Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Standards
2.2. Bee Pollen Sample Collection
2.3. Preparation of Bee Pollen Extracts
2.4. UHPLC-QTOF/MS-Based Non-Targeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.5. Targeted Quantification of ECG and L-Theanine in CBP
3. Results
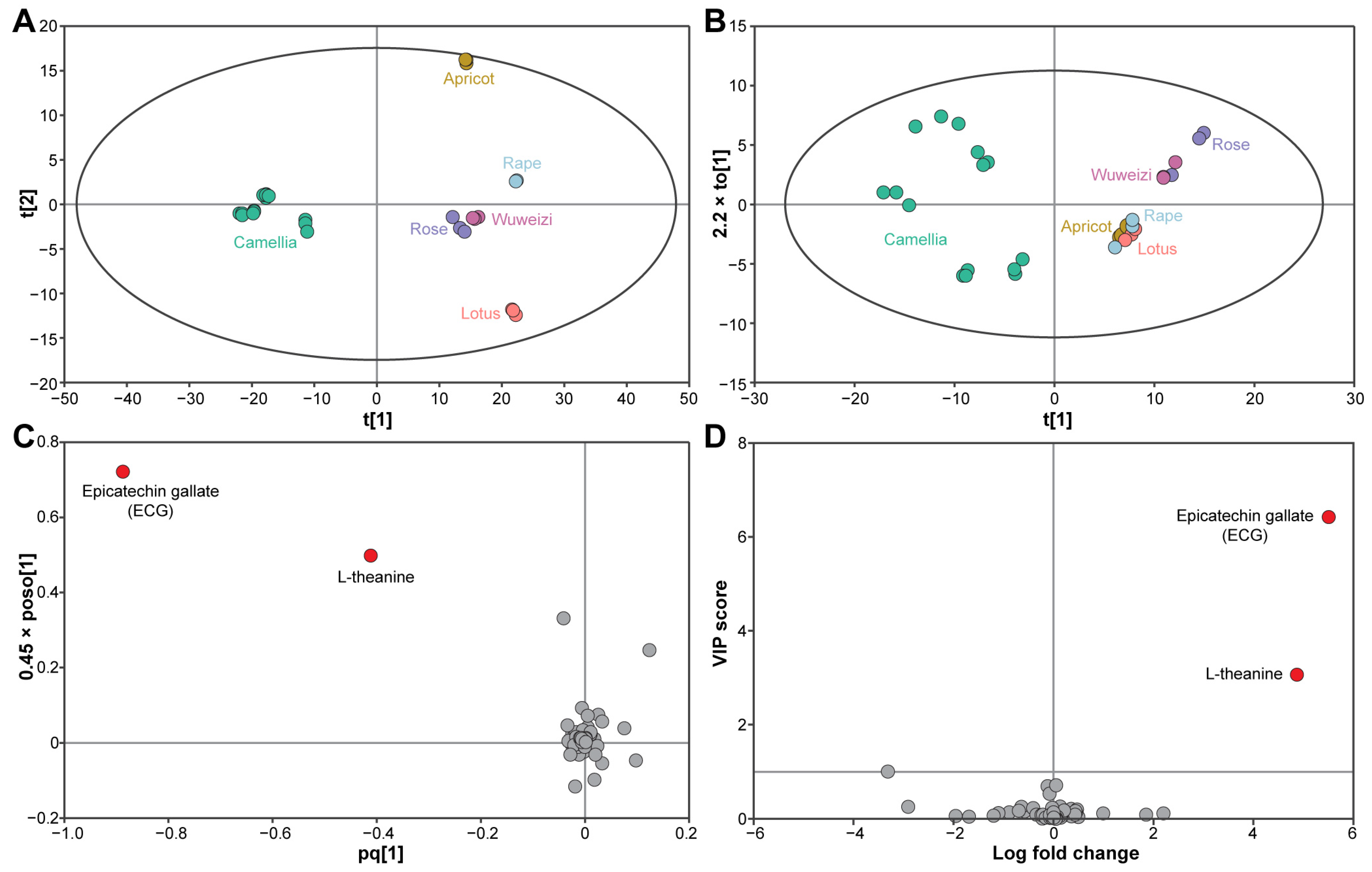
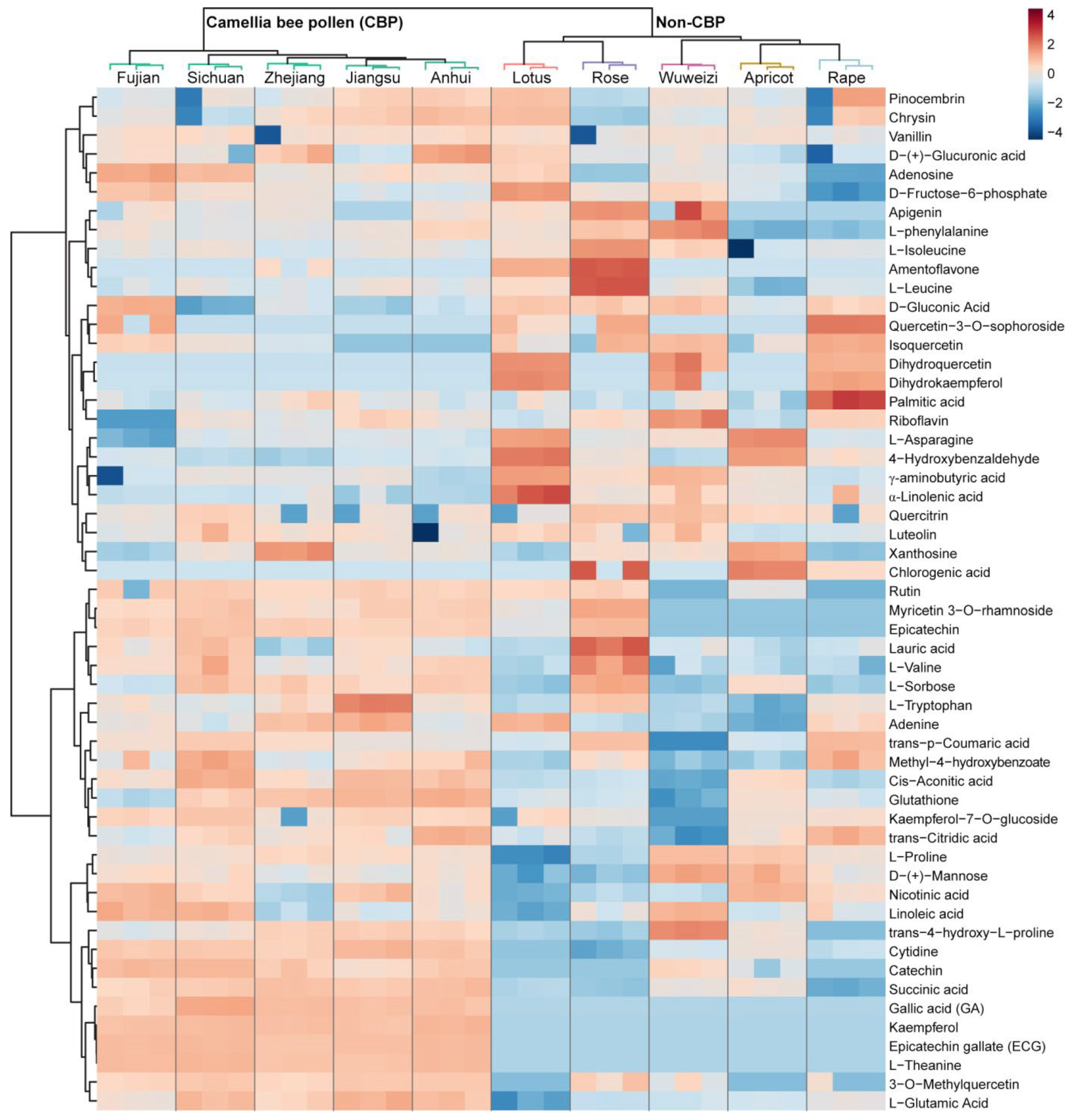
3.1. Overall Metabolic Profiles of the Bee Pollen
3.2. Metabolite Identification
3.3. Marker Compound Selection of CBP
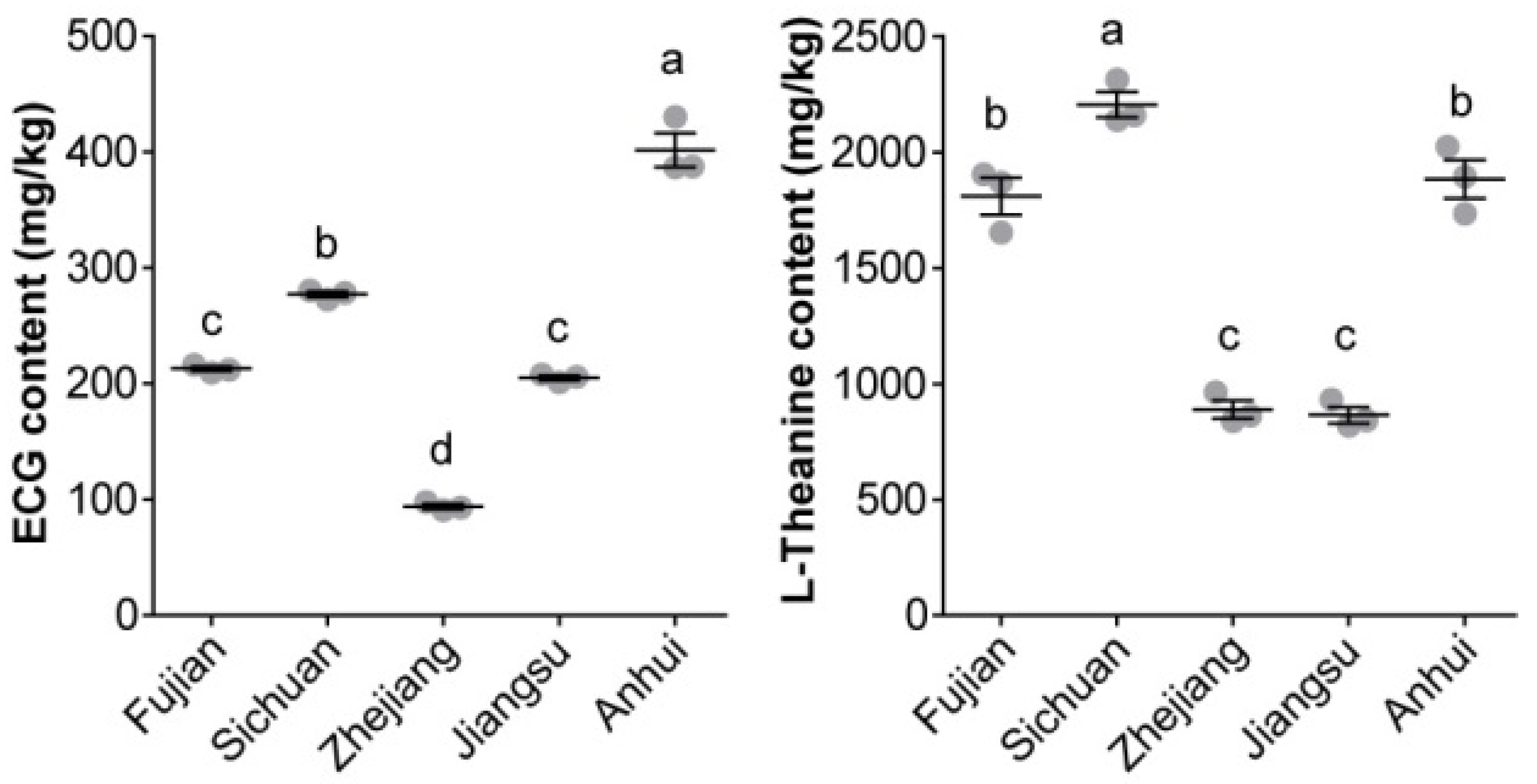
3.4. ECG and L-Theanine Quantification
4. Discussion
4.1. Distinctive Metabolic Profiles of CBP
4.2. ECG and L-Theanine as Maker Compounds of CBP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thakur, M.; Nanda, V. Composition and functionality of bee pollen: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 98, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, D.; Gabriele, M.; Summa, M.; Colosimo, R.; Leonardi, D.; Domenici, V.; Pucci, L. Antioxidant, nutraceutical properties, and fluorescence spectral profiles of bee pollen samples from different botanical origins. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algethami, J.S.; Abd El-Wahed, A.A.; Elashal, M.H.; Ahmed, H.R.; Elshafiey, E.H.; Omar, E.M.; Al Naggar, Y.; Algethami, A.F.; Shou, Q.Y.; Alsharif, S.M.; et al. Bee pollen: Clinical trials and patent applications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, S.A.M.; Elashal, M.H.; Yosri, N.; Du, M.; Musharraf, S.G.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D.; Guo, Z.M.; Cao, W.; Zou, X.B.; et al. Bee pollen: Current status and therapeutic potential. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaoan, R.; Strant, M.; Varadi, A.; Topal, E.; Yucel, B.; Cornea-Cipcigan, M.; Campos, M.G.; Vodnar, D.C. Bee collected pollen and bee bread: Bioactive constituents and health benefits. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostic, A.Z.; Milincic, D.D.; Barac, M.B.; Ali Shariati, M.; Tesic, Z.L.; Pesic, M.B. The application of pollen as a functional food and feed ingredient-The present and perspectives. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baky, M.H.; Abouelela, M.B.; Wang, K.; Farag, M.A. Bee pollen and bread as a super-food: A comparative review of their metabolome composition and quality assessment in the context of best recovery conditions. Molecules 2023, 28, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Chen, G.J.