Functional Enhancement of Guar Gum−Based Hydrogel by Polydopamine and Nanocellulose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Gel−PDA
2.3. Characterization of Gel−PDA
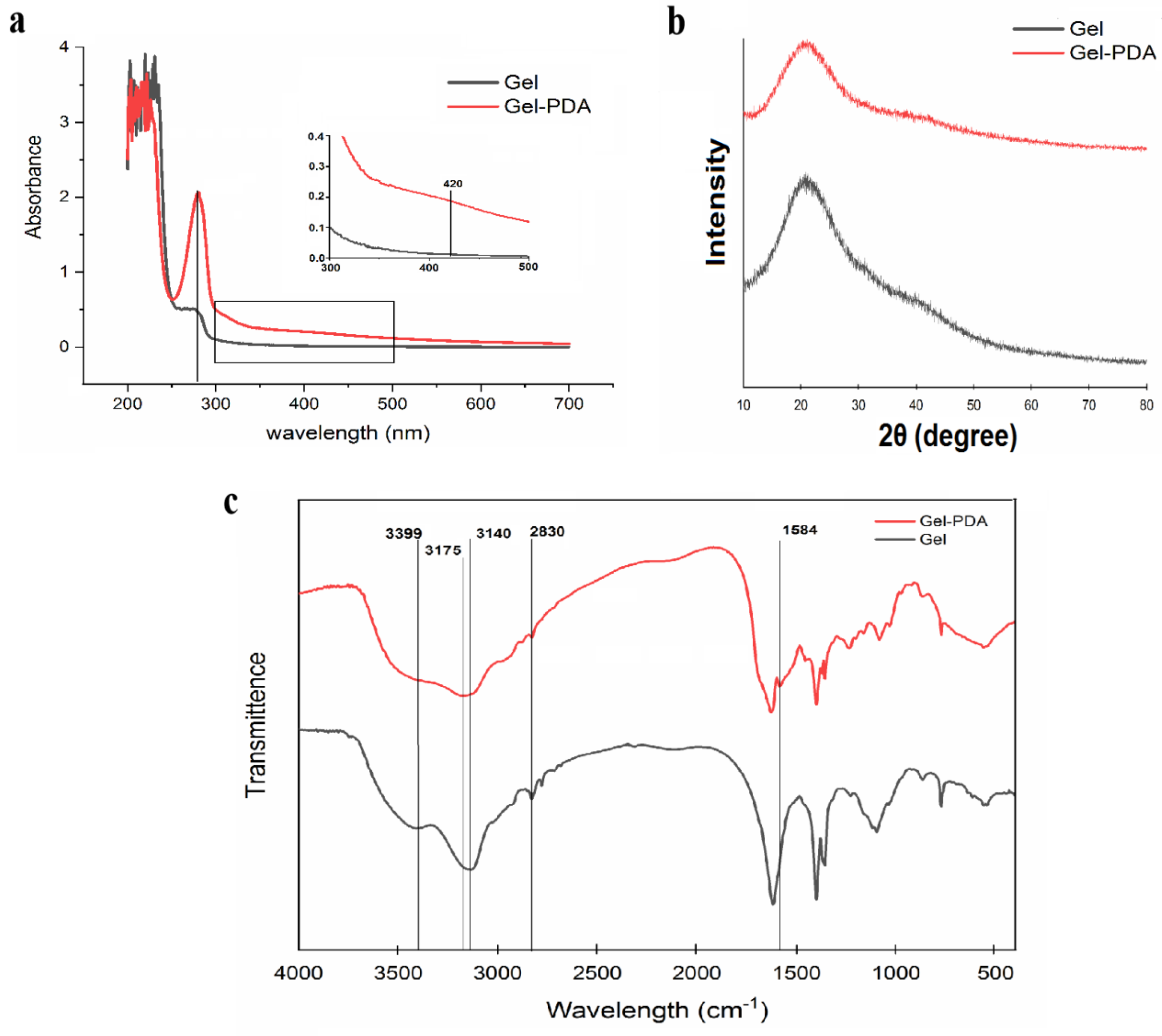
2.3.1. Ultraviolet−Visible (UV–Vis) Spectroscopic Analysis
2.3.2. Fourier−Transform Infrared Spectroscopic Analysis
2.3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.4. Fabrication of Gel−PDA+Guar Gum+CNC Hydrogel
2.5. Characterization of Hydrogel
2.5.1. Morphological and Structural analysis
2.5.2. Rheology and Self−Healing Test
2.5.3. Tissue Adhesive Test
2.5.4. Anti−Oxidant Activity Assay
2.5.5. Hemolysis and Hemostasis Assay
2.5.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PDA Coating on the Gelatin Matrix
3.2. Fabrication and Characterization of Hydrogel
3.3. Rheology, Self−Healing, and Injectability of Hydrogel
3.4. Tissue Adhesion and Anti−Oxidant Capacity
3.5. Hemostasis, Hemolysis, and Cytotoxicity of Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nele, V.; Wojciechowski, J.P.; Armstrong, J.P.K.; Stevens, M.M. Tailoring Gelation Mechanisms for Advanced Hydrogel Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.P.; Huang, Y.; He, J.H.; Han, Y.; Guo, B.L. Physical Double−Network Hydrogel Adhesives with Rapid Shape Adaptability, Fast Self−Healing, Antioxidant and NIR/pH Stimulus−Responsiveness for Multidrug−Resistant Bacterial Infection and Removable Wound Dressing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1901748–1901765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Long, L.Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.M.; Wang, Y.B. Dual−crosslinked mussel−inspired smart hydrogels with enhanced antibacterial and angiogenic properties for chronic infected diabetic wound treatment via pH−responsive quick cargo release. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128564–128578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.X.; Li, J.Y.; Han, F.; Meng, Q.C.; Wang, H.; Qiang, W.; Li, Z.X.; Li, F.F.; Xie, E.; Qin, X.Y.; et al. A Multifunctional Composite Hydrogel That Rescues the ROS Microenvironment and Guides the Immune Response for Repair of Osteoporotic Bone Defects. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201067–2201084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Rehman, H.U.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Liu, H. Ultratough, Self−Healing, and Tissue−Adhesive Hydrogel for Wound Dressing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33523–33531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J. Conductive, Self−Healing, Adhesive, and Antibacterial Hydrogels Based on Lignin/Cellulose for Rapid MRSA−Infected Wound Repairing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 52333–52345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, H.J.; Ryplida, B.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, G.; Ryu, J.H.; Park, S.Y. Diselenide−Bridged Carbon−Dot−Mediated Self−Healing, Conductive, and Adhesive Wireless Hydrogel Sensors for Label−Free Breast Cancer Detection. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8409–8420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, C.; Fan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Guan, P.; Tian, Y.; Xing, J.; Li, X.; et al. Injectable Self−Healing Natural Biopolymer−Based Hydrogel Adhesive with Thermoresponsive Reversible Adhesion for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007457–2007469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J.L.; Li, J. Injectable Thermoresponsive Hydrogel Formed by Alginate−g−Poly(N−isopropylacrylamide) That Releases Doxorubicin−Encapsulated Micelles as a Smart Drug Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35673–35682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Long, L.; Yang, L.; Fu, D.; Hu, C.; Kong, Q. Inflammation−Responsive Drug−Loaded Hydrogels with Sequential Hemostasis, Antibacterial, and Anti−Inflammatory Behavior for Chronically Infected Diabetic Wound Treatment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33584–33599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Liu, C.; Chen, W. Facile Access to Guar Gum Based Supramolecular Hydrogels with Rapid Self−Healing Ability and Multistimuli Responsive Gel–Sol Transitions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, M.; Bu, T.