Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Property Changes of Potato Starch after Continuous and Repeated Dry Heat Modification and Its Comparative Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
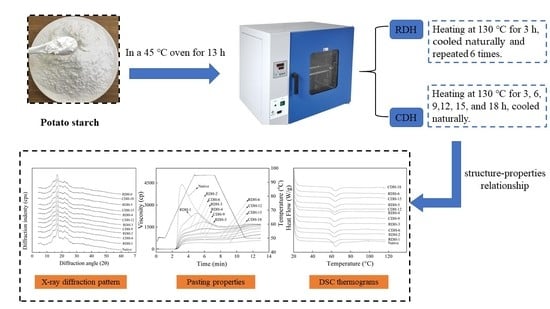
2.2. Dry-Heat Treatments
2.3. Microscopy Analysis
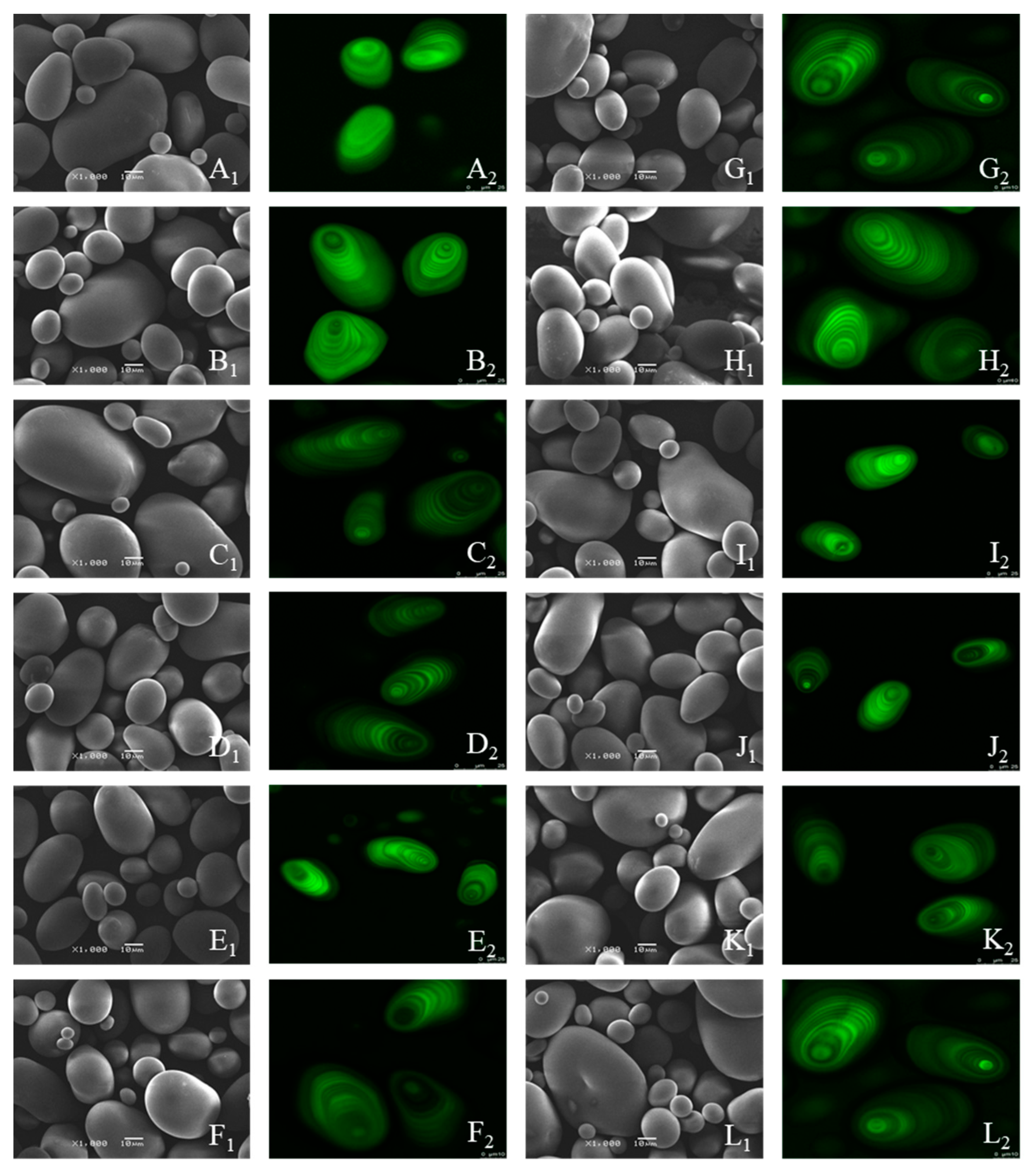
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
2.4. Determination of Molecular Weight Distribution
2.5. X-ray Diffraction (XDR) Analysis
2.6. Solubility (S) and Swelling Power (SP) Measurement
2.7. Light Transmittance Measurement
2.8. Pasting Properties Analysis
2.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.10. In Vitro Digestibility Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphological Structure
3.2. Molecular Weight (Mw) Analysis
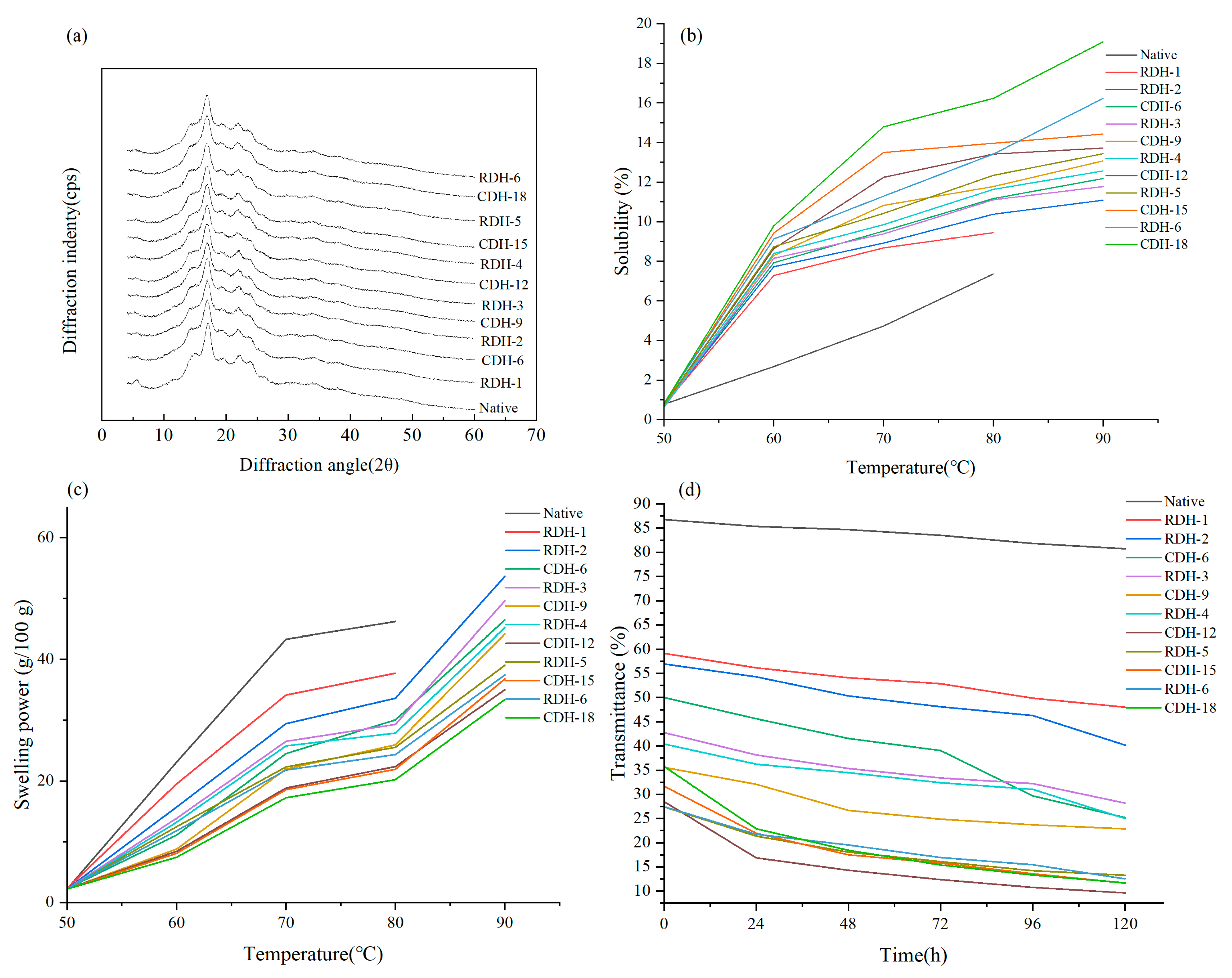
3.3. X-ray Diffraction Patterns
3.4. Starch Solubility and Swelling Power
3.5. Light Transmittance
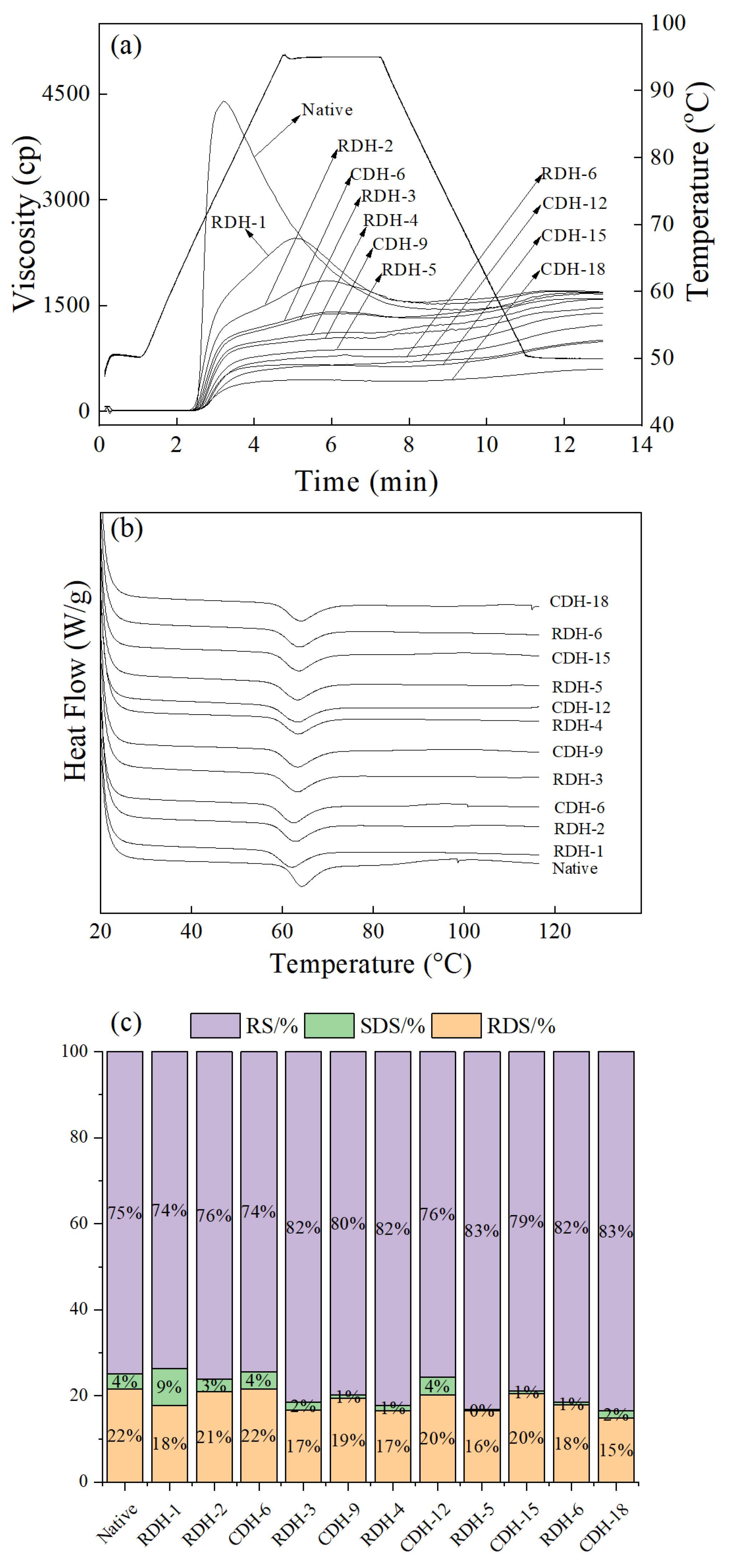
3.6. Pasting Properties
3.7. DSC Analysis
3.8. In Vitro Digestibility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojogbo, E.; Ogunsona, E.O.; Mekonnen, T.H. Chemical and Physical Modifications of Starch for Renewable Polymeric Materials. Mater. Today Sustain. 2020, 7–8, 100028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsik, P.V.; Mazumder, N. Structural and chemical characterization of rice and potato starch granules using microscopy and spectroscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2018, 81, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, P.; D’Agostino, D.; Assif, M.; Todorovic, M.; Pereira, L.S. Assessing potato transpiration, yield and water productivity under various water regimes and planting dates using the FAO dual Kc approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 195, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zeng, X.A.; Yu, S.J.; Zhang, B.S.; Chen, X.D. Effects of pulsed electric fields (PEF) treatment on physicochemical properties of potato starch. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 10, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praznik, W.; Burdicek, G.; Beck, R.H.F. Molecular composition of starches from growing potato tubers. Starch/Stärke 1986, 38, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.J.; Si, F.M.; Xiong, L.; Chu, L.J. Effect of dry heating with ionic gums on physicochemical properties of starch. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarahi, M.; Shahidi, F.; Hedayati, S. Physicochemical, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Native Corn Starch-Mung Bean Protein Isolate Composites. Gels 2022, 8, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.J.; Gong, M.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L. Effect of dry heat treatment on the physicochemical properties and structure of proso millet flour and starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 110, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Sindhu, R.; Panwar, S. Morphology and functionality of dry heat-treated and oxidized quinoa starches. J. Food Process. Pres. 2022, 46, e16672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.Y.; Chai, S.; Xu, M.H.; Ji, J.Y.; Mao, H.J.; Yan, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.G. Effect of dry heating treatment on multi-levels of structure and physicochemical properties of maize starch: A thermodynamic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.Y.; Su, C.Y.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B.; Ge, X.Z.; Li, W.H. Repeated and continuous dry heat treatments induce changes in physicochemical and digestive properties of mung bean starch. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xu, M.J.; Tang, W.; Wen, L.R.; Yang, B. Modification of structural, physicochemical and digestive properties of normal maize starch by thermal treatment. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, I.K.; Bae, I.Y.; Lee, H.G. Effect of dry heat treatment on physical property and in vitro starch digestibility of high amylose rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xu, M.J.; Tian, J.; Li, B. Impact of continuous and repeated dry heating treatments on the physicochemical and structural properties of waxy corn starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, M.; Wu, H.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Jing, L.Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Su, C.Y.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.H. Effects of repeated and continuous dry heat treatments on properties of sweet potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Cui, L.H.; You, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.H.; Qu, W.H.; Liu, P.D.; Ma, D.Y.; Cui, Y.Y. Effects of repeated and continuous dry heat treatments on the physicochemical and structural properties of quinoa starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; Su, C.Y.; Ge, X.Z.; Shen, H.S.; Han, L.H.; Yu, X.Z.; Li, W.H. The influence of repeated versus continuous dry-heating on the performance of wheat starch with different amylose content. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 136, 110380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Guan, L.; Seib, P.A.; Shi, Y.C. Settling volume and morphology changes in cross-linked and unmodified starches from wheat, waxy wheat, and waxy maize in relation to their pasting properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englyst, H.N.; Kingman, S.M.; Cummings, J.H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesan, S.; Govindaraju, I.; Mazumder, N. An Insight into the Ultrastructural and Physiochemical Characterization of Potato Starch: A Review. Am. J. Potato Res. 2020, 97, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Tian, Y.; Wei, B.; Chen, L.; Bi, Y.; Jin, Z. Effect of reaction solvents on the multi-scale structure of potato starch during acid treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandanasree, D.; Khalid Gul, K.; Riar, C.S. Effect of hydrocolloids and dry heat modification on physicochemical, thermal, pasting and morphological characteristics of cassava (Manihot esculenta) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.; Bertoft, E. The molecular structures of starch components and their contribution to the architecture of starch granules: A comprehensive review. Starch/Stärke 2010, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaran, S.; Hoover, R.; Donner, E.; Liu, Q. Composition, structure, morphology and physicochemical properties of lablab bean, navy bean, rice bean, tepary bean and velvet bean starches. Food Chem. 2014, 152, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.H.; Gopal, A.; Malleshi, N.G.; Tharanathan, R.N. Characteristics of native and enzymatically hydrolyzed ragi (Eleusine coracana) and rice (Oryza sativa) starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.J.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Gong, B.; Li, B.; Jing, L.Z.; Gou, M.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.H. The effect of repeated versus continuous annealing on structural, physicochemical, and digestive properties of potato starch. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Liu, J.B.; Zhang, Q.R.; Lin, Q.; Liu, R.; Xing, Y.N.; Jiang, H. 3D printing performance using radio frequency electro-magnetic wave modified potato starch. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2022, 80, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.L.; Ezequiel, D.C.; Leonel, M.D. Crystallinity, thermal and pasting properties of starches from different potato cultivars grown in brazil. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 144–149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.M.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wang, R.R.; Li, J.W.; Pan, W.T.; Zhang, X.W.; Xiao, W.H.; Wen, H.L.; Xie, J.H. Chestnut starch modification with dry heat treatment and addition of xanthan gum: Gelatinization, structural and functional properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Hao, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Q.Y. Effects of dry heat treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of waxy potato starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, S. Influence of heat-moisture treatment (HMT) on physicochemical and functional properties of starches from different Indian oat (Avena sativa L.) cultivars. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.H.; Gao, J.M.; Wu, G.L.; Zheng, J.M.; Ouyang, S.H.; Luo, Q.G.; Zhang, G.Q. Physicochemical and structural properties of A- and B-starch isolated from normal and waxy wheat: Effects of lipids removal. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 60, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Yang, Y.J.; Chung, H.J.; Lim, S.T. Effect of Dry Heating on Physicochemical Properties of Pregelatinized Rice Starch. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, H.; Mahanta, C.L.; Singh, V.; Das, B.B.; Rahman, N. Physical, physicochemical and nutritional characteristics of Bhoja chaul, a traditional ready-to-eat dry heat parboiled rice product processed by an improvised soaking technique. Food Chem. 2016, 191, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, B.R.; Abraão, A.S.; Lemos, A.M.; Nunes, F.M. Chemical composition and functional properties of native chestnut starch (Castanea sativa Mill). Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Shen, M.Y.; Li, E.P.; Xiao, Y.H.; Wen, H.L.; Ren, Y.M.; Xie, J.H. Effect of Mesona chinensis polysaccharide on pasting, rheological and structural properties of corn starches varying in amylose contents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 230, 115713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Xu, M.J.; Li, B.; Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Ouyang, S.H.; Li, W.H. Repeated heat-moisture treatment exhibits superiorities in modification of structural, physicochemical and digestibility properties of red adzuki bean starch compared to continuous heat-moisture way. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, K.L.; Brand-Miller, J.; Copeland, L. Glycemic effect of potatoes. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.E.; Shoemaker, C.F.; Xu, Z.T.; Zhu, S.; Zhong, F. Effect of dry heat treatment with xanthan on waxy rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.; Gidley, M.J. Loss of crystalline and molecular order during starch gelatinisation: Origin of the enthalpic transition. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 227, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.J.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Liu, Y.; Jing, L.Z.; Zhao, K.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Yang, S.O.; Li, W.H. The Changes in Structural, Physicochemical, and Digestive Properties of Red Adzuki Bean Starch after Repeated and Continuous Annealing Treatments. Starch/Stärke 2018, 70, 1700322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.T.; Zhou, D.N.; Jin, Z.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Chen, H.Q. Effect of repeated heat-moisture treatments on digestibility, physicochemical and structural properties of sweet potato starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Jing, L.Z.; Wu, H.; Gou, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Li, W.H. The molecular mechanism for morphological, crystal, physicochemical and digestible property modification of wheat starch after repeated versus continuous heat-moisture treatment. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamadevan, V.; Bertoft, E.B. Impact of different structural types of amylopectin on retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 80, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Molecular Weight g·mol−1 | RC (%) | Crystal Type | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Ι | Peak II | |||
| Native | 1.75 × 1020 | 3.26 × 1012 | 27.27 ± 0.30 g | B |
| RDH-1 | 2.93 × 1019 | 3.57 × 1012 | 36.42 ± 0.30 e | B |
| RDH-2 | 1.89 × 1019 | 3.57 × 1012 | 43.25 ± 0.17 c | B |
| CDH-6 | 1.23 × 1019 | 2.07 × 1012 | 32.40 ± 0.18 f | B |
| RDH-3 | 6.65 × 1017 | 1.29 × 1011 | 44.60 ± 0.33 b | B |
| CDH-9 | 3.95 × 1018 | 1.02 × 1012 | 19.68 ± 0.25 i | B |
| RDH-4 | 5.61 × 1016 | 7.47 × 1010 | 46.74 ± 0.21 a | B |
| CDH-12 | 1.78 × 1017 | 5.51 × 1010 | 25.01 ± 0.44 h | B |
| RDH-5 | 6.03 × 1018 | 1.29 × 1011 | 37.82 ± 0.06 d | B |
