Quality of Refrigerated Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Subjected to High-Pressure Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Microbial Media
2.2. Preparation of Mint Extract and Time-Kill Profile Study
2.3. Inactivation of Planktonic Cells by High-Pressure Processing
2.4. Preparation of Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Combined with HPP
2.5. Analyses
2.5.1. Microbial Analysis
2.5.2. Chemical Analysis
- Total Volatile Base (TVB) and Trimethylamine (TMA) Contents
- pH Value
- Peroxide Value (PV) and Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
2.5.3. Weight Loss and Cooking Loss
2.5.4. Texture Analysis
2.5.5. Sensory Evaluation
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time-Kill Profile of ME against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Shewanella spp.
3.2. Inactivation of Planktonic Cells by HPP
3.3. Quality Changes of Squid Mantle Cut Treated with ME and HPP during Refrigerated Storage
3.3.1. Microbiological Changes
3.3.2. Total Volatile Base (TVB) and Trimethylamine (TMA) Contents
3.3.3. pH
3.3.4. PV and TBARS Value
3.3.5. Weight and Cooking Losses
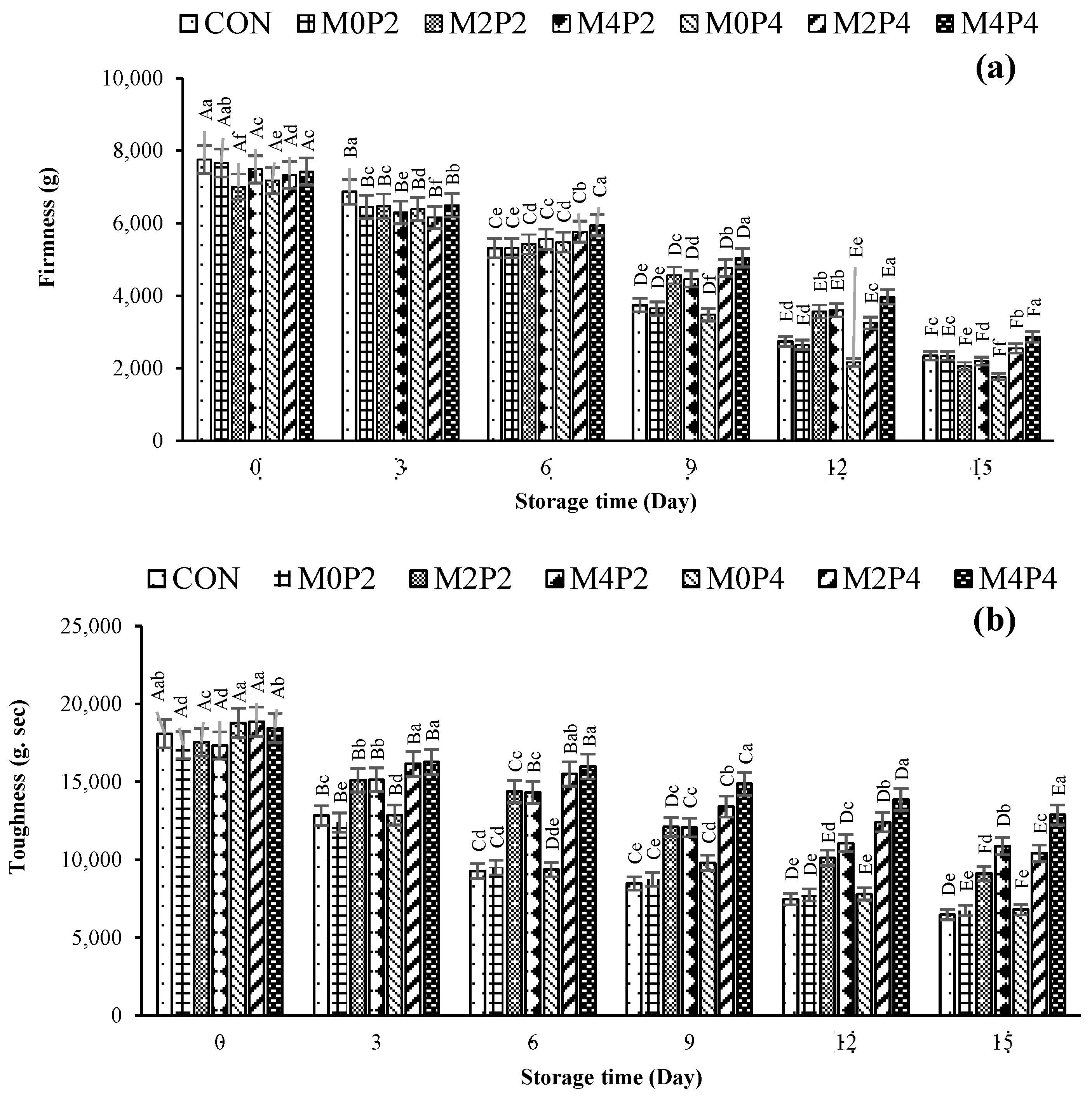
3.3.6. Textural Property
3.3.7. Sensorial Property
3.4. Microbial Community in SMC and the Selected ME and HPP-Treated SMC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Alba, M.; Pérez-Andrés, J.M.; Harrison, S.M.; Brunton, N.P.; Burgess, C.M.; Tiwari, B.K. High pressure processing on microbial inactivation, quality parameters and nutritional quality indices of mackerel fillets. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 55, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roobab, U.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Arshad, R.N.; Khan, A.W.; Zeng, X.-A.; Bhat, Z.F.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Batool, Z.; Aadil, R.M. High-pressure processing of fish and shellfish products: Safety, quality, and research prospects. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3297–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romulo, A. The impact of high pressure processing treatment on microbial inactivation of seafood—A review. Food Res. 2021, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rode, T.M.; Hovda, M.B. High pressure processing extend the shelf life of fresh salmon, cod and mackerel. Food Control 2016, 70, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, F.; Simonin, H.; Guyon, C.; Jung, S.; de Lamballerie, M. Chapter 3—High-pressure processing of meats and seafood. In Emerging Technologies for Food Processing, 2nd ed.; Sun, D.-W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 35–63. [Google Scholar]
- Grossi, A.; Bolumar, T.; Søltoft-Jensen, J.; Orlien, V. High pressure treatment of brine enhanced pork semitendinosus: Effect on microbial stability, drip loss, lipid and protein oxidation, and sensory properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, J.; Lee, H.-Y.; Ahn, J. Effect of high pressure processing on the quality of squid (Todarodes pacificus) during refrigerated storage. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, M.; Maqsood, S.; Siliveru, K. Emerging non-thermal technology applications for sustainable food processing. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1190320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Huang, H.-W.; Hsu, C.-P.; Yang, B.B. Recent advances in food processing using high hydrostatic pressure technology. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. Antibacterial mechanism of lactobionic acid against Shewanella baltica and Shewanella putrefaciens and its application on refrigerated shrimp. Food Biosci. 2023, 51, 102291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cebrino, F.; Durán, R.; Delgado-Adámez, J.; Contador, R.; Ramírez, R. Changes after high-pressure processing on physicochemical parameters, bioactive compounds, and polyphenol oxidase activity of red flesh and peel plum purée. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hygreeva, D.; Pandey, M.C. Novel approaches in improving the quality and safety aspects of processed meat products through high pressure processing technology—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, X. High-pressure processing as emergent technology for the extraction of bioactive ingredients from plant materials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naher, J.; Nilsuwan, K.; Palamae, S.; Hong, H.; Zhang, B.; Osako, K.; Benjakul, S. Ethanolic extracts from mint (Mentha arvensis) and basil (Ocimum basilicum) leaves: Antioxidant, antimicrobial capacities and shelf-life extension of refrigerated squid mantle cut. Int. Aquat. Res. 2023, 15, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Mittal, A.; Buatong, J.; Zhang, B.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Chitooligosaccharide-catechin conjugate: Antimicrobial mechanisms toward Vibrio parahaemolyticus and its use in shucked Asian green mussel. Food Control 2023, 151, 109794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Zhang, B.; Visessanguan, W.; Benjakul, S. Chitooligosaccharide conjugates prepared using several phenolic compounds via ascorbic acid/H2O2 free radical grafting: Characteristics, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antimicrobial activities. Foods 2022, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamae, S.; Temdee, W.; Buatong, J.; Suyapoh, W.; Sornying, P.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Benjakul, S. Use of high pressure processing in combination with acidic electrolyzed water depuration for the shelf-life extension of blood clam (Tegillarca granosa). Food Control 2024, 156, 110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temdee, W.; Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. Rapid quality deterioration of harpiosquillid mantis shrimp (Harpiosquilla raphidea) during iced storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmal, N.P.; Benjakul, S. Retardation of quality changes of Pacific white shrimp by green tea extract treatment and modified atmosphere packaging during refrigerated storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilgaard, M.C.; Carr, B.T.; Civille, G.V. Sensory Evaluation Techniques; CRC press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chayanupatkul, M.; Somanawat, K.; Chuaypen, N.; Klaikeaw, N.; Wanpiyarat, N.; Siriviriyakul, P.; Tumwasorn, S.; Werawatganon, D. Probiotics and their beneficial effects on alcohol-induced liver injury in a rat model: The role of fecal microbiota. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2022, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogana, R.; Adhikari, A.; Tzar, M.N.; Ramliza, R.; Wiart, C. Antibacterial activities of the extracts, fractions and isolated compounds from Canarium patentinervium Miq. against bacterial clinical isolates. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehrawat, R.; Kaur, B.P.; Nema, P.K.; Tewari, S.; Kumar, L. Microbial inactivation by high pressure processing: Principle, mechanism and factors responsible. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K. Cold plasma combined with liposomal ethanolic coconut husk extract: A potential hurdle technology for shelf-life extension of Asian sea bass slices packaged under modified atmosphere. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 65, 102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefzi, K.; Ben Jemaa, M.; Baraket, M.; Dakhlaoui, S.; Msaada, K.; Nasr, Z. In vitro antioxidant, antibacterial and mechanisms of action of ethanolic extracts of five Tunisian plants against bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolak, H.; Czyżowska, A.; Kręgiel, D. Activity of Mentha piperita L. ethanol extract against acetic acid bacteria Asaia spp. Foods 2018, 7, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayebah, B.; Hung, Y.-C.; Kim, C.; Frank, J.F. Efficacy of electrolyzed water in the inactivation of planktonic and biofilm Listeria monocytogenes in the presence of organic matter. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2143–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.-W.; Chen, Y.-A.; Chang, H.-Y.; Huang, T.-C.; Chen, T.