Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling and Study Setting
2.2. Bacterial Isolation
2.3. Characterization of Staphylococcus spp.
2.4. Testing the Susceptibility of Staphylococcus spp. Isolates to Antimicrobials
2.5. Whole Genome Sequencing and Prediction of Resistome and Virulome
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
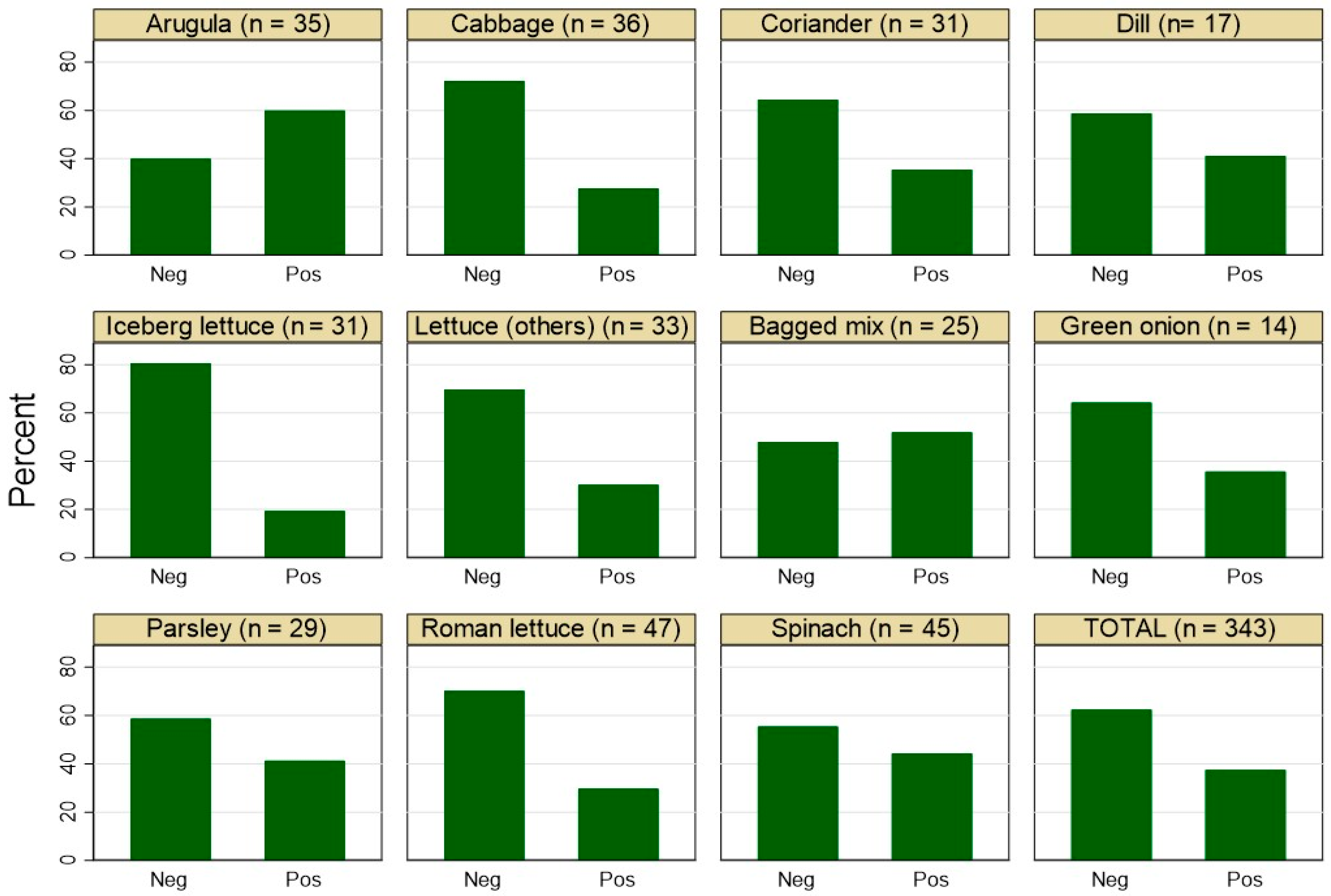
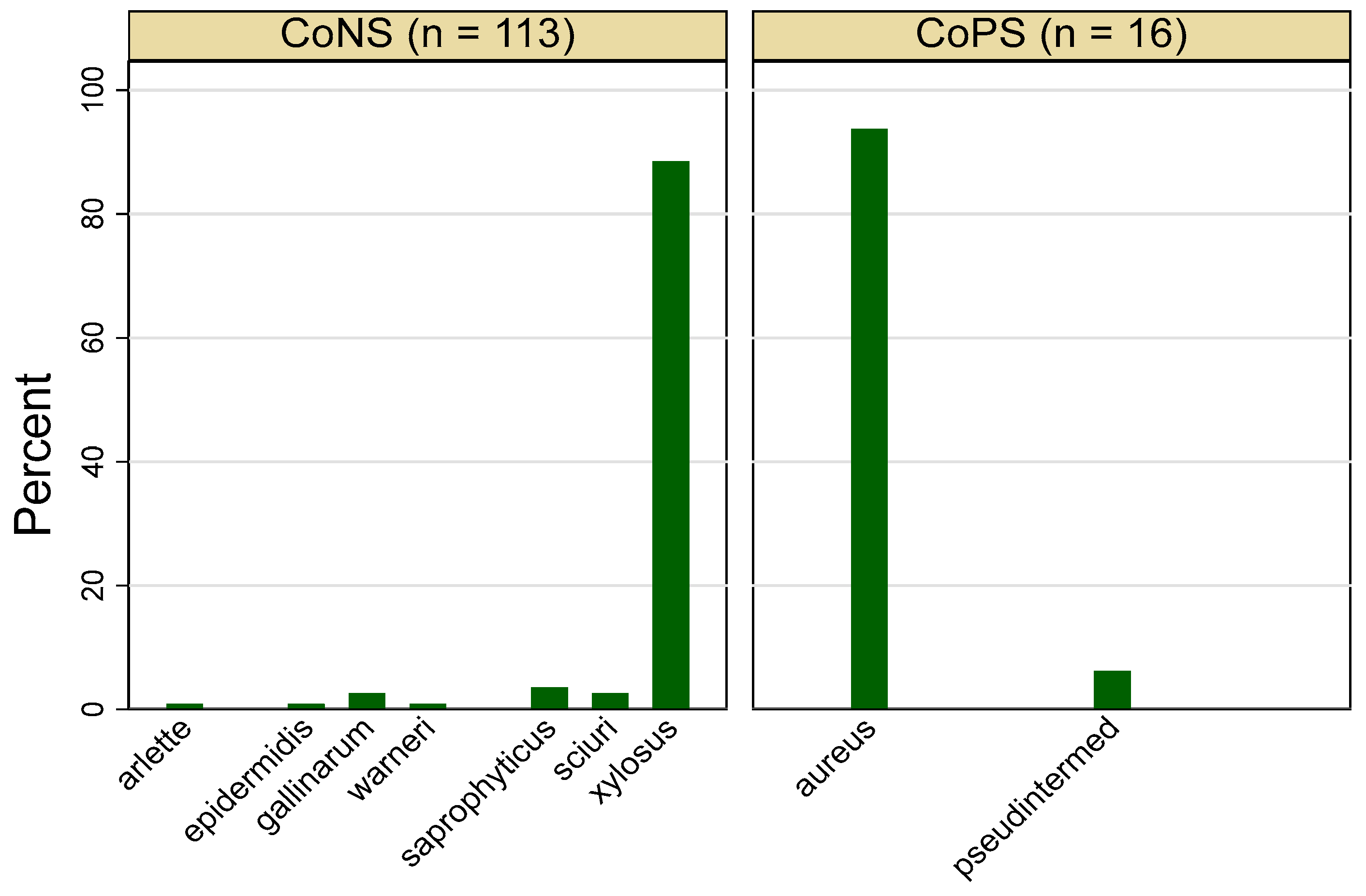
3.1. Frequency of Staphylococcus spp.
3.2. Screening of Antimicrobial Phenotypic Resistance
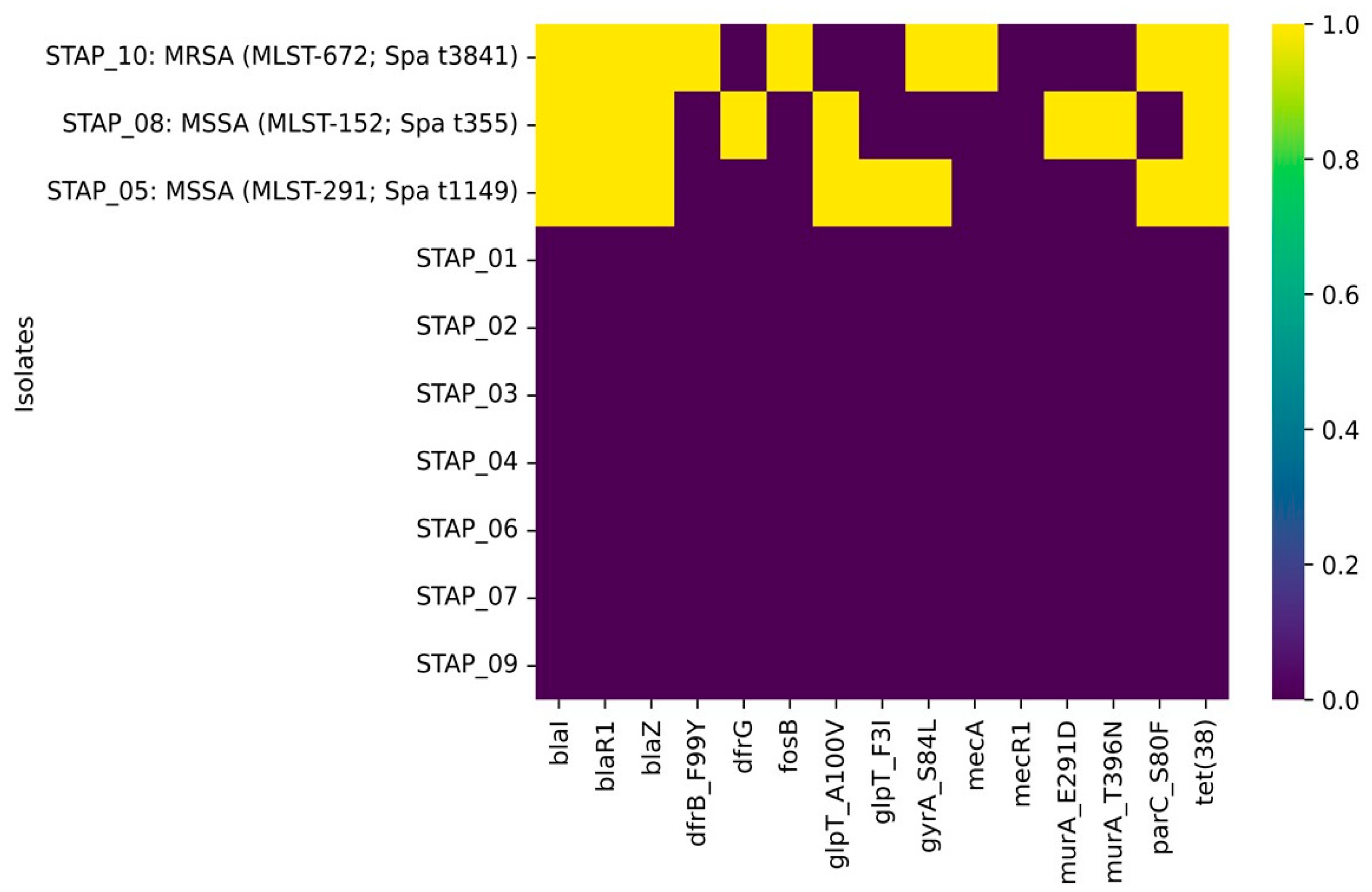
3.3. Genomic Insight on Antimicrobial Resistance Determinants
3.4. Genomic Insight on Toxin-Related Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olaimat, A.N.; Abu Ghoush, M.; Al-Holy, M.; Abu Hilal, H.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Osaili, T.M.; Ayyash, M.; Holley, R.A. Survival and Growth of Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus in Ready-to-Eat Mediterranean Vegetable Salads: Impact of Storage Temperature and Food Matrix. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 346, 109149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhout, C.; Elgroud, R.; Butaye, P. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Other Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococci and Mammaliicoccus (MRNaS) Associated with Animals and Food Products in Arab Countries: A Review. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombari, V.; Mayer, M.D.B.; Laicini, Z.M.; Mamizuka, E.; Franco, B.D.G.M.; Destro, M.T.; Landgraf, M. Foodborne Outbreak Caused by Staphylococcus aureus: Phenotypic and Genotypic Characterization of Strains of Food and Human Sources. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 489–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Gu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; An, L.; Bai, L.; Chen, Y.; Cui, S. Genome-Based Surveillance Reveals Cross-Transmission of MRSA ST59 between Humans and Retail Livestock Products in Hanzhong, China. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1392134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asante, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Somboro, A.M.; Govinden, U.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Review of Clinically and Epidemiologically Relevant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Africa. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 26, 951–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ashker, M.; Gwida, M.