Acid–Heat-Induced Fabrication of Nisin-Loaded Egg White Protein Nanoparticles: Enhanced Structural and Antibacterial Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
2.3. Determination of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
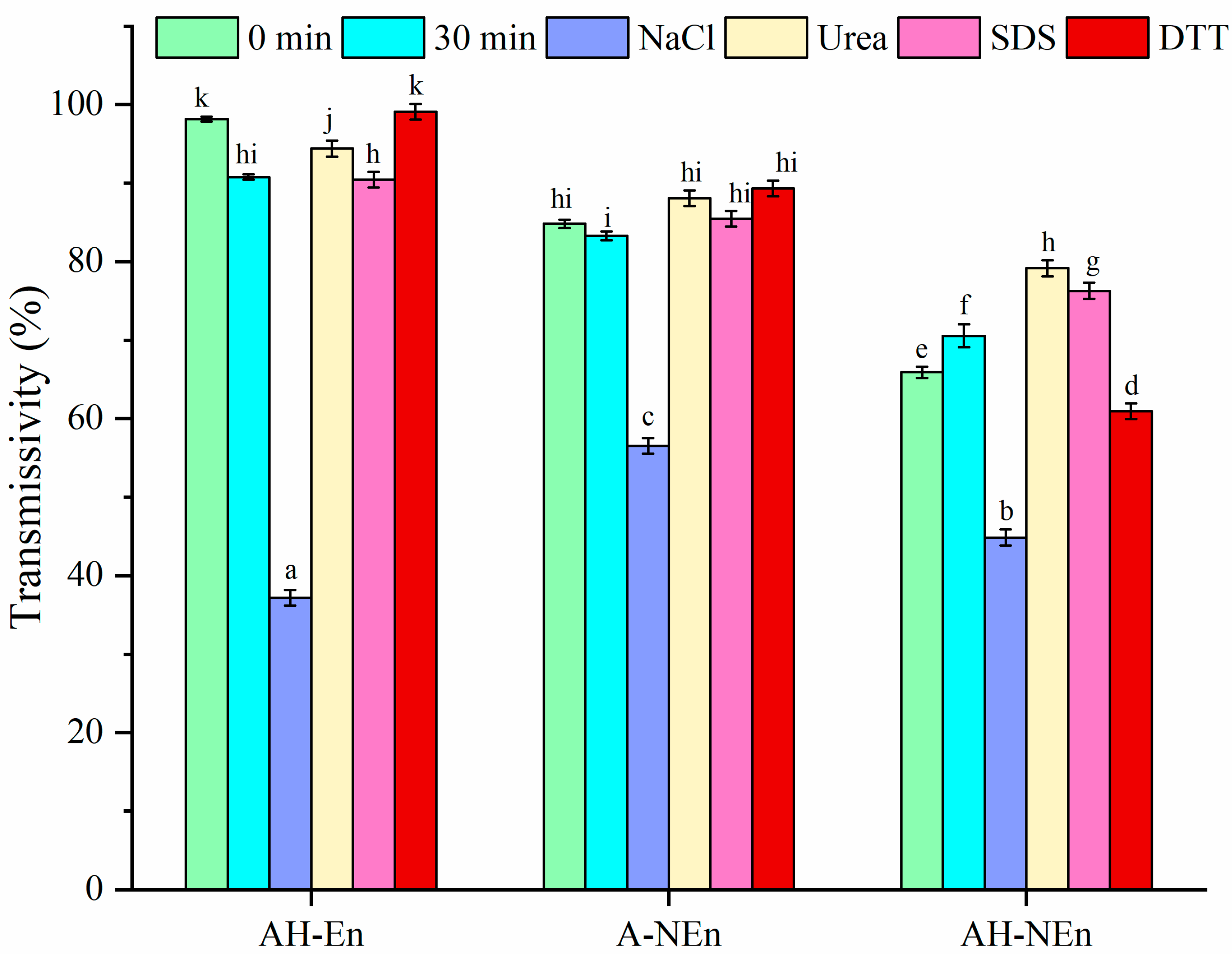
2.4. Measurement of Turbidity
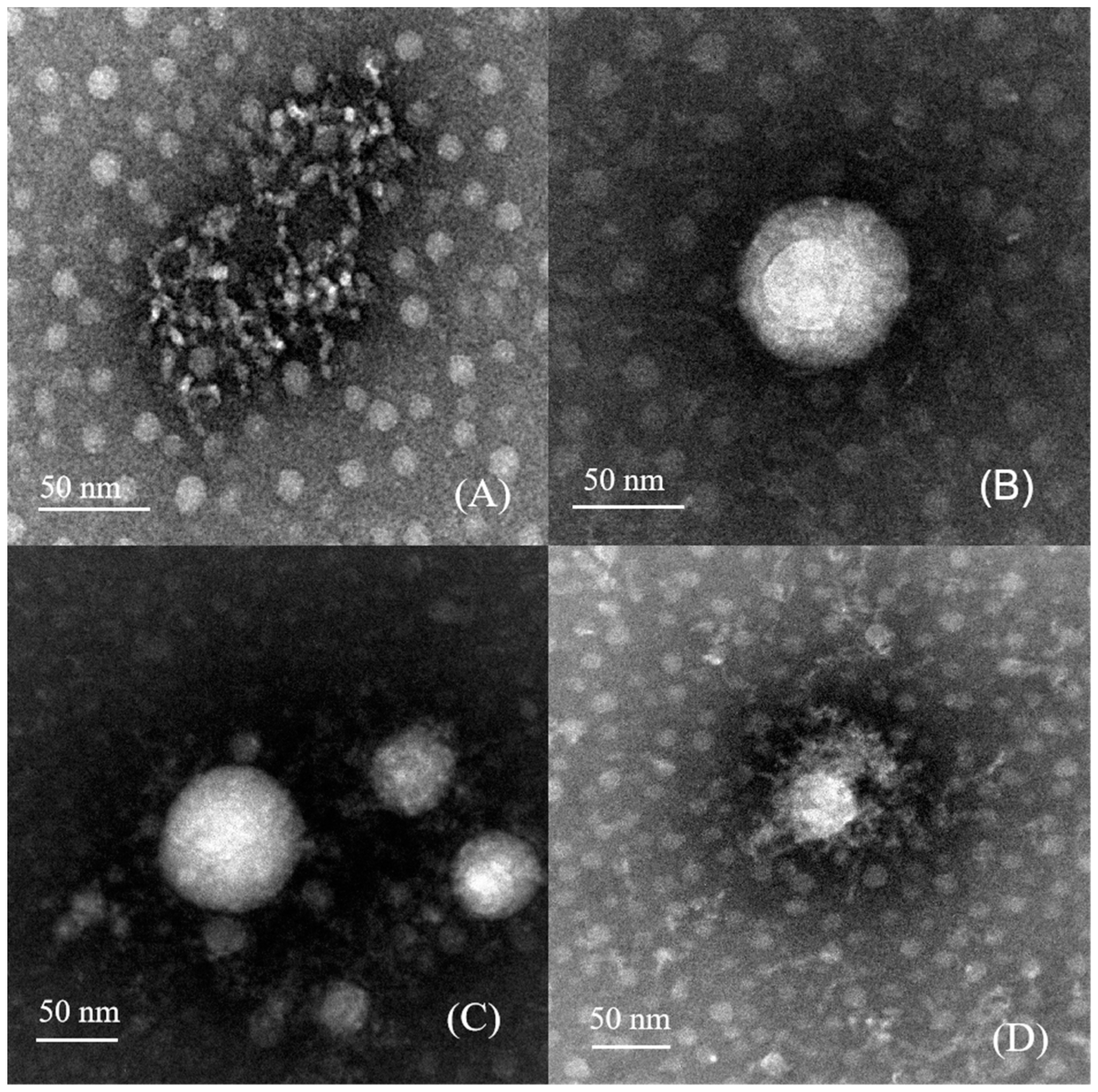
2.5. Observation of Morphology
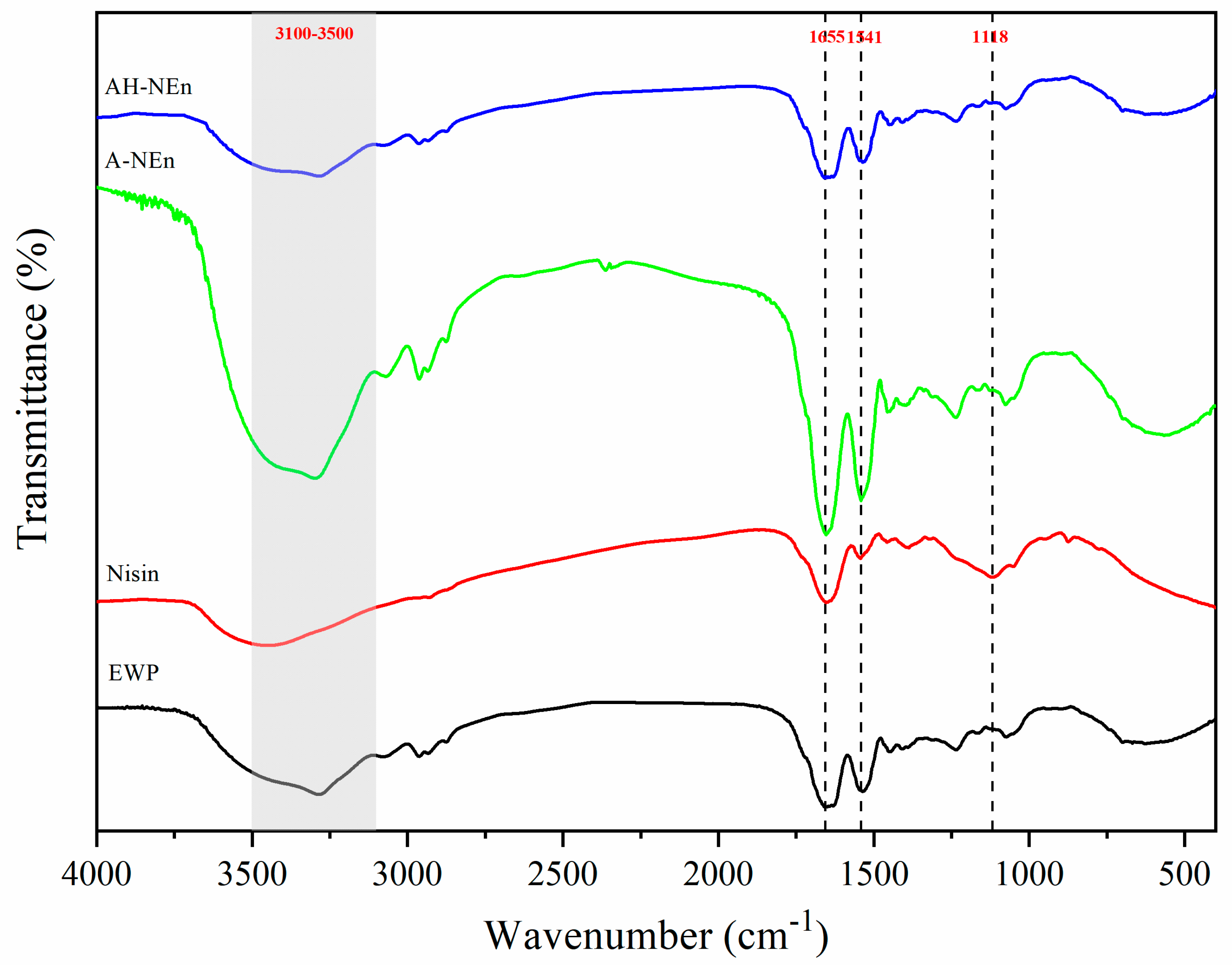
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
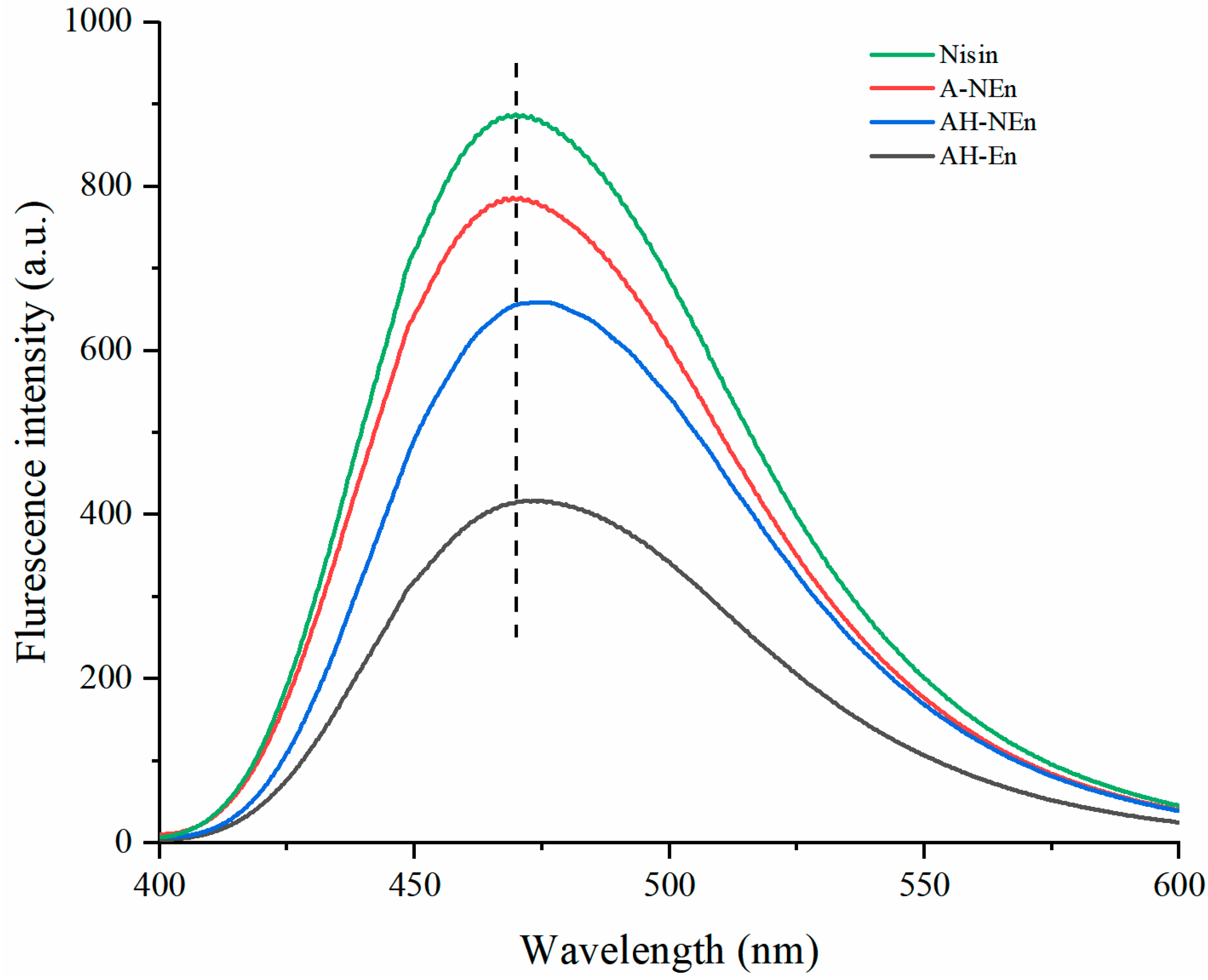
2.7. Determination of Fluorescence Spectra
2.8. Characterization of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.9. Characterization of X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.10. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency and Loading Capacity
2.11. Measurement of Antibacterial Activity
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Z-Average Diameter, PDI, and Zeta Potential
3.2. Analysis of Intermolecular Interaction Force
3.3. Morphological Structure Analysis
3.4. FTIR Analysis of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
3.5. Fluorescence Spectra Analysis of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
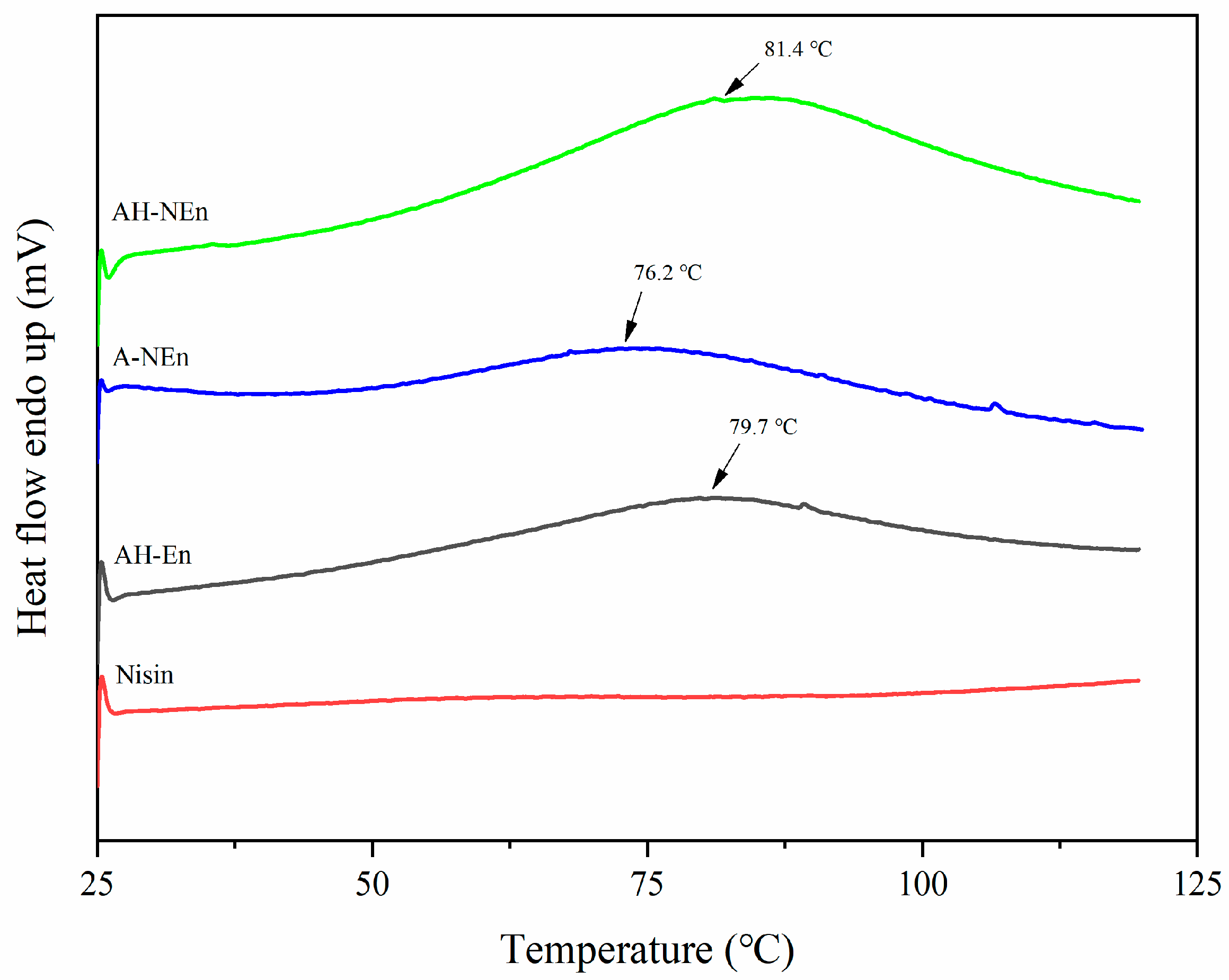
3.6. DSC Analysis of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
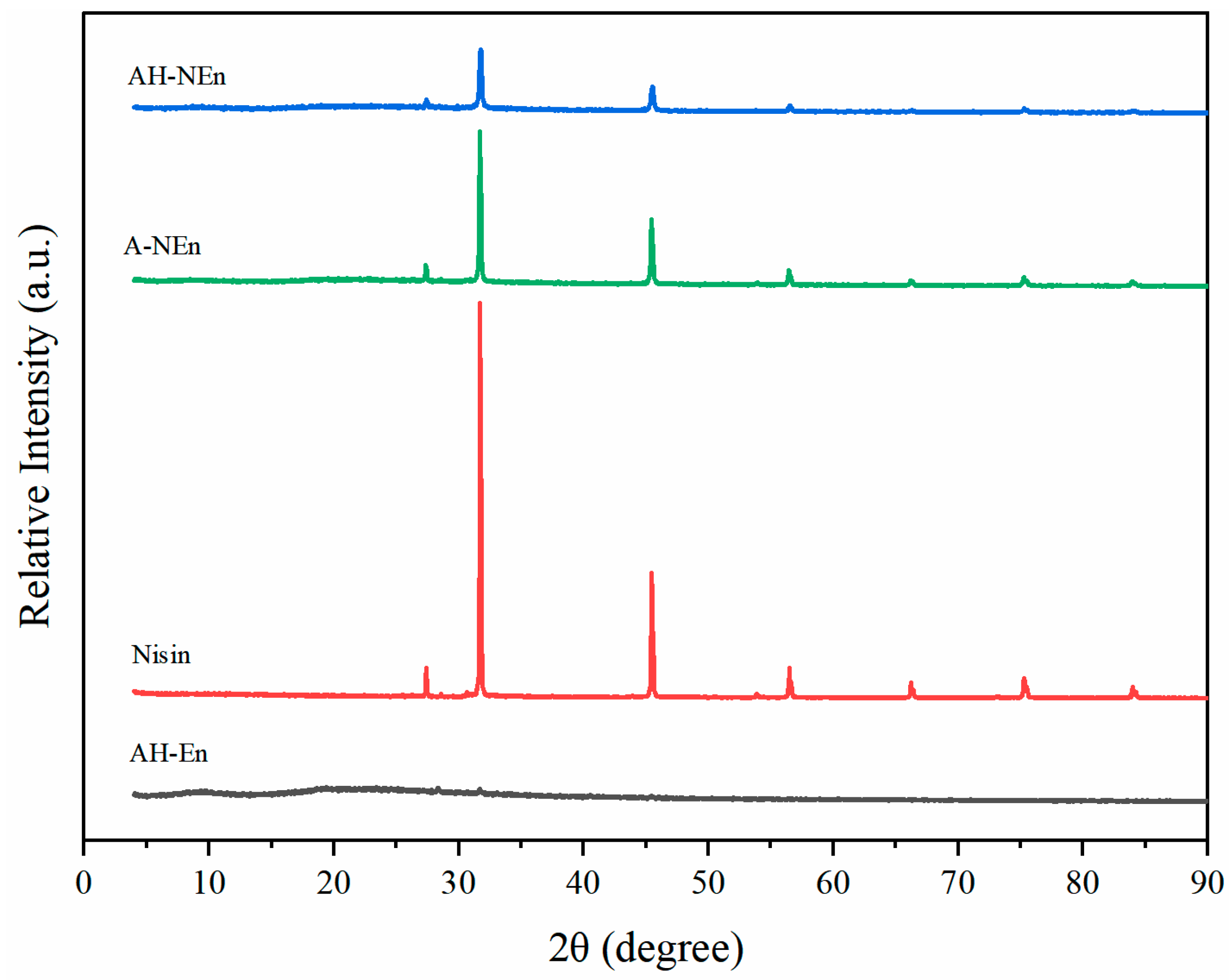
3.7. XRD Analysis of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
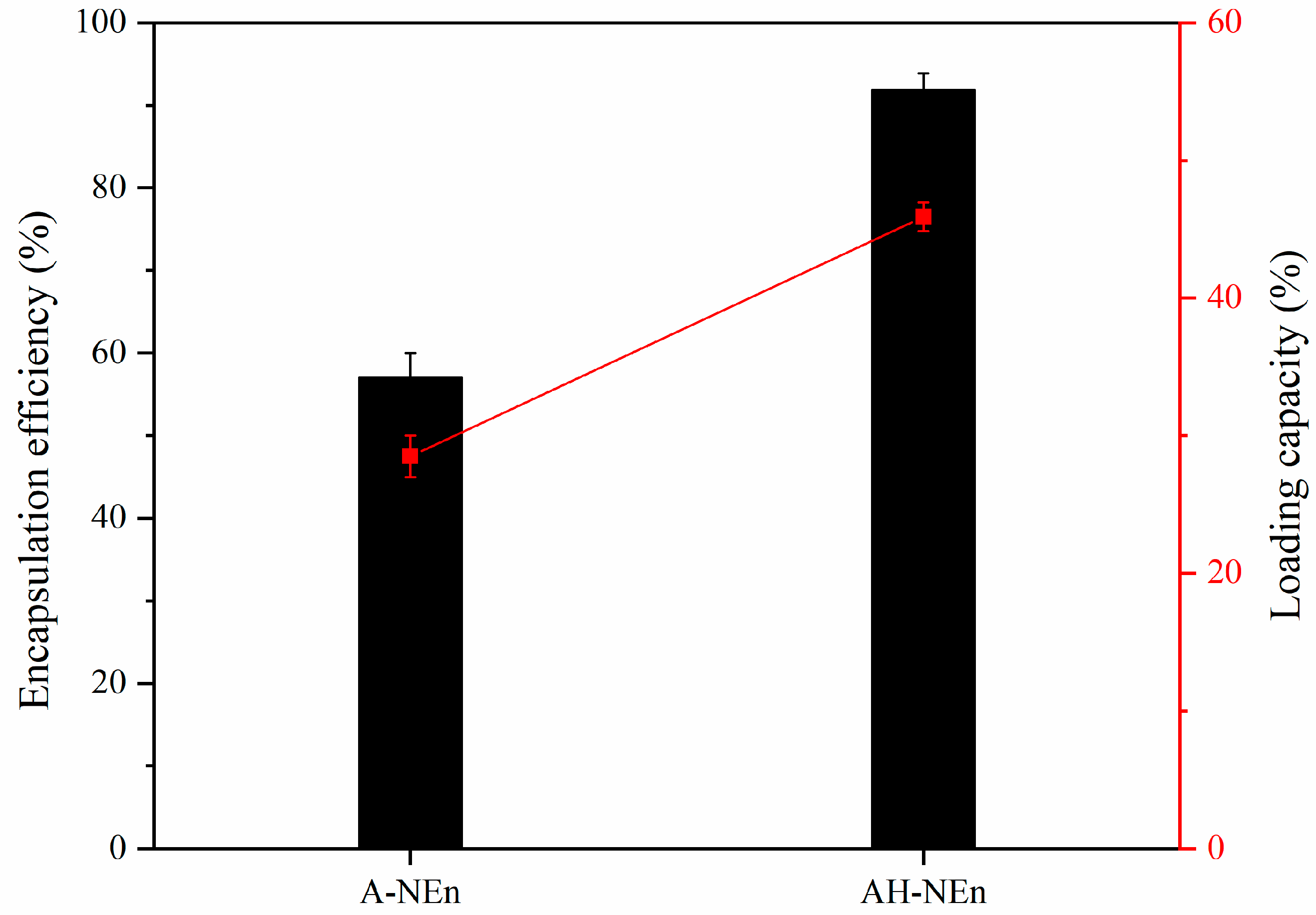
3.8. Encapsulation Capacity of EWP Nanoparticles
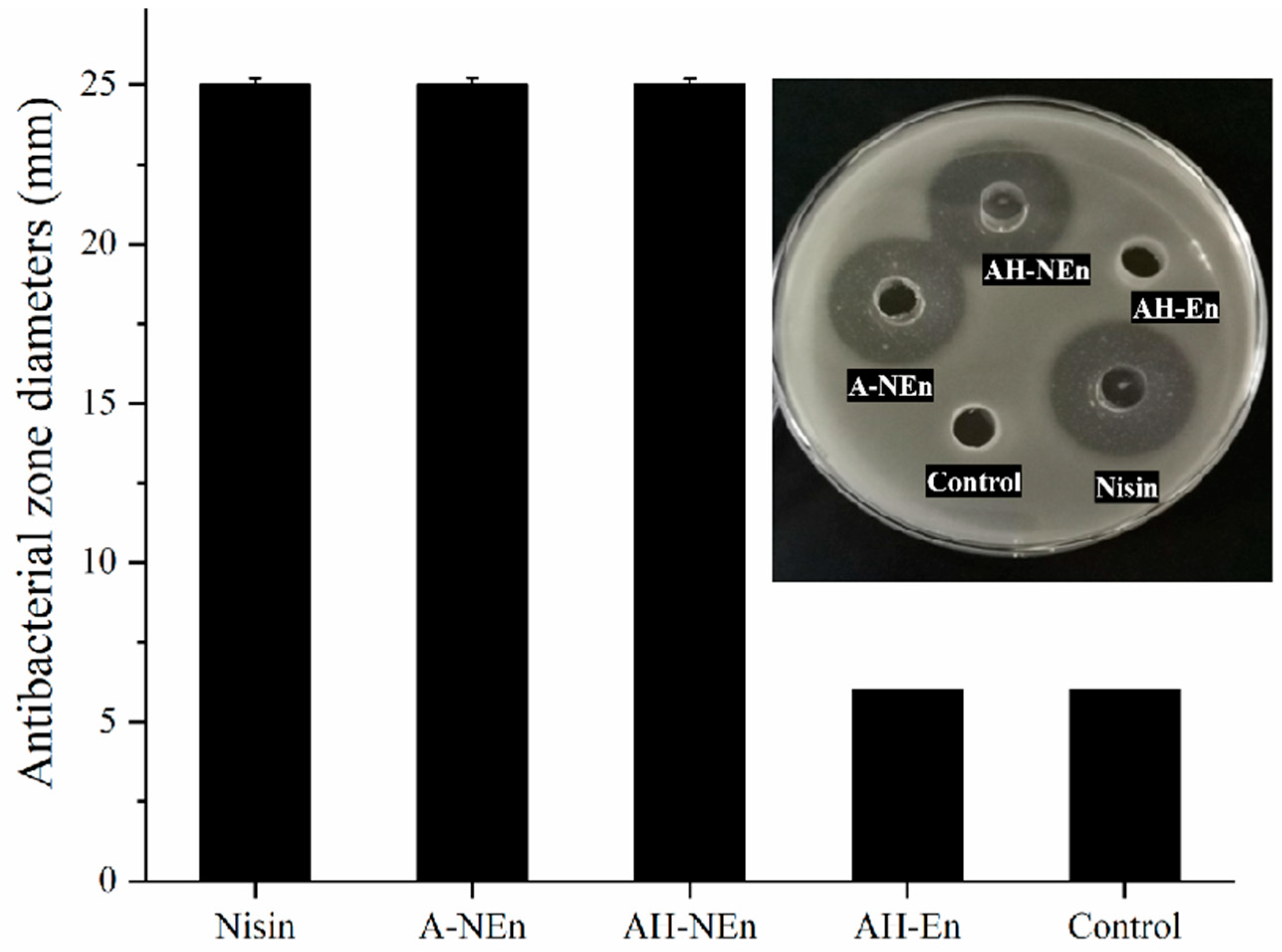
3.9. Antibacterial Properties Analysis of Nisin-Loaded EWP Nanoparticles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Farid, M. A review on recent development in non-conventional food sterilization technologies. J. Food Eng. 2016, 182, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Wang, L.H.; Zeng, X.A.; Han, Z.; Brennan, C.S. Non-thermal technologies and its current and future application in the food industry: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Cai, R.; Yue, T.; Gao, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z. Application of nanostructures as antimicrobials in the control of foodborne pathogen. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Qian, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhou, C. Polymeric Antimicrobial Food Packaging and Its Applications. Polymers 2019, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloui, H.; Khwaldia, K. Natural Antimicrobial Edible Coatings for Microbial Safety and Food Quality Enhancement. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 1080–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Lei, Y.; Wei, M.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Xie, P.; Sun, B. Preservation of stewed beef chunks by using calcium propionate and tea polyphenols. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 176, 114491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, K.; Raorane, C.J.; Ramkumar, V.; Ulagesan, S.; Santhamoorthy, M.; Raj, V.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Phan, T.T.; Kim, S.C. Update on Chitosan-Based Hydrogels: Preparation, Characterization, and Its Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Applications. Gels 2022, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaam, O.E.; Fliss, I.; Aider, M. Effect of electro-activated aqueous solutions, nisin and moderate heat treatment on the inactivation of Clostridium sporogenes PA 3679 spores in green beans puree and whole green beans. Anaerobe 2017, 47, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Gwak, J.W.; Kamarajan, P.; Fenno, J.C.; Rickard, A.H.; Kapila, Y.L. Biomedical applications of