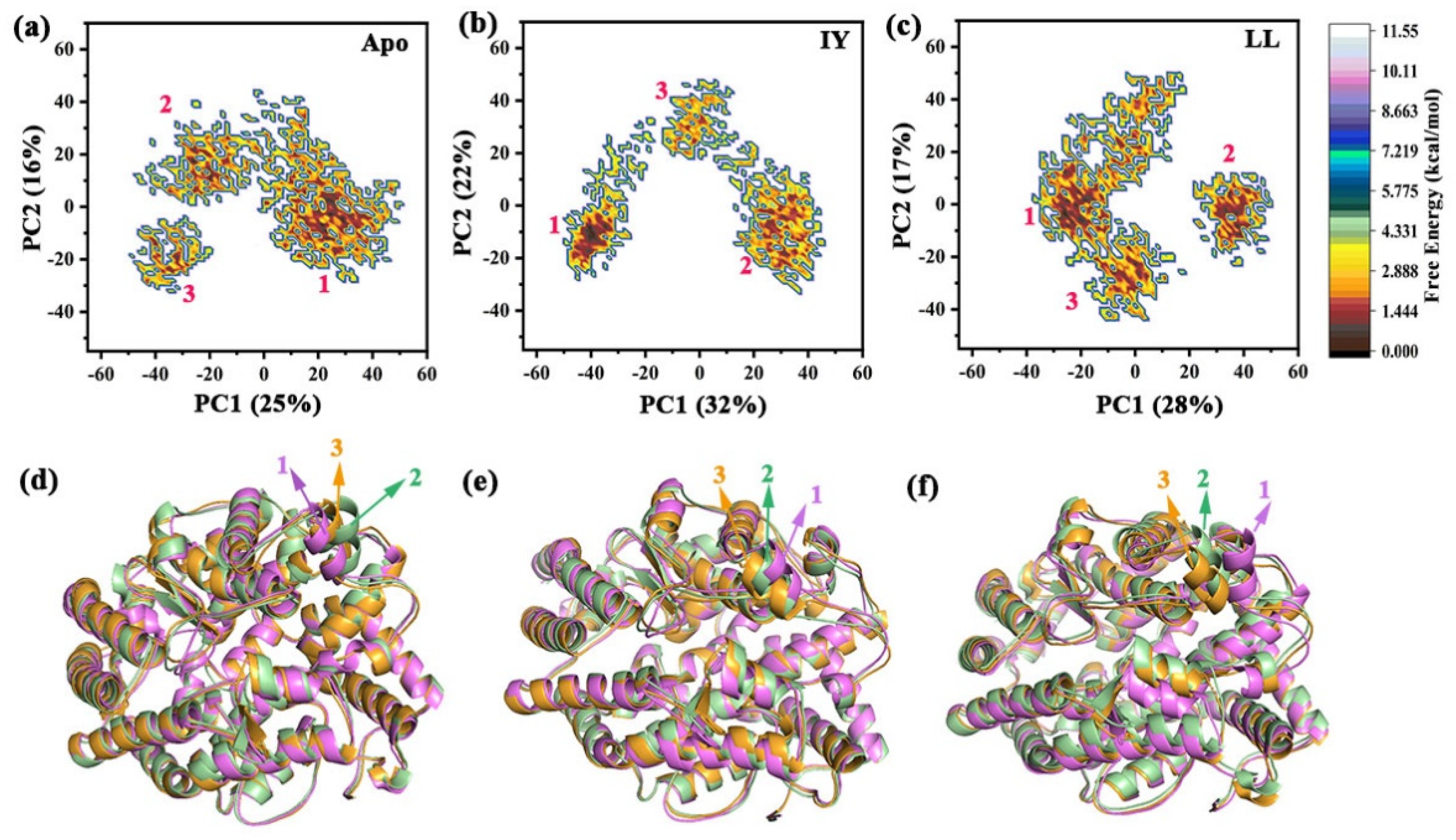
3.4.3. Motions of Protein via Principal Component Analysis
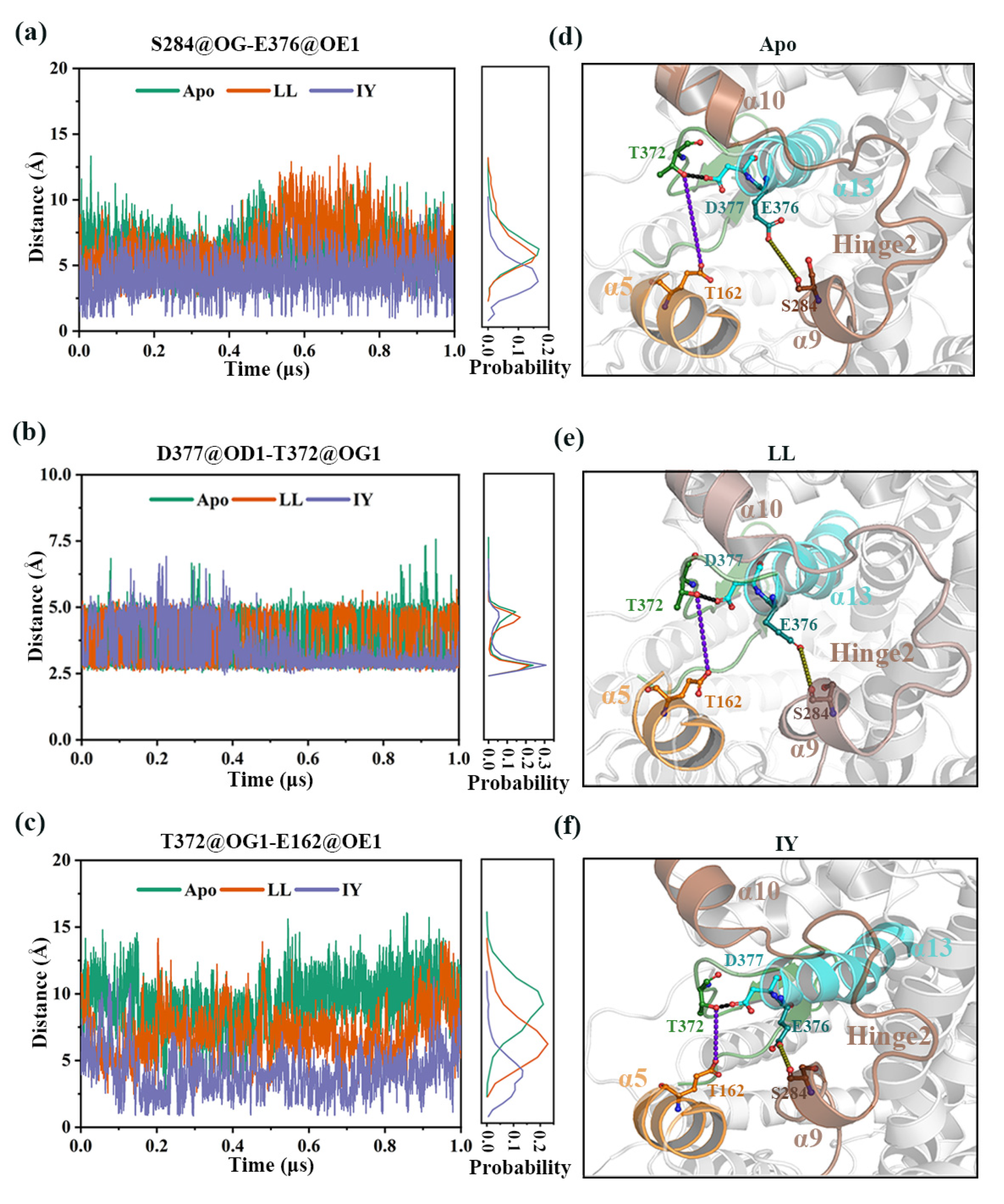
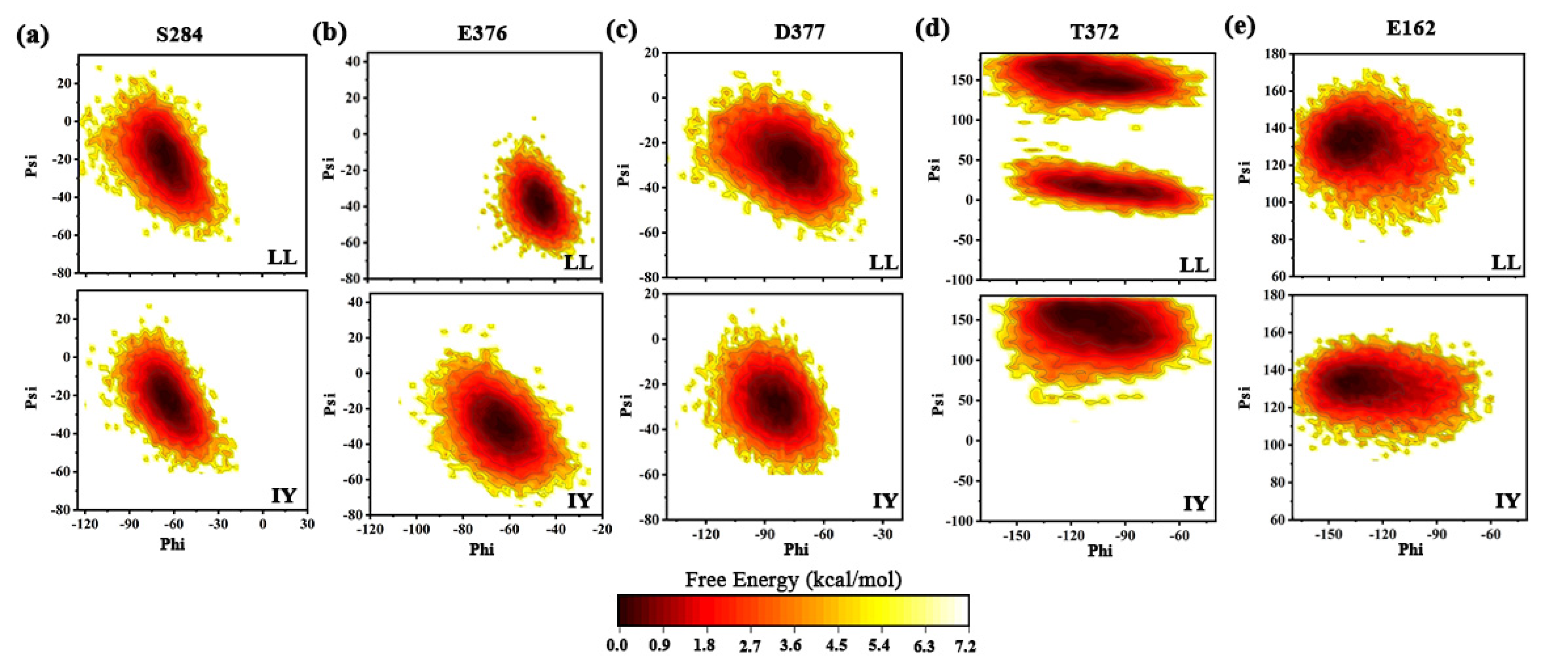
3.4.4. The Molecular Mechanism behind the Different States of the Active Site
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallumrd, S.; Oddvang, T.K.; Severinsson, E. The Evidence of Interdisciplinary Teamwork in the Rehabilitation of Stroke Patients with Aphasia. Open J. Nurs. 2016, 06, 793–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obirikorang, Y.; Obirikorang, C.; Acheampong, E.; Anto, E.O.; Asiwu, R.Y. Adherence to Lifestyle Modification among Hypertensive Clients: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study. Open Access Libr. J. 2018, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyvratt, M.J.; Patchett, A.A. Recent developments in the design of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Med. Res. Rev. 1985, 5, 483–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natesh, R.; Schwager, S.L.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. Crystal structure of the human angiotensin-converting enzyme-lisinopril complex. Nature 2003, 421, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, J.H.; Hayashi, M.A.; Camargo, A.C.; Neshich, G. Structural basis of the lisinopril-binding specificity in N- and C-domains of human somatic ACE. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 308, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, N.; Fernandes, P.A.; Ramos, M.J. QM/MM Study and MD Simulations on the Hypertension Regulator Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 