-Y. Combined impact of high-pressure processing and slightly acidic electrolysed water on Listeria monocytogenes proteomes. Food Res. Int. 2021, 147, 110494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathanasriwong, K.; Wannawisarn, N.; Pratheepthinthong, S.; Sane, A.; Suppakul, P. Development of a novel Mohr’s salt-based indicator for monitoring sea bass (Lates calcarifer) fillet spoilage in chilled storage. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2020, 54, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Marques, A.; Mendes, R.; Gonçalves, A.; Fidalgo, L.; Oliveira, M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Effects of high-pressure processing on the quality of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets during refrigerated storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Rao, L.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liao, X. High pressure processing combined with selected hurdles: Enhancement in the inactivation of vegetative microorganisms. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1800–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisés, S.G.; Guamis, B.; Roig-Sagués, A.X.; Codina-Torrella, I.; Hernández-Herrero, M.M. Effect of ultra-high-pressure homogenization processing on the microbiological, physicochemical, and sensory characteristics of fish broth. Foods 2022, 11, 3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lan, W.; Sun, X. Effect of chlorogenic acid grafted chitosan on microbiological compositions of sea bass (Lateolabrax japonicus) fillets: Dominant spoilage bacteria, inhibition activity and membrane damage mechanisms. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 411, 110540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basaran-Akgul, N.; Mousavi-Hesary, M.; Basaran, P.; Shin, J.H.; Swanson, B.G.; Rasco, B.A. High pressure processing inactivation of listeria innocua in minced trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2010, 34, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, M.; Grèbol, N.; Aymerich, M.T.; Monfort, J.M.; Hugas, M. Microbial inactivation after high-pressure processing at 600 MPa in commercial meat products over its shelf life. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2004, 5, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margesin, R. Effect of temperature on growth parameters of psychrophilic bacteria and yeasts. Extremophiles 2009, 13, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gram, L.; Huss, H.H. Microbiological spoilage of fish and fish products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 33, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Michailidou, S.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Sakellariou, A.K.; Pasentsis, K.; Psomopoulos, F.; Argiriou, A.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Boziaris, I.S. Microbial spoilage investigation of thawed common cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) stored at 2 °C using next generation sequencing and volatilome analysis. Food Microbiol. 2018, 76, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaz-Pires, P.; Seixas, P.; Mota, M.; Lapa-Guimarães, J.; Pickova, J.; Lindo, A.; Silva, T. Sensory, microbiological, physical and chemical properties of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) and broadtail shortfin squid (Illex coindetii) stored in ice. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paarup, T.; Sanchez, J.A.; Peláez, C.; Moral, A. Sensory, chemical and bacteriological changes in vacuum-packed pressurised squid mantle (Todaropsis eblanae) stored at 4 °C. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletzer, D.; Blimkie Travis, M.; Wolfmeier, H.; Li, Y.; Baghela, A.; Lee Amy, H.Y.; Falsafi, R.; Hancock Robert, E.W. The stringent stress response controls proteases and global regulators under optimal growth conditions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mSystems 2020, 5, 1110–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aganovic, K.; Hertel, C.; Vogel, R.F.; Johne, R.; Schlüter, O.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Jäger, H.; Holzhauser, T.; Bergmair, J.; Roth, A.; et al. Aspects of high hydrostatic pressure food processing: Perspectives on technology and food safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3225–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.L.G.; Rosário, D.K.A.; Torres Neto, L.