| CDH-15 | 3.00 × 1016 | 6.41 × 1010 | 32.50 ± 0.43 f | B |
| RDH-6 | 1.50 × 1018 | 6.09 × 1011 | 36.35 ± 0.11 e | B |
| CDH-18 | 1.20 × 1017 | 5.14 × 1011 | 36.77 ± 0.13 e | B |
| Sample | PV/cp | TV/cp | FV/cp | BD/cp | SB/cp | PT/min | GT/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | 4437 ± 53 a | 1444 ± 9 b | 1667 ± 6 a | 2994 ± 45 a | 223 ± 3 e | 3.20 ± 0.00 f | 67.80 ± 0.07 cde |
| RDH-1 | 2451 ± 1 b | 1517 ± 35 a | 1683 ± 14 a | 935 ± 33 b | 167 ± 21 f | 5.10 ± 0.04 e | 66.50 ± 0.64 f |
| RDH-2 | 1843 ± 13 c | 1470 ± 68 ab | 1665 ± 25 a | 373 ± 55 c | 195 ± 43 ef | 5.70 ± 0.24 de | 66.97 ± 0.04 ef |
| CDH-6 | 1420 ± 19 d | 1327 ± 9 c | 1597 ± 9 b | 93 ± 10 d | 271 ± 1 d | 6.00 ± 0.18 bcd | 67.42 ± 0.67 def |
| RDH-3 | 1354 ± 44 e | 1297 ± 50 c | 1655 ± 30 a | 58 ± 6 de | 358 ± 20 c | 6.07 ± 0.19 bcd | 67.80 ± 0.07 cde |
| CDH-9 | 1028 ± 23 g | 1009 ± 38 e | 1463 ± 9 c | 19 ± 16 e | 454 ± 29 b | 5.77 ± 0.71 cde | 68.22 ± 0.60 cd |
| RDH-4 | 1112 ± 12 f | 1097 ± 14 d | 1566 ± 32 b | 15 ± 2 e | 465 ± 18 b | 6.53 ± 0.28 abc | 67.80 ± 0.07 cde |
| CDH-12 | 668 ± 8 j | 656 ± 0 h | 1012 ± 10 f | 12 ± 8 e | 356 ± 10 c | 6.67 ± 0.19 ab | 70.17 ± 0.04 a |
| RDH-5 | 872 ± 7 h | 865 ± 6 f | 1387 ± 5 d | 8 ± 1 e | 522 ± 1 a | 6.97 ± 0.05 a | 68.60 ± 0.07 bc |
| CDH-15 | 661 ± 2 j | 631 ± 2 h | 979 ± 9 f | 30 ± 0 e | 349 ± 6 c | 5.04 ± 0.05 e | 69.37 ± 0.11 ab |
| RDH-6 | 778 ± 32 i | 758 ± 16 g | 1211 ± 13 e | 20 ± 16 e | 454 ± 4 b | 6.07 ± 0.37 bcd | 69.40 ± 1.06 ab |
| CDH-18 | 458 ± 16 k | 437 ± 18 i | 628 ± 45 g | 22 ± 2 e | 192 ± 28 ef | 5.97 ± 0.62 bcd | 70.25 ± 0.00 a |
| Sample | To/°C | Tp/°C | Tc/°C | ΔT/°C | ΔH/J·g−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native | 60.83 ± 0.31 a | 64.05 ± 0.25 a | 72.21 ± 0.18 ab | 11.38 ± 0.49 d | 14.10 ± 0.15 a |
| RDH-1 | 57.18 ± 0.08 e | 61.80 ± 0.23 g | 69.72 ± 0.69 d | 12.54 ± 0.61 bc | 12.33 ± 0.24 f |
| RDH-2 | 58.20 ± 0.23 cd | 62.71 ± 0.27 f | 70.66 ± 0.50 cd | 12.46 ± 0.27 c | 12.72 ± 0.10 ef |
| CDH-6 | 57.79 ± 0.13 d | 62.54 ± 0.20 f | 71.28 ± 0.25 bc | 13.49 ± 0.37 ab | 13.65 ± 0.40 abc |
| RDH-3 | 58.63 ± 0.05 b | 63.13 ± 0.10 de | 71.77 ± 0.81 ab | 13.14 ± 0.86 abc | 13.33 ± 0.18 bcde |
| CDH-9 | 58.50 ± 0.15 bc | 62.87 ± 0.30 ef | 71.81 ± 0.75 ab | 13.32 ± 0.60 abc | 13.43 ± 0.35 abcd |
| RDH-4 | 58.70 ± 0.11 b | 63.36 ± 0.04 cd | 72.39 ± 0.19 a | 13.69 ± 0.30 a | 12.86 ± 0.42 def |
| CDH-12 | 58.12 ± 0.13 cd | 63.29 ± 0.06 d | 72.12 ± 0.44 ab | 14.00 ± 0.57 a | 13.13 ± 0.52 cde |
