Daily Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum KACC91563 Alleviates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in an Animal Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Preparation of Bifidobacterium longum
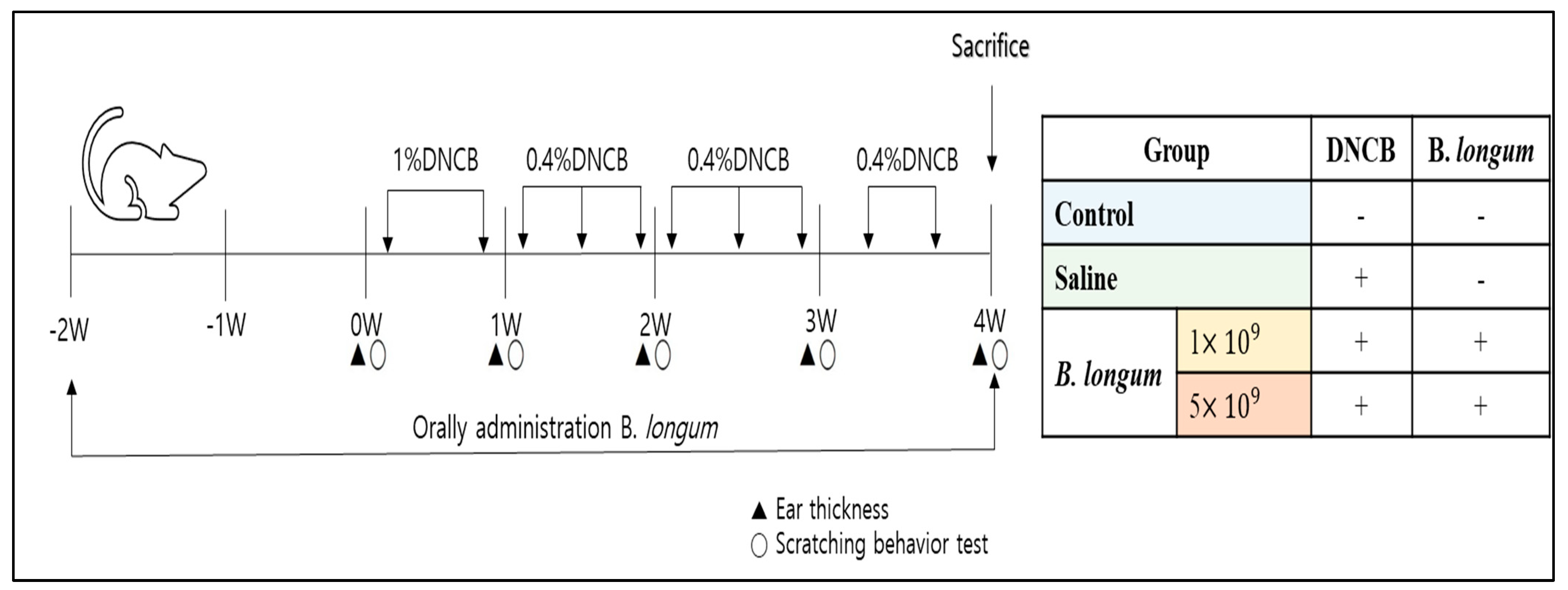
2.4. ACD Model Induction and Treatment with B. longum
2.5. Assays for the ACD
2.5.1. Body Weight and Symptoms Measurement
2.5.2. Histopathological Analysis
2.6. Serum IgE Measurement
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
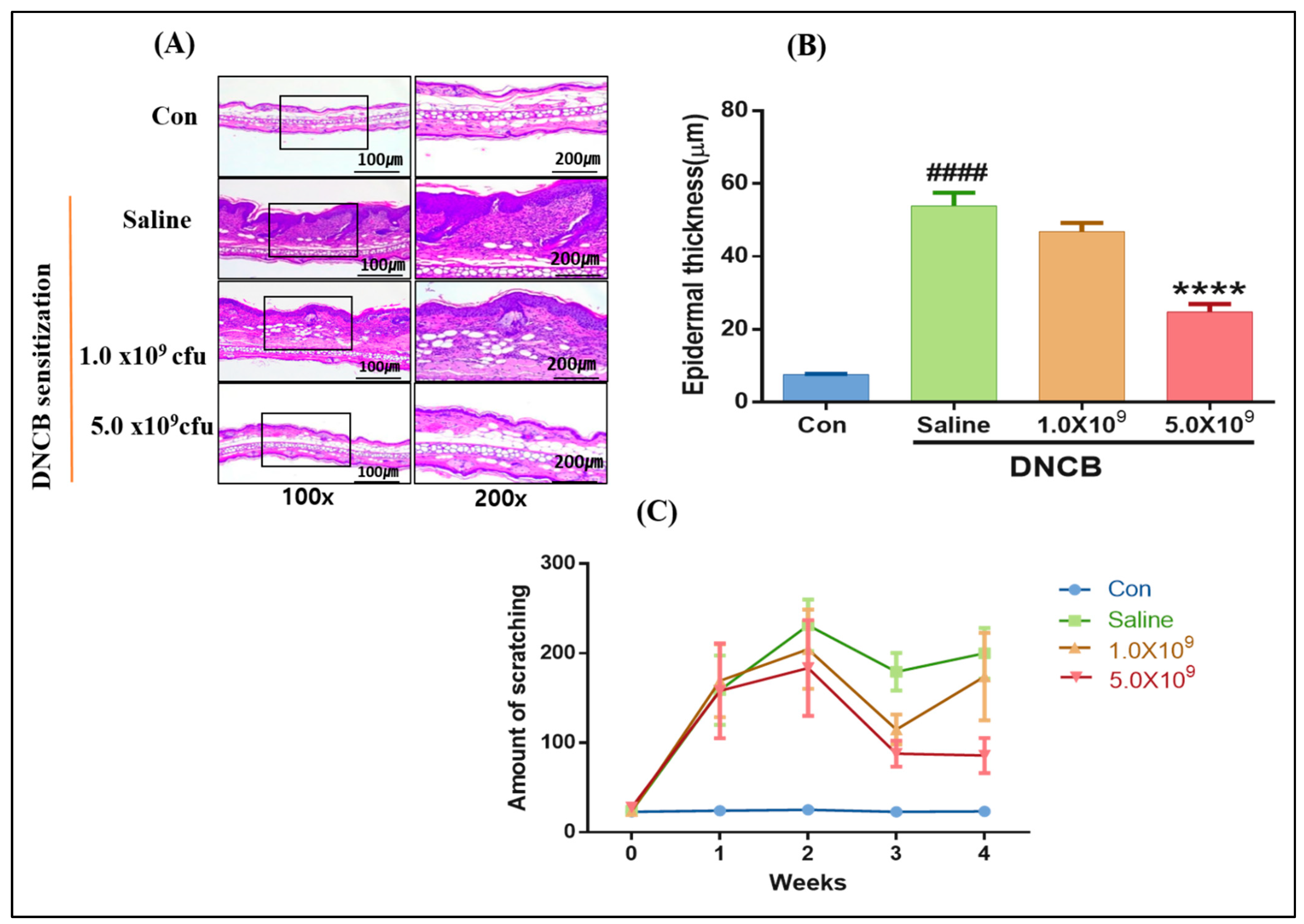
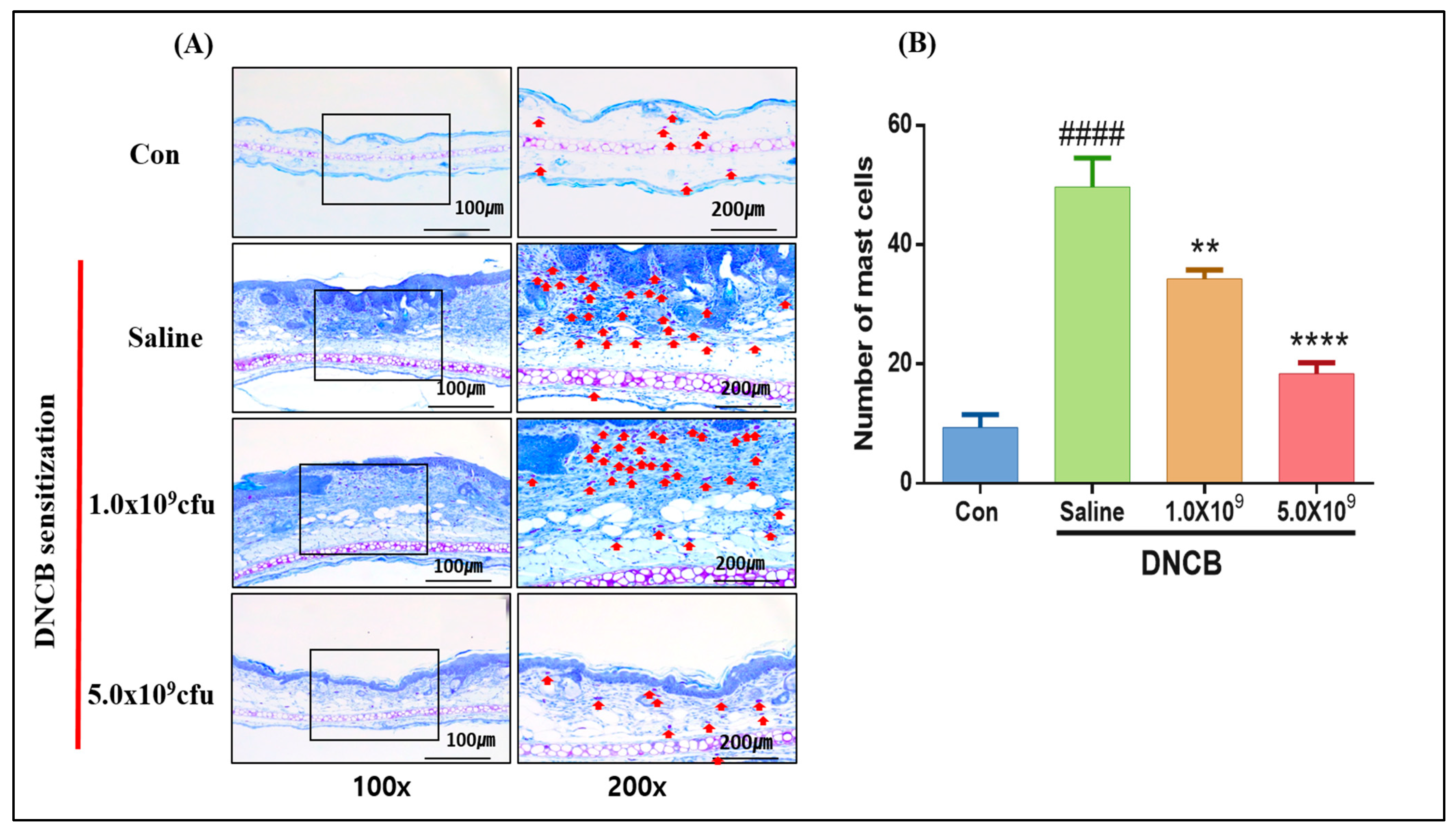
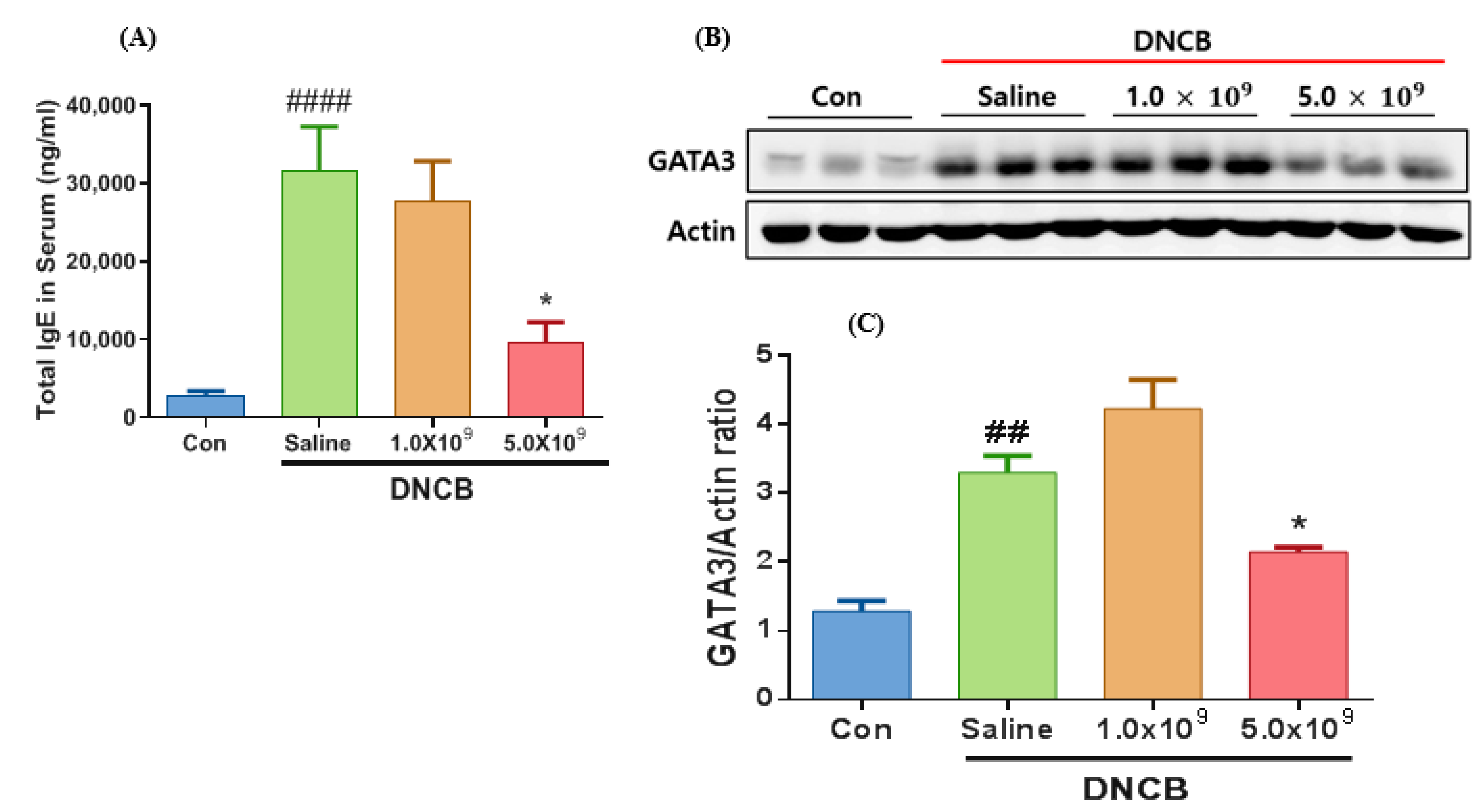
3.1. Daily Supplementation with Probiotic B. longum Attenuates the ACD Symptom, Skin Barrier Damage, and Immune Responses
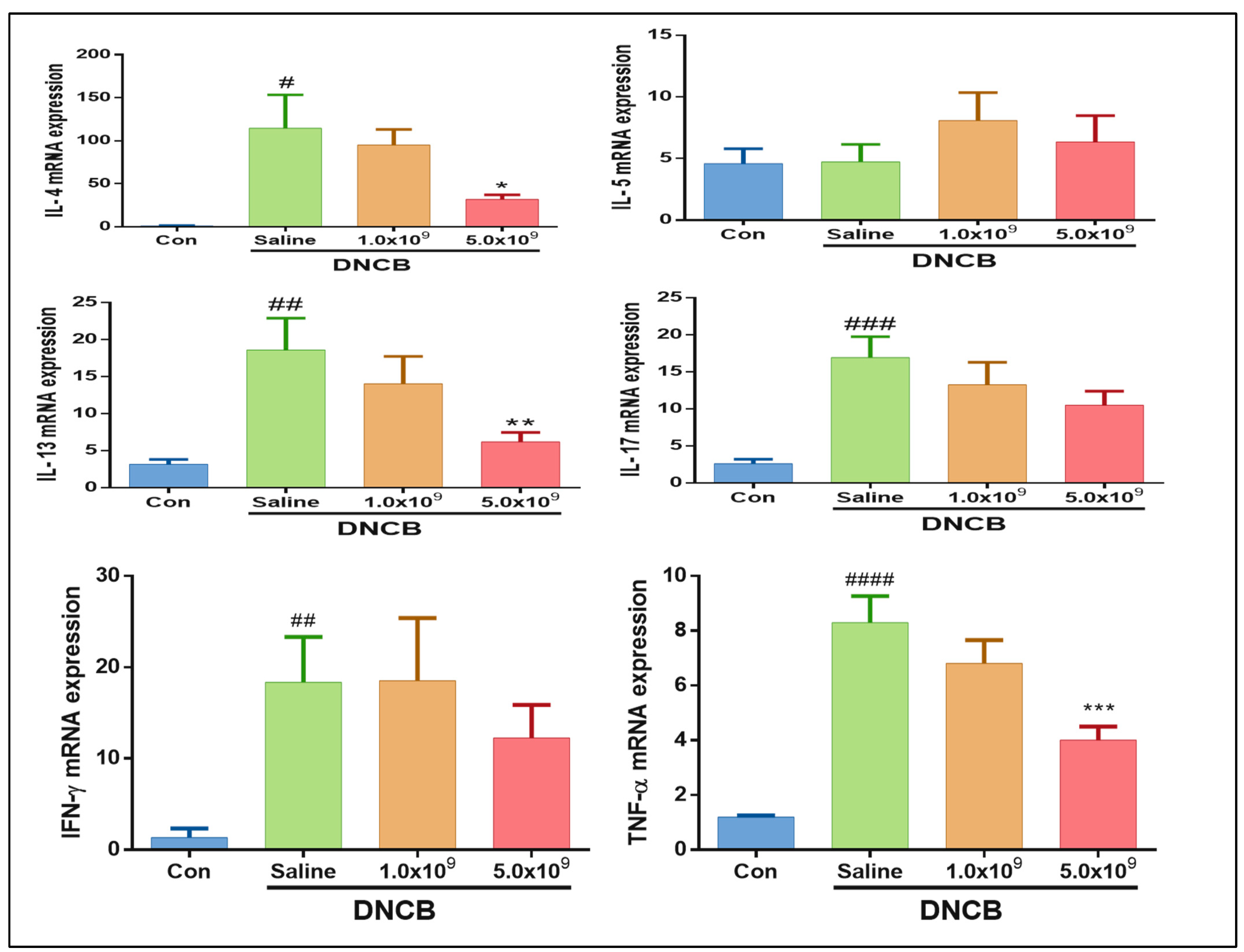
3.2. Daily Supplementation with Probiotic B. longum Suppresses the Inflammatory Cytokine Production
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santeramo, F.G.; Carlucci, D.; De-Devitiis, B.; Seccia, A.; Stasi, A.; Viscecchia, R.; Nardone, G. Emerging trends in European food, diets and food industry. Food Res. Int. 2018, 104, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Deng, F.; Qu, M.; Yang, P.; Yang, B. Association between dietary patterns and chronic diseases among Chinese adults in Baoji. Int. J. Chronic Dis. 2014, 2014, 548269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Allen, N.B.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Black, T.; Brewer, L.C.; Foraker, R.E.; Grandner, M.A.; Lavretsky, H.; Perak, A.M.; Sharma, G.; et al. Life’s Essential 8: Updating and enhancing the American heart association’s construct of cardiovascular health: A presidential advisory from the American heart association. Circulation 2022, 146, e18–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, L.F.M.; Ferrari, G.; Lee, D.H.; Aune, D.; Liao, B.; Huang, W.; Nie, J.; Wang, Y.; Giovannucci, E. Lifestyle risk factors and all-cause and cause specific mortality: Assessing the influence of reverse causation in a prospective cohort of 457,021 US adults. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 37, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, M.B.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Fung, T.T.