Trypsin from Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass: Purification, Characterization, and Its Use in the Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Preparation of Pyloric Caeca Crude Extract
2.3. Purification of Trypsin
2.3.1. Preparation of Ammonium Sulphate Fraction
2.3.2. Purification of Trypsin
2.4. Trypsin Activity Assay
2.5. Characterization of Trypsin
2.5.1. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Substrate–Gel Electrophoresis
2.5.2. pH and Temperature Profile
2.5.3. pH and Thermal Stability
2.5.4. Effect of Inhibitors
2.6. Kinetic Studies
2.7. Determination of Protein Content
2.8. Extraction of Acid-Soluble Collagen (ASC) from Asian Seabass Skin
2.9. Comparative Study on Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen (ASC) by Partially Purified Seabass Trypsin (PPST) and Commercial Porcine Trypsin (CPT)
2.9.1. Hydrolysis of ASC
2.9.2. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
2.9.3. SDS–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.9.4. Size Distribution of Hydrolyzed Collagen
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Purification of Trypsin from Asian Seabass Pyloric Caeca (ASPC)
3.2. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Substrate-Gel Electrophoresis
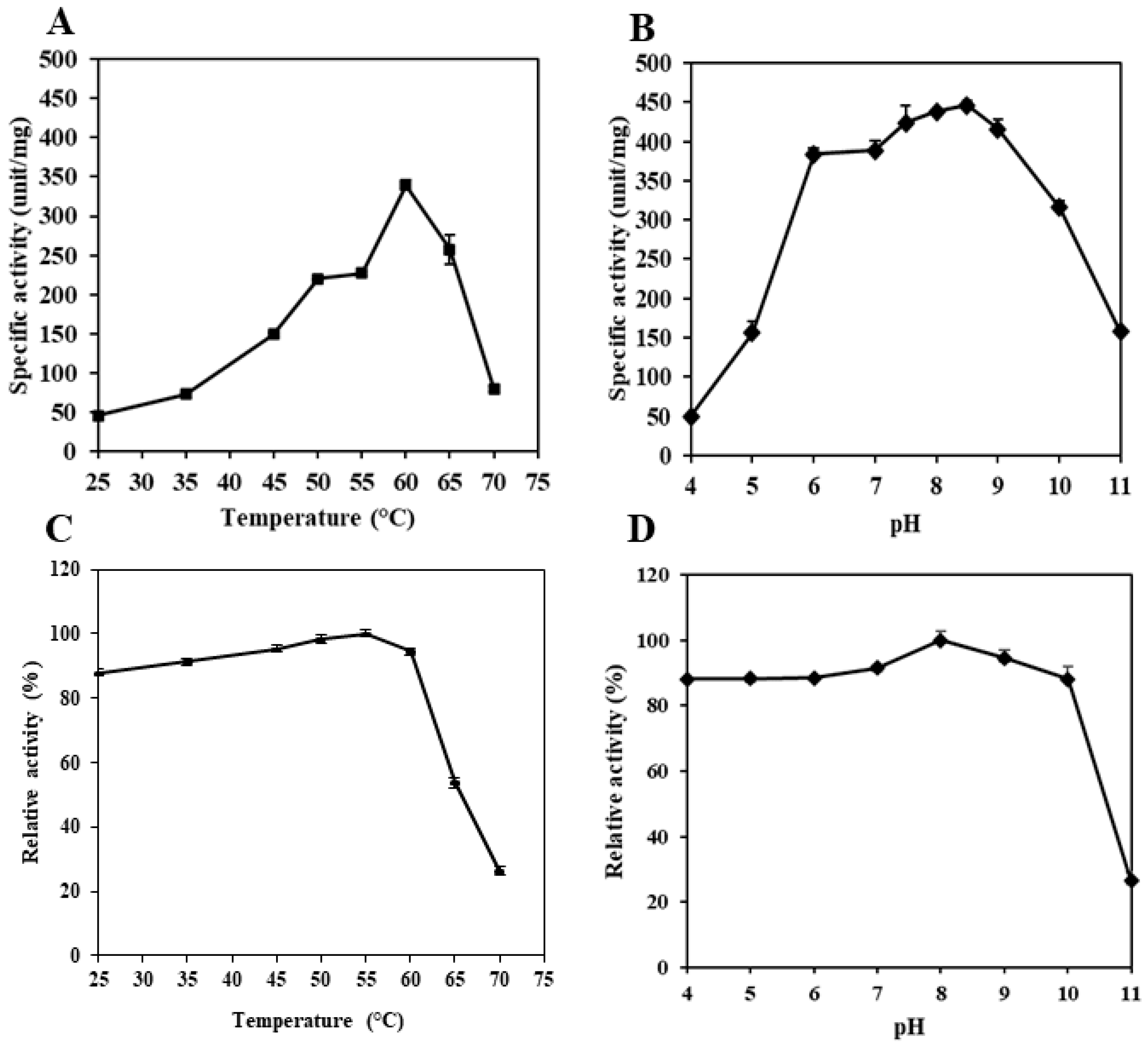
3.3. pH and Temperature Profile
3.4. pH and Thermal Stability
3.5. Effects of Various Protease Inhibitors on the Activity of Trypsin from the Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass
3.6. Enzyme Kinetics
3.7. Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen (ASC) by Partially Purified Seabass Trypsin (PPST) and Commercial Porcine Trypsin (CPT)
3.7.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH)
3.7.2. Protein Pattern
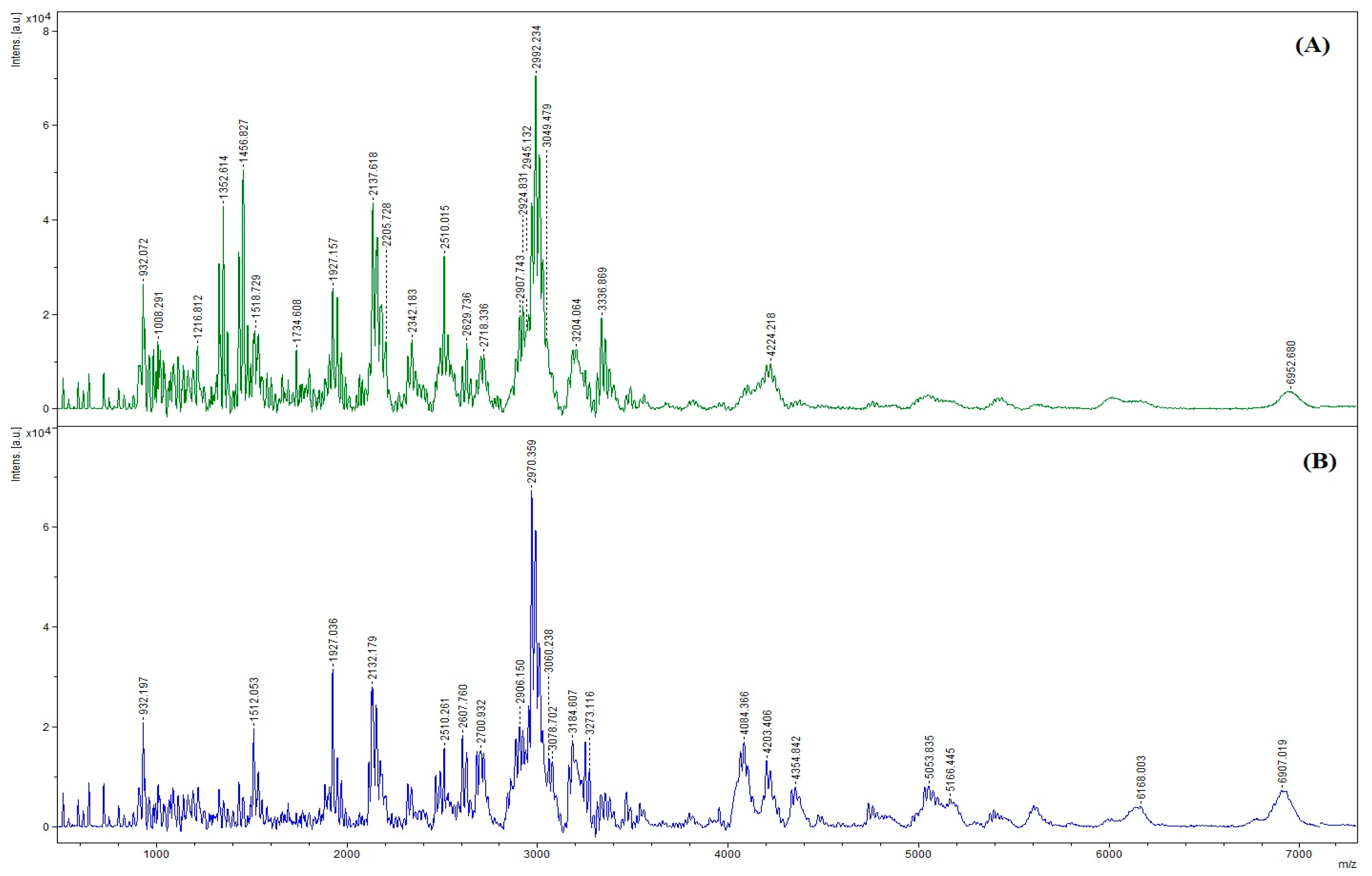
3.7.3. Size Distribution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klompong, V.; Benjakul, S.; Kantachote, D.; Shahidi, F. Antioxidative activity and functional properties of protein hydrolysate of yellow stripe trevally (Selaroides leptolepis) as influenced by the degree of hydrolysis and enzyme type. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.; Saetang, J.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Use of tuna visceral pepsin in combination with trypsin as digestion aid: Enhanced protein hydrolysis and bioavailability. Foods 2022, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigogliuso, S.; Campora, S.; Notarbartolo, M.; Ghersi, G. Recovery of bioactive compounds from marine organisms: Focus on the future perspectives for pharmacological, biomedical and regenerative medicine applications of marine collagen. Molecules 2023, 28, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, K.A.; Singh, A.; Pudtikajorn, K.; Benjakul, S. Lipases from different yeast strains: Production and application for n-3 fatty acid enrichment of tuna eyeball oil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol 2023, 48, 102651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K. Chitin and chitosan: Functional biopolymers from marine crustaceans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 203–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, U.; Nagarajarao, R.C.; Balange, A.K.