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Exploring high hydrostatic pressure for enhancing the preservation of white and dark muscle fish fillets stored at different packaging systems under refrigeration. Food Control 2024, 155, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Burke, C.M.; Bolch, C.J.S.; Stanley, R. Evaluation of spoilage potential and volatile metabolites production by Shewanella baltica isolated from modified atmosphere packaged live mussels. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsironi, T.; Anjos, L.; Pinto, P.I.S.; Dimopoulos, G.; Santos, S.; Santa, C.; Manadas, B.; Canario, A.; Taoukis, P.; Power, D. High pressure processing of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets and tools for flesh quality and shelf life monitoring. J. Food Eng. 2019, 262, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Romero, M.; Kelly, A.L.; Kerry, J.P. Effects of high-pressure treatment on the microflora of oysters (Crassostrea gigas) during chilled storage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2008, 9, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diachkova, A.; Tikhonov, S.; Tikhonova, N. The effect of high pressure processing on the shelf life of chilled meat and fish. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2019, 8, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, T.M.; Rotabakk, B.T. Extending shelf life of desalted cod by high pressure processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 69, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Zhou, M.; Qiao, Y.; Xiong, G.; Wei, L.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Shi, L.; Ding, A.; Li, X. Effects of ozone water combined with ultra-high pressure on quality and microorganism of catfish fillets (Lctalurus punctatus) during refrigeration. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 880370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Mechanisms of fish protein degradation caused by grass carp spoilage bacteria: A bottom-up exploration from the molecular level, muscle microstructure level, to related quality changes. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.L.G.; Mársico, E.T.; Mano, S.B.; da Silveira Alvares, T.; Rosenthal, A.; Lemos, M.; Ferrari, E.; Lázaro, C.A.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Combined effect of high hydrostatic pressure and ultraviolet radiation on quality parameters of refrigerated vacuum-packed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) fillets. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.-D.A.; Holman, B.W.B.; Giteru, S.G.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) and its role in meat spoilage: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 280–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantasuttikul, A.; Kijroongrojana, K.; Benjakul, S. Quality indices of squid (Photololigo duvaucelii) and cuttlefish (Sepia aculeata) stored in ice. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2011, 20, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okur, I.; Oztop, M.H.; Alpas, H. Optimization and comparison of high-pressure-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from olive pomace. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Aslam, R.; Makroo, H.A. High pressure extraction and its application in the extraction of bio-active compounds: A review. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e12896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howgate, P. Traditional Methods. In Fishery Products; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 19–41. [Google Scholar]
