Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ginsenosides Extracted from Forest-Grown Wild Panax quinquefolius L.
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction of Active Components of Forest-Grown Wild American Ginseng
2.3. Composition of AGGs Evaluated by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS
2.4. Contents of AGGs Analyzed by HPLC
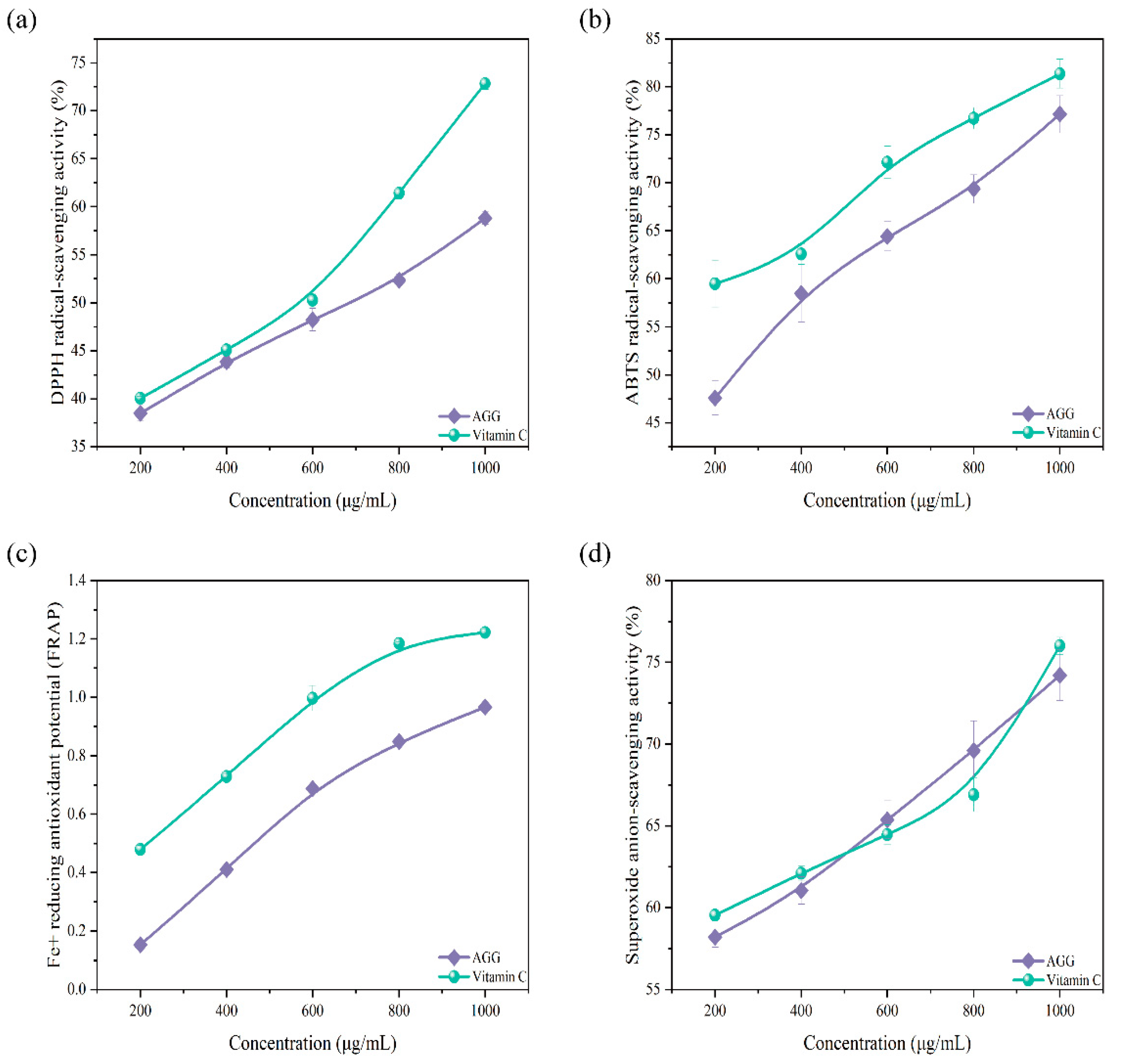
2.5. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis
2.5.1. Assay of Scavenging Activity on DPPH Free Radicals
2.5.2. Assay of Anion-Scavenging Activity on Superoxide Radicals
2.5.3. Assay of Scavenging Activity on ABTS Radicals
2.5.4. Assay of Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Potential (FRAP)
2.6. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of AGGs on RAW 264.7 Macrophages
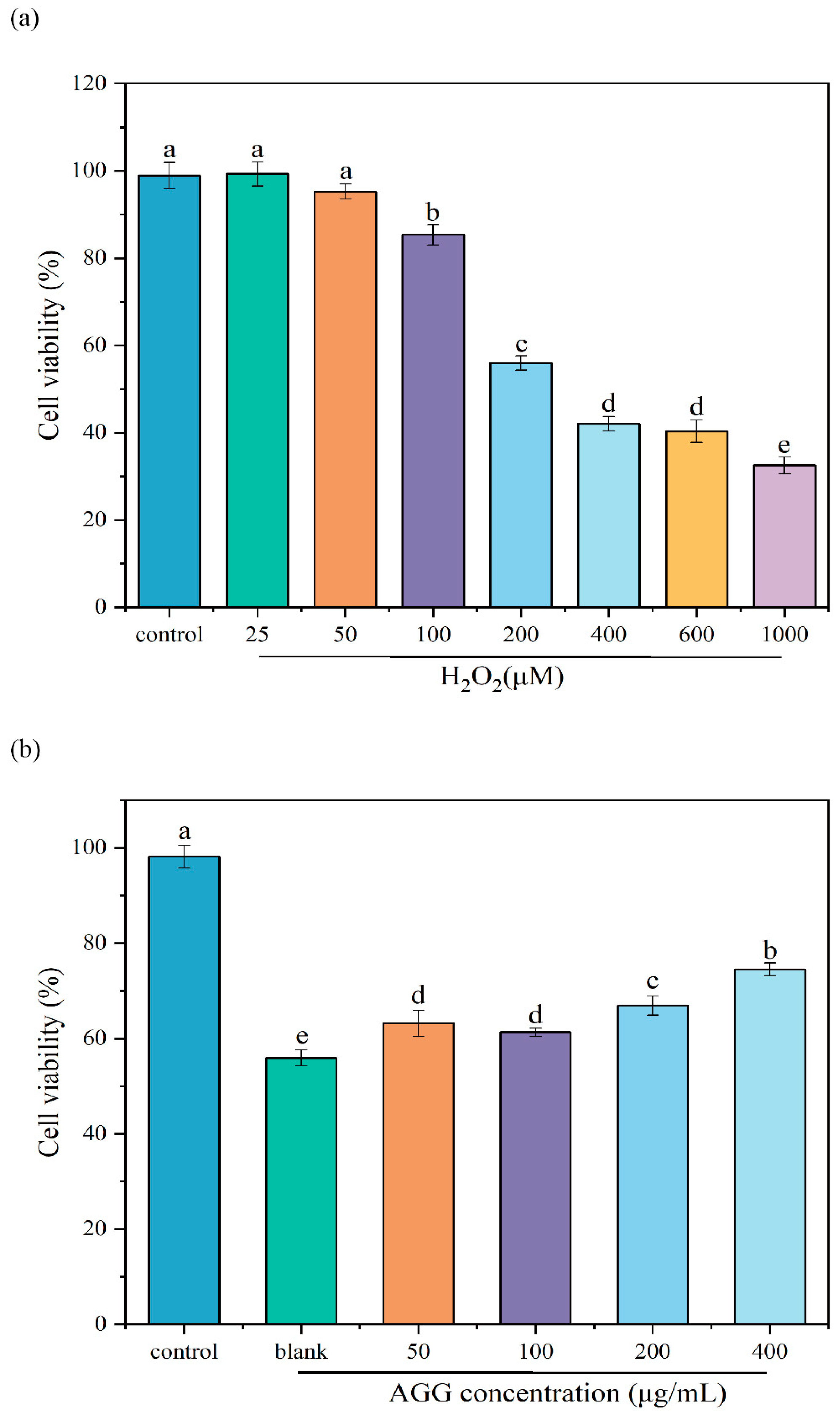
2.6.1. Cytotoxicity of AGGs
2.6.2. The Protective Effect of AGGs on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury
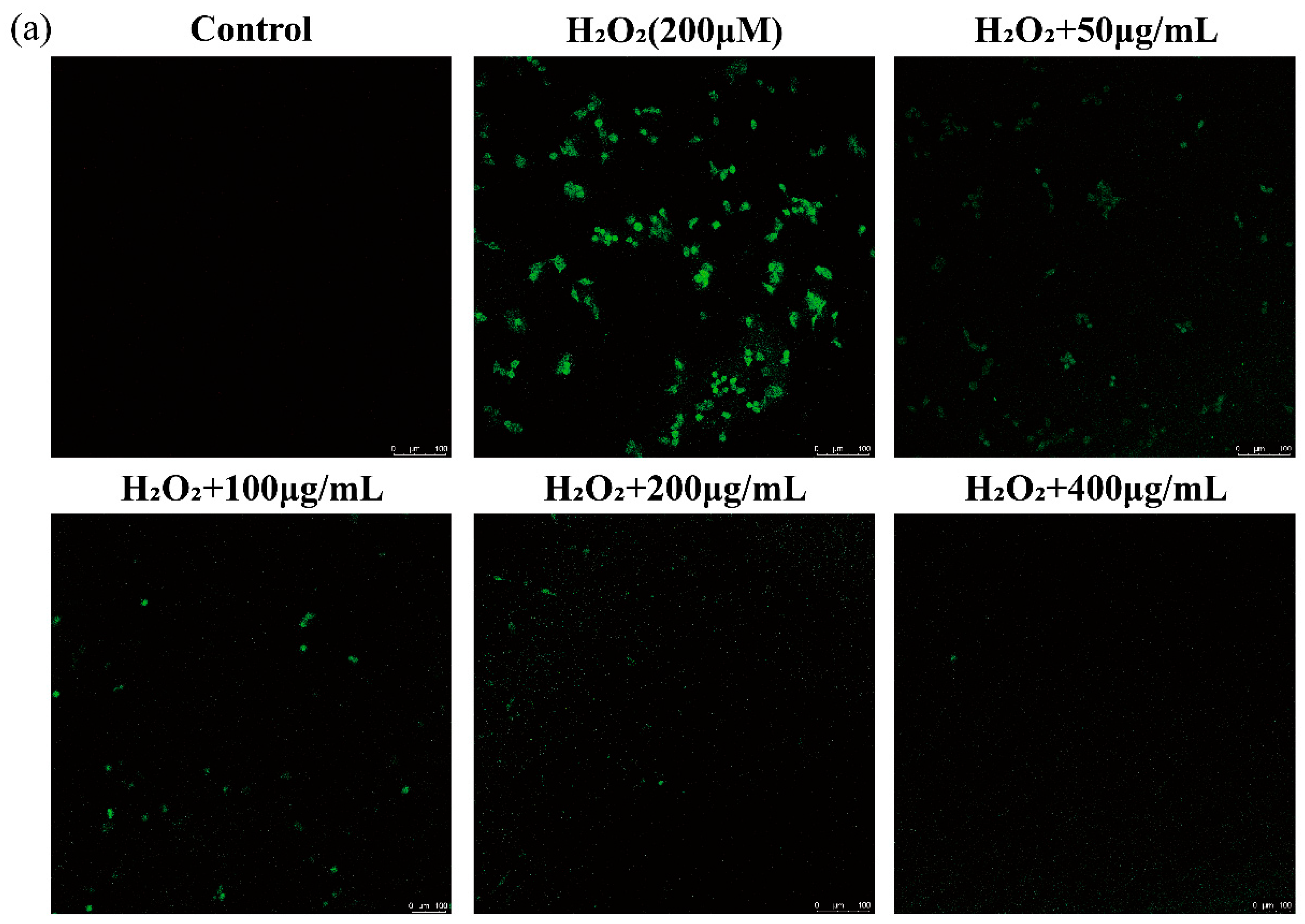
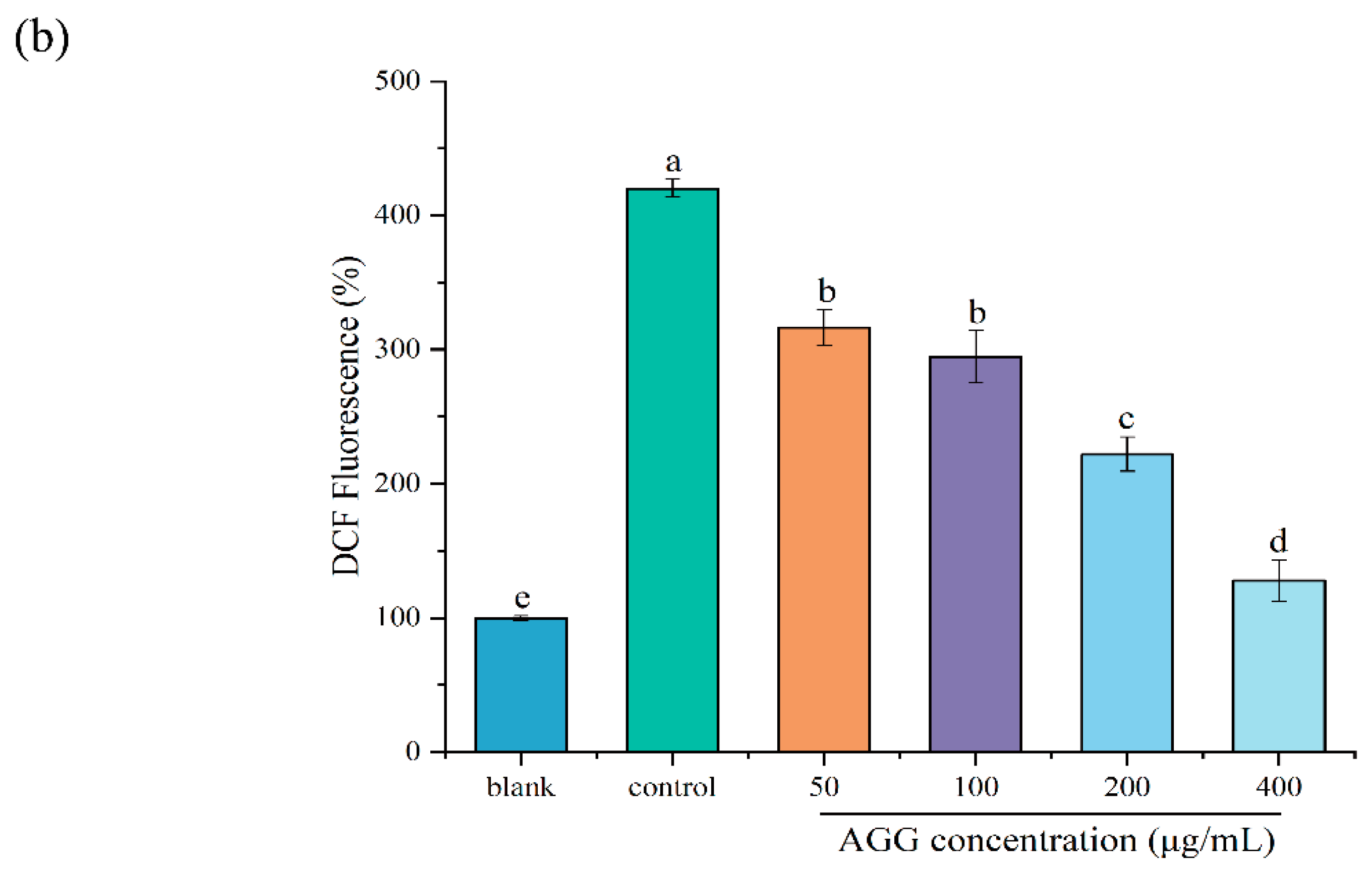
2.6.3. Effects of AGGs on Intracellular ROS of RAW 264.7 Macrophages
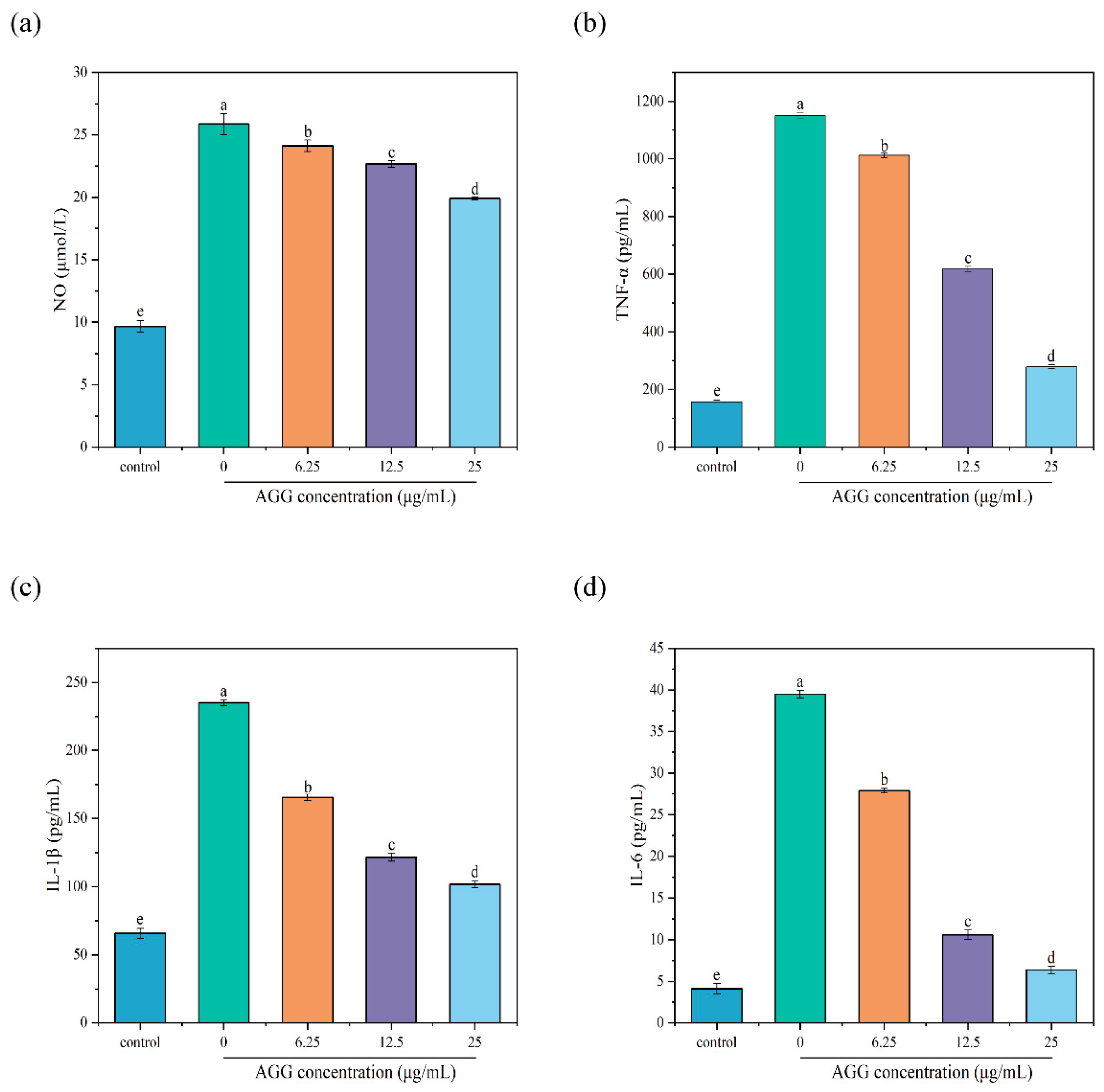
2.6.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of AGGs in LPS-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Identification of Terpenoids in Panax quinquefolius L. by LC-MS
3.2. In Vitro Antioxidant Activity Analysis of AGGs
3.3. Protective Effect of AGGs on H2O2-Induced Oxidative Injury in RAW 264.7 Macrophages
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of AGGs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGGs | American ginseng ginsenosides |
| FRAP | Ferric-reducing antioxidant potential |
| TPTZ | Tripyridyltriazine |
| ABTS | Aiammonium salt |
| PMS | Phenazine methosulphate |
| DPPH | 1,1-Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl |
| NBT | Nitroblue tetrazolium |
| CCK8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| Vc | Ascorbic acid |
References
- Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Q.; Li, N. In vitro antioxidant analysis of flavonoids extracted from Artemisia argyi stem and their anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheban, K.C.; Woodbury, D.J.; Duguid, M.C. Importance of environmental factors on plantings of wild-simulated American Ginseng. Agrofor. Syst. 2022, 96, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Abid, S.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Panax ginseng cultivars in Korea and China. Molecules 2020, 25, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hofseth, A.B.; Cui, X.; Windust, A.J.; Poudyal, D.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Matesic, L.E.; Singh, N.P.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. American ginseng suppresses colitis through p53-mediated apoptosis of inflammatory cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 3, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Han, M.; Yang, L. Differences in the Quality, Yield, and Soil Microecology of Ginseng in Different Planting Environments. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratan, Z.A.; Haidere, M.F.; Hong, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Lee, J.-O.; Lee, J.; Cho, J.Y. Pharmacological potential of ginseng and its major component ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.-Y.; Zhang, P.-P.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zheng, Y.-Y.; Huang, Y.-R.; Zheng, G.-Q.; Lin, Y. Preclinical systematic review of ginsenoside Rg1 for cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Aging 2021, 13, 7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, W.; Wang, Z.; Tian, L.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, T. Pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 975784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, G.N.; Hong, F.X.; Peng, D.; Ming, T. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates isoflurane/surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction via inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2017, 30, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Seog, H.M.; Choi, I.W.; Park, M.W.; Cho, H.Y. Antioxidant properties of various solvent extracts from wild ginseng leaves. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 39, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.H.; Seog, H.M.; Choi, I.W.; Cho, H.Y. Antioxidant activities of cultivated and wild Korean ginseng leaves. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Xie, Z.; Huang, S.; Tai, Y.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, W.; Sun, J.; Yuan, Y. Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharides extracted from Lilium lancifolium Thunb. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 52, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Yang, X.-W.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.-J.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.-P. Application of UPLC-Triple TOF-MS/MS metabolomics strategy to reveal the dynamic changes of triterpenoid saponins during the decocting process of Asian ginseng and American ginseng. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Q.; Liu, Z. Determination of Total Saponins in Araliaceae Functional Food. Shandong Chem. Ind. 2021, 50, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, W.A.; Hendel, J.G.; Elmi, J. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography determination of ginsenosides of Panax quinquefolium. J. Chromatogr. A 1996, 755, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.E.-M.M.R.; Hassan, H.M.M. Free radical scavenging activity of three different flowers-Hibiscus rosa-sinensis, Quisqualis indica and Senna surattensis. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Ye, H.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, X. Production, characterization and antioxidant activities in vitro of exopolysaccharides from endophytic bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa EJS-3. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 78, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Laura, T.; Liang, X.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X. Determination of polyphenolic content and antioxidant activity of kudingcha made from Ilex kudingcha CJ Tseng. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lü, Y.; Ma, G.; Chen, J.; Liu, D.; Ye, X. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacities of bayberry juices. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Xie, M.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Hu, B.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.; Liu, Z. Evaluation of chemical property, cytotoxicity and antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of polysaccharides from Fuzhuan brick teas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmers, M.A.; Guerrero-Medina, J.L.; Esposito, D.; Grace, M.H.; Paredes-Lopez, O.; Garcia-Saucedo, P.A.; Ann Lila, M. Characterization of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Activities from Mamuyo (Styrax ramirezii Greenm.) Fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10459–10465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; Cha, S.; Kim, M.-Y.; Cho, J.Y. Ginsenosides are active ingredients in Panax ginseng with immunomodulatory properties from cellular to organismal levels. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wang, C.-Z.; He, T.-C.; Yuan, C.-S.; Du, W. Antioxidants potentiate American ginseng-induced killing of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 289, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, R.S.; Abdel-Latif, M.S.; Abd El Baky, H.H.; Tawfeek, L.S. Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of some medicinal plants’ crude juices. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 28, e00536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-del-Río, I.; López-Ibáñez, S.; Magadán-Corpas, P.; Fernández-Calleja, L.; Pérez-Valero, Á.; Tuñón-Granda, M.