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L. Multifunctional Injectable Hydrogel Dressings for Effectively Accelerating Wound Healing: Enhancing Biomineralization Strategy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenlo, F.; Moreira, R.; Silva, C. Rheological behaviour of aqueous systems of tragacanth and guar gums with storage time. J. Food Eng. 2010, 96, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, D.; Barak, S.; Khatkar, B.S. Guar gum: Processing, properties and food applications−A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdel−Halim, E.S.; Al−Deyab, S.S. Electrically conducting silver/guar gum/poly(acrylic acid) nanocomposite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidarian, P.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Kaynak, A.; Paulino, M.; Nasri−Nasrabadi, B.; Varley, R. Double dynamic cellulose nanocom−posite hydrogels with environmentally adaptive self−healing and pH−tuning properties. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1407–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L.; Sgambato, A.; Visone, R.; Occhetta, P.; Moretti, M.; Rasponi, M.; Nicotra, F.; Cipolla, L. Gelatin hydrogels via thiol−ene chemistry. Mon. Für Chem. Chem. Monthly. 2015, 147, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Yuan, L.; Ge, L.; Li, D.; Mu, C. Facile Fabrication of Biocompatible Gelatin−Based Self−Healing Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1350–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhurakkat Perikamana, S.K.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.B.; Shin, Y.M.; Lee, E.J.; Mikos, A.G.; Shin, H. Materials from Mussel Inspired Chemistry for Cell and Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2541–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.Y.; Lei, X.X.; Hu, J.J.; Jiang, Y.L.; Li, Q.J.; Song, Y.T.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Li−Ling, J.; Xie, H.Q. Multi−crosslinking hydrogels with robust bio−adhesion and pro−coagulant activity for first−aid hemostasis and infected wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Seidi, F.; Li, C.; Wan, Z.; Jin, Y.; Song, J.; Xiao, H. Antimicrobial/Biocompatible Hydrogels Dual−Reinforced by Cellulose as Ultrastretchable and Rapid Self−Healing Wound Dressing. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y. Polyphenol scaffolds in tissue engineering. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 8, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; Meng, L.; Wang, M.; Cui, C.; Wang, B.; Han, C.-R.; Xu, F.; Yang, J. Mimicking Dynamic Adhesiveness and Strain−Stiffening Behavior of Biological Tissues in Tough and Self−Healable Cellulose Nanocomposite Hydrogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Cao, S.; Shen, F.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Wang, X. Rapid self−healing, stretchable, moldable, antioxidant and antibacterial tannic acid−cellulose nanofibril composite hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 224, 115147–115160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, F. Cellulose Nanofibrils Enhanced, Strong, Stretchable, Freezing−Tolerant Ionic Conductive Organohydrogel for Multi−Functional Sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003430–2003441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Gèze, A.; Wouessidjewe, D.; Huang, J.; Dufresne, A. Biocompatible Double−Membrane Hydrogels from Cationic Cellulose Nanocrystals and Anionic Alginate as Complexing Drugs Codelivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 6880–6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, T.; Ni, R.; Jia, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, T.