Study on the Characteristics of Fine Rice Flour by Micro-Crushing and Its Effects on the Quality Improvement of Rice Cakes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Fine Rice Flour Preparation
2.3. Fine Rice Flour Characterization
2.3.1. Basic Components
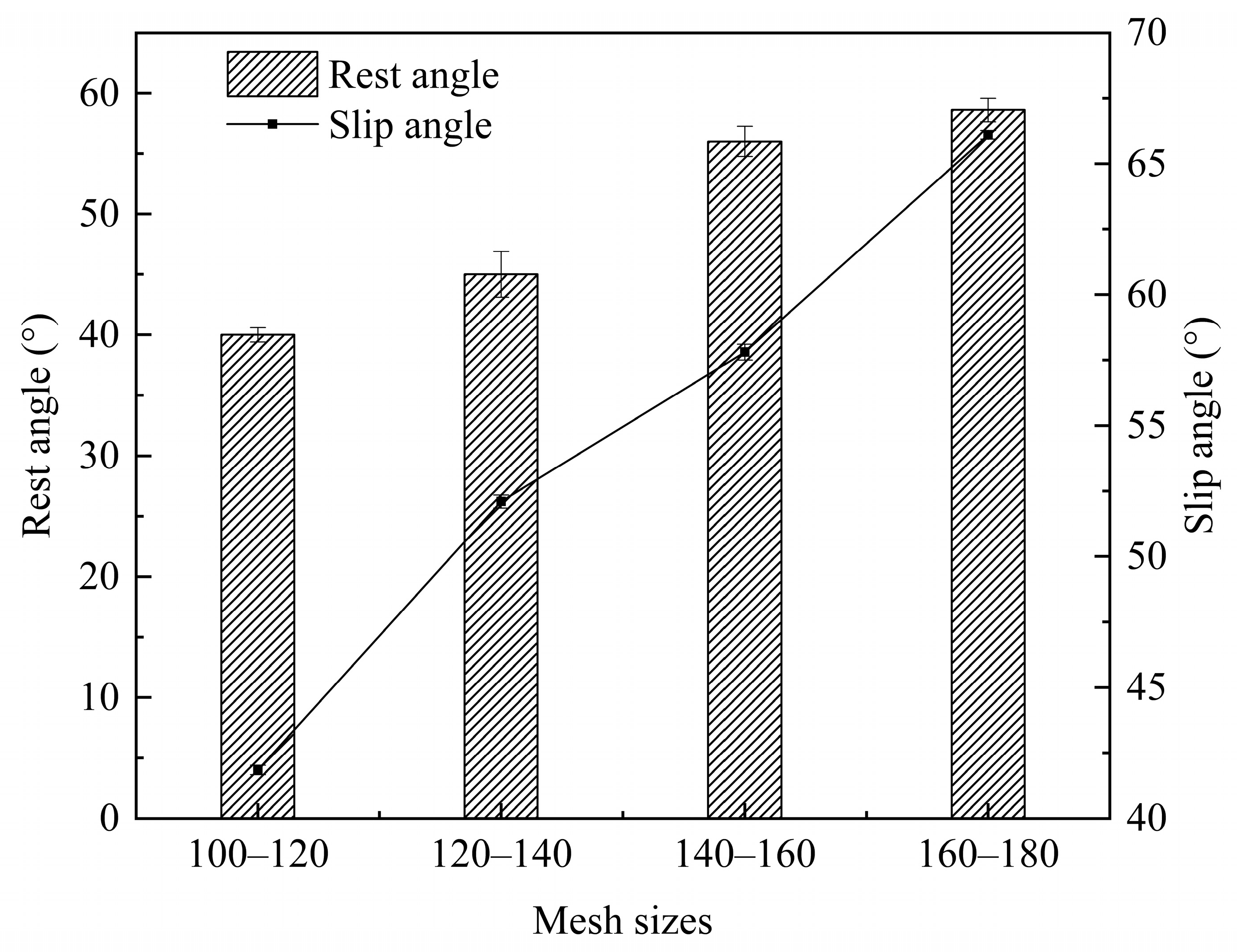
2.3.2. Rest Angle and Slip Angle
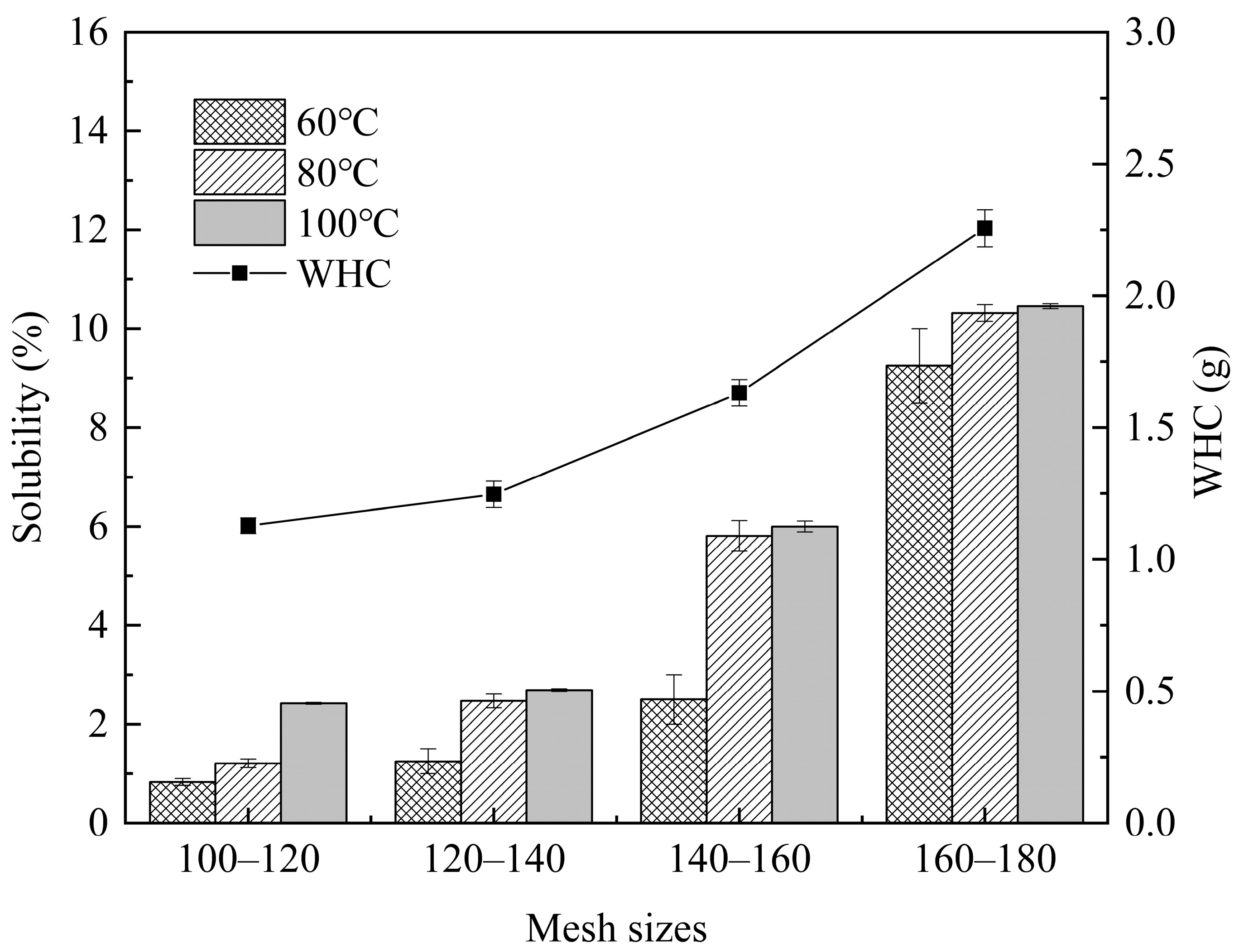
2.3.3. Solubility and WHC
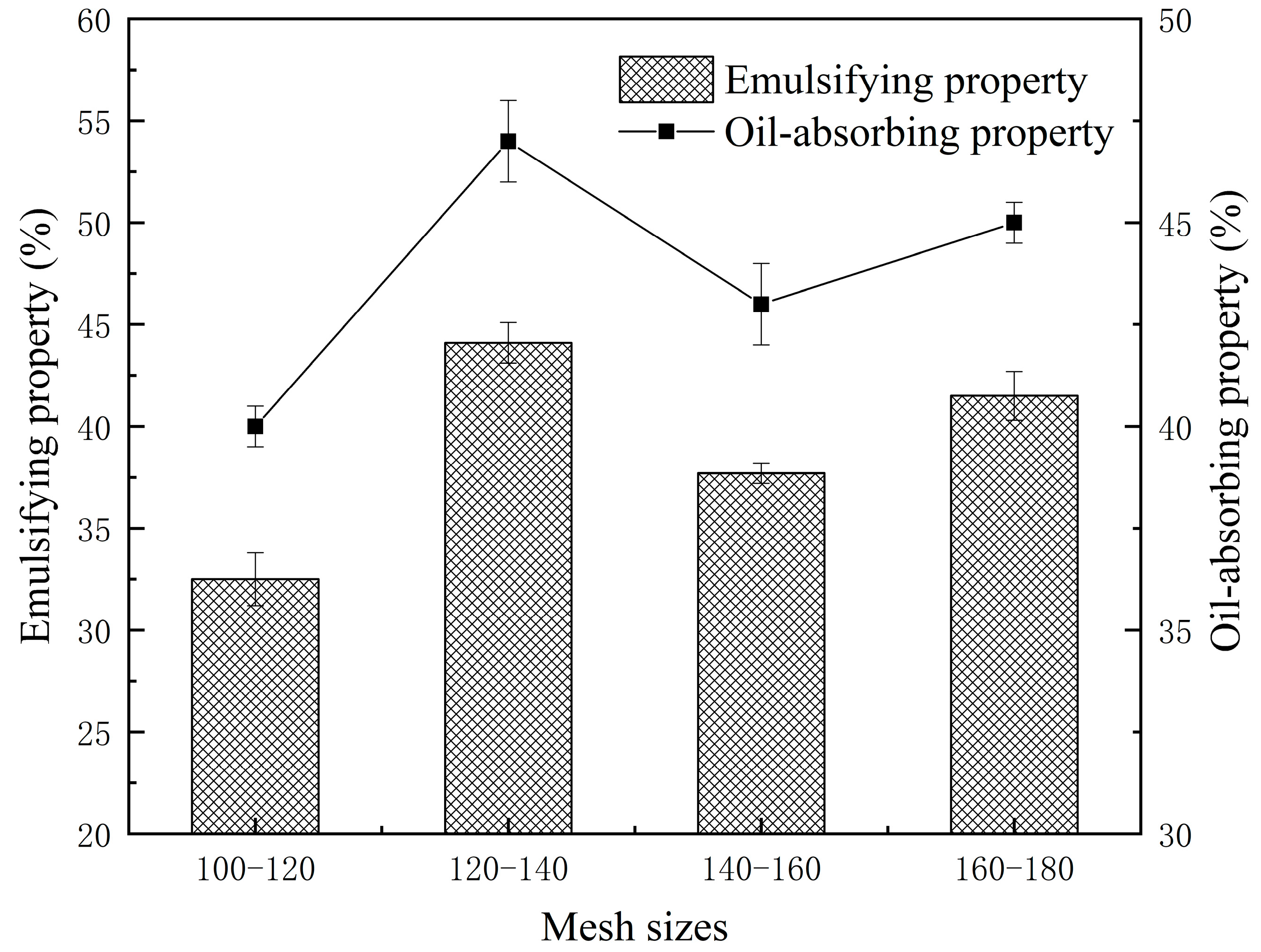
2.3.4. Emulsifying Property and Oil-Absorbing Property
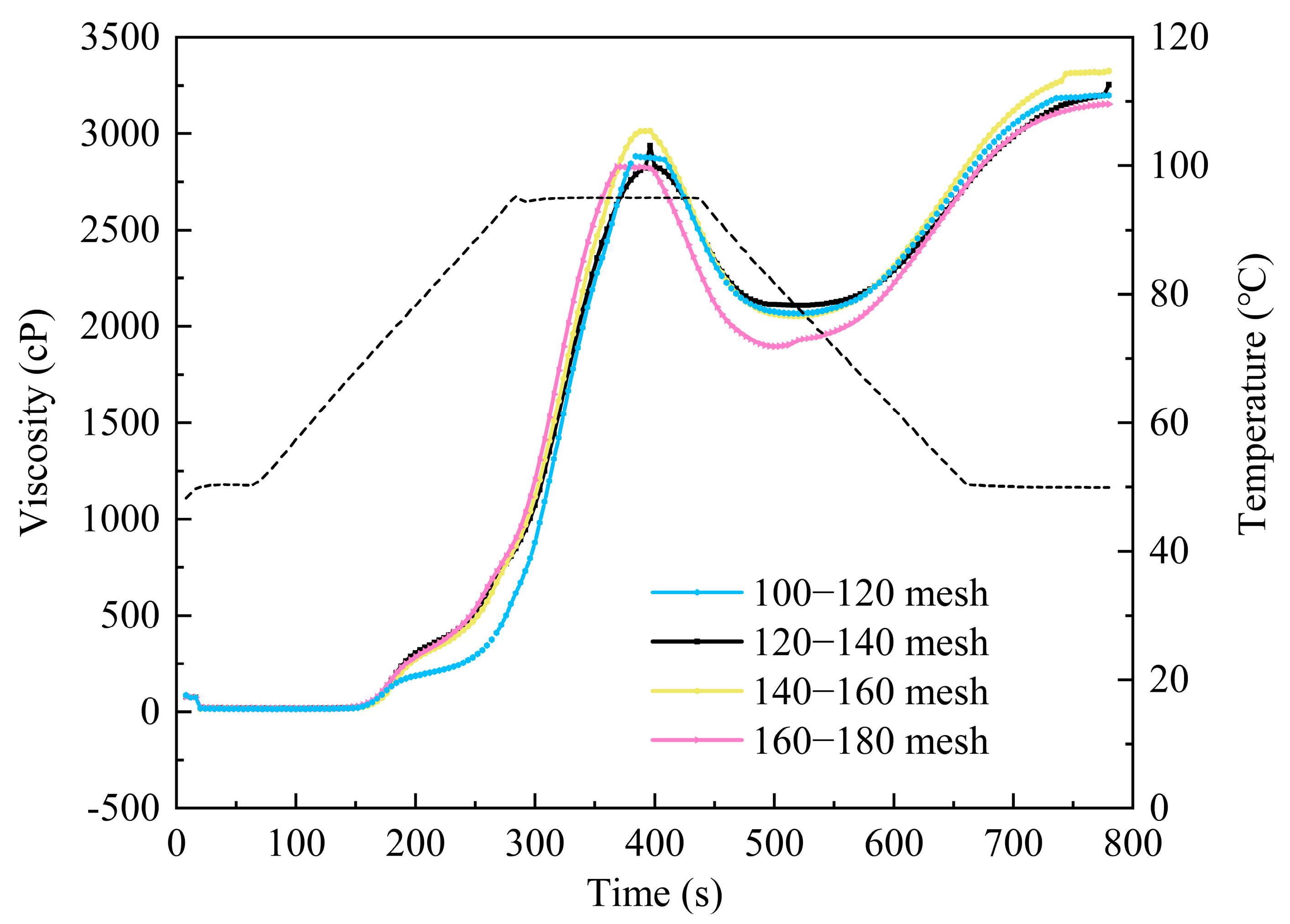
2.3.5. Electrical Conductivity and Pasting Properties
2.4. Rice Cake Preparation
2.5. Rice Cake Characterization
2.5.1. Texture Analysis and Specific Volume
2.5.2. Color Analysis and Sensory Assessment
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Mesh Size on Properties of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.1. Basic Components of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.2. The Flowability of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.3. Solubility and Water Holding Capacity (WHC) of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.4. Emulsifying and Oil-Absorbing Properties of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.5. The Conductivity of Fine Rice Flour
3.1.6. Gelatinizing Properties of Fine Rice Flour
3.2. Effect of Mesh Sizes on the Properties of Rice Cakes
3.2.1. Texture Properties
3.2.2. Specific Volume and Porosity
3.2.3. Color Analysis and Sensory Evaluations
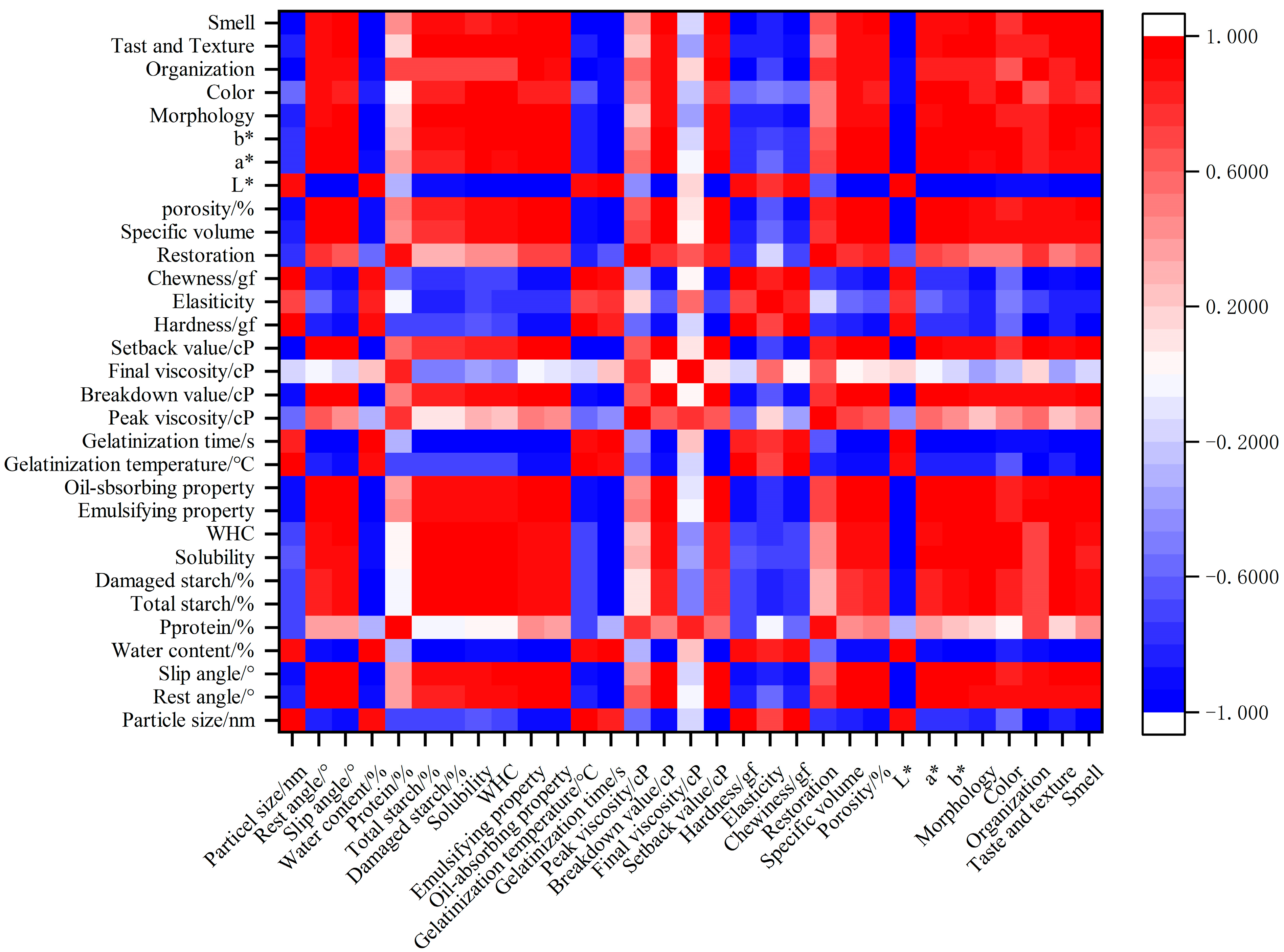
3.2.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardo, A.; Churruca, I.; Lasa, A. Nutritional imbalances in adult celiac patients following a gluten-free diet. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Insight into protein-starch ratio on the gelatinization and retrogradation characteristics of reconstituted rice flour. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, H.Z.; Jiao, Y.; Fei, X.J.; Xu, J.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Shi, L.J. Analysis of processing quality of rice with three different grain shapes within the range of milling. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 28–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, W.Z.; Xiao, H.X.; Tang, Q.; Lin, Q.L.; Han, W.F.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S.G.; Yang, Q.L. Effect of multiple wet heat treatment on the structure and properties of rice starch. J. Chin. Cereals Oils Assoc. 