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.X.; Ye, H. Physiological genetics, chemical composition, health benefits and toxicology of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) flower: A review. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, e109584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Q.; Sun, M.H.; Wan, Z.R.; Liang, J.S.; Betti, M.; Hrynets, Y.; Xue, X.F.; Wu, L.M.; Wang, K. Bee pollen extracts modulate serum metabolism in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury mice with anti-inflammatory effects. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7855–7868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, X.Y.; Lu, Q.; Liu, R. Antioxidant and anti-tyrosinase activities of bee pollen and identification of active components. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.C.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, C.Y. Antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory properties of aqueous ethanol extracts from monofloral bee pollen. J. Apic. Sci. 2015, 59, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Sun, X.; Ni, H.; Du, X.P.; Chen, F.; Jiang, Z.D.; Li, Q.B. Identification and characterization of the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of caffeine from Camellia pollen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12741–12751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Huang, G.L.; Chen, Y.H.; Du, X.P.; Jiang, Z.D.; Chen, F.; Ni, H. Isolation and purification of two tyrosinase inhibitors from camellia pollen by high-speed counter-current chromatography. Acta Chromatogr. 2017, 29, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Lai, X.Y.; Lai, G.Y.; Jiang, Z.D.; Ni, H.; Chen, F. Purification and characterization of a tyrosinase inhibitor from Camellia pollen. J. Funct. Food. 2016, 27, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Ren, P.P.; Wu, Y.N.; He, Q.H. Recent advances in analytical techniques for the detection of adulteration and authenticity of bee products—A review. Food Addit. Contam. Part A-Chem. 2021, 38, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, O.M.; Freitas, A.S.; Oliveira, E.S.; Silva, R.A.; Maester, F.M.; Andrella, R.R.S.; Cardozo, G.M.B.Q. Evaluation of the botanical origin of commercial dry bee pollen load batches using pollen analysis: A proposal for technical standardization. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2010, 82, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.H.; Qi, Y.T.; Ritho, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zheng, X.W.; Wu, L.M.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.P. Flavonoid glycosides as floral origin markers to discriminate of unifloral bee pollen by LC-MS/MS. Food Control. 2015, 57, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansari, E.; Zarre, S.; Alizadeh, K.; Attar, F.; Aghabeigi, F.; Salmaki, Y. Pollen morphology of Campanula (Campanulaceae) and allied genera in Iran with special focus on its systematic implication. Flora 2012, 207, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Yu, W.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Ye, N. Micromorphological observation on pollen of 14 cultivars of tea tree (Camellia sinensis). J. South. Agric. 2018, 49, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhu, X.L.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.H.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of rape bee pollen after fermentation and their correlation with chemical components by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics. Food Chem. 2023, 409, e135342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Ma, B.; Li, J.; Fang, Y. Changes in chemical composition and antioxidant activity of royal jelly produced at different floral periods during migratory beekeeping. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, e111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Qiao, N.; Ning, F.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Luo, L.P. Identification and characterization of plant-derived biomarkers and physicochemical variations in the maturation process of Triadica cochinchinensis honey based on UPLC-QTOF-MS metabolomics analysis. Food Chem. 2023, 408, e135197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, M.I.; Termentzi, A.; Kasiotis, K.M.; Cheilari, A.; Stathopoulou, K.; Machera, K.; Aligiannis, N. Untargeted ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-hybrid quadrupole-orbitrap mass spectrometry (UHPLC-HRMS) metabolomics reveals propolis markers of Greek and Chinese origin. Molecules 2021, 26, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamat, J.; Rozani, N.A.A.; Murugesu, S. Application of the metabolomics approach in food authentication. Molecules 2021, 26, 7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.B.; Tian, Y.F.; Jiang, P.Y.Z.