Abstract
Fermentation is an effective method for ameliorating the gelation properties of freshwater fish surimi, but the formation of biogenic amines (BAs) during fermentation should also be controlled. In this study, the BAs in fermented tilapia surimi were inhibited by the collaborative fermentation of Latilactobacillus sakei and Pediococcus acidilactici, followed by the revelation of the BA inhibition mechanism. Most of the BAs, and the total BA, as well as their precusor free amino acids (FAAs), were significantly reduced, while the umami FAAs, including glutamic acid and aspartic acid, were significantly enhanced after cooperative fermentation with starters. The high-throughput sequencing found that the spoilage microorganisms such as Acinetobacter, Micrococcus, and Streptococcus as well as Pediococcus were significantly inhibited, while Latilactobacillus rapidly became the dominant genus after cooperative fermentation, suggesting the better environment adaptability of L. sakei than P. acidilactici. The group-dimension correlation analysis suggested that Lactiplantibacillus had the greatest influence on the decrease in BAss. The quick acidification of starters, especially L. sakei, could inhibit the growth and metabolism of spoilage microorganisms to reduce BAs. L. sakei and P. acidilactici can be developed as the special starters to control the BA production in the fermented tilapia surimi through collaborative fermentation.
1. Introduction
Surimi products are famous worldwide because of their special mouthfeel from the gelation property [1]. In order to form a good gel, the surimi products are mainly produced from sea fish, due to their better gel strength than freshwater fish. However, as the demand for surimi products increases, more freshwater fish are used as raw material, and need to improve the gelation property [2]. As one of the main freshwater fish worldwide, tilapia are usually processed into filets [3,4], resulting in a low added value. The low gelation properties limit the processing of tilapia into surimi products. The addition of additives, such as protease inhibitors [5], microbial transglutaminase [6], and polysaccharides [7] is a traditional method to improve the gelation properties of surimi. Fermentation through lactic acid bacteria (LAB) is an effective method to enhance the gelation properties of freshwater fish surimi through acidification [8]. Previous studies have found that the gel property of tilapia surimi can be significantly improved by microbial fermentation [8]. However, most studies only focus on the improvement of flavor and gelation properties of tilapia surimi by fermentation with various strains of LAB, such as Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pentosaceus [9,10], but ignore the formation of biogenic amines (BAs) during fermentation.
BAs in fermented foods are generally produced through the decarboxylation of free amino acids by microorganisms [11]. An excessive intake of BAs can result in severe harm to human health. Dietary exposure to foods containing high levels of histamine and tyramine is associated with many adverse health effects, including elevated blood pressure, migraines, and tachycardia [12], while the toxicity of cadaverine and putrescine in aquatic organisms has also been reported [13], indicating the importance to control BAs in foods. High concentrations of BAs have been found in fermented surimi because of the high free amino acids (FAAs) and active microbial metabolisms [8,14]. Natural microbial communities and even starters are involved in the production of BAs [14,15]. Therefore, it is important to select good starters to control the formation of BAs during fermentation. Many starters have been found to have a good BA reduction ability, such as the strains of LAB [16].
Therefore, in this study, in order to inhibit the production of BAs in the tilapia surimi, two strains of LAB were selected and used for collaborative fermentation. The changes in eight BAs during the collaborative fermentation process were studied and compared with those during the natural fermentation, followed by the study of FAAs and microbial community. The correlation networks in the group dimension were constructed to reveal the inhibition mechanism of BAs by collaborative fermentation. This work is expected to provide a useful way to enhance the food safety of fermented tilapia surimi.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Starter Strains
The starter strains Latilactobacillus sakei H30-5 and Pediococcus acidilactici H30-21 were isolated from tilapia surimi in the natural fermentation process [2]. Both strains stored in the magnetic beads at −80 °C were anaerobically incubated into the de Man, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) medium (Guangdong Huankai Microbial Sci. & Tech. CO., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) at 30 °C for 24 h, respectively. After centrifugation at 4 °C and 10,000× g for 5 min, the precipitation was resuspended into 0.9% NaCl solution as starters.
2.2. Tilapia Surimi Fermentation
The tilapia surimi was fermented according to the previous study [17]. Briefly, the minced tilapia muscle was mixed with 0.5% sucrose, 0.5% glucose, 2% salt, and 5% water. The starter strains (1 × 106 CFU/g) were added into the mixture. After blending for 5 min at ice temperature, the mixture was added into the plastic casings (Φ = 3 cm) and then fermented at 25 °C. The tilapia surimi fermented with starters at various time (18, 30, and 45 h) was taken as the CM group. The tilapia surimi fermented naturally was chosen as the CK group.
