Techno-Functional and Sensory Characterization of Commercial Plant Protein Powders
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Commercial Protein Powders
2.2. Color Analysis
2.3. Water Solubility after Heat Treatment at Native pH and pH 4.5
2.4. Water Solubility Index, Water-Holding Capacity, and Oil-Holding Capacity
2.5. Foam Capacity and Stability
2.6. Emulsion Activity and Stability
2.7. Rheological Properties
2.8. Sensory Evaluation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Commercial Protein Powders
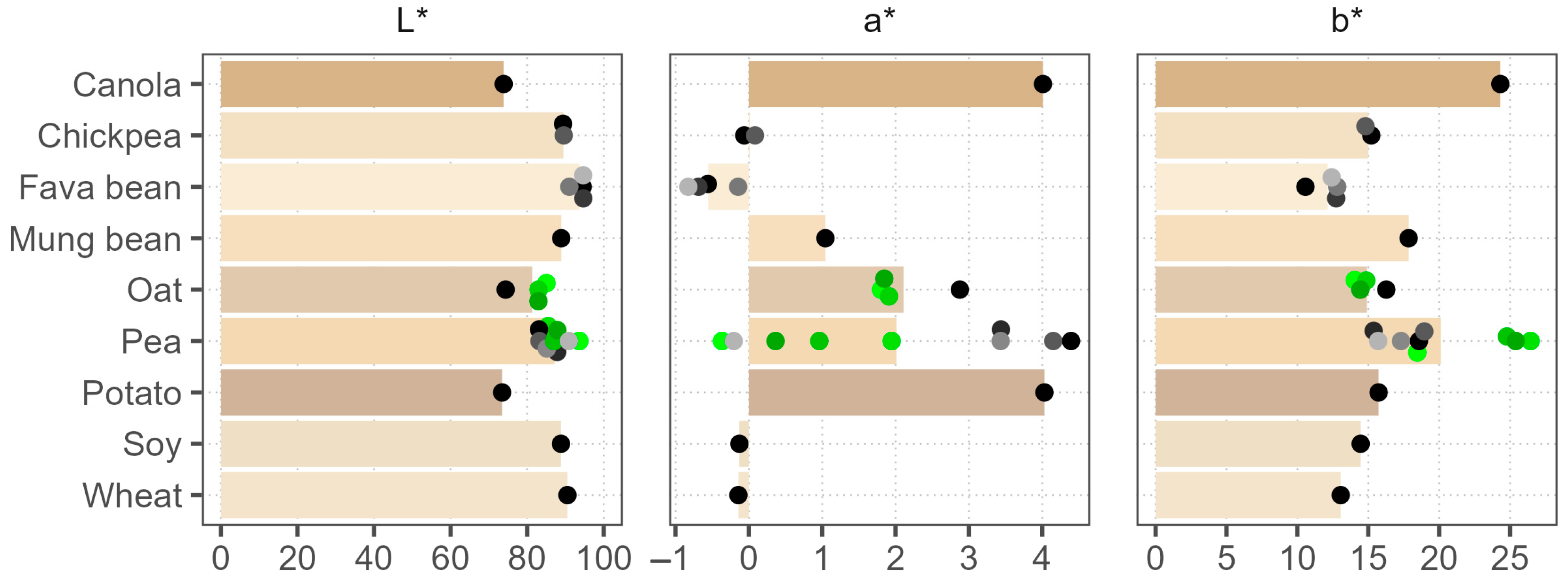
3.2. Color Analysis
3.3. pH and Solubility
3.3.1. Native pH
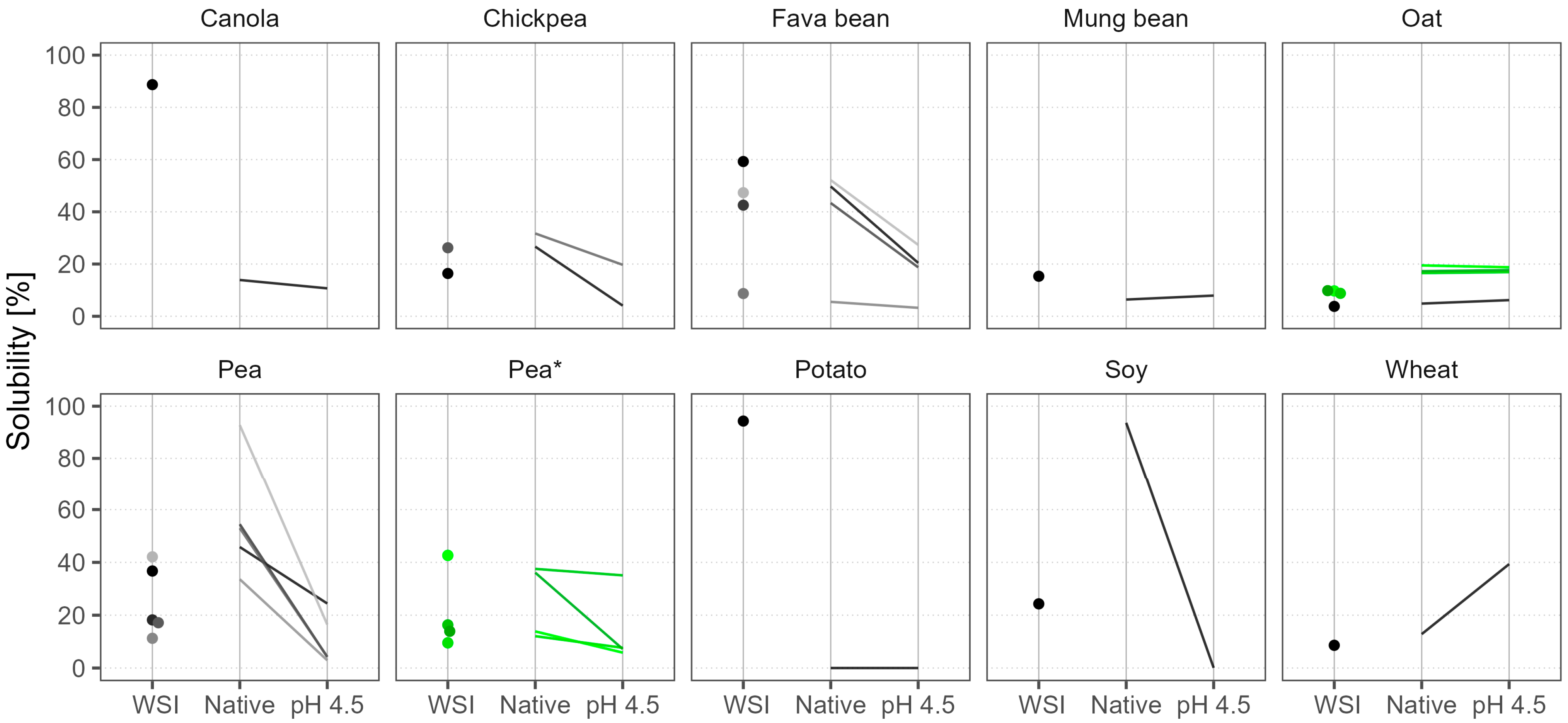
3.3.2. Solubility
3.4. Water- and Oil-Holding Capacities
3.5. Foaming and Emulsification Properties
3.6. Visco-Thermal Analysis
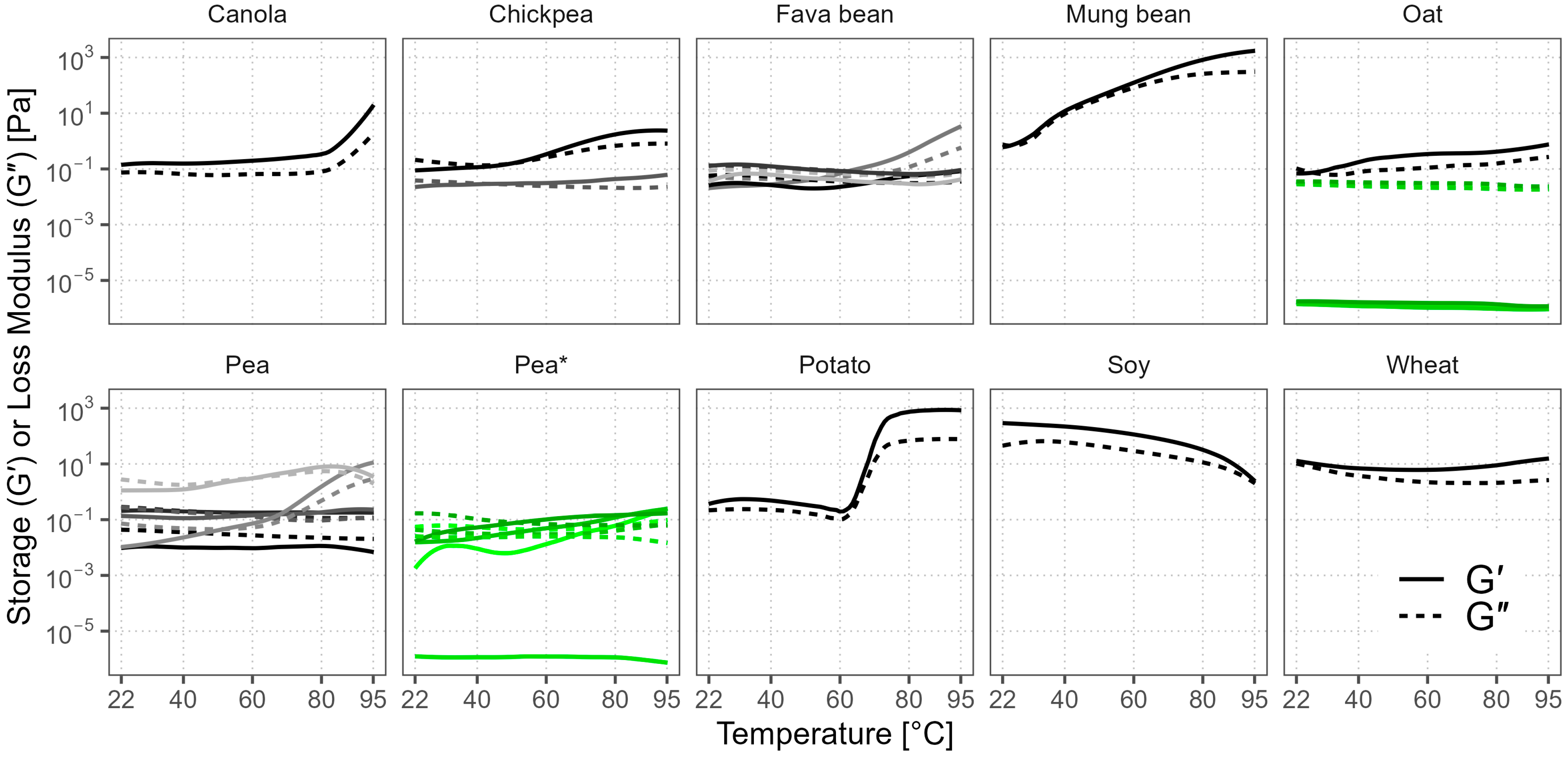
3.7. Gelation Behavior
3.8. Sensory Evaluation
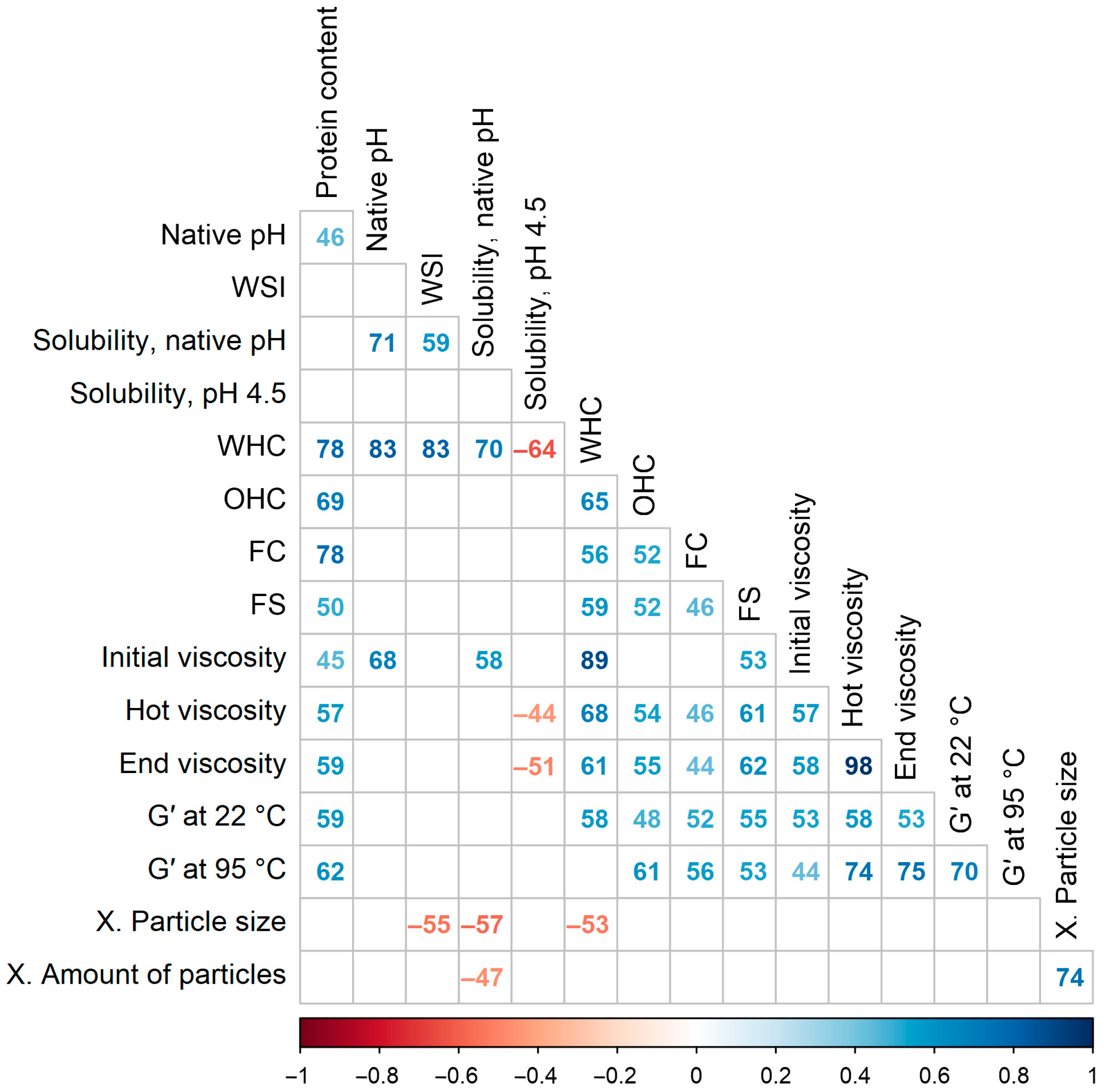
3.9. Correlations
3.10. General Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boukid, F. Plant-Based Meat Analogues: From Niche to Mainstream. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 247, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Evans, N.M.; Liu, H.; Shao, S. A Review of Research on Plant-Based Meat Alternatives: Driving Forces, History, Manufacturing, and Consumer Attitudes. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2639–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. A Brief Review of the Science behind the Design of Healthy and Sustainable Plant-Based Foods. NPJ Sci. Food 2021, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.K.; Greis, M.; Lu, J.; Nolden, A.A.; McClements, D.J.; Kinchla, A.J. Functional Performance of Plant Proteins. Foods 2022, 11, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, S.; Gibis, M.; Terjung, N.; Weiss, J. Survey of Aqueous Solubility, Appearance, and PH of Plant Protein Powders from Carbohydrate and Vegetable Oil Production. LWT 2020, 133, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea Protein Isolates: Structure, Extraction, and Functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.K.; Avarmenko, N.A.; Warkentin, T.D.; Nickerson, M.T. Functional Properties of Protein Isolates from Different Pea Cultivars. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. The Science of Plant-based Foods: Constructing Next-generation Meat, Fish, Milk, and Egg Analogs. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 4049–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, L.