Synergistic and Antagonistic Activity of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Cardiac H9c2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
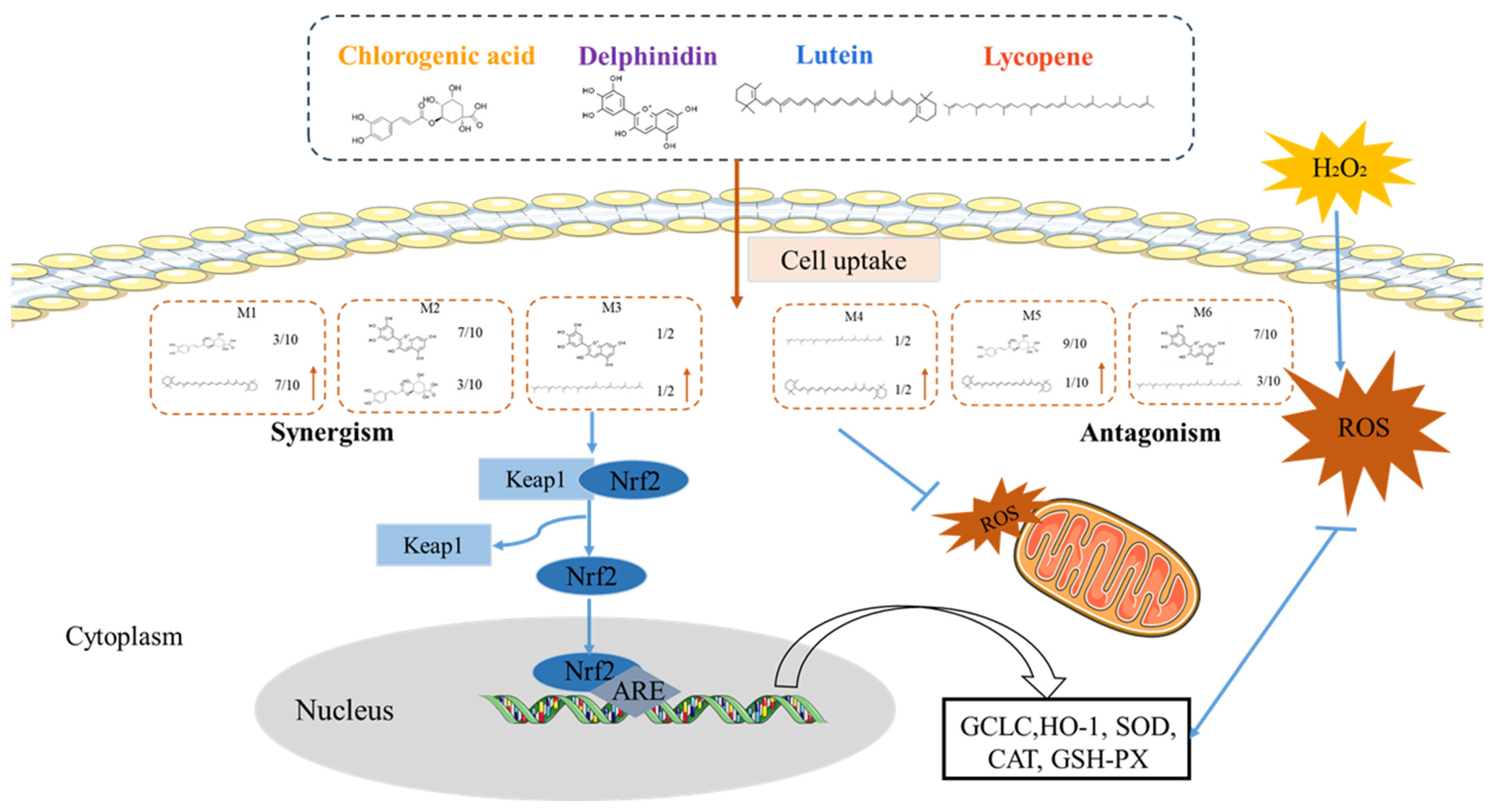
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Phytochemical Stock Preparation
2.2.2. General Cell Culture Condition
2.2.3. Cell Viability
2.2.4. Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA) Assay
2.2.5. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production
2.2.6. The Activity of SOD, CAT, and GSH-Px Enzymes
2.2.7. Western Blot Analysis for Nrf2, HO-1, and GCLC Expression
2.2.8. Immunofluorescence Staining for the Localization of Nrf2 in Cells
2.2.9. The Effects of the Inhibitor ATRA on Nrf2, HO-1, and GCLC Expression
2.2.10. JC-1 Staining for Membrane Potential Differences in the Mitochondrial Function of H9C2 Cells
2.2.11. Degradation and Absorption of Lycopene and Lutein in H9c2 Cells
2.2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability
3.2. Cellular Antioxidant Activity (CAA)
3.3. Interaction Effects of Phytochemical Combinations on the Inhibition of Intracellular ROS Generation
3.4. Interaction Effects of Phytochemical Combinations on SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT Enzyme Activities
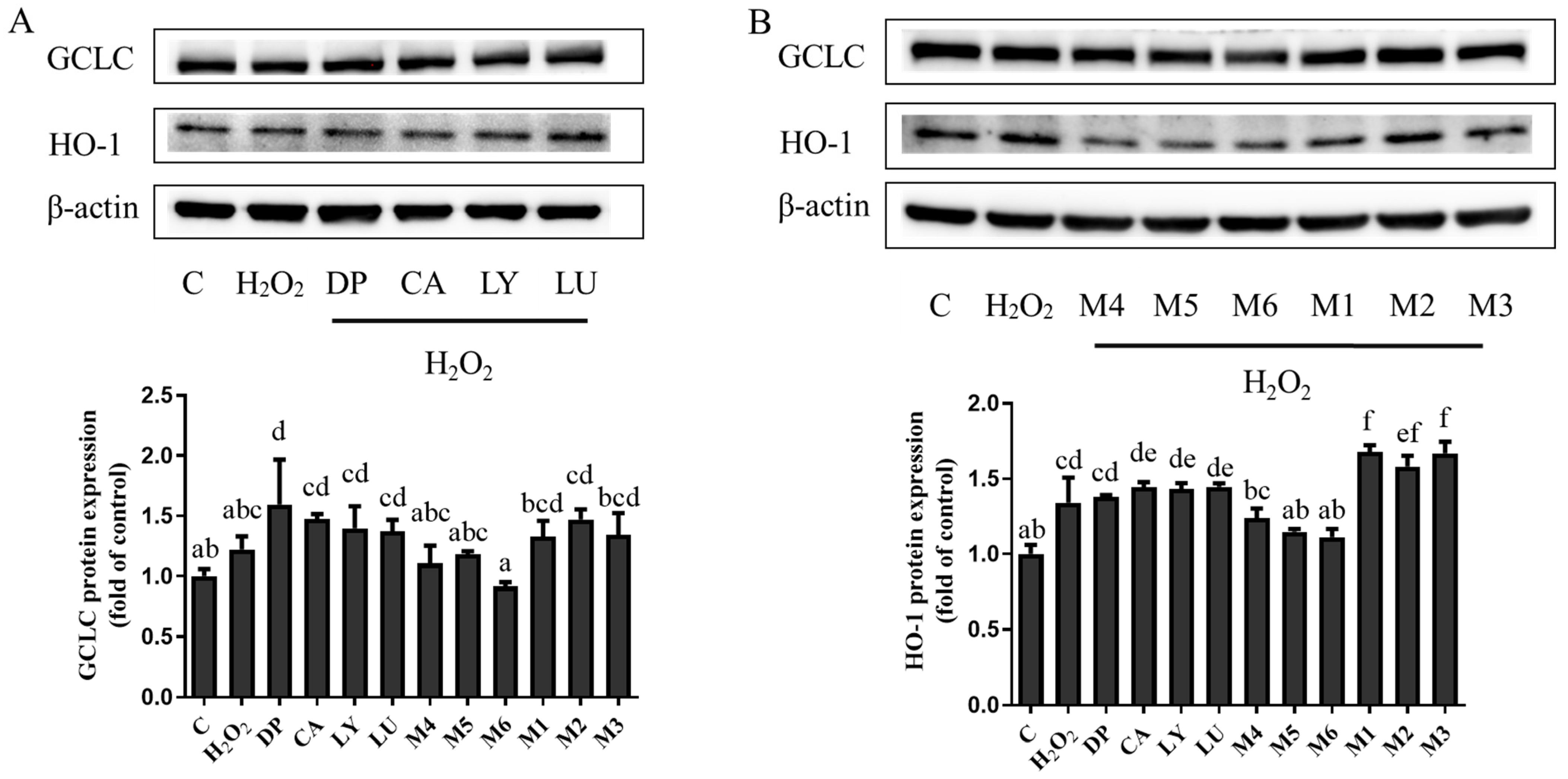
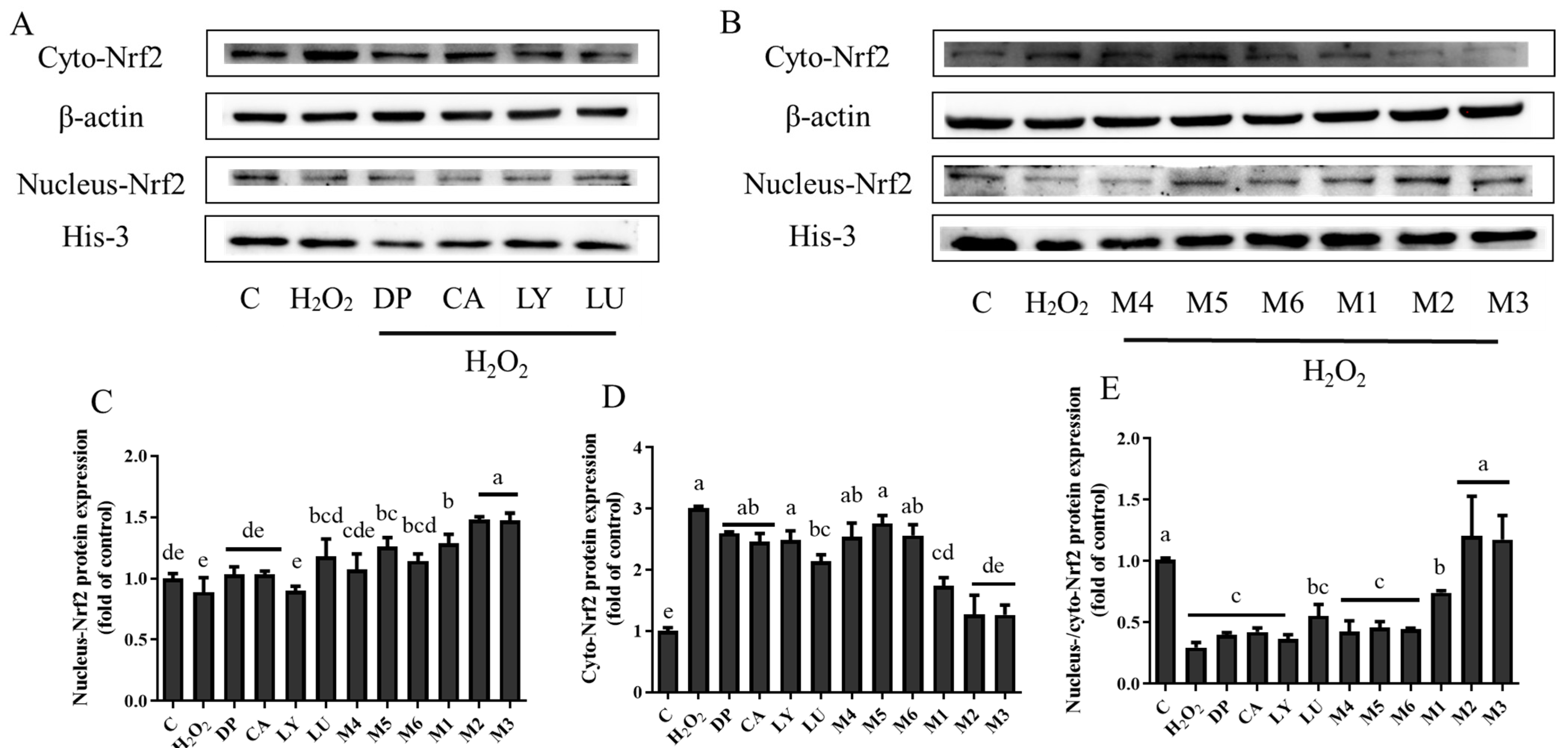
3.5. Interaction Effects of Phytochemical Combinations on the Expression of Nrf2 and Its Downstream Antioxidant Proteins
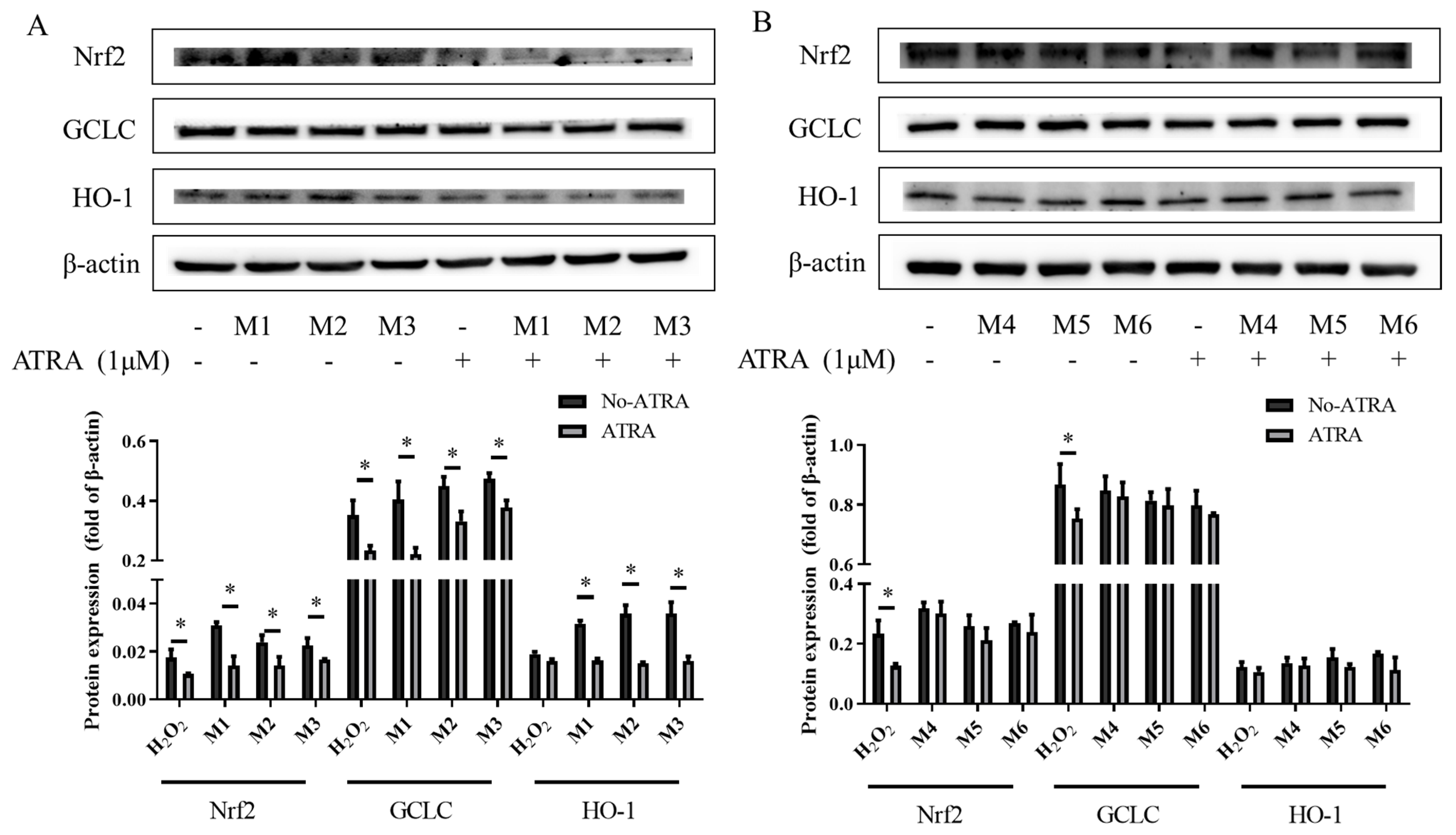
3.6. The Effects of the Inhibitor ATRA on Nrf2, HO-1, and GCLC Protein Expression
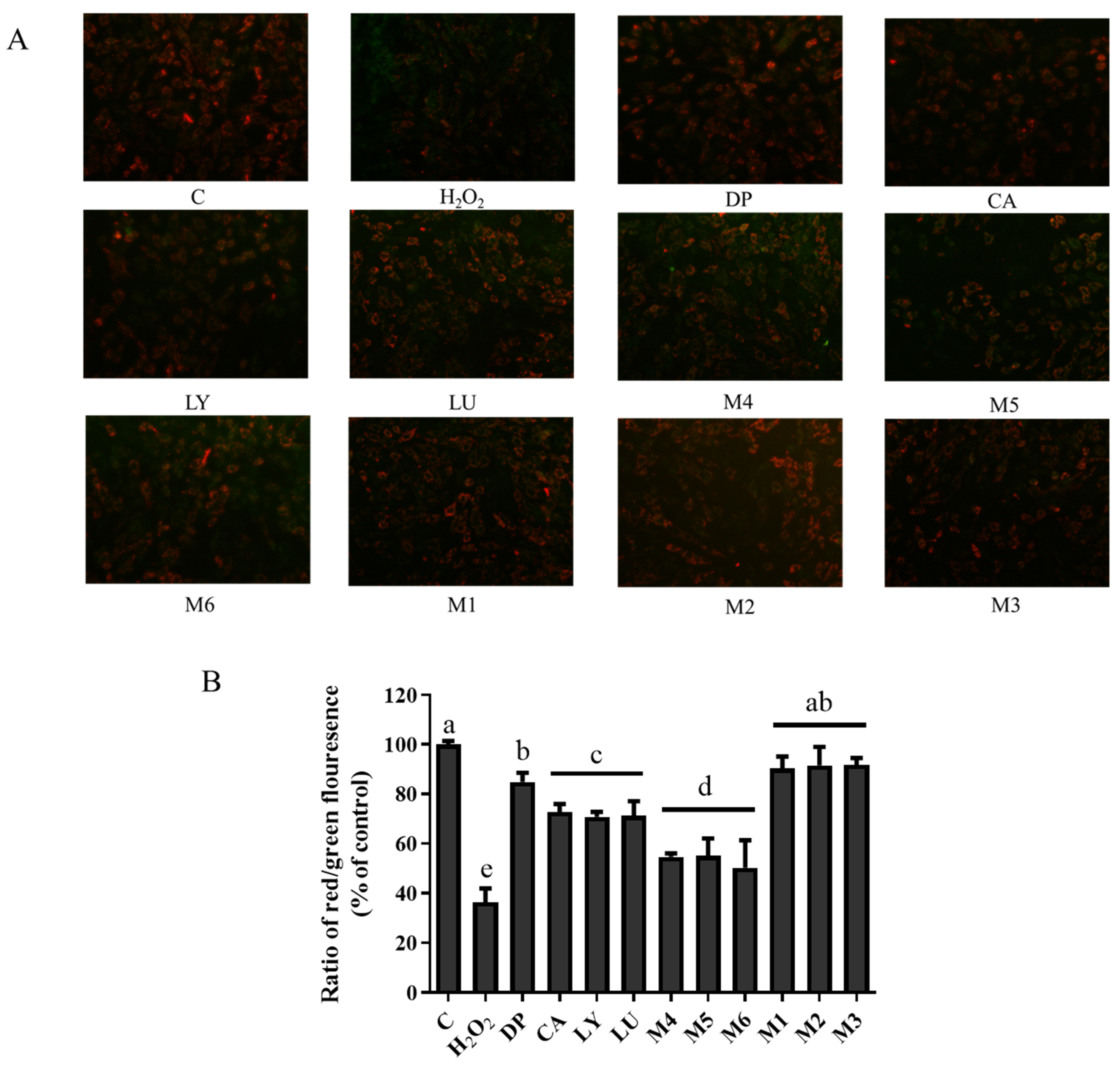
3.7. Interaction Effects of Phytochemical Combinations on Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
3.8. The Effects of Phytochemical Combinations on Cell Absorption of Lycopene and Lutein
4. Discussion