2.3. Detection of BAs
The tilapia surimi (5.0 g) was homogenized with 0.4 mol/L HClO4 solution. After centrifugation for 5 min at 10,000× g and 4 °C, the supernatant was taken to determine the content of BAs [8]. Briefly, the samples were first derived by dansyl chloride (Anpel Laboratory Technologies Inc., Shanghai, China), and were then detected through the LC-20AD HPLC system (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) with the ChromCore™ C18A reversed-phase chromatographic column (250 × 4.6 mm; Nano Chrom, Suzhou, China) by an ultraviolet detector at 254 nm. The content of BAs was then calculated through the standard curves of 8 BAs (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.4. Detection of FAAs
The tilapia surimi (5.0 g) was first homogenized with 45 mL water. After centrifugation for 5 min at 10,000× g and 4 °C, the supernatant was taken to analyze the content of FAAs [8]. Briefly, the samples were derived by 9-fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and o-phthalaldehyde (OPA; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), respectively. The FAAs were then analyzed by the Agilent 1100 Series HPLC System (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with the ZORBAX Eclipse AAA column (150 mm × 4.6 mm; Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The derived FAAs by FMOC were detected through a fluorescence detector (excitation at 266 nm and emission at 305 nm), while the derived FAAs by OPA were detected through an ultraviolet detector at 338 nm. The content of FAAs was calculated through the standard curves of 25 FAAs (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.5. Analysis of Microbial Community
The tilapia surimi (3.0 g) was first homogenized with 0.9% NaCl solution. The homogenized solution was then centrifuged for 5 min at 10,000× g and 4 °C. After genomic DNA extraction from the precipitation, the 16S rRNA gene high-throughput sequencing was used to analyze the microbial community according to the previous study [18]. Briefly, the V3-V4 regions of 16S rRNA genes were amplified by the PCR through the primer pair, 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). After purification, the PCR amplicons were paired-end sequenced through the MiSeq PE300 platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were collected under 97% sequence similarity by UPARSE v7.0.1090. The taxonomy was analyzed by RDP Classifier v2.11 using the OTUs.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was performed in triplicate. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The content heatmap and correlation heatmap were constructed by MetaboAnalyst v6.0. The correlation network was drawn through Cytoscape v3.8.1. The influence of genus on the decrease in BA (Ig) was calculated through the equation below according to the previous study [2] with some modification:
where r is the Pearson’s correlation coefficient between BA and genus (p < 0.05), and Ag is the mean abundance of genus for Pearson’s correlation analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in BAs After Collaborative Fermentation
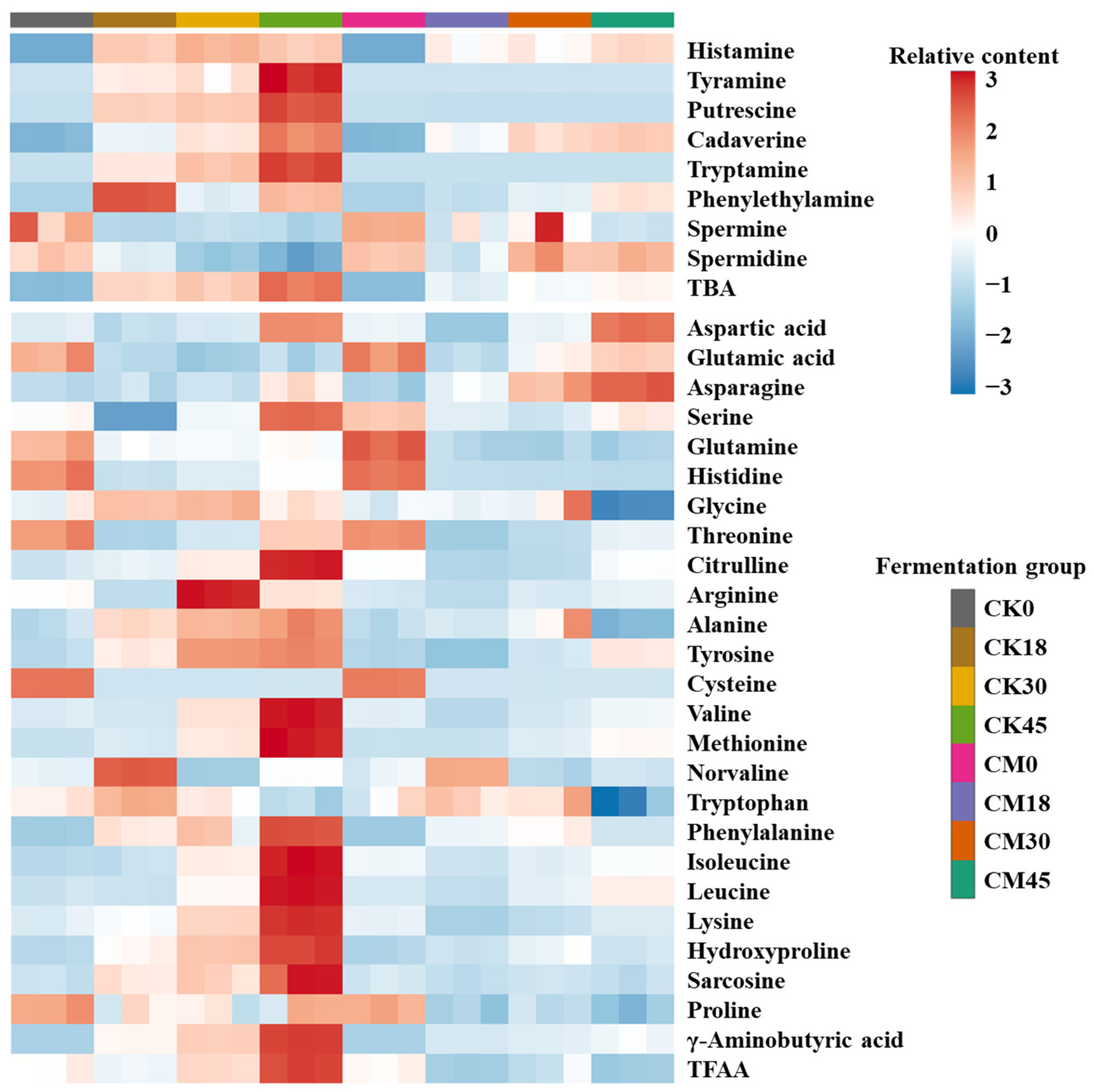
BAs are one of the most important food safety indexes in fermented foods. In this work, the changes in eight BAs during the fermentation process were studied in both the CM and CK groups (Figure 1 and Table S1). Most of the BAs in both groups were obviously enhanced along with fermentation and maximized at 45 h. Histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, and tyramine were the main BAs in the fermented tilapia surimi. These BAs are also reported as the main BAs in fish sauce [18]. In contrast, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, spermine, and spermidine had relatively low contents (<10 mg/kg). As the most toxic BA, histamine is abundant in fermented food and is required to be limited to 50 mg/kg in aquatic products by the Food and Drug Administration of USA. In this study, less histamine was found in the tilapia surimi before fermentation (<1 mg/kg), but the histamine content after natural fermentation for 18, 30, and 45 h increased to 38.66, 44.18, and 39.09 mg/kg, respectively, with a risk of exceeding the standard. After collaborative fermentation, the histamine content was reduced by 25.84%, 33.59%, and 8.73% at 18, 30, and 45 h, respectively, suggesting good histamine inhibition by starters, especially at 30 h. As another toxic BA, tyramine was relatively low before natural fermentation for 30 h (<10 mg/kg), but was significantly elevated after natural fermentation for 45 h, reaching 20.99 mg/kg. Interestingly, the tyramine content obviously decreased to below 0.2 mg/kg during the whole collaborative fermentation process. Putrescine and cadaverine can not only evaluate the freshness of aquatic products, but also enhance the toxicity of histamine by protecting it from degradation [8]. Although a high content of putrescine was found after natural fermentation for 18–45 h (>10 mg/kg), its production is completely suppressed by collaborative fermentation with starters. There was no obvious change in the cadaverine content between the CK and CM groups before 30 h, but its content significantly decreased by 27.97% at 45 h after collaborative fermentation with starters. Similar to putrescine, the tryptamine is completely suppressed by collaborative fermentation with starters. There was no obvious change in the contents of phenylethylamine, spermine, and spermidine between the CM and CK groups. The total BA (TBA) significantly increased during the natural fermentation and reached the maximum (399.72 mg/kg) at 45 h. Interestingly, the TBA decreased by 42.37%, 35.86%, and 48.89% after collaborative fermentation with starters for 18, 30, and 45 h, respectively. The results suggested that the collaborative fermentation with starters could effectively inhibit the BA formation in the tilapia surimi.
