Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeys from Tropical Forests of Colombia: Apis mellifera and Melipona eburnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
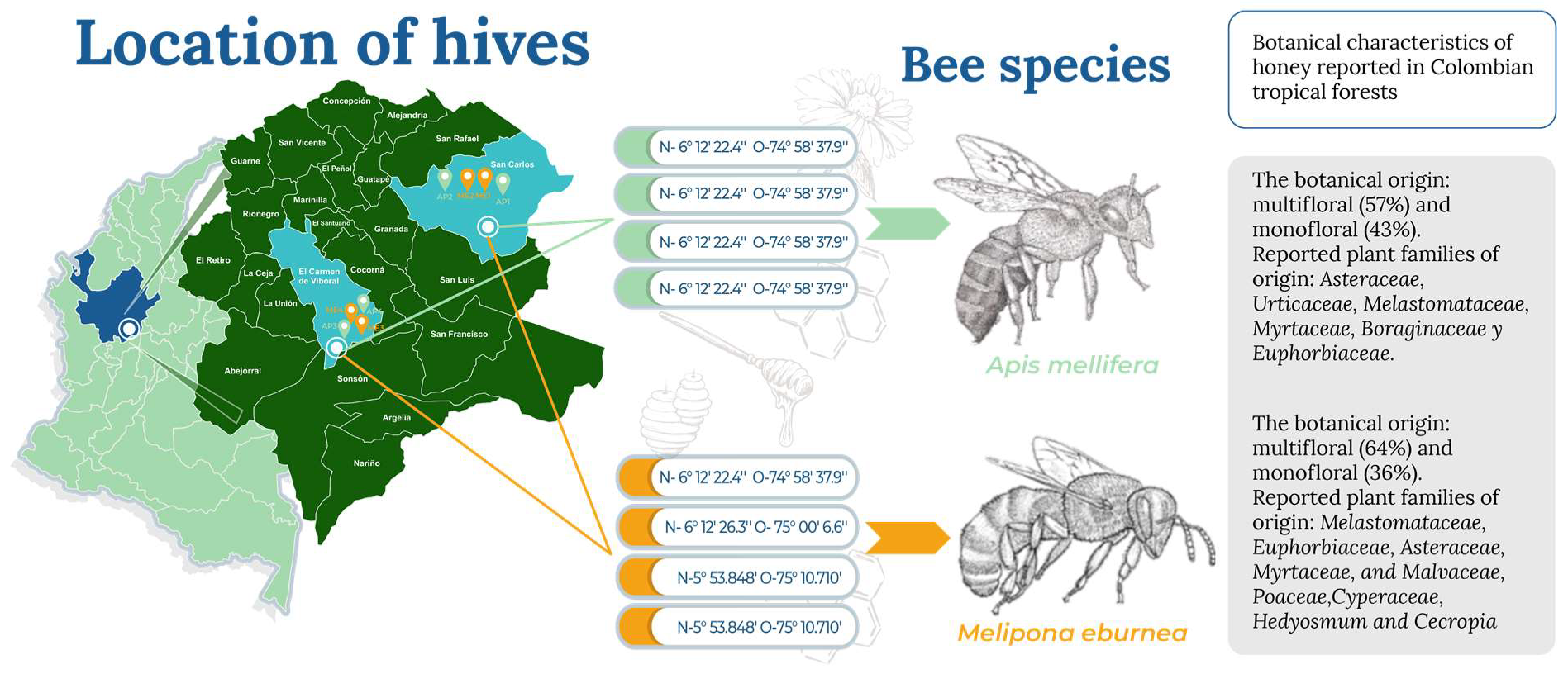
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Obtaining the Samples
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization
2.3.1. Diastase and HMF Activity
2.3.2. HMF Activity
2.3.3. Sugars
2.4. Determination of Total Phenols Content
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity Analysis
2.5.1. DPPH Free Radical Trapping Activity
2.5.2. ABTS Free-Radical-Trapping Activity
2.5.3. FRAP (Reducing Capacity)
2.6. Antimicrobial Activity
2.7. Statistic Analysis
- Determination of Data Normality Criteria
- Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) and Multiple Range Tests
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Correlation Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
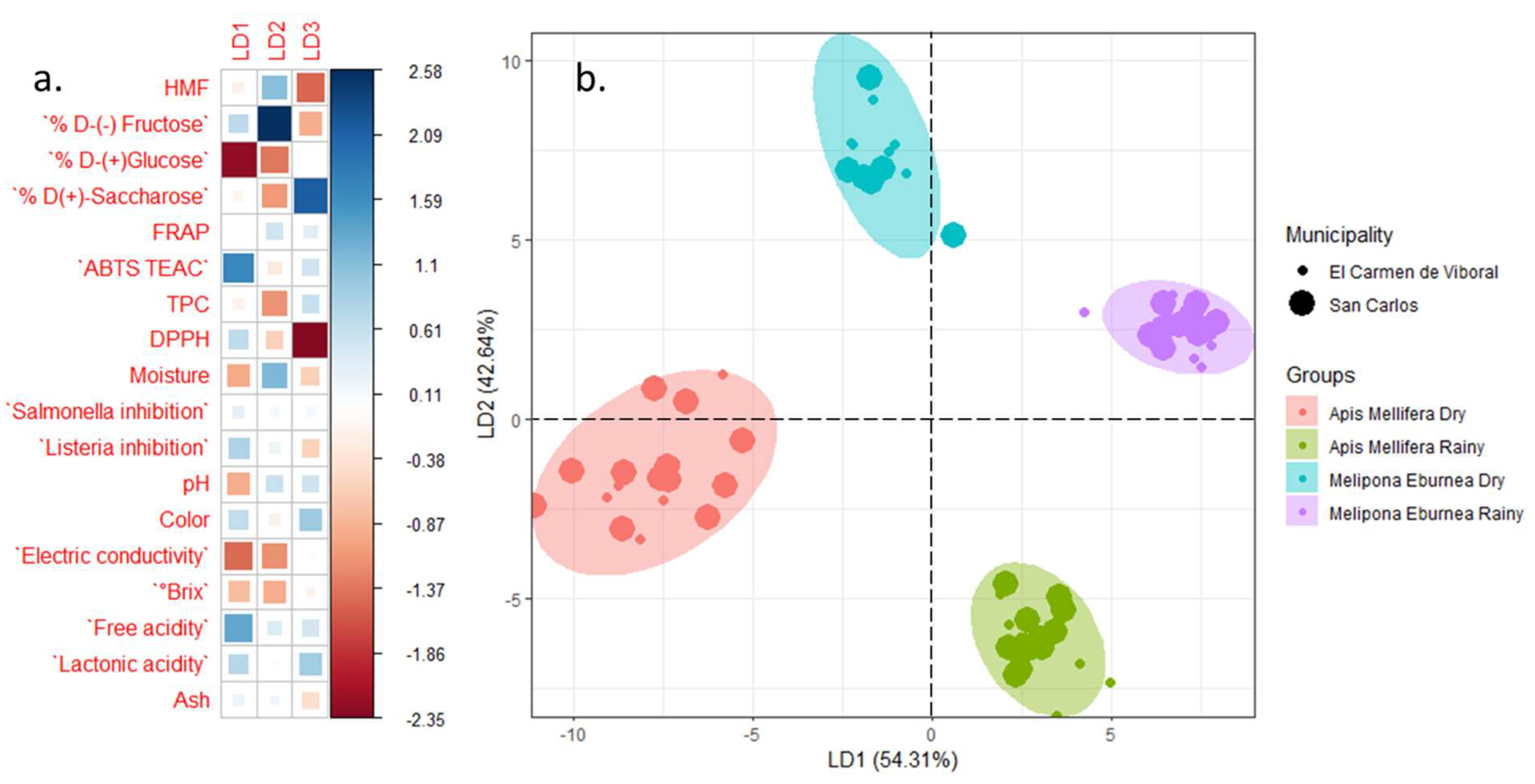
3.1. Influence of the Bee Species and the Time of Collection on the Quality Characteristics and Biological Activities of the Two Kinds of Honey Produced in Tropical Forests of Colombia
3.1.1. Physical–Chemical Analysis
3.1.2. Biological Analysis
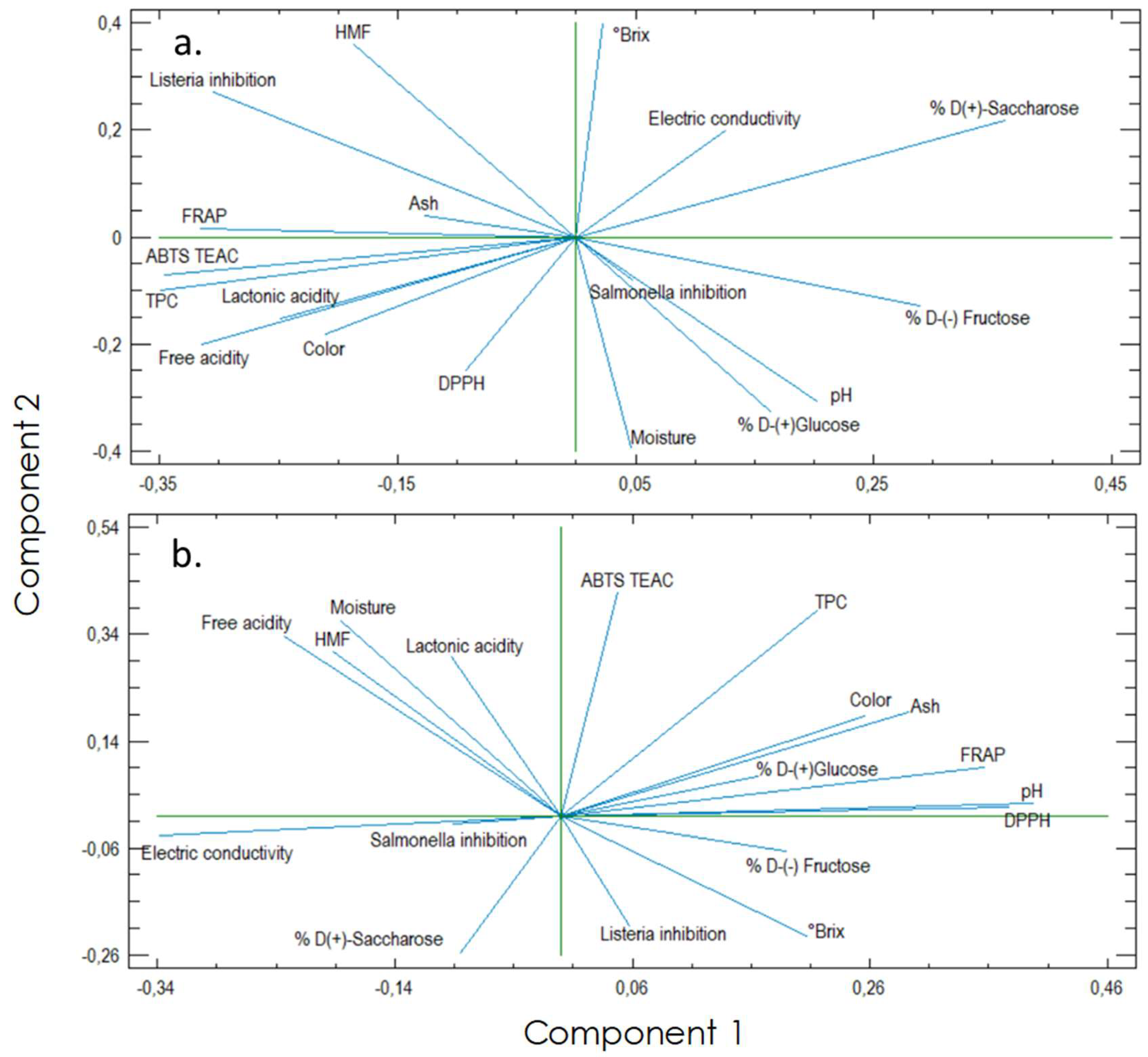
3.2. Principal Components Analysis
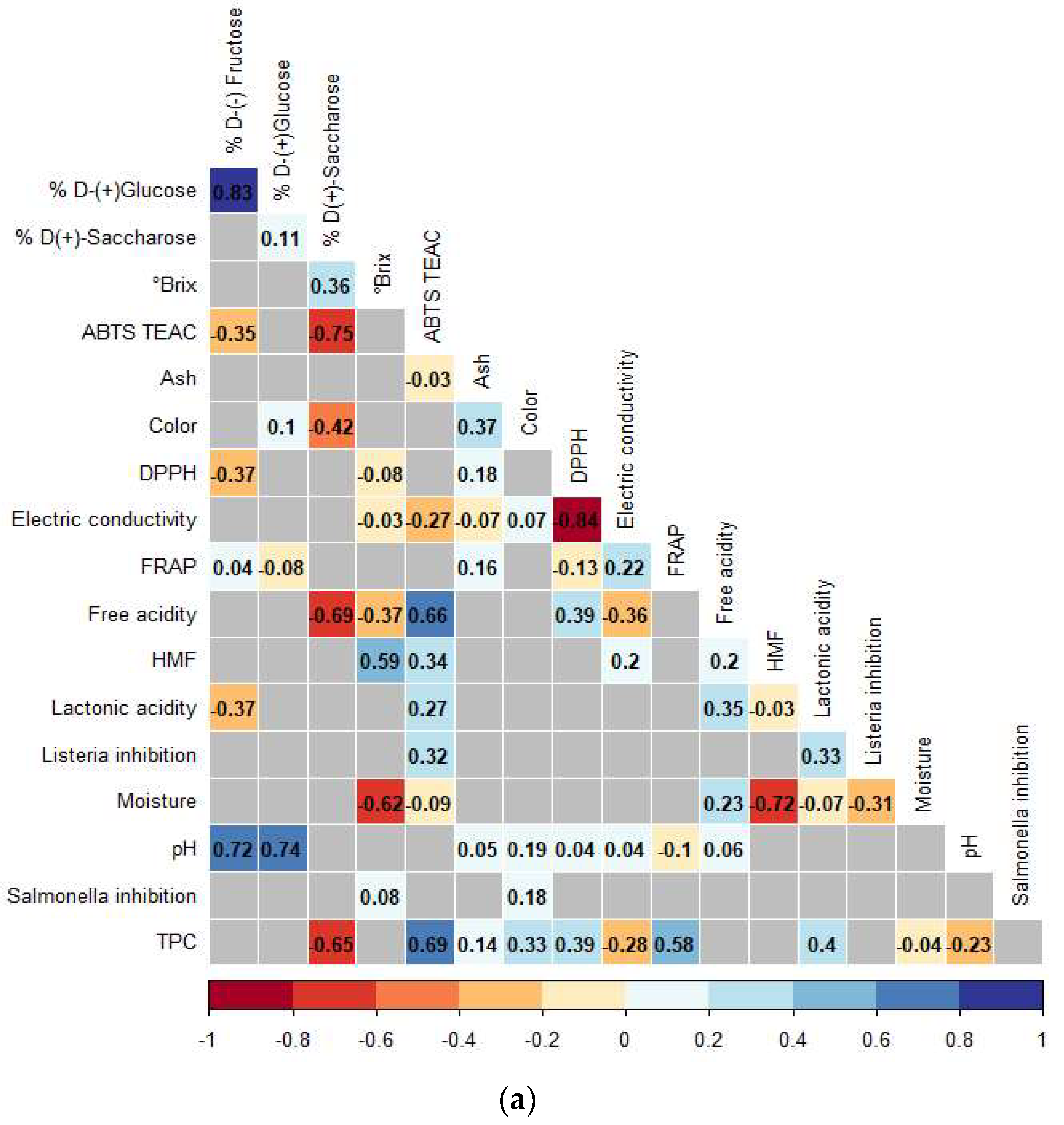
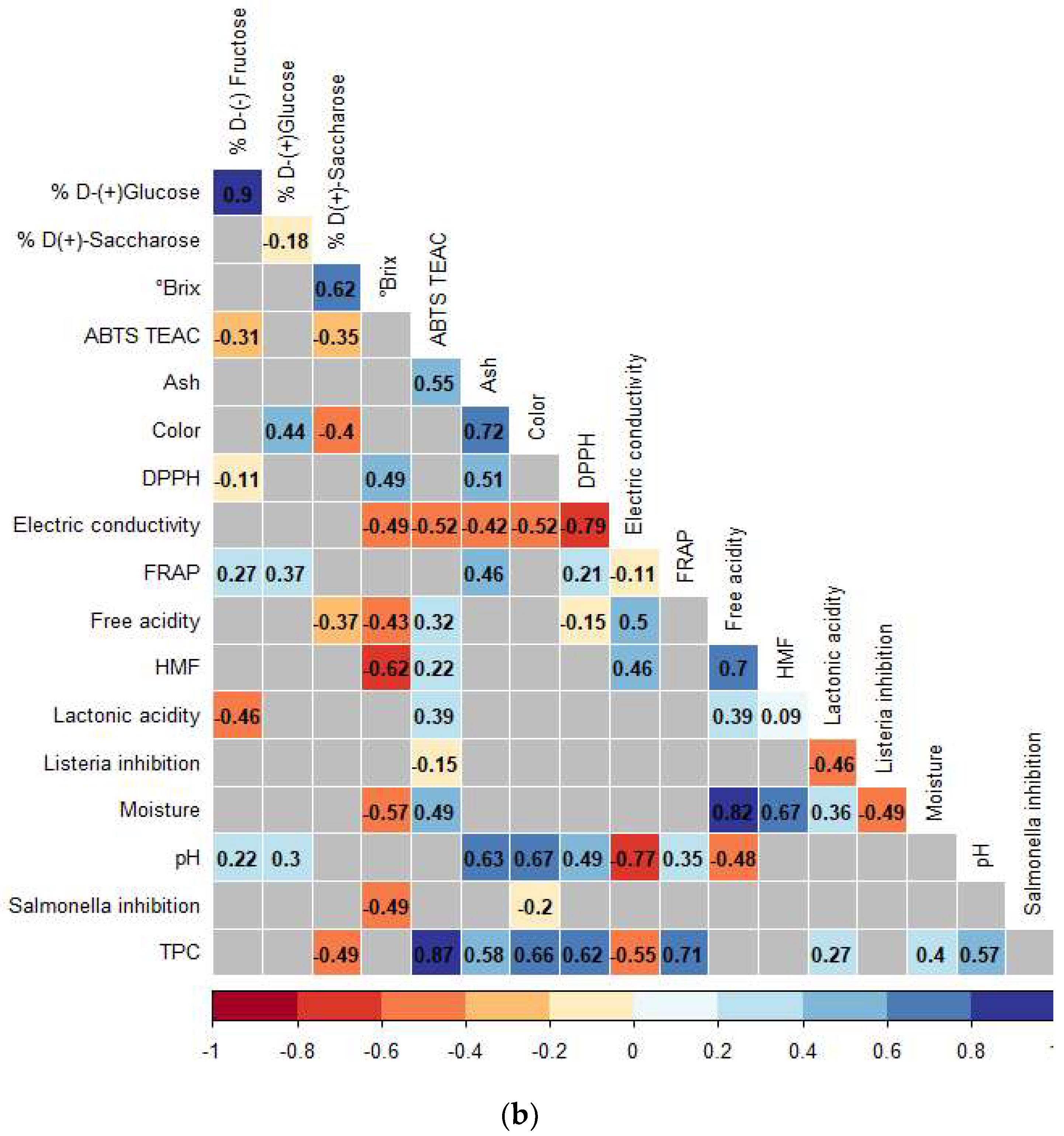
3.3. Correlations Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schencke, C.; Vásquez, B.; Sandoval, C.; del Sol, M. El Rol de La Miel En Los Procesos Morfofisiológicos de Reparación de Heridas. Int. J. Morphol. 