MCT/LCT Mixed Oil Phase Enhances the Rheological Property and Freeze-Thawing Stability of Emulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Stock Modified Starch Stabilized Emulsions
2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetric Analysis of Mixed Oil
2.4. Small Deformation Rheology
2.5. Freeze-Thawing Treatment
2.6. Stability Analysis
2.7. Particle Size Analysis
2.8. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
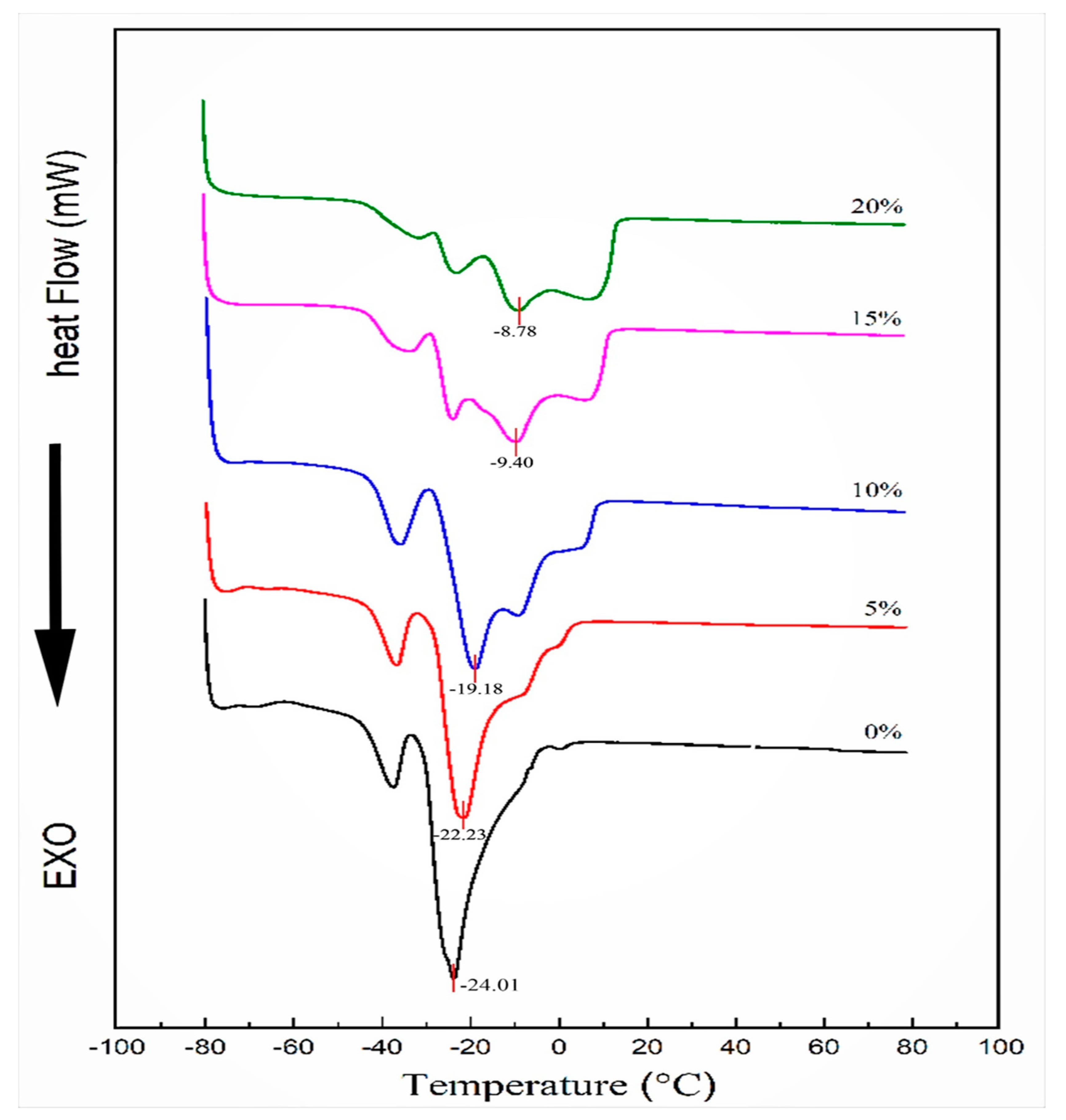
3.1. Thermal Analysis by DSC
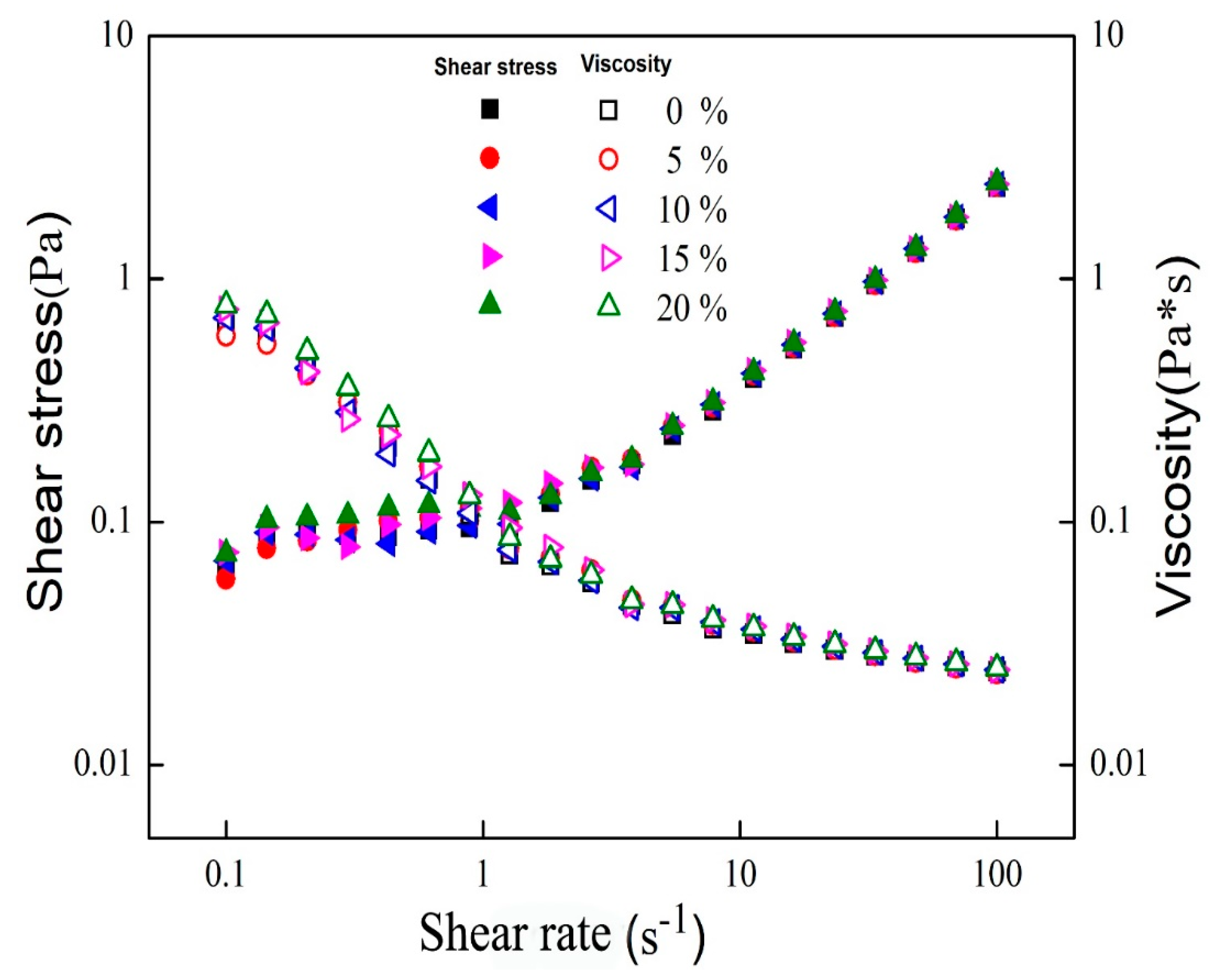
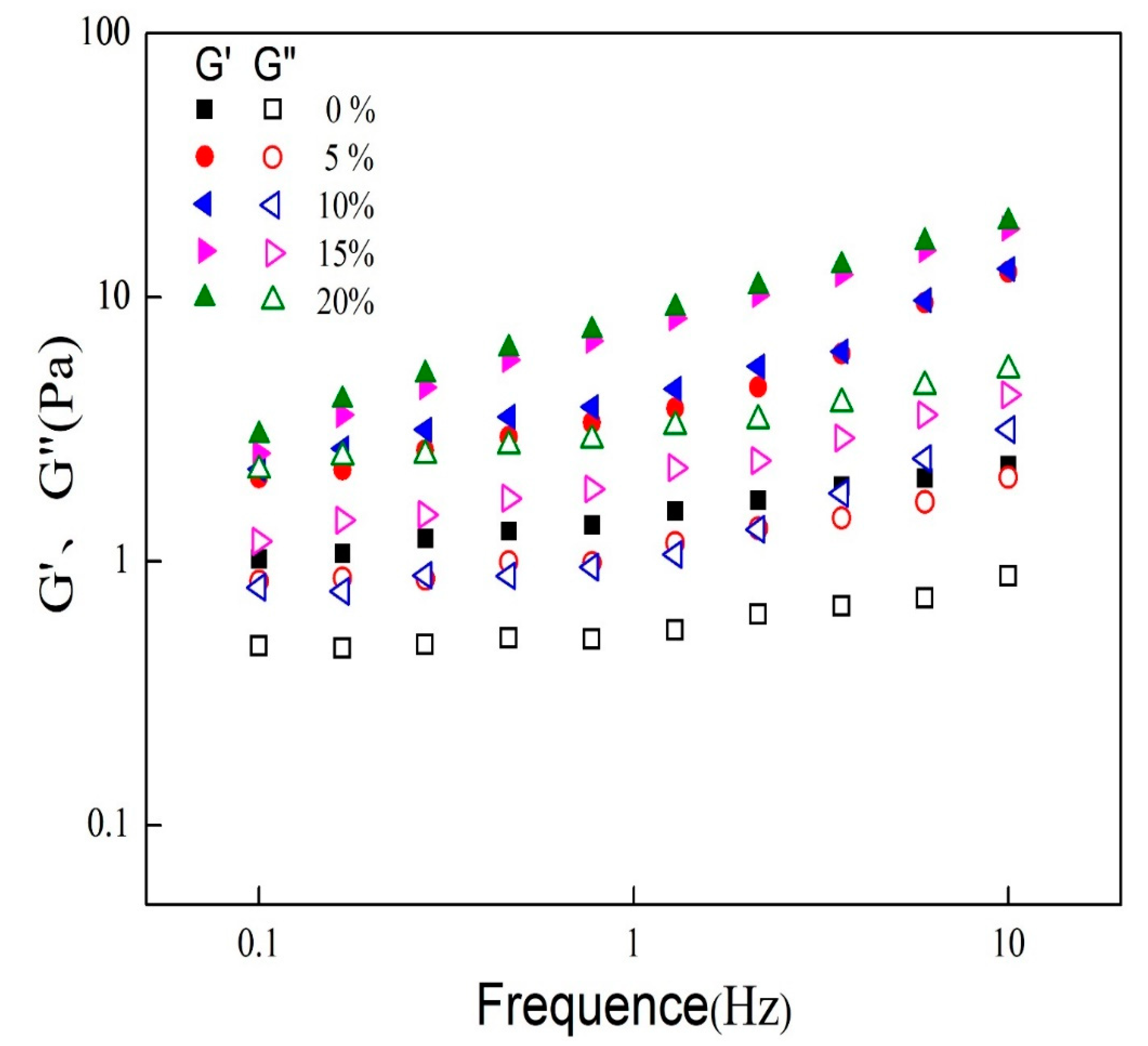
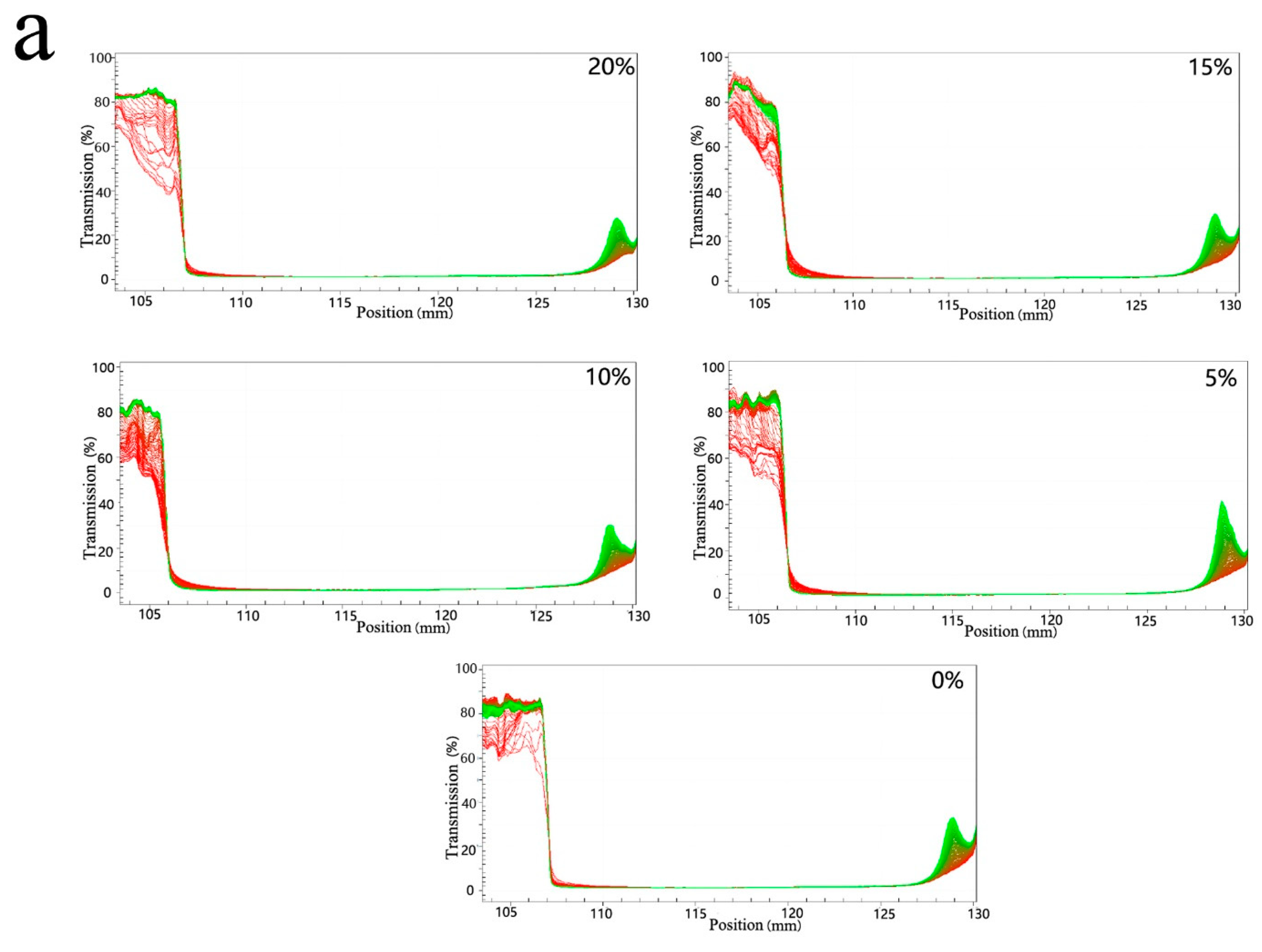
3.2. Rheological Properties of Mixed Oil Phase Emulsions
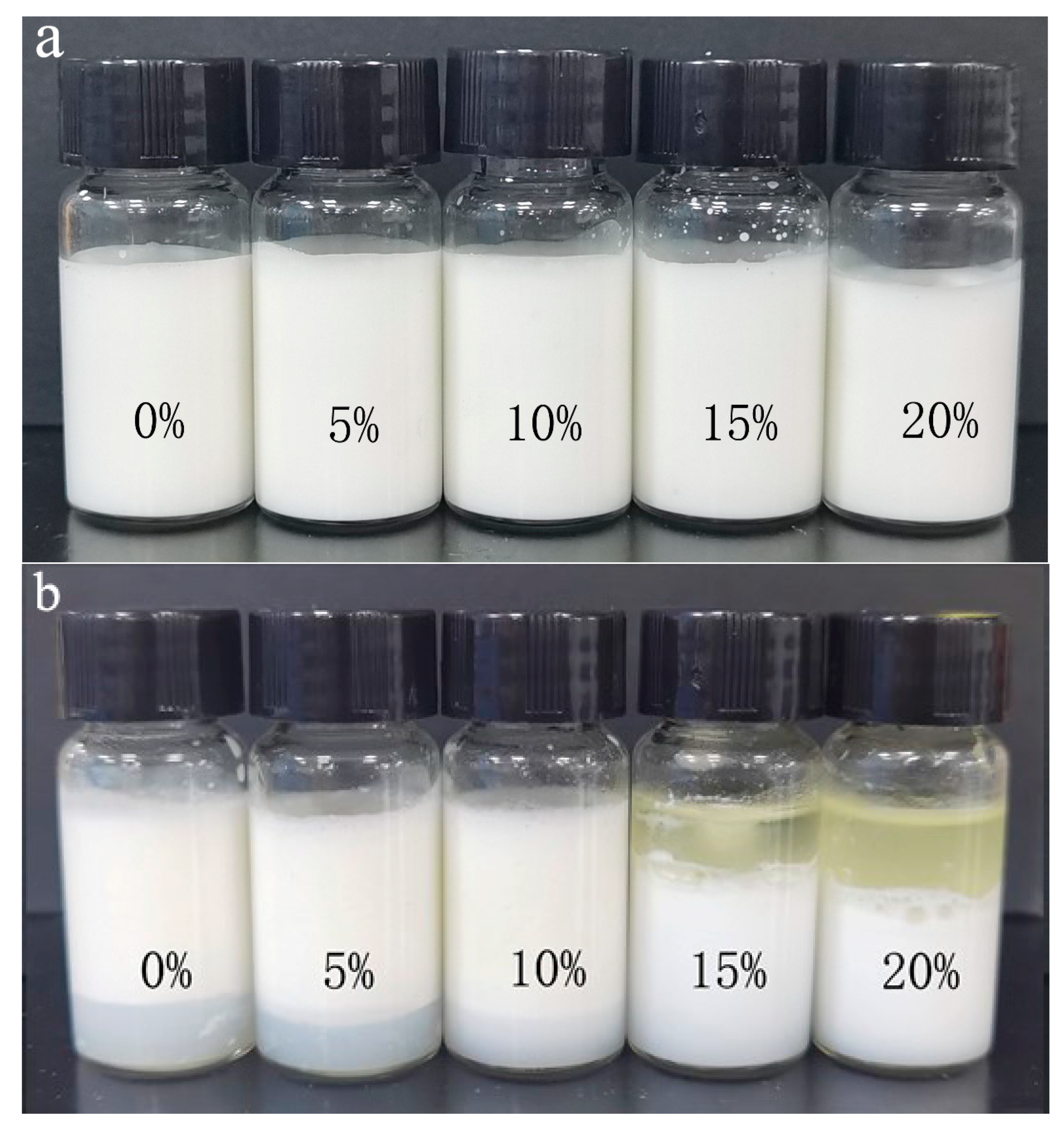
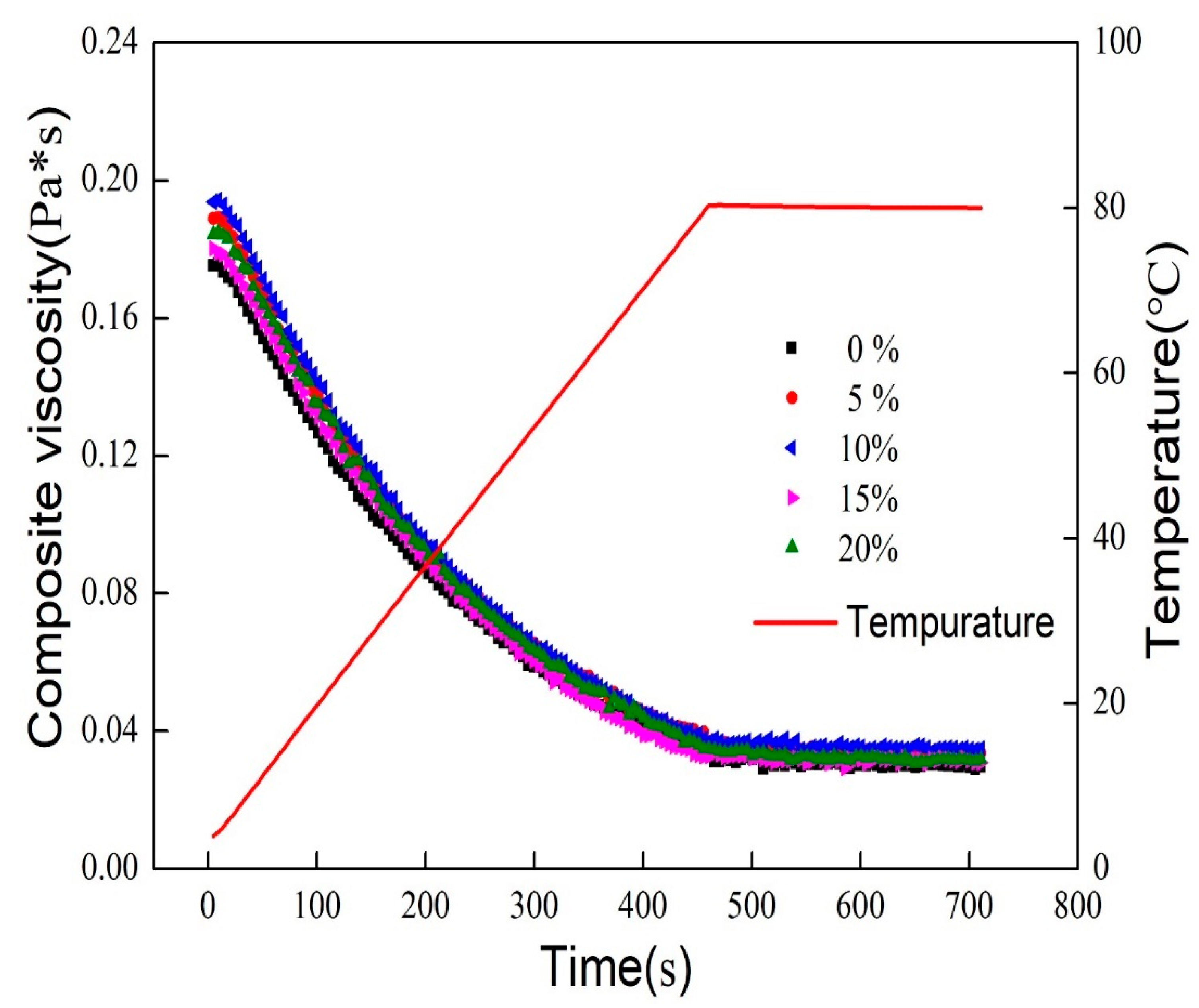
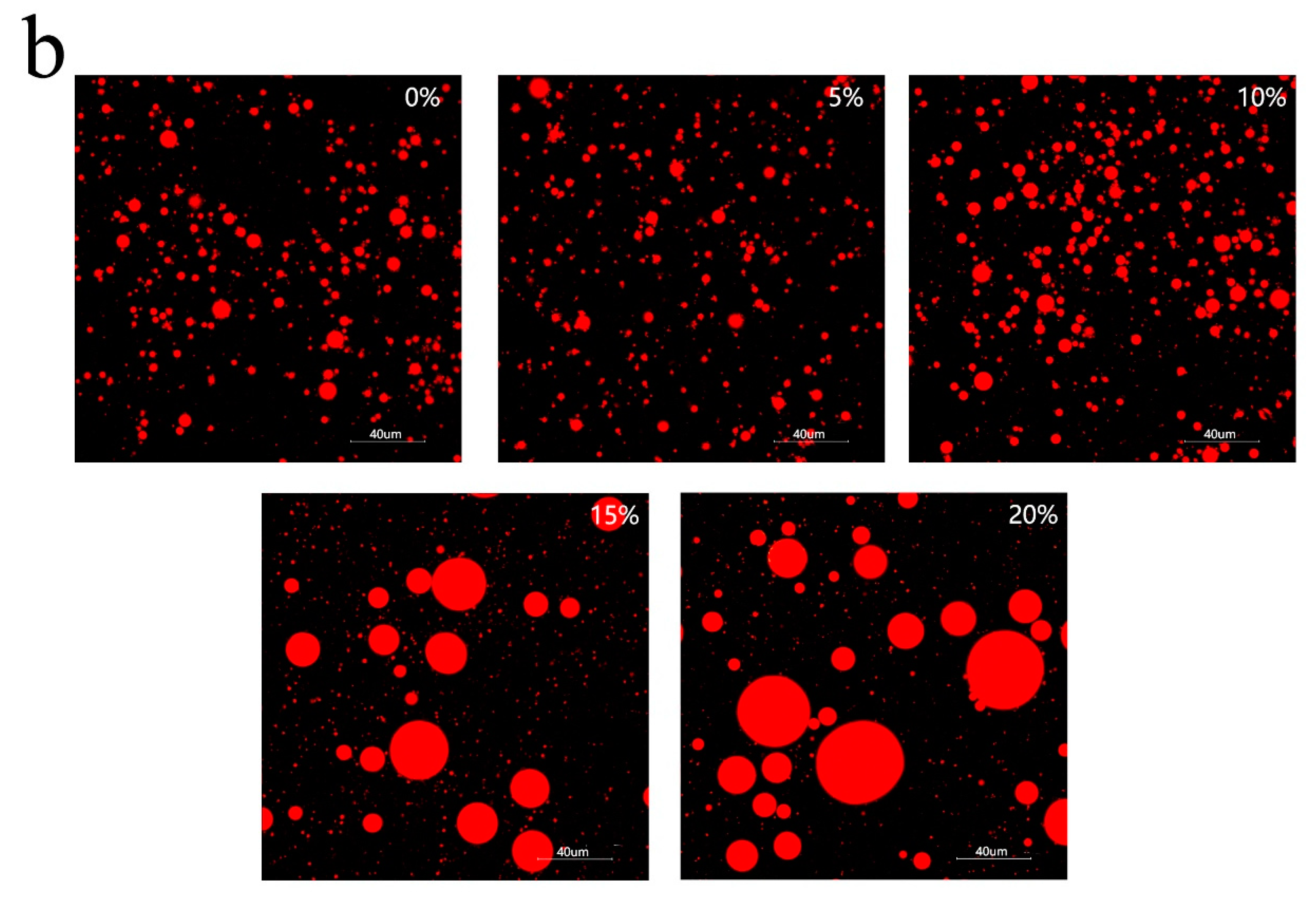
3.3. Freeze-Thawing Stability of Mixed Oil Phase Emulsions
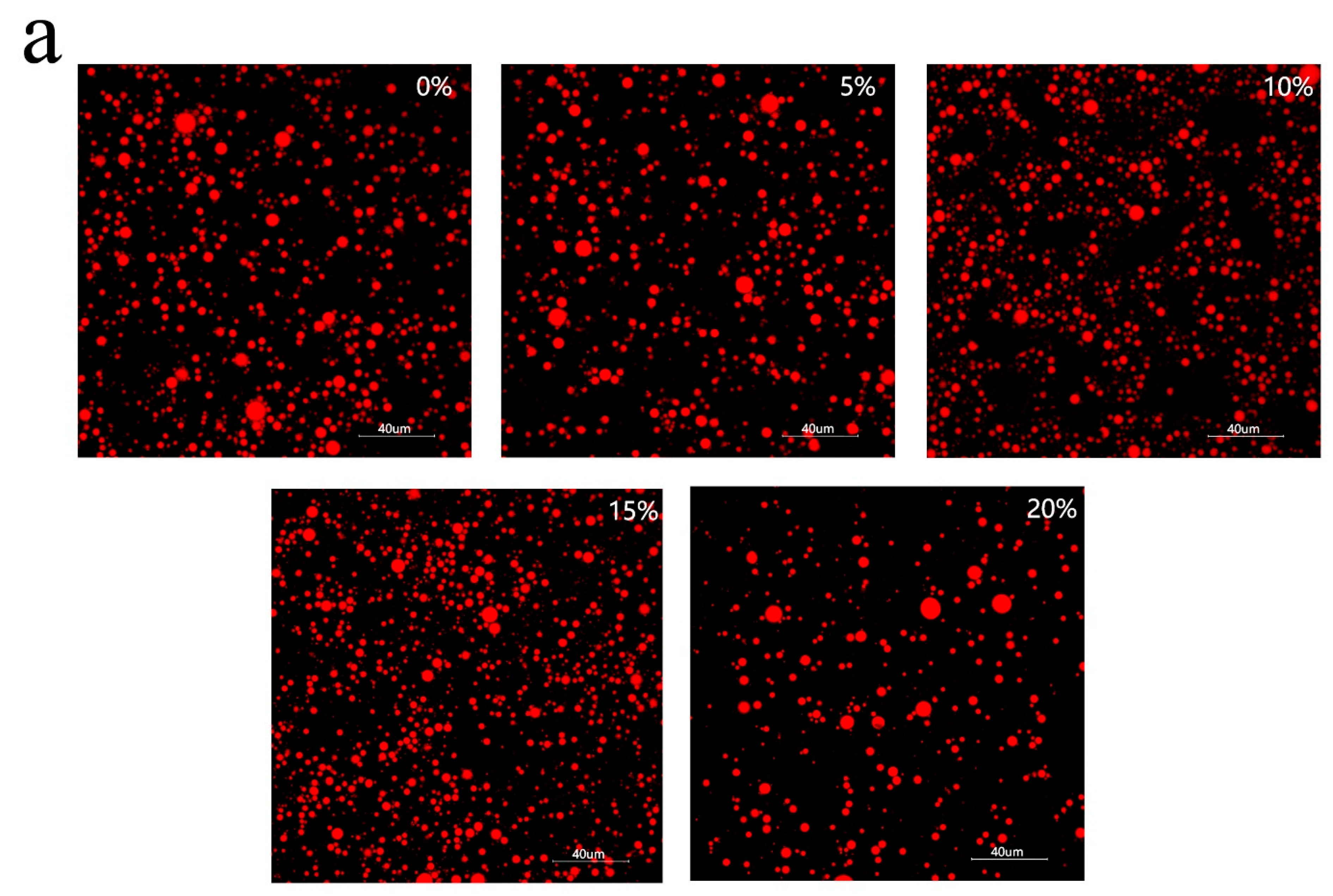
3.4. Characteristics of Emulsion Particles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sandrou, D.K.; Arvanitoyannis, I.S. Low-Fat/Calorie Foods: Current state and perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2010, 40, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, C.E.; Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.J.; Chen, L.; Tong, Q.Y.; McClements, D.J. Designing hydrogel particles for controlled or targeted release of lipophilic bioactive agents in the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 72, 698–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Matsuo, M.; Kssai, M.; Takeuchi, H. Effects of a liquid diet supplement contain in structured medium- and long-chain triacylglycerols on bodyfat accumulation in healthy young subjects. Asia. Pacific. J. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 10, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Yu, X.; Jing, H.; et al. Consumption of medium- and long-chain triacylglycerols decreases body fat and blood triglyceride in Chinese hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 63, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marten, B.; Pfeuffer, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Medium-chain triglycerides. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M. Study on the Effect of Oil Bases on Cellular Antioxidant Activities of Lipid Concomitants. Master’s Thesis, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, W.; French, D.; Wong, A.; Drasner, K.; Wu, A.H.B. A mixed (long- and medium-chain) triglyceride lipid emulsion extracts local anesthetic from human rerum in vitro more effectively than a long-chain emulsion. Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fioramonti, S.A.; Arzeni, C.; Pilosof, A.M.R.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Santiago, L.G. Influence of freezing temperature and maltodextrin concentration on stability of linseed oil-in-water multilayer emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2015, 156, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, C.; Hondoh, H.; Ueno, S. Influence of morphology and polymorphic transformation of fat crystals on the freeze-thaw stability of mayonnaise-type oil-in-water emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 604–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, G.; Vliet, T.V.; Stuart, M.C.; Velde, F.V.D.; Aken, G.A.V. Deformation and fracture of emulsion-filled gels: Effect of gelling agent concentration and oil droplet size. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1853–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusson, E.C.; Rosén, C.; Nilsson, L. Freeze-thaw stability of mayonnaise type oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agama Acevedo, E.; Perez, L.B. Starch as an emulsions stability: The case of octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) starch. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, D.; Kiwatashi, R.; Askura, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Shimada, Y.; Otake, k.; Shono, A. Physics Procedia: Effects of Operational Conditions on Preparation of Oil in Water Emulsion Using Ultrasound; AOCS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 70, pp. 1043–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Mana, Y.B.C.; Haryati, T.; Ghazali, H.M.; Asbi, B.A. Composition and thermal profile of crude palm oil and its products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Li, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, F.; Yadav, M.P.; Zhang, H. A comparison of corn fiber gum, hydrophobically modified starch, gum arabic and soybean soluble polysaccharide: Interfacial dynamics, viscoelastic response at oil/water interfaces and emulsion stabilization mechanisms. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, E.; Maria, E.; Roberto, J.; Santos, K.; Santana, S.; Alves, C.E.; Sucupira, M.I. Fatty acid in raw and heated coconut oil in eleven coconut oil food preparations analysed by gas chromatography. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2021, 24, 10329. [Google Scholar]
- Ghari, O.M.; Hassani, F.S.A.; Mezhkoun, M.E.M.; Zari, N.; Bouhfid, R.; Qaiss, A.E.K. Elaboration of a composite material based on plaster reinforced with phase change material/Oakum Fiber physical, thermal and mechanical properties. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayard, M.; Calderon, F.L.; Cansell, M. Free fatty acids and their esters modulate isothermal crystallization of anhydrous milk fat. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Sha, G.; Zhao, S.; Xie, Z.; Chang, X.; Shen, P. The viscosifying behavior of W/O emulsion and its underlying mechanisms: Considering the interfacial adsorption of heavy components. Colloid Surf. A 2022, 632, 127794. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.; Nicoli, T.; Benyahia, L.; Nicol, E. Utilization of xanthan to stabilize water in water emulsions and modulate their