Biomonitoring–Health Risk Nexus of Potentially Toxic Metals on Cerithidea obtusa: A Biomonitoring Study from Peninsular Malaysia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
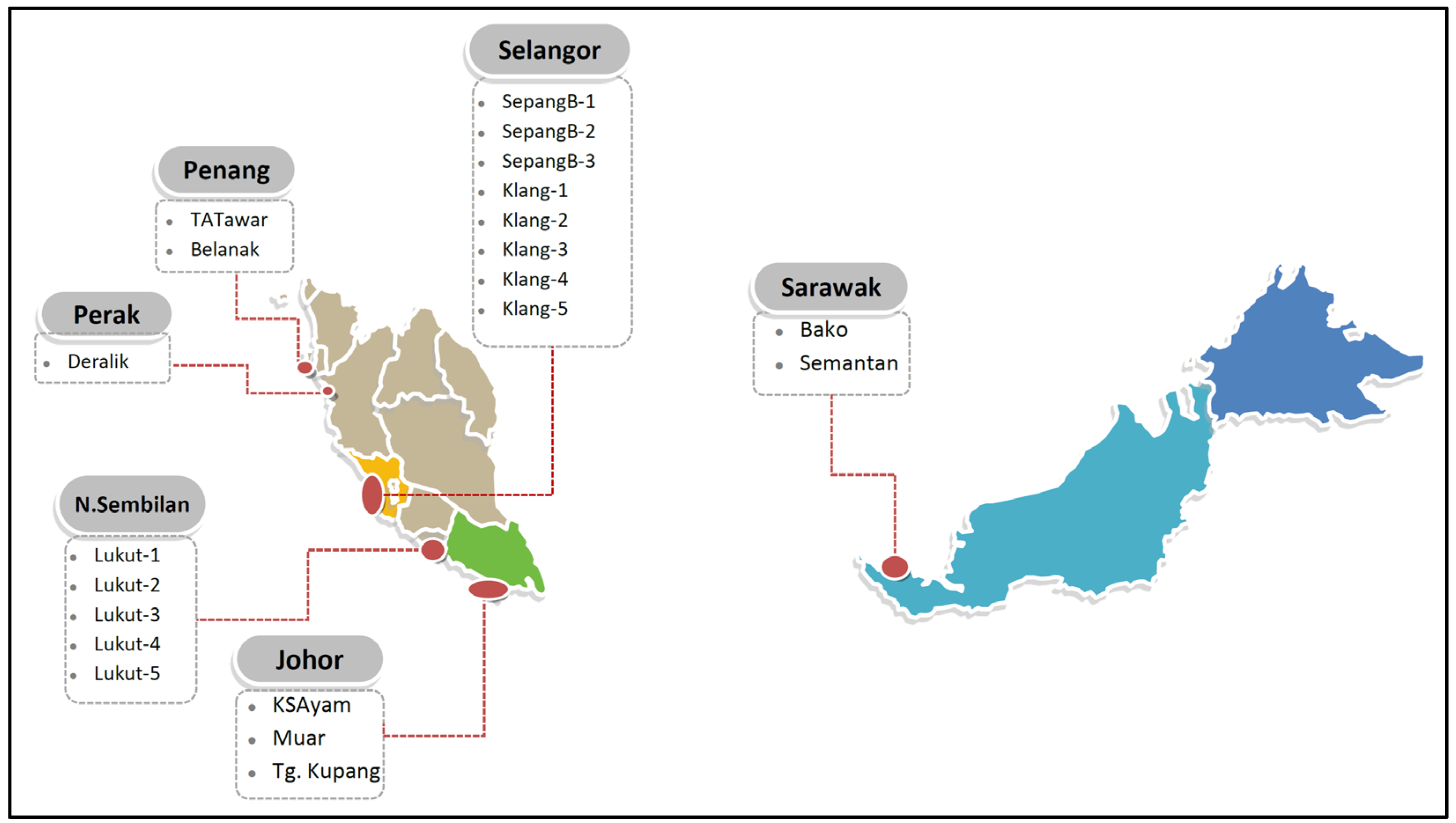
2.1. Samplings
2.2. Sample Preparation and Metal Analysis
2.3. Quality Monitoring and Assurance
2.4. Human Health Risk Assessments
2.4.1. Direct Comparisons with Seafood Safety Guidelines
2.4.2. Target Hazard Quotient
2.4.3. Comparisons between Estimated Weekly Intake (EWI) and Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake (PTWI)
2.5. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
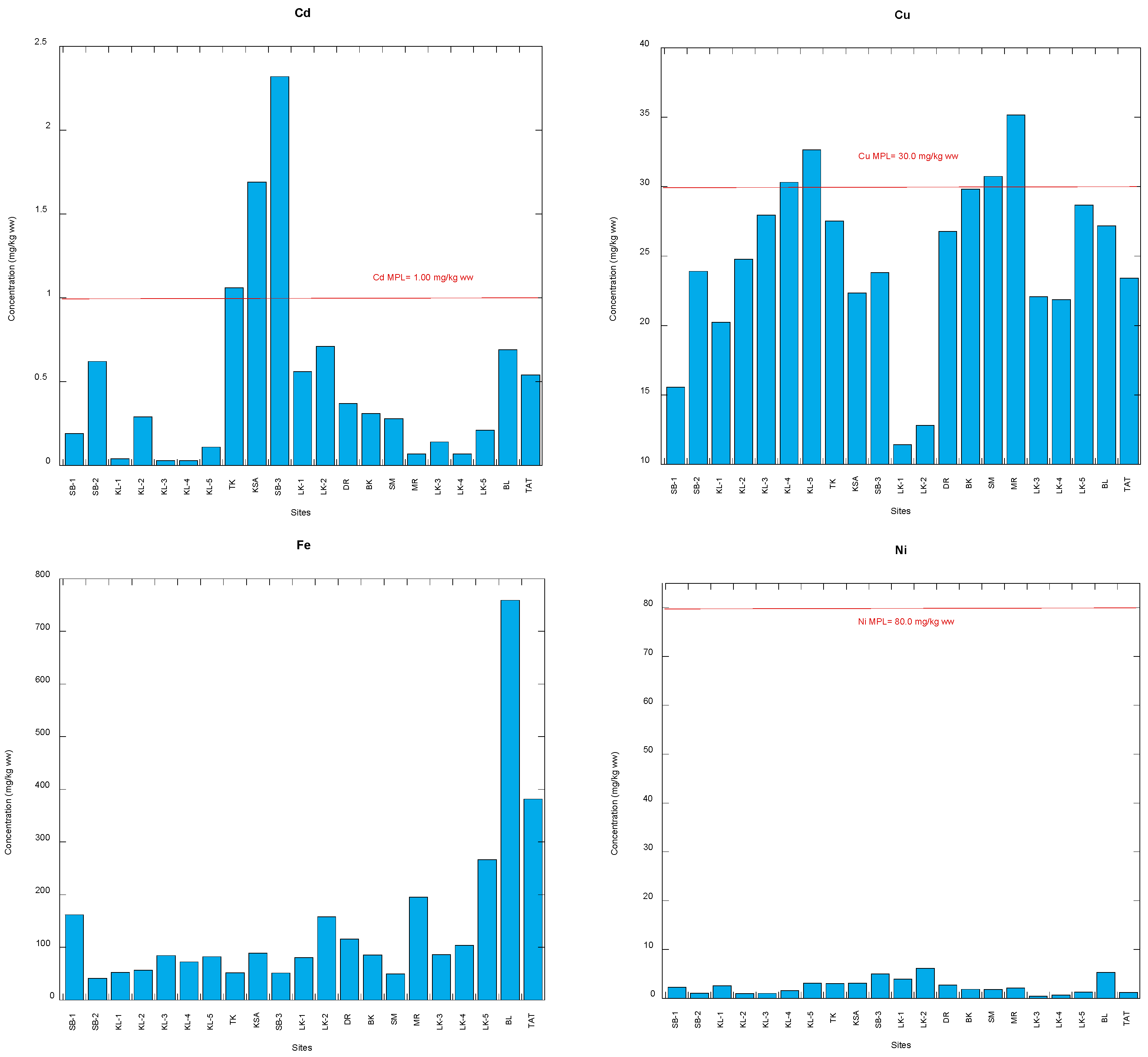
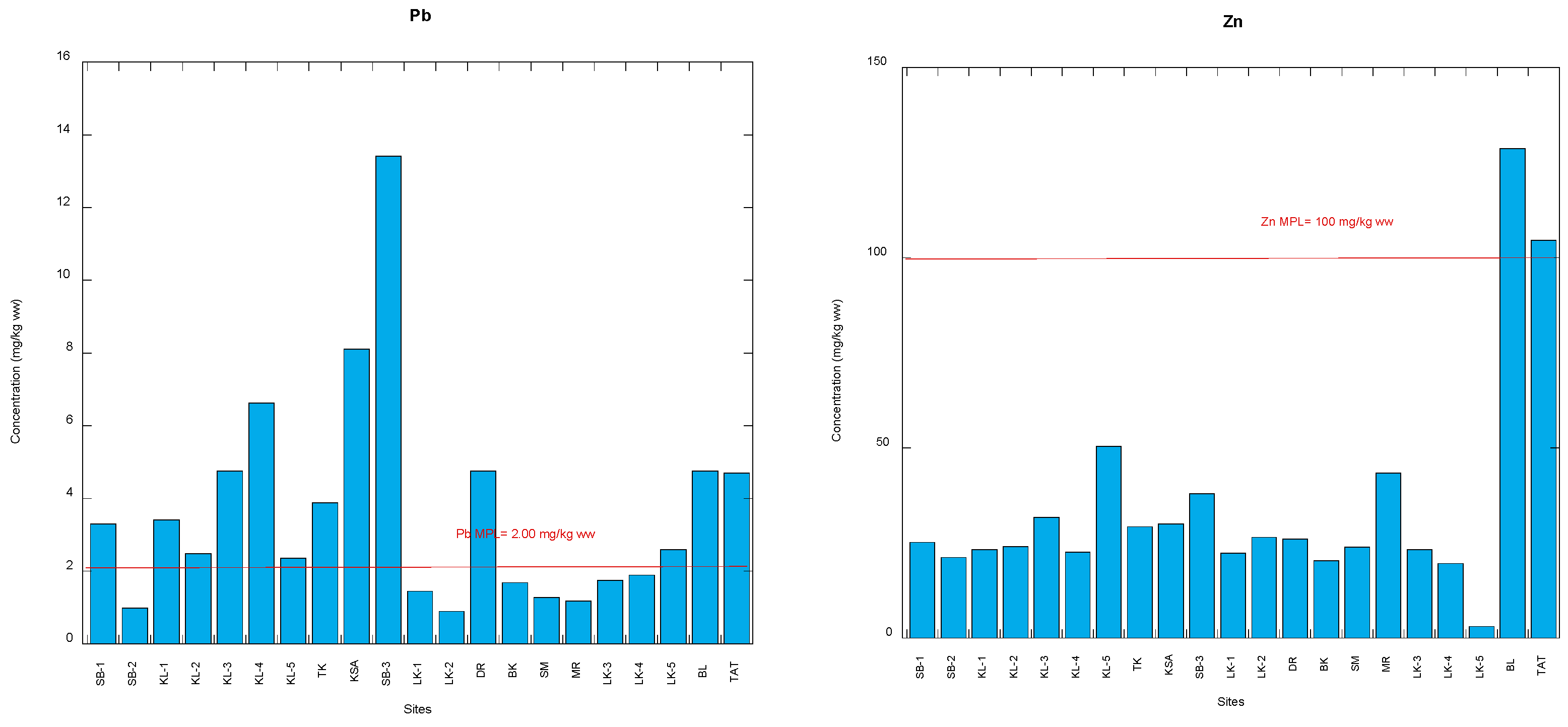
3.1. Comparison with Food Safety Guidelines of Potentially Toxic Metals
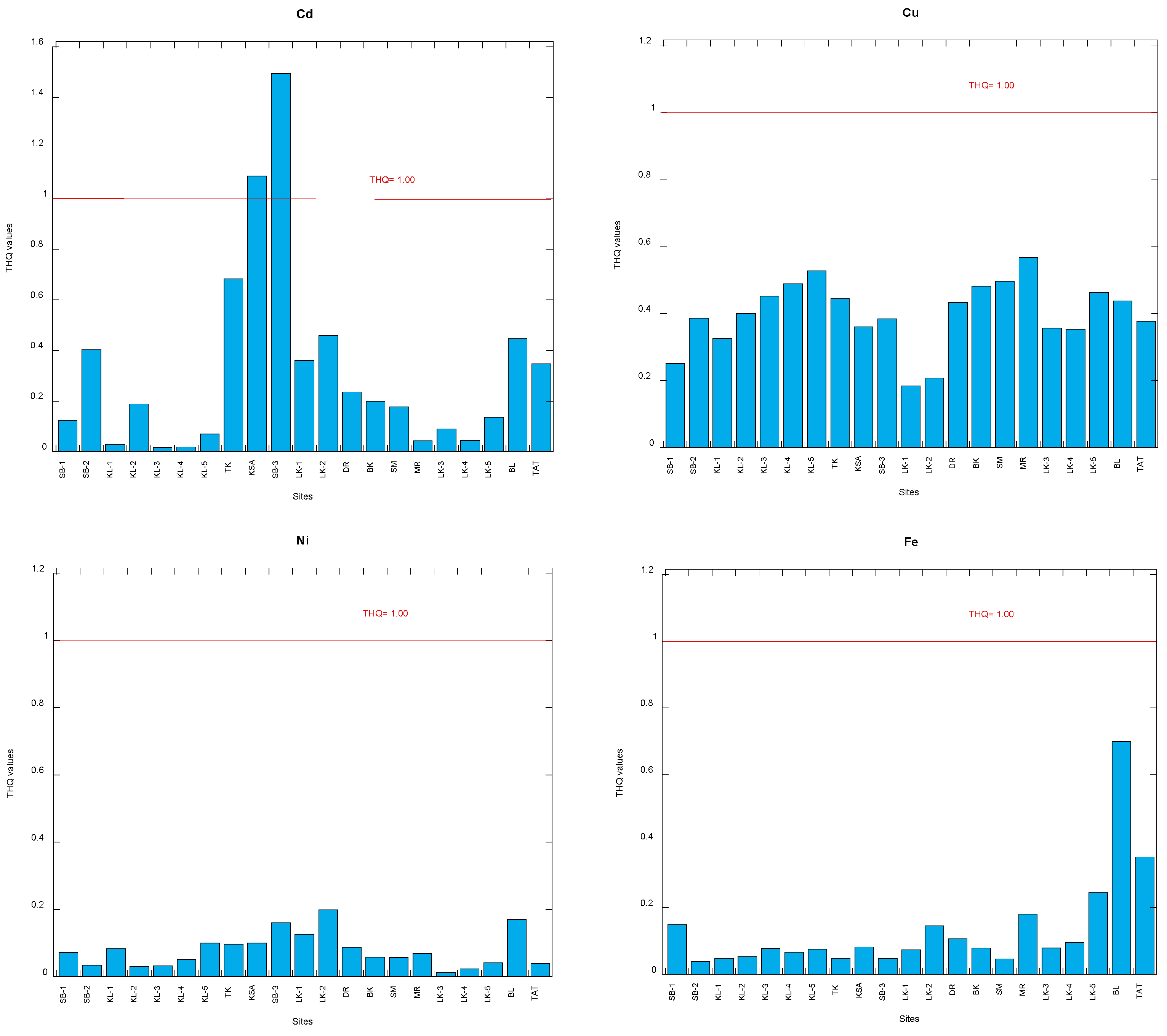
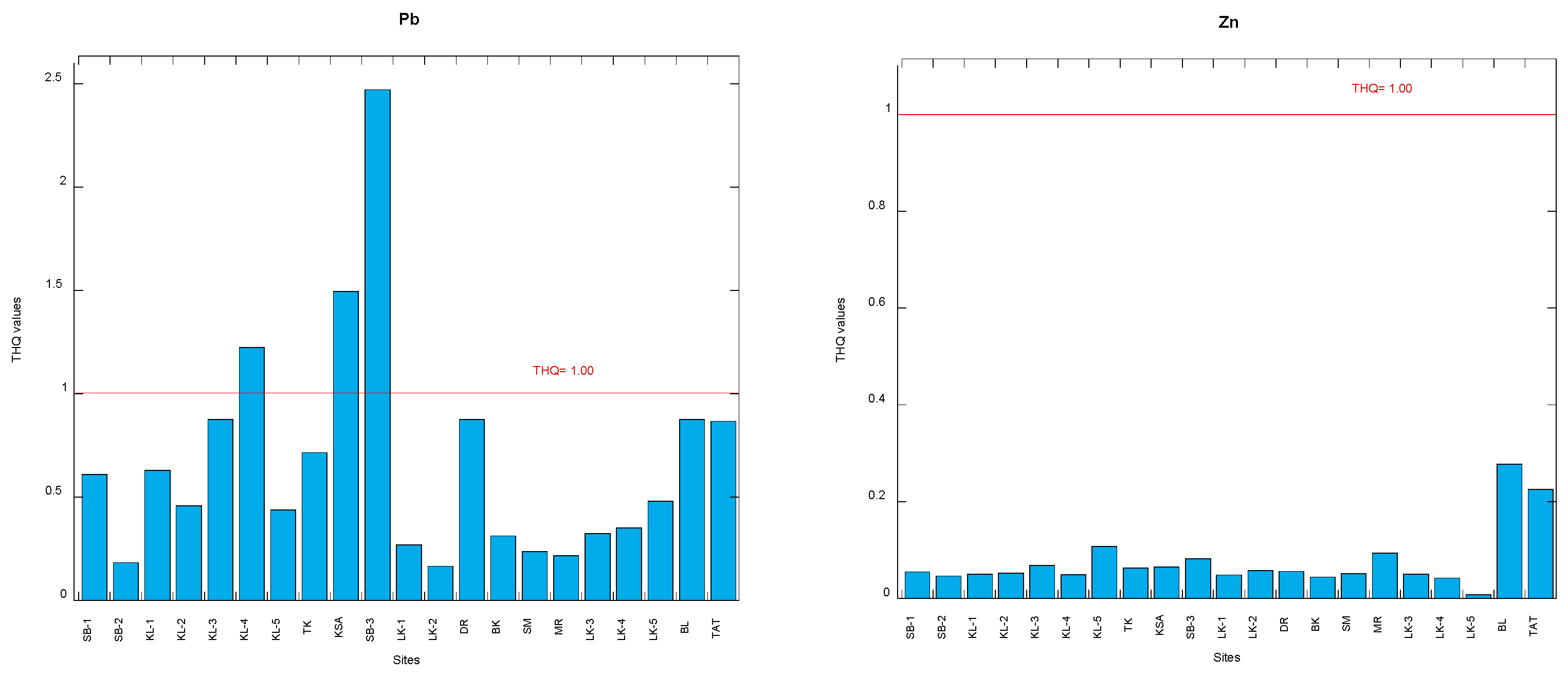
3.2. Target Hazard Quotients
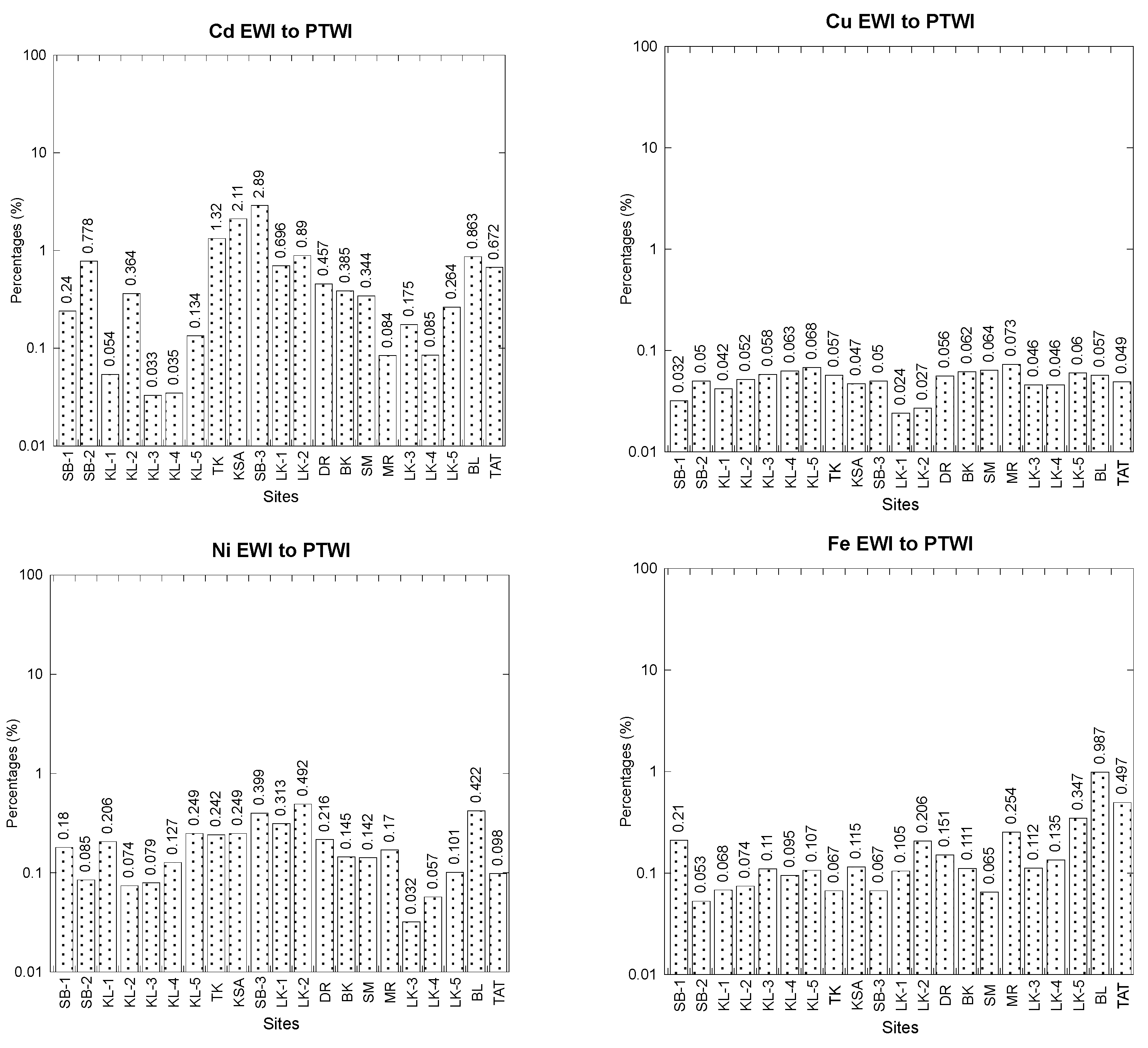
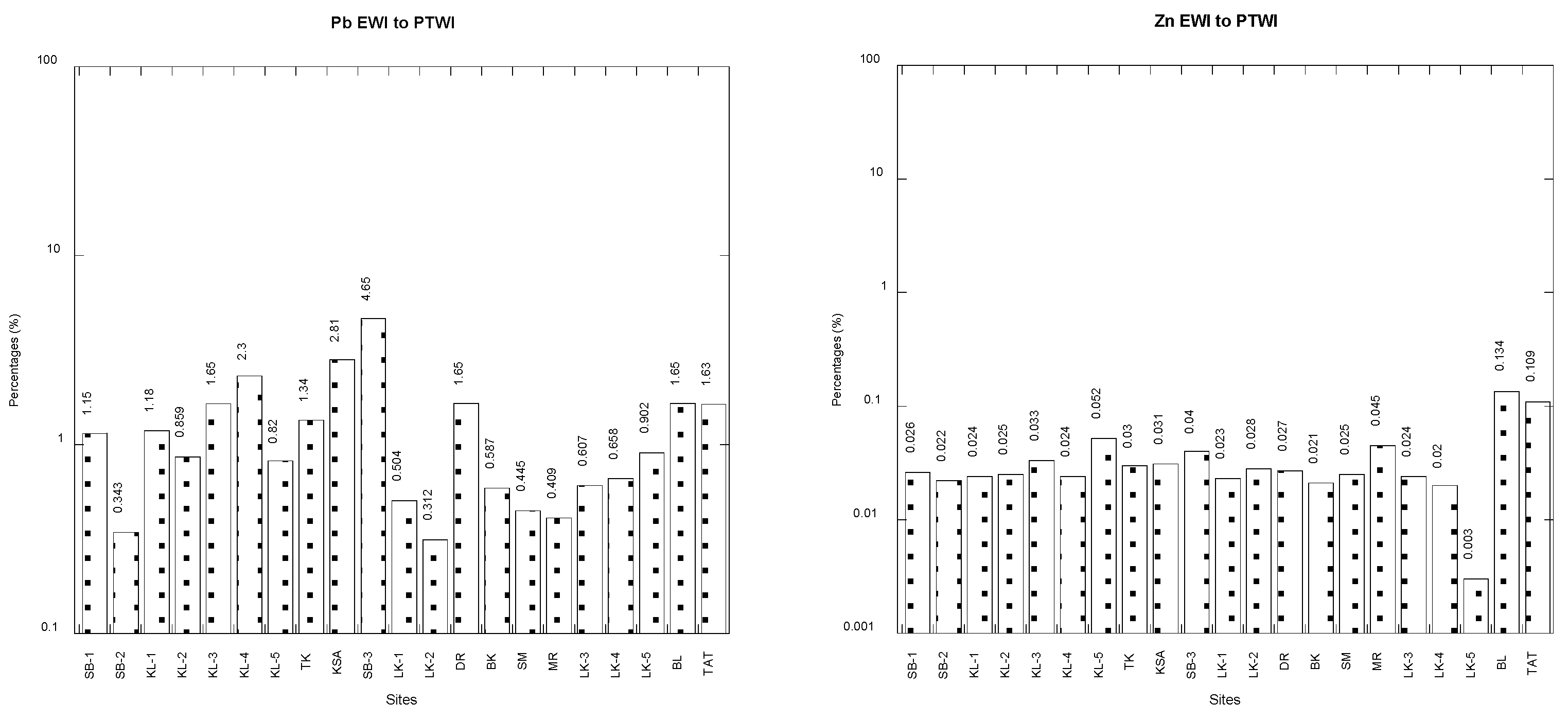
3.3. Comparisons between Estimated Weekly Intake (EWI) and Provisional Tolerable Weekly Intake (PTWI)
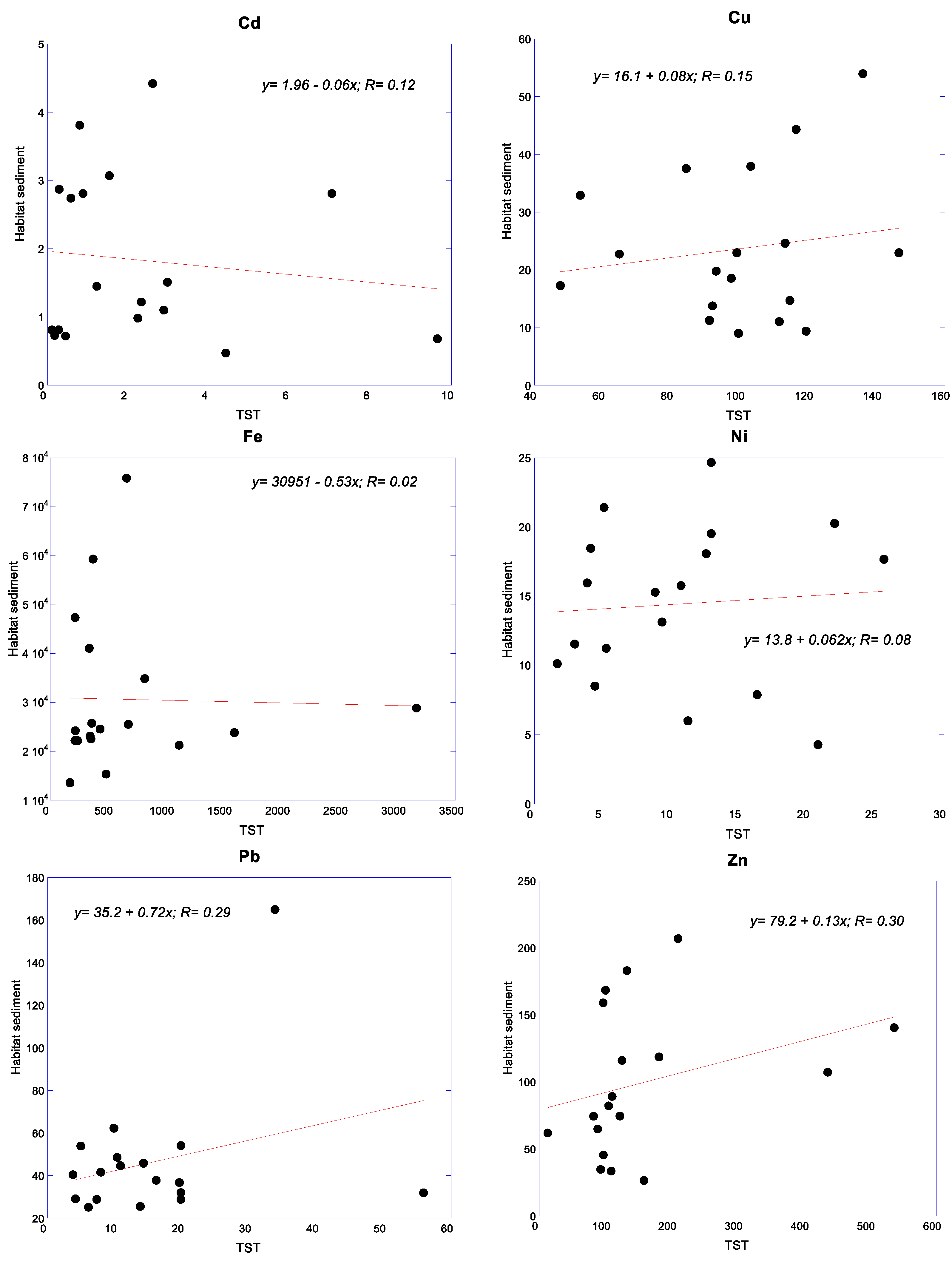
3.4. Relationships of Metals between Snails and Their Habitat Sediments
4. Discussion
4.1. General Low Health Risks with a Localized Elevation of Potentially Toxic Metals
4.2. Biomonitoring of Potentially Toxic Metals Using Cerithidea obtusa for Effective Mangrove Ecosystem Management
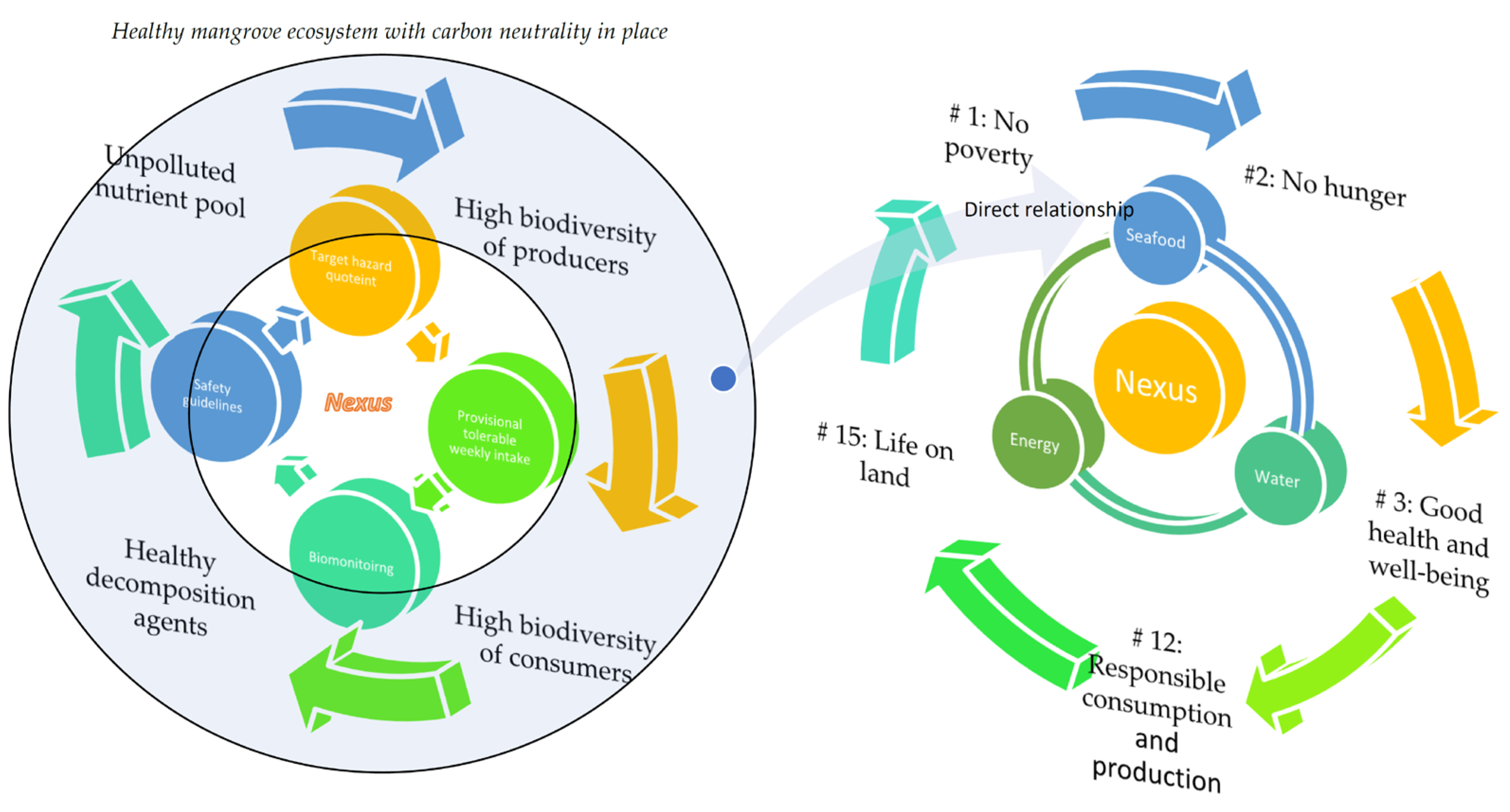
4.3. Health Risk–Biomonitoring Nexus versus Seafood–Water–Energy Nexus
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haseeb-ur-Rehman, M.; Munshi, A.B.; Atique, U.; Kalsoom, S. Metal pollution and potential human health risk assessment in major seafood items (fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanhan, P.; Lansubsakul, N.; Phaochoosak, N.; Sirinupong, P.; Yeesin, P.; Imsilp, K. Human Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal Concentration in Seafood Collected from Pattani Bay, Thailand. Toxics 2023, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, P.D.A.; Ferrari, R.G.; do Rosário, D.K.A.; de Almeida, C.C.; Saint’Pierre, T.D.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; dos Santos, L.N.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Toxic metal and metalloid contamination in seafood from an eutrophic Brazilian estuary and associated public health risks. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, J.; Jovetic, M.; Štulić, M.; Vujadinović, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Iammarino, M.; Djekic, I.V.; Tomasevic, I. Exposure assessment in the Serbian population and occurrence of histamine and heavy metals in fish and seafood. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7517–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Cao, H.; Hu, Y.; Du, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, H. Differences and risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood and freshwater products. J. Fish China 2022, 46, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Esau, B.S.; Ogbo, B.A.; Egbuna, C.; Ibeabuchi, C.G.; Orajiaka-Uchegbu, C. Health Risk Assessment of Hazardous Metals in Seafood from Ka-Bangha River, Khana, Rivers State, Nigeria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2022, 26, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandion, K.; Khalith, S.B.M.; Ravindran, B.; Chandrasekaran, M.; Rajagopal, R.; Alfarhan, A.; Chang, S.W.; Ayyamperumal, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Arunachalam, K.D. Potential health risk caused by heavy metal associated with seafood consumption around coastal area. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu-Olayan, A.H.; Thomas, B.V. Heavy metal accumulation in the gastropod, Cerithium scabridum l.; from the Kuwait Coast. