An Improved GC-MS Method for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection: Avoiding the Effects of Nitrite in Foods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Standard Solutions
2.3. MDA-Nitrite Mixed Solutions and Meat Samples
2.4. Hydrolysis Treatments on Tested Samples
2.5. MDA Detection Assays
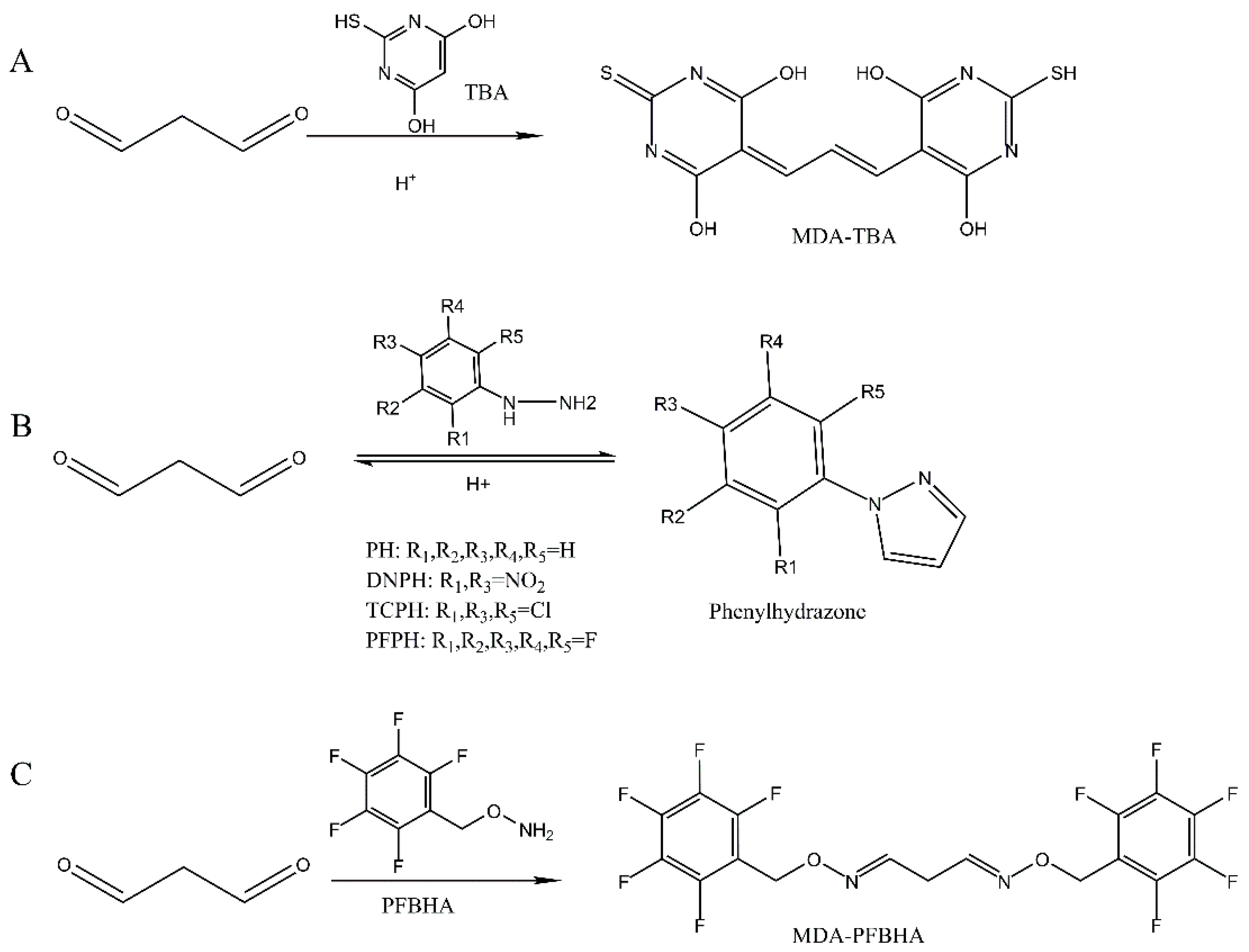
2.5.1. Detection of MDA by Conventional TBA Assay
2.5.2. Detection of MDA Directly by HPLC-UV Assay
2.5.3. Detection of MDA-DNPH by HPLC-UV Assay
2.5.4. Detection of MDA-PFPH by GC-MS Assay
2.6. Analyte Solution Stability and Method Validation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison among Three External Standard Methods
3.2. Comparison among Four Internal Standard Methods
3.3. Optimization of the Deuterated Internal Standard Method
3.4. Comparison among Detection Methods Applied in Food Samples
3.5. Analyte Stability and Method Validation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dimitrios, T. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation by Measuring Malondialdehyde (Mda) and Relatives in Biological Samples: Analytical and Biological Challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ganhão, R.; Estévez, M.; Morcuende, D. Suitability of the Tba Method for Assessing Lipid Oxidation in a Meat System with Added Phenolic-Rich Materials. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D.; Rothmann, S.; Schneider, J.Y.; Suchy, M.-T.; Trettin, A.; Modun, D.; Stuke, N.; Maassen, N.; Frölich, J.C. Development, Validation and Biomedical Applications of Stable-Isotope Dilution Gc–Ms and Gc–Ms/Ms Techniques for Circulating Malondialdehyde (Mda) after Pentafluorobenzyl Bromide Derivatization: Mda as a Biomarker of Oxidative Stress and Its Relation to 15(S)-8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α and Nitric Oxide (No). J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1019, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán Merás, I.; Periañez Llorente, C.; Pilo Ramajo, J.; Martín Tornero, E.; Espinosa-Mansilla, A. Optimization of the Thiobarbituric Acid-Malonaldehyde Reaction in Non-Aqueous Medium. Direct Analysis of Malonaldehyde in Oil Samples by Hplc with Fluorimetric Detection. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.; Linares, M.; Egea, M.; Auqui, S.; Garrido, M. Tbars Distillation Method: Revision to Minimize the Interference from Yellow Pigments in Meat Products. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonios, P.; Edward, M.; Herman, V.L.; Bruno, D.M. Malondialdehyde Measurement in Oxidized Foods: Evaluation of the Spectrophotometric Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (Tbars) Test in Various Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9589–9594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, G. Simultaneous Analysis of Malondialdehyde, 4-Hydroxy-2-Hexenal, and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal in Vegetable Oil by Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11320–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Cardoso, C.; Pestana, C. Measurement of Malondialdehyde in Fish: A Comparison Study between Hplc Methods and the Traditional Spectrophotometric Test. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domijan, A.-M.; Ralić, J.; Radić-Brkanac, S.; Rumora, L.; Žanić-Grubišić, T. Quantification of Malondialdehyde by Hplc-Fl—Application to Various Biological Samples. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolín, J.; Joy, M.; Blanco, M. Malondialdehyde Determination in Raw and Processed Meat Products by Uplc-Dad and Uplc-Fld. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, K.; Shibamoto, T. Improved Malonaldehyde Assay Using Headspace Solid-Phase Microextraction and Its Application to the Measurement of the Antioxidant Activity of Phytochemicals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4708–4713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konidari, C.N.; Giannopoulos, T.S.; Nanos, C.G.; Stalikas, C.D. Determination of Plasma, Urine, and Bovine Serum Albumin Low-Molecular-Weight Carbonyl Levels by Capillary Gas Chromatography with Electron-Capture and Mass-Selective Detection. Anal. Biochem. 