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.L.; Yang, H.S. Recent advances in the application of metabolomics for food safety control and food quality analyses. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1448–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.C.; Wang, K.; Shan, J.H.; Xue, X.F. A metabolomics approach revealed an Amadori compound distinguishes artificially heated and naturally matured acacia honey. Food Chem. 2022, 385, e132631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchetti, G.; Castiglioni, S.; Maldarizzi, G.; Carloni, P.; Lucini, L. UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS phenolic profiling and antioxidant capacity of bee pollen from different botanical origin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Yu, M.H.; Zhu, X.L.; Liu, R.; Lu, Q. Metabolomics reveals that phenolamides are the main chemical components contributing to the anti-tyrosinase activity of bee pollen. Food Chem. 2022, 389, e133071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.T.; Dong, F.; Tu, Y.Y.; Yang, Z.Y. Occurrence of functional molecules in the flowers of tea (Camellia sinensis) plants: Evidence for a second resource. Molecules 2018, 23, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, E.; Joshi, R.; Gulati, A. L-Theanine: An astounding sui generis integrant in tea. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Kenaan, A.; Geng, F.; Li, H.B.; Gunaratne, A.; Li, H.; Gan, R.Y. L-theanine: A unique functional amino acid in tea (Camellia sinensis L.) with multiple health benefits and food applications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, e853846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.J.; Li, W.F.; Xiao, X.; Huang, Q.X.; Yu, J.B.; Yang, Y.J.; Han, T.F.; Zhang, D.Z.; Niu, X.F. (-)-Epicatechin gallate blocks the development of atherosclerosis by regulating oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 8715–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullon, B.; Lu-Chau, T.A.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M.; Eibes, G. Rutin: A review on extraction, identification and purification methods, biological activities and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahkeshani, N.; Farzaei, F.; Fotouhi, M.; Alavi, S.S.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Naseri, R.; Momtaz, S.