4.1. Lycopene, Lutein, Chlorogenic Acid, and Delphinidin Showed Antioxidant Activities at Low Concentrations but Pro-Oxidant Activities at High Concentrations
4.2. Antioxidant Interactions Were Influenced by the Effects of Combined Phytochemicals at Different Ratios on H9c2 Cells Damaged by Oxidation Stress
4.3. The Expression of Antioxidant Enzymes May Not Be Consistent with the Changes in Antioxidant Activities Caused by the Interactions of Phytochemical Combinations
4.4. TheAntioxidant Interaction of Synergistic Groups (M1, M2, and M3 Groups) Were Mediated by the Activation of the Nrf2 Pathway in H9C2 Cells
4.5. Mitochondria Are a Primary Target of Antioxidant Interactions of Phytochemical Mixtures
4.6. The Stability of Carotenoids in the Medium Doe Not Directly Affect Cell Absorption, and the Absorption of Phytochemicals Is Closely Related to Antioxidant Interactions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmad, S.; Kumar, R. An update of new/potential cardiovascular markers: A narrative review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beg, M.A.; Huang, M.; Vick, L.; Rao, K.N.S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y. Targeting mitochondrial dynamics and redox regulation in cardiovascular diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; Giusti, M.M. Anthocyanins: Natural Colorants with Health-Promoting Properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 163–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Gull, N.; Hussain, L.; Bazmi, R.R.; Jamshed, A.; Siddique, R.; Riaz, M.; Rahman, H.M.A. The Emerging Trend of Phytochemicals and Nutraceuticals-Based Traditional Medicines and Their Role in Chronic Disease Management. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2024, 38, 31–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ouahabi, S.; Loukili, E.H.; Daoudi, N.E.; Chebaibi, M.; Ramdani, M.; Rahhou, I.; Bnouham, M.