Effect and Mechanism of Soluble Starch on Bovine Serum Albumin Cold-Set Gel Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase: A Significantly Improved Carrier for Active Substances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of BSA-SS Cold-Set Gel
2.3. Characteristics of BSA-SS Cold Gel
2.3.1. Texture Determination
2.3.2. Rheological Analysis
2.3.3. Microstructure
2.3.4. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.3.5. Determination of Water Binding State
2.4. Interaction between SS and BSA in the Gel
2.4.1. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.4.2. Zeta Potential
2.4.3. Fluorescence Spectrum Analysis
2.4.4. BSA Secondary Structure by Circular Dichroism (CD)
2.5. Performance Evaluation of BSA-SS Cold-Set Gel as Carrier
2.5.1. Determination of Embedding Efficiency (EE) on Quercetin
2.5.2. In Vitro Simulated Release of Quercetin
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of SS on BSA Cold-Set Gel
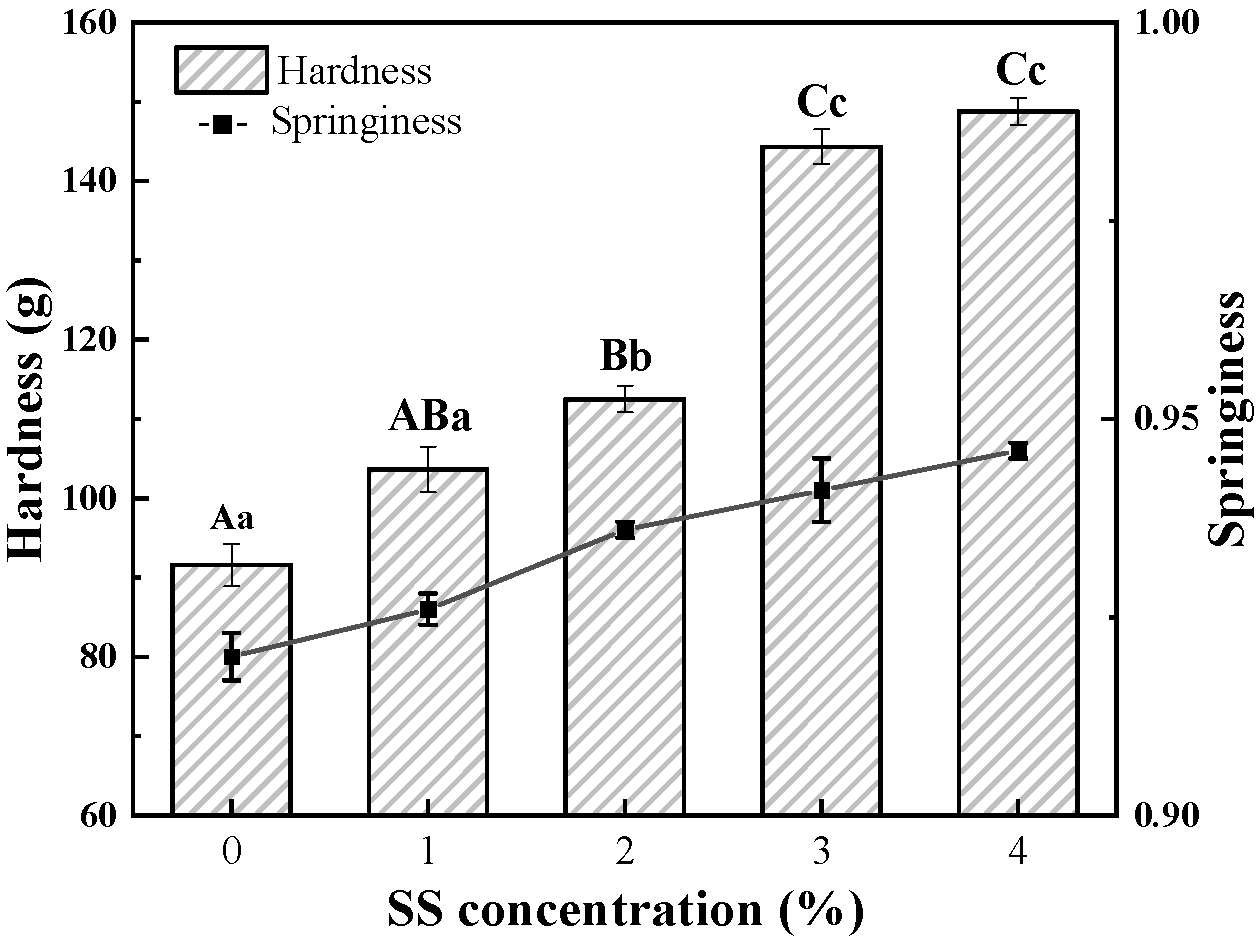
3.1.1. Texture Profile Analysis
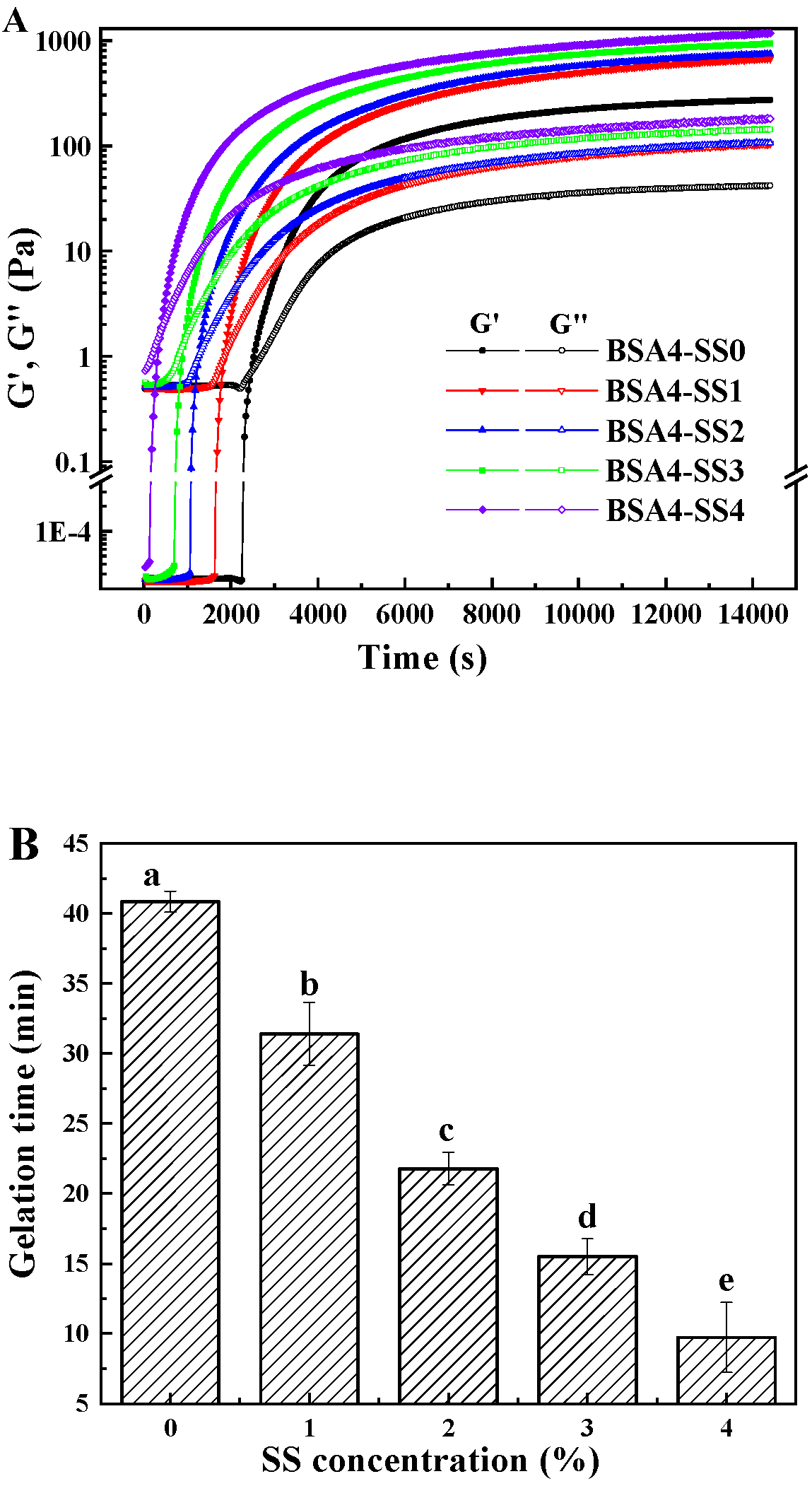
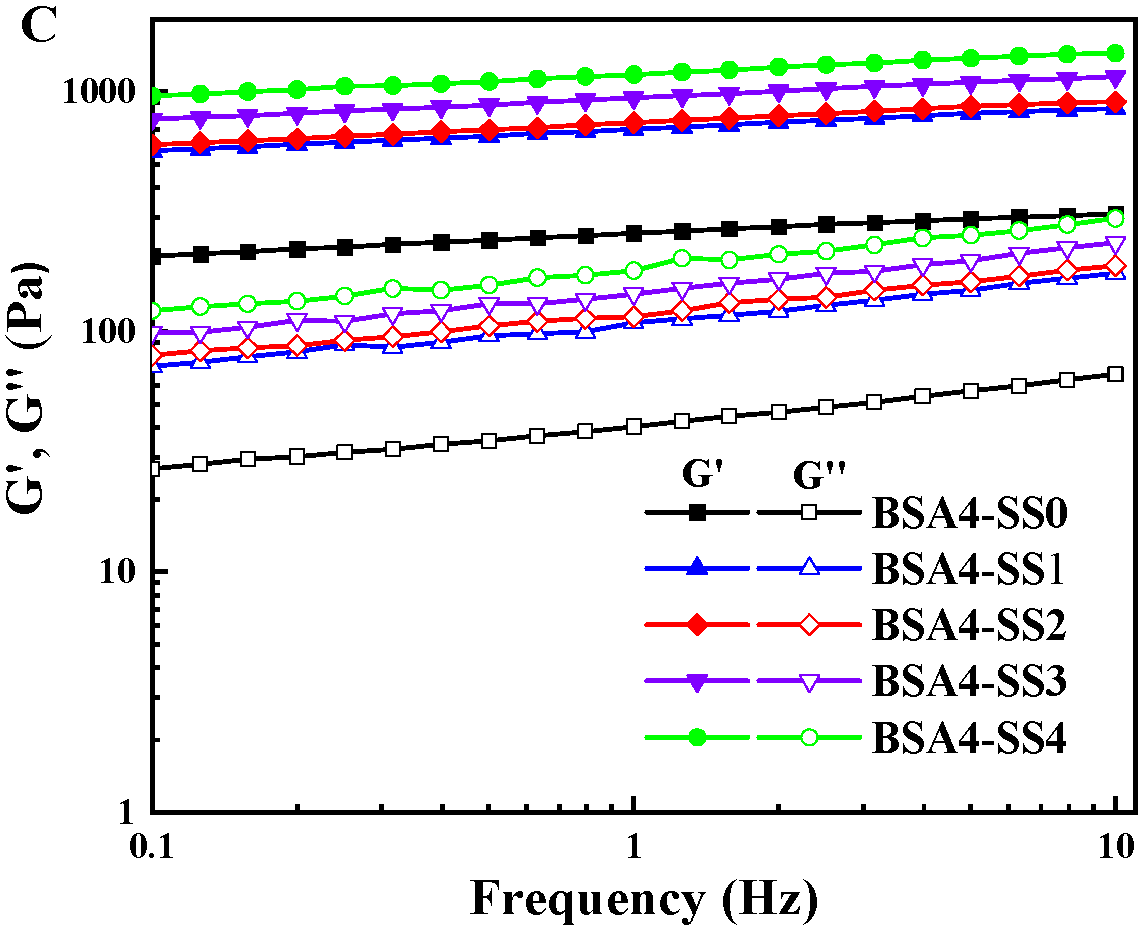
3.1.2. Changes in Rheological Characteristics during Gelation
3.1.3. Microstructure of the Cold-Set Gels
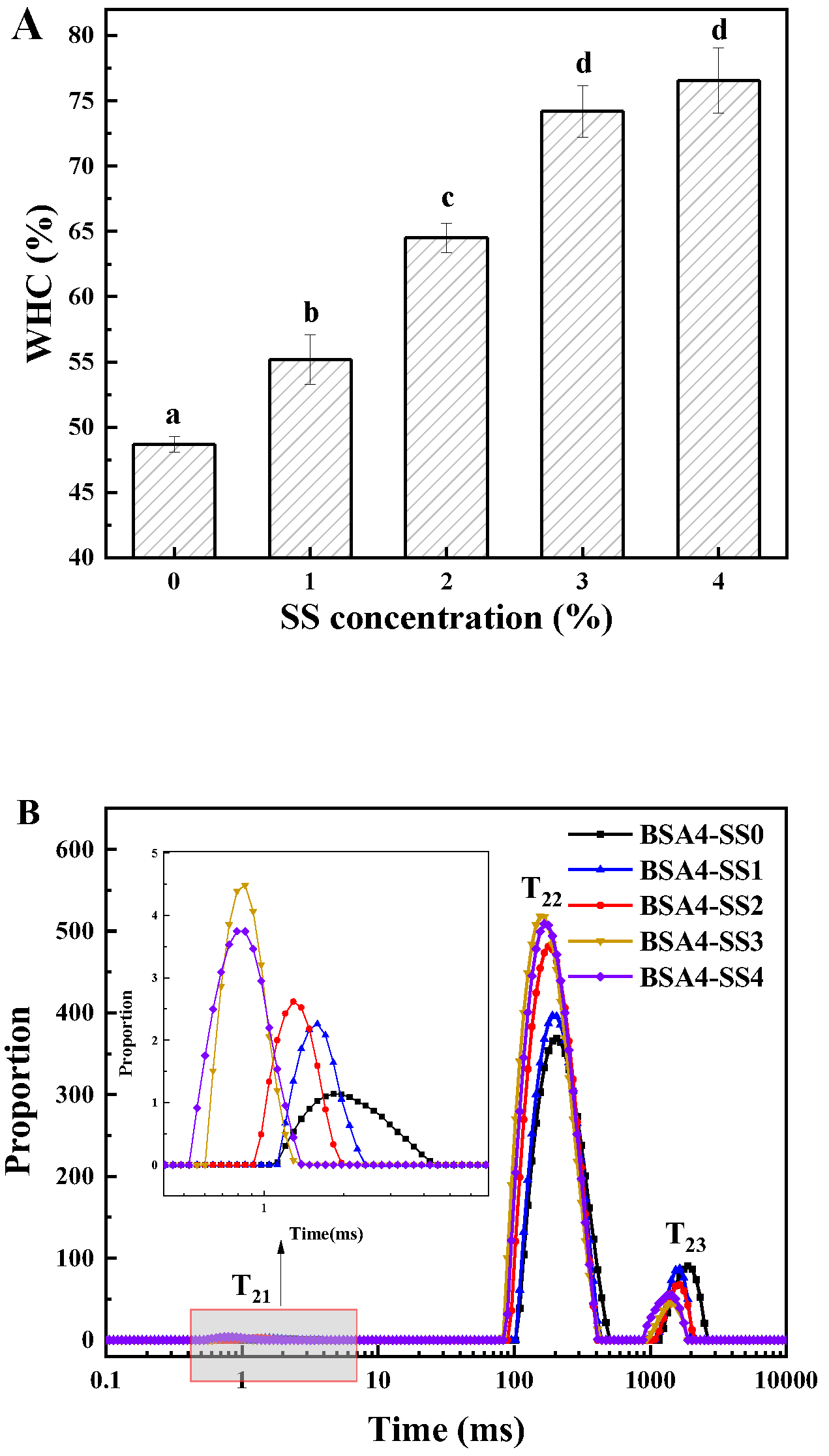
3.1.4. Change in WHC and Water Binding State
3.2. Acceleration Mechanism and Performance Improvement of BSA Cold-Set Gelation by SS
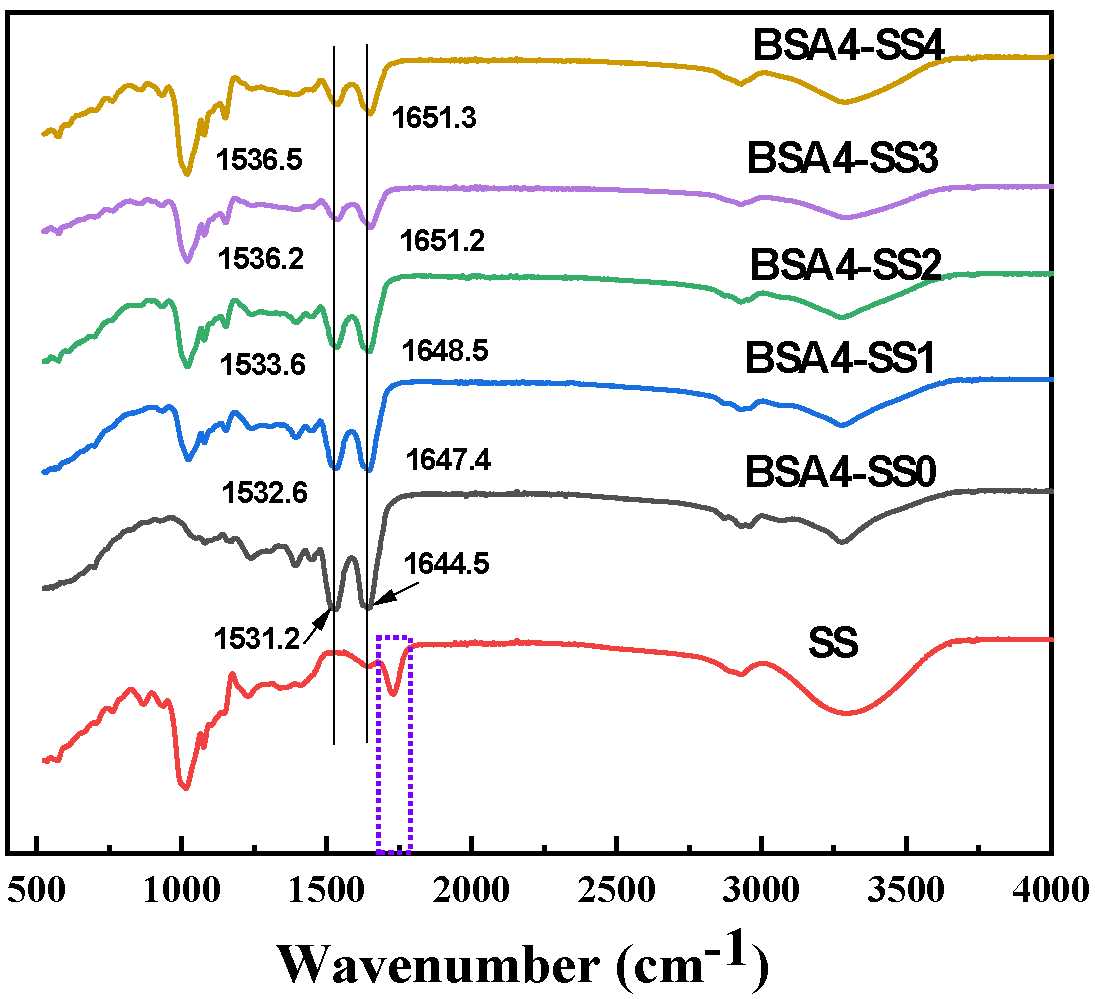
3.2.1. FTIR Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2.2. Zeta Potential of BSA-SS System
3.2.3. Fluorescence Quenching Analysis
3.2.4. Circular Dichroism Analysis
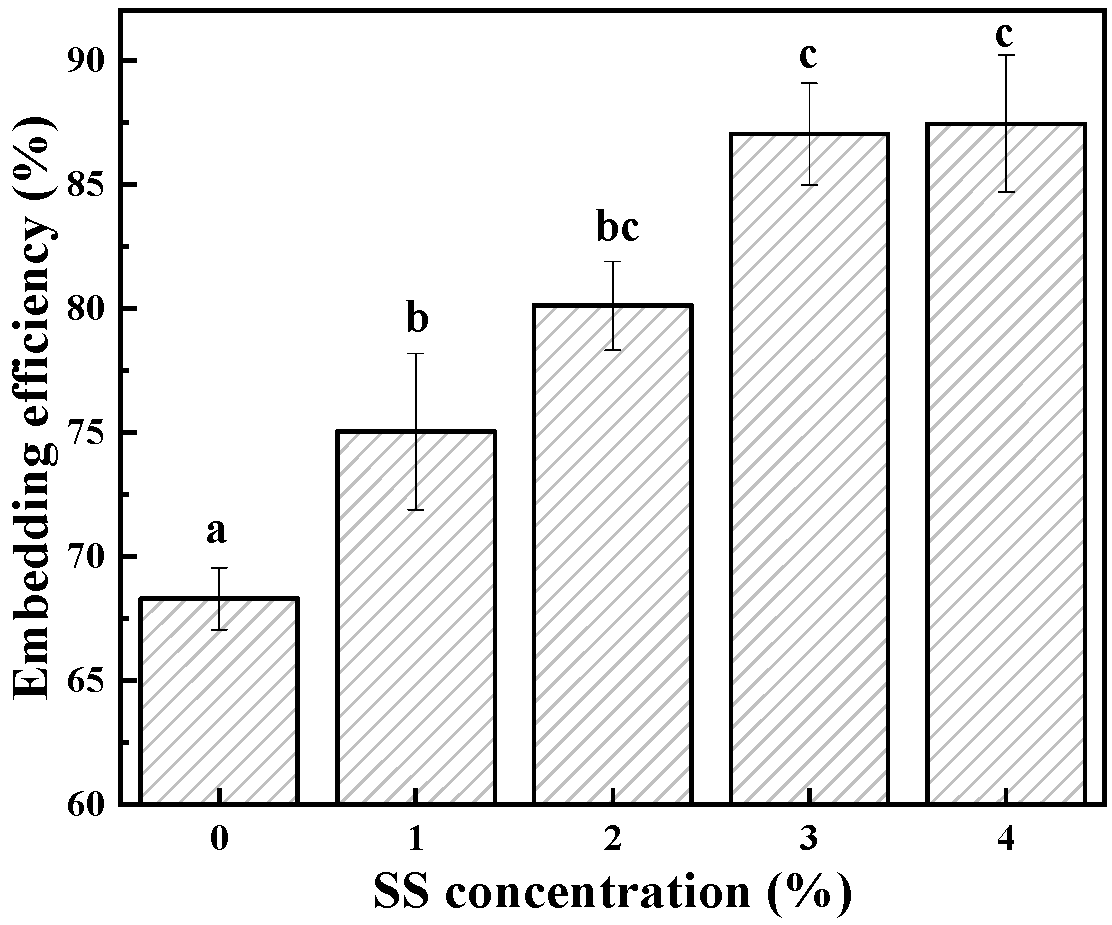
3.3. Embedding Ability of BSA-SS Cold-Set Gel
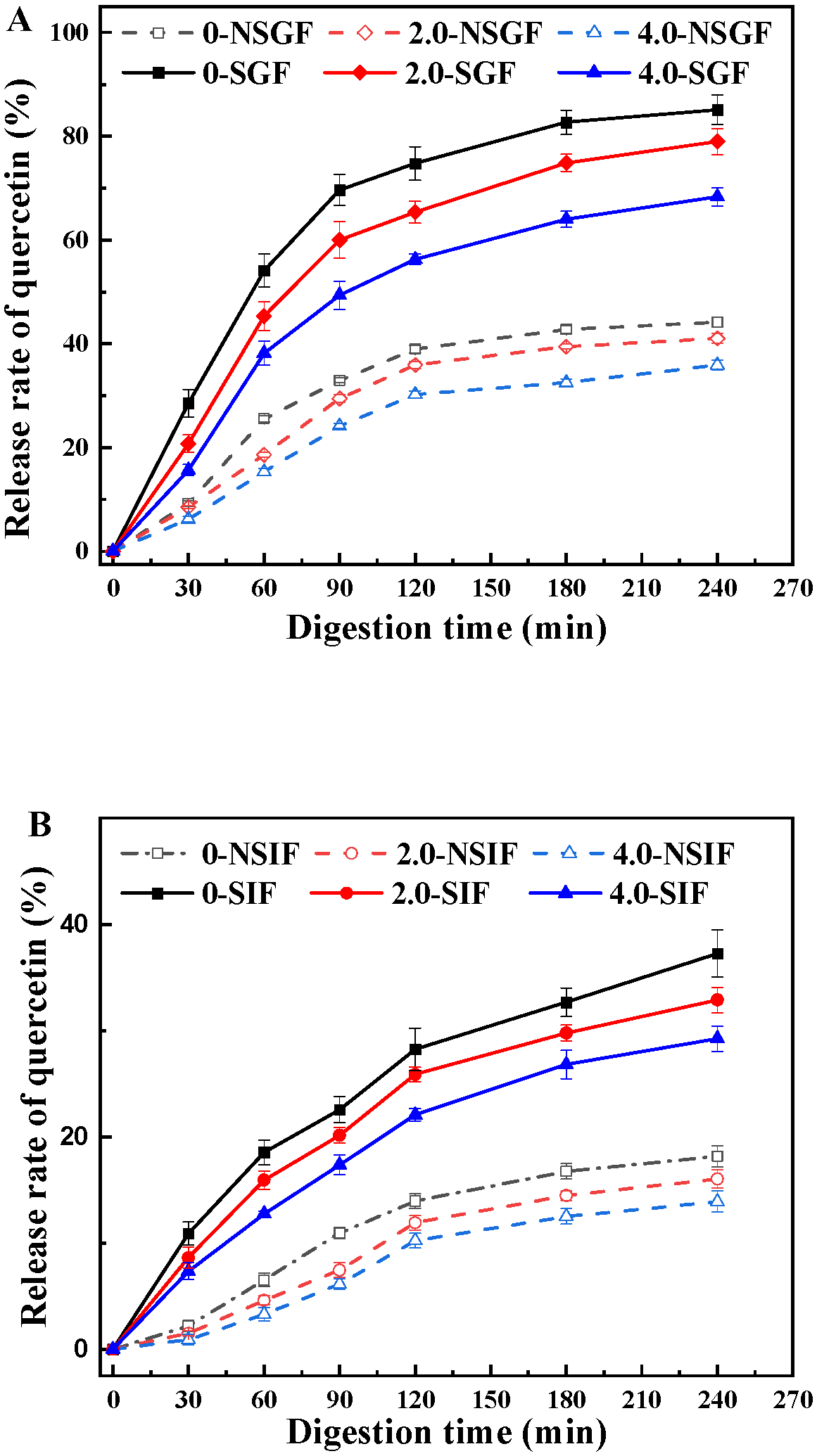
3.4. In Vitro Release of Quercetin in BSA-SS Composite Cold-Set Gel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gregersen, S.B.; Glover, Z.J.; Wiking, L.; Simonsen, A.C.; Bertelsen, K.; Pedersen, B.; Poulsen, K.R.; Andersen, U.; Hammershoj, M. Microstructure and rheology of acid milk gels and stirred yoghurts-quantification of process-induced changes by auto- and cross correlation image analysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabbasi, N.