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Proteolytic activity and characteristics of skipjack tuna trypsin loaded alginate–chitosan beads as affected by drying methods and trehalose/glycerol. Int. J. Food Sci. 2022, 58, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesekara, I. Development and biological activities of marine-derived bioactive peptides: A review. J. Funct. Foods 2010, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinanon, S.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Purification and biochemical properties of pepsins from the stomach of skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.; Benjakul, S. Comparative study on extraction of virgin coconut oil with the aid of partially purified protease from seabass pyloric caeca and commercial trypsin. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohmadlae, P.; Worawattanamateekul, W.; Hinsui, J. Characterization of acidic tuna protease and its application for extraction of tilapia collagen hydrolysate. CMUJ. Nat. Sci. 2020, 19, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Budge, S.M.; Ghaly, A.E.; Brooks, M.S.; Dave, D. Extraction, purification and characterization of fish pepsin: A critical review. J. Food Process. Technol 2011, 2, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khangembam, B.K.; Chakrabarti, R. Trypsin from the digestive system of carp Cirrhinus mrigala: Purification, characterization and its potential application. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.; Rezaei, M.; Madani, R.; Habibi Rezaie, M. Trypsin enzyme from viscera of common kilka (Clupeonella cultriventris caspia): Purification, characterization, and its compatibility with oxidants and surfactants. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2014, 23, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas-Júnior, A.C.V.; da Costa, H.M.S.; Marcuschi, M.; Icimoto, M.Y.; Machado, M.F.; Machado, M.F.; Ferreira, J.C.; de Oliveira, V.M.; Buarque, D.S.; Bezerra, R.S. Substrate specificity, physicochemical and kinetic properties of a trypsin from the giant Amazonian fish pirarucu (Arapaima gigas). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol 2021, 35, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aissaoui, N.; Marzouki, M.N.; Abidi, F. Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel intestinal protease from Scorpaena notata. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S. Two trypsin isoforms from albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) liver: Purification and physicochemical and biochemical characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, C.W.V.; da Costa Marques, M.E.; de Araújo Tenório, H.; de Miranda, E.C.; Pereira, H.J.V. Purification and characterization of trypsin from Luphiosilurus alexandri pyloric cecum. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 8, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Félix, M.L.; De La Reé-Rodríguez, C.; Perez-Velazquez, M. Partial characterization, quantification and optimum activity of trypsin and lipase from the sciaenids Cynoscion othonopterus, Cynoscion parvipinnis and Cynoscion xanthulus. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2020, 72, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Yáñez, F.J.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; García-Carreño, F.L.; de los Ángeles Navarrete-Del, M. Isolation and characterization of trypsin from pyloric caeca of Monterey sardine Sardinops sagax caerulea. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 140, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, D.M.R.C.; dos Santos, C.W.V.; de Souza, C.B.; de Albuquerque, F.S.; dos Santos Oliveira, J.M.; Pereira, H.J.V. Trypsin purified from Coryphaena hippurus (common dolphinfish): Purification, characterization, and application in commercial detergents. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol 2020, 25, 101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K. Proteolytic degradation of sardine (Sardinella gibbosa) proteins by trypsin from skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) spleen. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ktari, N.; Khaled, H.B.; Nasri, R.; Jellouli, K.; Ghorbel, S.; Nasri, M. Trypsin from zebra blenny (Salaria basilisca) viscera: Purification, characterisation and potential application as a detergent additive. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khaled, H.; Jellouli, K.; Souissi, N.; Ghorbel, S.; Barkia, A.; Nasri, M. Purification and characterization of three trypsin isoforms from viscera of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K. 29 kDa trypsin from the pyloric ceca of Atlantic bonito (Sarda sarda): Recovery and characterization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4548–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, R.S.; Santos, J.F.; Paiva, P.M.; Correia, M.T.; Coelho, L.C.; Vieira, V.L.; Carvalho, L.B., Jr. Partial purification and characterization of a thermostable trypsin from pyloric caeca of tambaqui (Colossoma macropomum). J. Food Biochem. 2001, 25, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K.; Saeki, H. Trypsins from yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacores) spleen: Purification and characterization. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 144, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, A.; Khajavi, M.; Abedian Kenari, A.; Haghbin Nazarpak, M.; Solouk, A.; Esmaeili, M.; Gisbert, E. Physicochemical and biochemical properties of trypsin-like enzyme from two sturgeon species. Animals 2023, 13, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketnawa, S.; Martínez-Alvarez, O.; Benjakul, S.; Rawdkuen, S. Gelatin hydrolysates from farmed Giant catfish skin using alkaline proteases and its antioxidative function of simulated gastro-intestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buamard, N.; Aluko, R.E.; Benjakul, S. Stability of tuna trypsin-loaded alginate-chitosan beads in acidic stomach fluid and the release of active enzyme in a simulated intestinal tract environment. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm, T.; Eggum, B.O. Nutritional value of fish viscera silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1981, 32, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Aluko, R.E.; Benjakul, S. Hydrolyzed collagen from porcine lipase-defatted seabass skin: Antioxidant, fibroblast cell proliferation, and collagen production activities. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Binlateh, T.; Hutamekalin, P.; Sukketsiri, W.; Aluko, R.E.; Benjakul, S. Hydrolyzed collagen from defatted sea bass skin and its conjugate with epigallocatechin gallate: In vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and anti-obesity activities. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khantaphant, S.; Benjakul, S. Comparative study on the proteases from fish pyloric caeca and the use for production of gelatin hydrolysate with antioxidative activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 151, 410–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khantaphant, S.; Benjakul, S. Purification and characterization of trypsin from the pyloric caeca of brownstripe red snapper (Lutjanus vitta). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, U.; Benjakul, S. Use of protease from seabass pyloric caeca in combination with repeated freeze–thawing cycles increases the production efficiency of virgin coconut oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121, 1800460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senphan, T.; Benjakul, S.; Kishimura, H. Purification and characterization of trypsin from hepatopancreas of Pacific white shrimp. J. Food Biochem. 2015, 39, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hau, P.; Benjakul, S. Purification and characterization of trypsin from pyloric caeca of bigeye snapper (Pricanthus macracanthus). J. Food Biochem. 2006, 30, 478–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lineweaver, H.; Burk, D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1934, 56, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, H.W.; Hogden, C.G. The biuret reaction in the determination of serum proteins. A study of the conditions necessary for the production of a stable color which bears a quantitative relationship to the protein concentration. J. Biol. Chem. 1940, 135, 707–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsuwan, K.; Patil, U.; Tu, C.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Salmon Skin Acid-Soluble Collagen produced by a simplified recovery process: Yield, compositions, and molecular characteristics. Fishes 2022, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Morrissey, M.T. Protein hydrolysates from Pacific whiting solid wastes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjakul, S.; Karnjanapratum, S.; Visessanguan, W. Hydrolysed collagen from Lates calcarifer skin: Its acute toxicity and impact on cell proliferation and collagen production of fibroblasts. Int. J. Food Sci. 2018, 53, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Benjakul, S. Trypsin from Unicorn leatherjacket (Aluterus monoceros) pyloric caeca: Purification and its use for preparation of fish protein hydrolysate with antioxidative activity. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poonsin, T.; Simpson, B.K.; Visessanguan, W.; Yoshida, A.; Klomklao, S. Optimal immobilization of trypsin from the spleen of albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) and its characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Marshall, S.N.; Simpson, B.K. Purification and characterization of trypsin from the pyloric ceca of the New Zealand hoki fish (Macruronus novaezealandiae). J. Food Biochem. 2007, 31, 772–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtovic, I.; Marshall, S.; Simpson, B. Isolation and characterization of a trypsin fraction from the pyloric ceca of chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Comp. Biochem. Physiol.B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 143, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimura, H.; Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Chun, B.S. Characteristics of trypsin from the pyloric ceca of walleye pollock (Theragra chalcogramma). Food Chem. 2008, 106, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, B.K. Digestive proteinases from marine animals. In Seafood Enzymes: Utilization and Influence on Postharvest Seafood Quality; Haard, N.F., Simpson, B.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 191–214. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.A.; Amaral, I.P.; Santo, A.R.E.; Carvalho, L.B., Jr.; Bezerra, R.S. Trypsin-like enzyme from intestine and pyloric caeca of spotted goatfish (Pseudupeneus maculatus). Food Chem. 2007, 100, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonsin, T.; Simpson, B.K.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Yoshida, A.; Klomklao, S. Carotenoprotein from Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) shells extracted using trypsin from albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga) spleen: Antioxidant activity and its potential in model systems. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, e12462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Kamil, Y.J. Enzymes from fish and aquatic invertebrates and their application in the food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2001, 12, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K. Trypsin from the pyloric caeca of bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 148, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, B. A guide to the Michaelis–Menten equation: Steady state and beyond. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 6086–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrisman, M.A.; Goldcamp, M.J.; Rhodes, A.N.; Riffle, J. Exploring Michaelis–Menten kinetics and the inhibition of catalysis in a synthetic mimic of catechol oxidase: An experiment for the inorganic chemistry or biochemistry laboratory. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Villalba, A.G.; Ramírez-Suárez, J.C.; Valenzuela-Soto, E.M.; Sánchez, G.G.; Ruiz, G.C.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R. Trypsin from viscera of vermiculated sailfin catfish, Pterygoplichthys disjunctivus, Weber, 1991: Its purification and characterization. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heu, M.; Kim, H.; Pyeun, J. Comparison of trypsin and chymotrypsin from the viscera of anchovy, Engraulis japonica. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 112, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomklao, S.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Kishimura, H.; Simpson, B.K. Purification and characterization of trypsin from the spleen of tongol tuna (Thunnus tonggol). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5617–5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Aldhahri, M.; Almulaiky, Y.Q. Dual immobilization of α-amylase and horseradish peroxidase via electrospinning: A proof of concept study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Han, X.-Q.; Synowiecki, J. Production and characteristics of protein hydrolysates from capelin (Mallotus villosus). Food Chem. 1995, 53, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, H.G.; Rasco, B.A. Fish protein hydrolysates: Production, biochemical, and functional properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2000, 40, 43–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.M.M.; Kishimura, H.; Benjakul, S. Extraction efficiency and characteristics of acid and pepsin soluble collagens from the skin of golden carp (Probarbus Jullieni) as affected by ultrasonication. Process Biochem. 2018, 66, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chotphruethipong, L.; Binlateh, T.; Hutamekalin, P.; Aluko, R.E.; Tepaamorndech, S.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Impact of hydrolyzed collagen from defatted seabass skin on proliferation and differentiation of preosteoblast MC3T3-E1 cells. Foods 2021, 10, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, U.; Nikoo, M.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Freeze-dried tuna pepsin powder stabilized by some cryoprotectants: In vitro simulated gastric digestion toward different proteins and its storage stability. Foods 2022, 11, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibilla, S.; Godfrey, M.; Brewer, S.; Budh-Raja, A.; Genovese, L. An overview of the beneficial effects of hydrolysed collagen as a nutraceutical on skin properties: Scientific background and clinical studies. Open Nutraceuticals J. 2015, 8, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Guo, Z.; Wei, J.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.-l.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, W. Extraction of low molecular weight peptides from bovine bone using ultrasound-assisted double enzyme hydrolysis: Impact on the antioxidant activities of the extracted peptides. LWT 2021, 146, 111470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, R.-Z.; Li, C.-Y.; Liu, W.-Y.; Yi, W.-X.; Cai, M.-Y. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of low-molecular-weight peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) skin. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1536–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, S.; Balange, A.K.; Nagarajarao, R.C.; Zhao, Q.; Benjakul, S. Microcapsules of shrimp oil using kidney bean protein isolate and κ-carrageenan as wall materials with the aid of ultrasonication or high-pressure microfluidization: Characteristics and oxidative stability. Foods 2022, 11, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; You, S.-G.; Kim, S.-M. Functional activities of low molecular weight peptides purified from enzymatic hydrolysates of seaweeds. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 34, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar]