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Hammouti, B.; Rhazi, L.; et al. Study of the Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant Properties, and In Vitro Anti-Diabetic Efficacy of Gracilaria bursa-pastoris Extracts. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goran, B.; Dimitrinka, N.; Lise, L.G. Mortality in Randomized Trials of Antioxidant Supplements for Primary and Secondary Prevention Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2007, 297, 842–857. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, M.A.T.; Bucknall, M.P.; Arcot, J. Interferences of anthocyanins with the uptake of lycopene in Caco-2 cells, and their interactive effects on anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation in vitro and ex vivo. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasa, M.; Angelino, D.; Gennari, L.; Ninfali, P. The cellular antioxidant activity in red blood cells (CAA-RBC): A new approach to bioavailability and synergy of phytochemicals and botanical extracts. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Deng, Z.Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y.W. Synergistic antioxidant effects of phenolic acids and carotenes on H2O2-induced H9c2 cells: Role of cell membrane transporters. Food Chem. 2020, 341, 128000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y.W. Antioxidant interactions between hydrophilic and lipophilic phytochemicals are influenced by their ratios and total concentrations. Food Biosci. 2022, 45, 101456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.L.; Liu, R.H. Cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) assay for assessing antioxidants, foods, and dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8896–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, D.L.; Thomas, C.A. Organelle-specific probe JC-1 identifies membrane potential differences in the mitochondrial function of bovine sperm. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 53, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, K.; Tong, K.I.; Yamamoto, M. Molecular mechanism activating Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in regulation of adaptive response to electrophiles. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2004, 36, 1208–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satué-Gracia, M.T.; Heinonen, M.; Frankel, E.N. Anthocyanins as Antioxidants on Human Low-Density Lipoprotein and Lecithin-Liposome Systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 3362–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.L.; Hu, M.L. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant effects of lycopene in comparison with β-carotene on oxidant-induced damage in Hs68 cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subagio, A.; Morita, N. Prooxidant activity of lutein and its dimyristate esters in corn triacylglyceride. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagdas, D.; Etoz, B.C.; Gul, Z. In vivo systemic chlorogenic acid therapy under diabetic conditions: Wound healing effects and cytotoxicity/genotoxicity profile. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 81, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, S.; Shamim, U.; Ullah, M.F. The anthocyanidin delphinidin mobilizes endogenous copper ions from human lymphocytes leading to oxidative degradation of cellular DNA. Toxicology 2008, 249, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliwell, B. Free radicals and antioxidants: Updating a personal view. Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treml, J.; Smejkal, K. Flavonoids as Potent Scavengers of Hydroxyl Radicals. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 720–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.J.; Hu, C.H. Mechanism of Chain Termination in Lipid Peroxidation by Carotenes: A Theoretical Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 16948–16958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, E.; Mariutti, L.R.B.; Chisté, R.C.; Mercadante, A.Z. Development of a Novel Micro-Assay for Evaluation of Peroxyl Radical Scavenger Capacity: Application to Carotenoids and Structure-Activity Relationship. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisté, R.C.; Freitas, M.; Mercadante, A.Z.; Fernandes, E. Carotenoids Inhibit Lipid Peroxidation and Hemoglobin Oxidation, but Not the Depletion of Glutathione Induced by ROS in Human Erythrocytes. Life Sci. 2014, 99, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, M.A.T.; Bucknall, M.; Arcot, J. Interactive effects of β-carotene and anthocyanins on cellular uptake, antioxidant activity and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro and ex vivo. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 45, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.A.T.; Bucknall, M.; Arcot, J. Effect of Different Anthocyanidin Glucosides on Lutein Uptake by Caco-2 Cells, and Their Combined Activities on Anti-Oxidation and Anti-Inflammation In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Molecules 2018, 23, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.W.; Li, H.Y.; Yu, C.W.; Yang, T.T.; Hu, J.N.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z.Y. The Evaluation of Antioxidant Interactions among 4 Common Vegetables using Isobolographic Analysis. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.L.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.S. Role of Resveratrol in Regulation of Cellular Defense Systems against Oxidative Stress. BioFactors 2018, 44, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babin, A.; Saciat, C.; Teixeira, M.; Troussard, J.P.; Motreuil, S.; Moreau, J.; Moret, Y. Limiting immunopathology: Interaction between carotenoids and enzymatic antioxidant defences. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 49, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, S.W.; Cui, G.; Leung, G.P.H. Icaritin protects against oxidative stress-induced injury in cardiac H9c2 cells via Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 and calcium signalling pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Ren, B.; Guo, R. Supplementation of lycopene attenuates oxidative stress induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment via Nrf2/NF-κB transcriptional pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, M.A.; Elkhateeb, S.A.; Abd, E.B.; Kattaia, A.A.; Mohamed, E.M.; Atteia, H.H. Lycopene ameliorates atrazine-induced oxidative damage in adrenal cortex of male rats by activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 15262–15274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, K.; Zhang, S. NrF2/ARE and NF-κB pathway regulation may be the mechanism for lutein inhibition of human breast cancer cell. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Li, J.; Zha, D.; Zhang, L.; Gao, P.; Yao, T.; Wu, X. Chlorogenic acid prevents diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation through modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 54, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, B.; Yang, Y.; Pham, T.X.; Park, Y.-K.; Manatou, J.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K.; Lee, J.-Y. Berry anthocyanins suppress the expression and secretion of proinflammatory mediators in macrophages by inhibiting nuclear translocation of NF-κB independent of NRF2-mediated mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2014, 25, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anna, O.; Adam, S. Mitochondria as a pharmacological target: Magnum overview. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas, E.; Davies, K.J. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanong, C.B.; Dean, N.; Ronggui, L.; Katarina, L.; Joseph, W.; De, P. Thyromimetic Action of the Peroxisome Proliferators Clofibrate, Perfluorooctanoic Acid, and Acetylsalicylic Acid Includes Changes in mRNA Levels for Certain Genes Involved in Mitochondrial Biogenesis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1996, 325, 107–112. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz, B.; Schlter, T.; Bohnensack, R.; Pergande, G.; Muller, W.E.G. Effect of flupirtine on cell death of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirakosyan, A.; Seymour, E.M.; Noon, K.R.; Llanes, D.E.U.; Kaufman, P.B.; Warber, S.L.; Bolling, S.F. Interactions of antioxidants isolated from tart cherry (Prunus cerasus) fruits. Food Chem. 2010, 122, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Combination of Materials 2 | Fraction 3 | CI25 4 |
|---|---|---|
| DP-LY | F 1/10 | 0.91 ± 0.08 b |
| F 3/10 | 0.91 ± 0.13 b | |
| F 5/10 | 0.57 ± 0.04 b | |
| F 7/10 | 4.54 ± 1.52 a | |
| F 9/10 | 0.75 ± 0.18 b | |
| CA-LU | F 1/10 | 0.88 ± 0.21 ab |
| F 3/10 | 0.27 ± 0.15 a | |
| F 5/10 | 0.85 ± 0.16 ab | |
| F 7/10 | 0.71 ± 0.01 ab | |
| F 9/10 | 6.40 ± 5.01 a | |
| CA-LY | F 1/10 | 0.84 ± 0.09 ab |
| F 3/10 | 0.74 ± 0.18 b | |
| F 5/10 | 0.94 ± 0.25 ab | |
| F 7/10 | 2.38 ± 1.27 a | |
| F 9/10 | 1.07 ± 0.05 ab | |
| DP-CA | F 1/10 | 1.16 ± 0.16 a |
| F 3/10 | 0.62 ± 0.12 b | |
| F 5/10 | 0.96 ± 0.34 ab | |
| F 7/10 | 0.53 ± 0.01 b | |
| F 9/10 | 0.67 ± 0.02 b | |
| DP-LU | F 1/10 | 4.3 ± 1.29 a |
| F 3/10 | 0.97 ± 0.36 b | |
| F 5/10 | 0.71 ± 0.04 b | |
| F 7/10 | 2.19 ± 0.72 b | |
| F 9/10 | 1.35 ± 0.14 b | |
| LY-LU | F 1/10 | 2.46 ± 1.93 c |
| F 3/10 | 14.33 ± 0.75 b | |
| F 5/10 | 22.85 ± 1.93 a | |
| F 7/10 | 1.35 ± 0.67 c | |
| F 9/10 | 0.59 ± 0.19 c |
