Quantitative Textural and Rheological Data on Different Levels of Texture-Modified Food and Thickened Liquids Classified Using the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) Guideline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Dysphagia
1.2. Diet Modification
1.3. International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative
1.4. Purpose of the Current Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and IDDSI Level Determination
2.2. Instrumentation and Measurement Procedures
2.2.1. Texture Profile Analysis
2.2.2. Rheology Analysis
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Texture Profile Analysis
3.2. Rheology Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Texture Profile Analysis
4.1.1. Comparison of Hardness to International Standard
4.1.2. Adhesiveness and Cohesiveness
4.1.3. Concerning Descriptive Properties
4.2. Rheology Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsuo, K.; Palmer, J.B. Anatomy and Physiology of Feeding and Swallowing: Normal and Abnormal. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 19, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logemann Jeri, A. Evaluation and Treatment of Swallowing Disorders, 2nd ed.; PRO-ED: Austin, TX, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, I.; Hamad, A.; Sasegbon, A.; Hamdy, S. Advances in the Treatment of Dysphagia in Neurological Disorders: A Review of Current Evidence and Future Considerations. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2022, 18, 2251–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.M.; Chambers, E. Managing Dysphagia Through Diet Modifications. Am. J. Nurs. 2010, 110, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, M.; Marchese-Ragona, R.; Masiero, S.; Restivo, D.A. Dysphagia in neurological diseases: A literature review. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 3067–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadde, E.K.; Chen, J. Texture and texture assessment of thickened fluids and texture-modified food for dysphagia management. J. Texture Stud. 2021, 52, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, H.; Hori, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsujimura, T.; Ono, T.; Inoue, M. Biomechanics of human tongue movement during bolus compression and swallowing. J. Oral. Sci. 2013, 55, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stading, M. Bolus rheology of texture-modified food: Effect of degree of modification. J. Texture Stud. 2021, 52, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.M.; Alsanei, W.A.; Ayanikalath, S.; Barbon, C.E.A.; Chen, J.; Cichero, J.A.Y.; Coutts, K.; Dantas, R.O.; Duivestein, J.; Giosa, L.; et al. The Influence of Food Texture and Liquid Consistency Modification on Swallowing Physiology and Function: A Systematic Review. Dysphagia 2015, 30, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichero, J.A.; Lam, P.; Steele, C.M.; Hanson, B.; Chen, J.; Dantas, R.O.; Duivestein, J.; Kayashita, J.; Lecko, C.; Murray, J.; et al. Development of International Terminology and Definitions for Texture-Modified Foods and Thickened Fluids Used in Dysphagia Management: The IDDSI Framework. Dysphagia 2017, 32, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadde, E.K.; Prakash, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Instrumental texture assessment of IDDSI texture levels for dysphagia management. Part 1: Thickened fluids. J. Texture Stud. 2022, 53, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.Y.; Ng, M.L.; Tong, E.T.S. How Accurate Are the Consistency Labels Used in Hong Kong? An Objective Study of the Consistency of Thickened Liquids Using International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative and Consistometric Measurements. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2022, 74, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, E.; Tse, S.K. Application of a Manufacturer’s Guideline and an IDDSI-Driven Guideline to Thickening of Some Non-water Beverages: A Rheological Study. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunimaru, W.; Ito, S.; Motohashi, R.; Arai, E. Ease of swallowing potato paste in people with dysphagia: Effect of potato variety. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EZTest Compact Table-Top Universal Tester: Evaluation of Food Texture. Application Data Sheet No. 12. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/sites/shimadzu.com.an/files/pim/pim_document_file/applications/application_note/12414/jpi313005.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Overview of Texture Profile Analysis. Available online: https://texturetechnologies.com/resources/texture-profile-analysis (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Momosaki, R.; Abo, M.; Kobayashi, K. Swallowing Analysis for Semisolid Food Texture in Poststroke Dysphagic Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Dysphagia Diet Task Force; American Dietetic Association. The National Dysphagia Diet (NDD): Standardization for Optimal Care, 1st ed.; American Dietetic Association: Chicago, IL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, J.M.; Chambers, E., 4th; Matta, Z.; Clark, M. Viscosity measurements of nectar- and honey-thick liquids: Product, liquid, and time comparisons. Dysphagia 2005, 20, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, C.; Methven, L.; Fairfield, C.; Bell, A. Consistently inconsistent: Commercially available starch-based dysphagia products. Dysphagia 2011, 26, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Universal Design Food Classification Table. Available online: https://www.udf.jp/outline/udf.html#table (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Kang, A.J.; Kim, D.K.; Kang, S.H.; Seo, K.M.; Park, H.S.; Park, K.H. EMG Activity of Masseter Muscles in the Elderly According to Rheological Properties of Solid Food. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2016, 40, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Industry Research and Development Institute (FIRDI). 2020 Annual Report; Food Industry Research and Development Institute (FIRDI): Hsinchu, Taiwan, 2020; Available online: https://www.firdi.org.tw/PageData/Reports/109%E5%B9%B4/pdf/en.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2021).