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Terpenoids and polyphenols as natural antioxidant agents in food preservation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saw, C.L.L.; Yang, A.Y.; Cheng, D.C.; Boyanapalli, S.S.-S.; Su, Z.-Y.; Khor, T.O.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Kong, A.-N.T. Pharmacodynamics of ginsenosides: Antioxidant activities, activation of Nrf2, and potential synergistic effects of combinations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Wu, L.; Li, C.-R.; Wang, X.-W.; Ma, Y.-J.; Zhong, Z.-y.; Zhao, H.-B.; Cui, J.; Xun, S.-F.; Huang, X.-L.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 Protects Rat Cardiomyocyte From Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Oxidative Injury Via Antioxidant and Intracellular Calcium Homeostasis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 108, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.-W.; Chung, Y.-C.; Shih, I.P.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chou, S.-T.; Hsu, C.-K. Red Bean Extract Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation and H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in RAW 264.7 Macrophages. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, W.; Yuan, Q.; Ye, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X. Box-Behnken design for extraction optimization, characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of Cicer arietinum L. hull polysaccharides. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh Dieu, V.; Quang Ngoc, N.; Van-Long, T. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects of combination between sulforaphane and acetaminophen in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2019, 41, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, M.-J.; Jeong, W.-S.; Kim, K.-B. Detoxifying effect of fermented black ginseng on H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1516–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Siddiqi, M.H.; Aceituno, V.C.; Simu, S.Y.; Yang, D.C. Suppression of MAPKs/NF-beta B Activation Induces Intestinal Anti-Inflammatory Action of Ginsenoside Rf in HT-29 and RAW264.7 Cells. Immunol. Investig. 