2005, 338, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiamegos, Y.C.; Stalikas, C.D. Gas Chromatographic Determination of Carbonyl Compounds in Biological and Oil Samples by Headspace Single-Drop Microextraction with in-Drop Derivatisation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 609, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shestivska, V.; Antonowicz, S.S.; Dryahina, K.; Kubišta, J.; Smith, D.; Španěl, P. Direct Detection and Quantification of Malondialdehyde Vapour in Humid Air Using Selected Ion Flow Tube Mass Spectrometry Supported by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruan, E.D.; Aalhus, J.; Juárez, M. A Rapid, Sensitive and Solvent-Less Method for Determination of Malonaldehyde in Meat by Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Coupled Thermal Desorption and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with in Situ Derivatization. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 2723–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D.; Rothmann, S.; Schneider, J.Y.; Gutzki, F.-M.; Beckmann, B.; Frölich, J.C. Simultaneous Gc-Ms/Ms Measurement of Malondialdehyde and 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal in Human Plasma: Effects of Long-Term L-Arginine Administration. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanff, E.; Eisenga, M.F.; Beckmann, B.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Tsikas, D. Simultaneous Pentafluorobenzyl Derivatization and Gc-Ecnici-Ms Measurement of Nitrite and Malondialdehyde in Human Urine: Close Positive Correlation between These Disparate Oxidative Stress Biomarkers. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1043, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelzer, S.; Oberreither, R.; Bernecker, C.; Stelzer, I.; Truschnig-Wilders, M.; Fauler, G. Measurement of Total and Free Malondialdehyde by Gas–Chromatography Mass Spectrometry—Comparison with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Methology. Free Radic. Res. 2013, 47, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Ding, Y.; Li, G.; Wu, Y. Typical Reactive Carbonyl Compounds in Food Products: Formation, Influence on Food Quality, and Detection Methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 503–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Pegg, R.B.; Harris, R. Effects of Nitrite and Sulfanilamide on the 2-Thiobarbituric Acid (Tba) Values in Aqueous Model and Cured Meat Systems. J. Muscle Foods 1991, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Nam, K.C.; Jo, C. Detection of Malondialdehyde in Processed Meat Products without Interference from the Ingredients. Food Chem. 2016, 209, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giera, M.; Lingeman, H.; Niessen, W.M.A. Recent Advancements in the Lc- and Gc-Based Analysis of Malondialdehyde (Mda): A Brief Overview. Chromatographia 2012, 75, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, X. Measurement of Malonaldehyde in Apple Juice Using Gc–Ms and a Comparison to the Thiobarbituric Acid Assay. Food Chem. 2002, 77, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejska, I.; Skonieczny, S.; Rubin, L.J. Malondialdehyde-Nitrite Interactions in Meat and Model Systems. J. Food Sci. 1990, 55, 926–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trufelli, H.; Palma, P.; Famiglini, G.; Cappiello, A. An Overview of Matrix Effects in Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cyronak, M.; Yang, E. Does a Stable Isotopically Labeled Internal Standard Always Correct Analyte Response?: A Matrix Effect Study on a Lc/Ms/Ms Method for the Determination of Carvedilol Enantiomers in Human Plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotto, D.; Maria, L.S.; Valentini, J.; Paniz, C.; Schmitt, G.; Garcia, S.C.; Pomblum, V.J.; Rocha, J.B.T.; Farina, M. Importance of the Lipid Peroxidation Biomarkers and Methodological Aspects for Malondialdehyde Quantification. Quim. Nova 2009, 32, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano, M.; Gallego, M.; Silva, M. Analysis of Endogenous Aldehydes in