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Rahimi, R.; Farzaei, M.H.; et al. Pharmacological effects of gallic acid in health and diseases: A mechanistic review. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oelschlaegel, S.; Gruner, M.; Wang, P.N.; Boettcher, A.; Koelling-Speer, I.; Speer, K. Classification and characterization of manuka honeys based on phenolic compounds and methylglyoxal. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7229–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanisevic, J.; Want, E.J. From samples to insights into metabolism: Uncovering biologically relevant information in LC-HRMS metabolomics data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.R.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.Z.; Zhou, J.H. Analytical strategies for LC-MS-based untargeted and targeted metabolomics approaches reveal the entomological origins of honey. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.X.; Xia, Z.Q.; Li, H.J.; Jiang, X.H.; Qin, D.D.; Wang, Q.S.; Wang, Q.; Pan, C.D.; Li, B.; Wu, H.L. Genome-wide association analysis identified molecular markers associated with important tea flavor-related metabolites. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, e42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.D.; Lian, S.B.; Wu, N.N.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhao, S.Q.; Zhang, L.M.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, H.Y. Integrated transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis of catechins, caffeine and theanine biosynthesis in tea plant (Camellia sinensis) over the course of seasons. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, e294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, D.; Lu, M.; Li, J.; Ma, C. Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen. Foods 2023, 12, 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142661
Qi D, Lu M, Li J, Ma C. Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142661
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Dandan, Meiling Lu, Jianke Li, and Chuan Ma. 2023. "Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen" Foods 12, no. 14: 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142661
APA StyleQi, D., Lu, M., Li, J., & Ma, C. (2023). Metabolomics Reveals Distinctive Metabolic Profiles and Marker Compounds of Camellia (Camellia sinensis L.) Bee Pollen. Foods, 12(14), 2661. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142661






