Effect of Mild Alkali Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Normal and Waxy Rice Starches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rice Starch Extraction
2.3. Alkali Treatment
2.4. Starch Granule-Associated Protein Content
2.5. X-ray Diffraction
2.6. Swelling Power and Solubility
2.7. Thermal Properties
2.8. Pasting Properties
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SGAP Content
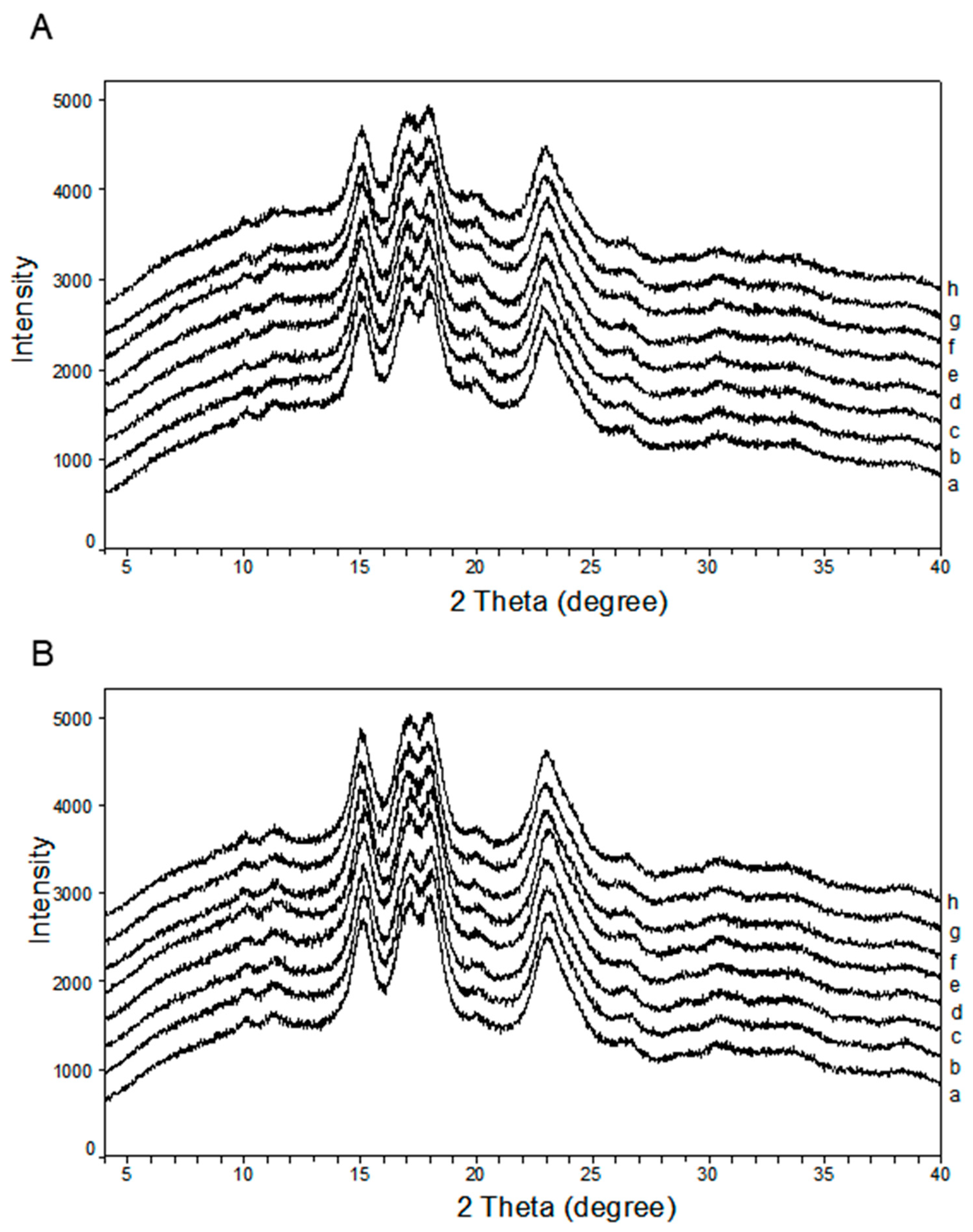
3.2. Crystalline Structure
3.3. Swelling Power and Solubility
3.4. Thermal Properties
3.5. Pasting Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wani, A.A.; Singh, P.; Shah, M.A.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Gul, K.; Wani, I.A. Rice starch diversity: Effects on structural, morphological, thermal, and physicochemical properties—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, A.; Jonathan, O.R.; Alan, L.K.; James, A.O.M. Chemistry, structure, functionality and applications of rice starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 70, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Bergman, C.J. The functionality of rice starch. In Starch in Food; Eliasson, A.C., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 258–294. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, F.F. An update on the use of co-products from the milling of rice in value-added food products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Nadiha, M.Z.; Fazilah, A.; Bhat, R.; Karim, A.A. Comparative susceptibilities of sago, potato and corn starches to alkali treatment. Food Chem. 2010, 121, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Gao, W.; Li, X.; Man, S.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. Comparative susceptibilities to alkali-treatment of A-, B- and C-type starches of Dioscorea zingiberensis, Dioscorea persimilis and Dioscorea opposita. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 39, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.A.; Lim, S.T. Structural changes in corn starches during alkaline dissolution by vortexing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 55, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Fazilah, A.; Karim, A.A. Alcoholic-alkaline treatment of sago starch and its effect on physicochemical properties. Food Bioprod. Process. 2011, 89, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Romero-Manilla, R.; Paredes-López, O. Preparation and properties of physically modified banana starch prepared by alcoholic-alkaline treatment. Starch-Stärke 2000, 52, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, I.; Singh, S.; Saxena, D.C. Influence of alkali treatment on physicochemical, pasting, morphological and structural properties of mango kernel starches derived from Indian cultivars. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Nadiha, M.Z.; Chen, F.K.; Phuah, Y.P.; Chui, Y.M.; Fazilah, A. Pasting and retrogradation properties of alkali-treated sago (Metroxylon sagu) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, M.; Schwurack, B.; Flöter, E. Alkaline dissolution of native potato starch − impact of the preparation conditions on the solution properties determined by means of SEC-MALS. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragheb, A.A.; Abdel-Thalouth, I.; Tawfik, S. Gelatinization of starch in aqueous alkaline solutions. Starch-Stärke 1995, 47, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Wang, S. Alkali-induced changes in functional properties and in vitro digestibility of wheat starch: The role of surface proteins and lipids. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, S.I.; Singh, S.; Saxena, D.C. Effect of alkali-treatment on physicochemical, pasting, thermal, morphological and structural properties of Horse Chestnut (Aesculus indica) starch. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2016, 10, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.A.; BeMiller, J.N. Influence of reaction conditions on the location of reactions in waxy maize starch granules reacted with a propylene oxide analog at low substitution levels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 60, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, S.; Min, G.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, B.; Niu, M.; Jia, C.; Xu, Y.; Lin, Q. Starch-protein interplay varies the multi-scale structures of starch undergoing thermal processing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, P.M. Starch granule-associated proteins and polypeptides: A review. Starch-Stärke 2001, 53, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, Z. The role of starch granule-associated proteins in enhancing the strength of indica rice starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Chen, X.; Zhou, R.; Li, H.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Surface microstructure of rice starch is altered by removal of granule-associated proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.B.; Putaux, J.L.; Samios, D.; da Silveira, N.P. Influence of alkali concentration on the deproteinization and/or gelatinization of rice starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 70, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, I.W.M. The temperature-dependence of elementary reaction rates: Beyond Arrhenius. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Ei Halal, S.L.M.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.D. Physical modification of starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing and their applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavareze, E.D.; Dias, A.R.G. Impact of heat-moisture treatment and annealing in starches: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Wei, C.; Zhou, G.; Huo, Z. Effects of nitrogen level on structure and physicochemical properties of rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AACC method 46-11A; Crude Protein—Improved Kjeldahl Method, Copper Catalyst Modification. American Association of Cereal Chemists: St Paul, MN, USA, 2000.
