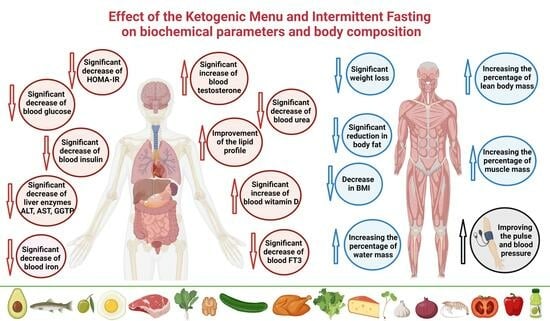
Keto Menu–Effect of Ketogenic Menu and Intermittent Fasting on the Biochemical Markers and Body Composition in a Physically Active Man—A Controlled Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Report
2.2. Diet Applied
2.3. Physical Activity
2.4. Supplementation
2.5. Biochemical Parameter Measurements
2.5.1. Measurements of the Biochemical Parameters before and after 13 Weeks on Ketogenic Diet
2.5.2. Cyclic Measurements of the Biochemical Parameters during 13 Weeks on the Ketogenic Diet
2.6. Measurements of the Anthropometric Parameters (Body Composition)
2.7. Measurements of the Heart Rate and Arterial Pressure
3. Results
3.1. Biochemical Parameters (before (P0) and after (P1) the Intervention)
3.1.1. Blood Cell Count
3.1.2. The Remaining Biochemical Parameters
3.2. Biochemical Parameters Measured Periodically
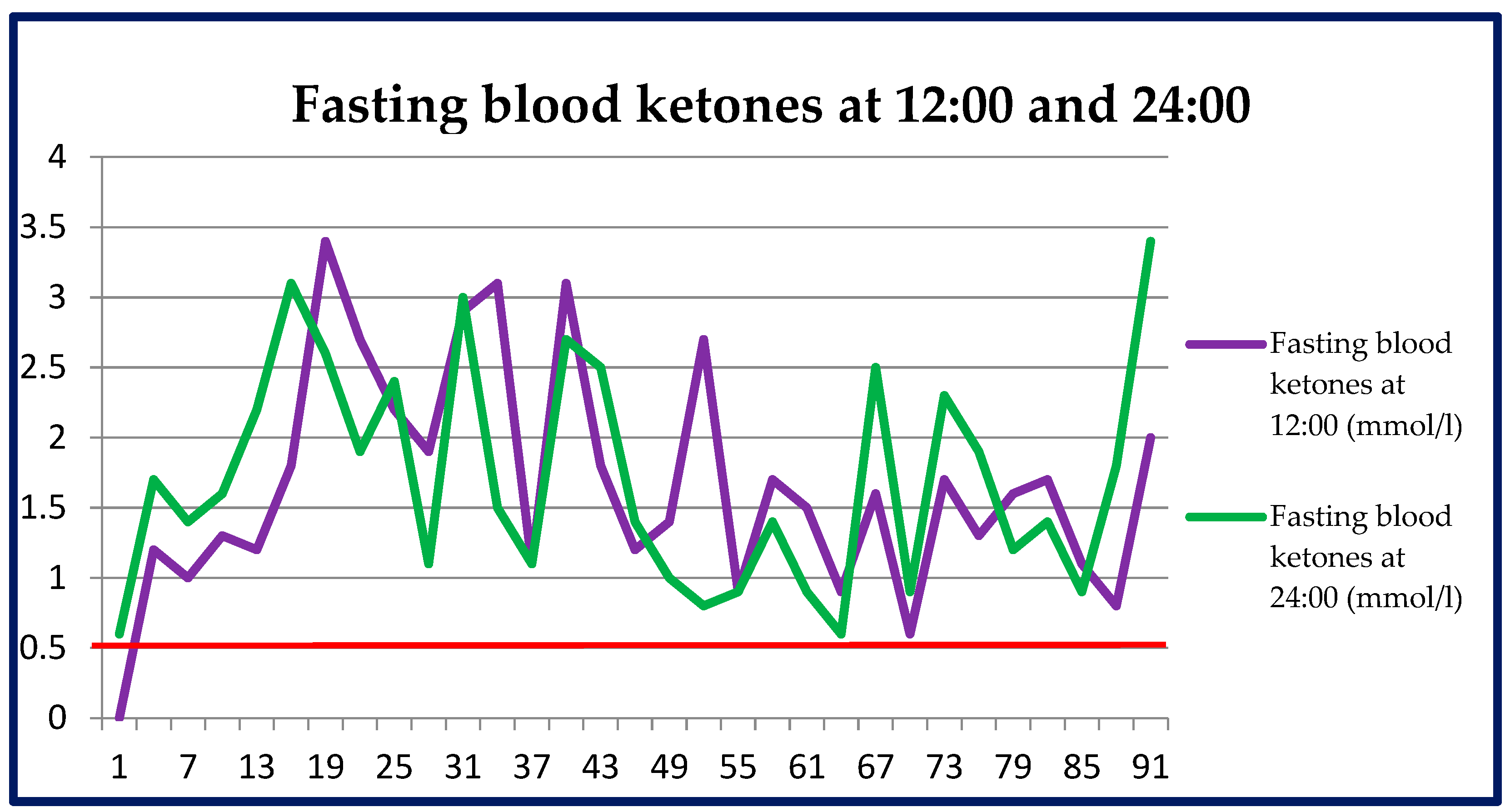
3.2.1. Measurements of Ketone Bodies in Blood
3.2.2. Measurements of Ketone Bodies in Urine
3.2.3. Blood Glucose Measurements
3.3. Anthropometric Parameters
3.3.1. Body Mass
3.3.2. Adipose Tissue Mass
3.3.3. Muscular Tissue Mass
3.3.4. Lean Tissue Mass
3.3.5. Water Mass
3.3.6. Bone Mass and Level of Visceral Adipose Tissue
3.3.7. Body Mass Index (BMI) and Metabolic Age
3.4. Arterial Pressure and Heart Rate
3.4.1. Systolic and Diastolic Pressure in the Morning and Evening
3.4.2. Heart Rate in the Morning and Evening
4. Discussion
4.1. Biochemical Parameters
4.1.1. Testosterone
4.1.2. Carbohydrate Metabolism Parameters (HOMA-IR, Glucose, Insulin, HbA1c)
4.1.3. Liver Function Parameters (ALT, AST, GGTP, Bilirubin)
4.1.4. Iron Metabolism Parameters (Iron, Ferritin, Transferrin)
4.1.5. Thyroid Function Parameters (TSH, FT3, FT4)
4.1.6. Lipid Profile (Total Cholesterol, HDL, LDL, Triglycerides)
4.1.7. Renal Function Parameters (Urea, Creatinine, Uric Acid)
4.1.8. Vitamin D 25(OH)D
4.1.9. Microelements (Sodium, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Phosphorus)
4.2. Body Composition
4.3. Arterial Pressure and Pulse Rate
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lloyd, G.E.R. (Ed.) Hippocratic Writings; Chadwick, J.; Lonie, I.M.; Mann, W.N.; Withington, E.T., Translators; Penguin: Harmondsworth, UK, 1983; p. 149. ISBN 0-14-044451-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kossoff, E.; Cervenka, M. Ketogenic Dietary Therapy Controversies for Its Second Century. Epilepsy Curr. 2020, 20, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, M.; Ros, E.; Allen, K.; Sikand, G.; Agarwala, A.; Aspry, K.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Devries, S.; Reddy, K.; Singh, T.; et al. Controversial Dietary Patterns: A High Yield Primer for Clinicians. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pondel, N.; Liśkiewicz, A.; Liśkiewicz, D. Dieta ketogeniczna—Mechanizm działania i perspektywy zastosowania w terapii: Dane z badań klinicznych. Postępy Biochem. 2020, 66, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.; Lowery, R. The Ketogenic Bible; Victory Belt Publishing Inc.: Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2017; ISBN 13:978-1-628601-04-6. [Google Scholar]
- Aragon, A.A.; Schoenfeld, B.J. Does Timing Matter? A Narrative Review of Intermittent Fasting Variants and Their Effects on Bodyweight and Body Composition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasim, I.; Majeed, C.N.; DeBoer, M.D. Intermittent Fasting and Metabolic Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, F.; Osaili, T.; Obaid, R.S.; Naja, F.; Radwan, H.; Cheikh Ismail, L.; Hasan, H.; Hashim, M.; Alam, I.; Sehar, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Time-Restricted Feeding/Eating: A Targeted Biomarker and Approach in Precision Nutrition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocchi, A.; Rebelos, E.; Dardano, A.; Mantuano, M.; Daniele, G. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Brain Metabolism. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabel, K.; Cienfuegos, S.; Kalam, F.; Ezpeleta, M.; Varady, K.A. Time-Restricted Eating to Improve Cardiovascular Health. Curr. Atheroscler Rep. 2021, 23, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, J.; Huang, R.; Guo, M.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, L. The role and its mechanism of intermittent fasting in tumors: Friend or foe? Cancer Biol. Med. 2021, 18, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cabo, R.; Mattson, M.P. Effects of Intermittent Fasting on Health, Aging, and Disease. N. Engl J Med. 2019, 381, 2541–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarosz, M. Normy Żywienia dla Populacji Polski i ich Zastosowanie; Narodowy Instytut Zdrowia Publicznego–Państwowy Zakład Higieny: Warsaw, Poland, 2020; ISBN 978-83-65870-28-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stergiou, G.S.; Palatini, P.; Parati, G.; O’Brien, E.; Januszewicz, A.; Lurbe, E.; Persu, A.; Mancia, G.; Kreutz, R. European Society of Hypertension Council and the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Variability. 2021 European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for office and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. J. Hypertens. 