2016, 45, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Khajuria, A.; Taneja, S.C.; Khajuria, R.K.; Singh, J.; Johri, R.K.; Qazi, G.N. The gastric ulcer protective effect of boswellic acids, a leukotriene inhibitor from Boswellia serrata, in rats. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-Y.; Jeong, J.-J.; Eun, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and its metabolites ginsenoside Rh1 and 20(S)-protopanaxatriol in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 762, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Yoo, E.S.; Baik, K.U.; Park, M.H.; Han, B.H. In vitro inhibitory effect of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production and its modulation by known TNF-alpha antagonists. Planta Med. 2001, 67, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budamagunta, V.; Manohar-Sindhu, S.; Yang, Y.; He, Y.; Traktuev, D.O.; Foster, T.C.; Zhou, D. Senescence-associated hyper-activation to inflammatory stimuli in vitro. Aging 2021, 13, 19088–19107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-S.; Lee, E.-J.; Lee, J.-C.; Kim, W.-K.; Kim, H.-S. Anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids in IFN-γ-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells: Involvement of NF-κB and ERK signaling pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joh, E.-H.; Lee, I.-A.; Jung, I.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1 activation-The key step of inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 82, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, R.; Yang, Q.; Kong, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Shi, M.; Xiong, L.; et al. Ginsenoside Rd attenuates early oxidative damage and sequential inflammatory response after transient focal ischemia in rats. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.-A.; Hyam, S.R.; Jang, S.-E.; Han, M.J.; Kim, D.