- Wang, I.C. International Classification Systems for Texture-Modified Foods. Hu Li Za Zhi 2020, 67, 24–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.M.; Li, L.Y. Comparative Study of Chemical Composition and Texture Profile Analysis between Camembert Cheese and Chinese Sufu. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, M.H. The Hardness, Adhesiveness and Cohesiveness of Commercial Foods in Taiwan: A Primary Study Applied in Dysphagia. J. Cardinal Tien Coll. Nurs. 2018, 16, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.W.; Lee, S.; Yoo, B.; Nam, K. Effects of texture properties of semi-solid food on the sensory test for pharyngeal swallowing effort in the older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, B.; Howes, T.; Bhandari, B.R.; Truong, V. Stickiness in Foods: A Review of Mechanisms and Test Methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2001, 4, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buma, T.J. Free Fat in Spray Dried Whole Milk 5. Cohesion: Determination, Influence of Particle Size, Moisture Content and Free Fat Content. Neth. Milk. Dairy J. 1971, 25, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Rennie, P.R.; Chen, X.D.; Hargreaves, C.; Mackereth, A.R. A Study of the Cohesion of Dairy Powders. J. Food Eng. 1999, 39, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fitzgerald, M.A.; Prakash, S.; Nicholson, T.M.; Gilbert, R.G. The molecular structural features controlling stickiness in cooked rice, a major palatability determinant. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep43713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, Y.; Kayashita, J. Evaluation of the Japanese Dysphagia Diet 2013 by the JSDR Dysphagia Diet Committee (Thickened Liquid) by Using Several Types of Thickened Liquids. Jpn. J. Dysphagia Rehabil. 2015, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Diamante, L.M.; Lan, T. Absolute Viscosities of Vegetable Oils at Different Temperatures and Shear Rate Range of 64.5 to 4835 s−1. J. Food Process. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopade, P.A.; Halley, P.J.; Cichero, J.A.; Ward, L.C. Rheological characterization of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. I: Water and cordial. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopade, P.A.; Halley, P.J.; Cichero, J.A.; Ward, L.C.; Hui, L.S.; Teo, K.H. Rheological characterisation of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. II. Milk as a dispersing medium. J. Food Eng. 2008, 84, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopade, P.A.; Halley, P.J.; Cichero, J.A.; Ward, L.C.; Liu, J.; Varliveli, S. Rheological characterization of food thickeners marketed in Australia in various media for the management of dysphagia. III. Fruit juice as a dispersing medium. J. Food Eng. 2008, 86, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Spindle | Sample Volume (mL) | Shear Rate Constant (SRC) | RPM at 50 s−1 Shear Rate | Full Scale Viscosity Range (cP) at 50 s−1 Shear Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UL | 16 | 1.223 | 40.9 | 15.6–156.544 |
| SC4-21 | 7.1 | 0.93 | 53.8 | 93–930 |
| SC4-28 | 11.0 | 0.28 | 178.6 | 280–2800 |
| Type | IDDSI Level | Hardness (×103 N/m2) | Adhesiveness (g·s) | Cohesiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | ||||
| Fish and meat | 7 | 53.97–131.76 | (−25.06)–0.00 | 0.36–0.73 |
| 6 | 14.49–48.52 | (−8.03)–0.00 | 0.55–0.76 | |
| 5 | 8.22–12.53 | (−4.61)–0.00 | 0.51–0.70 | |
| 4 | 0.85–3.52 | (−58.19)–(−22.63) | 0.53–0.74 | |
| Vegetables | 7 | 11.00–392.50 | (−120.48)–0.00 | 0.08–0.83 |
| 6 | 1.97–49.49 | (−26.18)–(−1.13) | 0.09–0.72 | |
| 5 | 1.66–17.08 | (−22.66)–(−1.16) | 0.18–0.55 | |
| 4 | 0.51–2.19 | (−50.69)–(−16.13) | 0.64–0.89 | |
| Fruits | 7 | 40.27–347.15 | (−84.40)–(−7.31) | 0.08–0.26 |
| 6 | 17.84–47.12 | (−20.66)–(−2.35) | 0.12–0.30 | |
| 5 | 1.56–13.92 | (−19.58)–(−1.61) | 0.23–0.49 | |
| 4 | 0.45–4.84 | (−42.20)–(−17.70) | 0.59–0.78 | |
| High-protein food | 7 | 5.18–370.10 | (−32.75)–0.00 | 0.55–0.79 |
| 6 | 3.70–46.98 | (−23.16)–0.00 | 0.54–0.74 | |
| 5 | 0.89–9.05 | (−24.42)–(−3.06) | 0.38–0.63 | |
| 4 | 0.67–3.94 | (−53.03)–(−5.51) | 0.52–0.74 | |
| High-starch food | 7 | 5.09–287.07 | (−165.12)–(−0.94) | 0.09–0.67 |
| 6 | 3.14–45.05 | (−75.95)–(−0.94) | 0.11–0.63 | |
| 5 | 3.75–18.85 | (−91.72)–(−3.23) | 0.15–0.53 | |
| 4 | 0.61–3.03 | (−89.16)–(−18.59) | 0.68–0.88 | |
| Dishes | ||||
| Fish | 7 | 34.84–303.80 | (−62.14)–0.00 | 0.41–0.75 |
| 6 | 8.66–47.76 | (−24.91)–(−3.14) | 0.40–0.66 | |
| 5 | 7.30–16.01 | (−33.29)–(−14.57) | 0.30–0.46 | |
| 4 (soft meal) | 3.05–4.91 | (−20.16)–(−11.38) | 0.43–0.57 | |
| 4 (puree) | 0.72–2.44 | (−66.40)–(−20.12) | 0.62–0.74 | |
| Meat | 7 | 85.68–151.07 | (−223.65)–(−4.31) | 0.08–0.62 |
| 6 | 9.41–25.98 | (−23.60)–(−5.92) | 0.48–0.59 | |
| 5 | 1.32–18.94 | (−26.00)–(−12.57) | 0.36–0.58 | |
| 4 (soft meal) | 2.16–3.71 | (−14.60)–(−9.11) | 0.41–0.89 | |
| 4 (puree) | 0.93–4.55 | (−39.16)–(−11.14) | 0.49–0.99 | |
| Condiments | 7 | 13.56–108.19 | (−29.94)–(−2.29) | 0.28–0.49 |
| 6 | 13.56–26.27 | (−29.94)–(−2.29) | 0.30–0.49 | |
| 5 | 6.75–13.84 | (−17.66)–(−15.26) | 0.26–0.41 | |