2021, 39, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damian, D.; Katarzyna, K. Wpływ Diety Ketogennej na Glikemię i Wartości ciał Ketonowych w Moczu. Archaegraph. Dietetyka i Medycyna- Współczesne Problemy. pp. 63–77. Available online: https://www.archaegraph.pl (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Santos, H.O. Ketogenic diet and testosterone increase: Is the increased cholesterol intake responsible? to what extent and under what circumstances can there be benefits? Hormones 2017, 16, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cangemi, R.; Friedmann, A.J.; Holloszy, J.O.; Fontana, L. Long-term effects of calorie restriction on serum sex-hormone concentrations in men. Aging Cell 2010, 9, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cienfuegos, S.; Corapi, S.; Gabel, K.; Ezpeleta, M.; Kalam, F.; Lin, S.; Pavlou, V.; Varady, K.A. Effect of Intermittent Fasting on Reproductive Hormone Levels in Females and Males: A Review of Human Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarelli, A.; Santi, D.; Genchi, V.A.; Conte, E.; Giordano, F.; Di Leo, S.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; Perrini, S. Very low-calorie ketogenic diet rapidly augments testosterone levels in non-diabetic obese subjects. Andrology 2023, 11, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furini, C.; Spaggiari, G.; Simoni, M.; Greco, C.; Santi, D. Ketogenic state improves testosterone serum levels-results from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine 2022, 79, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; Lowery, R.P.; Roberts, M.D.; Sharp, M.H.; Joy, J.M.; Shields, K.A.; Partl, J.M.; Volek, J.S.; D’Agostino, D.P. Effects of Ketogenic Dieting on Body Composition, Strength, Power, and Hormonal Profiles in Resistance Training Men. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3463–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cenci, L.; Pompei, P.; Sahin, N.; Bianco, A.; Neri, M.; Caprio, M.; Moro, T. Effects of Two Months of Very Low Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, Muscle Area, and Blood Parameters in Competitive Natural Body Builders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, G.N.; Leslie, S.W. Physiology, Testosterone. [Updated 2023 Jan 2]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK526128/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Kelly, D.M.; Jones, T.H. Testosterone: A metabolic hormone in health and disease. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 217, R25–R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yan, A.F.; Cheskin, L.J.; Shi, Z. Higher SerumTestosterone Level Was Associatedwith a Lower Risk of Prediabetes inUS Adults: Findings from NationallyRepresentative Data. Nutrients 2023, 15, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalczyk, M.M.; Klonek, G.; Maszczyk, A.; Zajac, A. The Effects of a Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet on Glycaemic Control Variables in Hyperinsulinemic Overweight/Obese Females. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, A.M.; Horgan, G.W.; Murison, S.D.; Bremner, D.M.; Lobley, G.E. Effects of a high-protein ketogenic diet on hunger, appetite, and weight loss in obese men feeding ad libitum. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, T.L.; Sutherland, J.P.; Wolfe, P.; Allian-Sauer, M.; Capell, W.H.; Talley, N.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Foster, G.D.; Hill, J.O.; Eckel, R.H. Lack of suppression of circulating free fatty acids and hypercholesterolemia during weight loss on a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myette-Côté, É.; Durrer, C.; Neudorf, H.; Bammert, T.D.; Botezelli, J.D.; Johnson, J.D.; DeSouza, C.A.; Little, J.P. The effect of a short-term low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet with or without postmeal walks on glycemic control and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. American Journal of physiology. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1210–R1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partsalaki, I.; Karvela, A.; Spiliotis, B.E. Metabolic impact of a ketogenic diet compared to a hypocaloric diet in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavo, L.; Pilone, V.; Rossetti, G.; Barbarisi, A.; Cesaretti, M.; Iannelli, A. A 4-Week Preoperative Ketogenic MicronutrientEnriched Diet Is Effective in Reducing Body Weight, Left Hepatic Lobe Volume, and Micronutrient Deficiencies in PatientsUndergoing Bariatric Surgery: A Prospective Pilot Study. Obes. Surg. 2018, 28, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, C.R.; Messina, A.; Cibelli, G.; Messina, G.; Polito, R.; Losavio, F.; Torre, E.L.; Monda, V.; Monda, M.; Quiete, S.; et al. Italian Ketogenic Mediterranean Diet in Overweight and Obese Patients with Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallberg, S.J.; McKenzie, A.L.; Williams, P.T.; Bhanpuri, N.H.; Peters, A.L.; Campbell, W.W.; Hazbun, T.L.; Volk, B.M.; McCarter, J.; Phinney, S.D.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of a Novel Care Model for the Management of Type 2 Diabetes at 1 Year:An Open-Label, Non-Randomized, Controlled Study. Diabetes Ther. 2018, 9, 583–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyńka, D.; Kowalcze, K.; Ambrozkiewicz, F.; Paziewska, A. Effect of the Ketogenic Diet on the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of the Meta-Analyses and Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsou, S.; Zacharodimos, N.; Poulia, K.