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Han, L.; Lu, X. Adhesive Gelatin−Catechol Complex Reinforced Poly(Acrylic Acid) Hydrogel with Enhanced Toughness and Cell Affinity for Cartilage Regeneration. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4366–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazerian, H.; Baidya, A.; Haghniaz, R.; Davoodi, E.; Ahadian, S.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A.; Weiss, P.S. Stretchable and Bioadhesive Gelatin Methacryloyl−Based Hydrogels Enabled by in Situ Dopamine Polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 40290–40301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Zuo, G.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; He, F.; Ren, K.; Luo, H. Preparation and characterization of nano−platelet−like hydroxyapatite/gelatin nanocomposites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Song, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, M.; Wei, J.; Qin, J.; Peng, W.; Lasaosa, F.L.; He, Y.; Mao, H.; et al. Injectable Adhesive Self−Healing Multicross−Linked Double−Network Hydrogel Facilitates Full−Thickness Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 57782–57797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Noncompressible Hemostasis and Bone Regeneration Induced by an Absorbable Bioadhesive Self−Healing Hydrogel. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009189–2009203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Bai, Q.; Zeng, Q.; Sun, N.; Zheng, C.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T. A multifunctional mussel−inspired hydrogel with antioxidant, electrical conductivity and photothermal activity loaded with mupirocin for burn healing. Mater. Des. 2022, 217, 110598–110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Tang, K. Multi−Crosslinked Hydrogels with Instant Self−Healing and Tissue Adhesive Properties for Biomedical Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 22, 2100443–2100451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, W.; Tian, M.; Wei, J.; Song, Q.; Qiao, W. Mussel−inspired hydrogels as tissue adhesives for hemostasis with fast−forming and self−healing properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 148, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, L.; You, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, F. Synthesis and biological evaluation of surface−modified nanocellulose hydrogel loaded with paclitaxel. Life Sci. 2019, 241, 117137–117743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Gan, L.; Ma, X.; Huang, J. Polydopamine−coated cellulose nanocrystals as an active ingredient in poly(vinyl alcohol) films towards intensifying packaging application potential. Cellulose 2019, 26, 9599–9612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.C.; Gu, Z.P.; Xiong, S.B.; An, Y.Q.; Hu, Y. Fabrication of a novel bio−inspired collagen−polydopamine hydrogel and insights into the formation mechanism for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 6, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wei, T.; Ge, Y. Preparation and characterization of novel Ce(III)−gelatin complex. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 108, 3804–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Du, X.; Hou, W.; Liu, X.J.; Zhu, C.; Gao, B.B.; Sun, L.D.; Li, Q.W.; Liao, J.L.; Levkin, P.A.; et al. UV−Triggered Polydopamine Secondary Modification: Fast Deposition and Removal of Metal Nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.J.; Li, J.; Saini, P.; Paterson, J.R.; Sharples, G.J.; Badyal, J.P.S. Bioinspired and eco−friendly high efficacy cinnamaldehyde antibacterial surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2918–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, Y.F.; Meng, X.X.; Liu, G.H.; Hu, S.; Pan, F.S.