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Askari, G.; Salami, M. Pinto bean protein-based acid-induced cold-set gels as carriers for curcumin delivery: Fabrication and characterization. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2021, 1, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Lu, Z.H.; Yin, L.J.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Li, L.T. Effect of preheating temperature and calcium ions on the properties of cold-set soybean protein gel. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.L.; Fan, C.; Yan, P.; Kang, X. Fabrication and characteristics of porcine plasma protein cold-set gel: Influence of the aggregates produced by glucono-5-lactone acidification on microbial transglutaminase catalysis. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, T.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Assembly of soy protein-corn starch composite gels by thermal induction: Structure, and properties. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Mena, N.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Pérez-Won, M.; Herrera-Lavados, C.; Lemus-Mondaca, R.; Moreno-Osorio, L. Evaluation of physicochemical properties of starch-protein gels: Printability and postprocessing. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 182, 114797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Johansson, D.; Ström, A.; Rydén, J.; Nilsson, K.; Karlsson, J.; Moriana, R.; Langton, M. Effect of starch and fibre on faba bean protein gel characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burey, P.; Bhandari, B.R.; Howes, T.; Gidley, M.J. Hydrocolloid gel particles: Formation, characterization, and application. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.M.; Yuan, J.L.; Li, R.X.; Kang, X. Characterization and embedding potential of bovine serum albumin cold-set gel induced by glucono-delta-lactone and sodium chloride. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.X.; Yuan, J.L.; Ding, C.S.; Kang, X. Bovine serum albumin cold-set emulsion gel mediated by transglutaminase/glucono-delta-lactone coupling precursors: Fabrication, characteristics and embedding efficiency of hydrophobic bioactive components. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.H.; Donner, E.; Yada, R.Y.; Liu, Q. Physicochemical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of potato starch/protein blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Ren, F.; Zhao, H.B.; Cui, B.; Liu, P.F. Effects of native starch and modified starches on the textural, rheological and microstructural characteristics of soybean protein gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoisier, A.; Aguilera, J.M. Starch gelatinization inside a whey protein gel formed by cold gelation. J. Food Eng. 2019, 256, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Q.M.; Pan, L.H.; Qian, X.P.; Zhang, H.L.; Zha, X.Q.; Luo, J.P. The effects of lotus root amylopectin on the formation of whey protein isolate gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Effect of rice protein on the water mobility, water migration and microstructure of rice starch during retrogradation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.Y.; Wu, L.Y.; Xiao, J.H. Inhibition of gelatinized rice starch retrogradation by rice bran protein hydrolysates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 175, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, N.F.; Zhou, Y.B. Effect of rice protein hydrolysates on the short-term and long-term retrogradation of wheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.T. Characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by glucono-delta-lactone: Effects of the protein concentration during preheating. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, W. Low frequency magnetic field plus high pH promote the quality of pork myofibrillar protein gel: A novel study combined with low field NMR and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zha, X.Q.; Shen, W.D.; Li, Q.M.; Pan, L.H.; Luo, J.P. The hydrogel of whey protein isolate coated by lotus root amylopectin enhance the stability and bioavailability of quercetin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, C.; Ma, W.H.; Kuang, J.W.; Huang, J.R.; Xiong, Y.L. Textural properties, microstructure and digestibility of mungbean starch–flaxseed protein composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Wang, S. Effect of modified tapioca starches on the gelling properties of whey protein isolate. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.-H.; Li, D.; Wang, L.-J.; Adhikari, B. Effect of LBG on the gel properties of acid-induced SPI gels. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Influence of Mesona blumes polysaccharide on the gel properties and microstructure of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Chem. 2020, 313, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallieri, A.L.F.; da Cunha, R.L. The effects of acidification rate, pH and ageing time on the acidic cold set gelation of whey proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Degner, B.; McClements, D.J. Creating novel food textures: Modifying rheology of starch granule suspensions by cold-set whey protein gelation. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Hemar, Y.; Mo, G.; de Campo, L.; Gilbert, E.P. Effect of porous waxy rice starch addition on acid milk gels: Structural and physicochemical functionality. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 109, 106092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.N.; Ingrassia, R.; Busti, P.; Wagner, J.; Boeris, V.; Spelzini, D. Acid-induced aggregation and gelation of heat-treated chia proteins. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.X.; Han, G.; Wen, R.X.