2020, 35, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.L.; Sun, B.Y.; Wang, L.C. Study on optimization of gluten-free rice flour sponge cake process by response surface method. Agric. Prod. Process. 2017, 10, 21–24+29. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Shin, M. Effects of particle size distributions of rice flour on the quality of gluten-free rice cupcakes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Tay, S.H.; Yang, H.S. Replacement of eggs with soybean protein isolates and polysaccharides to prepare yellow cakes suitable for vegetarians. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.Q.; Huang, N.Z.; Teng, J.W. Effects of micro-pulverization on physicochemical properties and functional activity of passion fruit peel fiber powder. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2021, 42, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Y. Effect and Application of Micro-Crushing Synergistic Extrusion Treatment on Oat Bran Characteristics. Master’s Thesis, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, Hohhot, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, M. Size-dependent physicochemical property and functionality of insoluble dietary fiber derived from wheat bran. LWT 2024, 193, 115747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 5009.3-2016; National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China, Determination of Moisture in Foods. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.5-2016; China Food and Drug Administration, Determination of Protein in Foods. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2016.
- GB 5009.9-2023; State Administration for Market Regulation, Determination of Starch in Foods. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Leewatchararongjaroen, J.; Anuntagool, J. Effects of dry-milling and wet-milling on chemical, physical and gelatinization properties of rice flour. Rice Sci. 2016, 23, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Du, F.L.; Zhu, Q.J. Effect of superfine pulverization on properties of Astragalus membranaceus powder. Powder Technol. 2010, 203, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.H.; Dou, B.X. Effects of ultrafine crushing on physical and chemical characteristics of soybean, corn and germinated brown rice. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 45, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Lin, Z.; Wang, A. Influence of damaged starch on the properties of rice flour and quality attributes of gluten-free rice bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Oh, I.; Jeong, S. Particle size effect of rice flour in a rice-zein noodle system for gluten-free noodles slit from sheeted doughs. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 86, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, J.R.; Zhao, Z.L. Insights into Ultrasonication Treatment on the Characteristics of Cereal Proteins: Functionality, Conformational and Physicochemical Characteristics. Foods 2023, 12, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.L.; Wang, Y. Research on recipe of rice cake. Grain Process. 2016, 41, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hasjim, J.; Li, E.; Dhital, S. Milling of rice grains: Effects of starch/flour structures on gelatinization and pasting properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Q.Y.; Liu, Y.M. Effects of rice noodle type and addition amount on cake quality. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2013, 34, 153–156+159. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, N.; Kataoka, T.; Nishiba, Y. Crucial role of amylose in the rising of gluten-and additive-free rice bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 92, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.S.; He, Z.K.; Song, G.W. Determination of DNA by use of the molecular “light switch” complex of Ru(bipy)2(dppz)2+. Microchim. Acta 2000, 134, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.; He, Z.; Song, G. High sensitive determination of DNA by use of molecular “light switch” complex of Ru(phen)2(dppx)2+. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 436, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ji, J.; Yang, L.; Lei, N.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Structural and physicochemical property changes during pyroconversion of native maize starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyakul, S.; Jangchud, K.; Jangchud, A. Effect of extrusion conditions on physical and chemical properties of high protein glutinous rice-based snack. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Chen, L.; Li, L. Konjac Variation of Crystal Structure of Potato Starch in the Process of Micronization Milling. Fine Chem. 2002, 19, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akharume, F.; Santra, D.; Adedeji, A. Physicochemical and functional properties of proso millet storage protein fractions. Food Hydrocolloids 2020, 108, 105497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H. Effect of Extrusion on Starch Properties of Millet. Master’s Thesis, Tianjin University of Commerce, Tianjin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareifard, M.; Ramaswamy, H.; Trigui, M. Ohmic heating behaviour and electrical conductivity of two-phase food systems. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2003, 4, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, L.; Li, Z. Determination of starch gelatinization temperature by ohmic heating. J. Food Eng. 2004, 62, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewicki, P.P. Water as the determinant of food engineering properties. A review. J. Food Eng. 2004, 61, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghinezhad, E.; Khoshtaghaza, M.H.; Suzuki, T. Quantifying the relationship between rice starch gelatinization and moisture-electrical conductivity of paddy during soaking. J. Food Process Eng. 2016, 39, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, E.M.; Martinez, M.G.; Reyes-Vega, M.L. Electrical conductivity and kinetic parameters of rice starch. J. Food Process Eng. 2007, 30, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiwanichsiri, S.; Ohnishi, S.; Suzuki, T. Measurement of electrical conductivity, differential scanning calorimetry and viscosity of starch and flour suspensions during gelatinisation process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2001, 81, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, L.; Gomez, M.; Martinez, M.M. Mesoscale structuring of gluten-free bread with starch. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 38, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J. Insights into the multiscale structure and pasting properties of ball-milled waxy maize and waxy rice starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, M.; Handa, S.; Mridula, D. Physicochemical, functional and rheological properties of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) flour as influenced by particle size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.L. Effect of Peeling Rate on Quality of Wheat Flour, Dough and Steamed Bread. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, Xianyang, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tian, J.Z.; Li, J.J. Study on the effect of grain size of wheat flour on its gelatinization properties. Mod. Flour Milling Ind. 2012, 26, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Lebesi, M.D.; Tzia, C. Effect of the Addition of Different Dietary Fiber and Edible Cereal Bran Sources on the Baking and Sensory Characteristics of Cupcakes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011, 4, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Sohn, H.K.; Yoon, M. Effect of the shape of rice starch granules on flour characteristics and gluten-free bread quality. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burešová, I.; Tokár, M.; Mareček, J. The comparison of the effect of added amaranth, buckwheat, chickpea, corn, millet and quinoa flour on rice dough rheological characteristics, textural and sensory quality of bread. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gao, J.; Jin, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Ying, J.; Zhou, W. Whole-wheat flour particle size influences dough properties, bread structure and in vitro starch digestibility. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3610–3620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, H.; Baranyai, L.; Badak-Kerti, K. Influence of Baking Temperature and Formulation on Physical, Sensorial, and Morphological Properties of Pogácsa Cake: An Image Analysis Study. Foods 2022, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, T.; Rouaud, O.; Jury, V. Bread baking using ohmic heating technology; a comprehensive study based on experiments and modelling. J. Food Eng. 2016, 190, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N. Study on the Structural Properties of Wheat Damaged Starch and the Quality Characteristics of Gluten-Free Model Dough Bread. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]

| Item | Scoring Criteria | Scores |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Neat and full in shape, with a smooth surface and a flat bottom without damage or shrinkage. | 15~20 |
| Relatively neat in shape, with a slight collapse on the top and some minor surface damage. | 10~15 | |
| Irregular in shape, uneven in thickness, with a rough surface, and collapse or shrinkage on the top. | <10 | |
| Color | The surface is light yellow, and the interior is white, with uniform color, exhibiting the characteristic color features of this variety. | 15~20 |
