Influence of Roasting Temperature on the Detectability of Potentially Allergenic Lupin by SDS-PAGE, ELISAs, LC-MS/MS, and Real-Time PCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Protein Analysis
2.2.1. Sample Preparation for SDS-PAGE and ELISAs
2.2.2. SDS-PAGE
2.2.3. ELISAs
2.2.4. Sample Preparation for LC-MS/MS
2.2.5. LC-MS/MS
2.3. DNA Analysis
2.3.1. Sample Preparation for Real-Time PCR
2.3.2. Real-Time PCR Assay for Lupin
2.3.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Protein Analysis
3.1.1. Protein Extraction
3.1.2. SDS-PAGE
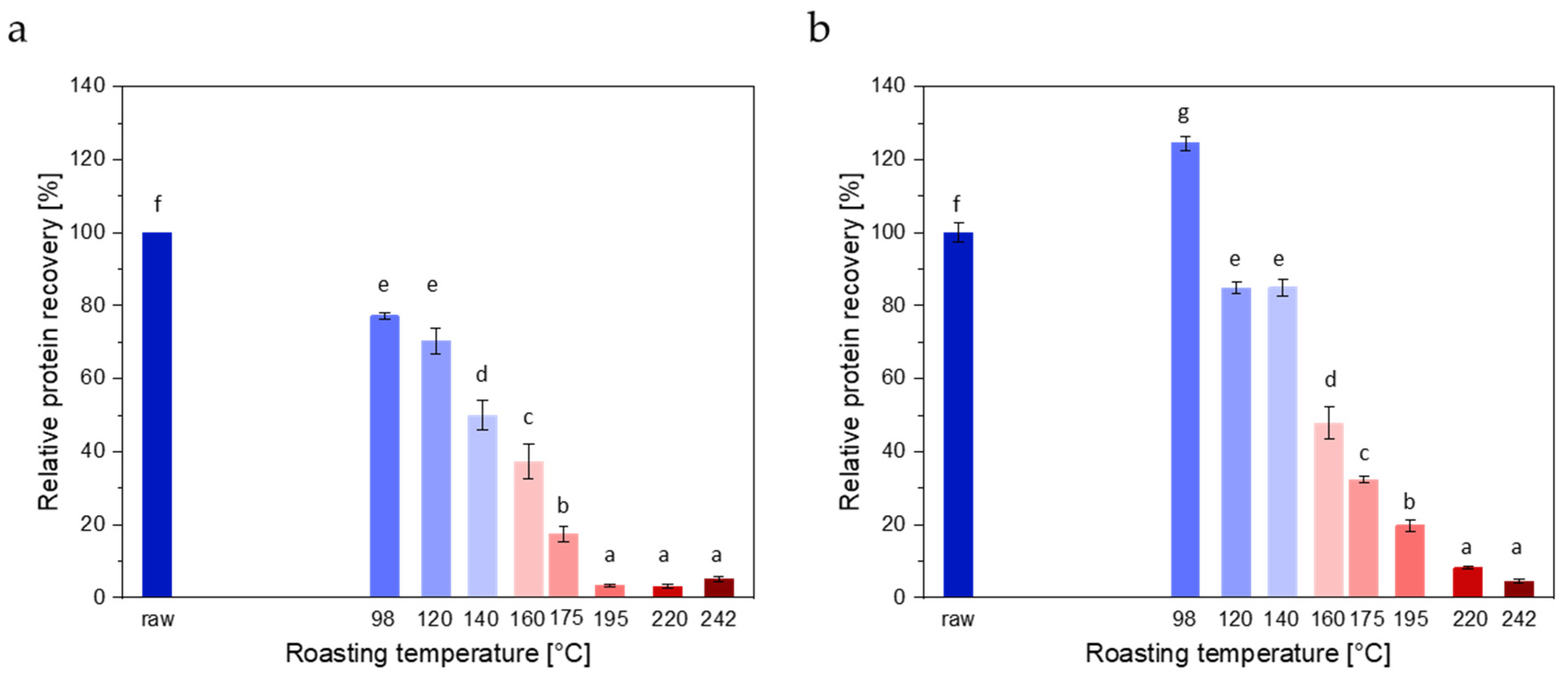
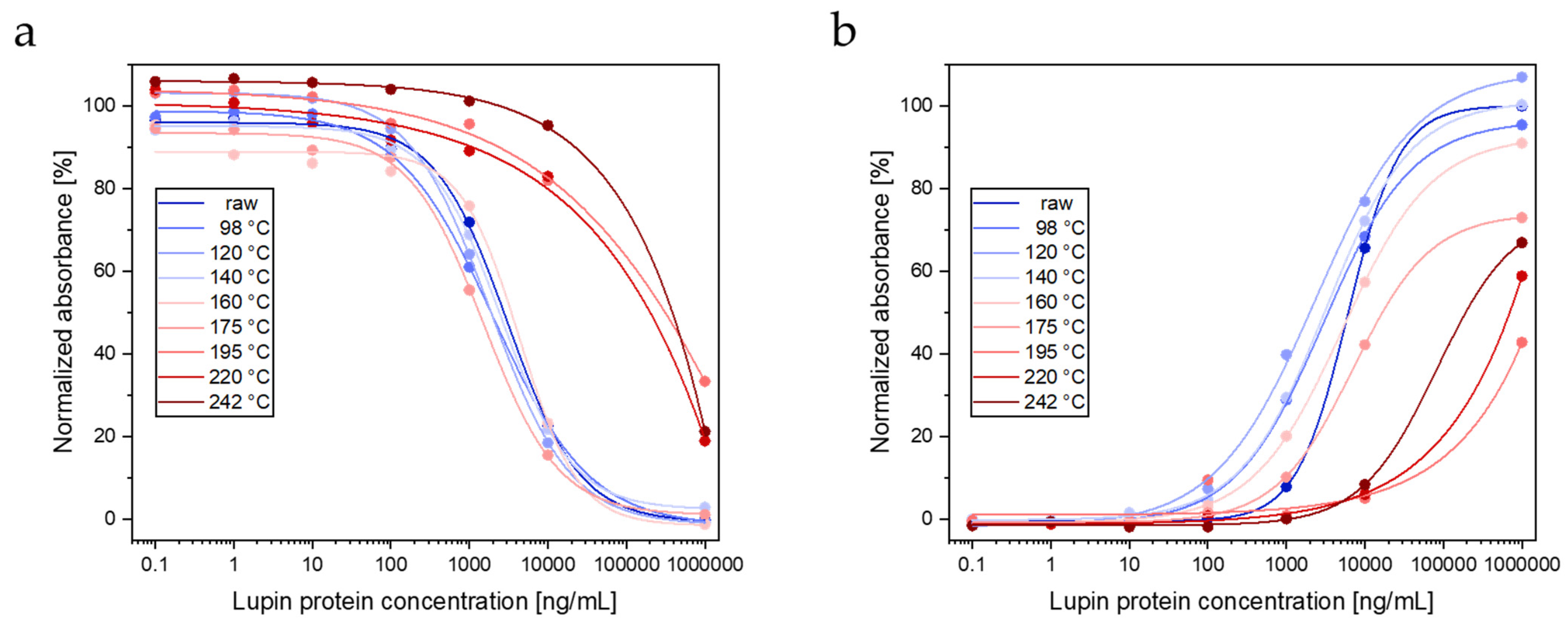
3.1.3. ELISAs
3.1.4. LC-MS/MS
3.2. DNA Analysis
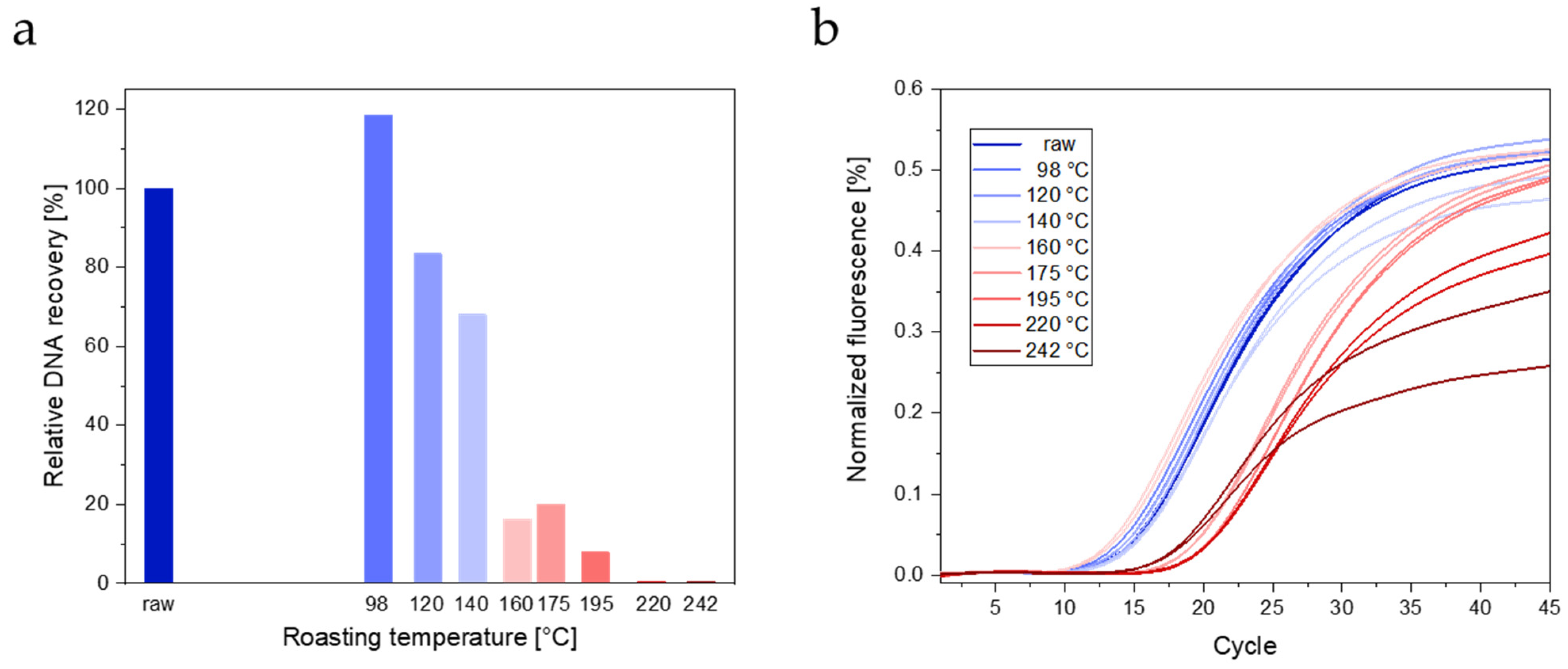
3.2.1. DNA Extraction
3.2.2. Real-Time PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alcorta, A.; Porta, A.; Tárrega, A.; Alvarez, M.D.; Vaquero, M.P. Foods for plant-based diets: Challenges and innovations. Foods 2021, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Qureshi, S.; Akbar, M.H.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Gani, A.; Mushtaq, M.; Hassan, I.; Dhull, S.B. Plant-based meat alternatives: Compositional analysis, current development and challenges. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Lopez, J.C.; Foley, R.C.; Brear, E.; Clarke, V.C.; Lima-Cabello, E.; Florido, J.F.; Singh, K.B.; Alché, J.D.; Smith, P.M.C. Characterization of narrow-leaf lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) recombinant major allergen IgE-binding proteins and the natural β-conglutin counterparts in sweet lupin seed species. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemus-Conejo, A.; Rivero-Pino, F.; Montserrat-de la Paz, S.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Nutritional composition and biological activity of narrow-leafed lupins (Lupinus angustifolius L.) hydrolysates and seeds. Food Chem. 2023, 420, 136104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukid, F.; Pasqualone, A. Lupine (Lupinus spp.) proteins: Characteristics, safety and food applications. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2022, 248, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bähr, M.; Fechner, A.; Kiehntopf, M.; Jahreis, G. Consuming a mixed diet enriched with lupin protein beneficially affects plasma lipids in hypercholesterolemic subjects: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, R.F.; García Pérez, R.; González Díaz, A.; Liñán González, A. Therapeutic Applications and Effects of Lupinus angustifolius (Blue Lupin) and Its Components: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Foods 2023, 12, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Lopez, J.C. Narrow-leafed