Investigation on 3D Printing of Shrimp Surimi Adding Three Edible Oils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Surimi
2.3. The 3D Printability
2.4. Rheological Properties
2.5. Textural Properties
2.6. Water Distribution
2.7. Water-Holding Capacity
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
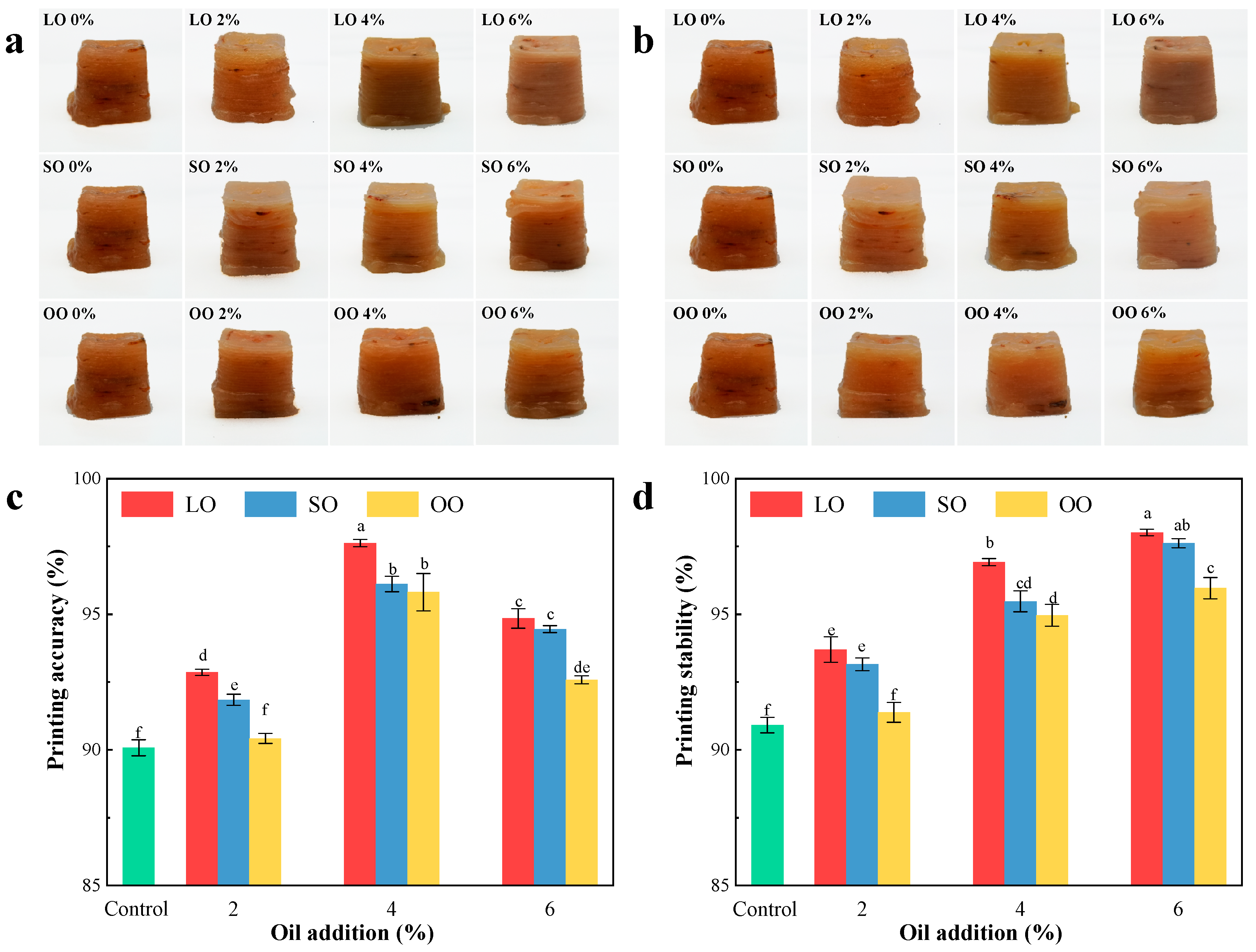
3.1. The 3D Printability
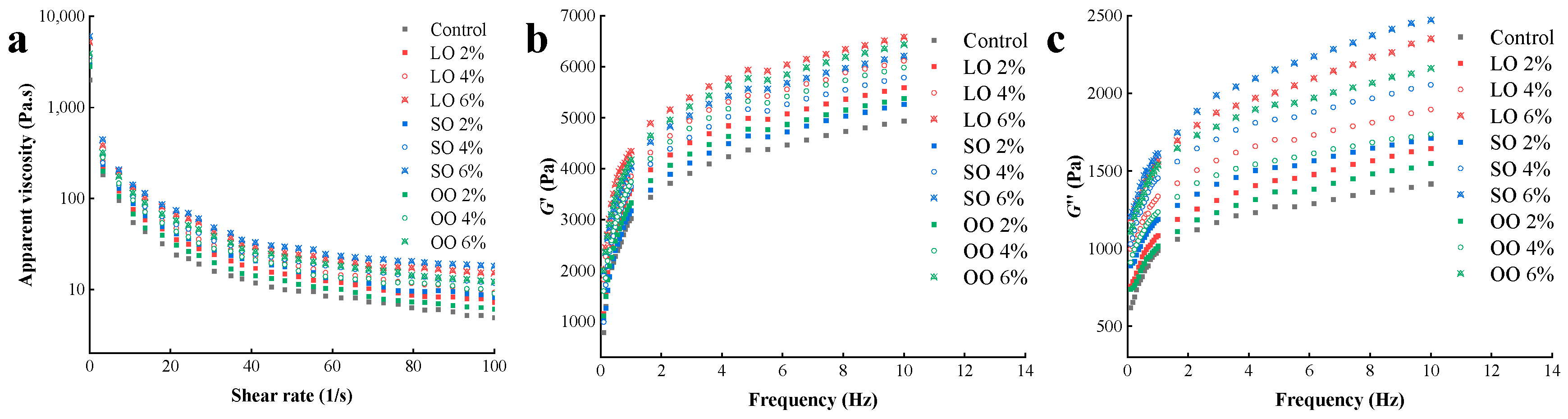
3.2. Rheological Properties
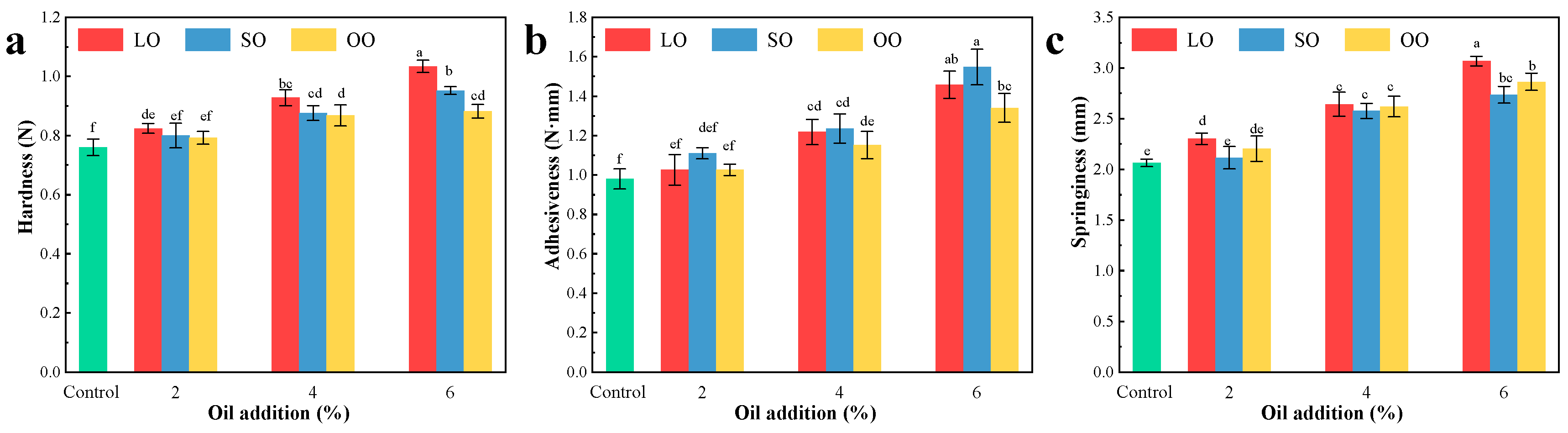
3.3. Textural Properties
3.4. Water Distribution
3.5. Water-Holding Capacity
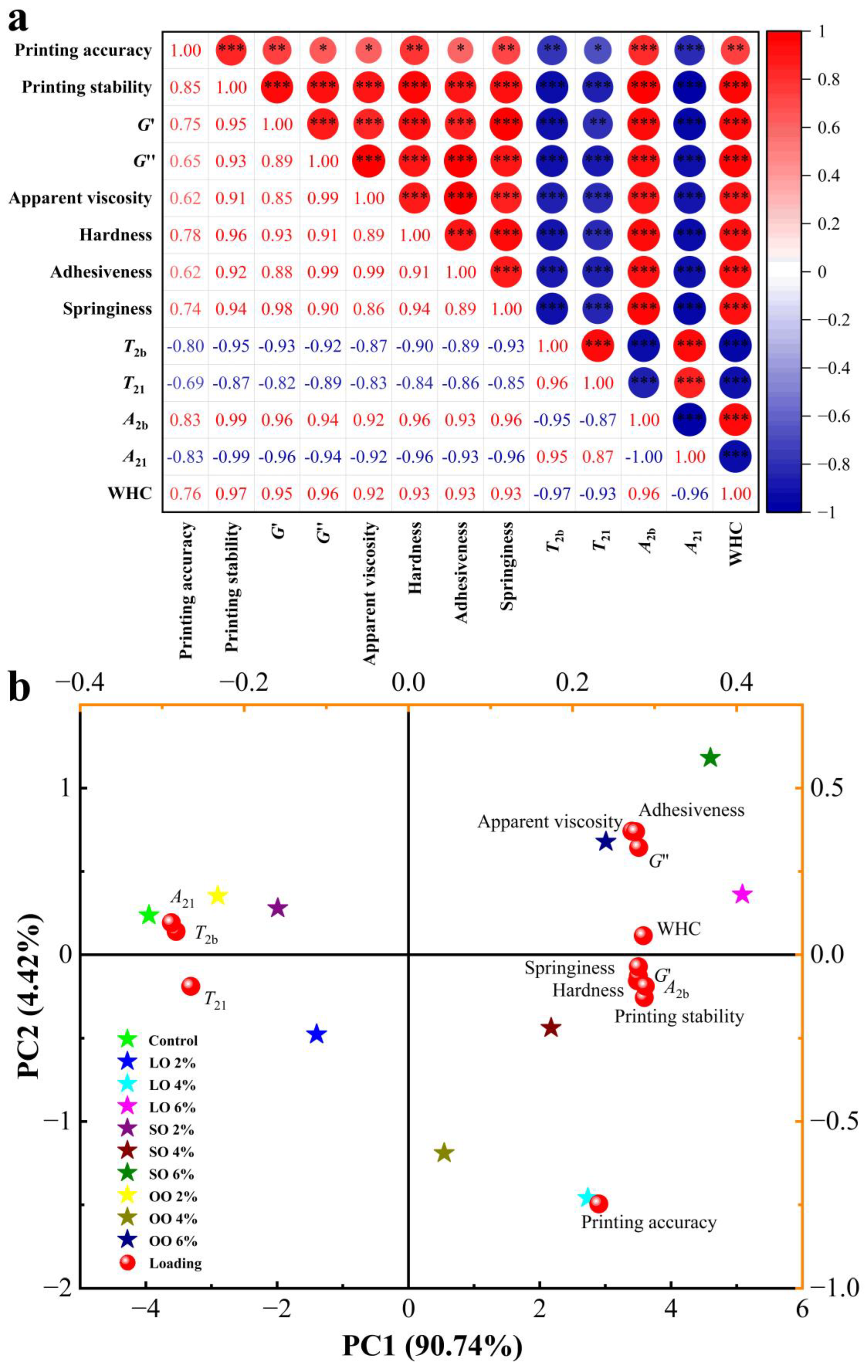
3.6. The Correlation and Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pant, A.; Lee, A.Y.; Karyappa, R.; Lee, C.P.; An, J.; Hashimoto, M.; Tan, U.-X.; Wong, G.; Chua, C.K.; Zhang, Y. 3D food printing of fresh vegetables using food hydrocolloids for dysphagic patients. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 114, 106546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Chitrakar, B.; Hati, S.; Xie, S.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Mo, H. Development of black fungus-based 3D printed foods as dysphagia diet: Effect of gums incorporation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantihal, S.; Prakash, S.; Godoi, F.C.; Bhandari, B. Effect of additives on thermal, rheological and tribological properties of 3D printed dark chocolate. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Prakash, S.; Zhang, M. Creation of internal structure of mashed potato construct by 3D printing and its textural properties. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhu, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, F. Rheological & 3D printing properties of potato starch composite gels. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuhongsung, P.; Zhang, M.; Devahastin, S. Investigation on 3D printing ability of soybean protein isolate gels and correlations with their rheological and textural properties via LF-NMR spectroscopic characteristics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 122, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Su, W.; Tan, M. Advancements in precision nutrition: Steady-state targeted delivery of food functional factors for nutrition intervention of chronic diseases. Food Saf. Health 2023, 1, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Soria-Lopez, A.; Barba, F.J.