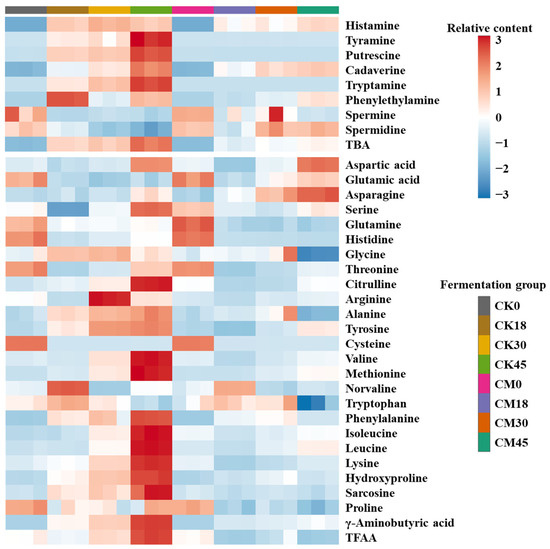
Figure 1.
Changes in BAs and FAAs in tilapia surimi during the fermentation process of CM and CK groups.
3.2. Changes in FAAs After Collaborative Fermentation
As the raw material of BAs, the content of FAAs has great influence on the production of BAs. In this work, the changes in 25 FAAs during the fermentation process were studied in both the CM and CK groups (Figure 1 and Table S2). Most FAAs in the CK group were obviously enhanced along with fermentation and maximized at the end of fermentation, while most FAAs in the CM group changed little in the fermentation process. Glycine and alanine were the most abundant FAAs and accounted for over 50% of the total FAAs, contributing to the sweet taste of tilapia surimi. This result was similar to other fermented freshwater fish surimi [14,19]. Compared with those in the CK group, most FAAs in the CM groups were reduced, suggesting a decrease in proteolytic activity by microorganisms. Interestingly, glutamic acid and aspartic acid were significantly elevated by collaborative fermentation, especially at the end of fermentation, resulting in an increase in the umami taste of tilapia surimi. In addition, the asparagine content was also significantly elevated in the CM group compared with that in the CK group, contributing to the increasing sweet taste of tilapia surimi. As the precusor of histamine, the histidine content significantly reduced with the increase in time in both groups, mainly due to the use in the production of high content of histamine. An obvious reduction in histidine was also observed in the previous study. Compared with those in the CK group, the contents of histidine, tyrosine, arginine, lysine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine were lower in the CM groups, contributing to the decrease in the corresponding BAs after collaborative fermentation. Similarly, the total FAA (TFAA) decreased by 11.84%, 12.66%, and 33.56% after collaborative fermentation with starters for 18, 30, and 45 h, respectively. The decrease in proteolytic activity after collaborative fermentation with starters was an important reason for the decrease in BAs.
3.3. Changes in Microbial Composition After Collaborative Fermentation
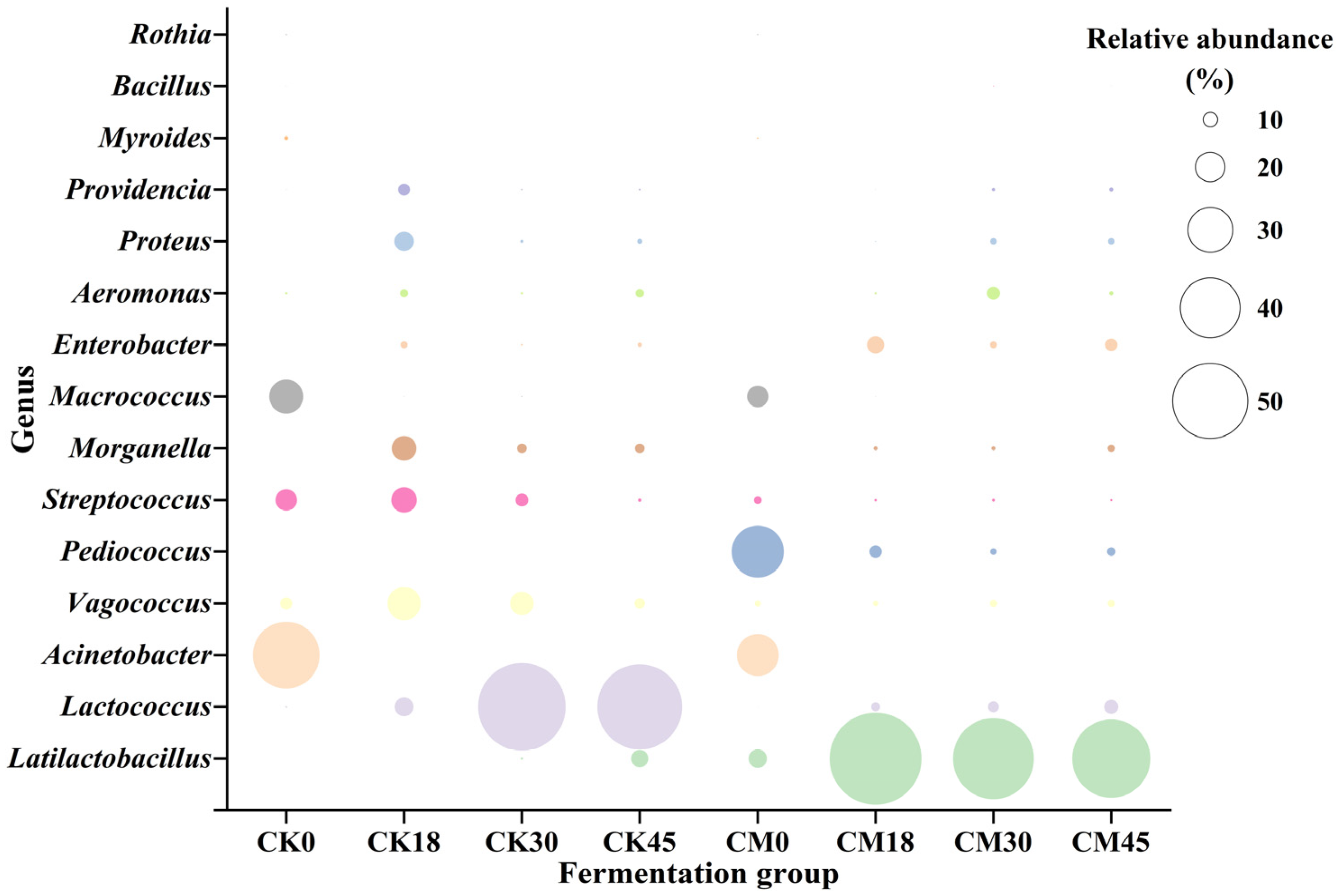