2016, 34, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godebo, G.; Kibru, G.; Tassew, H. Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Isolates in Infected Wounds at Jimma University Specialized Hospital, Ethiopia. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2013, 12, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Grabek-Lejko, D.; Swacha, S.; Tomczyk, M.; Bednarska, S.; Kapusta, I. Physicochemical Quality Parameters, Antibacterial Properties and Cellular Antioxidant Activity of Polish Buckwheat Honey. Food Biosci. 2020, 34, 100538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, S.; Selamat, J.; Sanny, M.; Abd Razak, S.-B.; Jambari, N.N.; Mian, Z.; Khatib, A. Influence of Origins and Bee Species on Physicochemical, Antioxidant Properties and Botanical Discrimination of Stingless Bee Honey. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Forestier, J.; Gómez, M.; Montenegro, G. Secreción de néctar de quillay. Una herramienta para una apicultura sustentable. Agron. Y For. 2008, 35, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- Barth, O.M.; Freitas, A.S.; Sousa, G.L.; Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Pollen and Physicochemical Analysis of Apis and Tetragonisca (Apidae) Honey. Interciencia 2013, 38, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Brosi, B.J. The Complex Responses of Social Stingless Bees (Apidae: Meliponini) to Tropical Deforestation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagran, E.; Henao-Rojas, J.C.; Franco, G. Thermo-Environmental Performance of Four Different Shapes of Solar Greenhouse Dryer with Free Convection Operating Principle and No Load on Product. Fluids 2021, 6, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, E.A.; Bertin, G.; Armand, P.; Durand, M.D.