-A.; Karatzi, K.; Dimitriadis, G.; Papakonstantinou, E. Effects of Time-Restricted Feeding and Ramadan Fasting on Body Weight, Body Composition, Glucose Responses, and Insulin Resistance: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, H.; Elsabaawy, M.; Sakr, A.; Eltahawy, M.; Elsayed, M.; Elsabaawy, D.M.; Abdelkreem, M. Impact of intermittent fasting on laboratory, radiological, and anthropometric parameters in NAFLD patients. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 8, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, H.A.; Iftikhar, H.; Abdalrubb, A.; Al-Marri, N.D.R.; Abdelrahim, M.G.; Fayed, M.; Elgassim, M.A.M.; Elarref, M.A. Clinical Assessment of Intermittent Fasting with Ketogenic Diet in Glycemic Control and Weight Reduction in Patients With Type II Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e30879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Guisado, J.; Munoz-Serrano, A. The effect of the Spanish Ketogenic Mediterranean Diet on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot study. J. Med. Food. 2011, 14, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basciani, S.; Camajani, E.; Contini, S.; Persichetti, A.; Risi, R.; Bertoldi, L.; Strigari, L.; Prossomariti, G.; Watanabe, M.; Mariani, S.; et al. Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diets with Whey, Vegetable, or Animal Protein in Patients with Obesity: A Randomized Pilot Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gepner, Y.; Shelef, I.; Komy, O.; Cohen, N.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Bril, N.; Rein, M.; Serfaty, D.; Kenigsbuch, S.; Zelicha, H.; et al. The beneficial effects of Mediterranean diet over low-fat diet may be mediated by decreasing hepatic fat content. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cenci, L.; Grimaldi, K.A. Effect of ketogenic Mediterranean diet with phytoextracts and low carbohydrates/high-protein meals on weight, cardiovascular risk factors, body composition and diet compliance in Italian council employees. Nutr. J. 2011, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruci, A.; Tuccinardi, D.; Tozzi, R.; Balena, A.; Santucci, S.; Frontani, R.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Safe and Effective Tool for Weight Loss in Patients with Obesity and Mild Kidney Failure. Nutrients 2020, 12, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, C.; Clemens, Z. Gilbert’s Syndrome Successfully Treated with the Paleolithic Ketogenic Diet. Am. J. Med. Case Rep. 2015, 3, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Tozzi, R.; Risi, R.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. Beneficial effects of the ketogenic diet on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klement, R.J.; Frobel, T.; Albers, T.; Fikenzer, S.; Prinzhausen, J.; Kämmerer, U. A pilot case study on the impact of a self-prescribed ketogenic diet on biochemical parameters and running performance in healthy and physically active individuals. Nutr. Med. 2013, 1, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- McKay, A.K.A.; Peeling, P.; Pyne, D.B.; Welvaert, M.; Tee, N.; Leckey, J.J.; Sharma, A.P.; Ross, M.L.R.; Garvican-Lewis, L.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; et al. Chronic adherence to a ketogenic diet modifies iron metabolismin elite athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kose, E.; Guzel, O.; Arslan, N. Analysis of hematological parameters in patients treated with ketogenic diet due to drug-resistant epilepsy. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkus, D.L.; Murray-Kolb, L.E.; de Souza, M.J. The unexplored crossroads of the female athlete triad and iron deficiency: A narrative review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1721–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, A.K.A.; Pyne, D.B.; Burke, L.M.; Peeling, P. Iron Metabolism: Interactions with Energy and Carbohydrate Availability. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovides, S.; Maloney, S.K.; Bhana, S.; Angamia, Z.; Meiring, R.M. Could the ketogenic diet induce a shift in thyroid function and support a metabolic advantage in healthy participants? A pilot randomized-controlled-crossover trial. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteberg, E.; Thorsby, P.M.; Kverneland, M.; Iversen, P.O.; Selmer, K.K.; Nakken, K.O.; Taubøll, E. Effects of modified Atkins diet on thyroid function in adult patients with pharmacoresistant epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 111, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, T.; Tinsley, G.; Bianco, A.; Marcolin, G.; Pacelli, Q.F.; Battaglia, G.; Palma, A.; Gentil, P.; Neri, M.; Paoli, A. Effects of eight weeks of time-restricted feeding (16/8) on basal metabolism, maximal strength, body composition, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors in resistance-trained males. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liang, L.; Bray, G.A.; Qi, L.; Hu, F.B.; Rood, J.; Sacks, F.M.; Sun, Q. Thyroid hormones and changes in body weight and metabolic parameters in response to weight loss diets: The POUNDS LOST trial. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Most, J.; Redman, L.M. Impact of calorie restriction on energy metabolism in humans. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 133, 110875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Al-Zaid, N.S.; Mathew, T.C.; Al-Mousawi, M.; Talib, H.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.I. Long term effects of ketogenic diet in obese subjects with high cholesterol level. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2006, 286, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowis, K.; Banga, S. The Potential Health Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burén, J.; Ericsson, M.; Damasceno, N.R.T.; Sjödin, A. A Ketogenic Low-Carbohydrate High-Fat Diet Increases LDL Cholesterol in Healthy, Young, Normal-Weight Women: A Randomized Controlled Feeding Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbain, P.; Strom, L.; Morawski, L.; Wehrle, A.; Deibert, P.; Bertz, H. Impact of a 6-week non-energy-restricted ketogenic diet on physical fitness, body composition and biochemical parameters in healthy adults. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Mathew, T.C.; Khadada, M.; Al-Mousawi, M.; Talib, H.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.I.; Al-Zaid, N.S. Beneficial effects of ketogenic diet in obese diabetic subjects. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2007, 302, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, H.M.; Mathew, T.C.; Hussein, T.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.; Khoursheed, M.A.; Al-Sayer, H.M.; Bo-Abbas, Y.Y.; Al-Zaid, N.S. Long-term effects of a ketogenic diet in obese patients. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 9, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Jin, H.; Xian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Bai, X. Effect of Ketogenic Diets on Body Composition and Metabolic Parameters of Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloch, M.; Perveen, B.; Khan, K.S.; Imtiaz, F. Ketogenic diet to alleviate symptoms of gout. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, E.L.; Asher, J.L.; Molony, R.D.; Shaw, A.C.; Zeiss, C.J.; Wang, C.; Morozova-Roche, L.A.; Herzog, R.I.; Iwasaki, A.; Dixit, V.D. β-Hydroxybutyrate Deactivates Neutrophil NLRP3 Inflammasome to Relieve Gout Flares. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.A.; Mathew, T.C.; Dashti, A.A.; Asfar, S.; Al-Zaid, N.; Dashti, H.M. Effect of low-calorie versus low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet in type 2 diabetes. Nutrition 2012, 28, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perticone, M.; Maio, R.; Sciacqua, A.; Suraci, E.; Pinto, A.; Pujia, R.; Zito, R.; Gigliotti, S.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Ketogenic Diet-Induced Weight Loss is Associated with an Increase in Vitamin D Levels in Obese Adults. Molecules 2019, 24, 2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscemi, S.; Buscemi, C.; Corleo, D.; De Pergola, G.; Caldarella, R.; Meli, F.; Randazzo, C.; Milazzo, S.; Barile, A.M.; Rosafio, G.; et al. Obesity and Circulating Levels of Vitamin D before and after Weight Loss Induced by a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almsaid, H.; Khalfa, H.M. The effect of Ketogenic diet on vitamin D3 and testosterone hormone in patients with diabetes mellitus type 2. Curr. Issues Pharm. Med. Sci. 2020, 33, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenig, S.; Petelin, A.; Poklar Vatovec, T.; Mohorko, N.; Jenko-Pražnikar, Z. Assessment of micronutrients in a 12-wk ketogenic diet in obese adults. Nutrition 2019, 67–68, 110522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulides, S.S.; Neal, E.G.; Fitzsimmons, G.; Chaffe, H.M.; Jeanes, Y.M.; Aitkenhead, H.; Cross, J.H. The effect of the classical and medium chain triglyceride ketogenic diet on vitamin and mineral levels. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 25, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, Z. The paleolithic ketogenic diet may ensure adequate serum magnesium levels. J. Evol. Health: A Jt. Publ. Ancestral Health Soc. Soc. Evol. Med. Health 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondanelli, M.; Perna, S.; Ilyas, Z.; Peroni, G.; Bazire, P.; Sajuox, I.; Maugeri, R.; Nichetti, M.; Gasparri, C. Effect of very low-calorie ketogenic diet in combination with omega-3 on inflammation, satiety hormones, body composition, and metabolic markers. A pilot study in class I obese subjects. Endocrine 2022, 75, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, W.S., Jr.; Olsen, M.K.; Guyton, J.R.; Bakst, R.P.; Westman, E.C. A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet versus a low-fat diet to treat obesity and hyperlipidemia: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 140, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, G.M.; Guzman, G.; Correa De Mello, L.L.; Trein, B.; Spina, L.; Bussade, I.; Marques Prata, J.; Sajoux, I.; Countinho, W. Efficacy of a 2-Month Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) Compared to a Standard Low-Calorie Diet in