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B.H. Influence of lard-based diacylglycerol on rheological and physicochemical properties of thermally induced gels of porcine myofibrillar protein at different NaCl concentrations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 127, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Guo, X.Y.; Liu, Y.D.; Qi, X.M.; Lei, H.J.; Xu, H.D. Heat-induced whey protein isolate gels improved by cellulose nanocrystals: Gelling properties and microstructure. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 231, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Min, G.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Q. Starch-protein interplay varies the multi-scale structures of starch undergoing thermal processing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollakup, R.; Pongburoos, S.; Boonsong, W.; Khanoonkon, N.; Kongsin, K.; Sothornvit, R.; Sukyai, P.; Sukatta, U.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of cassava starch and whey protein blend films containing rambutan peel extract and cinnamon oil for active packaging. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koupantsis, T.; Pavlidou, E.; Paraskevopoulou, A. Glycerol and tannic acid as applied in the preparation of milk proteins—CMC complex coavervates for flavour encapsulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenhof, M.-A.; MacNaughtan, W.; Farhat, I.A. FTIR study of state and phase transitions of low moisture sucrose and lactose. Carbohydr. Res. 2003, 338, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.B.; Miao, Z.C.; Qi, Q.; Zheng, Q.H.; Mao, Y.X.; Chu, Z.J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.Y.; Zheng, M.Z.; Liu, J.S. Interactions of soy protein isolate with common and waxy corn starches and their effects on acid-induced cold gelation properties of complexes. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.L.; Yang, L.C.; Li, J.G.; Lin, L.Z.; Zheng, G.D. Effect of Smilax china L. starch on the gel properties and interactions of calcium sulfate-induced soy protein isolate gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamul, D.K.; Lupano, C.E. Whey protein concentrate gels with honey and wheat flour. Food Res. Int. 2005, 38, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Hu, T.; Zhao, S.; Xiong, S.; Xie, J.; Huang, Q. Gel characteristics and microstructure of fish myofibrillar protein/cassava starch composites. Food Chem. 2017, 218, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Fang, F.; Federici, E.; Campanella, O.; Jones, O.G. Rheology, microstructure and phase behavior of potato starch-protein fibril mixed gel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergfeldt, K.; Piculell, L.; Linse, P. Segregation and Association in Mixed Polymer Solutions from Flory−Huggins Model Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 3680–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhong, J.; Luo, L.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, L. Binding interaction between rice glutelin and amylose: Hydrophobic interaction and conformational changes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Chen, R.; Dai, T.; Liu, Y.; Luo, S.; Liu, C. Soluble starch/whey protein isolate complex-stabilized high internal phase emulsion: Interaction and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Qiu, C.; Li, X.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Study on the interaction between bovine serum albumin and starch nanoparticles prepared by isoamylolysis and recrystallization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.N.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.X.; Yu, Q.S.; Feng, W. Impact of binding interaction characteristics on physicochemical, structural, and rheological properties of waxy rice flour. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.M.; Guo, X.P.; Zhou, F.; Xiao, L.; Liu, J.J.; Jiang, C.J.; Xing, M.Y.; Yao, P. Quercetin alleviates ethanol-induced liver steatosis associated with improvement of lipophagy. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 125, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.D.; Verma, P.R.P.; Singh, S.K. Development and evaluation of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for the effective delivery of quercetin using a quality by design approach. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Du, C.W.; Zhao, N.; Jiang, W.Q.; Yu, X.Z.; Du, S.K. Preparation and characterization of quinoa starch nanoparticles as quercetin carriers. Food Chem. 2022, 369, 130895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.Y.; Feng, Y.L.; Tang, H.H.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, J.M. Cold-set oat protein isolate—Gellan gum binary gels with various microstructures: Fabrication, characterization, formation mechanism, and controlled release properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhong, F.; Yokoyama, W.; Huang, D.J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Y. Interactions in starch co-gelatinized with phenolic compound systems: Effect of complexity of phenolic compounds and amylose content of starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.L.; Yan, P.; Liu, X.C.; Kang, X.; Jin, Y.G.; Sheng, L.; Xia, J.X. Enhancing solid-like characteristics of porcine plasma protein-carrageenan-based high internal phase emulsion: As solid fat alternative of loading curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 139, 108528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, A.; Remondetto, G.E.; Subirade, M. Soy protein cold-set hydrogels as controlled delivery devices for nutraceutical compounds. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Z.; Liu, C.Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.Z.; Yuan, Y.K.; Wang, D.F.; Xu, Y. Fabrication and characterization of cold-gelation whey protein-chitosan complex hydrogels for the controlled release of curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Reyes, S.V.; Garcia-Suarez, F.J.; Jimenez, M.T.; San Martin-Gonzalez, M.F.; Bello-Perez, L.A. Protection of L. rhamnosus by spray-drying using two prebiotics colloids to enhance the viability. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | T21 (ms) | T22 (ms) | T23 (ms) | PT21 (%) | PT22 (%) | PT23 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.82 ± 0.03 d | 204.94 ± 0.14 d | 1889.65 ± 1.73 d | 0.30 ± 0.03 a | 87.65 ± 0.17 a | 12.05 ± 0.10 a |