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 68, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Dayal, S.R.; Siddiqua, S.A.; Muhib, M.I.; Bhowmik, S.; Kabir, M.M.; Rak, A.A.L.E.; Srzednicki, G. Risk assessment of heavy metals in marine fish and seafood from Kedah and Selangor coastal regions of Malaysia: A high-risk health concern for consumers. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55166–55175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulajfene, W.; Strogyloudi, E.; Catsiki, V.-A.; El Mlayah, A.; Tlig-Zouari, S. Bio-monitoring of metal impact on metallothioneins levels in the gastropod Phorcus turbinatus (Born, 1778) in the northeastern and the eastern coasts of Tunisia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 120, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Le, N.; Ha Hoang, T.T.; Phung, V.P.; Nguyen, T.L.; Duong, T.T.; Dinh, L.M.; Huong Pham, T.M.; Binh Phung, T.X.; Nguyen, T.D.; Duong, T.N.; et al. Trace Metal Element Analysis in Some Seafood in the Coastal Zone of the Red River (Ba Lat Estuary, Vietnam) by Green Sample Preparation and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). J. Anal. Meth. Chem. 2021, 2021, 6649362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djedjibegovic, J.; Marjanovic, A.; Tahirovic, D.; Caklovica, K.; Turalic, A.; Lugusic, A.; Omeragic, E.; Sober, M.; Caklovica, F. Heavy metals in commercial fish and seafood products and risk assessment in adult population in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orajiaka-Uchegbu, C.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Ogbo, A.B.; Egbuna, C. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals and potential health risk through consumption of seafoods from selected creeks in rivers state, Nigeria. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 1033–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, C.; Traina, A.; Giosuè, C.; Carpintieri, D.; Lo Dico, G.M.; Bellante, A.; Del Core, M.; Falco, F.; Gherardi, S.; Uccello, M.M.; et al. Heavy Metals and PAHs in Meat, Milk, and Seafood from Augusta Area (Southern Italy): Contamination Levels, Dietary Intake, and Human Exposure Assessment. Front. Publ. Health 2020, 8, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soceanu, A.; Dobrinas, S.; Carazeanu Popovici, I.; Jitariu, D. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2020, 21, 490–497. [Google Scholar]
- Milenkovic, B.; Stajic, J.M.; Stojic, N.; Pucarevic, M.; Strbac, S. Evaluation of heavy metals and radionuclides in fish and seafood products. Chemosphere 2019, 229, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saher, N.U.; Kanwal, N. Assessment of some heavy metal accumulation and nutritional quality of shellfish with reference to human health and cancer risk assessment: A seafood safety approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 5189–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazrouh, M.M.; Mourad, M.H. Biochemical composition and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in some seafood in the mediterranean coast of Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Jin, H.; Feng, H.; Shen, G.; Cao, Y.; Yu, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal variation and potential risks of seven heavy metals in seawater, sediment, and seafood in Xiangshan Bay, China (2011–2016). Chemosphere 2018, 212, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehel, J.; Bartha, A.; Dankó, D.; Lányi, K.; Laczay, P. Heavy metals in seafood purchased from a fishery market in Hungary. Food Addit. Contam. Part B Surveil. 2018, 11, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liao, Y.; Shou, L. Concentration and potential health risk of heavy metals in seafoods collected from Sanmen Bay and its adjacent areas, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 131, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuplulu, O.; Iplikcioglu Cil, G.; Korkmaz, S.D.; Aykut, O.; Ozansoy, G. Determination of metal contamination in seafood from the Black, Marmara, Aegean and Mediterranean sea metal contamination in seafood. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2018, 69, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satapathy, S.; Panda, C.R. Toxic metal ion in seafood: Meta-analysis of human carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic threat assessment, a geomedical study from Dhamra and Puri, Odisha. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2017, 23, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Yan, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.; Hu, D.; Guo, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Fan, C. Seafood consumption among Chinese coastal residents and health risk assessment of heavy metals in seafood. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 16834–16844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkpaa, K.W.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C.; Wegwu, M.O.; Essien, E.B. Health risk assessment of hazardous metals for population via consumption of seafood from Ogoniland, Rivers State, Nigeria; A case study of Kaa, B-Dere, and Bodo City. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.K.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Comparative study of potentially toxic nickel and their potential human health risks in seafood (fish and mollusks) from Peninsular Malaysia. Biology 2022, 11, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.K. Mussel Watch in Malaysia Past, Present and Future; UPM Press: Serdang, Malaysia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, A.; Iwok, E.; Ekanem, S. Public health threats of heavy metals due to the consumption of Achachatina marginata (African giant land snail) from a partially remediated site in Ikot Ada Udo, Akwa Ibom State, South-South Nigeria. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soegianto, A.; Putranto, T.W.C.; Payus, C.M.; Zarqasi, F.R.; Syafitrirulla, P.P.; Muchlisin, M.I.; Ramdhani, S.; Nosafandra, A.S.; Wibisono, A.D. Metals in the tissues of the East Java Coast Indonesian green mussel (Perna viridis Linnaeus, 1758) and associated health risks. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 48, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montojo, U.M.; Baldoza, B.J.S.; Cambia, F.D.; Benitez, K.C.D.; Perelonia, K.B.S.; Rivera, A.T.F. Levels and health risk assessment of mercury, cadmium, and lead in green mussel (Perna viridis) and oyster (Crassostrea iredalei) harvested around Manila Bay, Philippines. Food Control 2021, 124, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Carocci, A.; Lauria, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Catalano, A. Nickel: Human health and environmental toxicology. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.K.; Reddy, R.C.; Bagoji, I.B.; Das, S.; Bagali, S.; Mullur, L.; Khodnapur, J.P.; Biradar, M.S. Primary concept of nickel toxicity—An overview. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, S.; Garman, E.; Heim, K.E.; Lyons-Darden, T.; Schlekat, C.E.; Taylor, M.D.; Oller, A.R. Concise review of nickel human health toxicology and rcotoxicology. Inorganics 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Leston, J.; Mendez, J.; Pasaro, E.; Laffon, B. Genotoxic effects of lead: An updated review. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovic, M.; Stankovic, S. Human exposure to trace metals and possible public health risks via consumption of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Adriatic coastal area. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 70, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield, R.L.; Henderson, C.R.; Cory-Slechta, D.A.; Cox, C.; Jusko, T.A.; Lanphear, B.P. Intellectual impairment in children with blood lead concentrations below 10 lg per deciliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Qu, L.; Yao, S. Health risk assessment of eight heavy metals in nine varieties of edible vegetable oils consumed in China. Food Chem Toxicol. 