The metabolism of spoilage microorganisms is the main source of BAs. In this study, the changes in various microbial genera during the fermentation process were studied in both the CM and CK groups (Figure 2). A total of 15 genera (relative abundance > 0.5%) were detected. Acinetobacter (44.03%), Micrococcus (22.61%), and Streptococcus (14.15%) were the main genera in the raw tilapia surimi, in accordance with the previous result [8]. However, after natural fermentation, their abundance significantly decreased, while the abundance of LAB, including Lactococcus and Latilactobacillus, was markedly elevated, reaching 55.88% and 11.31% at the end of fermentation, respectively. In the CM group, besides Acinetobacter, Micrococcus, and Streptococcus, Pediococcus and Latilactobacillus were the dominant genera before fermentation due to the addition of starters. Similarly, along with the fermentation, spoilage microorganisms such as Acinetobacter, Micrococcus, and Streptococcus were remarkedly reduced after collaborative fermentation, and decreased to only 0.01%, 0.26%, and 1.56% at 45 h, respectively. The abundance of Pediococcus also obviously decreased, and its relative abundance was only 5.64% at 45 h, indicating the low adaptability of starter P. acidilactici to the tilapia surimi environment. In contrast, Latilactobacillus rapidly became the dominant genus after 18 h to 45 h of collaborative fermentation, with relative abundance > 50%. In addition, Lactococcus and Enterobacter were also abundant after collaborative fermentation, and their relative abundance reached 9.40% and 8.27% at the end of fermentation. It suggested that the surimi fermentation environment was more suitable for the growth of LAB, especially the starter L. sakei. A similar result has also been found in other studies [9,10].
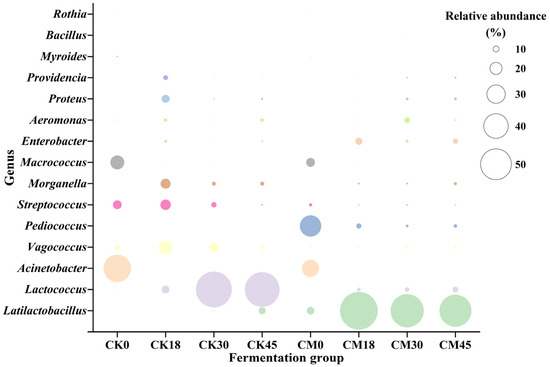
Figure 2.
Changes in microbial taxonomic compositions in the tilapia surimi during the fermentation process of the CM and CK groups.
3.4. Correlation of Core Microbial Genus with BAs and FAAs in Group Dimension
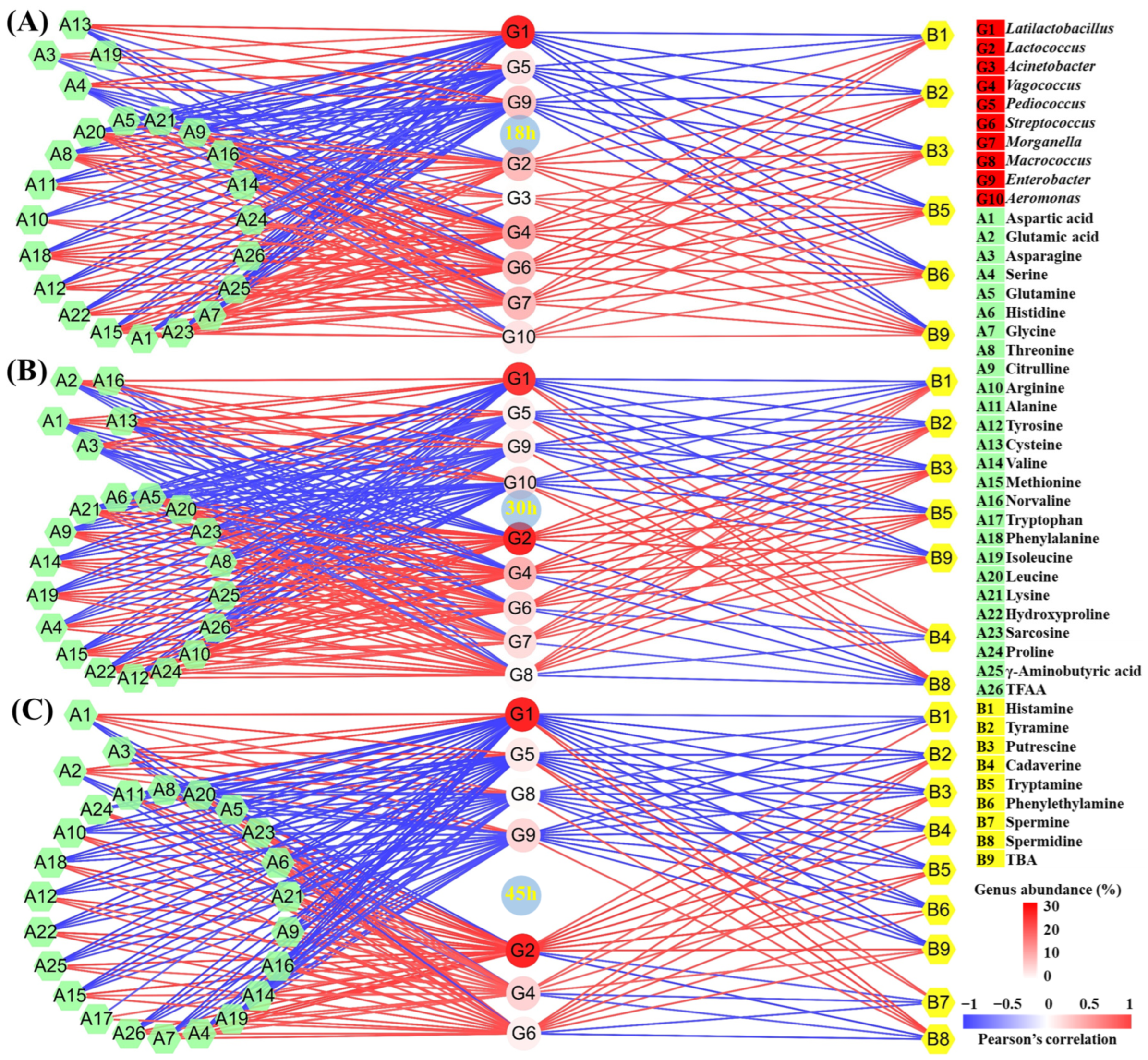
The microbial community and quality indexes of fermented food will change when the starter is added. The group-dimension correlation analysis can uncover the change mechanisms of various qualities induced by the microbial community [17,20]. However, most studies only perform the correlation analysis at the end of fermentation, resulting in the incomplete disclosure mechanisms [2,20]. In this study, the correlation analysis among 10 core microbial genera, 8 BAs, and 26 FAAs over different fermentation times between the CM and CK groups was performed through the Pearson’s correlation analysis (Figure S1), followed by the making of correlation networks (Figure 3).