- Sui, Z.; Huber, K.C.; BeMiller, J.N. Effects of the order of addition of reagents and catalyst on modification of maize starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.Z.; Hamaker, B.R. Partial leaching of granule-associated proteins from rice starch during alkaline extraction and subsequent gelatinization. Starch-Stärke 2002, 54, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Meng, D.; Wu, Z.; Chen, J.; Xue, L. Modification and solubility enhancement of rice protein and its application in food processing: A review. Molecules 2023, 28, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Corso, M.; Baraldi, I.; Colla, E.; Canan, C. Obtaining concentrated rice bran protein by alkaline extraction and stirring—Optimization of conditions. Int. Food Res. J. 2018, 25, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar]
- Mistry, A.H.; Schmidt, S.J.; Eckhoff, S.R.; Sutherland, J.W. Alkali Extraction of Starch from Corn Flour. Starch-Stärke 1992, 44, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malumba, P.; Delatte, S.; Doran, L.; Blecker, C. The effect of annealing under acid or alkaline environment on the physicochemical and functional properties of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thys, R.C.S.; Westfahl, H., Jr.; Noreña, C.P.Z.; Marczak, L.D.F.; Silveira, N.P.; Cardoso, M.B. Effect of the alkaline treatment on the ultrastructure of C-type starch granules. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1894–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Gilbert, R.G.; Malde, A.K. Understanding the binding of starch fragments to granule-bound starch synthase. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 4730–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.-Z.; Campanella, O.H.; Guan, H.; Keeling, P.L.; Hamaker, B.R. Influence of maize starch granule-associated protein on the rheological properties of starch pastes. Part I. Large deformation measurements of paste properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.-Z.; Campanella, O.H.; Guan, H.; Keeling, P.L.; Hamaker, B.R. Influence of maize starch granule-associated protein on the rheological properties of starch pastes. Part II. Dynamic measurements of viscoelastic properties of starch pastes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, R.F.; Debon, S.J.J. Annealing of starch—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2000, 27, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, D. Amylose in starch: Towards an understanding of biosynthesis, structure and function. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 1490–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Yu, G. Effects of endogenous proteins and lipids on structural, thermal, rheological, and pasting properties and digestibility of adlay seed (Coix lacryma-jobi L.) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Qi, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, B. Potential relation between starch granule-associated proteins and retrogradation properties of buckwheat starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 265, 130686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Removal of starch granule-associated proteins alters the physicochemical properties of diverse small granule starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Alakli Treatment | Protein Content % | RC % | SP (g/g) | SOL % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal rice | native | - | 0.76 ± 0.02 ab | 22.0 ± 0.5 a | 11.4 ± 0.1 e | 4.1 ± 0.1 de |