lupin (Lupinus angustifolius L.) β-conglutin: A multifunctional family of proteins with roles in plant defence, human health benefits, and potential uses as functional food. Legume Sci. 2020, 2, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarino, C.B.J.; Jayasena, V.; Coorey, R.; Chakrabarti-Bell, S.; Johnson, S.K. Nutritional, Health, and Technological Functionality of Lupin Flour Addition to Bread and Other Baked Products: Benefits and Challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 835–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Hag, L.V.; Haritos, V.S.; Dhital, S. Lupin proteins: Structure, isolation and application. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krois. Available online: https://steirerkaffee.at/ (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Peeters, K.A.B.M.; Nordlee, J.A.; Penninks, A.H.; Chen, L.; Goodman, R.E.; Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C.A.F.M.; Hefle, S.L.; Taylor, S.L.; Knulst, A.C. Lupine allergy: Not simply cross-reactivity with peanut or soy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 120, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamón, E.; Rodríguez, J.; Burbano, C.; Muzquiz, M.; Pedrosa, M.M.; Cabanillas, B.; Crespo, J.F.; Sancho, A.I.; Mills, E.N.C.; Cuadrado, C. Characterization of lupin major allergens (Lupinus albus L.). Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 1668–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Jappe, U.; Novak, N. Allergy to Peanut, Soybean, and Other Legumes: Recent Advances in Allergen Characterization, Stability to Processing and IgE Cross-Reactivity. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappe, U.; Vieths, S. Lupine, a source of new as well as hidden food allergens. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jappe, U.; Karstedt, A.; Warneke, D.; Hellmig, S.; Böttger, M.; Riffelmann, F.W.; Treudler, R.; Lange, L.; Abraham, S.; Dölle-Bierke, S.; et al. Identification and purification of novel low-molecular-weight lupine allergens as components for personalized diagnostics. Nutrients 2021, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duranti, M.; Consonni, A.; Magni, C.; Sessa, F.; Scarafoni, A. The major proteins of lupin seed: Characterisation and molecular properties for use as functional and nutraceutical ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I. Lupine allergens: Clinical relevance, molecular characterization, cross-reactivity, and detection strategies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 3886–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO/IUIS. Available online: http://allergen.org/index.php (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Aguilera-Insunza, R.; Iturriaga, C.; Mariñanco, A.; Venegas, L.; Aravena, G.; Perez-Mateluna, G.; Baptista-Dias, N.; Borzutzky, A.; Wandersleben, T. High prevalence of lupin allergy among patients with peanut allergy: Identification of γ-conglutin as major allergen. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023, 130, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers, amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2011:304:0018:0063:en:PDF (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Holden, L.; Fæste, C.K.; Egaas, E. Quantitative sandwich ELISA for the determination of lupine (Lupinus spp.) in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5866–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, L.; Moen, L.H.; Sletten, G.B.G.; Dooper, M.M.B.W. Novel polyclonal-monoclonal-based ELISA utilized to examine lupine (Lupinus species) content in food products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaw, C.H.; Hefle, S.L.; Taylor, S.L. Sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of lupine residues in foods. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, T135–T140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, C.; Ertl, A.; Cichna-Markl, M. Development and Validation of Two Competitive ELISAs for the Detection of Potentially Allergenic Lupine (Lupinus Species) in Food. Food Anal. Methods 2013, 6, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, C.; Cichna-Markl, M. Development and validation of a sandwich ELISA for the determination of potentially allergenic lupine in food. Food Chem. 2012, 130, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Cabello, E.; Alché, J.D.; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C. Narrow-leafed lupin main allergen β-conglutin (Lup an 1) detection and quantification assessment in natural and processed foods. Foods 2019, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmel, A.; Hupfer, C.; Hampe, E.I.; Busch, U.; Engel, K.H. Development of a real-time PCR for the detection of lupine DNA (Lupinus species) in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4328–4332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarafoni, A.; Ronchi, A.; Duranti, M. A real-time PCR method for the detection and quantification of lupin flour in wheat flour-based matrices. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, A.M.G.; Brohée, M.; De Andrade Silva, E.; Van Hengel, A.J.; Chassaigne, H. Development of a real-time PCR method for the simultaneous detection of soya and lupin mitochondrial DNA as markers for the presence of allergens in processed food. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, B.; Münch, S.; Schwägele, F.; Neusüß, C.; Jira, W. A sensitive HPLC-MS/MS screening method for the simultaneous detection of lupine, pea, and soy proteins in meat products. Food Control 2017, 71, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, L.S.; Schreiber, A.; Stahl-Zeng, J.; Liu, H.F. Simultaneous analysis of multiple allergens in food products by LC-MS/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.H.; Khuda, S.E.; Pereira, M.; Ross, M.M.; Fu, T.J.; Fan, X.; Wu, Y.; Williams, K.M.; DeVries, J.; Pulvermacher, B.; et al. Multi-allergen Quantitation and the Impact of Thermal Treatment in Industry-Processed Baked Goods by ELISA and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10669–10680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Álvarez, J.; Guillamón, E.; Crespo, J.F.; Cuadrado, C.; Burbano, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Fernández, C.; Muzquiz, M. Effects of extrusion, boiling, autoclaving, and microwave heating on lupine allergenicity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capraro, J.; Magni, C.; Fontanesi, M.; Budelli, A.; Duranti, M. Application of two-dimensional electrophoresis to industrial process analysis of proteins in lupin-based pasta. LWT 2008, 41, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, C.; Moura, M.B.M.V.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I. Immunoreactivity of lupine and soybean allergens in foods as affected by thermal processing. Foods 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirtori, E.; Resta, D.; Brambilla, F.; Zacherl, C.; Arnoldi, A. The effects of various processing conditions on a protein isolate from Lupinus angustifolius. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmel, A.; Hupfer, C.; Busch, U.; Engel, K.H. Detection of lupine (Lupinus spp.) DNA in processed foods using real-time PCR. Food Control 2011, 22, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrottin, J.; Pilolli, R.; Huet, A.C.; van Poucke, C.; Nitride, C.; De Loose, M.; Tranquet, O.; Larré, C.; Adel-Patient, K.; Bernard, H.; et al. Optimization of a sample preparation workflow based on UHPLC-MS/MS method for multi-allergen detection in chocolate: An outcome of the ThRAll project. Food Control 2023, 143, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisslitz, S.; Islam, S.; Buck, L.; Grunwald-Gruber, C.; Sestili, F.; Camerlengo, F.; Masci, S.; D’Amico, S. Absolute and relative quantitation of amylase/trypsin-inhibitors by LC-MS/MS from wheat lines obtained by CRISPR-Cas9 and RNAi. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 974881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Xia, B.; Hu, L.T.; Ni, Z.J.; Thakur, K.; Wei, Z.J. Maillard conjugates and their potential in food and nutritional industries: A review. Food Front. 2020, 1, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzli, I.; Weiss, J.; Gibis, M. Glycation of plant proteins via Maillard reaction: Reaction chemistry, technofunctional properties, and potential food application. Foods 2021, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.R. Melanoidins produced by the Maillard reaction: Structure and biological activity. Food Chem 2011, 128, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, C.R.; Kwofie, E.M.; Adewale, P.; Lam, E.; Ngadi, M. Advances in legume protein extraction technologies: A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 82, 103199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y. Effects of ultrasonic treatment on the structural and functional properties of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) seed protein. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 97, 106465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, E.E.; Gökmen, V. Formation of Maillard reaction products in bread crust-like model system made of different whole cereal flours. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casal, S.; Mendes, E.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Ferreira, M.A. Roast effects on coffee amino acid enantiomers. Food Chem. 2005, 89, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, R.C.; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C.; Kamphuis, L.G.; Hane, J.K.; Melser, S.; Singh, K.B. Analysis of conglutin seed storage proteins across lupin species using transcriptomic, protein and comparative genomic approaches. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weder, J.K.P.; Sohns, S. Model studies on the heating of food proteins—Amino acid composition of lysozyme, ribonuclease and insulin after dry heating. Z. Lebensm. Unters. Forsch. 1983, 176, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tal, M.; Silberstein, A.; Nusser, E. Why does Coomassie Brilliant Blue R interact differently with different proteins? A partial answer. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 9976–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasian, A.; Juhász, A.; Broadbent, J.A.; Nye-Wood, M.G.; Le, T.T.; Colgrave, M.L. Evaluation of the Major Seed Storage Proteins, the Conglutins, Across Genetically Diverse Narrow-Leafed Lupin Varieties. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 842168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downs, M.L.; Baumert, J.L.; Taylor, S.L.; Mills, E.N.C. Mass spectrometric analysis of allergens in roasted walnuts. J. Proteom. 