2011, 49, 3081–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorell, J.M.; Johnson, C.C.; Rybicki, B.A.; Peterson, E.L.; Kortsha, G.X.; Brown, G.G. Occupational exposures to metals as risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 1997, 48, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JECFA. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants (Twenty-Seventh Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). WHO Technical Report Series, No. 696, 1983, and Corrigenda. 1983. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/39165 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- JECFA. Evaluation of Certain Food Additives and Contaminants (Twenty-Sixth Report of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives). WHO Technical Report Series, No. 683. 1982. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/41546 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Mertz, W. The essential trace elements. Science 1981, 213, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaro, N.; Juddy, O.; Murago, E.N.M.; Gitonga, E. The contents of Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd in meat in Nairobi, Kenya. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2007, 5, 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- AFS. Annual Fisheries Statistics of Malaysia Department of Fisheries Malaysia. 2021. Available online: https://www.dof.gov.my/en/resources/fisheries-statistics-i/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Amin, B.; Nurrachmi, I. Concentration, distribution, and correlation of heavy metals in seawater, sediment, and Cerithidea obtusa from coastal waters of Singkep Island, Riau Archipelago Province. Indon. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Duysak, Ö.; Azdural, K. Evaluation of heavy metal and aluminium accumulation in a gastropod, Patella caerulea L.; 1758 in Iskenderun Bay, Turkey. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamli, H.; Idris, M.H.; Hena, M.A.; Wong, S.K. Diversity of edible mollusc (Gastropoda and Bivalvia) at selected divison of Sarawak, Malaysia. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inform. Technol. 2012, 2, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, M.H.; Hamli, H.; Kamal, A.H.M.; Lah, R.A.; Jaafar, N.M.S.N. Study of diversity and morphometry in edible bivalves and gastropods from a coastal wetland in Sarawak. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 43, 889–896. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, T.U.R.; Ramesh, K.B. Heavy Metal Risk Assessment in Bhavanapadu Creek Using Three Potamidid Snails-Telescopium telescopium, Cerithidea obtusa and Cerithidea cingulata. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 1000385. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, K.; Saion, E.; Yap, C.K.; As, N. Bioaccumulation of Metals in Mangrove Snail (Cerithidea obtusa) from Southwest Johor, Malaysia. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2022, 10, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Saion, E.; Yap, C.K.; Balu, P.; Cheng, W.H.; Chong, M.Y. Distribution of heavy metals in sediments and soft tissues of the Cerithidea obtusa from Sepang River, Malaysia. Indon. J. Chem. 2022, 22, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, P.; Hong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X.; Ma, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, Y. Metal loadings in estuarine bivalve and gastropod shellfish in response to socio-economic development in watershed. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 176, 105593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, M.; Mohanraj, R.V.B.J.; Prasath, R.V.A. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in a gastropod species at the Kole wetland agroecosystem, a Ramsar site. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 329, 117027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primost, M.A.; Gil, M.N.; Bigatti, G. High bioaccumulation of cadmium and other metals in Patagonian edible gastropods. Mar. Biol. Res. 2017, 13, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragi, A.S.; Leena, P.P.; Cheriyan, E.; Nair, S.M. Heavy metal concentrations in some gastropods and bivalves collected from the fishing zone of South India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 118, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabushko, V.I.; Toichkin, A.M.; Kapranov, S.V. Heavy Metals and Arsenic in Soft Tissues of the Gastropod Rapana venosa (Valenciennes, 1846) Collected on a Mollusk Farm Off Sevastopol (Southwestern Crimea, Black Sea): Assessing Human Health Risk and Locating Regional Contamination Areas. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumanti, S.; Siregar, Y.I. Annalysis of Pb, Cu and Zn Metal Contents in Red Chut-chut Snail (Cerithidea obtusa) and Sediment in Mendol Island Kuala Kampar of Riau Province. Asian J. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 2, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh-Nho, N.; Marchand, C.; Strady, E.; Huu-Phat, N.; Nhu-Trang, T.T. Bioaccumulation of some trace elements in tropical mangrove plants and snails (Can Gio, Vietnam). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wariski, I.; Siregar, Y.I.; Amin, B. Heavy Metal Content in Sediment and Hora Shell (Cerithidea obtusa) in Panipahan Waters, Rokan Hilir, Riau. J. Nat. Indon. 2021, 9, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Edward, F.B. Distribution of heavy metals in the different parts of Cerithidea obtusa and the relationships between metal distribution and allometric parameters of the snail. Environ. Asia 2010, 3, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Edward, F.B. Heavy metal distribution in the different parts of Cerithidea obtusa by using multivariate analysis. Malay. J. Sci. 2009, 28, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.H.; Yap, C.K. Potential human health risks from toxic metals via mangrove snail consumption and their ecological risk assessments in the habitat sediment from Peninsular Malaysia. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artalina, D.; Takarina, N.D. Metals Content in Edible Gastropod from Blanakan Silvofishery Ponds. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1245, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Hisyam, M.N.D.; Edward, F.B.; and Tan, S.G. Concentrations of heavy metal in the different parts of gastropod, Faunus ater collected from the intertidal area of Peninsular Malaysia. Pertanika J. Trop. Agric. Sci. 2010, 33, 45–60. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, C.K.; Ismail, A.; Tan, S.G.; Omar, H. Correlations between speciation of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn in sediment and their concentrations in total soft tissue of green-lipped mussel Perna viridis from the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US FDA/CFSAN National Shellfish Sanitation Program. Guide for the Control of Molluscan Shellfish. Guidance Documents Chapter II. Growing Areas: 04. Action Levels, Tolerances, and Guidance Levels for Poisonous or Deleterious Substances in Seafood, 2007 (2019 Revised Edition). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143238/download (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Food Safety and Quality Division of the Ministry of Health Malaysia. Malaysian Law on Food and Drugs; Malaysian Food Regulation; Malaysian Law Publishers: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of the European Parliament and the Council of 19 December 2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants In Foodstuffs. Official Journal of the European Communities, L364/18. 2006. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R1881&from=EN (accessed on 12 June 2015).
