Effect of Juglone and Other Allelochemicals in Walnut Leaves on Yield, Quality and Metabolites of Snack Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Growing Conditions
2.3. Chemicals, Plant Material, and Preparation of J. regia Leaf Extract
2.4. Sampling of the Plants
2.5. Extraction of the Phenolic Compounds
2.6. HPLC–Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Individual Phenolic Compounds
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of Individual Phenolic Compounds
3.2. Effects of Juglone Treatments on Cucumber Yield and Quality
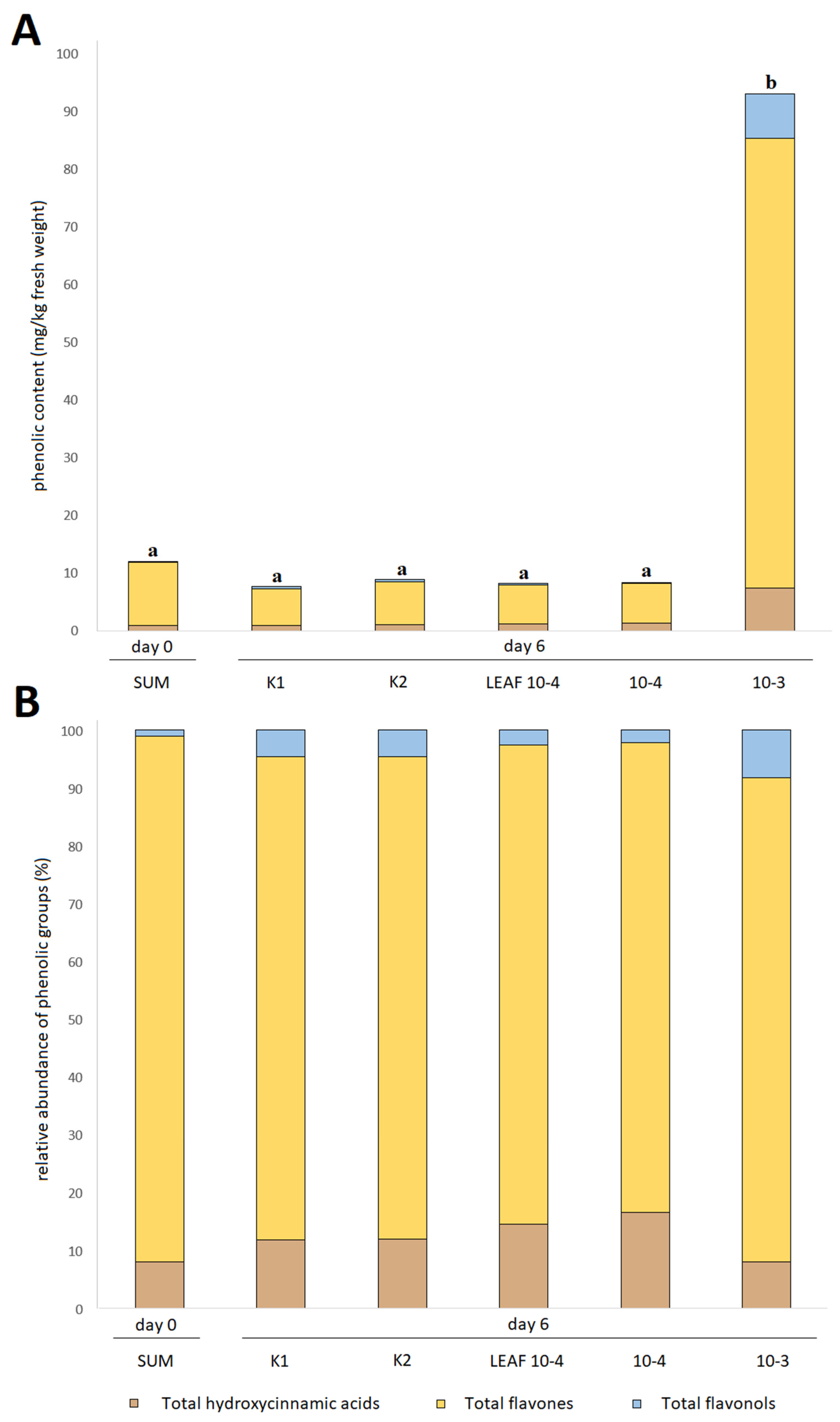
3.3. Effects of Juglone Treatments on Phenolic Composition of Cucumber Fruit
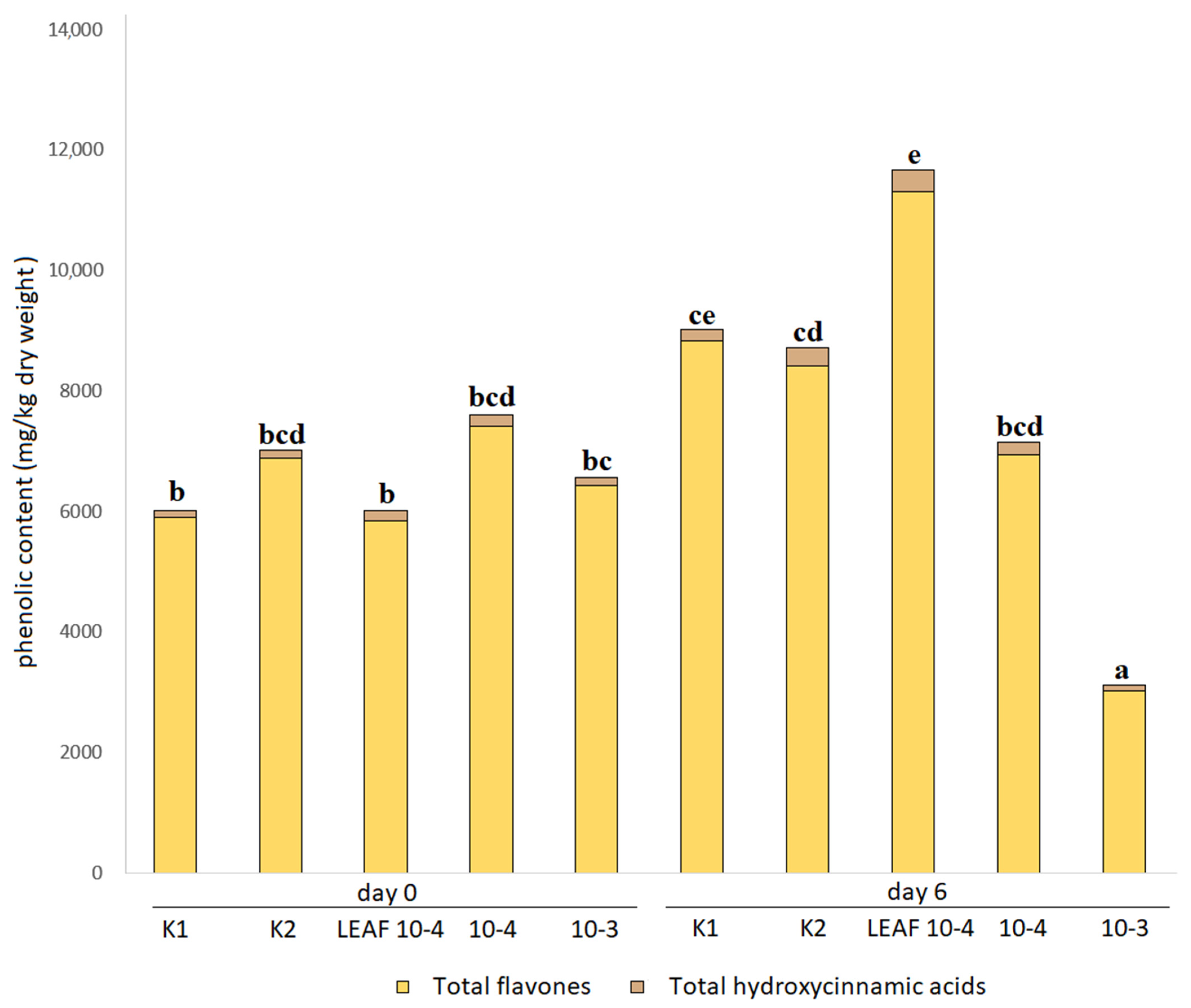
3.4. Effects of Juglone Treatments on Phenolic Composition of Cucumber Leaves
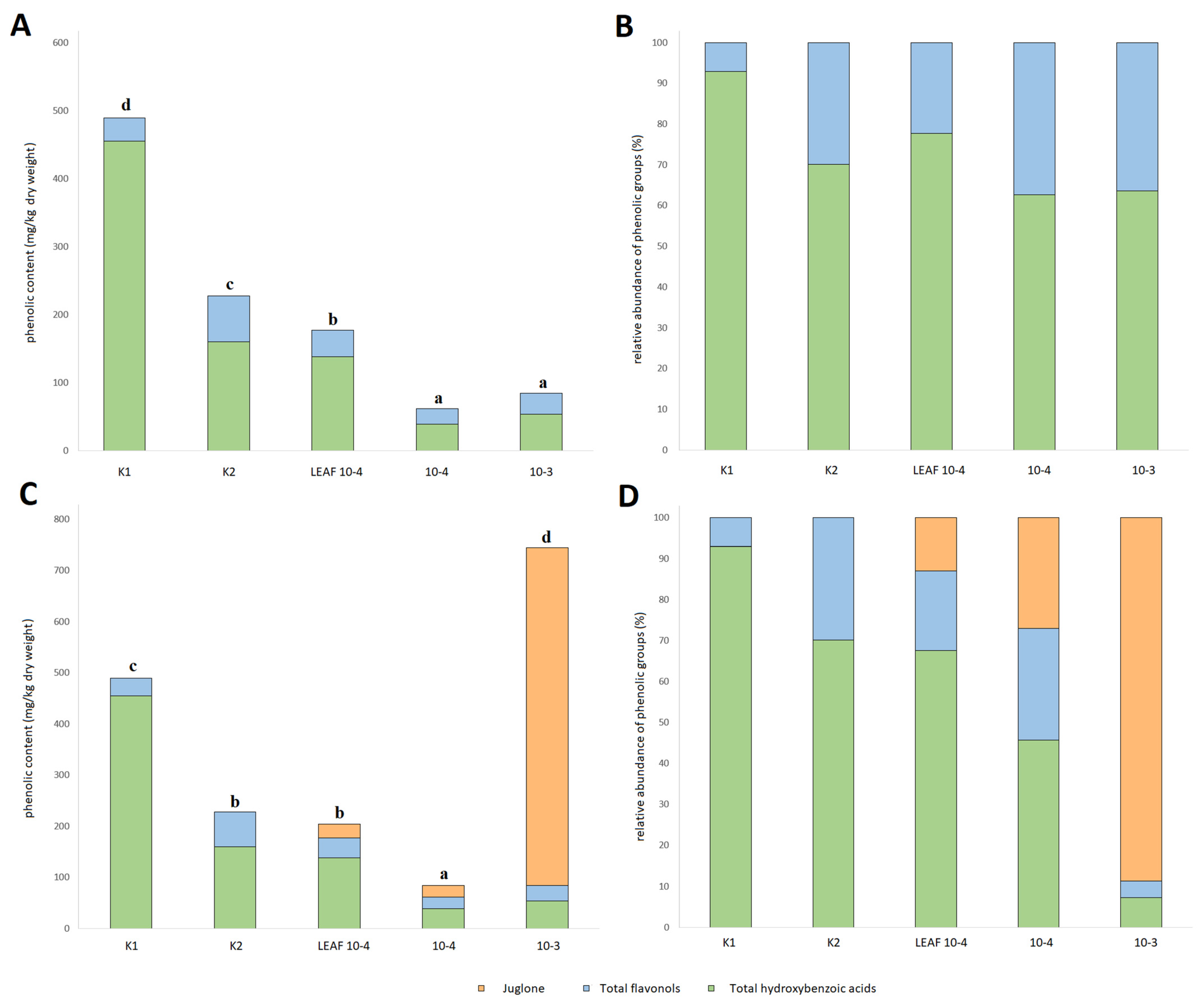
3.5. Effects of Juglone Treatments on Phenolic Composition of Cucumber Roots
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatlioglu, T. Cucumber: Cucumis sativus L. In Genetic Improvement of Vegetable Crops, 1st ed.; Kalloo, G., Bergh, B.O., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Exeter, UK, 1993; pp. 197–227. [Google Scholar]
- Staub, J.E.; Robbins, M.D.; Wehner, T.C. Cucumber. In Vegetables I: Asteraceae, Brassicaceae, Chenopodicaceae, and Cucurbitaceae; Prohens-Tomás, J., Nuez, F., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 241–282. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.; Shanks, C.B. Quality of Vegetables Based on Total Phenolic Concentration Is Lower in More Rural Consumer Food Environments in a Rural American State. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.H. Health-Promoting Components of Fruits and Vegetables in the Diet. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2013, 4, 384S–392S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, S.; Mussatto, S.I.; Martinez-Avila, G.; Montañez-Saenz, J.; Aguilar, C.N.; Teixeira, J.A. Bioactive phenolic compounds: Production and extraction by solid-state fermentation. A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Weng, Q.; Xu, M. Walnut Polyphenol Extract Protects against Fenitrothion-Induced Immunotoxicity in Murine Splenic Lymphocytes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Câmara, C.R.S.; Schlegel, V. A Review on the Potential Human Health Benefits of the Black Walnut: A Comparison with the English Walnuts and Other Tree Nuts. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 2175–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noia, J. Defining Powerhouse Fruits and Vegetables: A Nutrient Density Approach. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11, E95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medic, A.; Solar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R. Phenolic Response to Walnut Anthracnose (Ophiognomonia leptostyla) Infection in Different Parts of Juglans regia Husks, Using HPLC-MS/MS. Agriculture 2021, 11, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Stepp, J.R. Beyond yields: Climate change effects on specialty crop quality and agroecological management. Elementa Sci. Anthr. 2016, 4, 000092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.-H.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, X.; Pan, C.-D.; Jiang, D.-A. Phenolics and Plant Allelopathy. Molecules 2010, 15, 8933–8952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medic, A.; Zamljen, T.; Slatnar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R. Is Juglone the Only Naphthoquinone in Juglans regia L. with Allelopathic Effects? Agriculture 2021, 11, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mominul-Islam, A.K.M.; Widhalm, J.R. Agricultural Uses of Juglone: Opportunities and Challenges. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ercisli, S.; Turkkal, C. Allelopathic effects of juglone and walnut leaf extracts on growth, fruit yield and plant tissue composition in strawberry cvs. ‘Camarosa’ and ‘Sweet Charlie’. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2005, 80, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Scisciolo, B.; Leopold, D.J.; Walton, D.C. Seasonal patterns of juglone in soil beneath Juglans nigra (black walnut) and influence of J. nigra on understory vegetation. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 1111–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duroux, L.; Delmotte, F.M.; Lancelin, J.-M.; Kéravis, G.; Jay-Allemand, C. Insight into naphthoquinone metabolism: β-glucosidase-catalysed hydrolysis of hydrojuglone β-d-glucopyranoside. Biochem. J. 1998, 333, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubay, P.; Kunzelmann, J.; Ittzés, A.; Zámboriné, N.; Szabó, K. Allelopathic effects of leachates of Juglans regia L., Populus tremula L. and juglone on germination of temperate zone cultivated medicinal and aromatic plants. Agrofor. Syst. 2021, 95, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliskan, I.K.; Terzi, I. Allelopathic effects of walnut leaf extracts and juglone on seed germination and seedling growth. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, A.; Zamljen, T.; Grohar, M.C.; Slatnar, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R. Using HPLC–MS/MS to Assess the Quality of Beet, Mizuna, Lettuce and Corn Salad after Juglone and Walnut Leaf Extract Treatments. Agronomy 2022, 12, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamljen, T.; Medic, A.; Hudina, M.; Veberic, R.; Slatnar, A. Salt Stress Differentially Affects the Primary and Secondary Metabolism of Peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) According to the Genotype, Fruit Part, and Salinity Level. Plants 2022, 11, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suojala-Ahlfors, T. Fruit Firmness of Pickling Cucumber Cultivars. Horttechnology 2005, 15, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou-Zaid, M.M.; Lombardo, D.A.; Kite, G.C.; Grayer, R.J.; Veitch, N.C. Acylated flavone C-glycosides from Cucumis sativus. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Nema, N.K.; Maity, N.; Sarkar, B.K. Phytochemical and therapeutic potential of cucumber. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzat, S.M.; Raslan, M.; Salama, M.M.; Menze, E.T.; El Hawary, S.S. In vivo anti-inflammatory activity and UPLC-MS/MS profiling of the peels and pulps of Cucumis melo var. cantalupensis and Cucumis melo var. reticulatus. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 237, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Reidah, I.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. HPLC–ESI-Q-TOF-MS for a comprehensive characterization of bioactive phenolic compounds in cucumber whole fruit extract. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, F.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, M.N.; Shah, S.M.Z.; Kandel, R.C.; Aziz, N.; Adhikari, A.; Choudhary, M.I.; Ur-Rahman, A.; El-Seedi, H.R.; et al. Metabolite Profiling and Quantitation of Cucurbitacins in Cucurbitaceae Plants by Liquid Chromatography coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamljen, T.; Hudina, M.; Veberič, R.; Slatnar, A. Biostimulative effect of amino acids and green algae extract on capsaicinoid and other metabolite contents in fruits of Capsicum spp. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahyazadeh, M.; Nowak, M.; Kima, H.; Selmar, D. Horizontal natural product transfer: A potential source of alkaloidal contaminants in phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medic, A.; Jakopic, J.; Hudina, M.; Solar, A.; Veberic, R. Identification and quantification of major phenolic constituents in Juglans regia L. leaves: Healthy vs. infected leaves with Xanthomonas campestris pv. juglandis using HPLC-MS/MS. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.J.; Crespo, J.F.; Cabanillas, B. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strugstad, M.; Despotovski, S. A Summary of Extraction, Synthesis, Properties, and Potential Uses of Juglone: A Literature Review. J. Ecosyst. Manag. 2012, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | Rt (min) | [M-H]− (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | MS3 (m/z) | Fruit | Leaves | Roots |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeic acid derivative 1 | 10.21 | 447 | 401(100), 179(4) | 179(100) | x | ||