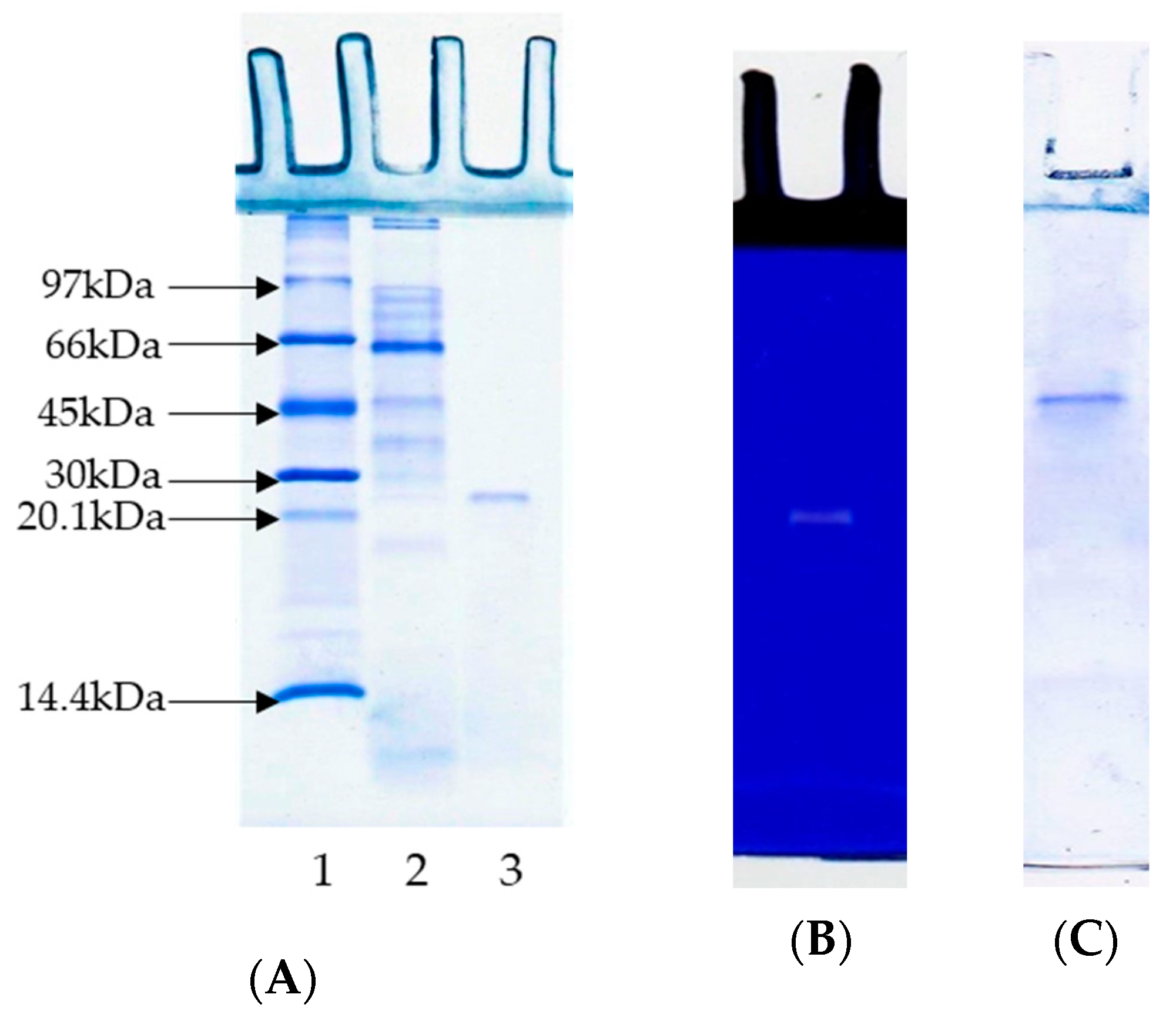


| Purification Fractions | Total Protein (mg) | Total Activity (unit a) | Specific Activity (unit/mg) | Yield (%) | Purity (fold) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASPC extract | 296 | 5357 | 18.1 | 100 | 1 |
| PPST | 11.4 | 1783 | 156.4 | 33.3 | 8.6 |
| PT | 2.43 | 814 | 335 | 15.2 | 18.5 |
| Inhibitors | Final Concentration | % Inhibition |
|---|---|---|
| E-64 | 0.1 mM | 3.55 ± 0.89 |
| Iodoacetic acid | 1 mM | 1.35 ± 1.01 |
| SBTI | 1 mg/mL | 99.47 ± 0.17 |
| TLCK | 5 mM | 93.62 ± 0.44 |
| TPCK | 5 mM | 3.44 ± 1.75 |
| EDTA | 2 mM | 6.15 ± 0.74 |
| Pepstatin A | 0.01 mM | 0.73 ± 0.72 |
| PMSF | 1 mM | 85.77 ± 0.92 |
| Substrate | Sources of Trypsin | Km A (mM) | Kcat A (s−1) | Kcat/Km (s−1mM−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAPNA | Lates calcarifer | 0.078 | 5.4 | 69.22 | This study |
| Coryphaena hippurus | 0.035 | 241.04 | 6886.85 | [20] | |
| P. disjunctivus | 0.13 | 1.46 | 11.23 | [56] | |
| Sardinella aurita | 0.083 | 1.21 | 14.61 | [23] | |
| Cirruhinus mrigala | 0.0672 | 6.17 | 92.09 | [12] | |
| Lutjanus vitta | 0.507 | 4.17 | 9.27 | [34] | |
| TAME | Lates calcarifer | 0.09 | 4.8 | 53.46 | This study |
| Lutjanus vitta | 0.328 | 112 | 341 | [34] | |
| M. novaezealandlae | 2.08 | 19.00 | 9.1 | [46] | |
| Thunnus tonggol | 0.25 | 200 | 800 | [58] | |
| Engraulis japonica | 0.84 | 39.67 | 47.2 | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, U.; Baloch, K.A.; Nile, S.H.; Kim, J.T.; Benjakul, S. Trypsin from Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass: Purification, Characterization, and Its Use in the Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen. Foods 2023, 12, 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152937
Patil U, Baloch KA, Nile SH, Kim JT, Benjakul S. Trypsin from Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass: Purification, Characterization, and Its Use in the Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen. Foods. 2023; 12(15):2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152937
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Umesh, Khurshid Ahmed Baloch, Shivraj Hariram Nile, Jun Tae Kim, and Soottawat Benjakul. 2023. "Trypsin from Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass: Purification, Characterization, and Its Use in the Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen" Foods 12, no. 15: 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152937
APA StylePatil, U., Baloch, K. A., Nile, S. H., Kim, J. T., & Benjakul, S. (2023). Trypsin from Pyloric Caeca of Asian Seabass: Purification, Characterization, and Its Use in the Hydrolysis of Acid-Soluble Collagen. Foods, 12(15), 2937. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12152937