| 4 (soft meal) | -- | -- | -- | |
| 4 (puree) | 0.92–3.18 | (−49.71)–(−33.97) | 0.70–0.80 | |
| Dessert | 7 | 17.01–115.15 | (−47.16)–(−15.81) | 0.14–0.80 |
| 6 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 5 | 0.89 | (−11.68) | 0.65 | |
| 4 (soft meal) | 1.44–4.61 | (−14.62)–(−9.93) | 0.50–0.62 | |
| 4 (puree) | -- | -- | -- | |
| Others | 7 | 27.22–114.07 | (−61.95)–(−20.66) | 0.57–0.64 |
| 6 | 9.05–30.29 | (−58.11)–(−2.70) | 0.52–0.84 | |
| 5 | 10.75–18.39 | (−9.10)–(−2.23) | 0.52–0.62 | |
| 4 (soft meal) | 1.75–4.79 | (−20.34)–(−12.35) | 0.36–0.49 | |
| 4 (puree) | 3.88–4.84 | (−31.33)–(−7.83) | 0.47–0.50 | |
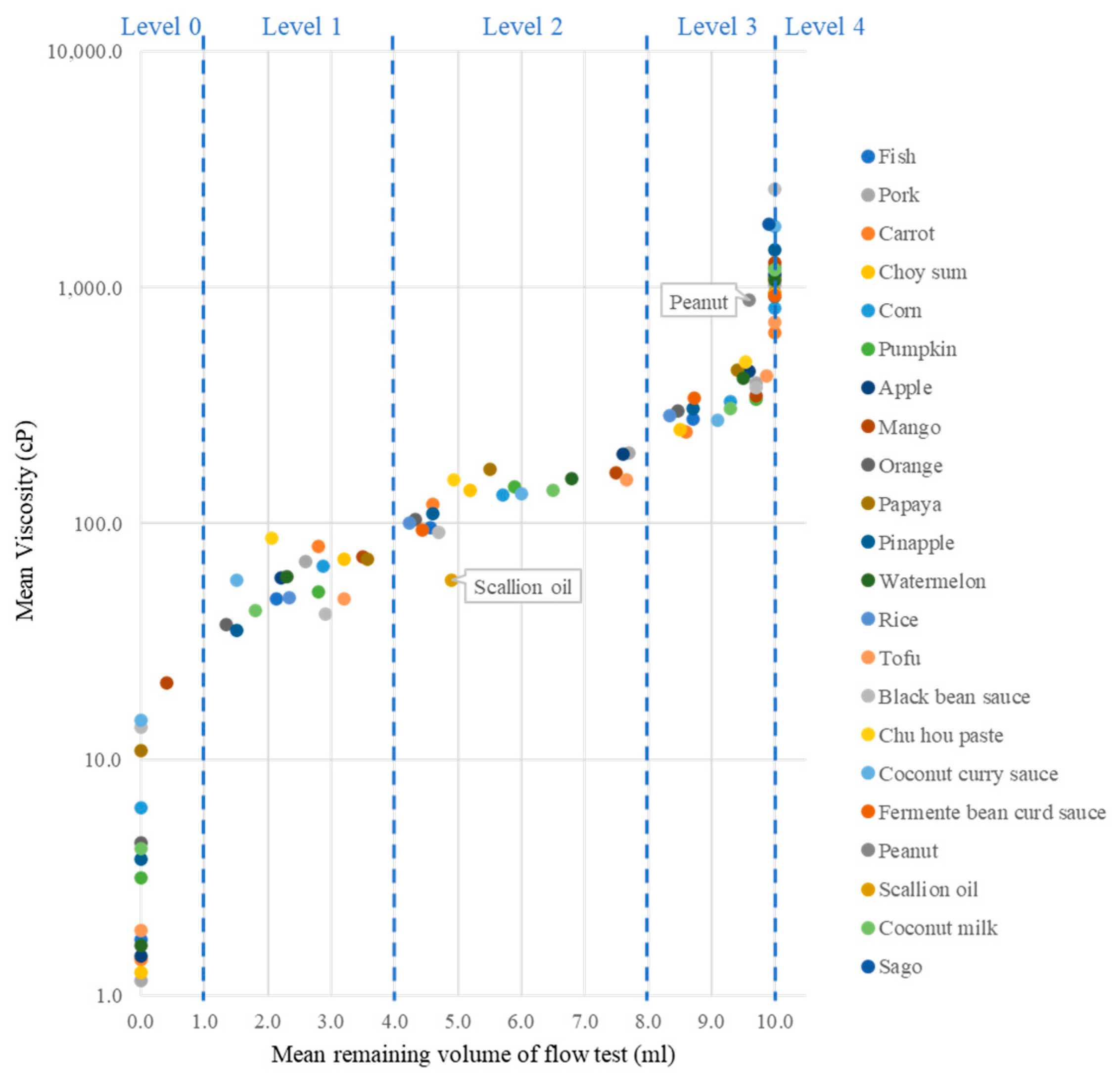
| Mean Viscosity (cP) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDDSI Level | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Thickened by Thick & EasyTM Clear | |||||
| Fish soup | 1101.3 | 275.6 | 95.8 | 47.8 | 1.7 |
| Pork soup | 1032.5 | 395.0 | 198.1 | 69.4 | 1.2 |
| Carrot juice | 645.5 | 244.0 | 120.2 | 79.9 | 1.4 |
| Choy sum soup | 1085.7 | 251.1 | 137.6 | 70.7 | 1.3 |
| Corn soup | 813.9 | 327.4 | 132.4 | 66.1 | 6.3 |
| Pumpkin soup | 1225.3 | 334.5 | 143.2 | 51.4 | 3.1 |
| Apple juice | 1132.0 | 442.1 | 197.8 | 58.8 | 1.5 |
| Mango juice | 1271.3 | 349.4 | 164.3 | 72.6 | 21.2 |
| Orange juice | 918.4 | 298.8 | 104.3 | 37.3 | 4.4 |
| Papaya juice | 945.5 | 446.7 | 169.3 | 70.6 | 10.9 |
| Pineapple juice | 1440.0 | 306.6 | 110.3 | 35.4 | 3.8 |
| Watermelon juice | 1071.7 | 413.3 | 154.7 | 59.9 | 1.6 |
| Soybean milk | 713.1 | 423.2 | 152.5 | 48.2 | 1.9 |
| Coconut milk | 1192.0 | 307.5 | 138.2 | 43.0 | 4.2 |
| Thickened by corn starch | |||||
| Black bean sauce | 2625.3 | 377.6 | 91.7 | 41.6 | 13.6 |
| Chu hou paste | 938.9 | 483.3 | 153.8 | 86.9 | |
| Coconut curry sauce | 1810.0 | 274.3 | 133.9 | 57.8 | 14.6 |
| Red fermented bean curd sauce | 929.6 | 340.4 | 94.2 | ||
| No thickener added | |||||
| Congee (rice) | 287.7 | 101.0 | 48.2 | ||
| Peanut sauce | 882.0 | ||||
| Scallion oil | 57.6 | ||||
| Scheme/Country | <Regular Food | Extensively Texture-Modified Food> | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universal Design Foods (UDF), Japan (Japan Care Food) [21,22] | Categories | Stage 1 Able to chew easily | Stage 2 Able to smash with gum | Stage 3 Able to smash with tongue | Stage 4 Able to swallow without chewing |
| Hardness (N/m2) | <5 × 105 | <5 × 104 | <2 × 104 | <5 × 103 | |
| Eatender, Taiwan [23,24] | Categories | Easy-to-chew | Gum-chewable | Tongue crushing | No chewing |
| Hardness (N/m2) | <5 × 105 | <5 × 104 | <2 × 104 | <5 × 103 | |