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Prieto, M.A. Aquaculture and agriculture-by products as sustainable sources of omega-3 fatty acids in the food industry. eFood 2021, 2, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Rao, Z. Effect of ultrasound-assisted thawing on gelling and 3D printing properties of silver carp surimi. Food Res. Int. 2021, 145, 110405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wei, S.; Xia, Q.; Pan, Y.; Ji, H.; Deng, C.; Hao, J.; Liu, S. Insight into the correlations among rheological behaviour, protein molecular structure and 3D printability during the processing of surimi from golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Yang, C. Investigation on fish surimi gel as promising food material for 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.W.; Cheng, W. Cloning and characterization of tyrosine decarboxylase (TDC) from Litopenaeus vannamei, and its roles in biogenic amines synthesis, immune regulation, and resistance to Vibrio alginolyticus by RNA interference. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2021, 123, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Xia, Q.; Zheng, O.; Liu, S.; Ji, H.; Deng, C.; Hao, J. The relationship between rheological and textural properties of shrimp surimi adding starch and 3D printability based on principal component analysis. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 2985–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, C.; Prakash, S.; Zhu, B.; Dong, X. Role of dietary fiber and flaxseed oil in altering the physicochemical properties and 3D printability of cod protein composite gel. J. Food Eng. 2022, 327, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, J.; Gu, S.; Pan, Z.; Ding, Y. Changes in physicochemical properties and protein structure of surimi enhanced with camellia tea oil. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, A.Q.; Xu, X.B.; Guo, Y.; Du, M.; Yu, C.P.; Wu, C. Fabrication of flavour oil high internal phase emulsions by casein/pectin hybrid particles: 3D printing performance. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Phuhongsung, P. Improving 3D/4D printing characteristics of natural food gels by novel additives: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ciftci, O.N. Effects of high oil compositions and printing parameters on food paste properties and printability in a 3D printing food processing model. J. Food Eng. 2021, 288, 110135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.; Lyu, F.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid encapsulation system: Physical and oxidative stability, and medical applications. Food Front. 