| RTC-8.5 | 25 °C 1 h pH 8.5 | 0.73 ± 0.01 bc | 22.0 ± 0.4 a | 13.1 ± 0.4 b | 6.7 ± 0.9 b | |
| RTC-9.9 | 25 °C 1 h pH 9.9 | 0.75 ± 0.01 abc | 22.1 ± 0.4 a | 12.0 ± 0.1 de | 4.2 ± 0.0 de | |
| RTC-11.3 | 25 °C 1 h pH 11.3 | 0.66 ± 0.04 d | 22.0 ± 0.6 a | 12.4 ± 0.4 cd | 4.7 ± 0.7 cde | |
| HTC-native | 50 °C 18 h | 0.79 ± 0.01 a | 22.2 ± 0.3 a | 11.4 ± 0.2 e | 3.6 ± 0.2 e | |
| HTC-8.5 | 50 °C 18 h pH 8.5 | 0.74 ± 0.04 abc | 21.9 ± 0.9 a | 12.7 ± 0.0 bc | 5.3 ± 0.2 c | |
| HTC-9.9 | 50 °C 18 h pH 9.9 | 0.70 ± 0.04 cd | 22.1 ± 0.3 a | 12.9 ± 0.1 bc | 4.9 ± 0.0 cd | |
| HTC-11.3 | 50 °C 18 h pH 11.3 | 0.23 ± 0.01 e | 21.8 ± 0.6 a | 22.9 ± 3.4 a | 10.8 ± 4.0 a | |
| Waxy rice | native | - | 0.96 ± 0.04 a | 26.5 ± 0.2 ab | 27.7 ± 1.2 ef | 12.5 ± 1.3 b |
| RTC-8.5 | 25 °C 1 h pH 8.5 | 0.89 ± 0.01 abc | 26.6 ± 0.2 ab | 31.6 ± 0.1 abc | 13.5 ± 0.0 b | |
| RTC-9.9 | 25 °C 1 h pH 9.9 | 0.88 ± 0.01 abc | 27.7 ± 0.1 a | 27.6 ± 0.4 f | 12.1 ± 0.2 bc | |
| RTC-11.3 | 25 °C 1 h pH 11.3 | 0.85 ± 0.01 bc | 26.5 ± 0.1 ab | 29.5 ± 0.8 de | 13.4 ± 0.0 b | |
| HTC-native | 50 °C 18 h | 0.94 ± 0.07 ab | 26.6 ± 0.4 ab | 30.5 ± 0.6 bcd | 10.5 ± 0.5 c | |
| HTC-8.5 | 50 °C 18 h pH 8.5 | 0.81 ± 0.01 c | 25.7 ± 0.0 bc | 29.8 ± 1.5 cd | 15.6 ± 0.3 a | |
| HTC-9.9 | 50 °C 18 h pH 9.9 | 0.91 ± 0.01 ab | 24.5 ± 1.5 c | 31.8 ± 0.3 ab | 16.2 ± 0.5 a | |
| HTC-11.3 | 50 °C 18 h pH 11.3 | 0.23 ± 0.05 d | 26.4 ± 1.0 ab | 33.3 ± 0.1 a | 15.9 ± 1.4 a | |
| Sample | ΔH (J/g) | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | Tc–Tp (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal rice | native | 11.25 ± 0.39 ab | 63.89 ± 0.01 e | 69.95 ± 0.04 c | 75.77 ± 0.15 ab | 11.88 ± 0.14 a |
| RTC-8.5 | 12.81 ± 0.98 a | 63.40 ± 0.06 f | 69.51 ± 0.11 d | 75.55 ± 0.05 bc | 12.15 ± 0.06 a | |
| RTC-9.9 | 11.43 ± 0.52 ab | 63.43 ± 0.02 f | 69.69 ± 0.06 cd | 75.37 ± 0.12 c | 11.94 ± 0.14 a | |
| RTC-11.3 | 10.86 ± 0.6 ab | 63.47 ± 0.08 f | 69.56 ± 0.10 d | 75.45 ± 0.13 bc | 11.97 ± 0.09 a | |
| HTC-native | 10.72 ± 0.54 b | 66.78 ± 0.04 a | 70.98 ± 0.13 a | 75.94 ± 0.16 a | 9.16 ± 0.18 e | |
| HTC-8.5 | 11.02 ± 0.48 ab | 65.97 ± 0.07 b | 70.71 ± 0.11 b | 75.69 ± 0.12 abc | 9.72 ± 0.04 d | |
| HTC-9.9 | 11.18 ± 1.60 ab | 65.63 ± 0.15 c | 70.60 ± 0.23 b | 75.73 ± 0.25 abc | 10.10 ± 0.18 c | |
| HTC-11.3 | 12.47 ± 1.25 ab | 64.65 ± 0.10 d | 69.93 ± 0.20 c | 75.57 ± 0.31 bc | 10.91 ± 0.38 b | |
| Waxy rice | native | 20.01 ± 1.68 c | 74.28 ± 0.20 b | 79.88 ± 0.08 bc | 87.13 ± 0.54 d | 12.85 ± 0.68 d |
| RTC-8.5 | 21.43 ± 2.15 bc | 73.75 ± 0.35 c | 79.65 ± 0.32 cd | 88.71 ± 1.21 c | 14.96 ± 1.49 bc | |