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 1 | 10.81 | 755 | 593(100), 455(71), 413(45), 293(12) | 473(100), 413(93), 293(20) | x | ||
| Caffeic acid derivative 2 | 11.50 | 447 | 401(100), 179(4) | 179(100) | x | ||
| Ferulic acid hexoside derivative | 12.12 | 401 | 355(100), 193(20) | 193(100) | x | x | |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 2 | 12.75 | 755 | 593(100), 455(71), 413(45), 293(12) | 473(100), 413(93), 293(20) | x | x | |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 13.65 | 785 | 623(100), 485(85), 443(42), 323(9) | 503(100), 443(69), 323(13) | x | ||
| Sinapic acid hexoside derivative | 14.34 | 431 | 385(100) | 205(100), 153(74), 223(54), 161(23) | x | x | |
| Feruoyl hexoside | 14.43 | 355 | 193(100) | x | |||
| Saponarin (isovitexin-7-O-glucoside)-4-O-glucoside | 14.49 | 623 | 503(100), 533(24), 341(3) | x | x | ||
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 14.83 | 961 | 799(100), 443(15), 323(5) | 443(100), 323(32), 413(26) | x | ||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 14.98 | 931 | 769(100), 413(7), 293(2) | 413(100), 593(70), 293(47) | x | x | |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 1 | 15.22 | 901 | 413(100), 739(98), 781(46), 293(40), 323(20), 341(19) | 293(100) | x | x | |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 15.78 | 961 | 799(100), 443(13), 323(4) | 443(100), 323(32), 413(26) | x | ||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 16.06 | 931 | 769(100), 413(7), 293(2) | 413(100), 593(70), 293(47) | x | x | |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 2 | 16.15 | 901 | 413(100), 739(84), 781(45), 293(34), 341(22), 323(17) | 293(100) | x | x | |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 16.60 | 961 | 799(100), 443(13), 323(3) | 443(100), 323(32), 413(26) | x | ||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 16.71 | 931 | 769(100), 413(7), 293(3) | 413(100), 593(70), 293(47) | x | ||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 3 | 16.96 | 901 | 413(100), 739(92), 781(47), 293(37), 323(18), 341(17) | 293(100) | x | ||
| Benzoic acid | 17.02 | 121 | 93(100), 92(17), 121(16), 75(8), 77(5) | x | |||
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside-glucoside | 17.43 | 947 | 785(100), 429(5) | x | |||
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside | 17.58 | 917 | 755(100) | x | |||
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside derivative | 17.84 | 1073 | 755(100), 911(98), 893(17), 867(15) | x | |||
| Isovitexin-8-C-galactoside | 18.18 | 593 | 413(100), 293(22) | 293(100) | x | ||
| Vicenin 2 (Isovitexin-8-C-glucoside) | 19.04 | 593 | 413(100), 293(21) | 293(100) | x | x | |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-glucoside | 19.54 | 623 | 443(100), 323(21) | 323(100), 365(4) | x | ||
| p-Coumaric acid | 20.41 | 163 | 119(100) | x | |||
| Quercetin-3-O-rutinoside | 20.43 | 609 | 301(100), 300(25), 179(3) | x | |||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-hexoside derivative | 21.10 | 897 | 853(100), 593(30), 413(5), 293(2) | 593(100), 413(17), 293(4) | x | ||
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-derivative | 21.41 | 799 | 443(100), 623(68), 323(31), 413(18), 593(15) | 323(100) | x | ||
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside | 21.68 | 769 | 623(100), 443(70), 413(11), 323(21) | 443(100), 323(22) | x | x | |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 21.83 | 769 | 413(100), 293(46), 593(65) | 293(100), 335(14) | x | ||
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | 21.99 | 739 | 593(100), 413(70), 293(26), 619(10) | 413(100), 293(27) | x | x | |
| Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside | 23.15 | 447 | 301(100), 300(20), 179(2) | x | |||
| Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside | 23.45 | 477 | 314(100), 315(38), 357(29) | x | |||
| Hydrogalic acid | 23.47 | 187 | 125(100) | x | |||
| Juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione) | 26.02 | 189 | 161(100) | x |
| Measurement | K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average weight (g) | 39.5 ± 5.6 c | 36.5 ± 5.4 bc | 49.1 ± 5.3 d | 35.2 ± 4.9 bc | 4.3 ± 1.0 a |