-N.; Elvire, G.; Farid, B.-M.; Madjid, A.; Latifou, L.; Victorien, D.; Lamine, B.-M. Polyphenolic Profile, and Antioxidant and Antifungal Activities of Honey Products in Benin. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 12, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, T. Diagnóstico de la actividad apícola y de la crianza de abejas en Colombia. Minist. Agric. Desarro. Rural.-MADR 2006, 4, 1–121. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, P.; Henao-Rojas, J.; Correa, G.; Aristizabal, A. Identification of Harvest Maturity Indicators for ‘Hass’ Avocado Adaptable to Field Conditions. HortTechnology 2018, 28, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Henao, D.; Quijano-Abril, M.; Giraldo Sánchez, C.E.; Calvo-Cardona, S.J.; Zapata-Vahos, I.C. Limited Foraging Overlap between Introduced Apis Mellifera and Native Melipona Eburnea in a Colombian Moist Forest as Revealed through Pollen Analysis. Palynology 2022, 46, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, L.; Díaz, M.; Machado, R.; Blanco, D.; Demedio, J.; García, A. Physical, chemical and organoleptic characterization of Melipona beecheii honey collected in agroforestry systems. Pastos Y Forrajes 2013, 36, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius International Standard for Honey CXS 12-19811 Adopted in 1981; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1981; pp. 1–8.
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 20th ed.; Latimer, G.W., AOAC International, Eds.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-0-935584-87-5. [Google Scholar]
