Bread Products from Blends of African Climate Resilient Crops: Baking Quality, Sensory Profile and Consumers’ Perception
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Water Binding Capacity of Native and Treated Flours
2.2.2. Thermal Analysis of Native and Treated Flours
2.2.3. Pasting Behaviour of Native and Treated Flours
2.2.4. Bread-Making Procedure
2.2.5. Instrumental Bread Quality Evaluation
2.2.6. Descriptive Sensory Analysis
2.2.7. Sensory Evaluation with Naive Consumers of a CRCs-Based Bread and of Wholemeal Wheat Bread
Subjects
Sensory Sessions
Hedonic Characterization and Rate-All-That-Apply (RATA)
2.2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Sorghum, Cowpea and Cassava Flours
3.2. Baking Quality of Breads Made from Blends of Cassava, Sorghum and Cowpea Flours
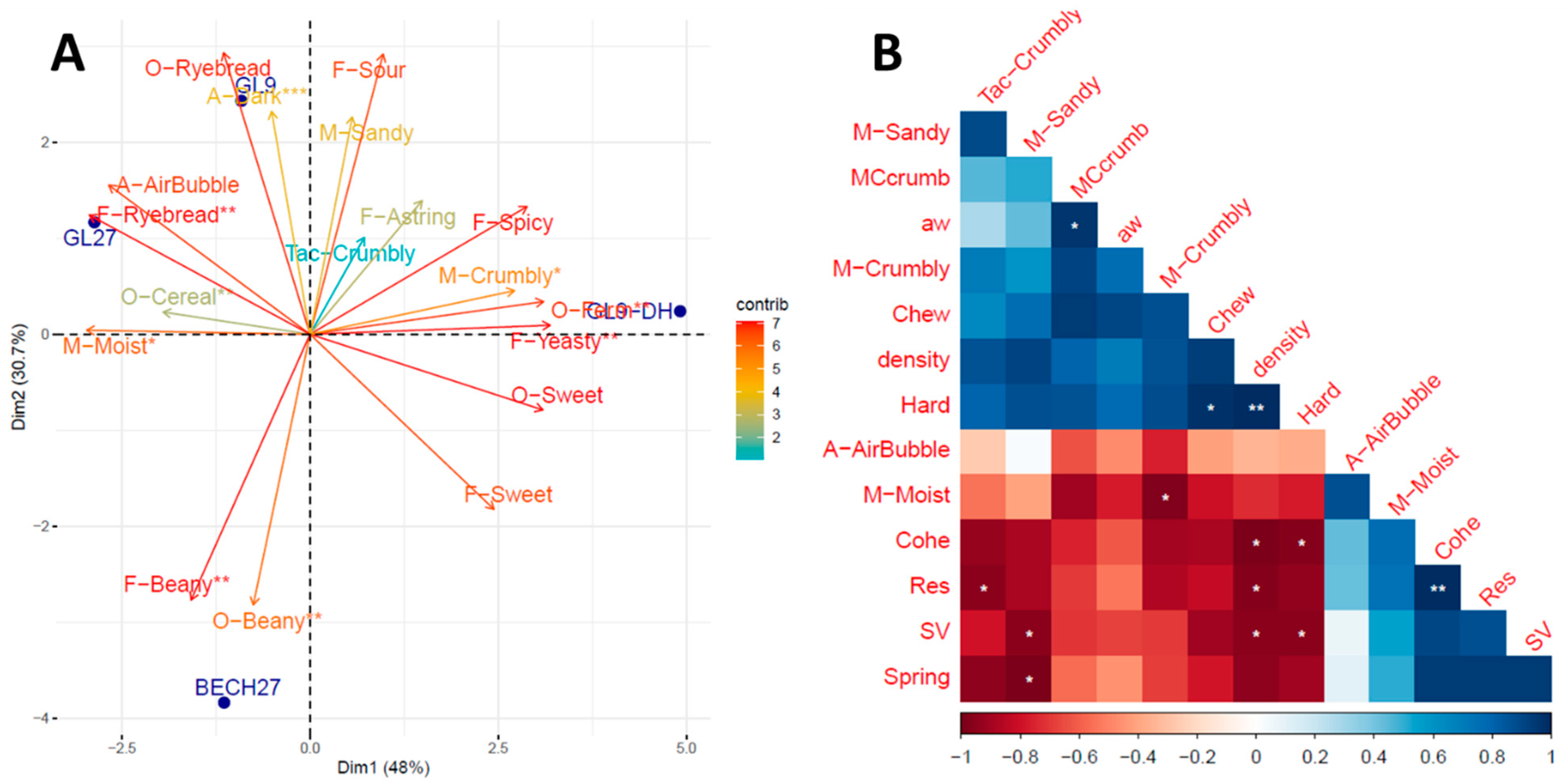
3.3. Descriptive Sensory Profiling of Bread
3.4. Consumers Evaluation of CRCs-Based Bread and Commercial Wholemeal Wheat Bread
3.5. Demonstration of Wheat Replacement in Real Life Conditions in SSA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ofori, S.A.; Cobbina, S.J.; Obiri, S. Climate Change, Land, Water, and Food Security: Perspectives From Sub-Saharan Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 680924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blekking, J.; Giroux, S.; Waldman, K.; Battersby, J.; Tuholske, C.; Robeson, S.M.; Siame, G. ScienceDirect the Impacts of Climate Change and Urbanization on Food Retailers in Urban Sub-Saharan Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2022, 55, 101169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J.E.; Hellin, J.; Sonder, K.; Araus, J.L.; MacRobert, J.F.; Thierfelder, C.; Prasanna, B.M. Adapting Maize Production to Climate Change in Sub-Saharan Africa. Food Secur. 2013, 5, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, N.M.; Jayne, T.S.; Shiferaw, B. Africa’s Rising Demand for Wheat: Trends, Drivers, and Policy Implications. Dev. Policy Rev. 2015, 33, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shew, A.M.; Tack, J.B.; Nalley, L.L.; Chaminuka, P. Yield Reduction under Climate Warming Varies among Wheat Cultivars in South Africa. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.; Pixley, K.; Zinyengere, N.; Meng, S.; Tufan, H.; Cichy, K.; Bizikova, L.; Isaacs, K.; Ghezzi-Kopel, K.; Porciello, J. A Scoping Review of Adoption of Climate-Resilient Crops by Small-Scale Producers in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhankher, O.P.; Foyer, C.H. Climate Resilient Crops for Improving Global Food Security and Safety. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndiaye, M.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; van Bruggen, A.H.C. Effect of Rotation of Cowpea (Vigna Unguiculata) with Fonio (Digitaria Exilis) and Millet (Pennisetum Glaucum) on Macrophomina Phaseolina Densities and Cowpea Yield. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Chimonyo, V.G.P.; Modi, A.T.; Mabhaudhi, T. Water Use and Productivity of a Sorghum-Cowpea-Bottle Gourd Intercrop System. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, D.; Dayoub, M.; Birech, R.; Nakiyemba, A. The Contribution of Cereal Grains to Food Security and Sustainability in Africa: Potential Application of UAV in Ghana, Nigeria, Uganda, and Namibia. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, M.W.J.; Renzetti, S.; Linderhof, V.; du Rand, G.E.; Marx-Pienaar, N.J.M.M.; de Kock, H.L.; Magano, N.; Taylor, J.R.N. Towards Sustainable Shifts to Healthy Diets and Food Security in Sub-Saharan Africa with Climate-Resilient Crops in Bread-Type Products: A Food System Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, J.; Bing, J.; Byrne, P.F.; Cassman, K.G.; Ciampitti, I.; Delmer, D.; Habben, J.; Lafitte, H.R.; Lidstrom, U.E.; Porter, D.O.; et al. Science-Based Intensive Agriculture: Sustainability, Food Security, and the Role of Technology. Glob. Food Sec. 2019, 23, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönfeldt, H.C.; Hall, N.G. Dietary Protein Quality and Malnutrition in Africa. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontieri, P.; Mamone, G.; de Caro, S.; Tuinstra, M.R.; Roemer, E.; Okot, J.; de Vita, P.; Ficco, D.B.M.; Alifano, P.; Pignone, D.; et al. Sorghum, a Healthy and Gluten-Free Food for Celiac Patients as Demonstrated by Genome, Biochemical, and Immunochemical Analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoako, D.; Awika, J.M. Polyphenol Interaction with Food Carbohydrates and Consequences on Availability of Dietary Glucose. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, L.; Capuano, E.; Oliviero, T.; Renzetti, S. Wheat Starch-Tannic Acid Complexes Modulate Physicochemical and Rheological Properties of Wheat Starch and Its Digestibility. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hamaker, B.R. Slowly Digestible Starch: Concept, Mechanism, and Proposed Extended Glycemic Index. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, J.L.; Greenspan, P.; Hartle, D.K.; Dowd, C. Inhibition of Aromatase and A-Amylase by Flavonoids and Proanthocyanidins from Sorghum Bicolor Bran Extracts. J. Med. Food 2011, 14, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, É.A.; Isabel, D.; Natal, G.; Aparecida, V.; Queiroz, V.; Eugene, R.; Roberto, P.; Oliveira, S.; Paula, D.; Benjamim, A.; et al. Sorghum Genotype May Reduce Low-Grade Inflammatory Response and Oxidative Stress and Maintains Jejunum Morphology of Rats Fed a Hyperlipidic Diet. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awika, J.M.; Duodu, K.G. Bioactive Polyphenols and Peptides in Cowpea (Vigna Unguiculata) and Their Health Promoting Properties: A Review. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 38, 686–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, C.; Visvanathan, R.; Deen, A.; Bangamuwage, R.; Jayawardana, B.C.; Nammi, S.; Liyanage, R. Cowpea: An Overview on Its Nutritional Facts and Health Benefits. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4793–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinyawiwatkul, W.; McWatters, K.H.; Beuchat, L.R.; Phillips, R.D. Cowpea Flour: A Potential Ingredient in Food Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996, 36, 413–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumler, R.; Schönlechner, R. Effect of Sorghum on Rheology and Final Quality of Western Style Breads: A Literature Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, T.; Ncube, T.; Ngoromani, N. Rheological Properties and Bread Making Quality of White Grain Sorghum-Wheat Flour Composites. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. Eng. 2015, 2015, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keregero, M.M.; Mtebe, K. Acceptability of Wheat-Sorghum Composite Flour Products: An Assessment. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 1994, 46, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ari Akin, P.; Demirkesen, I.; Bean, S.R.; Aramouni, F. Sorghum Flour Application in Bread: Technological Challenges and Opportunities. Foods 2022, 11, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyango, C.; Mutungi, C.; Unbehend, G.; Lindhauer, M.G. Modification of Gluten-Free Sorghum Batter and Bread Using Maize, Potato, Cassava or Rice Starch. LWT 2011, 44, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, T.J.; Messerschmidt, M.; Bean, S.R.; Park, S.H.; Arendt, E.K. Gluten-Free Bread from Sorghum: Quality Differences among Hybrids. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, A.B.; Awoyale, W.; Alenkhe, B.; Malu, N.; Asiru, B.W.; Manyong, V.; Sanginga, N. Can Food Technology Innovation Change the Status of a Food Security Crop? A Review of Cassava Transformation into “Bread” in Africa. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, M.; Marti, A.; Tuccio, M.G.; Bocchi, E.; Carini, E. Technological Functionality of Composite Flours from Sorghum, Tapioca and Cowpea. Int J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; Heetesonne, I.; Ngadze, R.T.; Linnemann, A.R. Dry Heating of Cowpea Flour below Biopolymer Melting Temperatures Improves the Physical Properties of Bread Made from Climate-Resilient Crops. Foods 2022, 11, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankwa, R.; Aisala, H.; Kayitesi, E.; de Kock, H.L. The Sensory Profiles of Flatbreads Made from Sorghum, Cassava, and Cowpea Flour Used as Wheat Flour Alternatives. Foods 2021, 10, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henshaw, F.O.; McWatters, K.H.; Akingbala, J.O.; Hung, Y.C. Functional Characterization of Flour of Selected Cowpea (Vigna Unguiculata) Varieties: Canonical Discriminant Analysis. Food Chem. 2002, 79, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoletti, M.; Marti, A.; Marengo, M.; Iametti, S.; Pagani, M.A.; Renzetti, S. Understanding the Influence of Buckwheat Bran on Wheat Dough Baking Performance: Mechanistic Insights from Molecular and Material Science Approaches. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; Theunissen, M.; Horrevorts, K. A Systematic Comparison of the Intrinsic Properties of Wheat and Oat Bran Fractions and Their Effects on Dough and Bread Properties: Elucidation of Chemical Mechanisms, Water Binding, and Steric Hindrance. Foods 2021, 10, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, A.P.; Miller, R.; Jaffe, T.; Koppel, K.; Ehmke, L. Sensory Profile and Quality of Chemically Leavened Gluten-Free Sorghum Bread Containing Different Starches and Hydrocolloids. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4391–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.S. Sensory Profile, Consumer Acceptance, and Physicochemical Properties of Pan Bread Made with Imported or Domestic Commercial Wheat Flour. J. Sens. Stud. 2019, 34, e12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyners, M.; Jaeger, S.R.; Ares, G. On the Analysis of Rate-All-That-Apply (RATA) Data. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppermann, A.K.L.; de Graaf, C.; Scholten, E.; Stieger, M.; Piqueras-Fiszman, B. Comparison of Rate-All-That-Apply (RATA) and Descriptive Sensory Analysis (DA) of Model Double Emulsions with Subtle Perceptual Differences. Food Qual. Prefer. 2017, 56, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husson, A.F.; Josse, J.; Le, S.; Mazet, J.; Husson, M.F. Package ‘FactoMineR’. 2022, pp. 1–106. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/FactoMineR/FactoMineR.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2022).
