Nano Filling Effect of Nonmeat Protein Emulsion on the Rheological Property of Myofibrillar Protein Gel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of MP
2.3. Preparation of Emulsion
2.4. Preparation of MP-Emulsified Soybean Oil Composite Sols
2.5. Preparation of Heat-Induced Gelation
2.6. Measurement of Drop Size of Emulsion
2.6.1. Measurement of Drop Size of Macro-Emulsion
2.6.2. Measurement of Drop Size of Nano-Emulsion
2.7. Measurement of Interfacial Tension
2.8. Viscosity and Heat Scanning Rheological Measurements
2.9. Gel Strength Measurement
2.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy Analyses
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Emulsions
3.1.1. Drop Size
3.1.2. Ability of Protein to Reduce the O/W Interfacial Tension
3.2. Viscosity of Emulsion-Filled Composite Sols
3.3. Heat Scanning Rheological Measurements
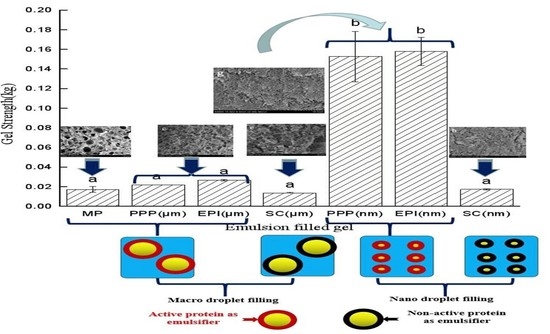
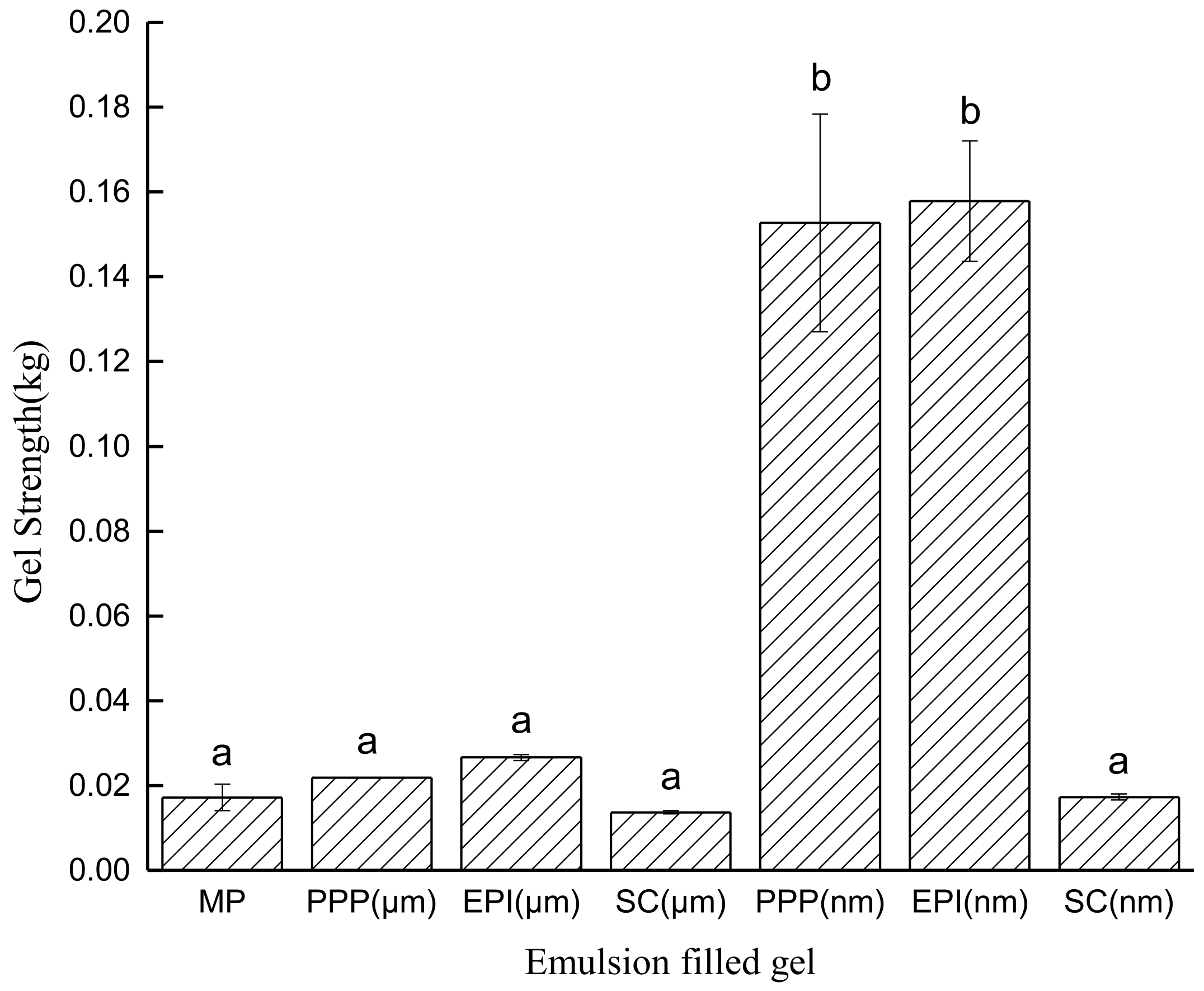
3.4. Strength of Emulsion-Filled Gels after Heating
3.5. Microstructure of Emulsion-Filled Gels after Heating
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herrero, A.M.; Carmona, P.; Pintado, T.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Lipid and protein structure analysis of frankfurters formulated with olive oil-in-water emulsion as animal fat replacer. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Herrero, A.; Pintado, T.; Solas, M.T.; Ruiz-Capillas, C. Influence of emulsified olive oil stabilizing system used for pork backfat replacement in frankfurters. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 2068–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.G.; Bibette, J.; Weitz, D.A. Elasticity of Compressed Emulsions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 2051–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbut, S. Importance of fat emulsification and protein matrix characteristics in meat batter stability. J. Muscle Foods 1995, 6, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremias-Andrade, I.M.; Souki, N.P.D.B.G.; Moraes, I.C.F.; Pinho, S.C. Rheological and mechanical characterization of curcumin-loaded emulsion-filled gels produced with whey protein isolate and xanthan gum. LWT 2017, 86, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windhab, E.J.; Dressler, M.; Feigl, K.; Fischer, P.; Megias-Alguacil, D. Emulsion processing—from single-drop deformation to design of complex processes and products. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 2101–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, M.; Solans, C.; González, C.; Martínez, A.; Guinart, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Studies of formation of W/O nano-emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2004, 249, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Belwal, T.; Liu, S.; Duan, Z.; Luo, Z. Novel multi-phase nano-emulsion preparation for co-loading hydrophilic arbutin and hydrophobic coumaric acid using hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltsa, O.; Spiliopoulou, N.; Yanniotis, S.; Mandala, I. Stability and physical properties of model macro- and nano/submicron emulsions containing fenugreek gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharat, M.; McClements, D.J. Recent advances in colloidal delivery systems for nutraceuticals: A case study—Delivery by Design of curcumin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 557, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaiko, J.; McClements, D.J. Food-grade nanoemulsion filled hydrogels formed by spontaneous emulsification and gelation: Optical properties, rheology, and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Li, Z.; Julian McClements, D.; Tang, Z.; Xiao, H. Design of nanoemulsion-based delivery systems to enhance intestinal lymphatic transport of lipophilic food bioactives: Influence of oil type. Food Chem. 2020, 317, 126229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Influence of particle size and interfacial interactions on the physical and mechanical properties of particle-filled myofibrillar protein gels. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60723–60735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravelle, A.J.; Marangoni, A.G.; Barbut, S. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel stability: Influencing texture and microstructure using a model hydrophilic filler. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, P.L.; Sala, G.; Stieger, M.; Scholten, E. Effect of oil droplet inhomogeneity at different length scales on mechanical and sensory properties of emulsion-filled gels: Length scale matters. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Chen, J.S. Heat-set whey protein emulsion gels: Role of active and inactive filler particles. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1999, 20, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yost, R.A.; Kinsella, J.E. Microstructure of Whey Protein Isolate Gels Containing Emulsified Butterfat Droplets. J. Food Sci. 1992, 57, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, P.; Kang, Z.L.; Li, K.; Xie, C.; Sun, J.X.; Xu, X.L. Effect of soybean oil emulsified and unemulsified with chicken plasma protein on the physicochemical properties of frankfurters. CyTA-J. Food 2015, 13, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paglarini, C.d.S.; Furtado, G.d.F.; Biachi, J.P.; Vidal, V.A.S.; Martini, S.; Forte, M.B.S.; Cunha, R.L.; Pollonio, M.A.R. Functional emulsion gels with potential application in meat products. J. Food Eng. 2018, 222, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.k.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, J.S.; Yim, D.G. Effect of diverse binder materials and their addition levels on physico-chemical characteristics of sausages. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, M.; Wang, P.; Xu, X. Rheological and nuclear magnetic resonance characterization of porcine plasma protein-stabilized gel-like emulsion affected by pH and heating. LWT 2017, 75, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Effect of microbial transglutaminase on NMR relaxometry and microstructure of pork myofibrillar protein gel. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Zou, Y.F.; Li, K.; Kang, Z.L.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Effect of pre-emulsification of plant lipid treated by pulsed ultrasound on the functional properties of chicken breast myofibrillar protein composite gel. Food Res. Int. 2014, 58, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Xiong, Y.L. Extreme pH treatments enhance the structure-reinforcement role of soy protein isolate and its emulsions in pork myofibrillar protein gels in the presence of microbial transglutaminase. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Xia, N.; Yang, X.Q.; Yin, S.W.; Qi, J.R.; He, X.T.; Yuan, D.-B.; Wang, L.-J. Adsorption and Dilatational Rheology of Heat-Treated Soy Protein at the Oil–Water Interface: Relationship to Structural Properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3302–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Zhou, G. Rheological and Microstructural Properties of Porcine Myofibrillar Protein–Lipid Emulsion Composite Gels. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, E207–E217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, T.; Zhao, X.; Cai, L.; Guanghong, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of salt content on gelation of normal and wooden breast myopathy chicken pectoralis major meat batters. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, G.; Xue, S.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Han, M. Improved gelation functionalities of myofibrillar protein from pale, soft and exudative chicken breast meat by nonenzymatic glycation with glucosamine. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2006–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Jaczynski, J. Protein Recovery from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Processing Byproducts via Isoelectric Solubilization/Precipitation and Its Gelation Properties As Affected by Functional Additives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 9079–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahergorabi, R.; Sivanandan, L.; Jaczynski, J. Dynamic rheology and endothermic transitions of proteins recovered from chicken-meat processing by-products using isoelectric solubilization/precipitation and addition of TiO2. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.L.; Brekke, C.J. Gelation properties of chicken myofibrils treated with calcium and magnesium chlorides1. J. Muscle Foods 1991, 2, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, E. Composite foods: From structure to sensory perception. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Kelly, A.L.; Maidannyk, V.; Miao, S. Effect of structuring emulsion gels by whey or soy protein isolate on the structure, mechanical properties, and in-vitro digestion of alginate-based emulsion gel beads. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; He, Y.; Bhandari, B. Production of sub-micron emulsions by ultrasound and microfluidization techniques. J. Food Eng. 2007, 82, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsmar, C.; Pradines, V.; Alahverdjieva, V.S.; Aksenenko, E.V.; Fainerman, V.B.; Kovalchuk, V.I.; Krägel, J.; Leser, M.E.; Noskov, B.A.; Miller, R. Thermodynamics, adsorption kinetics and rheology of mixed protein–surfactant interfacial layers. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 150, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.; Policova, Z.; Sedev, R.; Neumann, A.W. Relaxation behaviour of human albumin adsorbed at the solution/air interface. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1993, 76, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surh, J.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of pH and pectin type on properties and stability of sodium-caseinate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2006, 20, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strixner, T.; Kulozik, U. 7-Egg proteins. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Phillips, G.O., Williams, P.A., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 150–209. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Furlán, L.T.; Padilla, A.P.; Campderrós, M.E. Development of reduced fat minced meats using inulin and bovine plasma proteins as fat replacers. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, C.J. Quality of frankfurter-type sausages with added pig skin and wheat fiber mixture as fat replacers. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Miao, S.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Study on the textural and volatile characteristics of emulsion filled protein gels as influenced by different fat substitutes. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayum, A.; Hussain, M.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Shi, R.; Li, T.; Anwar, A.; Ahmed, Z.; Hou, J.; Jiang, Z. Gelling, microstructure and water-holding properties of alpha-lactalbumin emulsion gel: Impact of combined ultrasound pretreatment and laccase cross-linking. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, T.; Kuang, W.; Xu, J.; Zhao, M. Influence of xanthan gum on physical characteristics of sodium caseinate solutions and emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S.; Richards, M.P. Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of whey protein isolate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullet, M.S. Mixtures of Proteins and Protein-Stabilised Droplets: Rheology of Emulsions and Emulsion Gels. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, England, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Wu, N.; Sun, H.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. A comparative study of chemical composition, color, and thermal gelling properties of normal and PSE-like chicken breast meat. CyTA-J. Food 2015, 13, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Egelandsdal, B.; Fretheim, K.; Samejima, K. Dynamic rheological measurements on heat-induced myosin gels: Effect of ionic strength, protein concentration and addition of adenosine triphosphate or pyrophosphate. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1986, 37, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kelly, A.L.; Miao, S. Preparation, structure-property relationships and applications of different emulsion gels: Bulk emulsion gels, emulsion gel particles, and fluid emulsion gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalgleish, D.G. Adsorption of protein and the stability of emulsions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, T.; Madadlou, A. An overview on preparation of emulsion-filled gels and emulsion particulate gels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.H.; Wang, P.L.; Sun, D.Y.; Yan, Z.M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Gao, F. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on gelling and rheological properties of soybean protein isolate emulsion gel. J. Food Eng. 2020, 277, 109923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, P.; Han, M.; Xu, X. Nano Filling Effect of Nonmeat Protein Emulsion on the Rheological Property of Myofibrillar Protein Gel. Foods 2022, 11, 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050629
Cai R, Yang Z, Li Z, Wang P, Han M, Xu X. Nano Filling Effect of Nonmeat Protein Emulsion on the Rheological Property of Myofibrillar Protein Gel. Foods. 2022; 11(5):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050629
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ruying, Zongyun Yang, Zhen Li, Peng Wang, Minyi Han, and Xinglian Xu. 2022. "Nano Filling Effect of Nonmeat Protein Emulsion on the Rheological Property of Myofibrillar Protein Gel" Foods 11, no. 5: 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050629
APA StyleCai, R., Yang, Z., Li, Z., Wang, P., Han, M., & Xu, X. (2022). Nano Filling Effect of Nonmeat Protein Emulsion on the Rheological Property of Myofibrillar Protein Gel. Foods, 11(5), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050629