| Color is relatively uniform | 10~15 | |
| Color is not uniform | <10 | |
| Texture | Even fermentation, soft and fine texture, good elasticity, fine and non-grainy powder, no sugar lumps, powder lumps, etc., showing a fine and dense honeycomb-like cross-section. | 15~20 |
| Poor fermentation, coarse texture, with larger air holes, and slightly inferior elasticity. | 10~15 | |
| No fermentation, no elasticity, with sugar lumps, powder lumps, etc. | <10 | |
| Flavor and Taste | Soft and delicious, with a hint of egg aroma, non-sticky, moderate sweetness, with the unique flavor of the rice flour cake, no peculiar flavors, and a light rice aroma. | 15~20 |
| Light egg aroma, slightly hard texture, the unique flavor of rice flour cake is not prominent. | 10~15 | |
| Light egg aroma, poor texture, and the unique flavor of rice flour cake is not prominent. | <10 | |
| Smell | Pure, authentic, and rich in rice flour cake aroma. | 15~20 |
| The aroma is not strong, with a subtle rice flour cake aroma | 10~15 | |
| No cake aroma or presence of off-odors | <10 |
| Components | 100–120 Mesh | 120–140 Mesh | 140–160 Mesh | 160–180 Mesh |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water content (%) | 11.25 ± 0.08 a | 10.61 ± 0.04 b | 10.40 ± 0.11 c | 9.80 ± 0.14 d |
| Protein (%) | 7.52 ± 0.04 a | 7.63 ± 0.12 a | 7.83 ± 0.09 a | 7.21 ± 0.13 a |
| Damaged starch (%) | 18.01 ± 0.04 a | 19.07 ± 0.11 b | 20.08 ± 0.08 c | 26.05 ± 0.12 d |
| Total starch (%) | 74.03 ± 1.53 a | 73.47 ± 2.63 a | 74.37 ± 0.83 a | 74.27 ± 1.83 a |
| D50/μm | 125.30 ± 37.11 a | 103.30 ± 12.52 b | 82.70 ± 11.21 c | 71.60 ± 8.50 d |
| Microscope (×200) | 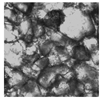 | 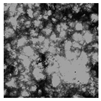 | 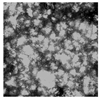 | 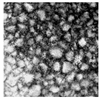 |
| Materials | Mesh Sizes | Moisture Volume Fraction (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | ||
| Rice flour | 100–120 mesh | 98.04 ± 3.51 d | 60.02 ± 1.36 d | 47.19 ± 1.32 c | 42.01 ± 0.01 d | 36.19 ± 0.83 d |
| 120–140 mesh | 99.04 ± 2.47 c | 67.05 ± 1.01 c | 54.09 ± 1.45 b | 46.06 ± 0.59 c | 41.67 ± 0.51 c | |
| 140–160 mesh | 102.03 ± 2.01 b | 70.06 ± 2.57 b | 54.05 ± 0.39 b | 45.06 ± 0.14 b | 40.66 ± 0.83 b | |
| 160–180 mesh | 108.01 ± 3.78 a | 71.13 ± 1.54 a | 56.08 ± 0.93 a | 47.17 ± 0.83 a | 43.04 ± 0.38 a | |