- Codex Alimentarius. International Food Standard. General Standard for Contaminants and Toxins in Food and Feed. Cxs 193-1995. Adopted in 1995 Revised in 1997, 2006, 2008 and 2009, Amended in 2010, 2012–2019. FAO and WHO. 66 pages. 1997. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/en/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B193-1995%252FCXS_193e.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- ANZFA. Australian and New Zealand Food Standards Code, Standard 1.4.1—Contaminants and Natural Toxicants (F2011C00052). 2015. Available online: https://www.comlaw.gov.au/Details/F2015C00052/Download (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Nauen, C. Compilation of Legal Limits for Hazardous Substances in Fish and Fishery Products. FAO Fisheries Circular, No. 464. 1983. Available online: https://agris.fao.org/agris-search/search.do?recordID=XF19840038090 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Ahmad, N.I.; Wan Mahiyuddin, W.R.; Tengku Mohamad, T.R.; Ling, C.Y.; Daud, S.F.; Hussein, N.C.; Abdullah, N.A.; Shaharudin, R.; Sulaiman, L.H. Fish Consumption Pattern among Adults of Different Ethnics in Peninsular Malaysia. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 32697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US EPA Human Health Risk Assessment.; Regional Screening Level (RSL)—Summary Table November 2021. Available online: https://semspub.epa.gov/work/HQ/401635.pdf (accessed on 26 December 2021).
- JECFA. Summary and Conclusions of the Seventy-Third Meeting of the JECFA.; Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Volume 1, Recommendations, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- JECFA. Evaluations of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). Includes All Updates Up to the 89th JECFA (June 2020). 2021. Available online: https://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/search.aspx?fcc=2 (accessed on 7 January 2022).
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain (CONTAM); Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; et al. Update of the Risk Assessment of Nickel in Food and Drinking Water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JECFA. Safety Evaluation of Certain Contaminants in Food/Prepared by the Seventy-Second Meeting of the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA). (WHO Food Additives Series; 63) FAO JECFA Monographs. 2011. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44520 (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Zar, J.H. Biostatistical Analysis, 3rd ed; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 662. [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi, H.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Machida, M.; Kayama, F. Dietary exposure to cadmium at close to the current provisional tolerable weekly intake does not affect renal function among female Japanese farmers. Environ. Res. 2004, 95, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberdorster, G.I. Pulmonary deposition, clearance and effects of inhalation soluble and insoluble cadmium compounds. IARC Sci. Publ. 1992, 118, 189–204. [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi, H.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Murakami, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Murata, K.; Kayama, F. Age-relevant renal effects of cadmium exposure through consumption of home-harvested rice in female Japanese farmers. Environ. Int. 2013, 56, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi, H.; Aoshima, K.; Oguma, E.; Sasaki, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Hosoi, Y.; Katoh, T.; Kayama, F. Latest status of cadmium accumulation and its effects on kidneys, bone, and erythropoiesis in inhabitants of the formerly cadmium-polluted Jinzu River Basin in Toyama, Japan, after restoration of rice paddies. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 2010, 83, 953–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium, and Zinc; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, D.J.H.; Rainbow, P.S. Strategies of trace metals sequestration in aquatic organisms. Mar. Environ. Res. 1989, 28, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S. Trace metal accumulation in marine invertebrates: Marine biology or marine chemistry. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 1997, 77, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.J.H. The chemistries and environmental fates of trace metals and organchlorines in aquatic ecosystems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, C.K.; Kumar, K.; Saion, E.; Kamari, H.M.; Wong, K.W.; Saito, M.; Nulit, R.; Shohaimi, S.; Bakhtiari, A.R.; Al-Shami, S.A. Association of Trace Metals (Cr, Co, Mn and Sc) between Surface Sediments and the Mangrove Snail Cerithedea Obtusa: Assessment of the Snail as a Biomonitor for Intertidal Mangrove Ecosystem Management; Nova Science: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 141–166. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, V.K. Snails as biological monitor (bioindicator). Asian J. Adv. Res. 2020, 5, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Arthur, M.; Viglia, S.; Xue, J.; Meng, F.; Lombardi, G.V. Seafood-energy-water nexus: A study on resource use efficiency and the environmental impact of seafood consumption in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C. Continental-scale spatial distribution, sources, and health risks of heavy metals in seafood: Challenge for the water-food-energy nexus sustainability in coastal regions? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 63815–63828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Hooper, T.; Swales, J.K.; Papathanasopoulou, E.; Austen, M.C.; Yan, X. Energy-food nexus in the marine environment: A macroeconomic analysis on offshore wind energy and seafood production in Scotland. Energy Policy 2021, 149, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, L. Food Safety Objectives: The Nexus among Preventive Controls, Validation, and Food Safety Assurance. Food Safety Magazine. 2022. Available online: https://www.food-safety.com/articles/8336-food-safety-objectives-the-nexus-among-preventive-controls-validation-and-food-safety-assurance (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Orimoloye, I.R. Water, energy and food nexus: Policy relevance and challenges. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 5, 824322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Geslin, V.; Turrero, P.; Rodriguez, N.; Machado-Schiaffino, G.; Ardura, A. Oceanic karma? Eco-ethical gaps in African EEE metal cycle may hit back through seafood contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gephart, J.A.; Troell, M.; Henriksson, P.J.G.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Verdegem, M.; Metian, M.; Mateos, L.D.; Deutsch, L. The ‘seafood gap’ in the food-water nexus literature—Issues surrounding freshwater use in seafood production chains. Adv. Wat. Res. 2017, 110, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nylen, N.G. Why federal dietary guidelines should acknowledge the food-choice/Environment Nexus: Examining the recommendation to eat more seafood. Ecol. Law Q. 2013, 40, 759–794. [Google Scholar]
| Cddw | Cdww | Cudw | Cuww | Fedw | Feww | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.11 | 0.03 | 47.6 | 11.4 | 171 | 40.9 |
| Max | 9.65 | 2.32 | 147 | 35.2 | 3162 | 759 |
| Mean | 2.05 | 0.49 | 103 | 24.7 | 600 | 144 |
| Median | 1.22 | 0.29 | 103 | 24.8 | 356 | 85.4 |
| SD | 2.42 | 0.58 | 25.6 | 6.15 | 681 | 163 |