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R.; Elsayed, M.; El-Gohary, F.; Reißig, A.; Müller, E.; Paul, A.; Igbinosa, E.O.; et al. Microarray-Based Detection of Resistance Genes in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Cattle and Buffalo with Mastitis in Egypt. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3855–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmann, C.; Ziebuhr, W.; Becker, K. Are Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Virulent? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.I.; Grácio, M.; Silva, M.C.; Pedroso, L.; Lima, A. One Health Perspectives on Food Safety in Minimally Processed Vegetables and Fruits: From Farm to Fork. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Qin, X.; Bu, X.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Dong, Q. Prevalence, Antibiotic Resistance and Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus in Ready-to-Eat Fruits and Vegetables in Shanghai, China. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osaili, T.M.; Hasan, F.; Al-Nabulsi, A.A.; Olaimat, A.N.; Ayyash, M.; Obaid, R.S.; Holley, R. A Worldwide Review of Illness Outbreaks Involving Mixed Salads/Dressings and Factors Influencing Product Safety and Shelf Life. Food Microbiol. 2023, 112, 104238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6888; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuff—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of CoagulasePositive Staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus and Other Species)—Part 1: Technique Using Baird-Parker Agar Medium. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999.
- Xiong, L.; Long, X.; Ni, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Guo, J.; Yang, C. Comparison of Autof Ms1000 and EXS3000 MALDI-TOF MS Platforms for Routine Identification of Microorganisms. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, N.; Magdalena, J.; Rottiers, S.; De Gheldre, Y.; Struelens, M.J. Evaluation of a Triplex PCR Assay To Discriminate Staphylococcus aureus from Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Determine Methicillin Resistance from Blood Cultures. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 33rd ed.; CLSI Supplement M100; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macori, G.; Bellio, A.; Bianchi, D.M.; Chiesa, F.; Gallina, S.; Romano, A.; Zuccon, F.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Cauquil, A.; Merda, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Profiling of Enterotoxigenic Staphylococcus aureus Strains Used for the Production of Naturally Contaminated Cheeses. Genes 2019, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyirifo, D.S.; Mensah, T.A.; Senya, A.S.Y.; Hounkpe, A.; Dornyoh, C.D.; Otwe, E.P. Dynamics of Antimicrobial Resistance and Virulence of Staphylococcal species Isolated from Foods Traded in the Cape Coast Metropolitan and Elmina Municipality of Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wan, T.