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nolden, A.; McClements, D.J. Standardized Methods for Testing the Quality Attributes of Plant-Based Foods: Milk and Cream Alternatives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2206–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Zhang, H.; Ikeda, S. Hydrocolloid Gels of Polysaccharides and Proteins. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 5, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zamani, S.; Liang, L.; Chen, L. Food Hydrocolloids Extraction Methods Significantly Impact Pea Protein Composition, Structure and Gelling Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assatory, A.; Vitelli, M.; Rajabzadeh, A.R.; Legge, R.L. Dry Fractionation Methods for Plant Protein, Starch and Fiber Enrichment: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bühler, J.M.; Dekkers, B.L.; Bruins, M.E.; Van Der Goot, A.J. Modifying Faba Bean Protein Concentrate Using Dry Heat to Increase Water Holding Capacity. Foods 2020, 9, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, T.G.; Singh, I.; Mayfield, C.; Baumert, J.L.; Zhang, Y. Comparison of Physicochemical and Emulsifying Properties of Commercial Pea Protein Powders. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2506–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, A.C.; Low, N.; Nickerson, M. Emulsifying Properties of Chickpea, Faba Bean, Lentil and Pea Proteins Produced by Isoelectric Precipitation and Salt Extraction. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Comparison of Wheat, Soybean, Rice, and Pea Protein Properties for Effective Applications in Food Products. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.K.; Grossmann, L.; Nolden, A.A.; McClements, D.J.; Kinchla, A.J. Functional and Physical Properties of Commercial Pulse Proteins Compared to Soy Derived Protein. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panescu, P.; Carter, M.; Cohen, M.; Gertner, D.; Ignaszewski, E.; Murray, S.; O’Donnell, M.; Pierce, B.; Voss, S. State of the Industry Report: Plant-Based Meat, Seafood, Eggs, and Dairy; Good Food Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, D. Soy Proteins. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2011; pp. 210–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, J.; Atkinson, C. Current Knowledge in Soybean Composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flynn, T.D.; Hogan, S.A.; Daly, D.F.M.; O’Mahony, J.A.; McCarthy, N.A. Rheological and Solubility Properties of Soy Protein Isolate. Molecules 2021, 26, 3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, R.; Sabapathy, S.N.; Bawa, A.S. Functional and Edible Uses of Soy Protein Products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2008, 7, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patisaul, H.B.; Jefferson, W. The Pros and Cons of Phytoestrogens. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2010, 31, 400–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suen, A.A.; Kenan, A.C.; Williams, C.J. Developmental Exposure to Phytoestrogens Found in Soy: New Findings and Clinical Implications. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 195, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukid, F.; Rosell, C.M.; Castellari, M. Pea Protein Ingredients: A Mainstream Ingredient to (Re)Formulate Innovative Foods and Beverages. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Composition, D.J.B. Composition, Physicochemical Properties of Pea Protein and Its Application in Functional Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2593–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Chen, Y.; Kaur, A.; Yu, L. Pulse Proteins: Secondary Structure, Functionality and Applications. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2787–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulbek, M.C.; Lam, R.S.H.; Wang, Y.C.; Asavajaru, P.; Lam, A. Pea: A Sustainable Vegetable Protein Crop; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780128027769. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, A.; Shahidi, S.; Rafe, A.; Naghizadeh Raeisi, S.; Ghorbani-HasanSaraei, A. Rheological Properties of Dairy Desserts: Effect of Rice Bran Protein and Fat Content. J. Food Sci. 2022, 87, 4977–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, O.E.; Sozer, N.; Ercili-Cura, D.; Poutanen, K. Protein From Oat. In Sustainable Protein Sources; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 105–119. [Google Scholar]
- Spaen, J.; Silva, J.V.C. Oat Proteins: Review of Extraction Methods and Techno-Functionality for Liquid and Semi-Solid Applications. LWT 2021, 147, 111478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukid, F.; Castellari, M. How Can Processing Technologies Boost the Application of Faba Bean (Vicia Faba L.) Proteins in Food Production? eFood 2022, 3, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojceska, V.; Ainsworth, P.; Plunkett, A.; Ibanoǧlu, Ş. The Effect of Extrusion Cooking Using Different Water Feed Rates on the Quality of Ready-to-Eat Snacks Made from Food by-Products. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brishti, F.H.; Zarei, M.; Muhammad, S.K.S.