Demulsification of Emulsion Using Heptanoic Acid during Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction and the Characterization of Peanut Oil and Proteins Extracted
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Preparation of Oil Body Emulsion and Protein from AEE
2.3. Measurement of the Main Composition
2.4. Oil Extracted by Different Demulsification Methods
2.4.1. Heptanoic Demulsification
2.4.2. Solvent Extraction (SE)
2.4.3. Freeze–Thaw and Heat Treatment (FHD)
2.4.4. Isoelectric Point Demulsification (IPD)
2.5. Optimization of Demulsification Conditions with Heptanoic Acid
2.5.1. Effects of Different Parameters on the FOY
2.5.2. Experiment Design for Optimizing
2.6. Determination of Composition of Fatty Acid
2.7. Physicochemical Properties and Determination of Oil
2.8. Amino Acid Composition Determination
2.9. Determination of Functional Properties of Peanut Protein
2.9.1. Solubility
2.9.2. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC) and Oil-Holding Capacity (OHC)
2.9.3. Emulsion Activity Index (EAI) and Emulsion Stability Index (ESI)
2.9.4. Foaming Capacity (FC) and Foaming Stability (FS)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Main Composition of Peanut and Oil Body Emulsion
3.2. Optimization of Demulsification of the Oil Body Emulsion
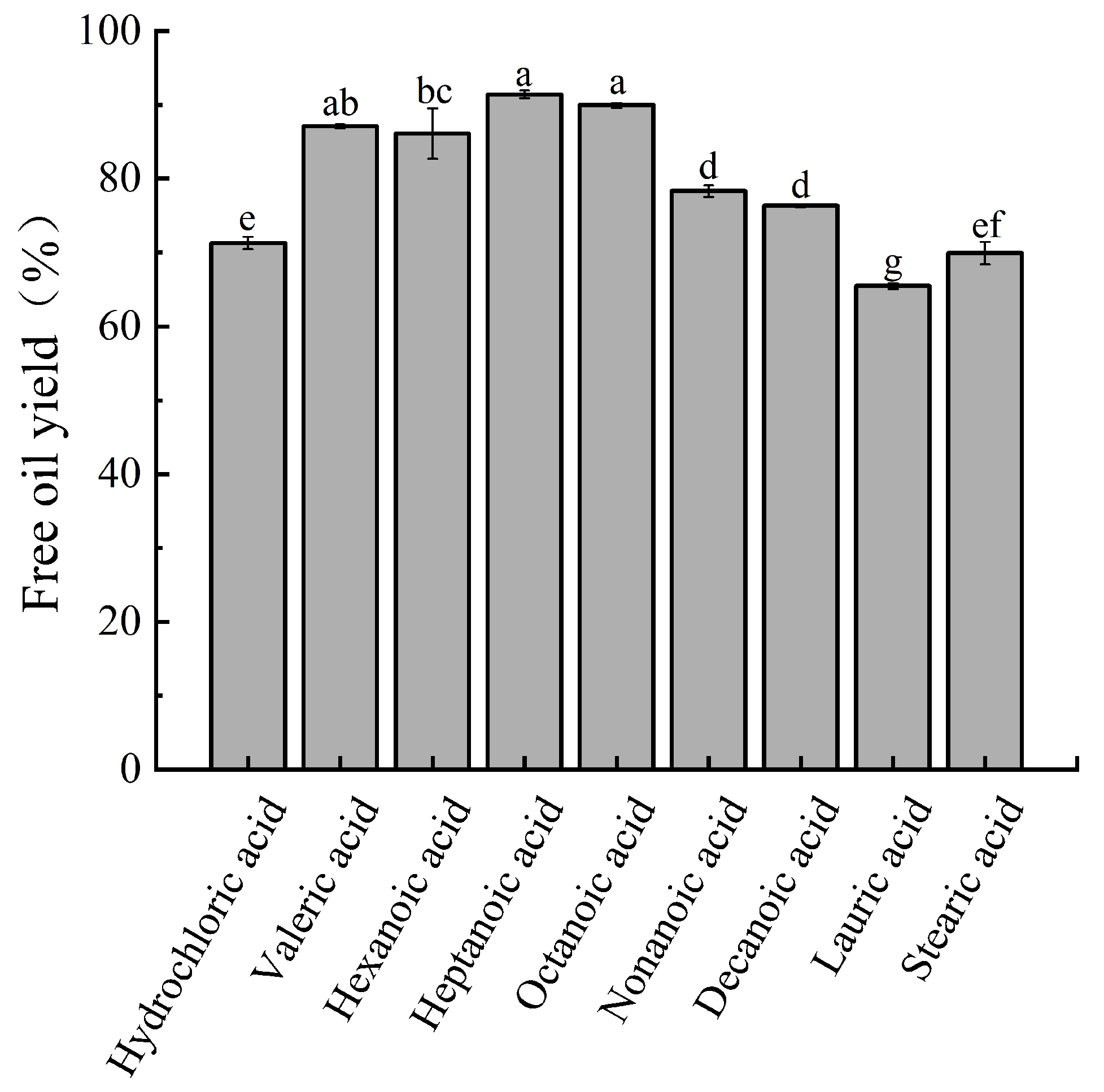
3.2.1. Selection of Fatty Acid for Demulsification by AEE
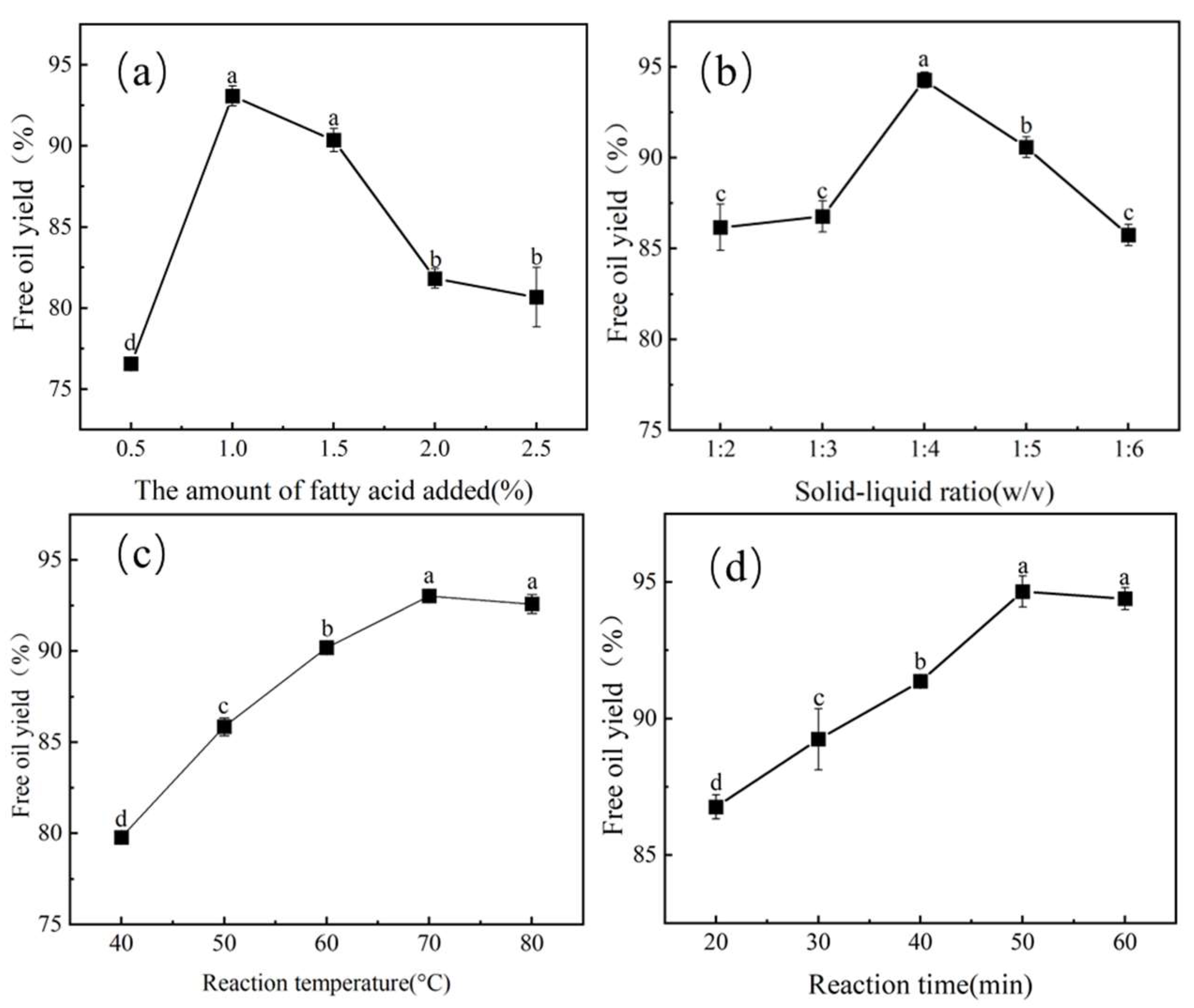
3.2.2. Effect of the Amount of Heptanoic Added on FOY
3.2.3. Effect of the Solid–Liquid Ratio on FOY
3.2.4. Effect of Reaction Temperature on FOY
3.2.5. Effect of Reaction Time on FOY
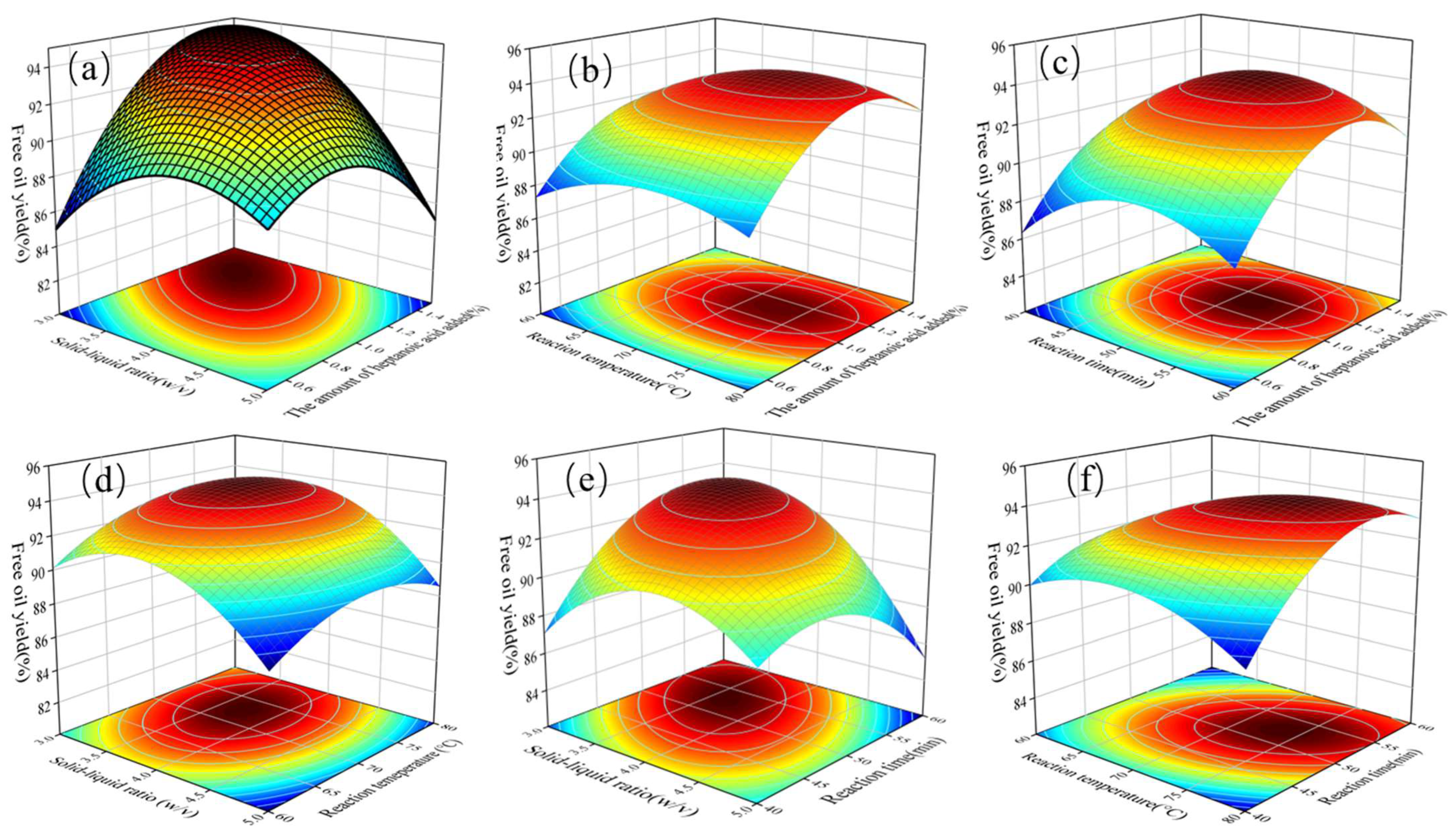
3.3. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Analysis
− 2.26X2X4 + 1.45X3X4 − 3.11X12 − 2.84X22 − 1.63X32 − 2.40X42
3.4. Effect of Parameter Interactions on FOY
3.5. Verification of the Optimal Condition
3.6. Oil Character Analsisy
3.6.1. Fatty Acid Composition Analysis of Different Oils
3.6.2. Physicochemical Character Analysis of Different Oils
3.7. Amino Acid Composition Determination
3.8. Functional Property of Proteins
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Settaluri, V.; Kandala, V.; Puppala, N.; Sundaram, J. Peanuts and their nutritional aspects—A review. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Chen, F.; Liu, C.; Duan, X. Composition and rheological properties of peanut oil bodies from aqueous enzymatic extraction. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, M.