| RTC-9.9 | 21.18 ± 2.9 bc | 73.64 ± 0.17 c | 79.72 ± 0.08 bcd | 87.38 ± 1.10 d | 13.74 ± 1.21 cd | |
| RTC-11.3 | 21.86 ± 2.38 bc | 73.75 ± 0.12 c | 79.51 ± 0.08 de | 87.49 ± 0.60 d | 13.75 ± 0.63 cd | |
| HTC-native | 23.12 ± 0.47 abc | 74.90 ± 0.11 a | 80.15 ± 0.12 a | 85.55 ± 0.43 e | 10.65 ± 0.43 e | |
| HTC-8.5 | 22.84 ± 2.70 bc | 74.16 ± 0.26 b | 82.55 ± 5.44 ab | 87.23 ± 4.42 bc | 13.06 ± 4.30 b | |
| HTC-9.9 | 23.76 ± 1.69 ab | 73.30 ± 0.23 d | 79.94 ± 0.17 ab | 90.05 ± 0.94 ab | 16.75 ± 1.15 a | |
| HTC-11.3 | 25.04 ± 0.70 a | 73.33 ± 0.14 d | 79.34 ± 0.15 e | 91.03 ± 0.87 a | 17.70 ± 0.84 a | |
| Sample | PV (mPa·s) | TV (mPa·s) | BD (mPa·s) | FV (mPa·s) | SB (mPa·s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal rice | native | 1639 ± 15 ab | 1223 ± 11 b | 416 ± 3 b | 1802 ± 6 c | 579 ± 5 bc |
| RTC-8.5 | 1658 ± 5 a | 1412 ± 11 a | 246 ± 6 d | 1949 ± 21 b | 537 ± 10 d | |
| RTC-9.9 | 1626 ± 5 ab | 1414 ± 1 a | 212 ± 4 d | 2010 ± 7 ab | 595 ± 8 abc | |
| RTC-11.3 | 1616 ± 4 ab | 1406 ± 5 a | 209 ± 1 d | 2026 ± 4 a | 619 ± 1 ab | |
| HTC-native | 1644 ± 31 b | 1237 ± 25 b | 406 ± 56 b | 1800 ± 28 c | 562 ± 3 cd | |
| HTC-8.5 | 1527 ± 62 ab | 1208 ± 19 b | 318 ± 43 c | 1809 ± 27 c | 600 ± 8 abc | |
| HTC-9.9 | 1490 ± 8 c | 1121 ± 28 c | 369 ± 20 bc | 1747 ± 29 c | 626 ± 1 a | |
| HTC-11.3 | 1590 ± 13 c | 829 ± 8 d | 760 ± 5 a | 1250 ± 54 d | 421 ± 47 e | |
| Waxy rice | native | 1171 ± 16 d | 663 ± 3 e | 508 ± 13 b | 810 ± 4 d | 146 ± 1 a |
| RTC-8.5 | 1211 ± 8 c | 720 ± 4 c | 491 ± 4 b | 844 ± 6 c | 124 ± 1 d | |
| RTC-9.9 | 1251 ± 1 b | 780 ± 0 b | 471 ± 1 c | 911 ± 2 b | 131.5 ± 2 c | |
| RTC-11.3 | 1111 ± 11 e | 673 ± 6 d | 437 ± 5 de | 813 ± 4 d | 139 ± 2 b | |
| HTC-native | 1539 ± 5 a | 887 ± 3 a | 652 ± 8 a | 984 ± 3 a | 97 ± 0 e | |
| HTC-8.5 | 1070 ± 10 f | 623 ± 3 f | 446 ± 6 d | 746 ± 2 e | 123 ± 1 d | |
| HTC-9.9 | 993 ± 11 g | 588 ± 3 g | 405 ± 7 f | 723 ± 7 f | 134 ± 3 c | |
| HTC-11.3 | 970 ± 10 h | 543 ± 1 h | 426 ± 9 e | 667 ± 1 g | 124 ± 0 d | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Ma, M.; Sui, Z.; Corke, H. Effect of Mild Alkali Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Normal and Waxy Rice Starches. Foods 2024, 13, 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152449
Xu Z, Liu X, Zhang C, Ma M, Sui Z, Corke H. Effect of Mild Alkali Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Normal and Waxy Rice Starches. Foods. 2024; 13(15):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152449
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zekun, Xiaoning Liu, Chuangchuang Zhang, Mengting Ma, Zhongquan Sui, and Harold Corke. 2024. "Effect of Mild Alkali Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Normal and Waxy Rice Starches" Foods 13, no. 15: 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152449
APA StyleXu, Z., Liu, X., Zhang, C., Ma, M., Sui, Z., & Corke, H. (2024). Effect of Mild Alkali Treatment on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Normal and Waxy Rice Starches. Foods, 13(15), 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13152449