- Gokoglu, N.; Topuz, O.K.; Yerlikaya, P.; Yatmaz, H.A.; Ucak, I. Effects of freezing and frozen storage on protein functionality and texture of some cephalopod muscles. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2018, 27, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Miao, J.; Lai, K. Effects of different salt concentrations on several freshness indicators of north Pacific squid (Ommastrephes sloani pacificus) during storage at 4 °C. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 1871–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, G.B.; Ofstad, R.; Lødemel, J.B.; Olsen, R.L. Changes in water-holding capacity of halibut muscle during cold storage. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-Y.; Park, S.-W.; Shin, H.-S. Fish freshness indicator for sensing fish quality during storage. Foods 2023, 12, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheftel, J.C. High-pressure, microbial inactivation and food preservation. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1995, 1, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smet, C.; Govaert, M.; Kyrylenko, A.; Easdani, M.; Walsh, J.L.; Van Impe, J.F. Inactivation of single strains of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium planktonic cells biofilms with plasma activated liquids. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 464002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zeng, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Zheng, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, H. Changes in quality characteristics based on protein oxidation and microbial action of ultra-high pressure-treated grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fillets during magnetic field storage. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, P.; Zhong, S.; Huang, J. Effect of temperature fluctuation on the freshness, water migration and quality of cold-storage Penaeus vannamei. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 193, 115771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouletis, A.D.; Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Neofitou, C.; Parlapani, F.F.; Gkagtzis, D.C. Quality changes of cuttlefish stored under various atmosphere modifications and vacuum packaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2882–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Zhan, H.; Zheng, J.; Liu, D.; Jia, P. High-pressure effects on cooking loss and histological structure of beef muscle. High Press. Res. 2010, 30, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, W.H.; Lipiński, M.R. Histological validation of morphological stages of sexual maturity in chokker squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii D’Orb (Cephalopoda: Loliginidae). S. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 1990, 9, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, S.; Lian, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of single- and two-cycle high hydrostatic pressure treatments on water properties, physicochemical and microbial qualities of minimally processed squids (Todarodes pacificus). J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, E1012–E1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabia-Sainz, H.M.; Torres-Arreola, W.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Santacruz-Ortega, H.C.; Rouzaud-Sández, O.; Valenzuela-Soto, E.M.; Burgara-Estrella, A.J.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M. Interrelation of collagen chemical structure and nanostructure with firmness of three body regions of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas). Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Lagarda, J.L.; García-Armenta, E.; Pacheco-Aguilar, R.; Gutiérrez-Dorado, R.; Mazorra-Manzano, M.Á.; Lugo-Sánchez, M.E.; Muy-Rangel, M.D. Relationships between morphometrical properties and the texture of an extrusion-expanded snack made from squid mantle (Dosidicus gigas). J. Texture Stud. 2018, 49, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.D.; Holley, R.A. High hydrostatic pressure effects on the texture of meat and meat products. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, R17–R23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, Y.A.; do Rosario, D.K.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Principles, application, and gaps of high-intensity ultrasound and high-pressure processing to improve meat texture. Foods 2023, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlapani, F.F. Microbial diversity of seafood. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syropoulou, F.; Parlapani, F.F.; Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Stamatiou, A.; Mallouchos, A.; Boziaris, I.S. Spoilage investigation of chill stored meagre (Argyrosomus regius) using modern microbiological and analytical techniques. Foods 2021, 10, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xin, X.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, C. Reduction of formaldehyde residues induced by the thermal decomposition of trimethylamine oxide during the processing and storage of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 97, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Hong, H.; Zhang, L.; Luo, Y. Spoilage-related microbiota in fish and crustaceans during storage: Research progress and future trends. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 252–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Storage Time (Day) | Weight Loss (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | M0P2 | M2P2 | M4P2 | M0P4 | M2P4 | M4P4 | |
| 0 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| 3 | 2.53 ± 0.05 *Be | 2.51 ± 0.01 Be | 2.45 ± 0.06 De | 2.48 ± 0.09 Ce | 2.51 ± 0.04 Be | 2.57 ± 0.06 Ae | 2.52 ± 0.02 Be |
| 6 | 4.76 ± 0.47 Bd | 4.65 ± 0.04 Cd | 5.32 ± 0.09 Ad | 5.34 ± 0.07 Ad | 3.98 ± 0.08 Dd | 3.75 ± 0.08 Ed | 3.03 ± 0.03 Fd |
| 9 | 7.86 ± 0.18 Bc | 7.67 ± 0.02 Cc | 6.81 ± 0.02 Dc | 7.89 ± 0.02 Ac | 5.92 ± 0.05 Ec | 5.89 ± 0.09 Fc | 4.35 ± 0.04 Gc |
| 12 | 9.96 ± 0.31 Ab | 8.78 ± 0.03 Bb | 8.22 ± 0.04 Db | 8.56 ± 0.06 Cb | 7.84 ± 0.06 Eb | 7.74 ± 0.07 Fb | 6.51 ± 0.07 Gb |
| 15 | 11.67 ± 0.37 Aa | 9.95 ± 0.02 Ba | 9.76 ± 0.05 Ca | 9.43 ± 0.02 Da | 9.22 ± 0.07 Ea | 9.04 ± 0.05 Fa | 7.18 ± 0.09 Ga |
| Storage Time (Day) | Cooking Loss (%) | ||||||
| CON | M0P2 | M2P2 | M4P2 | M0P4 | M2P4 | M4P4 | |
| 0 | 7.71 ± 0.21 *Bf | 7.31 ± 0.41 Cf | 7.35 ± 0.53 Cf | 7.29 ± 0.73 Df | 7.78 ± 0.63 Af | 7.22 ± 0.23 Ef | 7.09 ± 0.53 Ff |
| 3 | 9.52 ± 0.15 Be | 9.65 ± 0.31 Ae | 8.12 ± 0.45 Ee | 8.52 ± 0.92 De | 8.68 ± 0.84 Ce | 7.55 ± 0.85 Ge | 7.95 ± 0.63 Fe |
| 6 | 12.76 ± 0.26 Ad | 11.89 ± 0.21 Bd | 10.38 ± 0.32 Dd | 10.15 ± 0.71 Ed | 11.52 ± 0.34 Cd | 9.82 ± 0.24 Gd | 9.87 ± 0.83 Fd |
| 9 | 17.95 ± 0.27 Ac | 17.48 ± 0.24 Bc | 15.65 ± 0.24 Cc | 15.36 ± 0.63 Cc | 17.38 ± 0.21 Bc | 12.71 ± 0.17 Dc | 12.64 ± 0.75 Dc |
| 12 | 23.67 ± 0.21 Bb | 23.15 ± 0.23 Cab | 19.56 ± 0.12 Db | 19.13 ± 0.73 Eb | 24.18 ± 0.63 Ab | 17.44 ± 0.32 Fa | 17.34 ± 0.43 Gb |
| 15 | 30.78 ± 0.28 Aa | 25.45 ± 0.31 Ca | 23.39 ± 0.56 Da | 23.21 ± 0.12 Ea | 28.45 ± 0.63 Ba | 21.73 ± 0.52 Ea | 19.71 ± 0.73 Ga |
| Storage Time (Day) | Samples | Appearance | Color | Odor | Texture | Overall Acceptance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | CON | 8.07 ± 0.03 *a | 8.78 ± 0.13 a | 8.77 ± 0.09 a | 8.75 ± 0.10 a | 8.61 ± 0.19 a |
| M4P4 | 8.52 ± 0.02 a | 8.91 ± 0.11 a | 8.79 ± 0.06 a | 8.89 ± 0.12 a | 8.67 ± 0.21 a | |
| 12 | M4P4 | 7.12 ± 0.21 a | 7.73 ± 0.15 a | 6.03 ± 0.01 a | 6.83 ± 0.26 a | 6.45 ± 0.03 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nilsuwan, K.; Palamae, S.; Naher, J.; Buamard, N.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Quality of Refrigerated Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Subjected to High-Pressure Processing. Foods 2024, 13, 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081264
Nilsuwan K, Palamae S, Naher J, Buamard N, Zhang B, Benjakul S. Quality of Refrigerated Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Subjected to High-Pressure Processing. Foods. 2024; 13(8):1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081264
Chicago/Turabian StyleNilsuwan, Krisana, Suriya Palamae, Jasmin Naher, Natchaphol Buamard, Bin Zhang, and Soottawat Benjakul. 2024. "Quality of Refrigerated Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Subjected to High-Pressure Processing" Foods 13, no. 8: 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081264
APA StyleNilsuwan, K., Palamae, S., Naher, J., Buamard, N., Zhang, B., & Benjakul, S. (2024). Quality of Refrigerated Squid Mantle Cut Treated with Mint Extract Subjected to High-Pressure Processing. Foods, 13(8), 1264. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13081264