2016, 142, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, R.; Oberleitner, D.; Brockmeyer, J. Determination of food allergens by LC-MS: Impacts of sample preparation, food matrix, and thermal processing on peptide detectability and quantification. J. Proteom. 2019, 196, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, I.M.; Muth, C.; Drumm, R.; Kirchner, H.O.K. Thermal decomposition of the amino acids glycine, cysteine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, glutamine, arginine and histidine. BMC Biophys. 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima-Cabello, E.; Robles-Bolivar, P.; Alché, J.D.; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C. Narrow Leafed Lupin Beta-Conglutin Proteins Epitopes Identification and Molecular Features Analysis Involved in Cross-Allergenicity to Peanut and Other Legumes. Genom. Comput. Biol. 2023, 2, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yang, F.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lv, H.; Ji, X.; et al. Selection of specific nanobodies against lupine allergen Lup an 1 for immunoassay development. Foods 2021, 10, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beyer, B.; Obrist, D.; Czarda, P.; Pühringer, K.; Vymyslicky, F.; Siegmund, B.; D’Amico, S.; Cichna-Markl, M. Influence of Roasting Temperature on the Detectability of Potentially Allergenic Lupin by SDS-PAGE, ELISAs, LC-MS/MS, and Real-Time PCR. Foods 2024, 13, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050673
Beyer B, Obrist D, Czarda P, Pühringer K, Vymyslicky F, Siegmund B, D’Amico S, Cichna-Markl M. Influence of Roasting Temperature on the Detectability of Potentially Allergenic Lupin by SDS-PAGE, ELISAs, LC-MS/MS, and Real-Time PCR. Foods. 2024; 13(5):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050673
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeyer, Bruno, Dominik Obrist, Philipp Czarda, Katharina Pühringer, Filip Vymyslicky, Barbara Siegmund, Stefano D’Amico, and Margit Cichna-Markl. 2024. "Influence of Roasting Temperature on the Detectability of Potentially Allergenic Lupin by SDS-PAGE, ELISAs, LC-MS/MS, and Real-Time PCR" Foods 13, no. 5: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050673
APA StyleBeyer, B., Obrist, D., Czarda, P., Pühringer, K., Vymyslicky, F., Siegmund, B., D’Amico, S., & Cichna-Markl, M. (2024). Influence of Roasting Temperature on the Detectability of Potentially Allergenic Lupin by SDS-PAGE, ELISAs, LC-MS/MS, and Real-Time PCR. Foods, 13(5), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13050673