- Phillips, R.D.; Chinnan, M.S.; Branch, A.L.; Miller, J.; McWatters, K.H. Effects of Pretreatment Properties on Functional and Nutritional of Cowpea Meal. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisenga, S.M.; Workneh, T.S.; Bultosa, G.; Alimi, B.A. Progress in Research and Applications of Cassava Flour and Starch: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F. Structure, Physicochemical Properties, Modifications, and Uses of Sorghum Starch. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, M. Model Studies of Cake Baking-Cake Shrinkage and Shear Modulus of Cake Batter During Baking. Cereal Chem. 1985, 62, 242–246. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, L.; Gomez, M.; Martinez, M.M. Mesoscale Structuring of Gluten-Free Bread with Starch. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 38, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzetti, S.; van der Sman, R.G.M. Food Texture Design in Sugar Reduced Cakes: Predicting Batters Rheology and Physical Properties of Cakes from Physicochemical Principles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Ahmad, S.; Amarowicz, R.; De Feo, V. Antioxidant Activity of the Extracts of Some Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) Cultivars Commonly Consumed in Pakistan. Molecules 2013, 18, 2005–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjei-Fremah, S.; Jackai, L.E.; Worku, M. Analysis of Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Properties of Selected Cowpea Varieties Tested in Bovine Peripheral Blood. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2015, 10, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, W.S.U.; Pouvreau, L.; Curran, J.; Van De Velde, F.; De Kok, P.M.T. Flavor Aspects of Pulse Ingredients. Cereal Chem. 2017, 94, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khrisanapant, P.; Kebede, B.; Leong, S.Y.; Oey, I. A Comprehensive Characterisation of Volatile and Fatty Acid Profiles of Legume Seeds. Foods 2019, 8, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolkowski, A.; Guichard, E.; Briand, L.; Salles, C. Volatile Compounds in Pulses: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, W. Functional Foods: Consumer Willingness to Compromise on Taste for Health? Food Qual. Prefer. 2006, 17, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovski, B.; Seetharaman, K.; Duizer, L.M. Development of Soy-Based Bread with Acceptable Sensory Properties. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, R.; Ryland, D.; Sopiwnyk, E.; Aliani, M. Sensory and Physical Characteristics of Pan Bread Fortified with Thermally Treated Split Yellow Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Flour. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 3735–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotsiou, K.; Sacharidis, D.D.; Matsakidou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G.; Lazaridou, A. Impact of Roasted Yellow Split Pea Flour on Dough Rheology and Quality of Fortified Wheat Breads. Foods 2021, 10, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, J.; Bernal, J.; Gómez, M. Wheat Bread Aroma Compounds in Crumb and Crust: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 75, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Pal, J.