| ΔA | 2.2 ± 0.0 a | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.1 ± 0.0 a | 2.3 ± 0.1 b |
| Soluble solids content (°Bx) | 3.4 ± 0.2 a | 3.5 ± 0.1 a | 4.2 ± 0.1 b | 4.7 ± 0.1 b | 6.2 ± 0.5 c |
| Firmness (N) | 1.8 ± 0.3 a | 1.6 ± 0.2 a | 1.5 ± 0.3 a | 1.5 ± 0.2 a | 4.6 ± 0.6 b |
| Color parameters | |||||
| L* | 31.7 ± 1.1 a | 33.5 ± 0.5 ab | 31.8 ± 0.4 a | 31.6 ± 0.8 a | 35.9 ± 0.8 b |
| a* | −4.6 ± 0.2 a | −5.4 ± 0.1 a | −4.7 ± 0.1 a | −4.4 ± 0.2 a | −3.9 ± 0.2 b |
| b* | 17.1 ± 1.3 a | 20.5 ± 0.7 ab | 18.2 ± 0.5 ab | 17.1 ± 0.9 a | 21.7 ± 0.8 b |
| C* | 17.7 ± 1.4 a | 21.1 ± 0.7 ab | 18.9 ± 0.5 ab | 17.7 ± 0.9 a | 21.9 ± 0.8 b |
| h (°) | 105.0 ± 0.5 b | 104.9 ± 0.3 b | 104.8 ± 0.3 b | 104.6 ± 0.2 b | 100.1 ± 0.5 a |
| Phenolic Compound | Quantification According to Treatment (mg/kg Fresh Weight) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 3 | Day 6 | |||||||||
| SUM | K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | |
| Ferulic acid hexoside derivative | 0.41 ± 0.01 a | 0.67 ± 0.01 ac | 0.47 ± 0.01 ab | 1.07 ± 0.06 c | 0.63 ± 0.03 ab | 0.72 ± 0.05 ac | 0.46 ± 0.02 ab | 0.55 ± 0.01 ab | 0.61 ± 0.01 ab | 0.86 ± 0.04 bc | 5.10 ± 0.26 d |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) | 0.22 ± 0.06 a | 0.46 ± 0.06 a | 0.17 ± 0.11 a | 0.61 ± 0.01 a | 0.71 ± 0.04 a | 1.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.12 ± 0.06 a | 0.13 ± 0.05 a | 0.21 ± 0.05 a | 0.36 ± 0.04 a | 8.13 ± 0.70 b |
| Sinapic acid hexoside derivative | 0.51 ± 0.01 ab | 0.85 ± 0.02 d | 0.50 ± 0.00 ab | 0.60 ± 0.03 bc | 0.63 ± 0.01 bc | 0.72 ± 0.01 cd | 0.42 ± 0.02 a | 0.51 ± 0.02 ab | 0.56 ± 0.01 b | 0.50 ± 0.02 ab | 1.80 ± 0.08 e |
| Feruoyl hexoside | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.45 ± 0.03 b |
| Saponarin (isovitexin-7-O-glucoside)-4-O-glucoside | 0.07 ± 0.02 a | 0.41 ± 0.10 c | 0.14 ± 0.02 ab | 0.14 ± 0.09 ab | 0.15 ± 0.02 ab | 0.28 ± 0.00 bc | 0.09 ± 0.01 ab | 0.12 ± 0.01 ab | 0.17 ± 0.02 ab | 0.13 ± 0.04 ab | 1.40 ± 0.09 d |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 0.53 ± 0.08 ab | 0.71 ± 0.20 ab | 0.53 ± 0.04 ab | 0.84 ± 0.19 b | 1.00 ± 0.02 b | 0.46 ± 0.00 ab | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.41 ± 0.09 a | 0.57 ± 0.07 ab | 0.52 ± 0.06 ab | 7.82 ± 0.15 c |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 1 | 0.14 ± 0.0.03 ab | 0.19 ± 0.10 ab | 0.17 ± 0.01 ab | 0.22 ± 0.10 ab | 0.32 ± 0.02 b | 0.13 ± 0.01 ab | 0.01 ± 0.01 a | 0.06 ± 0.04 ab | 0.08 ± 0.03 ab | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 1.10 ± 0.10 c |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 4.23 ± 0.03 b | 7.50 ± 0.13 e | 4.37 ± 0.08 bc | 5.33 ± 0.26 cd | 5.56 ± 0.12 d | 5.71 ± 0.10 d | 2.60 ± 0.06 a | 3.05 ± 0.06 a | 2.67 ± 0.07 a | 2.50 ± 0.12 a | 22.16 ± 0.66 f |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 2 | 2.82 ± 0.02 b | 5.00 ± 0.09 e | 2.91 ± 0.05 bc | 3.55 ± 0.17 cd | 3.71 ± 0.08 d | 3.81 ± 0.07 d | 1.74 ± 0.04 a | 2.03 ± 0.04 a | 1.78 ± 0.05 a | 1.67 ± 0.08 a | 14.77 ± 0.43 f |
| Vicenin 2 (Isovitexin-8-C-glucoside) | 0.48 ± 0.02 e | 0.33 ± 0.01 bc | 0.34 ± 0.02 bc | 0.35 ± 0.02 bc | 0.44 ± 0.03 de | 0.27 ± 0.00 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.39 ± 0.02 cd |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside | 0.54 ± 0.02 a | 0.89 ± 0.04 a | 0.50 ± 0.00 a | 0.75 ± 0.04 a | 0.90 ± 0.01 a | 0.75 ± 0.01 a | 0.35 ± 0.02 a | 0.34 ± 0.00 a | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.39 ± 0.01 a | 8.36 ± 0.52 b |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | 1.91 ± 0.03 c | 2.49 ± 0.16 d | 1.61 ± 0.06 bc | 1.92 ± 0.11 c | 2.12 ± 0.05 cd | 1.83 ± 0.03 c | 1.00 ± 0.05 a | 1.14 ± 0.03 ab | 0.87 ± 0.03 a | 1.04 ± 0.03 ab | 13.79 ± 0.32 c |
| Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.90 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.06 ab | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | 0.32 ± 0.04 ab | 0.53 ± 0.14 ab | 0.35 ± 0.03 ab | 0.42 ± 0.00 ab | 0.22 ± 0.09 a | 0.18 ± 0.13 a | 7.47 ± 0.32 c |