Reducing Visceral and Liver Fat Accumulation in Patients with Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Castillo-García, A.; Lucia, A.; Naclerio, F. Effects of Combining a Ketogenic Diet with Resistance Training on Body Composition, Strength, and Mechanical Power in Trained Individuals: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steger, F.L.; Jamshed, H.; Bryan, D.R.; Richman, J.S.; Warriner, A.H.; Hanick, C.J.; Martin, C.K.; Salvy, S.J.; Peterson, C.M. Early time-restricted eating affects weight, metabolic health, mood, and sleep in adherent completers: A secondary analysis. Obesity 2023, 31 (Suppl. S1), 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia, J.M.; Santos, P.D.G.; Pezarat-Correia, P.; Minderico, C.S.; Infante, J.; Mendonca, G.V. Effect of Time-Restricted Eating and Resistance Training on High-Speed Strength and Body Composition. Nutrients 2023, 15, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Raimondo, D.; Buscemi, S.; Musiari, G.; Rizzo, G.; Pirera, E.; Corleo, D.; Pinto, A.; Tuttolomondo, A. Ketogenic Diet, Physical Activity, and Hypertension—A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, G.D.; Wyatt, H.R.; Hill, J.O.; Makris, A.P.; Rosenbaum, D.L.; Brill, C.; Stein, R.I.; Mohammed, B.S.; Miller, B.; Rader, D.J.; et al. Weight and metabolicoutcomes after 2 years on a low-carbohydrate versus low-fat dieta randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2010, 153, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, Y.; Özkan, G.; Ulusoy, Ş.; Arıcı, M.; Derici, Ü.; Şengül, Ş.; Sindel, Ş.; Ertürk, Ş. Turkish Society of Hypertension and Renal Diseases. The effect of intermittent fasting on blood pressure variability in patients with newly diagnosed hypertension or prehypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jafar, R.; Zografou Themeli, M.; Zaman, S.; Akbar, S.; Lhoste, V.; Khamliche, A.; Elliott, P.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Dehghan, A. Effect of Religious Fasting in Ramadan on Blood Pressure: Results from LORANS (London Ramadan Study) and a Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Blood Parameters | Baseline Values | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|
| Testosterone (nmol/L) | 24.2 | 9.90–27.90 nmol/L |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 173 | <190 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol HDL (mg/dL) | 53 | >40 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol LDL (mg/dL) | 99 | <100 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 107 | <150 mg/dL |
| Homocysteine (μmol/L) | 10.2 | 5.0–12.0 μmol/L |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 99 | 70–99 mg/dL |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 10.4 | 2.60–24.90 mU/L |
| HOMA-IR | 2.54 | <1 |
| ALT (U/L) | 54 | <41 U/L |
| AST (U/L) | 27 | <38 U/L |
| GGTP (IU/L) | 14 | 10–66 IU/L |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.9 | <1 mg/dL |
| TSH (mU/L) | 2.17 | 0.27–4.20 mU/L |
| FT3 (pmol/L) | 6.19 | 3.1–6.8 pmol/L |
| FT4 (pmol/L) | 19.22 | 12–22 pmol/L |
| CRP (mg/L) | <0.6 | <5 mg/L |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 93 | 62–106 μmol/L |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.8 | 3.4–7 mg/dL |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 28.2 | 16.6–48.5 mg/dL |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 181 | 30–400 ng/mL |
| Transferrin (mg/dL) | 286 | 200–360 mg/dL |
| Iron (μg/dL) | 202 | 59–158 μg/dL |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137 | 136–146 mmol/L |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.37 | 3.50–5.10 mmol/L |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 10.08 | 8.6–10 mg/dL |
| Magnesium (mEq/L) | 1.7 | 1.4–2.1 mEq/L |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.1 | 2.7–4.5 mg/dL |
| Vitamin B12 (pg/mL) | 540 | 197–771 pg/mL |
| Vitamin D 25(OH)D (ng/mL) | 78 | 30–100 ng/mL |
| Blood cell count | ||
| White blood cells (WBC) (g/L) | 7.81 | 3.50–10.00 (g/L) |
| Red blood cells (RBC) (T/L) | 5.52 | 4.50–5.70 (T/L) |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 16.8 | 12.0–16.8 (g/dL) |
| Haematocrit (%) | 47.4 | 40.0–49.5 (%) |
| MCV (fl) | 85.9 | 83.0–103.0 (fl) |
| MCH (pg) | 30.4 | 28.0–34.0 (pg) |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 35.4 | 32.0–36.0 (g/dL) |
| Platelets (G/L) | 275 | 150–400 (g/L) |
| RDW-CV (%) | 12 | 11.5–14.5 (%) |
| MPV (fl) | 11.4 | 9.0–12.6 (fl) |
| Neutrocytes (%) | 65.7 | 45–70 (%) |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 25.1 | 20–45 (%) |
| Monocytes (%) | 6.7 | 4.0–12.0 (%) |
| Eosinocytes (%) | 1.7 | <5.0 (%) |
| Basocytes (%) | 0.8 | <1.0 (%) |
| Neutrocytes (g/L) | 5.14 | 1.80–7.70 (g/L) |
| Lymphocytes (g/L) | 1.96 | 1–5 (g/L) |
| Monocytes (g/L) | 0.52 | <0.8 (g/L) |
| Eosinocytes (g/L) | 0.13 | <0.45 (g/L) |
| Basocytes (g/L) | 0.06 | <0.2 (g/L) |
| Anthropometric parameters | Baseline values | |
| Body mass | 86.8 kg | |
| Adipose tissue mass | 14.8 kg | |
| Muscular tissue mass | 68.4 kg | |
| Lean body mass | 72 kg | |
| Water mass | 49.8 kg | |
| Bone mass | 3.6 kg | |
| Visceral adipose tissue level | 4 | |
| Body mass index (BMI) | 26.5 kg/m2 | |
| Metabolic age | 20 years | |
