Fast and Reliable On-Site Quality Assessment of Essential Raw Brewing Materials Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Spectroscopic Analysis
2.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
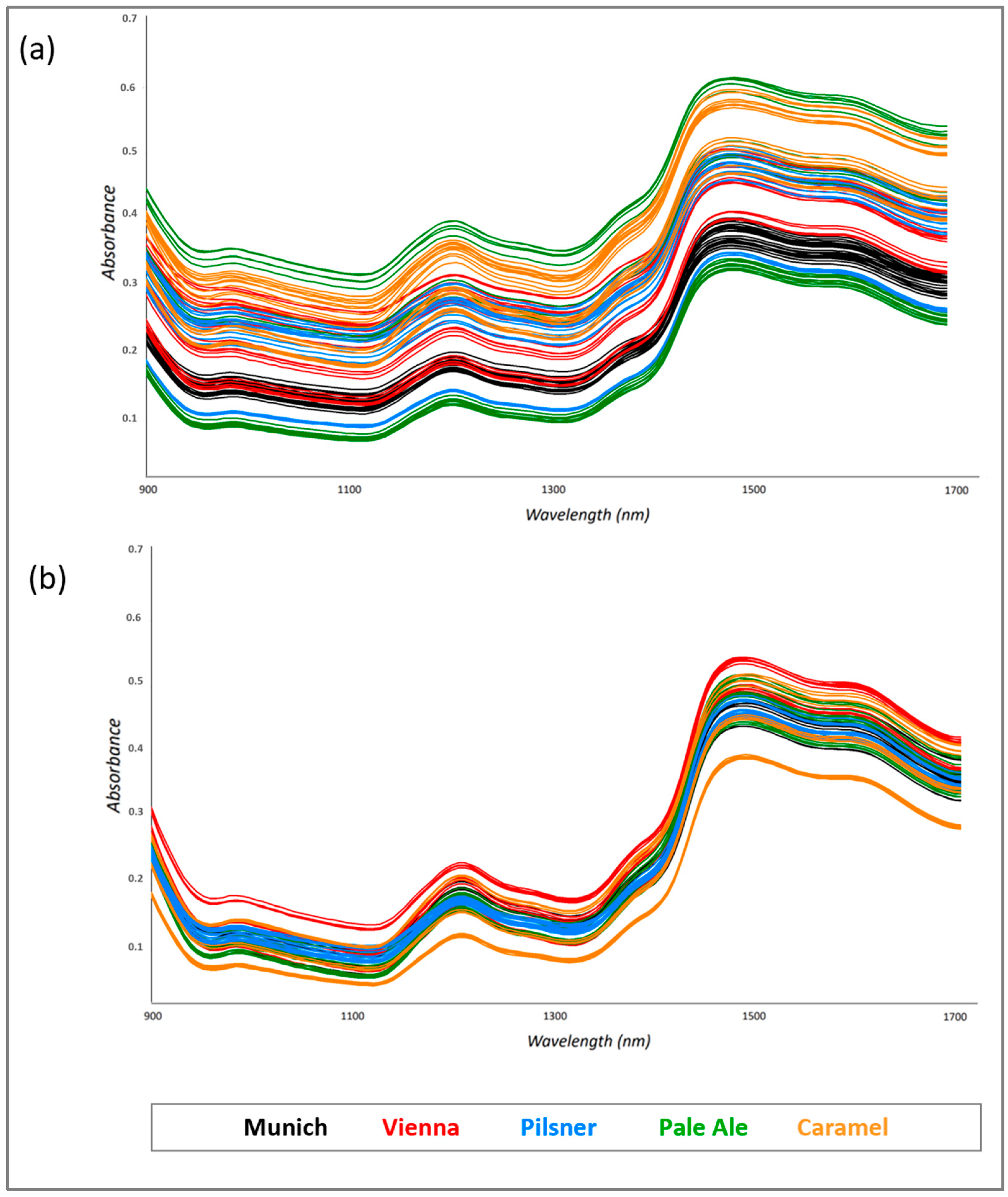
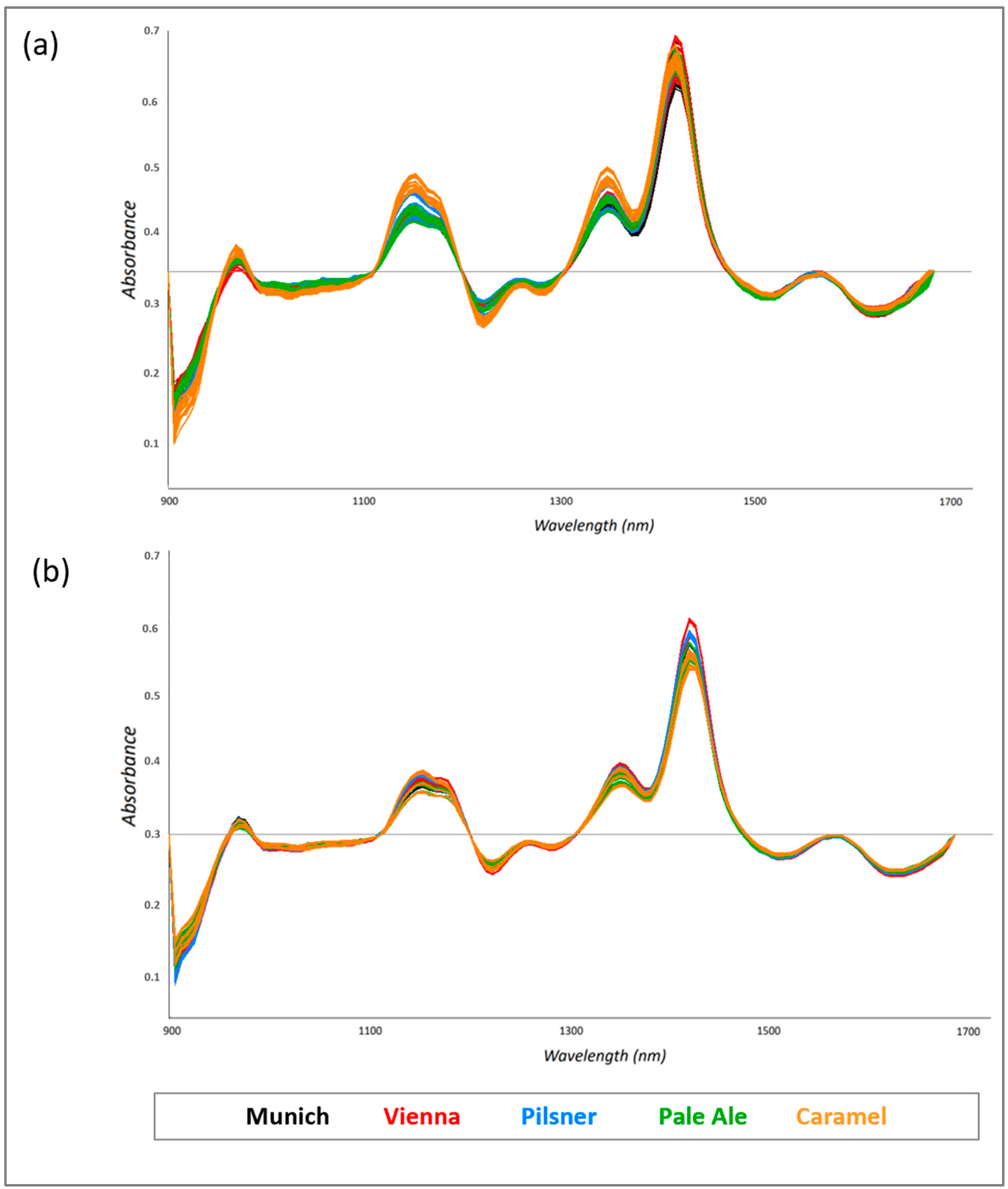
3.1. Optimization of an Analytical Protocol for Malt Grains Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics
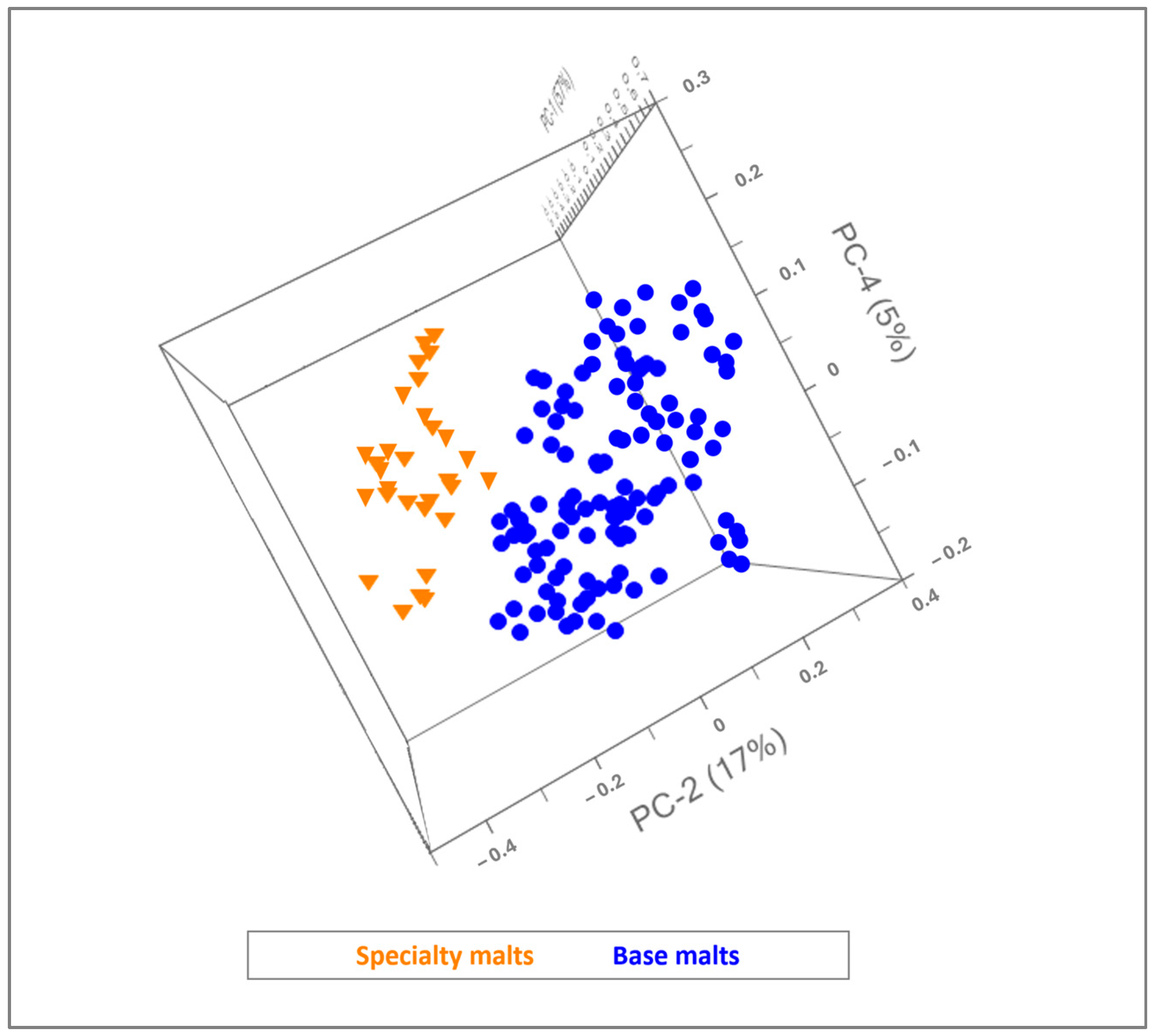
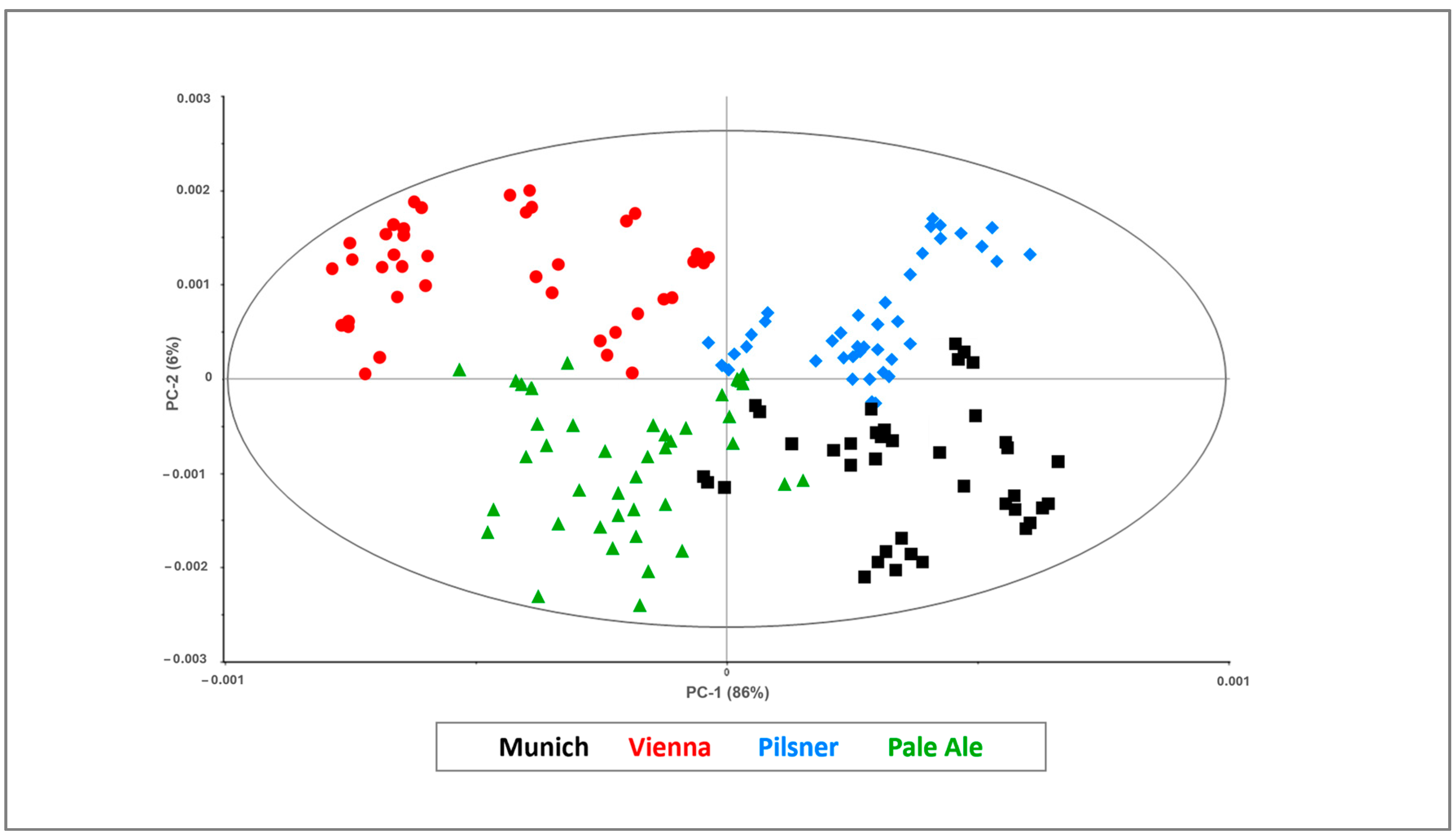
3.2. SIMCA Model Development
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O.; Peretti, G. Near-infrared Spectroscopy in the Brewing Industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2015, 55, 1771–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.O.; Goncalves, L.M.; Guido, L.F. Overall Antioxidant Properties of Malt and How They Are Influenced by the Individual Constituents of Barley and the Malting Process. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 927–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannenmacher, J.; Gastl, M.; Becker, T. Phenolic Substances in Beer: Structural Diversity, Reactive Potential and Relevance for Brewing Process and Beer Quality. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 953–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, D.O.; Guido, L.F. A review on the fate of phenolic compounds during malting and brewing: Technological strategies and beer styles. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozcan, M.M.; Aljuhaimi, F.; Uslu, N. Effect of malt process steps on bioactive properties and fatty acid composition of barley, green malt and malt grains. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yu, M.; Wu, S.; Ma, M.; Su, H.; Guo, F.; Bian, Q.; Du, T. Sensory lexicon and aroma volatiles analysis of brewing malt. NPJ Sci. Food 2022, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Piao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Hou, Y.; Shi, Z. Analysis of volatile compounds from a malting process using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction and GC–MS. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 783–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Brewery Convention. Analytica-EBC 4.17—Moisture and Total Nitrogen in Malt by Near Infrared Spectroscopy; 1997. Available online: https://brewup.eu/ebc-analytica/malt/moisture-and-total-nitrogen-in-malt-by-near-infrared-spectroscopy/4.17 (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Marte, L.; Belloni, P.; Genorini, E.; Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Montanari, L.; Marconi, O. Near infrared reflectance models for the rapid prediction of quality of brewing raw materials. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R.J. Evaluation of barley and malt quality using near-infrared reflectance techniques. J. Inst. Brew. 1985, 91, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileoni, V.; Perretti, G.; Marte, L.; Marconi, O.; Fantozzi, P. Near-infrared spectroscopy for proficient quality evaluation of malt and maize in beer industry. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Brewery Convention. Analytica-EBC 9.2.6—Alcohol in Beer by NIRS; 2008. Available online: https://brewup.eu/ebc-analytica/beer/alcohol-in-beer-by-near-infrared-spectroscopy/9.2.6 (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Nielsen, J.P.; Bro, R.; Larsen, J.; Munck, L. Application of fuzzy logic and near infrared spectroscopy for malt quality evaluation. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Evaluation of different validation strategies and long-term effects in NIR calibration models. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sileoni, V.; van den Berg, F.; Marconi, O.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Internal and External Validation Strategies for the Evaluation of Long-Term Effects in NIR Calibration Models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G. The Brewing Industry and the Opportunities for Real-Time Quality Analysis Using Infrared Spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilarska, A.A.; Boniecki, P.; Idzior-Haufa, M.; Zaborowicz, M.; Pilarski, K.; Przybylak, A.; Piekarska-Boniecka, H. Image Analysis Methods in Classifying Selected Malting Barley Varieties by Neural Modelling. Agriculture 2021, 11, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Miniaturized NIR Spectroscopy in Food Analysis and Quality Control: Promises, Challenges, and Perspectives. Foods 2022, 11, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Materazzi, S. Assessing the quality of milk using a multicomponent analytical platform MicroNIR/Chemometric. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 614718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, P.; Solanki, R.; Modi, V.; Basuri, T. A Brief Review on NIR Spectroscopy and its Pharmaceutical Applications. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Anal. 2016, 3, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, M. Near-infrared Spectroscopy Application to the Pharmaceutical Industry. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrógiewicz, M. Application of the near-infrared spectroscopy in the pharmaceutical technology. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 66, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, A.C.S.; Pereira, J.F.Q.; Honorato, R.S.; Bro, R.; Pimentel, M.F. Hierarchical classification models and Handheld NIR spectrometer to human blood stains identification on different floor tiles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 267, 120533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.F.Q.; Silva, C.S.; Vieira, M.J.L.; Pimentel, M.F.; Braz, A.; Honorato, R.S. Evaluation and identification of blood stains with handheld NIR spectrometer. Microchem. J. 2017, 133, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Fineschi, V.; Frati, P.; Materazzi, S. Application of innovative TGA/Chemometric approach for forensic purposes: The estimation of the time since death in contaminated specimens. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranenburg, R.F.; Ramaker, H.-J.; Sap, S.; van Asten, A.C. A calibration friendly approach to identify drugs of abuse mixtures with a portable near-infrared analyzer. Drug Test. Anal. 2022, 14, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deidda, R.; Coppey, F.; Damergi, D.; Schelling, C.; Coïc, L.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Sacréa, P.-Y.; De Bleyea, C.; Hubert, P.; Esseiva, P.; et al. New perspective for the in-field analysis of cannabis samples using handheld near-infrared spectroscopy: A case study focusing on the determination of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 202, 114150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, V.; Blasco, J.; Aleixos, N.; Cubero, S.; Talens, P. Monitoring strategies for quality control of agricultural products using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invernizzi, C.; Rovetta, T.; Licchelli, M.; Malagodi, M. Mid and Near-Infrared Reflection Spectral Database of Natural Organic Materials in the Cultural Heritage Field. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 2018, 7823248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catauro, M.; Naviglio, D.; Risoluti, R.; Ciprioti, S.V. Sol–gel synthesis and thermal behavior of bioactive ferrous citrate–silica hybrid materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Carcassi, E.; Masotti, A.; Materazzi, S. TGA/Chemometrics addressing innovative preparation strategies for functionalized carbon nanotubes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Fabiano, M.A.; Materazzi, S. Biomimetic complexes of Co(II), Mn(II), and Ni(II) with 2-propyl-4,5-imidazoledicarboxylic acid. EGA-MS characterization of the thermally induced decomposition. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2015, 85, 2374–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, A.; Morelato, M.; Roux, C.; Beavis, A. Review of the most common chemometric techniques in illicit drug profiling. Forensic Sci. Int. 2019, 302, 109911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Gullifa, G.; Battistini, A.; Materazzi, S. Development of a “single-click” analytical platform for the detection of cannabinoids in hemp seed oil. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 43394–43399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnan, A.; van den Berg, F.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitzky, M.J.; Golay, E. Smoothing and differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risoluti, R.; Caprari, P.; Gullifa, G.; Massimi, S.; Sorrentino, F.; Maffei, L.; Materazzi, S. Innovative screening test for the early detection of sickle cell anemia. Talanta 2020, 219, 121243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, R.J.; Dhanoa, M.S.; Lister, S.J. Standard normal variate transformation and detrending of near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 1989, 43, 772–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Provider | Country | Color (EBC) | Moisture (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Malts | Vienna | Bestmalz | Germany | 8–10 | 4.9 |