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Potential of Grain Legume Seeds: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascua, Y.; Koç, H.; Foegeding, E.A. Food Structure: Roles of Mechanical Properties and Oral Processing in Determining Sensory Texture of Soft Materials. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, L.; Carolas, A.L.; van Vliet, T.; van der Linden, E.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S.; van de Velde, F. Energy Storage Controls Crumbly Perception in Whey Proteins/Polysaccharide Mixed Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1404–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y.; Rosenthal, A. Human Oral Processing and Texture Profile Analysis Parameters: Bridging the Gap between the Sensory Evaluation and the Instrumental Measurements. J. Texture Stud. 2019, 50, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puerta, P.; Laguna, L.; Villegas, B.; Rizo, A.; Fiszman, S.; Tarrega, A. Oral Processing and Dynamics of Texture Perception in Commercial Gluten-Free Breads. Food Res. Int. 2020, 134, 109233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaro, A.; Varela, P.; Gimenez, A.; Aldrovandi, A.; Fiszman, S.M.; Hough, G. Textural Quality of White Pan Bread by Sensory and Instrumental Measurements. J. Texture Stud. 2002, 33, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, M.E.; Rosell, C.M. Relationship between Instrumental Parameters and Sensory Characteristics in Gluten-Free Breads. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 235, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, S.; Skibsted, L.H.; Kidmose, U.; Thybo, A.K. Addition of cassava flours in bread-making: Sensory and textural evaluation. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubaiwa, J.; Fogliano, V.; Chidewe, C.; Linnemann, A.R. Hard-to-Cook Phenomenon in Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Processing: Options to Improve Its Role in Providing Food Security. Food Rev. Int. 2017, 33, 167–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, E.; Lajolo, F.M. Starch Alterations in Hard-To-Cook Beans (Phaseolus Vulgaris). J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczak, W.; Doblado, R.; Frias, J.; Vidal-Valverde, C.; Sadowska, J.; Fornal, J. Microstructural and Biochemical Changes in Raw and Germinated Cowpea Seeds upon High-Pressure Treatment. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei-Fremah, S.; Worku, M.; De Erive, M.O.; He, F.; Wang, T.; Chen, G. Effect of Microfluidization on Microstructure, Protein Profile and Physicochemical Properties of Whole Cowpea Flours. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 57, 102207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duodu, K.G.; Nunes, A.; Delgadillo, I.; Parker, M.L.; Mills, E.N.C.; Belton, P.S.; Taylor, J.R.N. Effect of Grain Structure and Cooking on Sorghum and Maize in Vitro Protein Digestibility. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 35, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkhalifa, A.E.O.; Bernhardt, R.; Bonomi, F.; Iametti, S.; Pagani, M.A.; Zardi, M. Fermentation Modifies Protein/Protein and Protein/Starch Interactions in Sorghum Dough. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2006, 222, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, L.; Setser, C.; Sun, X.S. Sensory Characteristics of Sorghum Composite Bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2000, 35, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotong, V.; Chambers IV, E.; Chambers, D.H. Determination of the Sensory Attributes of Wheat Sourdough Bread. J. Sens. Stud. 2000, 15, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, A.T.; Botha, P.; Boonzaaier, C.C. Factors Contributing to Changes in Food Practices of a Black South African Community. J. Fam. Ecol. Consum. Sci. 2005, 33, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adikwu, O.; Ayoola, J.B.; Akerele, D. Factors Influencing the Use of High Quality Flour among Master Bakers in Makurdi Local Government Area, Benu State Nigeria. FUW Trends Sci. Technol. J. 2017, 2, 409–414. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, L.M. Cassava Bread in Nigeria: The Potential of ‘Orphan Crop’ Innovation for Building More Resilient Food Systems. Int. J. Technol. Glob. 2017, 8, 97–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients | Formulations in Baker’s % | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GL9 | GL27 | BECH27 | GL9-DH | BENCH9 ** | |
| Flours mixture * | |||||
| Sorghum | 45.7 | 27.4 | 27.4 | 45.7 | 45.7 |
| Cassava starch | 45.7 | 45.7 | 45.7 | 45.7 | 45.7 |
| GL | 8.7 | 26.9 | |||
| BECH | 26.9 | 8.7 | |||
| GL-DH | 8.7 | ||||
| Salt | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
| Dry yeast | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
| Rapeseed oil | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| Sucrose | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 3.7 |
| Psyllium flour | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.3 |
| Water | 108.7 | 108.7 | 108.7 | 108.7 | 108.7 |
| Attribute | Definition |
|---|---|
| Appearance | |
| Pore size | Size of holes inside a loaf |
| Homogeneity of pores | Observation of regular size of pores |
| Colour: dark | Perception of dark colour |
| Colour: red tone | Perception of red colour tones |
| Colour: yellow tone | Perception of yellow colour tones |
| Texture | |
| Hard | Related to the force required to bite |
| Soft | Related to the force required to bite |
| Dense | Tightly packed crumb structure, more closed crumb structure |
| Sticky | Adhering or sticking to oral cavity |
| Smooth | Degree of perceived smoothness of bread |
| Sandy | Sensation that describes presence of particles in oral cavity |
| Chewy | Related to the number of chews required before swallowing |
| Pasty | Sensation that describes the formation of a dough of the bolus |
| Crumbly | Easily breaking into small fragments |
| Dry | Degree of drying effect, amount of saliva absorbed by the sample |
| Moist | Amount of moisture perceived of the product |
| Taste | |
| Salty | Perception of salt |
| Sweet | Perception of sugar taste |
| Bitter | Perception of bitter taste |
| Sour | Perception of sour taste |
| Beany flavour | Having a flavour associated with cooked dry beans |
| Bland | Lacking taste |
| Tangy | Having a strong piquant flavour. |
| Yeasty flavour | Having a flavour associated with (dry) yeast |
| Cassava | Sorghum | BECH | GL | GL-DH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC (g/g) | 1.5 ± 0.1 a | 2.1 ± 0.2 b | 3.1 ± 0.2 c | 3.7 ± 0.3 d | 3.1 ± 0.2 cd |
| DSC parameters | |||||
| Tonset (°C) | 60.1 ± 0.2 a | 68.0 ± 0.2 d | 67.0 ± 0.6 cd | 64.6 ± 1.0 b | 66.1 ± 0.5 bc |
| Tpeak1 (starch) (°C) | 71.1 ± 0.1 a | 74.4 ± 0.1 b | 78.5 ± 0.1 d | 76.0 ± 0.2 c | 76.0 ± 0.1 c |