| Rice flour paste | 100–120 mesh | 168.35 ± 4.27 a | 133.21 ± 2.29 a | 116.75 ± 3.51 a | 87.2 ± 1.64 a | 72.01 ± 0.11 a |
| 120–140 mesh | 151.24 ± 4.01 b | 119.23 ± 1.51 b | 89.05 ± 2.82 b | 67.24 ± 1.74 b | 54.66 ± 0.07 b | |
| 140–160 mesh | 143.04 ± 2.76 c | 108.09 ± 1.57 c | 87.04 ± 1.83 c | 63.52 ± 1.83 c | 47.09 ± 1.53 c | |
| 160–180 mesh | 121.2 ± 1.71 d | 91.61 ± 0.35 d | 86.23 ± 1.71 d | 58.02 ± 0.51 d | 43.09 ± 1.71 d | |
| Rice cake batter | 100–120 mesh | 1540.68 ± 11.35 a | 1298.73 ± 7.66 a | 1161.53 ± 6.84 a | 1023.26 ± 10.43 a | 913.81 ± 6.47 a |
| 120–140 mesh | 1494.20 ± 8.44 b | 1281.29 ± 9.47 a | 1115.17 ± 9.25 b | 998.30 ± 8.45 b | 880.35 ± 7.79 b | |
| 140–160 mesh | 1525.45 ± 12.14 a | 1342.04 ± 11.35 b | 1144.33 ± 8.73 a | 1004.21 ± 7.62 c | 905.68 ± 6.88 a | |
| 160–180 mesh | 1522.37 ± 13.87 a | 1334.21 ± 10.92 b | 1163.46 ± 9.46 a | 1023.36 ± 11.25 a | 924.53 ± 7.57 a | |
| Sample | Gelatinization Temperature/ °C | Gelatinization Time/ s | Peak Viscosity/ cP | Breakdown Value/ cP | Final Viscosity/ cP | Setback Value/ cP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100–120 mesh | 76.63 ± 0.51 a | 6.6 ± 0.15 a | 2937 ± 50.61 a | 71.8 ± 0.26 a | 3254 ± 32.74 a | 1089 ± 15.84 a |
| 120–140 mesh | 72.61 ± 0.28 b | 6.53 ± 0.39 b | 3013 ± 48.01 b | 82.6 ± 0.41 b | 3325 ± 42.12 b | 1188 ± 36.73 b |
| 140–160 mesh | 71.8 ± 0.64 c | 6.47 ± 0.23 c | 3343 ± 49.32 c | 96.1 ± 0.42 c | 3427 ± 39.01 c | 1257 ± 26.81 c |
| 160–180 mesh | 71.61 ± 0.24 d | 6.4 ± 0.57 d | 3027 ± 38.21 d | 98.8 ± 0.27 d | 3166 ± 32.27 d | 1273 ± 37.74 d |
| Sample | Hardness/gf | Elasticity | Chewiness/gf | Restoration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100–120 mesh | 480.11 ± 12.36 a | 0.48 ± 0.01 a | 297.28 ± 13.21 a | 0.33 ± 0.01 b |
| 120–140 mesh | 349.77 ± 10.22 b | 0.51 ± 0.02 c | 217.194 ± 12.03 b | 0.35 ± 0.02 c |
| 140–160 mesh | 336.44 ± 13.38 c | 0.55 ± 0.02 b | 219.70 ± 9.42 b | 0.38 ± 0.01 a |
| 160–180 mesh | 324.91 ± 6.38 d | 0.57 ± 0.01 d | 195.01 ± 4.01 d | 0.38 ± 0.01 c |
| Samples | 100–120 Mesh | 120–140 Mesh | 140–160 Mesh | 160–180 Mesh |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice cake sectional view and black–white analytical view | 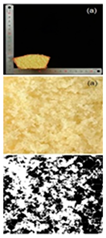 | 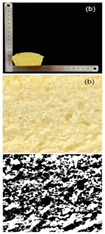 |  | 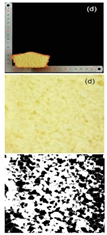 |
| Specific volume (mL/g) | 1.38 ± 0.03 d | 1.51 ± 0.02 c | 1.79 ± 0.01 b | 1.81 ± 0.01 a |