| Total hydroxycinnamic acids | 0.95 ± 0.01 a | 1.56 ± 0.02 bc | 0.98 ± 0.01 a | 1.68 ± 0.09 c | 1.27 ± 0.02 ac | 1.45 ± 0.05 ac | 0.89 ± 0.03 a | 1.06 ± 0.03 ab | 1.18 ± 0.01 ac | 1.37 ± 0.05 ac | 7.35 ± 0.36 d |
| Total flavones | 10.94 ± 0.17 cd | 17.99 ± 0.39 e | 10.74 ± 0.12 bd | 13.71 ± 0.85 de | 14.90 ± 0.29 de | 14.30 ± 0.23 de | 6.39 ± 0.13 a | 7.45 ± 0.25 abc | 6.80 ± 0.19 ab | 6.78 ± 0.34 ab | 77.93 ± 2.69 f |
| Total flavonols | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.90 ± 0.02 b | 0.31 ± 0.06 ab | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | 0.32 ± 0.04 ab | 0.53 ± 0.14 ab | 0.35 ± 0.03 ab | 0.42 ± 0.00 ab | 0.22 ± 0.09 a | 0.18 ± 0.13 a | 7.47 ± 0.32 c |
| TAPC | 12.02 ± 0.17 ab | 20.44 ± 0.43 c | 12.02 ± 0.18 ab | 15.47 ± 0.96 bc | 16.49 ± 0.30 bc | 16.28 ± 0.27 bc | 7.63 ± 0.14 a | 8.93 ± 0.27 a | 8.20 ± 0.27 a | 8.33 ± 0.53 a | 92.75 ± 3.34 d |
| Phenolic Compound | Quantification According to Treatment (mg/kg Dry Weight) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| day 0 | |||||
| K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | |
| Caffeic acid derivative 1 | 4.2 ± 1.1 a | 6.4 ± 2.0 ab | 7.5 ± 1.0 ac | 8.4 ± 1.4 ac | 6.2 ± 1.9 a |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 1 | 76.3 ± 17.8 ab | 100.3 ± 23.9 ab | 60.2 ± 11.8 a | 76.7 ± 6.8 ab | 110.0 ± 23.0 abc |
| Caffeic acid derivative 2 | 10.8 ± 4.4 abc | 17.2 ± 5.2 ad | 8.1 ± 2.3 ab | 15.1 ± 1.5 ad | 11.0 ± 2.5 abc |
| Ferulic acid hexoside derivative | 13.2 ± 5.0 ab | 15.1 ± 4.2 ab | 12.0 ± 3.9 ab | 18.0 ± 1.8 ab | 14.7 ± 4.3 ab |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 2 | 444.1 ± 61.8 bcd | 473.9 ± 35.5 cde | 331.9 ± 34.5 ac | 334.3 ± 18.3 ac | 570.9 ± 88.8 cde |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 246.2 ± 33.4 cf | 221.5 ± 14.7 ce | 179.6 ± 17.6 acd | 232.9 ± 11.3 cf | 282.1 ± 43.3 def |
| Sinapic acid hexoside derivative | 5.6 ± 2.7 a | 10.0 ± 2.4 a | 7.3 ± 2.2 a | 12.2 ± 2.4 ab | 7.5 ± 2.2 a |
| Saponarin (isovitexin-7-O-glucoside)-4-O-glucoside | 75.8 ± 20.4 ac | 113.2 ± 11.9 bcd | 80.1 ± 13.1 ac | 120.1 ± 11.8 bcd | 117.8 ± 22.5 bcd |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 294.7 ± 57.9 bc | 389.5 ± 5.5 cde | 279.4 ± 27.3 bc | 329.5 ± 13.5 bd | 400.2 ± 56.8 cde |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 354.1 ± 34.7 bc | 467.5 ± 5.7 cd | 338.1 ± 12.8 bc | 475.4 ± 17.0 cd | 362.0 ± 52.6 bc |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 1 | 339.0 ± 17.2 bc | 435.4 ± 10.2 bde | 359.8 ± 24.3 bc | 450.5 ± 26.8 bde | 392.0 ± 54.6 bc |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 302.6 ± 34.4 bd | 337.1 ± 22.2 cd | 237.3 ± 15.2 bc | 316.7 ± 17.0 cd | 303.6 ± 44.1 bd |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 1088.0 ± 185.3 c | 1229.0 ± 97.6 cd | 865.9 ± 86.4 bc | 1027.7 ± 19.2 bc | 872.7 ± 85.2 bc |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 2 | 615.5 ± 34.3 ac | 769.9 ± 14.9 bcd | 547.2 ± 26.9 ab | 734.7 ± 33.3 bcd | 764.3 ± 129.0 bcd |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 37.7 ± 13.0 ad | 62.4 ± 11.2 cd | 55.3 ± 7.9 bcd | 80.1 ± 15.0 d | 44.4 ± 10.5 bcd |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 75.4 ± 20.2 bc | 84.4 ± 13.2 bcd | 75.6 ± 10.2 bc | 94.2 ± 15.3 cd | 89.6 ± 19.3 bcd |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 3 | 85.6 ± 19.4 bd | 103.0 ± 14.1 be | 81.7 ± 8.4 bc | 93.3 ± 13.3 be | 99.1 ± 18.9 be |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside-glucoside | 88.0 ± 26.8 bcd | 98.3 ± 19.0 cd | 89.5 ± 9.9 bcd | 109.1 ± 16.1 cd | 103.0 ± 19.7 cd |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside | 74.6 ± 17.3 bcd | 63.9 ± 9.2 bcd | 74.0 ± 6.5 bcd | 84.3 ± 9.0 d | 80.1 ± 17.7 cd |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside derivative | 36.2 ± 19.4 acd | 88.5 ± 19.8 cf | 59.7 ± 10.1 acef | 75.4 ± 19.1 bcef | 63.7 ± 19.4 acef |
| Isovitexin-8-C-galactoside | 28.9 ± 20.6 ab | 33.8 ± 14.6 ab | 29.4 ± 5.9 ab | 32.1 ± 16.5 ab | 24.7 ± 9.1 ab |
| Vicenin 2 (Isovitexin-8-C-glucoside) | 533.8 ± 17.3 cde | 687.3 ± 25.8 efg | 864.8 ± 38.7 g | 1169.7 ± 44.3 h | 645.9 ± 85.5 df |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-glucoside | 74.2 ± 20.0 dg | 70.2 ± 15.3 def | 105.0 ± 4.8 fg | 125.7 ± 15.2 g | 73.6 ± 15.1 dg |