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.; Shi, J.; Jiang, Y. Effect of high-pressure homogenization on the functional property of peanut protein. J. Food Process Eng. 2011, 34, 2191–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.T.; Tu, Z.C.; Xiao, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.Q.; Liu, G.X.; Liu, C.M.; Shi, Y.; Fan, L.L.; Lin, D.R. Influence of ultrasonic treatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of peanut protein isolate. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Gasmalla, M.A.A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, R.; Aboagarib, E.A.A. Characterization and demulsification of cream emulsion from aqueous extraction of peanut. J. Food Eng. 2016, 185, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, B.P.; Johnson, L.A. Separating oil from aqueous extraction fractions of soybean. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, J.M.L.N.; Campbell, K.; Mahfuz, A.; Jung, S.; Glatz, C.E.; Johnson, L. Enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of oil and protein from soybeans and cream de-emulsification. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, S.; Han, F. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil and protein hydrolysates from peanut. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2008, 14, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.M.; Gordon, M.H.; Ezeh, O.; Niranjan, K. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of moringa oleifera oil. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.F.G.; De Almeida, N.M.; De Souza, T.S.P.; Taha, A.Y.; De Moura Bell, J.M.L.N. Characterization and demulsification of the oil-rich emulsion from the aqueous extraction process of almond flour. Processes 2020, 8, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, F.F.G.; de Moura Bell, J.M.L.N. Understanding the Impact of Enzyme-Assisted Aqueous Extraction on the Structural, Physicochemical, and Functional Properties of Protein Extracts from Full-Fat Almond Flour. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabrand, R.M.; Kim, H.; Zhang, C.; Glatz, C.E.; Jung, S. Destabilization of the emulsion formed during aqueous extraction of soybean oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Z.; Xin, Y.; Duan, X.; Wang, B.-Y. Effect of papain on the demulsification of peanut oil-body emulsion and the corresponding mechanism. J. Oleo Sci. 2020, 69, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.B.; Wang, T. Destabilization of emulsion formed during aqueous extraction of peanut oil: Synergistic effect of Tween 20 and pH. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Gasmalla, M.A.A.; Yang, R. Demulsification of oil-rich emulsion and characterization of protein hydrolysates from peanut cream emulsion of aqueous extraction processing. J. Food Eng. 2017, 204, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Johnson, L.A.; Jung, S. Demulsification of oil-rich emulsion from enzyme-assisted aqueous extraction of extruded soybean flakes. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.B.; Liu, X.J.; Lu, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Zhao, X. Enzymatic demulsification of the oil-rich emulsion obtained by aqueous extraction of peanut seeds. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2013, 90, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.M.; Gordon, M.H.; Niranjan, K. Aqueous enzyme assisted oil extraction from oilseeds and emulsion de-emulsifying methods: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 60–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y. Demulsification of peanut emulsion by aqueous enzymatic extraction using a combination of oleic and citric acids. LWT 2023, 180, 114658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, F.; Hao, L.; Du, Y.; Liu, C. Peanut oil-body composition and stability. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2812–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, F.; Xia, Y.; Liu, B. Physicochemical and rheological properties of peanut oil-body following alkaline pH treatment. LWT 2022, 154, 112590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xiao, B.; Yang, G.; Bi, Y.; Chen, F. Rapid salt-assisted microwave demulsification of oil-rich emulsion obtained by aqueous enzymatic extraction of peanut seeds. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 1900120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samira, H.H.; Somayeh, T.D. The study of ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of oil from peanut seeds using response surface methodology. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2018, 120, 1700252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Ding, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, W.; Hu, C.; He, D.; Wang, X. Characteristics and antioxidant activity of walnut oil using various pretreatment and processing technologies. Foods 2022, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Yao, F.; Chen, F. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of peanut oil-body and protein and evaluation of its physicochemical and functional properties. Int. J. Food Eng. 2021, 17, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamdar, S.N.; Rajalakshmi, V.; Pednekar, M.D.; Juan, F.; Yardi, V.; Sharma, A. Influence of degree of hydrolysis on functional properties, antioxidant activity and ace inhibitory activity of peanut protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, K.N.; Kinsella, J.E. Emulsifying properties of proteins: Evaluation of a turbidimetric technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1978, 26, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, F.; Chen, F. A Novel Strategy for the Demulsification of peanut oil-body by caproic acid. Foods 2023, 12, 3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, D.R.; Pathak, S.S.; Pradhan, R.C. Extraction of oil from terminalia chebula kernel by using ultrasound technology: Influence of process parameters on extraction kinetics. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 171, 113893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, C. Peanut oil and protein extraction using an aqueous enzymatic method and analysis of the characteristics of the emulsions produced. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100, 762–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, T.; Tang, G.; Song, G.; Li, L.; Yuan, T.; Zheng, F.; Gong, J. Ultrasound-assisted aqueous enzymatic extraction of gardenia fruits (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis) oil: Optimization and quality evaluation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 191, 116021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Luo, M.; Sun, A. Optimization of aqueous enzymatic extraction of castor (Ricinus communis) seeds oil using response surface methodology. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2019, 13, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvardi, M.; Rezaei, K.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E. Optimization of the aqueous enzymatic extraction of oil from iranian wild almond. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanock, L.R.; Baran, B.E.; Gentry, W.A.; Pattison, S.C.; Heggestad, E.D. Polynomial regression with response surface analysis: A powerful approach for examining moderation and overcoming limitations of difference scores. J. Bus. Psychol. 2010, 25, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, F.; Hao, L. Effect of physiochemical factors and peanut varieties on the charge stability of oil bodies extracted by aqueous method. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, M.; Sentí, M.; Elosua, R.; Vila, J.; Sala, J.; Masià, R.; Marrugat, J. Interaction between the Gln–Arg 192 variants of the paraoxonase gene and oleic acid intake as a determinant of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and paraoxonase activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 432, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.B.; Lunt, D.K.; Smith, D.R.; Walzem, R.L. Producing high-oleic acid beef and the impact of ground beef consumption on risk factors for cardiovascular disease: A review. Meat Sci. 2020, 163, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Hao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liang, D.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M. Physicochemical properties, fatty acid compositions, bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and thermal behavior of rice bran oil obtained with aqueous enzymatic extraction. LWT 2021, 149, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.P.; Price, K.M.; Dean, L.L.; Sweigart, D.S.; Cottonaro, J.M.; Sanders, T.H. Peanut Oil Stability and Physical Properties Across a Range of Industrially Relevant Oleic Acid/Linoleic Acid Ratios. Peanut Sci. 2016, 43, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.C.; Vuong, D.P.; Nguyen, N.T.T.; Nguyen, N.P.; Su, C.-H.; Wang, F.-M.; Juan, H.-Y. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of polyunsaturated fatty acid–rich sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) seed oil: An eco-friendly approach. LWT 2020, 133, 109992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, D.S.; Fanhani, A.; Stevanato, N.; Silva, C. Sunflower oil from enzymatic aqueous extraction process: Maximization of FOY and oil characterization. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e131691-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Suárez, P.; Rosales-Quintero, A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Pola-Sánchez, E.; Hernández-Cruz, M.C.; Ovando-Chacón, S.L.; Rodrigues, R.C.; Tacias-Pascacio, V.G. Aqueous enzymatic extraction of Ricinus communis seeds oil using Viscozyme L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 170, 113811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, H. An efficient ultrasound-assisted extraction method of pea protein and its effect on protein functional properties and biological activities. LWT 2020, 127, 109348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Functional properties and structural characteristics of phosphorylated pea protein isolate. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Factor Levels | Independent Variables | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | |
| amount of fatty acid added (%) | solid–liquid ratio (w/v) | reaction temperature (°C) | reaction time (min) | |
| −1 | 0.5 | 1:3 | 60 | 40 |