| Heart rate and arterial pressure | Measurement range | |
| Heart rate (morning) | 67–94 BPM | |
| Heart rate (evening) | 66–95 BPM | |
| Arterial pressure (morning) | 116/61–144/86 | |
| Arterial pressure (evening) | 117/64–146/88 | |
| Height | 181 cm | |
| Macrocomponents | First Stage | Second Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Protein | 100 g | 136 g |
| Fat | 220 g | 196 g |
| Carbohydrates | 20 g | 33–37 g 1 |
| Dietary fibre | 17–22 g 1 | 20–26 g 1 |
| Energy | 2460 kcal | ≈2450 kcal |
| Meal No. | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. (13:00) | -chicken eggs 168 g -avocado 70 g -homemade mayonnaise 25 g -spinach leaves 50 g -tomato 100 g -linseed 12 g -gouda cheese 35 g -smoked sprats 65 g -extra butter 32 g -Himalayan salt 2.5 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -pork shoulder 210 g -sour cream 30% fat 130 g -onion 30 g -garlic 5 g -spinach leaves 70 g -extra butter 50 g -Himalayan salt 3 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -chicken breast 170 g -sour cream 30% fat 120 g -brussels sprouts 85 g -coconut oil 30 g -spinach leaves 50 g -red pepper 70 g -extra butter 36 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -chicken eggs 168 g -smoked bacon 80 g -Brazil nuts 30 g -tomato 180 g -arugula 70 g -olive oil 38 mL -gouda cheese 30 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -chicken eggs 168 g -smoked sprats 91 g -arugula 40 g -homemade mayonnaise 35 g -pickled cucumbers 180 g -pumpkin seeds 35 g -olive oil 23 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -pork knuckle 200 g -sauerkraut 200 g -broccoli 220 g -marinated boletes 70 g -extra butter 40 g -olive oil 34 mL -highly mineralized water 1000 mL * | -pork neck 200 g -Chinese cabbage 190 g -homemade mayonnaise 40 g -tomato 150 g -linseed 25 g -avocado 70 g -olive oil 18 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * |
| 2. (17:00) | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -Roman salad 70 g -Iceberg lettuce 40 g -lamb’s lettuce 20 g -arugula 20 g -olive oil 33 mL -linseed 16 g -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -still mineral water 800 mL * -highly mineralized water 200 mL * | -coconut shrimp 20 g -coconut oil 30 g -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -Roman salad 40 g -Iceberg lettuce 30 g -tomato 30 g -lamb’s lettuce 20 g -arugula 20 g -olive oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * |
| 3. (21:00) | -pork shoulder 190 g -broccoli 270 g -sauerkraut 180 g -coconut oil 44 g -linseed oil 20 mL -Himalayan salt 2.5 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -chicken breast 130 g -tomato 120 g -cucumber 80 g -avocado 80 g -feta cheese 60 g -olive oil 38 mL -linseed 30 g -radish sprouts 24 g -Italian nuts 10 g -Himalayan salt 3 g -highly mineralized water 600 mL * -still mineral water 400 mL * | -chicken eggs 224 g -olive oil 10 mL -onion 30 g -arugula 60 g -Italian nuts 25 g -smoked mackerel 80 g -MCT oil 20 mL -Himalayan salt 3 g -highly mineralized water 1000 mL * | -chicken thigh 250 g -sauerkraut 100 g -Brussels sprouts 119 g -extra butter 38 g -parsley 50 g -linseed oil 20 mL -highly mineralized water 1000 mL * | -salmon 200 g -asparagus 180 g -extra butter 50 g -linseed 25 g -sauerkraut 250 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -Sirloin steak 200 g -coconut oil 22 g - Italian nuts 50 g -spinach lettuce 25 g -tomato 110 g -gouda cheese30 g -highly mineralized water 200 mL * -still mineral water 800 mL * | -shrimp 260 g -extra butter 50 g -garlic 10 g -dill 8 g -olive oil 24 mL -gouda cheese 50 g -still mineral water 500 mL * -highly mineralized water 500 mL * |
| Meal No. | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. (13:00) | -chicken eggs 336 g -avocado 70 g -homemade mayonnaise 25 g -spinach lettuce 50 g -tomato 180 g -linseed 12 g -gouda cheese 40 g -smoked sprats 39 g -still mineral water 1000 mL | -pork shoulder 280 g -sour cream 30% fat 130 g -onion 50 g -garlic 5 g -red pepper 70 g -spinach lettuce 40 g -extra butter 25 g -broccoli 200 g -still mineral water 1000 mL -Himalayan salt 3 g | -chicken breast 250 g -sour cream 30% fat 160 g -brussels 170 g -coconut oil 30 g -spinach lettuce 50 g -red pepper 70 g -still mineral water 1000 mL | -chicken eggs 336 g -smoked bacon 80 g -Brazil nuts 30 g -tomato 240 g -arugula 70 g -olive oil 5 mL -gouda cheese 30 g -still mineral water 1000 mL | -chicken eggs 336 g -smoked sprats 91 g -arugula 40 g -homemade mayonnaise 30 g -zucchini 300 g -pickled cucumbers 120 g -pumpkin seeds 10 g -olive oil 8 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL | -pork knuckle 300 g -sauerkraut 200 g -broccoli 250 g -marinated boletes 100 g -extra butter 30 g -olive oil 10 mL -highly mineralized water 1000 mL | -pork neck 300 g -Chinese cabbage 190 g -homemade mayonnaise 30 g - tomato 240 g -linseed 20 g -avocado 70 g -still mineral water 1000 mL |
| 2. (17:00) | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -Roman salad 70 g -Iceberg lettuce 40 g -lamb’s lettuce 20 g -arugula 20 g -olive oil 40 mL -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -coconut shrimp 20 g -coconut oil 30 g -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -MCT oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -black coffee brew (without sugar) 250 mL -tomato 50 g -Roman salad 40 g -Iceberg lettuce 30 g -lamb’s lettuce 20 g -arugula 20 g -olive oil 40 mL -still mineral water 1000 mL * |