| Group | Compound 2 | Low Concentration (nmol/mg Protein) 3 | High Concentration (nmol/mg Protein) 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LY | LY | 0.61 ± 0.007 b | 0.84 ± 0.018 b,* |
| M3 | 0.80 ± 0.075 a | 0.92 ± 0.024 a | |
| M4 | 0.38 ± 0.001 c | 0.62 ± 0.04 c,* | |
| M6 | 0.40 ± 0.006 c | 0.57 ± 0.011 c,* | |
| LU | LU | 0.07 ± 0.002 b | 0.18 ± 0.001 b,* |
| M1 | 0.20 ± 0.004 a | 0.36 ± 0.024 a | |
| M4 | 0.19 ± 0.006 a | 0.37 ± 0.007 a,* | |
| M5 | 0.13 ± 0.006 a | 0.19 ± 0.023 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, B.; Deng, Z.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y.; Li, H. Synergistic and Antagonistic Activity of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Cardiac H9c2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Foods 2024, 13, 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152440
Yu J, Xiao X, Chen B, Deng Z, Chen X, Fan Y, Li H. Synergistic and Antagonistic Activity of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Cardiac H9c2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Foods. 2024; 13(15):2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152440
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jingwen, Xiangwei Xiao, Baiying Chen, Zeyuan Deng, Xuan Chen, Yawei Fan, and Hongyan Li. 2024. "Synergistic and Antagonistic Activity of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Cardiac H9c2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway" Foods 13, no. 15: 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152440
APA StyleYu, J., Xiao, X., Chen, B., Deng, Z., Chen, X., Fan, Y., & Li, H. (2024). Synergistic and Antagonistic Activity of Selected Dietary Phytochemicals against Oxidative Stress-Induced Injury in Cardiac H9c2 Cells via the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Foods, 13(15), 2440. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152440