viscosity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, T.; Lin, W.; Tang, C.; Liu, R. Improving freeze-thaw stability of soy nanoparticle-stabilized emulsions through increasing particle size and surface hydrophobicity. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Wan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Yang, X. Wheat gluten-stabilized high internal phase emulsions as mayonnaise replacers. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.P.; Lai, O.M.; Abas, F.; Lim, H.K.; Tan, C.P. Stability of a concentrated oil-in-water emulsion model prepared using palm olein-based diacylglycerol/virgin coconut oil blends: Effects of the rheological properties, droplet size distribution and microstructure. Food Res. Int. 2014, 64, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanamai, R.; Mcclements, D.J. Depletion flocculation of beverage emulsions by gum arabic and modified starch. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, K.; Coudijzer, K.; Fredrick, E.; Campeneere, S.D.; Block, J.D.; Wouters, J.; Raes, K.; Dewettinck, K. Crystallization behavior of milk fat obtained from linseed-fed cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupongsak, S.; Sathitvorapojjana, S. Properties and storage stability of O/W emulsion replaced with medium-chain fatty acid oil. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayati, I.N.; Man, Y.B.C.; Tan, C.P.; Aini, I.N. Stability and rheology of concentrated O/W emulsions based on soybean oil/palm kernel olein blends. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, F.; Montanari, L.; Peressini, D.; Fantozzi, P. Influence of alginate concentration and molecular weight of functional properties of mayonnaise. LWT 2002, 35, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T. Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long- term physical stability of emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface 2004, 108–109, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangwal, K.; Sato, K. Structure-Function Analysis of Edible Fats: Nucleation and Crystallization Kinetics of Fats, 2nd ed.; AOCS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 21–72. [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, J.M.; Wagh, A.; Gioielli, L.A.; Silva, R.C.D.; Martini, S. Effects of high intensity ultrasound and emulsifiers on crystallization behavior of coconut oil and palm olein. Food Res. Int. 2016, 86, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.; Barey, P.; Veschambre, P.; Cansell, M. Physicochemical behavior of oil-in-water emulsions: Influence of milk protein mixtures, glycerol ester mixtures and fat characteristics. Colloids Surf. B 2005, 42, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, S.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L. MCT/LCT Mixed Oil Phase Enhances the Rheological Property and Freeze-Thawing Stability of Emulsion. Foods 2022, 11, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050712
Liu J, Han Y, Chen J, Zhang Z, Miao S, Zheng B, Zhang L. MCT/LCT Mixed Oil Phase Enhances the Rheological Property and Freeze-Thawing Stability of Emulsion. Foods. 2022; 11(5):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050712
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jiahao, Yi Han, Jiashi Chen, Zhigang Zhang, Song Miao, Baodong Zheng, and Longtao Zhang. 2022. "MCT/LCT Mixed Oil Phase Enhances the Rheological Property and Freeze-Thawing Stability of Emulsion" Foods 11, no. 5: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11050712