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R.; Shukri, R.; Saari, N. Evaluation of the Functional Properties of Mung Bean Protein Isolate for Development of Textured Vegetable Protein. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra, S.; Singh, S. Evaluation of Functional Properties of Composite Flours and Sensorial Attributes of Composite Flour Biscuits. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 3681–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumatsu, K.; Sawada, K.; Moritaka, S.; Misaki, M.; Toda, J.; Wada, T.; Ishii, K. Whipping and Emulsifying Properties of Soybean Products. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1972, 36, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onwulata, C.I.; Tunick, M.H.; Thomas-Gahring, A.E. Rapid Visco Analysis of Food Protein Pastes. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2014, 38, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Gelation Properties of Salt-Extracted Pea Protein Induced by Heat Treatment. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafe, A.; Vahedi, E.; Hasan-Sarei, A.G. Rheology and Microstructure of Binary Mixed Gel of Rice Bran Protein–Whey: Effect of Heating Rate and Whey Addition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 3890–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, S. Production of Protein-Rich Pulse Ingredients through Dry Fractionation: A Review. LWT 2021, 141, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, V.G.; Kraus, S.; Schott, M.; Muranyi, I.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P. Screening of Twelve Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Cultivars and Their Isolates Focusing on the Protein Characterization, Functionality, and Sensory Profiles. Foods 2021, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, N. Characterization of Protein Isolates from Different Indian Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) Cultivars. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharan, S.; Zanghelini, G.; Zotzel, J.; Bonerz, D.; Aschoff, J.; Saint-Eve, A.; Maillard, M. Fava Bean (Vicia faba L.) for Food Applications: From Seed to Ingredient Processing and Its Effect on Functional Properties, Antinutritional Factors, Flavor, and Color. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Aslam, N.; Sun, H.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Z.; He, S. Effects of Particle Size on Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Superfine Black Kidney Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) Powder. PeerJ 2019, 2019, e6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Guo, X.N.; Zhu, K.X.; Zhou, H.M. Effects of Alkali on Protein Polymerization and Textural Characteristics of Textured Wheat Protein. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R.; Toelstede, S.; Wild, F.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. High Moisture Extrusion Cooking of Pea Protein Isolates: Raw Material Characteristics, Extruder Responses, and Texture Properties. J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, P.; Dowling, K.; McKnight, S.; Barrow, C.J.; Wang, B.; Adhikari, B. Preparation, Characterization and Functional Properties of Flax Seed Protein Isolate. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Shi, J.; Scanlon, M.; Xue, S.J.; Lu, J. Effects of Pretreatments on Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Proteins Isolated from Canola Seeds after Oil Extraction by Supercritical-CO2 Process. LWT 2021, 137, 110415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmeister, H.; Meuser, F. Impact of Processing on Functional Properties of Protein Products from Wrinkled Peas. J. Food Eng. 2003, 56, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaleda, A.; Talvistu, K.; Vaikma, H.; Tammik, M.; Rosenvald, S.; Vilu, R. Physicochemical, Textural, and Sensorial Properties of Fibrous Meat Analogs from Oat-Pea Protein Blends Extruded at Different Moistures, Temperatures, and Screw Speeds. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafarga, T.; Álvarez, C.; Villaró, S.; Bobo, G.; Aguiló-Aguayo, I. Potential of Pulse-Derived Proteins for Developing Novel Vegan Edible Foams and Emulsions. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeżowski, P.; Polcyn, K.; Tomkowiak, A.; Rybicka, I.; Radzikowska, D. Technological and Antioxidant Properties of Proteins Obtained from Waste Potato Juice. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayas, J.F. Functionality of Proteins in Food; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; ISBN 978-3-642-63856-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Schilling, M.W.; Li, Y. Parallel Comparison of Functional and Physicochemical Properties of Common Pulse Proteins. LWT 2021, 146, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.Q.; Sontag-Strohm, T.; Salovaara, H.; Sibakov, J.; Kanerva, P.; Loponen, J. Oat Protein Solubility and Emulsion Properties Improved by Enzymatic Deamidation. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 64, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Kong, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Hua, Y. Effects of Heat Treatment on the Emulsifying Properties of Pea Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Grossmann, L. Next-Generation Plant-Based Foods; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-96763-5. [Google Scholar]