| Porosity (%) | 4.82 ± 0.11 d | 5.34 ± 0.08 c | 5.94 ± 0.02 b | 6.03 ± 0.12 a |
| Pore number | 152 ± 2.00 d | 191 ± 1.00 c | 214 ± 2.00 b | 247 ± 1.00 a |
| Total pore area/um2 | 6558.866 ± 435.86 d | 7123.926 ± 456.86 c | 8170.297 ± 367.15 b | 8593.641 ± 378.74 a |
| Pore area ratio/% | 4.938 ± 0.01 d | 5.494 ± 0.01 c | 6.139 ± 0.01 b | 6.641 ± 0.01 a |
| L* | a* | b* | h (°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice cake surface | ||||
| 100–120 mesh | 78.03 ± 1.41 a | 3.32 ± 1.34 d | 31.23 ± 0.31 d | 83.93 ± 1.01 a |
| 120–140 mesh | 74.80 ± 1.72 b | 4.69 ± 1.96 c | 33.04 ± 0.69 c | 81.92 ± 0.56 b |
| 140–160 mesh | 72.22 ± 2.31 c | 8.99 ± 2.06 b | 37.92 ± 0.82 b | 76.66 ± 0.32 c |
| 160–180 mesh | 69.32 ± 1.36 d | 10.08 ± 1.37 a | 40.98 ± 0.37 a | 76.18 ± 1.78 c |
| Rice cake core | ||||
| 100–120 mesh | 77.43 ± 0.47 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 d | 22.77 ± 0.01 d | 89.32 ± 1.29 a |
| 120–140 mesh | 73.59 ± 0.47 b | 0.34 ± 0.01 c | 24.31 ± 0.21 c | 89.20 ± 0.57 a |
| 140–160 mesh | 71.91 ± 0.41 c | 0.74 ± 0.01 b | 25.53 ± 0.07 b | 88.34 ± 2.38 b |
| 160–180 mesh | 67.17 ± 0.72 d | 2.79 ± 0.01 a | 32.31 ± 0.01 a | 85.06 ± 2.91 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, M.; Yang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Chen, F.; Hao, Y. Study on the Characteristics of Fine Rice Flour by Micro-Crushing and Its Effects on the Quality Improvement of Rice Cakes. Foods 2024, 13, 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223565
Lu M, Yang W, Zhang H, Yu Y, Chen F, Hao Y. Study on the Characteristics of Fine Rice Flour by Micro-Crushing and Its Effects on the Quality Improvement of Rice Cakes. Foods. 2024; 13(22):3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223565
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Mingshou, Wanshan Yang, Huining Zhang, Yang Yu, Fenglian Chen, and Yanling Hao. 2024. "Study on the Characteristics of Fine Rice Flour by Micro-Crushing and Its Effects on the Quality Improvement of Rice Cakes" Foods 13, no. 22: 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223565
APA StyleLu, M., Yang, W., Zhang, H., Yu, Y., Chen, F., & Hao, Y. (2024). Study on the Characteristics of Fine Rice Flour by Micro-Crushing and Its Effects on the Quality Improvement of Rice Cakes. Foods, 13(22), 3565. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223565