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Forouhi, N.G. Food based dietary patterns and chronic disease prevention. BMJ 2018, 361, k2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morze, J.; Danielewicz, A.; Hoffmann, G.; Schwingshackl, L. Diet quality as assessed by the healthy eating index, alternate healthy eating index, dietary approaches to stop hypertension score, and health outcomes: A second update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 1998–2031.e1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Song, M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Wang, M.; Fung, T.T.; Clinton, S.K.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.; Tabung, F.K.; et al. Optimal dietary patterns for prevention of chronic diseases. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiecka, A.; Macura, B.; Szczepanik, M. Modulation of allergic contact dermatitis via gut microbiota modified by diet, vitamins, probiotics, prebiotics, and antibiotics. Pharmacol. Rep. 2023, 75, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSweeney, S.M.; White, I.R.; Kimber, I.; McFadden, J.P.; Tziotzios, C. Contact allergy across the human lifespan. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1352–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, G.S.; Ferreira, I.; Sebastiao, A.I.; Silva, A.; Carrascal, M.; Neves, B.M.; Cruz, M.T. Allergic contact dermatitis: From pathophysiology to development of new preventive strategies. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brussow, H. Turning the inside out: The microbiology of atopic dermatitis. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustemeyer, T. Immunological mechanisms in allergic contact dermatitis. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy 2022, 9, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, I.; Nalawade, S.; Eagar, T.N.; Forsthuber, T.G. T cell subsets and their signature cytokines in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 2015, 74, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzępa, A.; Majewska-Szczepanik, M.; Lobo, F.M.; Wen, L.; Szczepanik, M. Broad spectrum antibiotic enrofloxacin modulates contact sensitivity through gut microbiota in a murine model. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pessemier, B.; Grine, L.; Debaere, M.; Maes, A.; Paetzold, B.; Callewaert, C. Gut-skin axis: Current knowledge of the interrelationship between microbial dysbiosis and skin conditions. Microorganisms 2021, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majamaa, H.; Isolauri, E. Probiotics: A novel approach in the management of food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1997, 99, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, I.A.; Bajpai, V.K.; Kumar, S.; Lim, J.; Paek, W.K.; Park, Y.H. Probiotics and atopic dermatitis: An overview. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Lee, S.Y.; Kang, M.J.; Kim, K.; Won, S.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, K.Y.; Kim, B.S.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, Y.; et al. Clostridia in the gut and onset of atopic dermatitis via eosinophilic inflammation. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 117, 91–92.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, S.; Halbert, A.; Richmond, P.; Prescott, S.L. Effects of probiotics on atopic dermatitis: A randomised controlled trial. Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakoeswa, C.R.S.; Herwanto, N.; Prameswari, R.; Astari, L.; Sawitri, S.; Hidayati, A.N.; Indramaya, D.M.; Kusumowidagdo, E.R.; Surono, I.S. Lactobacillus plantarum IS-10506 supplementation reduced SCORAD in children with atopic dermatitis. Benef. Microbes 2017, 8, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapat, L.; Chemin, K.; Dubois, B.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Kaiserlian, D. Lactobacillus casei reduces CD8+ T cell-mediated skin inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasajima, N.; Ogasawara, T.; Takemura, N.; Fujiwara, R.; Watanabe, J.; Sonoyama, K. Role of intestinal Bifidobacterium pseudolongum in dietary fructo-oligosaccharide inhibition of 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene- induced contact hypersensitivity in mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, J.S.; Lee, T.; Byun, M.J.; Lee, K.T.; Kim, M.K.; Han, G.S.; Jeong, S.G.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H. Complete genome sequence of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum KACC 91563. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.A.; Balciunas, E.M.; Converti, A.; Cotter, P.D.; De Souza Oliveira, R.P. Bacteriocin production by Bifidobacterium spp. A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, W.R.; Queiroz, A.G.; Mendes, E.; Casaro, M.B.; Nascimento, C.M.; Coelho, L.S.S.F.; Martins, F.S.; Leite-Silva, V.R.; Ferreira, C.M. Preventive oral supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum 51A alleviates oxazolone-induced allergic contact dermatitis-like skin inflammation in mice. Benef. Microbes 2021, 12, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.Y.; Hoa, V.B.; Park, W.S.; Yoo, J.H.; Kang, H.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, S.M.; Kim, B.M.; Oh, M.H.; Ham, J.S. Quality Characteristics of functional fermented Sausages added with encapsulated probiotic Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563. J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Park, W.S.; Yoo, J.; Han, G.S.; Kim, B.M.; Seong, P.N.; Oh, M.H.; Kim, K.W.; Ham, J.S. Characteristics of Kwark cheese supplemented with Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563. J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2017, 37, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, N.K.; Bae, C.H.; Park, D.C.; Paik, H.D.; Park, E. Immunomodulatory effects by Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563 in mouse splenocytes and macrophages. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera-Santander, V.E.; Hernández-Figueroa, R.H.; Jiménez-Munguía, M.T.; Mani-López, E.; López-Malo, A. Health Benefits of Consuming Foods with Bacterial Probiotics, Postbiotics, and Their Metabolites: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, A.; Chen, A.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, S.J.; Chen, D.; Yu, R. Lactobacillus for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis: Clinical and experimental evidence. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, U. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; SAGE Publications Sage UK: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.; Jang, H.Y.; Lee, S.M. Overexpression of tIK ameliorates DNCB-induced allergic contact dermatitis in BALB/c mice. Am. Assoc. Immnol. 2017, 198, 194.23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Han, S.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, N.R.; Lee, B.R.; Kim, H.; Kwon, M.; Ahn, K.; Noh, Y.; Kim, S.J.