| RDH-5 | 58.47 ± 0.28 bc | 63.39 ± 0.22 cd | 72.35 ± 0.37 a | 13.88 ± 0.10 a | 13.24 ± 0.19 bcde |
| CDH-15 | 58.74 ± 0.01 b | 63.54 ± 0.18 bcd | 72.26 ± 0.25 ab | 13.52 ± 0.26 ab | 13.85 ± 0.10 ab |
| RDH-6 | 58.83 ± 0.15 b | 63.72 ± 0.05 abc | 72.43 ± 0.25 a | 13.61 ± 0.40 a | 13.28 ± 0.35 bcde |
| CDH-18 | 58.84 ± 0.33 b | 63.85 ± 0.04 ab | 72.56 ± 0.44 a | 13.72 ± 0.11 a | 13.87 ± 0.40 ab |
| Sample | RDS/% | SDS/% | RS/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native | 21.55 ± 0.17 a | 3.57 ± 0.08 c | 74.88 ± 0.47 g |
| RDH-1 | 17.73 ± 0.14 f | 8.60 ± 0.10 a | 73.67 ± 0.22 i |
| RDH-2 | 20.96 ± 0.08 b | 3.00 ± 0.05 d | 76.04 ± 0.06 e |
| CDH-6 | 21.67 ± 0.08 a | 3.88 ± 0.06 b | 74.45 ± 0.12 h |
| RDH-3 | 16.74 ± 0.10 g | 1.74 ± 0.03 e | 81.52 ± 0.11 c |
| CDH-9 | 19.42 ± 0.06 d | 0.85 ± 0.06 g | 79.73 ± 0.08 d |
| RDH-4 | 16.55 ± 0.06 h | 1.18 ± 0.15 f | 82.27 ± 0.11 b |
| CDH-12 | 20.28 ± 0.06 c | 4.02 ± 0.19 b | 75.70 ± 0.17 f |
| RDH-5 | 16.49 ± 0.03 h | 0.30 ± 0.00 i | 83.21 ± 0.03 a |
| CDH-15 | 18.44 ± 0.08 e | 0.64 ± 0.00 h | 71.12 ± 0.17 j |
| RDH-6 | 17.82 ± 0.03 f | 0.63 ± 0.00 h | 81.47 ± 0.15 c |
| CDH-18 | 14.81 ± 0.06 i | 1.76 ± 0.12 e | 83.44 ± 0.08 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, W. Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Property Changes of Potato Starch after Continuous and Repeated Dry Heat Modification and Its Comparative Study. Foods 2023, 12, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020335
Guo S, Wu H, Liu X, Zhao W, Zheng J, Li W. Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Property Changes of Potato Starch after Continuous and Repeated Dry Heat Modification and Its Comparative Study. Foods. 2023; 12(2):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020335
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Shuangfeng, Hao Wu, Xinyue Liu, Wenqing Zhao, Jiayu Zheng, and Wenhao Li. 2023. "Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Property Changes of Potato Starch after Continuous and Repeated Dry Heat Modification and Its Comparative Study" Foods 12, no. 2: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020335
APA StyleGuo, S., Wu, H., Liu, X., Zhao, W., Zheng, J., & Li, W. (2023). Structural, Physicochemical and Digestive Property Changes of Potato Starch after Continuous and Repeated Dry Heat Modification and Its Comparative Study. Foods, 12(2), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020335