- Zappalà, M.; Fallico, B.; Arena, E.; Verzera, A. Methods for the Determination of HMF in Honey: A Comparison. Food Control 2005, 16, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaviria Montoya, C.; Hernández Arredondo, J.D.; Lobo Arias, M.; Medina Cano, C.I.; Rojano, B.A. Changes in the Antioxidant Activity in Mortiño Fruits (Vaccinium Meridionale Sw.) during Development and Ripening. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellín 2012, 65, 87–6495. [Google Scholar]
- Zapata, K.; Cortes, F.B.; Rojano, B.A. Polifenoles y Actividad Antioxidante Del Fruto de Guayaba Agria (Psidium Araca). Inf. Tecnol. 2013, 24, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudzicki, J. Kirby-Bauer Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Test Protocol; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; Volume 15, pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Henao-Rojas, J.C.; Osorio, E.; Isaza, S.; Madronero-Solarte, I.A.; Sierra, K.; Zapata-Vahos, I.C.; Betancur-Pérez, J.F.; Arboleda-Valencia, J.W.; Gallego, A.M. Towards Bioprospection of Commercial Materials of Mentha spicata L. Using a Combined Strategy of Metabolomics and Biological Activity Analyses. Molecules 2022, 27, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanza, M.; Mazza, S.; Martínez, G.; Giménez, L. Aplicación de Transformaciones Para El Cumplimiento de Los Supuestos de Normalidad y Homocedasticidad, a Concentraciones Foliares de N., P y K En Mandarino. Agrotecnia 2003, 11, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Qian, M.; Shao, Y. On Rotational Robustness of Shapiro-Wilk Type Tests for