| Durst Malz | Germany | 6–9 | 4.0 | ||
| Simpson Malt | UK | 5–10 | 3.5 | ||
| Crisp Malting | UK | 6–10 | 4.5 | ||
| Munich | Bestmalz | Germany | 11–20 | 4.9 | |
| Durst Malz | Germany | 20–25 | 4.0 | ||
| Rhön Malz | Germany | 23–26 | 3.0–4.5 | ||
| Simpson Malt | UK | 18–25 | 4.0 | ||
| Pilsner | Bestmalz | Germany | 3–4.9 | 4.9 | |
| Durst Malz | Germany | 2.5–3.3 | 4.5 | ||
| Rhön Malz | Germany | 2.8–3.8 | 4–4.5 | ||
| Dingemans | Belgium | 3.5 | 4.5 | ||
| Italmalt | Italy | 3.5–4.5 | 3–5 | ||
| Pale Ale | Bestmalz | Germany | 5–7 | 4.9 | |
| Simpson Malt | UK | 4–6 | 3.7 | ||
| Crisp Malting | UK | 5.5–7.5 | 3.5 | ||
| Muntons | UK | 5–7 | 3.7 | ||
| Thomas Fawcett & Sons | UK | 5–7.5 | 4.0 | ||
| Specialty Malts | Caramel | Bestmalz | Germany | 3–7 | 4.5 |
| Crystal | Simpson Malt | UK | 167–190 | 5.0 | |
| Number of Spectra | Calibration Set | Validation Set | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Munich | 160 | 120 | 40 |
| Vienna | 160 | 120 | 40 |
| Pilsner | 200 | 150 | 50 |
| Pale Ale | 200 | 150 | 50 |
| Caramel | 40 | 30 | 10 |
| Crystal | 40 | 30 | 10 |
| Equation | |
|---|---|
| Selectivity (%) | |
| Specificity (%) | |
| Efficiency (%) | |
| False positive rate (%) | |
| False negative rate (%) |
| PC Number | Selectivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Efficiency (%) | FPR (%) | FNR (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground malt grains | Munich | 7 | 87.50 | 66.67 | 70.71 | 4.29 | 0.13 |
| Vienna | 7 | 71.43 | 70.97 | 80.66 | 4.29 | 0.29 | |
| Pilsner | 7 | 75.00 | 67.57 | 75.04 | 3.75 | 0.25 | |
| Pale Ale | 6 | 70.00 | 72.73 | 76.28 | 3.95 | 0.30 | |
| Caramel | 6 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 3.75 | 0 | |