-W.; Wang, D.-Y.; Lin, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Teng, L.-J. Distribution of Antibiotic Resistance Genes among Staphylococcus species Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Foods. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, M.; Garrett-Sinha, L.A. Staphylococcus xylosus and Staphylococcus aureus as Commensals and Pathogens on Murine Skin. Lab. Anim. Res. 2023, 39, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freu, G.; Gioia, G.; Gross, B.; Biscarini, F.; Virkler, P.; Watters, R.; Addis, M.F.; Franklin-Guild, R.J.; Runyan, J.; Masroure, A.J.; et al. Frequency of Non-aureus Staphylococci and Mammaliicocci species Isolated from Quarter Clinical Mastitis: A 6-Year Retrospective Study. J. Dairy. Sci. 2024, 107, 3813–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Gajewska, J.; Zadernowska, A.; Randazzo, C.L.; Caggia, C. A Comprehensive Study on Antibiotic Resistance among Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Strains Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Food Served in Bars and Restaurants. Foods 2023, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, T.; Samir, M.; El-Mekkawy, R.M.; Ariny, E.; El-Sayed, S.R.; Enan, G.; Abdelatif, S.H.; Askora, A.; Merwad, A.M.A.; Tartor, Y.H. Methicillin- and Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Humans and Ready-to-Eat Meat: Characterization of Antimicrobial Resistance and Biofilm Formation Ability. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 735494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.; Liang, Z.; Wu, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, Q.; Gu, B. Global Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus in Food Products and Its Relationship with the Occurrence and Development of Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Adv. 2023, 1, 53–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindqvist, R.; Sylvén, S.; Vågsholm, I. Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment Exemplified by Staphylococcus aureus in Unripened Cheese Made from Raw Milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 78, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senok, A.C.; Somily, A.; Raji, M.; Garaween, G.; Kabil, M.; Shibl, A.; Monecke, S.; Ehricht, R. Genotyping of Staphylococcus aureus Associated with Nasal Colonization among Healthcare Workers Using DNA Microarray. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2018, 12, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, K.A.; Kooda, K.; Shirley, J.D.; Schuetz, A.N.; Abu Saleh, O.; Stevens, R.W. Failure of MecA/MecC PCR Testing to Accurately Predict Oxacillin Resistance in a Patient with Staphylococcus aureus Infective Endocarditis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e00437-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshaghi, A.; Bommersbach, C.; Zittermann, S.; Burnham, C.-A.D.; Patel, R.; Schuetz, A.N.; Patel, S.N.; Kus, J.V. Phenotypic and Genomic Profiling of Staphylococcus argenteus in Canada and the United States and Recommendations for Clinical Result Reporting. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergelidis, D.; Abrahim, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Soultos, N.; Martziou, E.; Koulourida, V.; Govaris, A.; Pexara, A.; Zdragas, A.; Papa, A. Isolation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus spp. from Ready-to-Eat Fish Products. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.; Rubin, J.E. Identification of Antimicrobial Resistant Bacteria from Plant-Based Food Products Imported into Canada. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 319, 108509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.U.; Kamal, M.; Swelum, A.A.; Khan, S.; los Ríos-Escalante, P.R.D.; Usman, T. Alarming Multidrug Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus Isolated from Raw Milk of Cows with Subclinical Mastitis: Antibiotic Resistance Patterns and Occurrence of Selected Resistance Genes. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, T.; Murakami, M.; Sonoda, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Hayashi, T. Occurrence and Quantitative Microbial Risk Assessment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a Sub-Catchment of the Yodo River Basin, Japan. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, C.; Layer-Nicolaou, F.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. A Look at Staphylococci from the One Health Perspective. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2024, 314, 151604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, P.S.; Gilmore, M.S. The Enterococcus Faecalis Cytolysin: A Novel Toxin Active against Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells. Cell Microbiol. 