nisin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1449–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slootweg, J.C.; Liskamp, R.M.; Rijkers, D.T. Scalable purification of the lantibiotic nisin and isolation of chemical/enzymatic cleavage fragments suitable for semi-synthesis. J. Pept. Sci. 2013, 19, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, G.; Nóbrega, C.M.; Converti, A.; Pinheiro, R. Kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of nisin thermoinactivation. J. Food Eng. 2020, 280, 109986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, N.A.; Barreto, C.M.; Brandelli, A. Antimicrobial activity of lysozyme-nisin co-encapsulated in liposomes coated with polysaccharides. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Remondetto, G.E.; Subirade, M. Food protein-based materials as nutraceutical delivery systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, N.; Mauser, A.; Ko, Y.; Lahann, J. Protein Nanoparticles: Uniting the Power of Proteins with Engineering Design Approaches. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 202104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, Y. Nanoparticulate systems for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Meikle, T.G.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Dekiwadia, C.; Drummond, C.J.; Conn, C.E.; Yang, Y. Encapsulation in egg white protein nanoparticles protects anti-oxidant activity of curcumin. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentini, F.F.; Sponton, O.E.; Perez, A.A.; Santiago, L.G. Formation and colloidal stability of ovalbumin-retinol nanocomplexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzeni, C.; Pilosof, A.M. Bioaccessibility of folic acid in egg white nanocarriers and protein digestion profile in solution and in emulsion. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, D.; Hao, L.; Lin, S.; Kang, Q.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Lu, J. Protective effects of soybean protein and egg white protein on the antibacterial activity of nisin in the presence of trypsin. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V. Effect of heat treatment on milk protein functionality at emulsion interfaces. A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2010, 24, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Niu, F.; Gu, L.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Formation of fibrous or granular egg white protein microparticles and properties of the integrated emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sponton, O.E.; Perez, A.A.; Ramel, J.V.; Santiago, L.G. Protein nanovehicles produced from egg white. Part 1: Effect of pH and heat treatment time on particle size and binding capacity. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 73, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, B.; Ma, L.; Yao, X.; Li, S.; Harlina, P.W.; Wang, J.; Geng, F. Inhibition of water-diluted precipitate formation from egg whites by ultrasonic pretreatment: Insights from quantitative proteomics analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 129973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Han, L.; Chang, C.; Zhang, W. Encapsulation of resveratrol in zein-polyglycerol conjugate stabilized O/W nanoemulsions: Chemical stability, in vitro gastrointestinal digestion, and antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 149, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Queiroz, L.J.; De Araújo, R.O.; Rodrigues, L.L.; De Medeiros, A.F.; Teixeira, A.F.; Santos, T.D.; Passos, T.S.; Maciel, B.L.; Dos Santos, E.A.; De Araújo, A.H. Chitosan-whey protein nanoparticles improve encapsulation efficiency and stability of a trypsin inhibitor isolated from Tamarindus indica L. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, N.; Wu, F.; Yu, D.; Elfalleh, W. Effects of (+)-catechin on a rice bran protein oil-in-water emulsion: Droplet size, zeta-potential, emulsifying properties, and rheological behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Wu, C.; Fang, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y. Effect of chitosan microcapsules loaded with nisin on the preservation of small yellow croaker. Food Control 2017, 79, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.; Okonkwo, C.E.; Zhou, C. Effect of molecular weight of chitosan on the formation and properties of zein-nisin-chitosan nanocomplexes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 292, 119664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivorotova, T.; Cirkovas, A.; Maciulyte, S.; Staneviciene, R.; Budriene, S.; Serviene, E.; Sereikaite, J. Nisin-loaded pectin nanoparticles for food preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ibarra-Sánchez, L.A.; Luu, L.; Miller, M.J.; Lee, Y. Co-assembly of nisin and zein in microfluidics for enhanced antilisterial activity in Queso Fresco. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, T.; Ching, Y.C.; Uyama, H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Chuah, C.H. Investigations on the interactions of proteins with nanocellulose produced via sulphuric acid hydrolysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, M.; Varidi, M.J.; Koocheki, A.; Varidi, M. Effect of heat treatment on the structure and stability of Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) protein isolate/Alyssum homolocarpum seed gum nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Wang, T.; Hu, Q.; Luo, Y. Zein/caseinate/pectin complex nanoparticles: Formation and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.H.; Zheng, J.; Xu, Y.T.; Yin, S.W.; Liu, F.; Tang, C.H. Surface modification improves fabrication of pickering high internal phase emulsions stabilized by cellulose nanocrystals. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 75, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaupt, R.; Heuberger, L.; Siqueira, G.; Gutt, B.; Zimmermann, T.; Maniura-Weber, K.; Salentinig, S.; Faccio, G. Enhanced Antimicrobial Activity and Structural Transitions of a Nanofibrillated Cellulose-Nisin Biocomposite Suspension. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20170–20181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Z. Enhancing the resistance of anthocyanins to environmental stress by constructing ovalbumin-propylene glycol alginate nanocarriers with novel configurations. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Brennan, J.D. Measurement of intrinsic fluorescence to probe the conformational flexibility and thermodynamic stability of a single tryptophan protein entrapped in a sol–gel derived glass matrix. Analyst 1998, 123, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Pei, Y.; Qiao, M.; Ma, F.; Ren, H.; Zhao, Q. Preparation and characterizations of Pickering emulsions stabilized by hydrophobic starch particles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 45, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Nafchi, A.; Tabatabaei, R.H.; Pashania, B.; Rajabi, H.Z.; Karim, A.A. Effects of ascorbic acid and sugars on solubility, thermal, and mechanical properties of egg white protein gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Kou, M.; Fan, J.; Pan, W.; Feng, Z.J.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W. Structural characteristics and rheological properties of ovalbumin-gum arabic complex coacervates. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, C. Effects of chitosan oligosaccharide-nisin conjugates formed by Maillard reaction on the intestinal microbiota of high-fat diet-induced obesity mice model. Food Qual. Saf. 2019, 3, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, J.; Ni, F.; Ren, G.; Xie, H. Complexation of beta-lactoglobulin with gum arabic: Effect of heat treatment and enhanced encapsulation efficiency. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.H.; Lin, Q.L.; Xiao, H.X. Effects of oxidative modification on thermal aggregation and gel properties of soy protein by peroxyl radicals. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 46, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, A.C.; Kim, L.; Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P.; Gharsallaoui, A. Using complexation for the microencapsulation of nisin in biopolymer matrices by spray-drying. Food Chem. 2017, 236, 32–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, F.; Qian, J.; Chen, Y.; Yao, S.; Tong, J.; Guo, H. Preparation and properties of gum arabic cross-link binding nisin microparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 197, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markley, J.L. High-resolution proton magnetic resonance studies of two trypsin inhibitors: Soybean trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz) and ovomucoid (hen egg white). Ann. N. Y. Acad Sci. 1973, 222, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Lu, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Preparation of extra-small nisin nanoparticles for enhanced antibacterial activity after autoclave treatment. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Z-Average Diameter (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nisin | 760.00 ± 4.55 d | 0.86 ± 0.06 d | 7.45 ± 0.98 a |