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Wang, B.Y.; Li, Z.X.; et al. Embedding dopamine nanoaggregates into a poly(dimethylsiloxane) membrane to confer controlled interactions and free volume for enhanced separation performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 3713–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.L.; Han, Q.; Liu, H.Q.; Shen, J.H.; Li, G.C.; Zhang, L.Z.; Yang, Y.M. Construction of injectable silk fibroin/polydopamine hydrogel for treatment of spinal cord injury. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 399, 125795–125802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Gong, C.; Li, B.; Wu, G. A pH, glucose, and dopamine triple−responsive, self−healable adhesive hydrogel formed by phenylborate–catechol complexation. Polym. Chem. 2017, 8, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Kong, Y.; Su, Y.; Kuss, M.A.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Xie, J.; Duan, B. Tannic acid−inspired, self−healing, and dual stimuliresponsive dynamic hydrogel with potent antibacterial and anti−oxidative properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7182–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Bai, Q.; Wu, W.; Sun, N.; Cui, N.; Lu, T. Gelatin−based adhesive hydrogel with self−healing, hemostasis, and electrical conductivity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2142–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Dong, W.; Zhao, S.; Du, T.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, D.; Zhang, M. An injectable adhesive antibacterial hydrogel wound dressing for infected skin wounds. Biomater. Adv. 2021, 134, 112584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Weng, L.-T.; Xu, J.; Weng, J.; et al. Tough, self−healable and tissue−adhesive hydrogel with tunable multifunctionality. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, Y.; Shen, S.; Fan, D. A physicochemical double cross−linked multifunctional hydrogel for dynamic burn wound healing: Shape adaptability, injectable self−healing property and enhanced adhesion. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 120838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Ren, Y.; Chang, R.; He, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guan, F.; Yao, M. Injectable Self−Healing Adhesive Chitosan Hydrogel with Antioxidative, Antibacterial, and Hemostatic Activities for Rapid Hemostasis and Skin Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 34455–34469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yao, W.; Tian, M.; Wei, J.; Song, Q.; Qiao, W. Mussel−inspired degradable antibacterial polydopamine/silica nanoparticle for rapid hemostasis. Biomaterials 2018, 179, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pak, S.; Chen, F. Functional Enhancement of Guar Gum−Based Hydrogel by Polydopamine and Nanocellulose. Foods 2023, 12, 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061304
Pak S, Chen F. Functional Enhancement of Guar Gum−Based Hydrogel by Polydopamine and Nanocellulose. Foods. 2023; 12(6):1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061304
Chicago/Turabian StylePak, SolJu, and Fang Chen. 2023. "Functional Enhancement of Guar Gum−Based Hydrogel by Polydopamine and Nanocellulose" Foods 12, no. 6: 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061304
APA StylePak, S., & Chen, F. (2023). Functional Enhancement of Guar Gum−Based Hydrogel by Polydopamine and Nanocellulose. Foods, 12(6), 1304. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061304