-H. Ginsenoside Re Ameliorates Inflammation by Inhibiting the Binding of Lipopolysaccharide to TLR4 on Macrophages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9595–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, H.; Guan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, C.; Mu, P.; et al. The composition and function of the soil microbial community and its driving factors before and after cultivation of Panax ginseng in farmland of different ages. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-K.; Jin, S.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.-R.; Han, Y.-H.; Song, I.-S. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, and compound K after single or multiple administration of red ginseng extract in human beings. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Chen, K.; Li, Z.; Fan, H.; Xu, B.; Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Xie, Z.; Liu, K.; Zhang, S. Pharmacokinetics and Oral Bioavailability of Panax Notoginseng Saponins Administered to Rats Using a Validated UPLC–MS/MS Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 71, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tao, F.; Yu, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, R.; Feng, J.; Zhai, Q.; Xue, P. Safety evaluation of rare ginsenosides of stems and leaves from American ginseng: 90-day exposure toxicity study combined with intestinal flora analysis and metabonomics in rats. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Hao, C.; Jin, W.; Dong, W.-W.; Quan, L.-H. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside F2 by recombinant β-glucosidase from rat intestinal Enterococcus gallinarum. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, C.-c. Ginsenoside Rb2: A review of pharmacokinetics and pharmacological effects. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
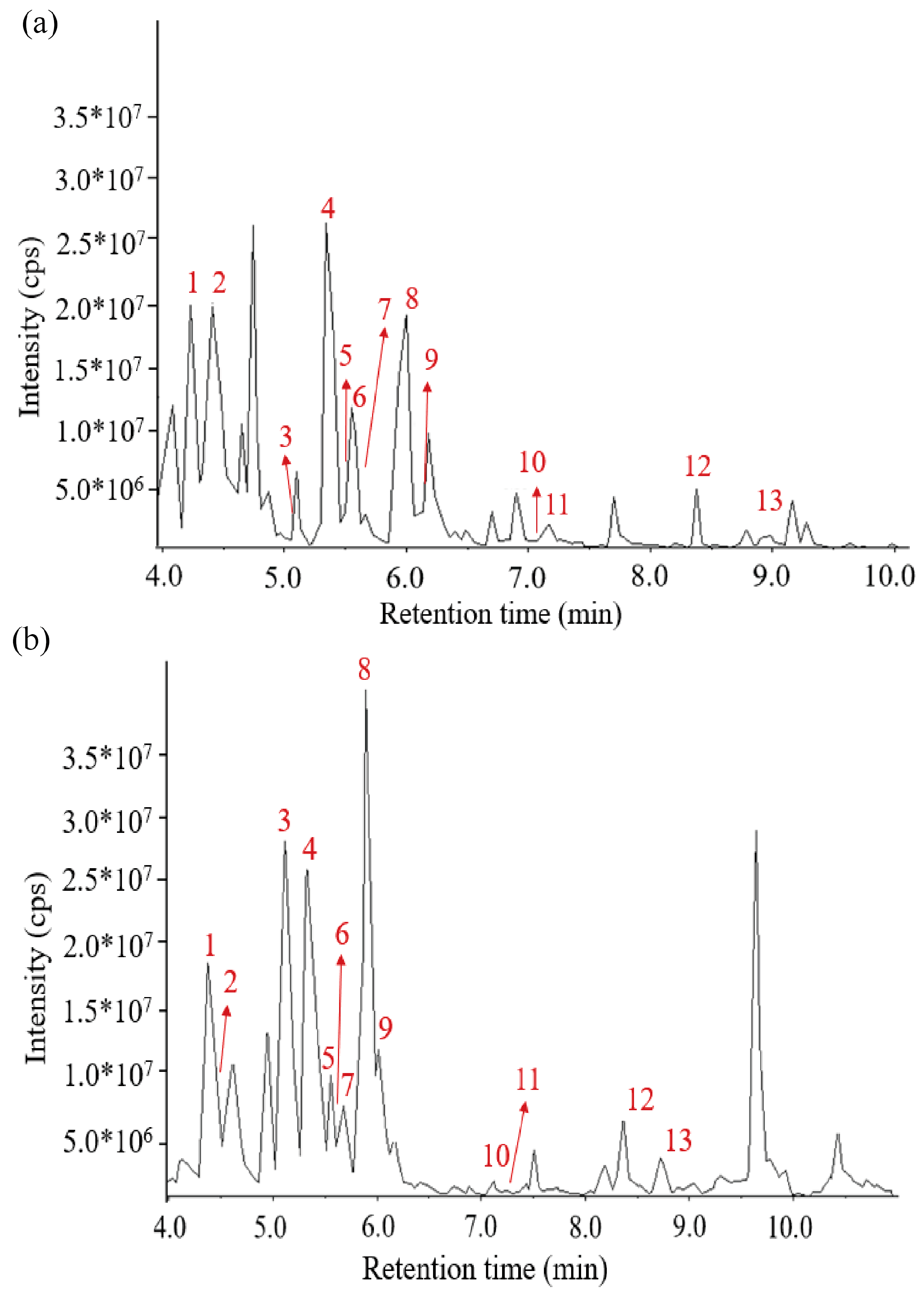
| No. | Molecular Formula | Q1 (Da) | Q3 (Da) | Retention Time | Component Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C48H82O18 | 945.54 | 783.49 | 4.37 | Ginsenoside Re |