Multivariate Normality. OJS 2014, 04, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappal, S. Data normalization using median median absolute deviation MMAD based Z-score for robust predictions vs. min–max normalization. Lond. J. Res. Sci. Nat. Form. 2019, 19, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Henao-Rojas, J.C.; Rosero-Alpala, M.G.; Ortiz-Muñoz, C.; Velásquez-Arroyo, C.E.; Leon-Rueda, W.A.; Ramírez-Gil, J.G. Machine Learning Applications and Optimization of Clustering Methods Improve the Selection of Descriptors in Blackberry Germplasm Banks. Plants 2021, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Shi, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Evaluation indicators of cultivated layer soil quality for red soil slope farmland based on cluster and PCA analysis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. R Package Version 2020, 1, 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, S.; Meyer, M.; Gregg, C.; Gerber, S. S-CorrPlot: An Interactive Scatterplot for Exploring Correlation. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2016, 25, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.E.; Finoia, M.G.; Fontana, L.; Mele, G.; Botrè, F.; Iavicoli, I. Characterization of Argentine Honeys on the Basis of Their Mineral Content and Some Typical Quality Parameters. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Agriculture, U. S. National Agricultural Statistics Service. 2011, Crop Production Summary. Available online: https://www.peanutsusa.com/phocadownload/CropProduction/Peanut%20Crop%20Production%20-%202011%20Annual%20Summary.pdf (accessed on 9 November 2022).