| 3. (21:00) | -pork shoulder 250 g -broccoli 300 g -sauerkraut 200 g -coconut oil 35 g -canned red beans 115 g -linseed oil 12 mL -still mineral water 750 mL -Himalayan salt 1 g -still mineral water 250 mL * | -chicken breast 200 g -tomato 100 g -cucumber 120 g -red pepper 70 g -avocado 70 g -feta cheese 60 g -Italian nuts 35 g -radish sprouts 24 g -olive oil 22 mL -linseed 10 g -Himalayan salt 2 g -highly mineralized water 600 mL * -still mineral water 400 mL * | -chicken eggs 280 g -olive oil 8 mL -onion 50 g -arugula 60 g -tomato juice 300 mL -Italian nuts 35 g -smoked mackerel 100 g -highly mineralized water 900 mL * -still mineral water 100 mL * | -chicken thigh 320 g -sauerkraut 100 g -brussels 119 g -extra butter 45 g -parsley 50 g -beetroot 150 g -highly mineralized water 600 mL * -still mineral water 400 mL * | -salmon 290 g -asparagus 180 g -extra butter 28 g -linseed 15 g -sauerkraut 180 g -still mineral water 1000 mL * | -Sirloin steak 260 g -coconut oil 8 g -canned red beans 120 g -Italian nuts 50 g -spinach lettuce 25 g -tomato 110 g -gouda cheese 30 g -highly mineralized water 200 mL * -still mineral water 800 mL * | -shrimp 350 g -extra butter 40 g -garlic 10 g -dill 8 g -red pepper 200 g -olive oil 20 mL -gouda cheese 50 g -highly mineralized water 500 mL * -still mineral water 500 mL * |
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nutrients of Diet | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | 0–4 Week | 5–13 Week | Norm * |
| Sodium (mg) | 2249.1 | 2202 | 2157.4 | 2064.5 | 2153.1 | 2535.1 | 2406.6 | 2755.4 | 3493.3 | 2959.6 | 2387.2 | 2954 | 2362.4 | 2901.8 | 1500 mg (AI) |
| Potassium (mg) | 3967.4 | 4923.2 | 3292.4 | 4770.3 | 3141.2 | 4626.3 | 3473.7 | 4597.8 | 3552.6 | 4983.1 | 3202.1 | 4027.9 | 3083.6 | 4293.8 | 3500 mg (AI) |
| Calcium (mg) | 1187.4 | 1197.5 | 916.2 | 982.3 | 901.4 | 946 | 942.6 | 1023.8 | 1065.6 | 1198.6 | 910.7 | 993.4 | 1040 | 1123.4 | 1000 mg (RDA) |
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1219.5 | 1841.7 | 1343.7 | 1744.8 | 1494.2 | 1863.3 | 1441.5 | 1960 | 1706.8 | 2022 | 1219 | 1617.6 | 1628.1 | 2061.5 | 700 mg (RDA) |
| Magnesium (mg) | 453.3 | 407.7 | 452 | 479.3 | 498.9 | 492.6 | 477 | 491.6 | 560 | 491.3 | 419.9 | 492.3 | 483.2 | 445.8 | 400 mg (RDA) |
| Iron (mg) | 13.2 | 19.9 | 11.2 | 13.1 | 13.7 | 17.2 | 12.9 | 19.7 | 19.6 | 22.5 | 17.7 | 23.1 | 9.7 | 12.3 | 10 mg (RDA) |
| Zinc (mg) | 12.9 | 18.7 | 11.3 | 14.3 | 9 | 11.7 | 12.6 | 17.4 | 12.4 | 15 | 14.9 | 19.6 | 14 | 18.7 | 11 mg (RDA) |
| Copper (mg) | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 0.9 mg (RDA) |
| Iodine (µg) | 82.6 | 105.3 | 26.2 | 56.5 | 72.3 | 87.8 | 36.7 | 55.7 | 121.8 | 187.1 | 63.6 | 69.1 | 32.6 | 35.9 | 150 µg (RDA) |
| Manganese (mg) | 2.5 | 3 | 2.2 | 3.7 | 2.7 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 3 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 2.3 mg (AI) |
| Thiamine (mg) | 2 | 2.6 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 3 | 1.3 mg (RDA) |
| Riboflavin (mg) | 2.1 | 3.6 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 3.3 | 2 | 3.1 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 1.6 | 1.3 mg (RDA) |
| Niacin (mg) | 18 | 23.2 | 35.8 | 51.2 | 33 | 46.5 | 17.5 | 20.8 | 21.5 | 29.3 | 25.1 | 34.1 | 21 | 31.4 | 16 mg (RDA) |
| Folates (µg) | 664.9 | 872.5 | 352.4 | 609.6 | 650.8 | 876.7 | 564.5 | 836.3 | 592.3 | 982.3 | 461.2 | 531.4 | 439 | 595.5 | 400 µg (RDA) |
| Vitamin B12 (µg) | 4.7 | 8 | 3 | 3.8 | 12.3 | 15.5 | 4.2 | 7.2 | 12.8 | 20 | 4.7 | 6.2 | 5.3 | 7 | 2.4 µg (RDA) |
| Vitamin B6 (mg) | 2.1 | 2.7 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 2.7 | 3.9 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 1.3 mg (RDA) |
| Vitamin A (µg) | 1711.5 | 2053.8 | 1478.5 | 2103.8 | 2528.4 | 2864.2 | 1267.8 | 1862.9 | 1240.7 | 1637.7 | 1069.5 | 1041.2 | 1458.7 | 2581.2 | (as retinol) |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 315.5 | 362.9 | 99 | 446.6 | 235.8 | 366.8 | 201.2 | 230 | 99 | 131.1 | 257.2 | 283.1 | 108.6 | 419.9 | 90 mg (RDA) |
| Vitamin D (µg) | 4.6 | 7.7 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 11.1 | 13.6 | 4.6 | 7.7 | 29.4 | 43.7 | 3 | 4 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 15 µg (AI) |
| Vitamin E (mg) | 14.6 | 16.8 | 12.6 | 17 | 14.4 | 19.7 | 14.4 | 12.8 | 29.9 | 23.6 | 12.6 | 10.3 | 27.3 | 30.8 | 10 mg (AI) |
| β-carotene (µg) | 5523.6 | 6225.9 | 4402.2 | 9255.5 | 10,928.5 | 13,033.9 | 2932 | 3382.5 | 2156.3 | 2607.3 | 4042.9 | 4280.9 | 6535.9 | 13,494 | - |
| Retinol (µg) | 791.8 | 1017.1 | 741.7 | 558.2 | 1190.2 | 1173.2 | 861.3 | 1381.5 | 930 | 1252.6 | 396.7 | 328.8 | 658 | 626.1 | 900 µg (RDA) |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 841.2 | 1406.8 | 518.7 | 540 | 1177.5 | 1386.8 | 979.1 | 1660.1 | 891.6 | 1501.5 | 380.5 | 457.7 | 637.1 | 781.2 | <300 mg |
| Ratio n3:n6 | 1:2:4 | 1:2:7 | 1:5 | 1:4:6 | 1:2:7 | 1:2:7 | 1:6:7 | 1:6:9 | 1:1:5 | 1:0:9 | 1:5:3 | 1:5 | 1:3:7 | 1:3:7 | 1:1–1:6 |
| Saturated fat (g) | 74.9 | 57.4 | 73.4 | 61.1 | 85.2 | 76.5 | 84.8 | 89.2 | 47.8 | 38.3 | 73.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 | 60.5 | <10% energy |