| p-Coumaric acid | 75.6 ± 3.3 bd | 85.1 ± 2.5 cd | 124.1 ± 4.4 g | 120.7 ± 4.3 fg | 95.0 ± 11.5 cde |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-hexoside derivative | 58.0 ± 12.6 ac | 89.0 ± 16.0 cd | 77.7 ± 7.1 bcd | 87.7 ± 9.6 cd | 60.8 ± 18.3 ac |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-derivative | 98.5 ± 8.6 ce | 81.3 ± 9.4 bcd | 100.7 ± 5.2 ce | 109.0 ± 9.1 ce | 98.5 ± 22.7 ce |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside | 150.0 ± 11.2 cdf | 102.6 ± 10.5 bc | 158.4 ± 8.5 cdf | 180.7 ± 9.6 ef | 151.7 ± 28.6 cdf |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 257.5 ± 2.6 bc | 296.8 ± 5.5 bde | 269.2 ± 10.6 bd | 338.8 ± 12.2 bf | 275.7 ± 36.9 bd |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | 466.8 ± 0.6 bc | 471.5 ± 9.8 bc | 525.3 ± 18.5 bc | 739.1 ± 19.4 e | 436.2 ± 56.8 bc |
| Total flavones | 5901.5 ± 485.6 bc | 6869.6 ± 377.2 bde | 5846.0 ± 352.9 bc | 7417.8 ± 372.3 bde | 6422.7 ± 968.9 bd |
| Total hydroxycinnamic acids | 109.3 ± 15.5 ad | 133.8 ± 14.1 bde | 158.9 ± 13.4 bde | 174.4 ± 11.3 cde | 134.3 ± 20.5 bde |
| TAPC | 6010.8 ± 501.1 c | 7003.4 ± 387.3 cde | 6004.9 ± 365.7 c | 7592.2 ± 383.5 cde | 6557.0 ± 988.1 cd |
| day 3 | |||||
| K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | |
| Caffeic acid derivative 1 | 16.3 ± 1.7 ac | 30.6 ± 1.8 c | 23.1 ± 3.7 ac | 9.9 ± 0.6 ac | 10.9 ± 0.6 ac |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 1 | 131.4 ± 3.3 abd | 241.5 ± 32.8 e | 167.1 ± 12.4 be | 78.1 ± 1.7 ab | 51.0 ± 6.4 a |
| Caffeic acid derivative 2 | 17.3 ± 1.4 ad | 26.4 ± 2.1 d | 14.8 ± 2.8 ad | 8.6 ± 0.1 ab | 5.3 ± 0.2 a |
| Ferulic acid hexoside derivative | 23.1 ± 4.8 ab | 26.3 ± 1.9 ab | 19.0 ± 5.2 ab | 11.7 ± 0.3 ab | 13.0 ± 0.6 a |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 2 | 587.4 ± 46.5 cde | 968.7 ± 87.8 fg | 729.1 ± 17.3 ef | 367.3 ± 9.5 bc | 81.7 ± 5.8 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 289.6 ± 16.6 ef | 271.9 ± 23.8 def | 242.1 ± 7.4 cf | 156.7 ± 2.2 ac | 76.9 ± 5.8 a |
| Sinapic acid hexoside derivative | 14.4 ± 1.0 abc | 15.2 ± 2.0 abc | 11.1 ± 0.8 ab | 13.3 ± 0.5 abc | 12.8 ± 0.8 ab |
| Saponarin (isovitexin-7-O-glucoside)-4-O-glucoside | 144.3 ± 10.5 ce | 159.3 ± 13.8 de | 113.4 ± 11.6 bcd | 68.3 ± 1.2 ab | 38.3 ± 12.7 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 352.7 ± 64.6 bd | 551.9 ± 43.1 ef | 462.0 ± 4.5 cde | 322.8 ± 6.3 bd | 75.9 ± 3.3 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 440.7 ± 15.6 bd | 653.2 ± 54.8 ef | 430.3 ± 9.7 bd | 408.1 ± 10.9 bd | 126.0 ± 7.3 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 1 | 420.0 ± 43.1 bd | 620.9 ± 52.7 ef | 496.7 ± 12.6 cde | 402.0 ± 15.8 bd | 123.8 ± 5.9 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 362.8 ± 22.9 cde | 325.1 ± 22.6 cd | 301.4 ± 6.6 bd | 275.2 ± 4.9 bd | 104.6 ± 4.4 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 1032.0 ± 143.7 bc | 1138.5 ± 84.1 cd | 1027.5 ± 98.5 bc | 1007.1 ± 51.8 bc | 329.9 ± 3.1 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 2 | 796.5 ± 67.4 bcd | 1419.5 ± 153.5 e | 905.2 ± 140.4 bcd | 688.4 ± 62.3 bc | 187.7 ± 22.0 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 62.1 ± 4.4 cd | 50.7 ± 6.4 bcd | 40.4 ± 6.7 ad | 30.0 ± 2.5 ac | 13.1 ± 0.8 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 113.3 ± 8.6 cd | 109.4 ± 12.3 cd | 93.3 ± 8.2 cd | 68.6 ± 3.7 ac | 16.7 ± 1.0 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 3 | 116.3 ± 7.7 cde | 149.8 ± 13.2 ef | 123.4 ± 6.9 cde | 96.2 ± 4.3 be | 21.6 ± 1.1 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside-glucoside | 124.7 ± 11.7 cd | 109.7 ± 12.6 cd | 91.6 ± 9.0 bcd | 74.2 ± 3.9 ad | 17.2 ± 2.0 a |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside | 89.1 ± 8.7 d | 70.7 ± 7.7 bcd | 81.7 ± 2.8 cd | 53.0 ± 4.2 ad | 16.9 ± 0.5 a |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside derivative | 83.5 ± 8.6 cf | 122.3 ± 16.0 f | 50.7 ± 8.6 ace | 52.7 ± 6.7 ace | 7.4 ± 1.3 a |
| Isovitexin-8-C-galactoside | 48.0 ± 5.3 ab | 67.7 ± 9.4 b | 26.8 ± 7.3 ab | 39.5 ± 4.4 ab | 21.2 ± 0.6 ab |