| SE | 0.53 | 0.13 | 5.59 | 1.34 | 149 | 35.7 |
| Skewness | 1.92 | 1.93 | −0.58 | −0.58 | 2.83 | 2.83 |
| Kurtosis | 3.20 | 3.22 | −0.13 | −0.13 | 7.81 | 7.81 |
| Nidw | Niww | Pbdw | Pbww | Zndw | Znww | |
| Min | 1.67 | 0.4 | 3.75 | 0.90 | 12.9 | 3.11 |
| Max | 25.6 | 6.14 | 55.9 | 13.4 | 536 | 129 |
| Mean | 10.1 | 2.43 | 15.1 | 3.63 | 146 | 35.1 |
| Median | 8.85 | 2.12 | 10.8 | 2.6 | 105 | 25.2 |
| SD | 6.57 | 1.58 | 12.3 | 2.96 | 121 | 28.9 |
| SE | 1.43 | 0.34 | 2.69 | 0.65 | 26.3 | 6.31 |
| Skewness | 0.90 | 0.90 | 1.89 | 1.90 | 2.33 | 2.33 |
| Kurtosis | −0.04 | −0.04 | 3.77 | 3.78 | 4.59 | 4.59 |
| Cd EDI | Cd THQ | Cu EDI | Cu THQ | Ni EDI | Ni THQ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.02 | 0.02 | 7.37 | 0.18 | 0.26 | 0.013 |
| Max | 1.49 | 1.49 | 22.7 | 0.57 | 3.96 | 0.198 |
| Mean | 0.32 | 0.32 | 15.9 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 0.08 |
| Median | 0.19 | 0.19 | 15.9 | 0.4 | 1.37 | 0.069 |
| SD | 0.38 | 0.38 | 3.97 | 0.10 | 1.02 | 0.05 |
| SE | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.87 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Skewness | 1.92 | 1.92 | −0.58 | −0.58 | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| Kurtosis | 3.20 | 3.20 | −0.13 | −0.13 | −0.04 | −0.04 |
| Fe EDI | Fe THQ | Pb EDI | Pb THQ | Zn EDI | Zn THQ | |
| Min | 26.4 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 0.16 | 2.01 | 0.01 |
| Max | 490 | 0.70 | 8.65 | 2.47 | 83.0 | 0.28 |
| Mean | 92.9 | 0.13 | 2.34 | 0.67 | 22.7 | 0.08 |
| Median | 55.1 | 0.08 | 1.68 | 0.48 | 16.3 | 0.05 |
| SD | 105 | 0.15 | 1.91 | 0.54 | 18.7 | 0.06 |
| SE | 23.0 | 0.03 | 0.42 | 0.12 | 4.07 | 0.01 |
| Skewness | 2.83 | 2.83 | 1.89 | 1.89 | 2.33 | 2.34 |
| Kurtosis | 7.81 | 7.80 | 3.77 | 3.77 | 4.59 | 4.61 |
| N = 21 | Cd EWI | Cu EWI | Ni EWI | Fe EWI | Pb EWI | Zn EWI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.12 | 51.5 | 1.81 | 185 | 4.06 | 14.1 |
| Max | 10.46 | 159 | 27.7 | 3427 | 60.6 | 581 |
| Mean | 2.22 | 112 | 10.9 | 651 | 16.4 | 159 |
| Median | 1.32 | 112 | 9.59 | 386 | 11.8 | 114 |
| SD | 2.63 | 27.8 | 7.12 | 738 | 13.4 | 131 |
| SE | 0.57 | 6.06 | 1.55 | 161 | 2.91 | 28.5 |
| Skewness | 1.93 | −0.58 | 0.90 | 2.83 | 1.90 | 2.33 |
| Kurtosis | 3.21 | −0.13 | −0.04 | 7.81 | 3.78 | 4.59 |
| Cd%EWI | Cu%EWI | Ni%EWI | Fe%EWI | Pb%EWI | Zn%EWI | |
| Min | 0.033 | 0.024 | 0.032 | 0.053 | 0.31 | 0.003 |
| Max | 2.893 | 0.073 | 0.492 | 0.987 | 4.65 | 0.134 |
| Mean | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 1.26 | 0.04 |
| Median | 0.364 | 0.052 | 0.17 | 0.111 | 0.90 | 0.026 |
| SD | 0.73 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 1.03 | 0.03 |
| SE | 0.16 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| Skewness | 1.92 | −0.61 | 0.90 | 2.83 | 1.90 | 2.33 |
| Kurtosis | 3.20 | −0.12 | −0.04 | 7.80 | 3.77 | 4.59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yap, C.K.; Al-Mutairi, K.A. Biomonitoring–Health Risk Nexus of Potentially Toxic Metals on Cerithidea obtusa: A Biomonitoring Study from Peninsular Malaysia. Foods 2023, 12, 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081575
Yap CK, Al-Mutairi KA. Biomonitoring–Health Risk Nexus of Potentially Toxic Metals on Cerithidea obtusa: A Biomonitoring Study from Peninsular Malaysia. Foods. 2023; 12(8):1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081575
Chicago/Turabian StyleYap, Chee Kong, and Khalid Awadh Al-Mutairi. 2023. "Biomonitoring–Health Risk Nexus of Potentially Toxic Metals on Cerithidea obtusa: A Biomonitoring Study from Peninsular Malaysia" Foods 12, no. 8: 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081575
APA StyleYap, C. K., & Al-Mutairi, K. A. (2023). Biomonitoring–Health Risk Nexus of Potentially Toxic Metals on Cerithidea obtusa: A Biomonitoring Study from Peninsular Malaysia. Foods, 12(8), 1575. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12081575