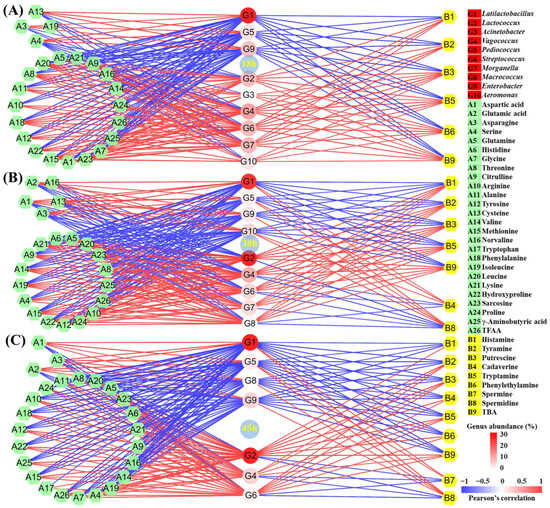
Figure 3.
Correlation network constructed by the Pearson’s correlation coefficient among the core microbial genera, BAs, and FAAs in the tilapia surimi in the group dimension in the (A) 18 h, (B) 30 h, and (C) 45 h periods. The red line and blue line, respectively, represent the significantly positive and negative correlation (|r| > 0.8 and p < 0.05).
In the 18 h period, a total of two genus clusters were found (Figure S1A), including 18 h-1 (Latilactobacillus, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, and Enterobacter) and 18 h-2 (Lactococcus, Acinetobacter, Vagococcus, Streptococcus, Morganella, and Aeromonas). Most BAs and FAAs were positively correlated with the cluster 18 h-2, but were negatively related with the cluster 18 h-1. In the cluster 18 h-1, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, and Enterobacter showed a significantly negative correlation with histamine, tyramine, putrescine, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, and TBA (Figure 3A). The rise in their abundance after collaborative fermentation contributed to the decrease in BA content in the tilapia surimi at 18 h. In addition, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, and Enterobacter also showed a significantly negative correlation with most FAAs, especially TFAA (Figure 3A), suggesting their important role in the decrease in FAA content at 18 h.
Similarly, in the 30 h period, two genus clusters were observed (Figure S1B), including 30 h-1 (Latilactobacillus, Acinetobacter, Pediococcus, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas) and 30 h-2 (Lactococcus, Vagococcus, Streptococcus, Morganella, and Macrococcus). Most BAs and FAAs exhibited a positive correlation with the cluster 30 h-2, but were negatively related with the cluster 30 h-1. In the cluster 30 h-1, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas exhibited a significantly negative correlation with histamine, tyramine, putrescine, tryptamine, and TBA (Figure 3B). The improvement in their abundance after collaborative fermentation was the main reason for the BA decrease at 30 h. In addition, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas were also significantly negatively correlated with most FAAs, especially TFAA (Figure 3B), suggesting their main role in the decrease in FAA content after collaborative fermentation for 30 h. In addition, the metabolism of these genera also led to the improvement in glutamic acid and aspartic acid at 30 h.