- Szołtysik, M.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Dąbrowska, A.; Zięba, T.; Bobak, Ł.; Chrzanowska, J. Effect of Two Combined Functional Additives on Yoghurt Properties. Foods 2021, 10, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, D.; Dogan, H.; Li, Y.; Alavi, S. Physico-Chemical Properties and Texturization of Pea, Wheat and Soy Proteins Using Extrusion and Their Application in Plant-Based Meat. Foods 2023, 12, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayar, S.; Koksel, H.; Turhan, M. The Effects of Protein-Rich Fraction and Defatting on Pasting Behavior of Chickpea Starch. Starch/Staerke 2005, 57, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Xiong, C.S.L. Functional and Pasting Properties of Pea Starch and Peanut Protein Isolate Blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.J.; Lucey, J.A. Structure and Physical Properties of Yogurt Gels: Effect of Inoculation Rate and Incubation Temperature. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3153–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahomud, M.S.; Haque, M.A.; Akhter, N.; Asaduzzaman, M. Effect of Milk PH at Heating on Protein Complex Formation and Ultimate Gel Properties of Free-Fat Yoghurt. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, J.; Zare, F.; Pletch, A. Pulse Proteins: Processing, Characterization, Functional Properties and Applications in Food and Feed. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 414–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Johansson, D.; Ström, A.; Rydén, J.; Nilsson, K.; Karlsson, J.; Moriana, R.; Langton, M. Effect of Starch and Fibre on Faba Bean Protein Gel Characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanvand, E.; Rafe, A. Rheological and Structural Properties of Rice Bran Protein-Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) Gum Complex Coacervates; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 83, ISBN 5135425365. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.B.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.P.; Liu, X.L. Effects of β-Glucans on Properties of Soya Bean Protein Isolate Thermal Gels. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, A.C.; Luning, P.A.; Weijzen, P.; Engels, W.; Kok, F.J.; de Graaf, C. Replacement of Meat by Meat Substitutes. A Survey on Person- and Product-Related Factors in Consumer Acceptance. Appetite 2011, 56, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.; Barker, S.; Falkeisen, A.; Gorman, M.; Knowles, S.; McSweeney, M.B. An Investigation into Consumer Perception and Attitudes towards Plant-Based Alternatives to Milk. Food Res. Int. 2022, 159, 111648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaikma, H.; Kaleda, A.; Rosend, J.; Rosenvald, S. Market Mapping of Plant-Based Milk Alternatives by Using Sensory (RATA) and GC Analysis. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaikma, H.; Metsoja, G.; Bljahhina, A.; Rosenvald, S. Individual Differences in Sensitivity to Bitterness Focusing on Oat and Pea Preparations. Future Foods 2022, 6, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.U.; Liu, C.; Sathe, S.K. Functional Properties of Select Seed Flours. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. High-Moisture Extrusion: Meat Analogues. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Fang, Z. Surmounting the Off-Flavor Challenge in Plant- Based Foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Protein Content, % dwb | Sample | Protein Content, % dwb | Sample | Protein Content, % dwb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canola | 90 | Mung bean | 85 | Pea 5 | 90 |
| Chickpea 1 | 89 | Oat 1 | 59 | Pea 6 *, 7 *, 8 *, 9 * | 80 |
| Chickpea 2 | 89 | Oat 2 *, 3 *, 4 * | 56 | Potato | 90 |
| Fava bean 1 | 60 | Pea 1 | 85 | Soy | 90 |
| Fava bean 2 | 60 | Pea 2 | 85 | Wheat | 82 |
| Fava bean 3 | 88 | Pea 3 | 84 | ||
| Fava bean 4 | 60 | Pea 4 | 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jakobson, K.; Kaleda, A.; Adra, K.; Tammik, M.-L.; Vaikma, H.; Kriščiunaite, T.; Vilu, R. Techno-Functional and Sensory Characterization of Commercial Plant Protein Powders. Foods 2023, 12, 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142805
Jakobson K, Kaleda A, Adra K, Tammik M-L, Vaikma H, Kriščiunaite T, Vilu R. Techno-Functional and Sensory Characterization of Commercial Plant Protein Powders. Foods. 2023; 12(14):2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142805
Chicago/Turabian StyleJakobson, Kadi, Aleksei Kaleda, Karl Adra, Mari-Liis Tammik, Helen Vaikma, Tiina Kriščiunaite, and Raivo Vilu. 2023. "Techno-Functional and Sensory Characterization of Commercial Plant Protein Powders" Foods 12, no. 14: 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142805
APA StyleJakobson, K., Kaleda, A., Adra, K., Tammik, M.-L., Vaikma, H., Kriščiunaite, T., & Vilu, R. (2023). Techno-Functional and Sensory Characterization of Commercial Plant Protein Powders. Foods, 12(14), 2805. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12142805