2022, 3, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, H.; Lyu, F.; Lin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, Y. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of fish myofibrillar protein-lipid composite gels: Effects of fat type and concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wei, S.; Xia, Q.; Pan, Y.; Liu, S.; Ji, H.; Deng, C.; Hao, J. LF-NMR as a tool for predicting the 3D printability of surimi-starch systems. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnicka, A.; Sala, G.; Kruif, C.G.; Velde, F. The interactions between oil droplets and gel matrix affect the lubrication properties of sheared emulsion-filled gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrowski, B.N.; Tahergorabi, R.; Jaczynski, J. Dynamic rheology and thermal transitions of surimi seafood enhanced with ω-3-rich oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Yi, X.; Xia, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Shen, X. Effects of fish oil on the gel properties and emulsifying stability of myofibrillar proteins: A comparative study of tilapia, hairtail and squid. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 161, 113373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Pollack, G.H. Healthy fats and exclusion-zone size. Food Chem. 2020, 316, 126305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.W.; Bae, H.; Park, H.J. Reprint of: Classification of the printability of selected food for 3D printing: Development of an assessment method using hydrocolloids as reference material. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.; Jӓger, H.; Chen, J.; Ettelaie, R. Construction of 3D printed reduced-fat meat analogue by emulsion gels. Part II: Printing performance, thermal, tribological, and dynamic sensory characterization of printed objects. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Choi, J.H.; Han, D.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, J.W.; Chung, H.J.; Kim, C.J. Optimization of replacing pork back fat with grape seed oil and rice bran fiber for reduced-fat meat emulsion systems. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fan, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W. Characterization of surimi particles stabilized novel pickering emulsions: Effect of particles concentration, pH and NaCl levels. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Chang, T.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Cui, M. Effects of vegetable oils on gel properties of surimi gels. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Sun, Y.; Tan, H.; Ma, L.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y. Effect of oil phases on the stability of myofibrillar protein microgel particles stabilized Pickering emulsions: The leading role of viscosity. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, X. Functional performance of a novel emulsion gel-based pork fat mimics in low-fat meat batter system: Incorporation of physicochemical and oral processing. Food Struct. 2023, 37, 100335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Xu, S.; Sun, J.; Yue, X.; Wu, Z.; Shao, J. Effects of fatty acid saturation degree on salt-soluble pork protein conformation and interfacial adsorption characteristics at the oil/water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Gao, Z. Effects of malondialdehyde-induced protein modification on water functionality and physicochemical state of fish myofibrillar protein gel. Food Res. Int. 2016, 86, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, J.; Petrović, L.; Sovilj, V.; Katona, J. Complex coacervation in gelatin/sodium caseinate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 37, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debusca, A.; Tahergorabi, R.; Beamer, S.K.; Partington, S.; Jaczynski, J. Interactions of dietary fibre and omega-3-rich oil with protein in surimi gels developed with salt substitute. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Khan, M.A.; Yu, X.; Zheng, H.; Han, M.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Changes in protein structures to improve the rheology and texture of reduced-fat sausages using high pressure processing. Meat Sci. 2016, 121, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, D.; Xiong, Y.L.; Castillo, M.; Payne, F.A.; Garrido, M.D. Textural and viscoelastic properties of pork frankfurters containing canola-olive oils, rice bran, and walnut. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xiong, Y.L.; Chen, J.; Tang, X.; Zhou, G. Rheological and microstructural properties of porcine myofibrillar protein-lipid emulsion composite gels. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, E207–E217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H. Effect of whey protein on the 3D printing performance of konjac hybrid gel. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 140, 110716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Deng, Y.; Song, L.; Batur, A.; Jia, N.; Liu, D. Investigation the effects of protein hydration states on the mobility water and fat in meat batters by LF-NMR technique. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, T.; Nie, Y.; Jiang, S.; Lin, L.; Lu, J. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of composite surimi gels: The effects of ultrasonic treatment and olive oil concentration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2022, 88, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chou, C.; Yu, Y.; Hsu, C.; Wang, S.; Ko, Y.; Chen, Y. Chicken surimi fortified by omega-3 fatty acid addition: Manufacturing and quality properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Li, L.; Peng, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, Q.; He, N.; Cai, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, X. Effects of different lipids on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of pale, soft and exudative (PSE)-like chicken meat gel. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 145, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, Y.; Durmus, M.; Ucar, Y.; Özogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M. Comparative study of nanoemulsions based on commercial oils (sunflower, canola, corn, olive, soybean, and hazelnut oils): Effect on microbial, sensory, and chemical qualities of refrigerated farmed sea bass. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B. Effect of addition of beeswax based oleogel on 3D printing of potato starch-protein system. Food Struct. 2021, 27, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wei, S.; Han, Z.; Zheng, O.; Ji, H.; Zhang, B.; Liu, S. Investigation on 3D Printing of Shrimp Surimi Adding Three Edible Oils. Foods 2024, 13, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030429
Pan Y, Sun Q, Liu Y, Wei S, Han Z, Zheng O, Ji H, Zhang B, Liu S. Investigation on 3D Printing of Shrimp Surimi Adding Three Edible Oils. Foods. 2024; 13(3):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030429
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Yanmo, Qinxiu Sun, Yang Liu, Shuai Wei, Zongyuan Han, Ouyang Zheng, Hongwu Ji, Bin Zhang, and Shucheng Liu. 2024. "Investigation on 3D Printing of Shrimp Surimi Adding Three Edible Oils" Foods 13, no. 3: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030429
APA StylePan, Y., Sun, Q., Liu, Y., Wei, S., Han, Z., Zheng, O., Ji, H., Zhang, B., & Liu, S. (2024). Investigation on 3D Printing of Shrimp Surimi Adding Three Edible Oils. Foods, 13(3), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13030429