| IDDSI [10] * | Categories | Level 7 Easy to chew | Level 6 Soft and bite size | Level 5 Minced and moist | Level 4 Pureed |
| Hardness assessed by fork pressure test | Can be broken down with pressure from fork; thumbnail blanches to white | Can be broken down with pressure from fork; thumbnail blanches to white | Particles easily come through the tines of a fork; thumbnail does not blanch to white | Tines of a fork make a clear pattern on the surface | |
| Current study | Hardness of tested food items (×103 N/m2) | 5.09–392.50 | 1.97–49.49 | 0.89–18.94 | 0.45–4.84 |
| IDDSI Level | Viscosity Ranges (cP) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Study | NDD | JSDR | ||
| Thickened by Thick & EasyTM Clear | Thickened by Corn Starch | |||
| 4 (Extremely thick) | 645.5–1440.0 | 929.6–2625.3 | >1750 | >500 |
| 3 (Moderately thick) | 244.0–446.7 | 274.3–483.3 | 351–1750 | 300–500 |
| 2 (Mildly thick) | 95.8–198.1 | 91.7–153.8 | 51–350 | 150–300 |
| 1 (Slightly thick) | 35.4–79.9 | 41.6–86.9 | 50–150 | |
| 0 (Thin) | 1.2–21.2 | 13.6–14.6 | <50 | <50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, M.C.; Chan, K.M.K.; Wong, T.T.; Tang, H.W.; Chung, H.Y.; Kwan, H.S. Quantitative Textural and Rheological Data on Different Levels of Texture-Modified Food and Thickened Liquids Classified Using the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) Guideline. Foods 2023, 12, 3765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203765
Wong MC, Chan KMK, Wong TT, Tang HW, Chung HY, Kwan HS. Quantitative Textural and Rheological Data on Different Levels of Texture-Modified Food and Thickened Liquids Classified Using the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) Guideline. Foods. 2023; 12(20):3765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203765
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Man Chun, Karen M. K. Chan, Tsz Ting Wong, Ho Wah Tang, Hau Yin Chung, and Hoi Shan Kwan. 2023. "Quantitative Textural and Rheological Data on Different Levels of Texture-Modified Food and Thickened Liquids Classified Using the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) Guideline" Foods 12, no. 20: 3765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203765
APA StyleWong, M. C., Chan, K. M. K., Wong, T. T., Tang, H. W., Chung, H. Y., & Kwan, H. S. (2023). Quantitative Textural and Rheological Data on Different Levels of Texture-Modified Food and Thickened Liquids Classified Using the International Dysphagia Diet Standardisation Initiative (IDDSI) Guideline. Foods, 12(20), 3765. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12203765