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum and Galactooligosaccharide Improve Skin Barrier Dysfunction and Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2022, 14, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuka, E.; Kawai, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nojima, H.; Kitagawa, K.; Shirai, Y.; Kamimura, K.; Kuraishi, Y. Roles of mast cells and histamine in mosquito bite-induced allergic itch-associated responses in mice. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 86, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Kenneth, D.; Livak, J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, Y.M.; Adhikari, B.; Kim, J.A.; Yu, D.Y.; Kim, G.I.; Lim, J.M.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Oral administration of β-glucan and Lactobacillus plantarum alleviates atopic dermatitis-like symptoms. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 1693–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, C.A.; Rorke, E.A.; Adhikary, G.; Xu, W.; Eckert, R.L. Loss of epidermal AP1 transcription factor function reduces filaggrin level, alters chemokine expression and produces an ichthyosis-related phenotype. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umborowati, M.A.; Damayanti, D.; Anggraeni, S. The role of probiotics in the treatment of adult atopic dermatitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2022, 41, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukasawa, T.; Yoshizaki-Ogawa, A.; Enomoto, A.; Miyagawa, K.; Sato, S.; Yoshizaki, A. Pharmacotherapy of itch-antihistamines and histamine receptor as G protein-coupled receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naclerio, R.M. Pathophysiology of perennial allergic rhinitis. Allergy 1997, 52, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K. The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerback, L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dyebinding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1966, 66, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.K.; Lee, C.G.; So, J.S.; Chae, C.S.; Hwang, J.S.; Sahoo, A.; Nam, J.H.; Rhee, J.H.; Hwang, K.-C.; Im, S.-H. Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2159–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jeun, E.J.; Hong, C.P.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, M.S.; Lee, E.