- González-Miret, M.L.; Terrab, A.; Hernanz, D.; Fernández-Recamales, M.Á.; Heredia, F.J. Multivariate Correlation between Color and Mineral Composition of Honeys and by Their Botanical Origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2574–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernanz, D.; Palomar, M.Á.; Moujanni, A.; Essamadi, A.; Heredia, F.J.; Terrab, A. Phenolic Compounds and Color of Labeled Resin Spurge Honey and Their Correlations with Pollen Content. LWT 2022, 169, 113987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku, M.; Tefera, W. Physicochemical Properties, Mineral and Heavy Metal Contents of Honey in Eastern Amhara Region, Ethiopia. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuttong, B.; Chanbang, Y.; Sringarm, K.; Burgett, M. Physicochemical Profiles of Stingless Bee (Apidae: Meliponini) Honey from South East Asia (Thailand). Food Chem. 2016, 192, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.; Roubik, D.; Barth, O.; Heard, T.; EnrÍquez, E.; Carvalho, C.; Villas-Bôas, J.; Marchini, L.; Locatelli, J.; Persano-Oddo, L.; et al. Composition of Stingless Bee Honey: Setting Quality Standards. Interciencia 2006, 31, 867–875. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, V.; Sarkar, B.C.; Sharma, H.K.; Bawa, A.S. Physico-Chemical Properties and Estimation of Mineral Content in Honey Produced from Different Plants in Northern India. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2003, 16, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, V.; Martin-Belloso, O.; Keener, L.; Astley, S.B.; Braun, S.; McMahon, H.; Lelieveld, H. Regulating Safety of Traditional and Ethnic Foods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-800620-7. [Google Scholar]
- Adgaba, N.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Getachew, A.; Tadesse, Y.; Belay, A.; Ansari, M.J.; Radloff, S.E.; Sharma, D. Characterization of Honeys by Their Botanical and Geographical Origins Based on Physico-Chemical Properties and Chemo-Metrics Analysis. Food Meas. 2017, 11, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pot-Honey: A Legacy of Stingless Bees; Vit, P., Pedro, S.R.M., Roubik, D.W., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4614-4959-1. [Google Scholar]
- do Nascimento, K.S.; Gasparotto Sattler, J.A.; Lauer Macedo, L.F.; Serna González, C.V.; Pereira de Melo, I.L.; da Silva Araújo, E.; Granato, D.; Sattler, A.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Phenolic Compounds, Antioxidant Capacity and Physicochemical Properties of Brazilian Apis Mellifera Honeys. LWT 2018, 91, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriceno, A.; Girelli, A.M.; Scuto, F.R.; Tarola, A.M. Determination of Furanic Compounds and Acidity for Italian Honey Quality. Flavour. Fragr. J. 2018, 33, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerrouk, S.; Bahloul, R. Palynological and Physicochemical Properties of Multifloral Honey Produced in Some Regions of Algeria. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, F.; Kongoli, R.; Malollari, I.; Tosti, T.; Milojković-Opsenica, D.; Tesic, Z. Analysis of Some Albanian Market Honey Based on 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) Content with Its Impact on Human Health. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2019, 20, 496–504. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Q.X. Chemical Composition, Characterization, and Differentiation of Honey Botanical and Geographical Origins. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 62, pp. 89–137. ISBN 978-0-12-385989-1. [Google Scholar]
- Besir, A.; Yazici, F.; Mortas, M.; Gul, O. A Novel Spectrophotometric Method Based on Seliwanoff Test to Determine 5-(Hydroxymethyl) Furfural (HMF) in Honey: Development, in House Validation and Application. LWT 2021, 139, 110602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Ye, D.; Li, X. Nondestructive Determination of Diastase Activity of Honey Based on Visible and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules 2019, 24, 1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vit, P.; Pulcini, P. Diastase and Invertase Activities in Meliponini and Trigonini Honeys from Venezuela. J. Apic. Res. 1996, 35, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escuredo, O.; Dobre, I.; Fernández-González, M.; Seijo, M.C. Contribution of Botanical Origin and Sugar Composition of Honeys on the Crystallization Phenomenon. Food Chem. 2014, 149, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, E.