| 0 | 1.0 | 1:4 | 70 | 50 |
| 1 | 1.5 | 1:5 | 80 | 60 |
| Oil (%) | Protein (%) | Water (%) | Ash (%) | Phospholipid (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peanut | 53.10 ± 0.24 | 21.05 ± 0.18 | 3.30 ± 0.06 | 2.37 ± 0.05 | 0.56 ± 0.04 |
| oil body emulsion | 69.30 ± 1.07 | 1.79 ± 0.24 | 23.29 ± 0.64 | 0.2 ± 0.01 | 0.75 ± 0.03 |
| Run | X1 (%) | X2 (w/v) | X3 (°C) | X4 (min) | Y (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 90.56 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 88.97 |
| 3 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 86.78 |
| 4 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 89.45 |
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 89.86 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.06 |
| 7 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 86.9 |
| 8 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 90.08 |
| 9 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 86.1 |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 93.51 |
| 11 | 0 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 93.8 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 89.32 |
| 13 | 0 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 89.97 |
| 14 | −1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 85.59 |
| 15 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 90.29 |
| 16 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 87.38 |
| 17 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 91.78 |
| 18 | 0 | 1 | 0 | −1 | 87.76 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 94.19 |
| 20 | 0 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 86.77 |
| 21 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 85.43 |
| 22 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 88.29 |
| 23 | 1 | −1 | 0 | 0 | 94.21 |
| 24 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0 | 92.64 |
| 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 93.56 |
| 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 93.2 |
| 27 | −1 | 0 | 0 | −1 | 86.56 |
| 28 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 95.45 |
| 29 | 0 | −1 | 0 | −1 | 86.43 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean of Square | F Value | p Value | Significant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 256.65 | 14 | 18.33 | 21.09 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X1 | 30.05 | 1 | 30.05 | 34.57 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X2 | 29.58 | 1 | 29.58 | 34.03 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X3 | 7.79 | 1 | 7.79 | 8.96 | 0.0097 | * |