| Vicenin 2 (Isovitexin-8-C-glucoside) | 508.2 ± 22.5 cde | 752.8 ± 59.3 fg | 469.2 ± 11.3 bd | 424.7 ± 16.1 bc | 34.3 ± 0.2 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-glucoside | 99.3 ± 14.2 eg | 59.4 ± 10.4 cdef | 57.1 ± 5.4 bdef | 34.6 ± 4.3 ad | 1.8 ± 0.2 a |
| p-Coumaric acid | 83.5 ± 2.5 cd | 97.7 ± 5.8 def | 111.6 ± 0.5 eg | 54.2 ± 3.0 b | 9.0 ± 0.6 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-hexoside derivative | 71.8 ± 9.2 bcd | 202.2 ± 23.0 e | 62.5 ± 2.0 ac | 76.7 ± 3.4 bcd | 9.2 ± 3.0 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-derivative | 124.1 ± 9.8 de | 75.5 ± 5.7 ac | 101.6 ± 0.4 ce | 76.2 ± 3.0 ac | 30.5 ± 3.4 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside | 166.5 ± 9.7 df | 133.7 ± 9.4 cde | 192.0 ± 3.0 f | 114.1 ± 2.8 cd | 39.1 ± 2.9 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 255.6 ± 11.8 b | 352.2 ± 20.2 bf | 363.4 ± 6.1 cdf | 283.5 ± 6.1 bde | 56.3 ± 4.3 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | 406.0 ± 15.9 b | 692.6 ± 40.5 de | 555.7 ± 8.1 cd | 447.5 ± 6.2 bc | 68.6 ± 6.0 a |
| Total flavones | 6826.0 ± 364.8 bde | 9299.3 ± 745.4 ef | 7184.3 ± 137.0 bde | 5645.5 ± 112.4 b | 1537.9 ± 91.9 a |
| Total hydroxycinnamic acids | 154.7 ± 8.8 bde | 196.2 ± 12.1 e | 179.7 ± 12.2 de | 97.7 ± 2.5 abc | 51.0 ± 2.1 a |
| TAPC | 6980.6 ± 373.4 cde | 9495.5 ± 756.5 ef | 7364.0 ± 146.4 cde | 5743.1 ± 114.5 bc | 1588.9 ± 94.0 a |
| day 6 | |||||
| K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | |
| Caffeic acid derivative 1 | 29.9 ± 2.1 bc | 145.6 ± 1.3 e | 152.7 ± 8.7 e | 80.0 ± 14.0 d | 24.5 ± 0.6 ac |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 1 | 256.1 ± 5.8 e | 212.1 ± 14.1 de | 383.0 ± 29.2 f | 197.6 ± 32.7 cde | 90.1 ± 6.4 ab |
| Caffeic acid derivative 2 | 22.7 ± 0.5 cd | 26.6 ± 2.1 d | 40.8 ± 2.0 e | 21.5 ± 4.0 bd | 10.9 ± 1.2 abc |
| Ferulic acid hexoside derivative | 30.6 ± 1.4 ab | 30.3 ± 3.9 ab | 54.7 ± 6.6 c | 33.0 ± 7.1 b | 16.2 ± 1.4 ab |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside) 2 | 1136.6 ± 42.1 gh | 910.4 ± 25.7 fg | 1334.1 ± 66.5 h | 718.9 ± 106.2 df | 172.3 ± 18.1 ab |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 299.4 ± 2.4 ef | 228.7 ± 13.0 cf | 335.7 ± 15.2 f | 212.0 ± 35.9 ac | 107.3 ± 11.8 a |
| Sinapic acid hexoside derivative | 24.5 ± 1.2 cd | 14.4 ± 3.2 abc | 27.6 ± 2.0 d | 22.3 ± 4.5 bd | 26.8 ± 1.3 d |
| Saponarin (isovitexin-7-O-glucoside)-4-O-glucoside | 129.3 ± 6.7 bce | 102.9 ± 13.1 acd | 199.3 ± 12.6 e | 100.4 ± 21.8 acd | 37.8 ± 3.9 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 564.4 ± 19.0 ef | 483.6 ± 11.9 df | 650.2 ± 11.9 f | 434.6 ± 64.3 cde | 169.5 ± 12.5 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 1 | 576.7 ± 15.1 df | 553.2 ± 12.8 de | 746.2 ± 30.2 f | 538.6 ± 84.2 de | 275.4 ± 19.8 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 1 | 591.8 ± 14.3 df | 521.0 ± 17.9 cde | 775.7 ± 26.3 f | 515.5 ± 88.8 cde | 261.7 ± 32.7 ab |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 380.4 ± 13.1 de | 289.5 ± 9.5 bd | 477.1 ± 16.9 e | 357.6 ± 55.5 cde | 187.8 ± 15.0 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 2 | 1371.7 ± 46.5 cd | 1292.1 ± 41.2 cd | 1646.5 ± 16.0 d | 1307.4 ± 194.6 cd | 556.0 ± 48.8 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 2 | 1133.5 ± 49.1 de | 1053.2 ± 10.4 ce | 1428.4 ± 121.0 e | 817.6 ± 132.0 bcd | 479.9 ± 24.0 ab |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 40.7 ± 4.9 ad | 30.0 ± 7.9 ac | 58.3 ± 4.6 bcd | 27.5 ± 5.0 ac | 18.8 ± 9.3 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-dihexoside 3 | 92.2 ± 5.5 cd | 78.3 ± 9.3 bc | 140.3 ± 7.4 d | 57.1 ± 8.4 ac | 32.4 ± 6.8 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-dihexoside 3 | 141.0 ± 3.9 de | 141.3 ± 7.7 de | 207.5 ± 8.2 f | 111.8 ± 16.8 cde | 47.7 ± 4.9 ab |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside-glucoside | 94.7 ± 7.3 bcd | 63.9 ± 7.0 ac | 131.4 ± 7.4 d | 62.6 ± 9.2 ac | 29.7 ± 1.8 ab |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside | 61.8 ± 3.7 ad | 45.7 ± 6.6 ad | 84.2 ± 4.4 d | 32.3 ± 4.3 ab | 38.2 ± 9.4 ac |