-K.A.; Al-Kahtani, S.; Taha, R. Comparison of the Physicochemical Characteristics of Sidr (Ziziphus spp.) Honey Produced by Apis Florea F. and Apis Mellifera L. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Montemayor, Á.-M.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Serrato-Villegas, L.E.; López-Pérez, M.G.; Montañez-Sáenz, J.C.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R. Honey and Syrups: Healthy and Natural Sweeteners with Functional Properties. In Natural Beverages; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 143–177. ISBN 978-0-12-816689-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moo-Huchin, V.; Aguilar, G.; Lira-Maas, J.; Estrada León, R.; Moo-Huchin, M.I.; Sauri, E. Physicochemical Properties of Melipona Beecheii Honey of the Yucatan Peninsula. J. Food Res. 2015, 4, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Palomino, L.R.; García, C.M.; Gil, J.H.; Rojano, B.A.; Durango, D.L. Determinación del contenido de fenoles y evaluación de la actividad antioxidante de propóleos recolectados en el departamento de Antioquia (Colombia). Vitae 2009, 16, 388–395. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Giampieri, F.; Brenciani, A.; Mazzoni, L.; Gasparrini, M.; González-Paramás, A.M.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Morroni, G.; Simoni, S.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; et al. Apis mellifera vs Melipona Beecheii Cuban Polifloral Honeys: A Comparison Based on Their Physicochemical Parameters, Chemical Composition and Biological Properties. LWT 2018, 87, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.V.; Krishnan, K.T.; Salleh, N.; Gan, S.H. Biological and Therapeutic Effects of Honey Produced by Honey Bees and Stingless Bees: A Comparative Review. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2016, 26, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, M.; Lupano, C.; Conforti, P.A. Color, cenizas y capacidad antioxidante de mieles de la provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina. Rev. La Fac. Agron. 2016, 115, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Tanleque-Alberto, F.; Juan-Borrás, M.; Escriche, I. Antioxidant Characteristics of Honey from Mozambique Based on Specific Flavonoids and Phenolic Acid Compounds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 86, 103377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodó, A.; Radványi, L.; Kőszegi, T.; Csepregi, R.; Nagy, D.U.; Farkas, Á.; Kocsis, M. Melissopalynology, Antioxidant Activity and Multielement Analysis of Two Types of Early Spring Honeys from Hungary. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, G.; Gil, F.; González, A.C.; Nieves, B.; Rojas, Y.; Rodríguez, M.A.; Vit, P. Evaluación de actividad antibacteriana de mieles de Apis mellifera, contra Escherichia coli y Staphylococcus aureus. Rev. Del Inst. Nac. Hig. Rafael Rangel 2009, 40, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Gamboa, V.; Figueroa-Ramírez, J. Poder antibacterial de mieles de Tetragonisca angustula, valorada por concentración mínima inhibitoria. Acta Biológica Colomb. 2009, 14, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Sagdic, O.; Silici, S.; Ekici, L. Evaluation of the Phenolic Content, Antiradical, Antioxidant, and Antimicrobial Activity of Different Floral Sources of Honey. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakman, P.H.S.; Zaat, S.A.J. Antibacterial Components of Honey. IUBMB Life 2012, 64, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemo, R.; Bacha, K. Microbial Quality, Physicochemical Characteristics, Proximate Analysis, and Antimicrobial Activities of Honey from Anfilo District. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainol, M.I.; Mohd Yusoff, K.; Mohd Yusof, M.Y. Antibacterial Activity of Selected Malaysian Honey. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braghini, F.; Biluca, F.C.; Schulz, M.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Costa, A.C.O.; Fett, R. Stingless Bee Honey: A Precious but Unregulated Product—Reality and Expectations. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 683–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulugeta, M.; Belay, A. Comb Honey and Processed Honey of Croton Macrostachyus and Schefflera Abyssinica Honey Differentiated by Enzymes and Antioxidant Properties, and Botanical Origin. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayinie, M.; Atlabachew, M.; Tesfaye, A.; Hilluf, W.; Reta, C. Quality Authentication and Geographical Origin Classification of Honey of Amhara Region, Ethiopia Based on Physicochemical Parameters. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncelj, J.; Doberšek, U.; Jamnik, M.; Golob, T. Evaluation of the Phenolic Content, Antioxidant Activity and Colour of Slovenian Honey. Food Chem. 2007, 105, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | A. mellifera × Dry | A. mellifera × Rainy | M. eburnea × Dry | M. eburnea × Rainy | p-Value KW Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color (mm PFund) | 72 ± 21.2 a | 48.21 ± 24.8 a | 60.83 ± 21.7 a | 49.69 ± 23.2 a | 0.186 |
| Ash (%) | 0.2 ± 0.09 a | 0.26 ± 0.14 a | 0.155 ± 0.02 a | 0.15 ± 0.1 a | 0.079 |
| Moisture (%) | 22.68 ± 2.9 a | 19.8 ± 2.6 a | 25.44 ± 1.7 b | 26.94 ± 2.2 b | 0.000 |
| pH | 4.15 ± 0.38 b | 3.55 ± 0.23 a | 4.48 ± 0.8 ab | 3.67 ± 0.24 a | 0.000 |
| Free acidity (meq acid. Kg−1) | 42.14 ± 7.4 a | 46.47 ± 7.01 a | 36.12 ± 27.3 a | 49.46 ± 25.2 a | 0.786 |
| Lactonic acidity (meq acid. Kg−1) | 0 ± 0.01 a | 0.2 ± 0.06 b | 0 ± 0.02 a | 0.5 ± 0.05 b | 0.000 |
| HMF (mg/Kg) | 4.82 ± 2.46 ab | 7.42 ± 2.19 b | 4.34 ± 2.7 ab | 3.8 ± 3.3 a | 0.032 |
| % D-(+) Glucose | 30.11 ± 2.41 b | 22.19 ± 4.34 a | 27.94 ± 1.37 b | 20.7 ± 3.45 a | 0.000 |
| % D-(−) Fructose | 36.63 ± 2.20 d | 27.74 ± 1.31 c | 32.94 ± 1.95 b | 24.63 ± 2.52 a | 0.000 |
| % D(+)-Saccharose | 2.73 ± 0.69 b | 0.9 ± 0.84 ab | 0.42 ± 0.4 ab | 0.19 ± 0.16 a | 0.000 |
| °Brix | 77.5 ± 1.94 b | 77.8 ± 2.70 a | 69.5 ± 2.23 ab | 71.95 ± 1.63 a | 0.007 |
| Electric conductivity (mS/cm) | 144.5 ± 21.89 ab | 134.4 ± 12.12 a | 152 ± 60.85 b | 126.80 ± 15.40 a | 0.007 |
| DPPH (mmol Equiv TX/100 g) | 0.76 ± 0.24 bc | 1.05 ± 0.23 c | 0.05 ± 0.26 ab | 0.095 ± 0.02 a | 0.000 |
| ABTS TEAC (mmol Equiv TX/100 g) | 4.12 ± 2.10 b | 9.97 ± 5.05 b | 0.36 ± 1.38 a | 2.25 ± 1.6 ab | 0.000 |
| FRAP (mg Equiv ascorbic acid/100 g) | 73.22 ± 28.50 b | 117.46 ± 29.99 b | 15.61 ± 14.25 ab | 10.79 ± 2.69 a | 0.000 |
| TPC (mg Equiv GAE/100 g) | 49.2 ± 6.94 b | 62.39 ± 12.23 b | 25.69 ± 9.44 a | 32.89 ± 13.14 a | 0.001 |
| S. typhimurium inhibition (mm) | 8.71 ± 0.85 a | 8.66 ± 0.71 a | 8.69 ± 1.03 a | 8.29 ± 2.84 a | 0.470 |
| Listeria inhibition (mm) | 10.49 ± 7.76 a | 26.03 ± 4.91 b | 25.56 ± 4.60 ab | 23.26 ± 6.28 ab | 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapata-Vahos, I.C.; Henao-Rojas, J.C.; Yepes-Betancur, D.P.; Marín-Henao, D.; Giraldo Sánchez, C.E.; Calvo-Cardona, S.J.; David, D.; Quijano-Abril, M. Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeys from Tropical Forests of Colombia: Apis mellifera and Melipona eburnea. Foods 2023, 12, 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051001
Zapata-Vahos IC, Henao-Rojas JC, Yepes-Betancur DP, Marín-Henao D, Giraldo Sánchez CE, Calvo-Cardona SJ, David D, Quijano-Abril M. Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeys from Tropical Forests of Colombia: Apis mellifera and Melipona eburnea. Foods. 2023; 12(5):1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051001
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapata-Vahos, Isabel Cristina, Juan Camilo Henao-Rojas, Diana Paola Yepes-Betancur, Daniela Marín-Henao, Carlos Eduardo Giraldo Sánchez, Samir Julián Calvo-Cardona, Dorely David, and Mario Quijano-Abril. 2023. "Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeys from Tropical Forests of Colombia: Apis mellifera and Melipona eburnea" Foods 12, no. 5: 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051001
APA StyleZapata-Vahos, I. C., Henao-Rojas, J. C., Yepes-Betancur, D. P., Marín-Henao, D., Giraldo Sánchez, C. E., Calvo-Cardona, S. J., David, D., & Quijano-Abril, M. (2023). Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity, and Antimicrobial Activity of Honeys from Tropical Forests of Colombia: Apis mellifera and Melipona eburnea. Foods, 12(5), 1001. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12051001