| X4 | 6.69 | 1 | 6.69 | 7.70 | 0.0149 | * |
| X1X2 | 39.94 | 1 | 39.94 | 45.95 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X1X3 | 0.3721 | 1 | 0.3721 | 0.4280 | 0.5236 | NS |
| X1X4 | 0.0110 | 1 | 0.0110 | 0.0127 | 0.9119 | NS |
| X2X3 | 0.3306 | 1 | 0.3306 | 0.3803 | 0.5473 | NS |
| X2X4 | 20.39 | 1 | 20.39 | 23.45 | 0.0003 | * |
| X3X4 | 8.35 | 1 | 8.35 | 9.61 | 0.0078 | * |
| X12 | 62.68 | 1 | 62.68 | 72.10 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X22 | 52.40 | 1 | 52.40 | 60.28 | <0.0001 | ** |
| X32 | 17.15 | 1 | 17.15 | 19.73 | 0.0006 | * |
| X42 | 37.51 | 1 | 37.51 | 43.15 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Residual | 12.17 | 14 | 0.8693 | |||
| Lack of fit | 9.24 | 10 | 0.9237 | 1.26 | 0.4447 | NS |
| Pure error | 2.93 | 4 | 0.7334 | |||
| Cor total | 268.82 | 28 | ||||
| R2 | 0.9547 | |||||
| Adj.R2 | 0.9095 | |||||
| Pre.R2 | 0.7850 | C.V. | 1.04 |
| Fatty Acids | SE | HD | FTHD | IPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmitic acid (16:0) | 12.32 ± 0.01 a | 11.97 ± 0.02 a | 11.95 ± 0.04 b | 12.00 ± 0.02 a |
| Stearic acid (18:0) | 4.01 ± 0.02 a | 3.95 ± 0.00 ab | 3.95 ± 0.01 b | 4.00 ± 0.04 ab |
| Oleic acid (18:1) | 37.90 ± 0.02 ab | 38.02 ± 0.04 a | 37.65 ± 0.13 c | 37.70 ± 0.1 bc |
| Linoleic acid (18:2) | 39.53 ± 0.03 c | 39.97 ± 0.01 b | 40.27 ± 0.07 a | 40.01 ± 0.01 b |
| Arachidic acid (20:0) | 1.56 ± 0.00 a | 1.56 ± 0.01 a | 1.55 ± 0.01 a | 1.57 ± 0.01 a |
| Arachidonic acid (20:1) | 0.83 ± 0.01 ab | 0.82 ± 0.02 b | 0.82 ± 0.00 ab | 0.86 ± 0.00 a |
| Behenic acid (22:0) | 2.48 ± 0.02 ab | 2.43 ± 0.01 b | 2.46 ± 0.04 ab | 2.52 ± 0.02 a |
| Tetracosanoic acid (24:0) | 1.37 ± 0.02 a | 1.28 ± 0.05 a | 1.35 ± 0.04 a | 1.34 ± 0.04 a |
| SFA | 21.74 | 21.19 | 21.25 | 21.43 |
| UFA | 78.26 | 78.81 | 78.75 | 78.56 |
| O/L | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.94 |
| Physicochemical Properties | SE | HD | FTHD | IPD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| acid value (mg KOH/g) | 0.43 ± 0.02 c | 0.63 ± 0.02 a | 0.39 ± 0.00 c | 0.55 ± 0.02 b |
| peroxide value (g/100 g) | 0.08 ± 0.00 c | 0.07 ± 0.00 d | 0.09 ± 0.00 b | 0.10 ± 0.00 a |
| saponification value (KOH/g) | 175.84 ± 0.11 c | 189.2 ± 0.07 a | 187.09 ± 1.32 a | 184.11 ± 0.67 b |
| iodine value (g I2/100 g) | 106.81 ± 1.21 ab | 109.33 ± 0.14 a | 108.39 ± 0.74 ab | 106.57 ± 1.1 b |
| Amino Acid | AEEP | CPPP |
|---|---|---|
| Aspartic acid (Asp) | 11.94 ± 0.01 a | 11.61 ± 0.01 b |
| * Threonine (Thr) | 3.23 ± 0.06 a | 3.31 ± 0.01 a |
| Serine (Ser) | 5.27 ± 0.01 a | 5.27 ± 0.01 a |
| Glutamic acid (Glu) | 18.06 ± 0.01 a | 17.86 ± 0.01 a |