| Meloside A (Isovitexin-2-O-glucoside)-glucoside derivative | 85.7 ± 9.2 cf | 96.2 ± 10.9 def | 102.5 ± 7.7 ef | 29.5 ± 1.6 ac | 13.4 ± 3.4 ab |
| Isovitexin-8-C-galactoside | 15.3 ± 7.7 a | 30.5 ± 4.3 ab | 45.4 ± 5.0 ab | 6.8 ± 1.7 a | 32.0 ± 3.0 ab |
| Vicenin 2 (Isovitexin-8-C-glucoside) | 597.6 ± 5.8 cdf | 779.2 ± 12.4 fg | 663.5 ± 25.7 ef | 318.0 ± 42.9 b | 58.3 ± 2.5 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-glucoside | 49.2 ± 7.5 ade | 54.6 ± 7.4 adef | 69.3 ± 5.0 def | 12.6 ± 4.8 abc | 3.8 ± 1.4 ab |
| p-Coumaric acid | 70.8 ± 3.0 bc | 98.9 ± 3.1 def | 81.7 ± 2.4 cd | 53.7 ± 8.4 b | 15.1 ± 0.6 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-hexoside derivative | 76.3 ± 1.3 bcd | 121.0 ± 5.4 d | 95.7 ± 7.2 cd | 28.3 ± 6.8 ab | 13.6 ± 4.1 a |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-derivative | 98.7 ± 2.9 ce | 72.0 ± 9.0 ac | 129.8 ± 7.5 e | 65.4 ± 8.3 ac | 46.7 ± 6.4 ab |
| Isoscoparin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-rhamnoside | 137.7 ± 1.9 cdf | 132.1 ± 3.8 cde | 176.0 ± 4.4 ef | 110.6 ± 18.4 bd | 54.7 ± 5.4 ab |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-feruoyl)-glucoside | 370.1 ± 7.1 df | 382.6 ± 4.7 ef | 542.9 ± 9.5 g | 407.6 ± 61.6 f | 148.0 ± 7.4 a |
| Isovitexin-2-O-(6-(E)-p-coumaroyl)-glucoside | 533.7 ± 9.2 bc | 729.9 ± 3.5 e | 889.9 ± 19.9 f | 469.5 ± 71.4 bc | 148.1 ± 8.3 a |
| Total flavones | 8834.5 ± 159.7 df | 8403.7 ± 235.8 cde | 11,312.8 ± 385.9 f | 6939.9 ± 1058.2 bde | 3023.0 ± 232.4 a |
| Total hydroxycinnamic acids | 178.5 ± 5.1 de | 315.8 ± 11.4 f | 357.6 ± 20.7 f | 210.5 ± 36.5 e | 93.5 ± 3.8 ab |
| TAPC | 9012.9 ± 155.0 df | 8719.6 ± 245.7 de | 11,670.4 ± 394.3 f | 7150.3 ± 1093.6 cde | 3116.5 ± 236.2 ab |
| Phenolic Compound | Quantification According to Treatment (mg/kg Dry Weight) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 6 | |||||
| K1 | K2 | LEAF 10-4 | 10-4 | 10-3 | |
| Benzoic acid | 435.8 ± 8.1 e | 125.3 ± 3.7 d | 39.6 ± 1.1 c | 28.0 ± 0.8 b | 12.7 ± 0.6 a |
| Quercetin-3-O-rutinoside | 26.4 ± 6.6 b | 27.2 ± 6.8 b | 2.4 ± 1.2 a | 9.6 ± 1.6 ab | 5.3 ± 0.6 a |
| Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside | 8.3 ± 0.9 a | 40.8 ± 0.3 e | 37.3 ± 0.2 d | 13.4 ± 0.4 b | 25.4 ± 1.4 c |
| Hydrogalic acid | 18.8 ± 0.7 b | 34.3 ± 0.3 c | 98.0 ± 0.5 e | 10.6 ± 0.5 d | 41.1 ± 2.0 a |
| Juglone (5-hydroxy-1,4-naphthalenedione) | nd | nd | 26.4 ± 1.3 a | 22.8 ± 0.7 a | 659.9 ± 18.1 b |
| Total hydroxybenzoic acids | 454.6 ± 7.9 d | 159.6 ± 3.9 c | 137.6 ± 1.5 b | 38.6 ± 1.1 a | 53.7 ± 1.8 a |
| Total flavonols | 34.7 ± 7.3 a | 68.0 ± 7.0 b | 39.6 ± 1.2 a | 23.0 ± 1.5 a | 30.7 ± 1.6 a |
| TAPCWJ | 489.3 ± 14.0 c | 227.6 ± 10.7 b | 177.2 ± 2.2 b | 84.4 ± 3.0 a | 744.3 ± 18.5 d |
| TAPC | 489.3 ± 14.0 d | 227.6 ± 10.7 c | 150.8 ± 2.1 b | 61.6 ± 2.7 a | 84.4 ± 2.4 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medic, A.; Zamljen, T.; Slatnar, A.; Hudina, M.; Grohar, M.C.; Veberic, R. Effect of Juglone and Other Allelochemicals in Walnut Leaves on Yield, Quality and Metabolites of Snack Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Foods 2023, 12, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020371
Medic A, Zamljen T, Slatnar A, Hudina M, Grohar MC, Veberic R. Effect of Juglone and Other Allelochemicals in Walnut Leaves on Yield, Quality and Metabolites of Snack Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Foods. 2023; 12(2):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020371
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedic, Aljaz, Tilen Zamljen, Ana Slatnar, Metka Hudina, Mariana Cecilia Grohar, and Robert Veberic. 2023. "Effect of Juglone and Other Allelochemicals in Walnut Leaves on Yield, Quality and Metabolites of Snack Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.)" Foods 12, no. 2: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020371
APA StyleMedic, A., Zamljen, T., Slatnar, A., Hudina, M., Grohar, M. C., & Veberic, R. (2023). Effect of Juglone and Other Allelochemicals in Walnut Leaves on Yield, Quality and Metabolites of Snack Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Foods, 12(2), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12020371