2587–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, S.E.; Coleman, J.J.; Ferner, R.E. Systematic review and meta-analysis of ethnic differences in risks of adverse reactions to drugs used in cardiovascular medicine. BMJ 2006, 332, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thurman, J.M.; Schrier, R.W. Comparative effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers on blood pressure and the kidney. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, A.B.; Morton, J.J.; Brown, J.J.; Davies, D.L.; Fraser, R.; Kelly, P.; Leckie, B.; Lever, A.F.; Robertson, J.I. Captopril in clinical hypertension. Changes in components of renin-angiotensin system and in body composition in relation to fall in blood pressure with a note on measurement of angiotensin II during converting enzyme inhibition. Br. Heart J. 2018, 44, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redelinghuys, P.; Nchinda, A.T.; Sturrock, E.D. Development of domain-selective angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1056, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrons, M.A.; Liggieri, C.S.; Trejo, S.A.; Bruno, M.A. ACE-inhibitory peptides from bovine caseins released with peptidases from Maclura pomifera latex. Food Res. Int. 2017, 93, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.R.; Ahmed, A.S.; Miyata, T. Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from caseins and whey proteins of goat milk. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootaert, C.; Matthijs, B.; Voorspoels, S.; Possemiers, S.; Smagghe, G.; Van Camp, J. Egg-derived bioactive peptides with ACE-inhibitory properties: A literature update. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3847–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, B.; Zarei, M.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Philip, R.; Bakar, J.; Abdul Hamid, A.; Saari, N. Purification and characterization of angiotensin converting enzyme-inhibitory peptides derived from Stichopus horrens: Stability study against the ACE and inhibition kinetics. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 20, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Zhang, C.; Ji, H. Two Novel Bioactive Peptides from Antarctic Krill with Dual Angiotensin Converting Enzyme and Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Activities. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 1742–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, X.; Li, D.; Sun, N.; Lin, S. Comprehensive Analysis of Mouse Hippocampal Lysine Acetylome Mediated by Sea Cucumber Peptides Preventing Memory Impairment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12333–12343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fang, L.; Min, W.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Exploration of the molecular interactions between angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) and the inhibitory peptides derived from hazelnut (Corylus heterophylla Fisch.). Food Chem. 2018, 245, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moayedi, A.; Mora, L.; Aristoy, M.C.; Safari, M.; Hashemi, M.; Toldra, F. Peptidomic analysis of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides obtained from tomato waste proteins fermented using Bacillus subtilis. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Liao, W.; Bai, J.; Wu, W.; Wu, J. Soy protein-derived ACE-inhibitory peptide LSW (Leu-Ser-Trp) shows anti-inflammatory activity on vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 4, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Hur, S.J. Antihypertensive peptides from animal products, marine organisms, and plants. Food Chem. 2017, 228, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.S.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q. Recent Research in Antihypertensive Activity of Food Protein-derived Hydrolyzates and Peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 760–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Li, D.S.; Ding, K. Purification and identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from fermented walnut residues. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 20, S3326–S3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.G.; Jaiswal, L.; Li, J.; Choi, J.H.; Moon, S.M.; Cho, J.Y.; Ham, K.S. Identification of four new angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from fermented anchovy sauce. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuanthong, M.; Gobba, C.D.; Sirinupong, N.; Youravong, W.; Otte, J. Purification and characterization of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatine produced by an enzymatic membrane reactor. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 36, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasnovas, R.; Limongelli, V.; Tiwary, P.; Carloni, P.; Parrinello, M. Unbinding Kinetics of a p38 MAP Kinase Type II Inhibitor from Metadynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4780–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Shen, M.; Li, D.; Kang, Y.; Hou, T. Characterizing Drug–Target Residence Time with Metadynamics: How To Achieve Dissociation Rate Efficiently without Losing Accuracy against Time-Consuming Approaches. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwary, P.; Limongelli, V.; Salvalaglio, M.; Parrinello, M. Kinetics of protein–ligand unbinding: Predicting pathways, rates, and rate-limiting steps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E386–E391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwary, P.; Mondal, J.; Morrone, J.A.; Berne, B.J. The role of water and steric constraints in the kinetics of cavity-ligand unbinding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12015–12019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, C.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhao, T.; Waterhouse, G.; Zhao, M.; Su, G. Identification of post-digestion angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from soybean protein Isolate: Their production conditions and in silico molecular docking with ACE. Food Chem. 2020, 345, 1873–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feher, V.A.; McCammon, J.A.; Miao, Y. Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics: Unconstrained Enhanced Sampling and Free Energy Calculation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3584–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; McCammon, J.A. Unconstrained Enhanced Sampling for Free Energy Calculations of Biomolecules: A Review. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Huang, Y.M.; Walker, R.C.; Mccammon, J.A.; Chang, C.E.A. Ligand Binding Pathways and Conformational Transitions of the HIV Protease. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.; Mccammon, J.A. Mechanism of the G-protein mimetic nanobody binding to a muscarinic G-protein-coupled receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3036–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.; Mccammon, J.A. Graded activation and free energy landscapes of a muscarinic G-protein-coupled receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 12162–12167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miao, Y.; Feixas, F.; Eun, C.; McCammon, J.A. Accelerated molecular dynamics simulations of protein folding. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kappel, K.; Miao, Y.; McCammon, J.A. Accelerated molecular dynamics simulations of ligand binding to a muscarinic G-protein-coupled receptor. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2015, 48, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Miao, Y. Mechanistic Insights into Specific G Protein Interactions with Adenosine Receptors. J. Phys. Chem. 2019, 123, 6462–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accelrys Software Inc., Discovery Studio Visualizer v21.1.0. Available online: https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scaknabu, G.; Baronw, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision, A.02.; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Corradi, H.R.; Chitapi, I.; Sewell, B.T.; Georgiadis, D.; Dive, V.; Sturrock, E.D.; Acharya, K.R. The structure of testis angiotensin-converting enzyme in complex with the C domain-specific inhibitor RXPA380. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 5473–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Case, D.A.; Cerutti, D.S.; Cheatham, T.E., III; Darden, T.A.; Duke, R.E.; Gohlke, H.; Goetz, A.W.; Homeyer, N.; Izadi, S.; Janowski, P.; et al. AMBER; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jorgensen, W.L.C.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N·log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: Software for Processing and Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Trajectory Data. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichiye, T.; Karplus, M. Collective motions in proteins: A covariance analysis of atomic fluctuations in molecular dynamics and normal mode simulations. Proteins 1991, 11, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Sinko, W.; Pierce, L.; Bucher, D.; Walker, R.C.; McCammon, J.A. Improved Reweighting of Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations for Free Energy Calculation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 2677–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalkute, C.B.; Barage, S.H.; Dhanavade, M.J.; Sonawane, K.D. Molecular dynamics simulation and molecular docking studies of Angiotensin converting enzyme with inhibitor lisinopril and amyloid Beta Peptide. Protein. J. 2013, 32, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Bian, X.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Insight into the binding of ACE-inhibitory peptides to angiotensin-converting enzyme: A molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2019, 45, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, T.A.; Naghibzadeh, S.; Jie, L. CASTp: Computed Atlas of Surface Topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3352–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
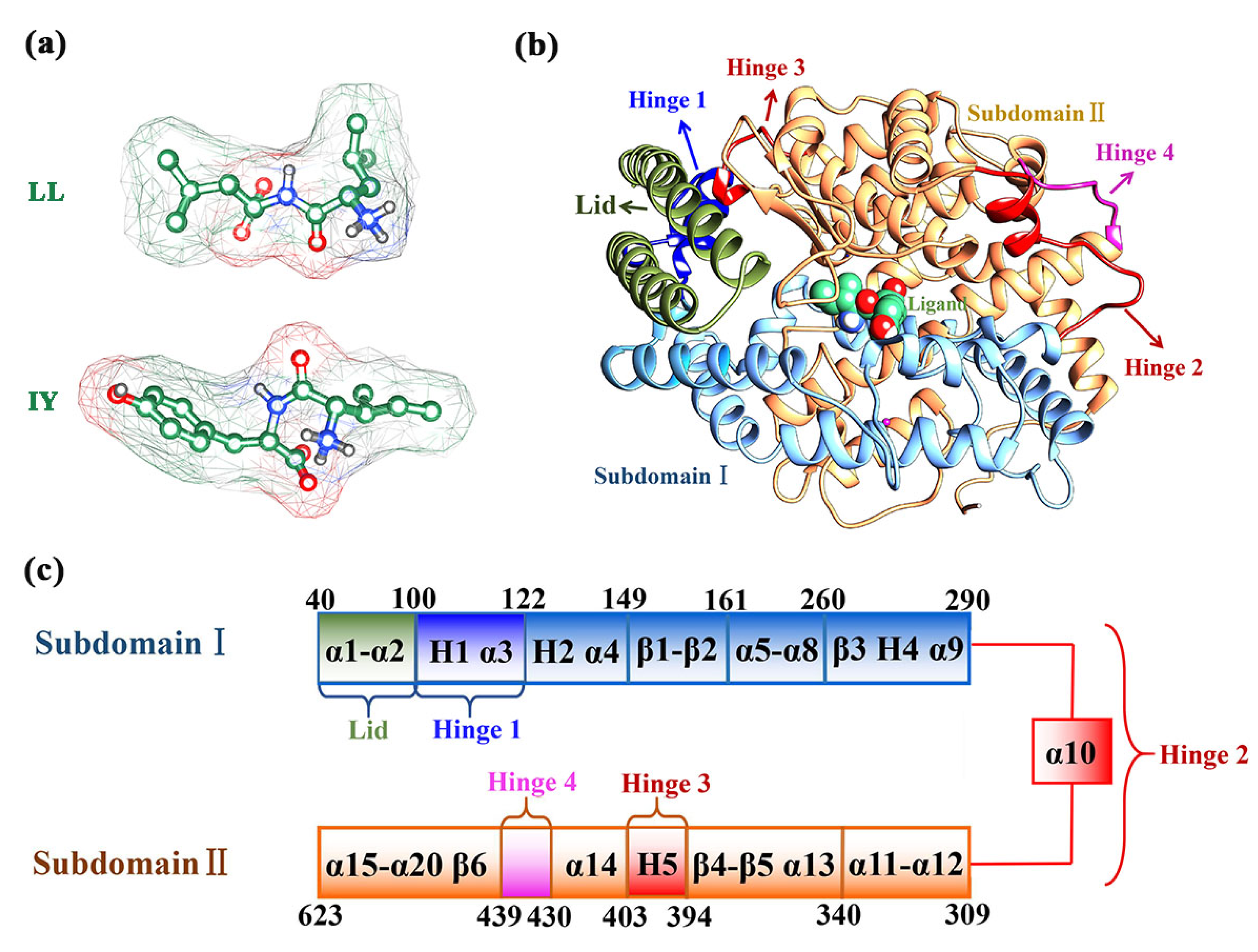
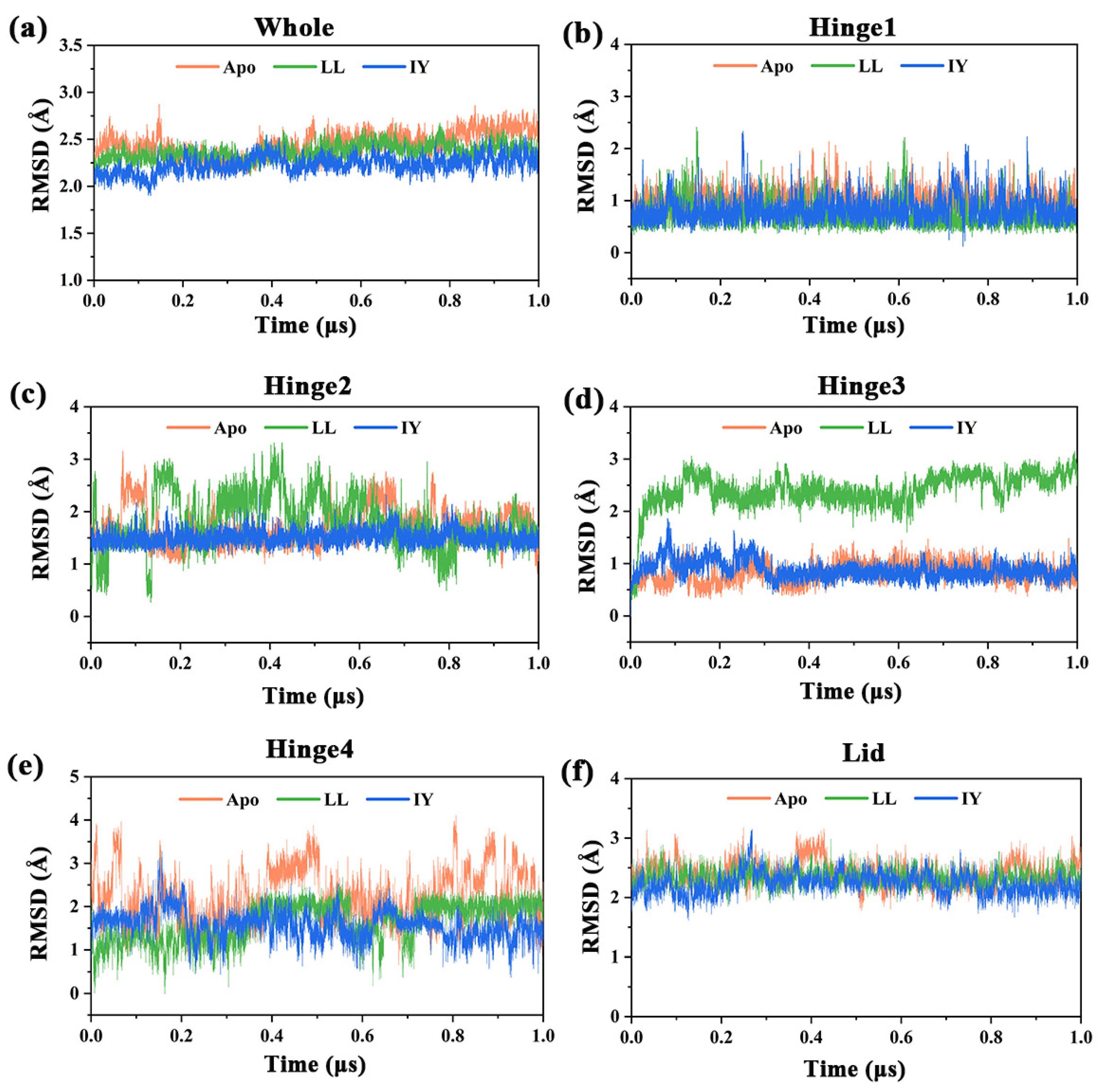
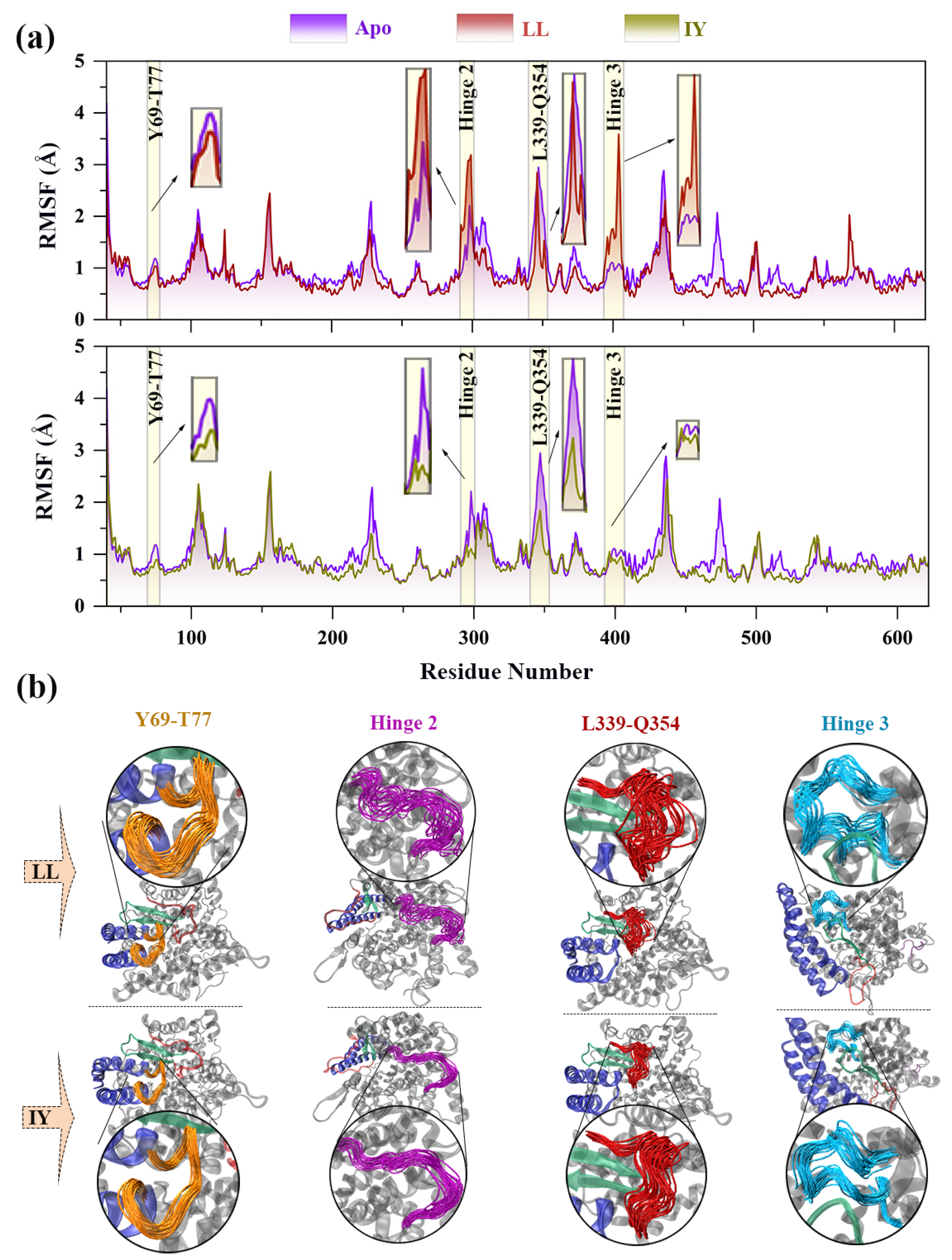
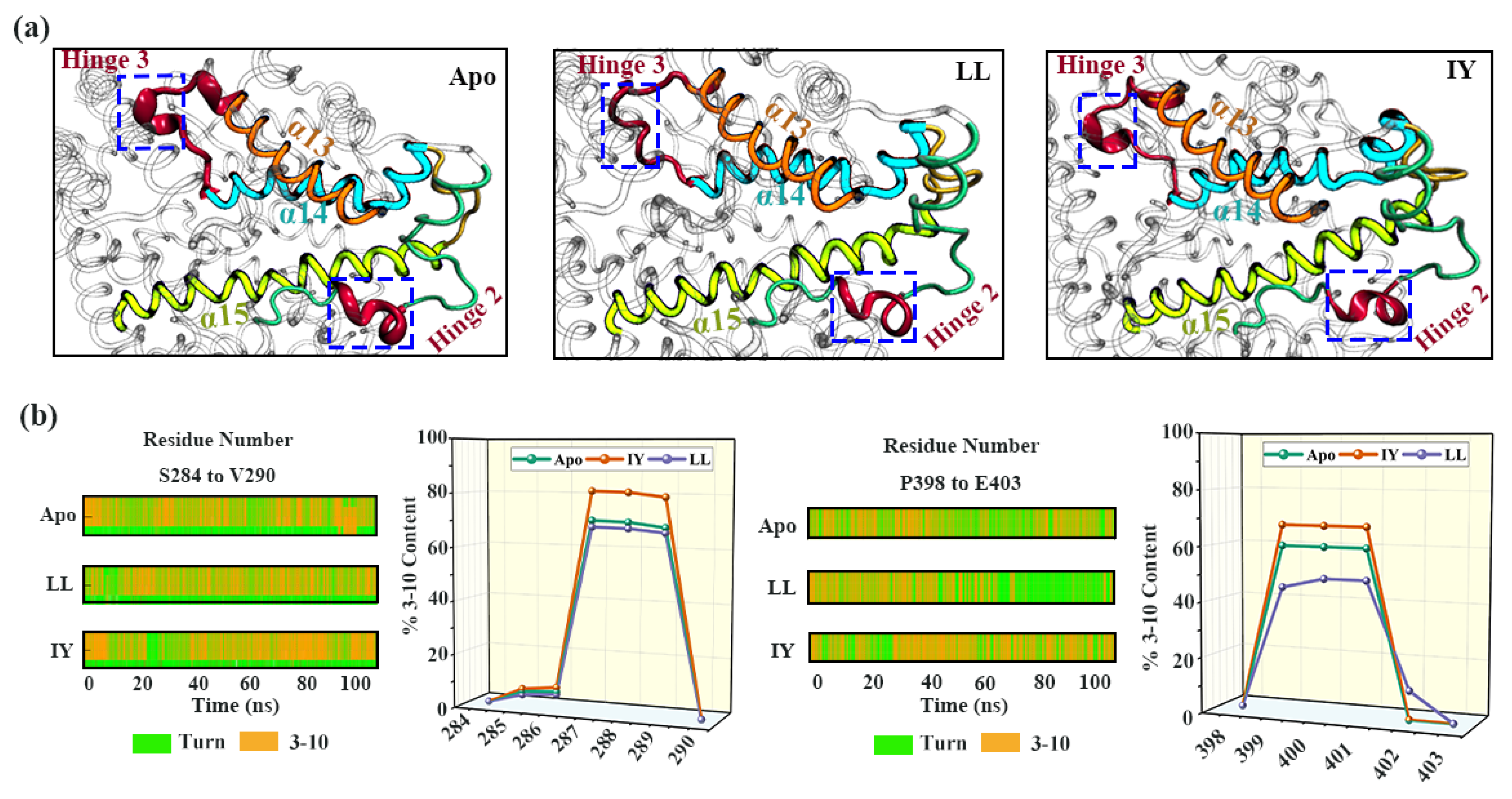
| Regions | Apo | ACE–LL | ACE–IY |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whole | 2.45 ± 0.13 | 2.37 ± 0.08 | 2.23 ± 0.09 |
| Hinge 1 | 1.01 ± 0.19 | 0.72 ± 0.24 | 0.82 ± 0.24 |
| Hinge 2 | 1.70 ± 0.35 | 1.80 ± 0.50 | 1.50 ± 0.14 |
| Hinge 3 | 0.84 ± 0.19 | 2.43 ± 0.35 | 0.88 ± 0.17 |
| Hinge 4 | 2.22 ± 0.62 | 1.63 ± 0.44 | 1.57 ± 0.33 |
| Lid | 2.40 ± 0.20 | 2.33 ± 0.14 | 2.23 ± 0.18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Liu, K.; Chen, S.; Han, L.; Han, W. Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides. Foods 2022, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030327
Li C, Liu K, Chen S, Han L, Han W. Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides. Foods. 2022; 11(3):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030327
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Congcong, Kaifeng Liu, Siao Chen, Lu Han, and Weiwei Han. 2022. "Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides" Foods 11, no. 3: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030327
APA StyleLi, C., Liu, K., Chen, S., Han, L., & Han, W. (2022). Gaussian Accelerated Molecular Dynamics Simulations Investigation on the Mechanism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) C-Domain Inhibition by Dipeptides. Foods, 11(3), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11030327