| PUFA (g) | 30.2 | 25.8 | 22.5 | 26.2 | 27.8 | 29.6 | 35.3 | 19.7 | 37.5 | 31.8 | 28.8 | 27.4 | 31.9 | 28.1 | 6–10% energy |
| MUFA (g) | 51 | 52.2 | 73.8 | 59.7 | 70.1 | 72.9 | 67.6 | 53 | 68.4 | 58.6 | 65.8 | 56.8 | 111.6 | 94.4 | 10–15% emergy |
| Blood Parameters | Measurements (P0) | Measurements (P1) | Change (%) | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White blood cells (WBC) (g/L) | 7.81 | 6.6 | (−) 15.5% | 3.50–10.00 (g/L) |
| Red blood cells (RBC) (T/L) | 5.52 | 5.53 | (+) 0.18% | 4.50–5.70 (T/L) |
| Haemoglobin (g/dL) | 16.8 | 16.8 | no change | 12.0–16.8 (g/dL) |
| Haematocrit (%) | 47.4 | 46.7 | (−) 1.48% | 40.0–49.5 (%) |
| MCV (fl) | 85.9 | 84.4 | (−) 1.75% | 83.0–103.0 (fl) |
| MCH (pg) | 30.4 | 30.4 | no change | 28.0–34.0 (pg) |
| MCHC (g/dL) | 35.4 | 36 | (+) 1.7% | 32.0–36.0 (g/dL) |
| Platelets (G/L) | 275 | 291 | (+) 5.82% | 150–400 (g/L) |
| RDW-CV (%) | 12 | 12 | no change | 11.5–14.5 (%) |
| MPV (fl) | 11.4 | 11.8 | (+) 3.51% | 9.0–12.6 (fl) |
| Neutrocytes (%) | 65.7 | 50.8 | (−) 22.68% | 45–70 (%) |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 25.1 | 36.2 | (+) 44.22% | 20–45 (%) |
| Monocytes (%) | 6.7 | 9.8 | (+) 46.27% | 4.0–12.0 (%) |
| Eosinocytes (%) | 1.7 | 2.4 | (+) 41.18% | < 5.0 (%) |
| Basocytes (%) | 0.8 | 0.8 | no change | <1.0 (%) |
| Neutrocytes (G/L) | 5.14 | 3.35 | (−) 34.82% | 1.80–7.70 (g/L) |
| Lymphocytes (G/L) | 1.96 | 2.39 | (+) 21.94% | 1–5 (g/L) |
| Monocytes (G/L) | 0.52 | 0.65 | (+) 25% | <0.8 (g/L) |
| Eosinocytes (G/L) | 0.13 | 0.16 | (+) 23.08% | <0.45 (g/L) |
| Basocytes (G/L) | 0.06 | 0.05 | (−) 16.67% | <0.2 (g/L) |
| Blood Parameters | Measurements (P0) | Measurements (P1) | Change (%) | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Testosterone (nmol/L) | 24.2 | 48 | (+) 98.3% | 9.90–27.90 nmol/L |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 173 | 175 | (+) 1.2% | <190 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol HDL (mg/dL) | 53 | 63 | (+) 18.9% | >40 mg/dL |
| Cholesterol LDL (mg/dL) | 99 | 89 | (−) 10.1% | <100 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 107 | 112 | (+) 4.7% | <150 mg/dL |
| Homocysteine (μmol/L) | 10.2 | 10.6 | (+) 3.9% | 5.0–12.0 μmol/L |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 99 | 71 | (−) 28.3% | 70–99 mg/dL |
| Insulin (mU/L) | 10.4 | 2.68 | (−) 74.2% | 2.60–24.90 mU/L |
| HOMA-IR | 2.54 | 0.47 | (−) 81.5% | <1 |
| HbA1c (%Hb) | - | 4.7 | - | <6% Hb |
| ALT (U/L) | 54 | 11 | (−) 79.6% | <41 U/L |
| AST (U/L) | 27 | 14 | (−) 48.1% | <38 U/L |
| GGTP (IU/L) | 14 | 8 | (−) 42.9% | 10–66 IU/L |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.9 | 0.7 | (−) 22.2% | <1 mg/dL |
| TSH (mU/L) | 2.17 | 2.36 | (+) 8.8% | 0.27–4.20 mU/L |
| FT3 (pmol/L) | 6.19 | 4.28 | (−) 30.9% | 3.1–6.8 pmol/L |
| FT4 (pmol/L) | 19.22 | 22.53 | (+) 17.2% | 12–22 pmol/L |
| CRP (mg/L) | <0.6 | <0.6 | - | <5 mg/L |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 93 | 82 | (−) 11.8% | 62–106 μmol/L |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.8 | 5.5 | (−) 5.2% | 3.4–7 mg/dL |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 28.2 | 17.1 | (−) 39.4% | 16.6–48.5 mg/dL |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 181 | 185 | (+) 2.2% | 30–400 ng/mL |
| Transferrin (mg/dL) | 286 | 233 | (−) 18.5% | 200–360 mg/dL |
| Iron (μg/dL) | 202 | 118 | (−) 41.6% | 59–158 μg/dL |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137 | 140 | (+) 2.2% | 136–146 mmol/L |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.37 | 4.59 | (+) 5% | 3.50–5.10 mmol/L |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 10.08 | 10.16 | (+) 0.8% | 8.6–10 mg/dL |
| Magnesium (mEq/L) | 1.7 | 1.6 | (−) 5.9% | 1.4–2.1 mEq/L |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.1 | 3.0 | (−) 3.2% | 2.7–4.5 mg/dL |
| Vitamin B12 (pg/mL) | 540 | 524 | (−) 3% | 197–771 pg/mL |
| Vitamin D 25(OH)D (ng/mL) | 78 | 125 | (+) 60.3% | 30–100 ng/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dyńka, D.; Paziewska, A.; Kowalcze, K. Keto Menu–Effect of Ketogenic Menu and Intermittent Fasting on the Biochemical Markers and Body Composition in a Physically Active Man—A Controlled Case Study. Foods 2023, 12, 3219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173219
Dyńka D, Paziewska A, Kowalcze K. Keto Menu–Effect of Ketogenic Menu and Intermittent Fasting on the Biochemical Markers and Body Composition in a Physically Active Man—A Controlled Case Study. Foods. 2023; 12(17):3219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173219
Chicago/Turabian StyleDyńka, Damian, Agnieszka Paziewska, and Katarzyna Kowalcze. 2023. "Keto Menu–Effect of Ketogenic Menu and Intermittent Fasting on the Biochemical Markers and Body Composition in a Physically Active Man—A Controlled Case Study" Foods 12, no. 17: 3219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173219
APA StyleDyńka, D., Paziewska, A., & Kowalcze, K. (2023). Keto Menu–Effect of Ketogenic Menu and Intermittent Fasting on the Biochemical Markers and Body Composition in a Physically Active Man—A Controlled Case Study. Foods, 12(17), 3219. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12173219