| Tpeak2 (protein) (°C) | - | - | 87.4 ± 1.1 | 88.3 ± 0.6 | 87.7 ± 0.9 |
| (kJ/mol) | 17.0 ± 0.5 b | 14.9 ± 1.6 b | 8.9 ± 1.2 a | 7.8 ± 0.5 a | 8.6 ± 0.6 a |
| RVA parameters | |||||
| PT (°C) | 70.7 ± 0.0 a | 92.2 ± 0.1 e | 86.6 ± 0.1 d | 80.3 ± 0.1 b | 82.8 ± 0.2 c |
| PV (cP) | 2397 ± 4 e | 487 ± 1 d | 219 ± 3 b | 277 ± 15 c | 130.5 ± 1 a |
| HV (cP) | 1094 ± 2 d | 484 ± 1 c | 216 ± 2 b | 247 ± 21 b | 129 ± 1 a |
| BD (cP) | 1303 ± 6 c | 4 ± 1 a | 4 ± 1 a | 30 ± 6 b | 1.5 ± 1 a |
| FV (cP) | 1471 ± 2 d | 967 ± 4 c | 363 ± 5 b | 342 ± 13 b | 174.5 ± 2 a |
| SB (cP) | 377 ± 0 d | 483 ± 2 e | 147 ± 3 c | 96 ± 8 b | 45.5 ± 1 a |
| GL9 | GL27 | BECH27 | GL9-DH | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SV (mL/g) | 1.73 ± 0.03 a | 1.82 ± 0.02 bc | 1.84 ± 0.00 c | 1.77 ± 0.03 ab |
| Crumb properties | ||||
| Moisture (%) | 52.5 ± 0.1 a | 52.4 ± 0.0 a | 52.4 ± 0.1 a | 52.5 ± 0.1 a |
| Hardness (N) | 21.1 ± 1.7 b | 16.2 ± 1.6 a | 16.4 ± 1.8 a | 20.6 ± 1.3 b |
| Springiness | 0.887 ± 0.012 a | 0.917 ± 0.018 b | 0.915 ± 0.009 b | 0.904 ± 0.010 b |
| Cohesiveness | 0.423 ± 0.017 a | 0.477 ± 0.012 b | 0.462 ± 0.016 b | 0.436 ± 0.008 a |
| Resilience | 0.191 ± 0.011 a | 0.225 ± 0.008 c | 0.213 ± 0.010 bc | 0.201 ± 0.005 ab |
| Attribute | GL9 | GL27 | BECH27 | GL9-DH | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | |||||
| Darkness | 4.74 bc | 6.28 a | 3.41 c | 4.94 ab | <0.001 |
| Pore size | 3.91 | 4.17 | 3.64 | 3.46 | 0.232 |
| Odour | |||||
| Cereal odour | 4.89 a | 3.51 ab | 4.20 ab | 2.78 b | 0.004 |
| Sweet odour | 2.52 | 2.24 | 2.84 | 3.70 | 0.056 |
| Ryebread odour | 3.79 | 3.86 | 2.92 | 3.3 | 0.452 |
| Beany odour | 1.67 b | 3.06 ab | 3.89 a | 2.54 ab | 0.009 |
| Fermented odour | 1.81 b | 1.59 b | 1.54 b | 5.46 a | <0.001 |
| Flavour/Taste | |||||
| Ryebread flavour | 3.32 a | 3.45 a | 2.69 ab | 1.91 b | 0.007 |
| Beany flavour | 2.17 b | 2.70 ab | 4.08 a | 1.94 b | 0.004 |
| Yeasty flavour | 1.88 b | 1.18 b | 1.73 b | 4.22 a | 0.001 |
| Spicy flavour | 2.12 | 1.84 | 1.56 | 2.94 | 0.122 |
| Sourness | 3.94 | 3.95 | 3.06 | 4.03 | 0.265 |
| Sweetness | 1.96 | 2.16 | 2.54 | 2.82 | 0.353 |
| Astringency | 2.18 | 2.56 | 2.06 | 2.65 | 0.390 |
| Texture | |||||
| Crumbliness tactile | 6.17 | 5.55 | 5.79 | 5.84 | 0.774 |
| Sandiness | 3.64 | 3.06 | 3.01 | 3.26 | 0.642 |
| Crumbliness mouthfeel | 5.61 ab | 4.56 b | 5.13 ab | 5.95 a | 0.019 |
| Moistness | 2.99 ab | 3.58 a | 3.13 ab | 2.55 b | 0.049 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renzetti, S.; Aisala, H.; Ngadze, R.T.; Linnemann, A.R.; Noort, M.W. Bread Products from Blends of African Climate Resilient Crops: Baking Quality, Sensory Profile and Consumers’ Perception. Foods 2023, 12, 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040689
Renzetti S, Aisala H, Ngadze RT, Linnemann AR, Noort MW. Bread Products from Blends of African Climate Resilient Crops: Baking Quality, Sensory Profile and Consumers’ Perception. Foods. 2023; 12(4):689. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040689
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenzetti, Stefano, Heikki Aisala, Ruth T. Ngadze, Anita R. Linnemann, and Martijn W. Noort. 2023. "Bread Products from Blends of African Climate Resilient Crops: Baking Quality, Sensory Profile and Consumers’ Perception" Foods 12, no. 4: 689. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12040689