2003, 5, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Loubet, P.; Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Molle, V. Staphylococcus aureus Toxins: An Update on Their Pathogenic Properties and Potential Treatments. Toxins 2021, 13, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, F.; Sudagidan, M.; Aydin, A.; Akyazi, I.; Bayrakal, G.M.; Yavuz, O.; Gurel, A. In Vivo Pathogenicity of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus Strains Carrying Panton–Valentine Leukocidin Gene. Life 2022, 12, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Burgold-Voigt, S.; Braun, S.D.; Diezel, C.; Liebler-Tenorio, E.M.; Müller, E.; Nassar, R.; Reinicke, M.; Reissig, A.; Senok, A.; et al. Characterisation of PVL-Positive Staphylococcus argenteus from the United Arab Emirates. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antimicrobials | Staphylococcus xylosus (n = 45) | Staphylococcus aureus (n = 10) | Other Staphylococci (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistant No. (%) | Resistant No. (%) | Resistant No. (Species) | |
| Benzylpenicillin | 1 (2.2) | 1 (10.0) | 2 (S. warneri, S. saprophyticus) |
| Oxacillin | 3 (6.6) | 1 (10.0) | 2 (S. warneri, S. gallinarum) |
| Gentamicin | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | — |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0 (0.0) | 2 (20.0) | — |
| Moxifloxacin | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | — |
| Erythromycin | 2 (4.4) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (S. arlette, S. warneri, S. saprophyticus, S. gallinarum) |
| Clindamycin | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (S. warneri, S. saprophyticus) |
| Linezolid | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | — |
| Teicoplanin | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Vancomycin | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Tetracycline | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Tigecycline | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Rifampicin | 1 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 0 (0.0) | 4 (40.0) | 1 (S. warneri) |
| Positive No. (%) | Positive No. (%) | Positive No. (%) | |
| Cefoxitin Screen test | 6 (13.3) | 1 (10.0) | 2 (S. warneri, S. gallinarum) |
| Inducible Clindamycin resistance | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (S. saprophyticus) |
| No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | |
| Multidrug-resistant | 1 (2.2) | 1 (10.0) | 2 (S. warneri, S. gallinarum) |
| Isolate | Species | Sample | Origin | Resistance Phenotypic Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAP_01 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Spinach | UAE | Cefoxitin screen test + ve |