In the 45 h period, two genus clusters were also observed (Figure S1C), including 45 h-1 (Latilactobacillus, Acinetobacter, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, and Enterobacter) and 45 h-2 (Lactococcus, Vagococcus, Streptococcus, Morganella, and Aeromonas). Most BAs and FAAs also showed a positive correlation with the cluster 45 h-2, but exhibited a negative correlation with the cluster 45 h-1. In cluster 45 h-1, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, and Enterobacter exhibited a significantly negative correlation with histamine, tyramine, putrescine, cadaverine, tryptamine, phenylethylamine, and TBA (Figure 3C). The increase in their abundance after collaborative fermentation was the main reason for the BA decrease at 45 h. In addition, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, and Enterobacter were also remarkedly negatively correlated with most FAAs, especially TFAA (Figure 3C), suggesting their main roles in the decrease in FAA content at 45 h. In addition, these genera also contributed to the increase in glutamic acid and aspartic acid at the end of fermentation after collaborative fermentation.
According to the correlation networks in different periods, Lactococcus, which possessed the highest mean abundance, showed a significantly positive correlation with most BAs in all three periods, suggesting its main role in the BA formation in the fermented tilapia surimi. Lactococcus is also found to show a correlation with BAs during the fermentation of different foods [8,21]. Many strains in the genus Lactococcus have been reported to produce BAs in the cheese [22]. Meanwhile, many spoilage microorganisms, especially Vagococcus and Streptococcus, were also responsible for the BA formation in the fermented tilapia surimi in the three periods. Similarly, Vagococcus is found to be related to the formation of BAs in vacuum-packaged large yellow croaker during ice storage [23]. Many strains in the genus Streptococcus isolated from homemade natural yogurt have been reported to produce BAs [24]. In this study, the decrease in these genera might be the main reason for the decrease in BAs after cooperative fermentation with starters. In addition, the strains in Lactococcus are famous for their proteolytic activity [25,26,27], followed by the strains in Streptococcus [28,29,30]. The inhibition of their proteolytic activity after cooperative fermentation with starters also contributed to the decrease in BAs in the fermented tilapia surimi.
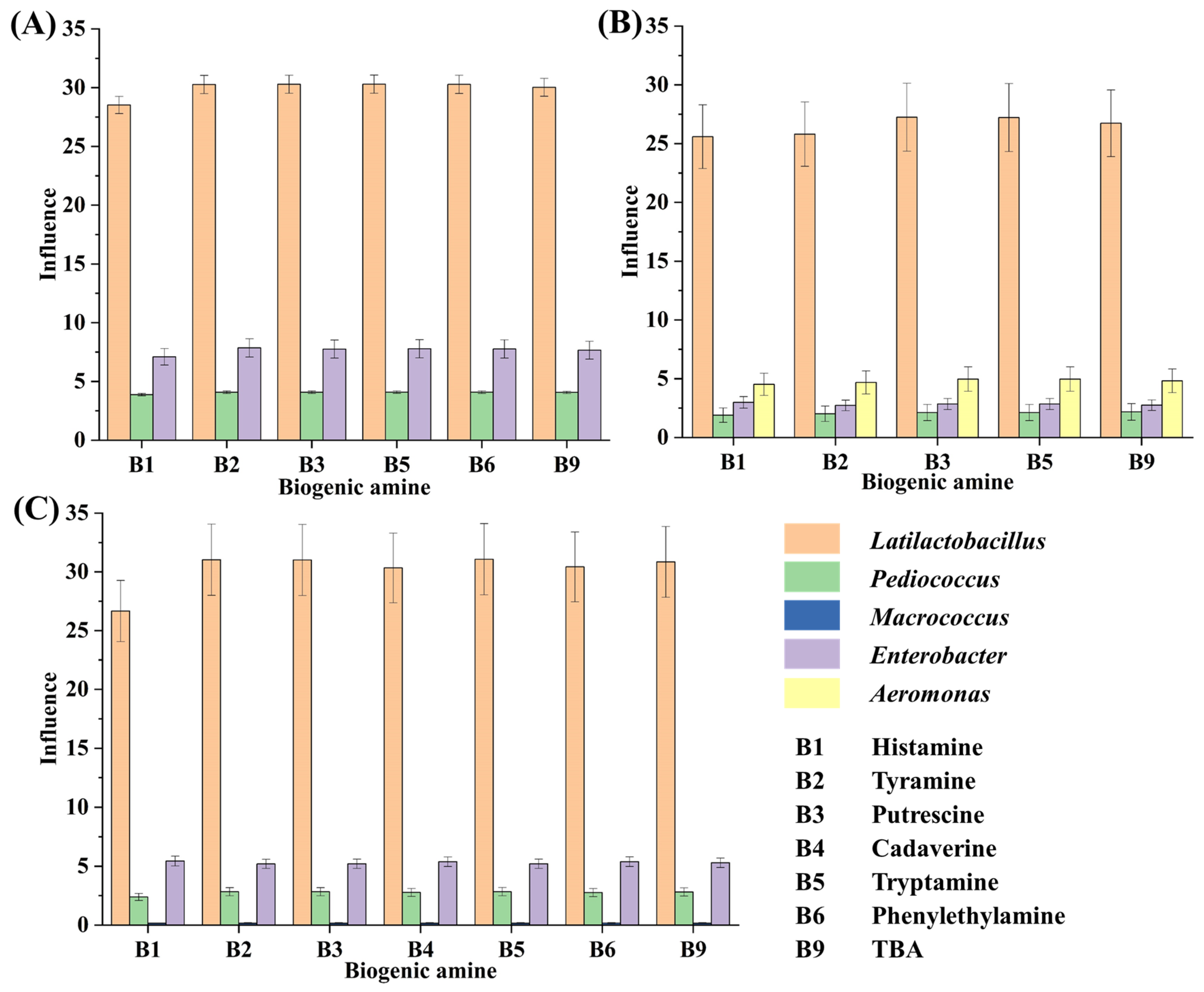
During the tilapia surimi fermentation in different periods, Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas played important roles in the decrease in BAs in different periods. The microorganisms in fermented food that are high in abundance and can obviously affect the food quality are considered the core ones [20,31]. In this work, after considering both factors, the influence of the genus was further calculated (Figure 4). According to the influence of these genera, Latilactobacillus contributed the most to the decrease in BAs, with a contribution over 71%, 73%, and 76% in the 18 h, 30 h, and 45 h periods, respectively. It suggested that the starter L. sakei H30-5 contributed the most to the decrease in BAs in the tilapia surimi. The acidification of LAB has been found to suppress the growth of spoilage microorganisms and their metabolisms [32], resulting in the inhibition of production of BAs. Similar results have reported that L. sakei can improve the food safety of fermented meat sausage [33,34]. Moreover, in this study, the high abundance of the starter P. acidilactici at the beginning of inoculation could quickly reduce the acidity of the fermentation environment, which was ideal for the starter L. sakei to grow and quickly reach a dominant position. The collaborative fermentation of these two starters kept the fermentation environment at a low pH and consequentially kept spoilage microorganisms at a low abundance. The collaborative fermentation of starters have also been reported to possess more advantages than a single starter in the formation of gel strength and flavor [2,17]. In addition, the inhibition of spoilage microorganisms by starters also led to the decrease in precusor FAAs of BAs, contributing to the decrease in BAs in the tilapia surimi. The collaborative metabolism of starters was useful in controlling the production of BAs from spoilage microorganisms.