| 2 | C42H72O14 | 799.48 | 637.43 | 4.46 | Ginsenoside Rg1 |
| 3 | C42H72O14 | 639.45 | 441.37 | 5.06 | Ginsenoside Rf |
| 4 | C54H92O23 | 1109.61 | 325.11 | 5.37 | Ginsenoside Rb1 |
| 5 | C56H92O25 | 1165.60 | 411.11 | 5.53 | Malonyl Ginsenoside Rc* |
| 6 | C42H72O13 | 783.49 | 475.38 | 5.62 | Ginsenoside Rg2 |
| 7 | C56H92O25 | 1165.60 | 411.11 | 5.66 | Malonyl Ginsenoside Rb2* |
| 8 | C48H82O18 | 947.56 | 325.11 | 5.93 | Ginsenoside Rd |
| 9 | C50H84O19 | 987.55 | 945.54 | 6.01 | 6″-Acetyl-ginsenoside Rd |
| 10 | C42H72O13 | 783.49 | 621.44 | 7.05 | Ginsenoside F2 |
| 11 | C42H72O13 | 783.49 | 459.38 | 7.38 | 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 |
| 12 | C42H70O12 | 765.48 | 603.43 | 8.50 | Ginsenoside Rk1 |
| 13 | C54H92O23 | 1109.61 | 325.11 | 8.94 | Ginsenoside Rb1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Yang, K.; Sun, Y.; Yang, R.; Hu, Y.; Chen, G.; Cai, H. Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ginsenosides Extracted from Forest-Grown Wild Panax quinquefolius L. Foods 2023, 12, 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234316
Yang Y, Xu S, Yang K, Sun Y, Yang R, Hu Y, Chen G, Cai H. Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ginsenosides Extracted from Forest-Grown Wild Panax quinquefolius L. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234316
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yang, Shan Xu, Kemeng Yang, Yuning Sun, Ruirui Yang, Yanan Hu, Guijie Chen, and Huimei Cai. 2023. "Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ginsenosides Extracted from Forest-Grown Wild Panax quinquefolius L." Foods 12, no. 23: 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234316
APA StyleYang, Y., Xu, S., Yang, K., Sun, Y., Yang, R., Hu, Y., Chen, G., & Cai, H. (2023). Characterization and In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Ginsenosides Extracted from Forest-Grown Wild Panax quinquefolius L. Foods, 12(23), 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234316