| Glycine (Gly) | 3.89 ± 0.01 a | 4.145 ± 0.05 b |
| Alanine (Ala) | 3.06 ± 0.01 a | 3.11 ± 0.01 a |
| Cystine (Cys) | 2.28 ± 0.06 a | 2.12 ± 0.01 a |
| * Valine (Val) | 3.66 ± 0.01 a | 3.79 ± 0.01 b |
| * Methionine (Met) | 2.755 ± 0.01 a | 2.7 ± 0.01 b |
| * Isoleucine (Ile) | 4.1 ± 0.01 a | 3.97 ± 0.01 b |
| * Leucine (Leu) | 6.83 ± 0.01 a | 6.62 ± 0.03 b |
| Tyrosine (Tyr) | 5.41 ± 0.01 a | 4.79 ± 0.03 a |
| * Phenylalanine (Phe) | 6 ± 0.01 a | 5.62 ± 0.01 a |
| Histidine (His) | 3.25 ± 0.01 a | 3.17 ± 0.01 b |
| Lysine (Lys) | 4.22 ± 0.01 a | 4.54 ± 0.01 b |
| Arginine (Arg) | 10.87 ± 0.04 a | 11.265 ± 0.04 b |
| Proline (Pro) | 5.16 ± 0.01 a | 6.13 ± 0.00 a |
| Essential AA | 30.80 ± 0.02 a | 30.54 ± 0.06 b |
| Hydrophobic AA | 35.46 ± 0.10 b | 36.08 ± 0.01 a |
| Functional Property | Solubility (%) | Water Holding (g/g) | Oil Holding (g/g) | Emulsifying Activity (m2/g) | Emulsifying Stability (%) | Foaming Property (%) | Foaming Stability (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEEP | 11.95 ± 0.16 b | 1.89 ± 0.11 a | 2.43 ± 0.01 a | 45.71 ± 0.12 a | 58.44 ± 1.79 a | 20.70 ± 0.14 a | 52.66 ± 0.32 a |
| CPPP | 12.96 ± 0.35 a | 1.41 ± 0.03 b | 2.25 ± 0.05 b | 39.70 ± 0.98 b | 53.29 ± 1.55 a | 19.60 ± 0.28 b | 51.55 ± 1.46 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Yang, C.; Liu, K.; Zhu, T.; Duan, X.; Xu, Y. Demulsification of Emulsion Using Heptanoic Acid during Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction and the Characterization of Peanut Oil and Proteins Extracted. Foods 2023, 12, 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193523
Li T, Yang C, Liu K, Zhu T, Duan X, Xu Y. Demulsification of Emulsion Using Heptanoic Acid during Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction and the Characterization of Peanut Oil and Proteins Extracted. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193523
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianci, Chenxian Yang, Kunlun Liu, Tingwei Zhu, Xiaojie Duan, and Yandong Xu. 2023. "Demulsification of Emulsion Using Heptanoic Acid during Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction and the Characterization of Peanut Oil and Proteins Extracted" Foods 12, no. 19: 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193523
APA StyleLi, T., Yang, C., Liu, K., Zhu, T., Duan, X., & Xu, Y. (2023). Demulsification of Emulsion Using Heptanoic Acid during Aqueous Enzymatic Extraction and the Characterization of Peanut Oil and Proteins Extracted. Foods, 12(19), 3523. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193523