Human Urine by Static Headspace Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1437, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwetha, B.; Siddalingaprasad, H.; Swamy, S.; Nagalakshmi, N.; Hariprasad, M. Mechanism of Haematotoxicity Induced by Phenylhydrazine: A Review. J. Appl. Pharm. Res. 2019, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonny, M.E.; Reineri, P.S.; Palma, G.A.; Nazareno, M.A. Development of an Analytical Method to Determine Malondialdehyde as an Oxidative Marker in Cryopreserved Bovine Semen. Anal. Methods 2015, 15, 6331–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Sánchez, A.; Hermosín, I.; Maya, I. Cleavage and Oligomerization of Malondialdehyde under Physiological Conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 4077–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, A.S.; Salonikas, C.; Naidoo, D.; Wilcken, D.E.L. Improved Method for Plasma Malondialdehyde Measurement by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Using Methyl Malondialdehyde as an Internal Standard. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotto, D.; Santa-Maria, L.D.; Boeira, S.; Valentini, J.; Charão, M.F.; Moro, A.M.; Nascimento, P.C.; Pomblum, V.J.; Garcia, S.C. Rapid Quantification of Malondialdehyde in Plasma by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Visible Detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Methods a | Meat Product Models with Different Addition Concentration of Sodium Nitrite | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.0005% | 0.003% | 0.015% | ||
| A1 | MDA-TBA adduct/UV-Vis/TCA | 0.704 ± 0.016 | 0.665 ± 0.009 * | 0.660 ± 0.032 * | 0.403 ± 0.013 * |
| B1 | MDA-DNPH adduct/HPLC-UV/TCA | 0.797 ± 0.068 | 0.522 ± 0.111 * | 0.325 ± 0.027 * | 0.281 ± 0.008 * |
| D1 | MDA-PFPH adduct (MDA-d2)/GC-MS/TCA | 0.850 ± 0.014 | 0.854 ± 0.018 | 0.844 ± 0.026 | 0.826 ± 0.003 |
| D2 | MDA-PFPH adduct (MDA-d2)/GC-MS/NaOH | 1.778 ± 0.019 | 1.748 ± 0.055 | 1.756 ± 0.026 | 1.773 ± 0.073 |
| F2 | MDA/HPLC-UV/NaOH | 2.659 ± 0.061 | 2.607 ± 0.100 | 2.731 ± 0.242 | 2.715 ± 0.179 |
| Meat Product Models with Different Addition Concentration of Sodium Nitrite | F2-MDA/HPLC-UV/NaOH a | D1-MDA-PFPH (MDA-d2)/GC/TCA | D2-MDA-PFPH (MDA-d2)/GC/NaOH | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recovery (%) | Intra CV (%) | Inter CV (%) | Recovery (%) | Intra CV (%) | Inter CV (%) | Recovery (%) | Intra CV (%) | Inter CV (%) | |
| Control b | 90.7 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 96.2 | 1.7 | 3.2 | 98.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| 0.0005% | 101.3 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 98.4 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 97.8 | 3.1 | 2.6 |
| 0.003% | 95.0 | 8.9 | 6.5 | 96.2 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 94.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| 0.015% | 93.4 | 6.6 | 4.9 | 98.3 | 0.3 | 1.0 | 93.9 | 4.1 | 3.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, X. An Improved GC-MS Method for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection: Avoiding the Effects of Nitrite in Foods. Foods 2022, 11, 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091176
Wang W, Zhang Z, Liu X, Cao X, Wang L, Ding Y, Zhou X. An Improved GC-MS Method for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection: Avoiding the Effects of Nitrite in Foods. Foods. 2022; 11(9):1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091176
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenjie, Zhiwen Zhang, Xiaoying Liu, Xiaoji Cao, Lianzhu Wang, Yuting Ding, and Xuxia Zhou. 2022. "An Improved GC-MS Method for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection: Avoiding the Effects of Nitrite in Foods" Foods 11, no. 9: 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091176
APA StyleWang, W., Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Cao, X., Wang, L., Ding, Y., & Zhou, X. (2022). An Improved GC-MS Method for Malondialdehyde (MDA) Detection: Avoiding the Effects of Nitrite in Foods. Foods, 11(9), 1176. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11091176