| Crystal | 5 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 91.29 | 3.75 | 0 | |
| Sieved malt grains | Munich | 7 | 75.00 | 82.35 | 84.89 | 2.50 | 0.25 |
| Vienna | 7 | 91.67 | 76.92 | 74.12 | 3.41 | 0.08 | |
| Pilsner | 6 | 83.33 | 88.24 | 81.35 | 2.50 | 0.17 | |
| Pale Ale | 7 | 80.00 | 77.78 | 73.79 | 2.78 | 0.20 | |
| Caramel | 7 | 100.00 | 80.00 | 89.44 | 2.50 | 0 | |
| Crystal | 7 | 83.33 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 2.52 | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gullifa, G.; Albertini, C.; Papa, E.; Petrucci, R.; Di Matteo, P.; Bortolami, M.; Materazzi, S.; Risoluti, R. Fast and Reliable On-Site Quality Assessment of Essential Raw Brewing Materials Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics. Foods 2024, 13, 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172728
Gullifa G, Albertini C, Papa E, Petrucci R, Di Matteo P, Bortolami M, Materazzi S, Risoluti R. Fast and Reliable On-Site Quality Assessment of Essential Raw Brewing Materials Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics. Foods. 2024; 13(17):2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172728
Chicago/Turabian StyleGullifa, Giuseppina, Chiara Albertini, Elena Papa, Rita Petrucci, Paola Di Matteo, Martina Bortolami, Stefano Materazzi, and Roberta Risoluti. 2024. "Fast and Reliable On-Site Quality Assessment of Essential Raw Brewing Materials Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics" Foods 13, no. 17: 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172728
APA StyleGullifa, G., Albertini, C., Papa, E., Petrucci, R., Di Matteo, P., Bortolami, M., Materazzi, S., & Risoluti, R. (2024). Fast and Reliable On-Site Quality Assessment of Essential Raw Brewing Materials Using MicroNIR and Chemometrics. Foods, 13(17), 2728. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172728