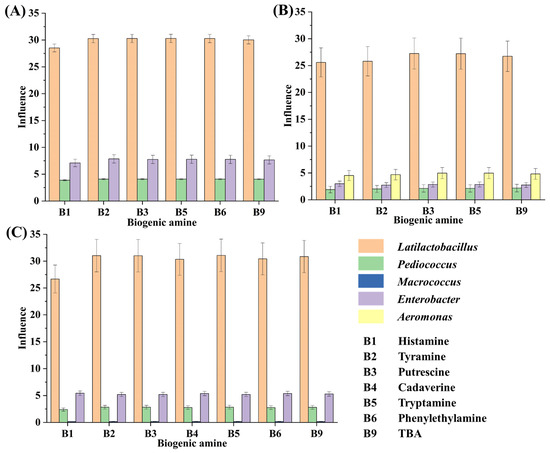
Figure 4.
The influence of the genus on the decrease in BAs in the tilapia surimi in the (A) 18 h, (B) 30 h, and (C) 45 h periods.
4. Conclusions
Most BAs in both the CK and CM groups were obviously enhanced during fermentation. Histamine, cadaverine, putrescine, and tyramine were the main BAs. Most BAs and the TBA were significantly inhibited through the collaborative fermentation with starters. Most FAAs, especially the precusors of the BAs, as well as TFAA, were significantly reduced, while the umami FAAs, including glutamic acid and aspartic acid, were significantly enhanced through the collaborative fermentation with starters. The spoilage microorganisms such as Acinetobacter, Micrococcus, and Streptococcus, as well as Pediococcus, were significantly inhibited after collaborative fermentation, while Latilactobacillus rapidly rose to the dominant abundance, suggesting the better environment adaptability of L. sakei compared to P. acidilactici. The group-dimension correlation network found that Lactiplantibacillus, Pediococcus, Macrococcus, Enterobacter, and Aeromonas played important roles in the decrease in BAs in different periods, especially Latilactobacillus, which had the greatest influence on the decrease in BAs. The acidification of LAB. especially the starter L. sakei, could suppress the growth of spoilage microorganisms and their metabolisms, resulting in the inhibition of the production of BAs. Collaborative fermentation with starters was first used to control the BAs in the tilapia surimi and exhibited good performance. L. sakei and P. acidilactici can be used as the special starters to enhance the food safety of fermented tilapia surimi in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/foods13203297/s1, Figure S1: Correlation analysis among the core microbial genera, BAs, and FAAs in the group dimension in the (A) 18 h, (B) 30 h, and (C) 45 h periods; Table S1: Changes in BAs (mg/kg) in the tilapia surimi during the fermentation process of the CM and CK groups; Table S2: Changes in FAAs (mg/kg) in the tilapia surimi during the fermentation process of the CM and CK groups.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L.; methodology, C.L.; validation, D.W., J.D. and H.H.; formal analysis, C.L.; investigation, C.W.; data curation, C.L.; writing—original draft preparation, C.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.Z.; visualization, C.L.; supervision, S.C.; project administration, D.W.; funding acquisition, C.L., H.H., Y.Z. and S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD2100903), the Earmarked fund for CARS (CARS-46), the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou of China (2023B03J1263), the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, South China Sea Fisheries Research Institute, CAFS (2024RC04), and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS (2023TD78).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, W.; Wen, L.; Xiong, S.; Xiao, S.; An, Y. Investigation of the Effect of Chemical Composition of Surimi and Gelling Temperature on the Odor Characteristics of Surimi Products Based on Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry/Olfactometry. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 135977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, C. Novel Insight into the Formation and Improvement Mechanism of Physical Property in Fermented Tilapia Sausage by Cooperative Fermentation of Newly Isolated Lactic Acid Bacteria Based on Microbial Contribution. Food Res. Int. 2024, 187, 114456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcântara, L.O.; Martins, M.E.d.O.; Sousa, J.R.; Cerqueira, M.Â.; Silva, A.L.C.; Souza Filho, M.d.S.M.; Souza, B.W.S. Wettability of Edible Coatings on Nile Tilapia Fillets (Oreochromis niloticus). J. Food Eng. 2019, 247, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Ruiz, E.I.; Maeda-Martinez, A.N.; Ocano-Higuera, V.M.; Sumaya-Martinez, M.T.; Sanchez-Herrera, L.M.; Fregoso-Aguirre, I.O.A.; Rincones-Lopez, J.E.; Palomino-Hermosillo, Y.A. Shelf Life of Fresh Fillets from Eviscerated Farmed Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Handled at Different Pre-Filleting Times. J. Food Process Preserv. 2020, 44, e14529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.B.; Park, J.W.; Jung, H. Effects of Potato Protein Isolated Using Ethanol on the Gelation and Anti-Proteolytic Properties in Pacific Whiting Surimi. Foods 2022, 11, 3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wu, C.; Yuan, C.; Ishimura, G.; Liu, W.; Chen, S. γ-PGA and MTGase Improve the Formation of ε-(γ-Glutamyl) Lysine Cross-Links within Hairtail (Trichiurus haumela) Surimi Protein. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasinnitiwong, N.; Benjakul, S.; Hong, H. Effects of κ-Carrageenan on Gel Quality of Threadfin Bream (Nemipterus spp.) Surimi Containing Salted Duck Egg White Powder. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Novel Insight into Physicochemical and Flavor Formation in Naturally Fermented Tilapia Sausage Based on Microbial Metabolic Network. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cui, Q.; Li, L.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y. Formation and Improvement Mechanism of Physical Property and Volatile Flavor of Fermented Tilapia Surimi by Newly Isolated Lactic Acid Bacteria Based on Two Dimensional Correlation Networks. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Contribution of Microbial Community to Flavor Formation in Tilapia Sausage during Fermentation with Pediococcus Pentosaceus. LWT 2022, 154, 112628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabade, D.S.; Jacxsens, L.; Miclotte, L.; Abatih, E.; Devlieghere, F.; De Meulenaer, B. Survey of Multiple Biogenic Amines and Correlation to Microbiological Quality and Free Amino Acids in Foods. Food Control 2021, 120, 107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turna, N.S.; Chung, R.; Mcintyre, L. A Review of Biogenic Amines in Fermented Foods: Occurrence and Health Effects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, A.P.A.; Vallim, J.H.; Castanha, R.F.; de Castro, V.L.S.S.; Marin-Morales, M.A. Toxicity Assessment of the Biogenic Amines Cadaverine and Putrescine in Aquatic Organisms. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, S. Biogenic Amine Accumulation in Silver Carp Sausage Inoculated with Lactobacillus Plantarum plus Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, T.; Li, Y. Biogenic Amines Are Important Indices for Characterizing the Freshness and Hygienic Quality of Aquatic Products: A Review. LWT 2024, 194, 115793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.H.; Mah, J.-H. Occurrence and Reduction of Biogenic Amines in Traditional Asian Fermented Soybean Foods: A Review. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, S.; Huang, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, Y. Improvement Mechanism of Volatile Flavor in Fermented Tilapia Surimi by Cooperative Fermentation of Pediococcus acidilactici and Latilactobacillus sakei: Quantization of Microbial Contribution through Influence of Genus. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.; Li, C.; Li, L.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, D.; Wu, Y. Novel Insight into Flavor and Quality Formation in Naturally Fermented Low-Salt Fish Sauce Based on Microbial Metabolism. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Q. Proteolytic Characterisation in Grass Carp Sausage Inoculated with Lactobacillus Plantarum and Pediococcus Pentosaceus. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y.; Qi, B. Microbial Community Changes Induced by a Newly Isolated Salt-Tolerant Tetragenococcus Muriaticus Improve the Volatile Flavor Formation in Low-Salt Fish Sauce. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Zhang, N.; Chu, J.; et al. Microbial Community Succession and Its Correlation with Quality Characteristics during Gray Sufu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flasarova, R.; Pachlova, V.; Bunkova, L.; Mensikova, A.; Georgova, N.; Drab, V.; Bunka, F. Biogenic Amine Production by Lactococcus lactis Subsp cremoris Strains in the Model System of Dutch-Type Cheese. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xie, J. Effects of ε-Polylysine and Rosemary Extract on Quality Attributes and Microbial Communities in Vacuum-Packaged Large Yellow Croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during Ice Storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezginc, Y.; Akyol, I.; Kuley, E.; Ozogul, F. Biogenic Amines Formation in Streptococcus thermophilus Isolated from Home-Made Natural Yogurt. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbowska, M.; Pluta, A.; Berthold-Pluta, A. Proteolytic and ACE-Inhibitory Activities of Dutch-Type Cheese Models Prepared with Different Strains of Lactococcus Lactis. Food Biosci. 2020, 35, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.; Pavunc, A.L.; Butorac, K.; Banic, M.; Culjak, N.; Rak, H.; Blazevic, M.; Iveljic, A.-M.; Suskovic, J.; Kos, B. Caseinolytic Proteases of Lactobacillus and Lactococcus Strains Isolated from Fermented Dairy Products. Mljekarstvo 2022, 72, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mecherfi, K.-E.; Lupi, R.; Cherkaoui, M.; Albuquerque, M.A.C.; Todorov, S.D.; Tranquet, O.; Klingebiel, C.; Rogniaux, H.; Denery-Papini, S.; Onno, B.; et al. Fermentation of Gluten by Lactococcus Lactis LLGKC18 Reduces Its Antigenicity and Allergenicity. Probiot. Antimicrob. Proteins 2022, 14, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Serrano, G.M.; Garcia-Garibay, M.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Gomez-Ruiz, L.; Ayala-Nino, A.; Castaneda-Ovando, A.; Gonzalez-Olivares, L.G. Proteolytic System of Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 28, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Analysis of the Proteolytic System of Streptococcus thermophilus Strains CS5, CS9, CS18 and CS20. Int. Dairy J. 2021, 118, 105025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Rosales, L.B.; Perez-Escalante, E.; Castaneda-Ovando, A.; Contreras-Lopez, E.; Cruz-Guerrero, A.E.; Regal-Lopez, P.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Gonzalez-Olivares, L.G. ACE-Inhibitory Activity of Whey Proteins Fractions Derived of Fermentation by Lacticaseibacillus Rhamnosus GG and Streptococcus thermophilus SY-102. Foods 2023, 12, 2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. The Potential Correlation between Bacterial Diversity and the Characteristic Volatile Flavour of Traditional Dry Sausages from Northeast China. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.V.; Seo, H.-W.; Seong, P.-N.; Kang, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Cho, S.-H.; Park, B.-Y.; Ham, J.-S.; Kim, J.-H. Lactobacillus Plantarum (KACC 92189) as a Potential Probiotic Starter Culture for Quality Improvement of Fermented Sausages. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2018, 38, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galante, N.; Palavecino Prpich, N.; Campos, C.; Cayré, M.E.; Castro, M. Alternative Culture Medium Design for Biomass Production of Autochthonous Meat Starter Latilactobacillus sakei Sp. Sakei ACU-2. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenmann, A.W.; Schiffer, C.J.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Impact of Different Sugars and Glycosyltransferases on the Assertiveness of Latilactobacillus sakei in Raw Sausage Fermentations. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 366, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).