| STAP_02 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Arugula | UAE | Cefoxitin screen test + ve Benzylpenicillin Oxacillin Erythromycin |
| STAP_03 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Bagged mix | UAE | Cefoxitin screen test + ve Oxacillin |
| STAP_04 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Iceberg lettuce | Spain | Cefoxitin screen test + ve |
| STAP_05 | Staphylococcus aureus | Parsley | UAE | Cefoxitin screen test − ve Ciprofloxacin |
| STAP_06 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Roman lettuce | Jordan | Cefoxitin screen test + ve Oxacillin Erythromycin Clindamycin Teicoplanin Vancomycin Rifampicin |
| STAP_07 | Staphylococcus xylosus | Cabbage | UAE | Cefoxitin screen test − ve |
| STAP_08 | Staphylococcus aureus | Arugula | Egypt | Cefoxitin screen test − ve Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole |
| STAP_09 | Staphylococcus warneri | Spinach | Egypt | Cefoxitin screen test + ve Benzylpenicillin Oxacillin Erythromycin Clindamycin Teicoplanin Vancomycin Tetracycline Tigecycline Rifampicin Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole |
| STAP_10 | Staphylococcus aureus | Dill | Egypt | Cefoxitin screen test + ve Benzylpenicillin Oxacillin Ciprofloxacin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, I.; Lakshmi, G.B.; Mohamed, M.-Y.I.; Ghazawi, A.; Khan, M.; Al-Rifai, R.H.; Abdalla, A.; Anes, F.; Elbediwi, M.; Khalifa, H.O.; et al. Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply. Foods 2024, 13, 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152439
Habib I, Lakshmi GB, Mohamed M-YI, Ghazawi A, Khan M, Al-Rifai RH, Abdalla A, Anes F, Elbediwi M, Khalifa HO, et al. Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply. Foods. 2024; 13(15):2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152439
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Ihab, Glindya Bhagya Lakshmi, Mohamed-Yousif Ibrahim Mohamed, Akela Ghazawi, Mushtaq Khan, Rami H. Al-Rifai, Afra Abdalla, Febin Anes, Mohammed Elbediwi, Hazim O. Khalifa, and et al. 2024. "Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply" Foods 13, no. 15: 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152439
APA StyleHabib, I., Lakshmi, G. B., Mohamed, M.-Y. I., Ghazawi, A., Khan, M., Al-Rifai, R. H., Abdalla, A., Anes, F., Elbediwi, M., Khalifa, H. O., & Senok, A. (2024). Staphylococcus spp. in Salad Vegetables: Biodiversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and First Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Strains in the United Arab Emirates Food Supply. Foods, 13(15), 2439. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152439