| 1.0% | 1.58 ± 0.04 c | 191.21 ± 2.25 c | 1644.67 ± 9.84 c | 0.34 ± 0.01 a | 90.15 ± 0.11 b | 9.51 ± 0.05 b |
| 2.0% | 1.28 ± 0.07 b | 178.34 ± 3.91 b | 1534.36 ± 11.73 b | 0.36 ± 0.05 a | 93.35 ± 0.24 c | 6.29 ± 0.14 c |
| 3.0% | 0.79 ± 0.14 a | 155.25 ± 4.73 a | 1431.45 ± 6.73 a | 0.38 ± 0.11 a | 96.14 ± 0.32 d | 3.48 ± 0.07 d |
| 4.0% | 0.85 ± 0.08 a | 160.79 ± 4.21 a | 1445.14 ± 5.75 a | 0.37 ± 0.04 a | 96.26 ± 0.19 d | 3.37± 0.07 d |
| Sample | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 27.17 ± 0.07 a | 18.03 ± 0.09 a | 21.03 ± 0.18 a | 33.77 ± 0.05 a |
| 2.0% | 27.00 ± 0.40 a | 18.13 ± 0.46 a | 21.11 ± 0.60 a | 33.76 ± 0.56 a |
| 4.0% | 26.73 ± 0.36 a | 18.30 ± 0.27 a | 21.23 ± 0.76 a | 33.74 ± 0.46 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Ding, C.; Yuan, J. Effect and Mechanism of Soluble Starch on Bovine Serum Albumin Cold-Set Gel Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase: A Significantly Improved Carrier for Active Substances. Foods 2023, 12, 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234313
Shi H, Ding C, Yuan J. Effect and Mechanism of Soluble Starch on Bovine Serum Albumin Cold-Set Gel Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase: A Significantly Improved Carrier for Active Substances. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234313
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Haoting, Changsheng Ding, and Jianglan Yuan. 2023. "Effect and Mechanism of Soluble Starch on Bovine Serum Albumin Cold-Set Gel Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase: A Significantly Improved Carrier for Active Substances" Foods 12, no. 23: 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234313
APA StyleShi, H., Ding, C., & Yuan, J. (2023). Effect and Mechanism of Soluble Starch on Bovine Serum Albumin Cold-Set Gel Induced by Microbial Transglutaminase: A Significantly Improved Carrier for Active Substances. Foods, 12(23), 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234313





