Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Fumonisin Family Mycotoxins on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
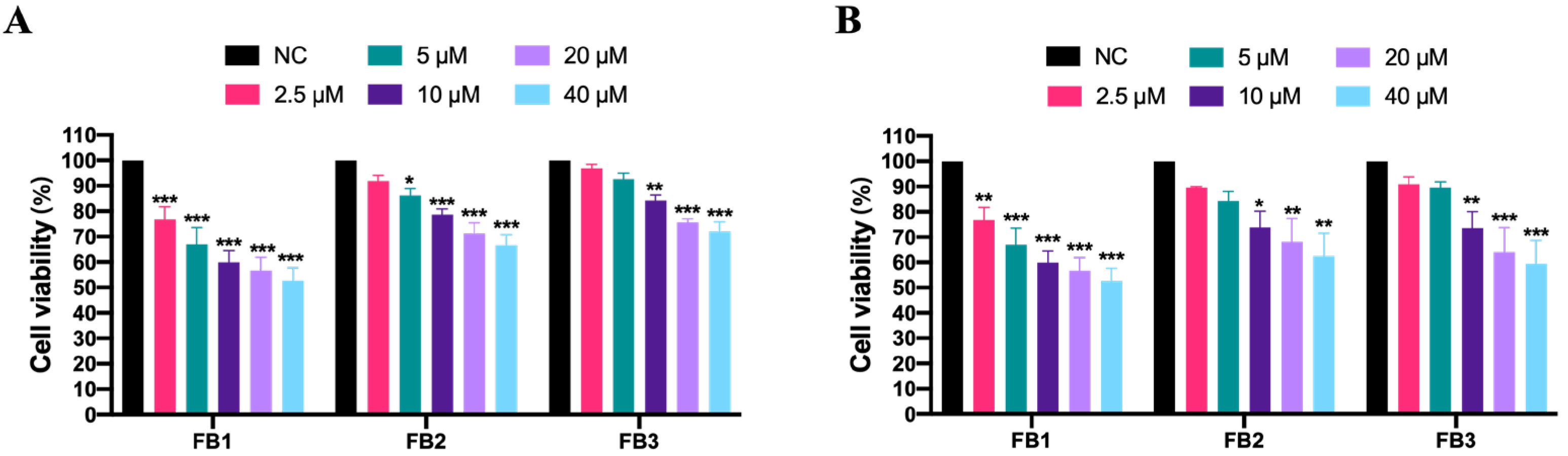
3.1. Effect of Fumonisins on Cell Viability in IPEC Cells
3.2. Combined Toxicity of Fumonisins in IPEC Cells
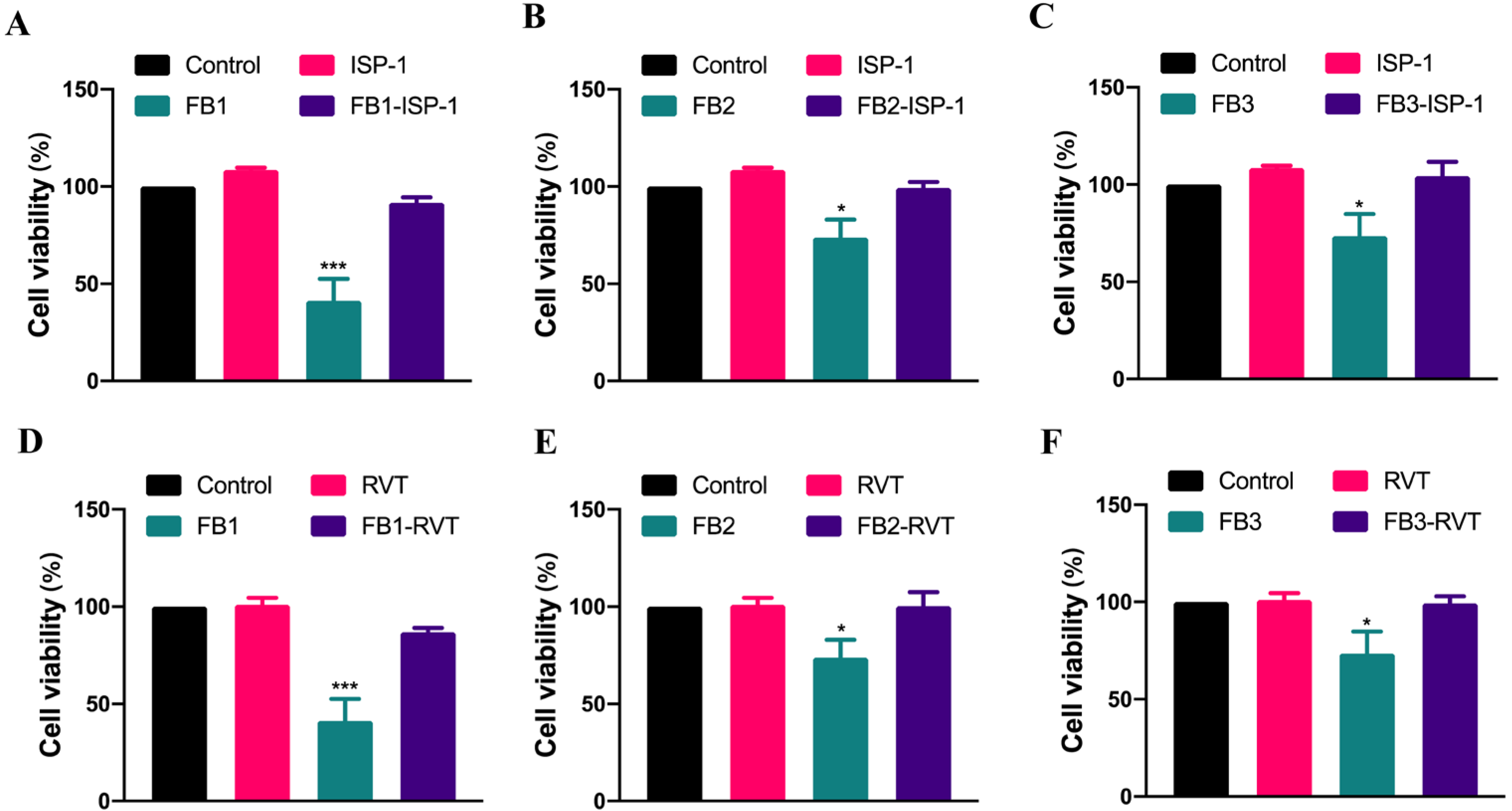
3.3. The Mitigation of FB-Induced Cytotoxicity by Natural Substances in IPEC Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FBs | Fumonisin Bs |
| FB1 | Fumonisin B1 |
| FB2 | Fumonisin B2 |
| FB3 | Fumonisin B3 |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| DRI | Dose reduction index |
| GES-1 | Human gastric epithelial cell line |
| IPEC | Porcine intestinal epithelial cells |
| ISP-1 | Myriocin |
| ID | Inhibitory does |
| RVT | Resveratrol |
References
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, D.; Cai, P.; Lin, H.; Ying, H.; Hu, Q.-N.; Wu, A. Elimination of Fusarium mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON) via microbial and enzymatic strategies: Current status and future perspectives. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Duan, C. The Major Fusarium Species Causing Maize Ear and Kernel Rot and Their Toxigenicity in Chongqing, China. Toxins 2018, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Rocha, M.E.B.; Da Chagas Oliveira Freire, F.; Maia, F.E.F.; Guedes, M.I.F.; Rondina, D. Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 2014, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Fumonisin B1: Mechanisms of toxicity and biological detoxification progress in animals. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waśkiewicz, A.; Beszterda, M.; Goliński, P. Occurrence of fumonisins in food—An interdisciplinary approach to the problem. Food Control 2012, 26, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wen, J.; Tang, Y.; Shi, J.; Mu, G.; Yan, R.; Cai, J.; Long, M. Research Progress on Fumonisin B1 Contamination and Toxicity: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-G.; Phat, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, C. Occurrence of Fusarium Mycotoxin Fumonisin B1 and B2 in Animal Feeds in Korea. Mycotoxin Res. 2013, 29, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jia, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, A. Involvement of PERK-CHOP pathway in fumonisin B1- induced cytotoxicity in human gastric epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jia, B.; Liu, N.; Yu, D.; Wu, A. Evaluation of the Individual and Combined Toxicity of Fumonisin Mycotoxins in Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, I.H.; Do, W.H.; Nam, W.S.; Li, H.; Jang, H.S.; Lee, C. Incidence and levels of deoxynivalenol, fumonisins and zearalenone contaminants in animal feeds used in Korea in 2012. Toxins 2013, 6, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Q.; Pang, M.; Liu, Y.; Dong, J. Fumonisins B1 and B2 in maize harvested in Hebei province, China, during 2011–2013. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2015, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Jiang, D.; Zheng, F.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Fumonisins B1, B2 and B3 in corn products, wheat flour and corn oil marketed in Shandong province of China. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2015, 8, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Jia, B.; Li, K.; Zhou, H.; Lai, W.; Tang, Y.; Yan, Z.; Sun, W.; Liu, N.; Yu, D.; et al. Pre-warning of abiotic factors in maize required for potential contamination of fusarium mycotoxins via response surface analysis. Food Control 2021, 121, 107570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.H.; Ding, S.T.; Chang, M.H. Effect of fumonisins on macrophage immune functions and gene expression of cytokines in broilers. Arch. Anim. Nutr. 2006, 60, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherbawy, Y.; Elhariry, H.; Kocsubé, S.; Bahobial, A.; Deeb, B.E.; Altalhi, A.; Varga, J.; Vágvölgyi, C. Molecular characterization of black Aspergillus species from onion and their potential for ochratoxin A and fumonisin B2 production. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, G.; De Girolamo, A.; Sarigiannis, Y.; Haidukowski, M.E.; Visconti, A. Occurrence of ochratoxin A, fumonisin B2 and black aspergilli in raisins from Western Greece regions in relation to environmental and geographical factors. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinl, S.; Hartinger, D.; Thamhesl, M.; Vekiru, E.; Krska, R.; Schatzmayr, G.; Moll, W.D.; Grabherr, R. Degradation of fumonisin B1 by the consecutive action of two bacterial enzymes. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 145, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B. The mechanism of Lactobacillus strains for their ability to remove fumonisins B1 and B2. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 97, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meoli, L.; Günzel, D. Channel functions of claudins in the organization of biological systems. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breugelmans, T.; Oosterlinck, B.; Arras, W.; Ceuleers, H.; De Man, J.; Hold, G.L.; De Winter, B.Y.; Smet, A. The role of mucins in gastrointestinal barrier function during health and disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Yuan, Q.; Su, J.; Yang, L.; Ning, L.; Lei, H. Fumonisin B(1) damages the barrier functions of porcine intestinal epithelial cells in vitro. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2019, 33, e22397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Tan, L.; Luo, Y.; Gao, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Fan, W.; DeSaeger, S.; Song, S. Fumonisin B(1) induced intestinal epithelial barrier damage through endoplasmic reticulum stress triggered by the ceramide synthase 2 depletion. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 166, 113263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Liu, S.; Ge, L.; Du, H.; Yue, D.; Hou, L.; Huang, K.; Chen, X. mTOR-Mediated Autophagy Regulates Fumonisin B(1)-Induced Intestinal Inflammation via Pyroptosis In Vivo and In Vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9187–9200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, S.; Wang, J.; Yin, P.; Liu, H.; Sun, C. Alginate oligosaccharides protect against fumonisin B1-induced intestinal damage via promoting gut microbiota homeostasis. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.V.B.; De Oliveira, C.A.F.; Ramalho, L.N.Z. Effects of Prenatal Exposure to Aflatoxin B1: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudyk, H.; Tomaszewska, E.; Arciszewski, M.B.; Muszyński, S.; Tomczyk-Warunek, A.; Dobrowolski, P.; Donaldson, J.; Brezvyn, O.; Kotsyumbas, I. Histomorphometrical changes in intestine structure and innervation following experimental fumonisins intoxication in male Wistar rats. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 23, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, T.; Chuturgoon, A.A. Toxicoepigenetic consequences of fumonisin B(1) exposure: Current knowledge and future perspective. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1849–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijó Corrêa, J.A.; Orso, P.B.; Bordin, K.; Hara, R.V.; Luciano, F.B. Toxicological effects of fumonisin B(1) in combination with other Fusarium toxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 121, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Jia, B.; Lin, H.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.; Liu, N.; Wu, A. Effects of Fumonisin B and Hydrolyzed Fumonisin B on Growth and Intestinal Microbiota in Broilers. Toxins 2022, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhet, S.; Oswald, I.P. The intestine as a possible target for fumonisin toxicity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, J.C. Drug Combination Studies and Their Synergy Quantification Using the Chou–Talalay Method—Letter. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, A.; Zikankuba, V.L. Mycotoxins contamination in maize alarms food safety in sub-Sahara Africa. Food Control 2018, 90, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 cytotoxicity against human intestinal Caco-2 cells is enhanced in the presence of other mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobral, M.M.C.; Faria, M.A.; Cunha, S.C.; Miladinovic, B.; Ferreira, I.M. Transport of mycotoxins across human gastric NCI–N87 and intestinal Caco-2 cell models. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonissen, G.; Croubels, S.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Eeckhaut, V.; Devreese, M.; Verlinden, M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Eeckhout, M.; De Saeger, S.; et al. Fumonisins affect the intestinal microbial homeostasis in broiler chickens, predisposing to necrotic enteritis. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonissen, G.; Van Immerseel, F.; Pasmans, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Janssens, G.P.; De Baere, S.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Su, S.; Wong, E.A.; De Meulenaer, B.; et al. Mycotoxins Deoxynivalenol and Fumonisins Alter the Extrinsic Component of Intestinal Barrier in Broiler Chickens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10846–10855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskeuas, V.; Griela, E.; Bouziotis, D.; Fegeros, K.; Antonissen, G.; Mountzouris, K.C. Effects of Deoxynivalenol and Fumonisins on Broiler Gut Cytoprotective Capacity. Toxins 2021, 13, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, M.; Boudry, G.; Sève, B.; Oswald, I.P.; Lallès, J.P. Intestinal physiology and peptidase activity in male pigs are modulated by consumption of corn culture extracts containing fumonisins. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assunção, R.; Pinhão, M.; Loureiro, S.; Alvito, P.; Silva, M.J. A multi-endpoint approach to the combined toxic effects of patulin and ochratoxin a in human intestinal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 313, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Jia, B.; Wu, A. Cytotoxicities of Co-occurring alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether and tenuazonic acid on human gastric epithelial cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 171, 113524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jaal, B.A.; Jaganjac, M.; Barcaru, A.; Horvatovich, P.; Latiff, A. Aflatoxin, fumonisin, ochratoxin, zearalenone and deoxynivalenol biomarkers in human biological fluids: A systematic literature review, 2001–2018. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 129, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, S.; Tan, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, A. Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Deoxynivalenol Family Mycotoxins on Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Toxins 2017, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Föllmann, W.; Behm, C.; Degen, G.H. Toxicity of the mycotoxin citrinin and its metabolite dihydrocitrinone and of mixtures of citrinin and ochratoxin A in vitro. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 88, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, J.B.; DesRochers, N.; Hoogstra, S.; Garnham, C.P.; Sumarah, M.W. Structure Activity Relationship for Fumonisin Phytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1604–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerre, P.; Matard-Mann, M.; Nyvall Collén, P. Targeted sphingolipid analysis in chickens suggests different mechanisms of fumonisin toxicity in kidney, lung, and brain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 170, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, P.C.; Couch, L.H.; Patton, R.E.; Eppley, R.M.; Doerge, D.R.; Churchwell, M.I.; Marques, M.M.; Okerberg, C.V. Comparison of the toxicity of several fumonisin derivatives in a 28-day feeding study with female B6C3F(1) mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2002, 185, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojjati, M.R.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Tang, S.; Huan, C.; Ooi, E.; Lu, S.; Jiang, X.C. Effect of myriocin on plasma sphingolipid metabolism and atherosclerosis in apoE-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 10284–10289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rachitha, P.; Krupashree, K.; Brindhadevi, K.; Pal, A.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Shanmuganathan, R.; Karuppusamy, I.; Raghavendra, V.B. Convalescent action of menthol against T-2 mycotoxin-induced toxicity: An in vitro study with HaCaT cells. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichinger, G.; Beisl, J.; Marko, D. Genistein and delphinidin antagonize the genotoxic effects of the mycotoxin alternariol in human colon carcinoma cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Che, S.; Ruan, Z.; Song, L.; Tang, R.; Zhang, L. Regulatory effects of flavonoids luteolin on BDE-209-induced intestinal epithelial barrier damage in Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 150, 112098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhai, S.; Jiang, X.; Meca, G.; Wang, S.; et al. Melatonin alleviates Ochratoxin A-induced liver inflammation involved intestinal microbiota homeostasis and microbiota-independent manner. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Wei, W.; Cao, R.; Lu, L.; Liang, S.; Xiong, M.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; Ma, Y. Resveratrol alleviates zea-induced decidualization disturbance in human endometrial stromal cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yu, H.; Shan, A.; Shen, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Resveratrol inhibits aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in bovine mammary epithelial cells and is involved the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Toxicon 2019, 164, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Ye, J.; Lv, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Z. Protection of Porcine Intestinal-Epithelial Cells from Deoxynivalenol-Induced Damage by Resveratrol via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1726–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