| AH-En | 231.90 ± 6.01 c | 0.51 ± 0.03 b | 15.60 ± 1.89 b |
| A-NEn | 184.30 ± 5.73 b | 0.73 ± 0.05 c | 18.50 ± 2.01 c |
| AH-NEn | 112.50 ± 2.85 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 a | 24.00 ± 1.18 d |
| Sample | MIC (μg/mL) | MBC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Nisin | 156.25 | 312.50 |
| A-NEn | 156.25 | 312.50 |
| AH-NEn | 156.25 | 312.50 |
| Treatment | Loss Rate of Bactericidal Activity (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nisin | A-NEn | AH-NEn | |
| Tryptic digestion | 87.50 ± 0.89 c | 2.50 ± 1.52 a | 12.50 ± 0.96 b |
| Heat treatment | 31.25 ± 1.12 c | 28.12 ± 1.33 b | 17.50 ± 1.03 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, S.; Jia, C.; Lu, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z. Acid–Heat-Induced Fabrication of Nisin-Loaded Egg White Protein Nanoparticles: Enhanced Structural and Antibacterial Stability. Foods 2024, 13, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111741
Rao S, Jia C, Lu X, Yu Y, Wang Z, Yang Z. Acid–Heat-Induced Fabrication of Nisin-Loaded Egg White Protein Nanoparticles: Enhanced Structural and Antibacterial Stability. Foods. 2024; 13(11):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111741
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Shengqi, Caochen Jia, Xiangning Lu, Yisheng Yu, Zhirong Wang, and Zhenquan Yang. 2024. "Acid–Heat-Induced Fabrication of Nisin-Loaded Egg White Protein Nanoparticles: Enhanced Structural and Antibacterial Stability" Foods 13, no. 11: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111741
APA StyleRao, S., Jia, C., Lu, X., Yu, Y., Wang, Z., & Yang, Z. (2024). Acid–Heat-Induced Fabrication of Nisin-Loaded Egg White Protein Nanoparticles: Enhanced Structural and Antibacterial Stability. Foods, 13(11), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111741