-J.; Moon, S.J.; Yun, C.H.; Im, S.-H.; Jeong, S.-G.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-derived protein from Bifidobacterium longum alleviates food allergy through mast cell suppression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, J.S.; Warrington, R.; Watson, W.; Kim, H.L. An introduction to immunology and immunopathology. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2018, 14, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, L.M.; Lavker, R.M.; Matis, W.L.; Murphy, G.F. Degranulation of human mast cells induces an endothelial antigen central to leukocyte adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8972–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ding, F.; Zhai, Y.; Tao, W.; Bic, J.; Fan, H.; Yin, N.; Wang, Z. IL-37 is protective in allergic contact dermatitis through mast cell inhibition. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 83, 106476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.B.; Yang, B.G.; Jang, G.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.; Oh, S.M.; Oh, N.; Lee, S.; Moon, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-A.; et al. Combined IgE neutralization and Bifidobacterium longum supplementation reduces the allergic response in models of food allergy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.H.; Cohn, L.; Ray, P.; Bottomly, K.; Ray, A. Transcription factor GATA-3 is differentially expressed in murine Th1 and Th2 cells and controls Th2-specific expression of the interleukin-5 gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21597–21603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.; Provot, S.; Werb, Z. GATA3 in development and cancer differentiation: Cells GATA have it. J. Cell Physiol. 2010, 222, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamauchi, H.; Amoh, Y.; Itoh, M.; Terashima, M.; Masuzawa, M.; Habu, S.; Katsuoka, K.; Iwabuchi, K. GATA-3 regulates contact hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of allergic dermatitis. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, Z.; Zang, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z. 3,3′-Diindolylmethane alleviates acute atopic dermatitis by regulating T cell differentiation in a mouse model. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 130, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, D.; Ahuja, N.; Kumar, S.; Kalra, R.; Nanduri, R.; Gupta, S.; Khare, A.K.; Bhagyaraj, E.; Arora, R.; Gupta, P. Nuclear receptor Nr1d1 alleviates asthma by abating GATA3 gene expression and Th2 cell differentiation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turmer, M.D. Cytokines and chemokines. At the crossroads of cell signaling and inflammatory diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2563–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitetta, E.S.; Ohara, J.; Myers, C.D.; Layton, J.E.; Krammer, P.H.; Paul, W.E. Serological, biochemical, and functional identity of B cell-stimulatory factor 1 and B cell differentiation factor for IgG1. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 162, 1726–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, K.; Tominaga, A.; Hamaoka, T. Antigen-induced T cell-replacing factor (TRF). I. Functional characterization of a TRF-producing helper T cell subset and genetic studies on TRF production. J. Immunol. 1980, 124, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperman, D.A.; Huang, X.; Koth, L.L.; Chang, G.H.; Dolganov, G.M.; Shu, Z.; Elias, J.A.; Sheppard, D.; Erle, D.J. Direct effects of interleukin-13 on epithelial cells cause airway hyperreactivity and mucus overproduction in asthma. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.S.; Lim, S.K.; Jang, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Park, H.K.; Kim, N.; Yun, M.; Shin, M.-Y.; Jo, H.E.; Oh, Y.J.; et al. Lactobacillus sakei WIKIM30 ameliorates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions by inducing regulatory T cells and altering gut microbiota structure in mice. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Slack, E.; Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D. The mucosal firewalls against commensal intestinal microbes. Semin. Immunopathol. 2009, 31, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, J.G.; Milani, C.; de Giori, G.S.; Sesma, F.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Bacteria as vitamin suppliers to their host: A gut microbiota perspective. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2013, 24, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Accession Number | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actin | NM_007393.5 | 5′-GAAATCGTGCGTGACATCAAAG-3′ | 5′-TGTAGTTTCATGGATGCCACAG-3′ |