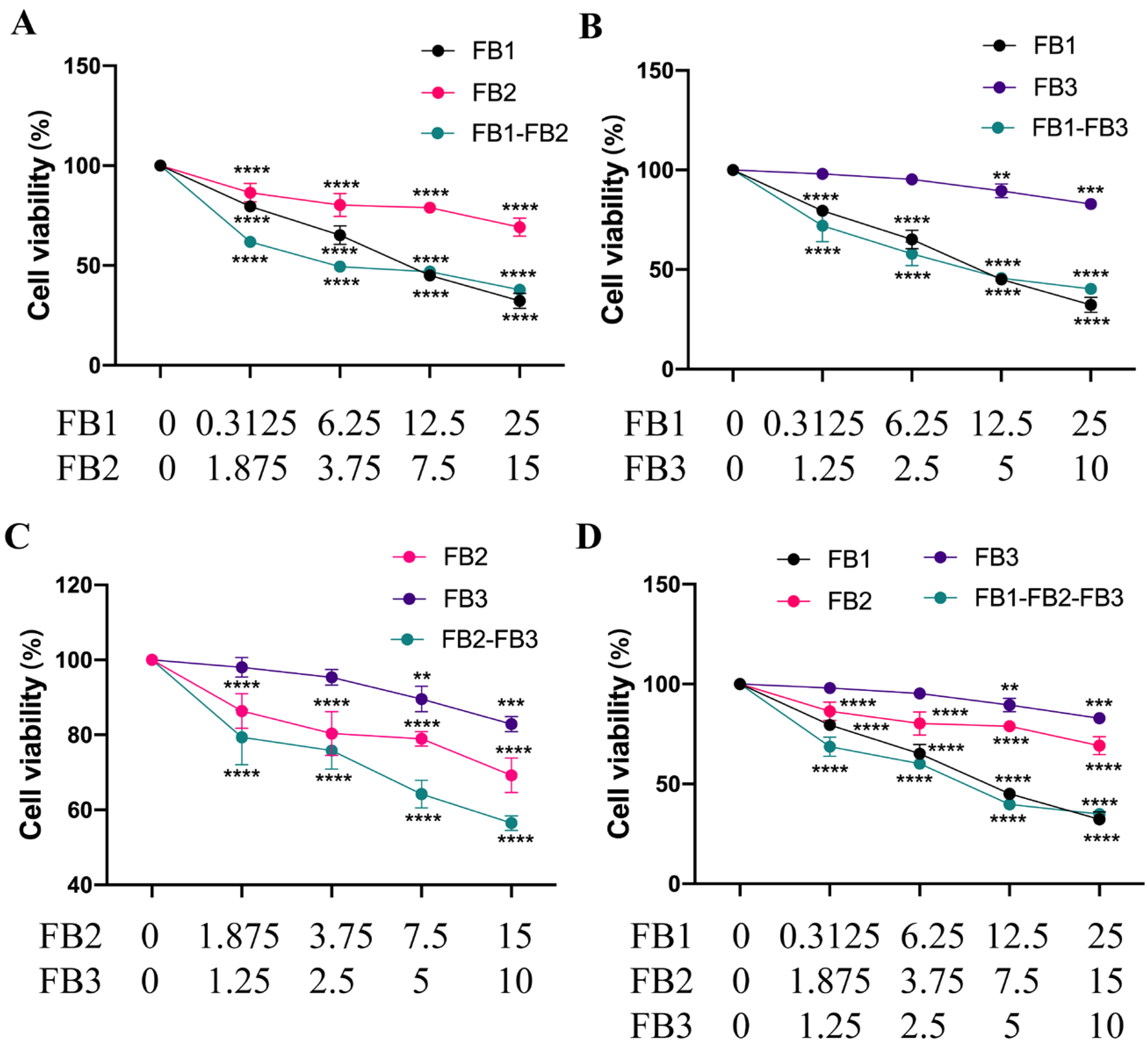
| Dm (μM) | M | r | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FB1 | 11.3967 | −1.0286 | 0.9968 |
| FB2 | 28.9756 | −0.4604 | 0.9699 |
| FB3 | 37.2595 | −1.1314 | 0.9955 |
| FB1-FB2 | 8.0753 | −0.4398 | 0.9719 |
| FB1-FB3 | 11.5549 | −0.6251 | 0.9795 |
| FB2-FB3 | 24.1793 | −0.5507 | 0.9859 |
| FB1-FB2-FB3 | 9.3569 | −0.7275 | 0.9756 |
| Fumonisin | Joint Ratio | ID10 | ID25 | ID50 | ID75 | ID90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combination Index | ||||||
| FB1-FB2 | 5:3 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.76 | 3.02 | 12.43 |
| FB1-FB3 | 5:2 | 0.33 | 0.61 | 1.14 | 2.13 | 3.99 |
| FB2-FB3 | 3:2 | 0.59 | 0.52 | 0.68 | 1.37 | 3.47 |
| FB1-FB2-FB3 | 5:3:2 | 0.70 | 0.72 | 0.98 | 1.47 | 2.92 |
| Fumonisin | Joint Ratio | ID10 | ID25 | ID50 | ID75 | ID90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dose Reduction Index | ||||||
| FB1 | 5:3 | 24.64 | 5.89 | 1.41 | 0.34 | 0.08 |
| FB2 | 25.55 | 22.85 | 20.42 | 18.26 | 16.33 | |
| FB1 | 5:2 | 3.39 | 1.83 | 0.99 | 0.53 | 0.29 |
| FB3 | 33.61 | 16.46 | 8.06 | 3.95 | 1.93 | |
| FB2 | 3:2 | 8.95 | 6.05 | 4.09 | 2.77 | 1.87 |
| FB3 | 17.92 | 6.44 | 2.31 | 0.83 | 0.30 | |
| FB1 | 5:3:2 | 2.95 | 1.89 | 1.22 | 0.78 | 0.37 |
| FB2 | 84.41 | 42.33 | 17.63 | 7.34 | 3.06 | |
| FB3 | 29.26 | 17.07 | 9.96 | 5.81 | 2.35 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Zou, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y. Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Fumonisin Family Mycotoxins on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell. Foods 2023, 12, 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132555
Yu S, Zou L, Zhao J, Zhu Y. Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Fumonisin Family Mycotoxins on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell. Foods. 2023; 12(13):2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132555
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Song, Lianpeng Zou, Jiawei Zhao, and Yiping Zhu. 2023. "Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Fumonisin Family Mycotoxins on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell" Foods 12, no. 13: 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132555
APA StyleYu, S., Zou, L., Zhao, J., & Zhu, Y. (2023). Individual and Combined Cytotoxic Effects of Co-Occurring Fumonisin Family Mycotoxins on Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cell. Foods, 12(13), 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12132555