| Interleukin 4 (IL-4) | NM_021283.2 | 5′-TCACTGACGGACCAGAGCTA-3′ | 5′- TGTGAGGACGTTTGGCACAT-3′ |
| Interleukin 5 (IL-5) | NM_010558.1 | 5′-CGTGGGGGTACTGTGGGAAAT-3′ | 5′-AATCCAGGAACTGCCTCGTC-3′ |
| Interleukin 13 (IL-13) | NM_008355.3 | 5′-TGCCATCTACAGGACCCAGA-3′ | 5′-CTCATTAGAAGGGGCCGTGG-3′ |
| Interleukin 17 (IL-17) | NM_010552.3 | F 5′-ACTACCTCAACCGTTCCACCT-3′ | 5′-TTCCCTCCGCATTGACACACT-3′ |
| Interferon γ (IFN-γ) | NM_008337.4 | 5′-GATGCATTCATGAGTATTGCCAAGT-3′ | 5′-GTGGACCACTCGGATGAGCTC-3′ |
| Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) | NM_013693.3 | F 5′-GAACTGGCAGAAGAGGCACT-3′ | 5′-AGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAACT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoa, V.-B.; Park, S.-H.; Ha, D.-H.; Son, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Park, W.-S.; Yoo, J.-Y.; Bae, I.-S.; Kim, H.-W.; Kang, H.-B.; et al. Daily Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum KACC91563 Alleviates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in an Animal Model. Foods 2024, 13, 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142190
Hoa V-B, Park S-H, Ha D-H, Son J-H, Lee K-H, Park W-S, Yoo J-Y, Bae I-S, Kim H-W, Kang H-B, et al. Daily Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum KACC91563 Alleviates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in an Animal Model. Foods. 2024; 13(14):2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142190
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoa, Van-Ba, So-Hyun Park, Do-Hyun Ha, Je-Hee Son, Kil-Ho Lee, Won-Seo Park, Ja-Yeon Yoo, In-Seon Bae, Hyoun-Wook Kim, Han-Byul Kang, and et al. 2024. "Daily Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum KACC91563 Alleviates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in an Animal Model" Foods 13, no. 14: 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142190
APA StyleHoa, V.-B., Park, S.-H., Ha, D.-H., Son, J.-H., Lee, K.-H., Park, W.-S., Yoo, J.-Y., Bae, I.-S., Kim, H.-W., Kang, H.-B., Lee, S.-M., & Ham, J.-S. (2024). Daily Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum KACC91563 Alleviates Allergic Contact Dermatitis in an Animal Model. Foods, 13(14), 2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13142190






