Sources of Lipopeptides and Their Applications in Food and Human Health: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Lipopeptide Source
2.1. Plant Sources
2.2. Animal Origin
2.3. Microbial Sources
2.3.1. Bacterial Sources
2.3.2. Algae Sources
2.3.3. Fungal Sources
2.4. Synthetic Sources
3. Lipopeptide Foods
3.1. Food Functionality of LPs
3.2. LPs and Food Packaging
3.3. Lipopeptide Food Taste
4. LPs and Human Health
4.1. Antibacterial Effects
4.2. Bioactivity and Immunomodulation
4.3. Nutrition and Metabolism
4.4. Lipopeptides Toxicity
5. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajijah, N.; Fiodor, A.; Pandey, A.K.; Rana, A.; Pranaw, K. Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) with Biofilm-Forming Ability: A Multifaceted Agent for Sustainable Agriculture. Diversity 2023, 15, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Saar, K.L.; Jacquat, R.; Hong, L.; Levin, A.; Gang, H.; Ye, R.; Mu, B.; Knowles, T.P.J. Mechanism of biosurfactant adsorption to oil/water interfaces from millisecond scale tensiometry measurements. Interface Focus 2017, 7, 20170013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambry, N.S.; Rusly, N.S.; Awang, M.S.; Md Noh, N.A.; Yahya, A.R.M. Production of lipopeptide biosurfactant in batch and fed-batch Streptomyces sp. PBD-410L cultures growing on palm oil. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 1577–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xu, L.; Ding, J.; Wang, M.; Ge, R.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, B.; Fan, J. Natural antimicrobial lipopeptides secreted by Bacillus spp. and their application in food preservation, a critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 127, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Kiran, G.S.; Selvin, J. Revealing the effect of lipopeptide on improving the probiotics characteristics: Flavor and texture enhancer in the formulated yogurt. Food Chem. 2022, 375, 131718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, A.B.; Worobo, R.W. The incidence and impact of microbial spoilage in the production of fruit and vegetable juices as reported by juice manufacturers. Food Control 2018, 85, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, K.R.; Kanwar, S.S. Lipopeptides as the antifungal and antibacterial agents: Applications in food safety and therapeutics. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 473050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, A.; Radoor, S.; C Nair, I.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Polyvinyl alcohol-nanocomposite films incorporated with clay nanoparticles and lipopeptides as active food wraps against food spoilage microbes. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 30, 100727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, M.; Cavelius, P.; Qoura, F.; Awad, D.; Brück, T. Lipopeptides development in cosmetics and pharmaceutical applications: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2023, 67, 108210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, C.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Gou, S.; Xie, J.; Yao, J.; Ni, J. Antimicrobial peptides conjugated with fatty acids on the side chain of D-amino acid promises antimicrobial potency against multidrug-resistant bacteria. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 141, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, K. Chapter 9—Natural Bioactive Cyclic Peptides and Peptidomimetics. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Attaur, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 62, pp. 343–376. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, J.; Abdalmegeed, D.; Tian, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, S.; Sedjoah, R.-C.A.-A.; Shao, Y.; Sun, S.; et al. Construction of lipopeptide mono-producing Bacillus strains and comparison of their antimicrobial activity. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-S.; Prodhan, Z.H.; Biswas, S.K.; Le, C.-F.; Sekaran, S.D. Antimicrobial peptides from different plant sources: Isolation, characterisation, and purification. Phytochemistry 2018, 154, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinski, J.M.L.N.; de Melo Franco, B.D.G.; Fonseca, G.G. 9—Plant-derived antimicrobial peptides. In Antimicrobial Peptides; Ajesh, K., Sreejith, K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 157–169. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.-Z.; Zeng, Y.-J.; Zong, M.-H.; Yang, J.-G.; Lou, W.-Y. Bioprospecting of a novel endophytic Bacillus velezensis FZ06 from leaves of Camellia assamica: Production of three groups of lipopeptides and the inhibition against food spoilage microorganisms. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-López, L.; Rincón-Fontán, M.; Vecino, X.; Cruz, J.M.; Moldes, A.B. Extraction, separation and characterization of lipopeptides and phospholipids from corn steep water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 248, 117076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamifar, S.; Abolmaali, S.; Mohsen Sohrabi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Shahmohammadi, M. Molecular characterization and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a plant defensin peptide derived from a gene of oat (Avena sativa L.). Phytochemistry 2021, 181, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.M.; Shahmohammadi, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Abdi, Z.; Shams, M.H.; Khanizadeh, S.; Kheirandish, F. Identification and functional characterization a cysteine-rich peptide from the garlic (Allium sativum L.). South Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 166, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chu, D.; Fan, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; You, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Production of antifungal iturins from vegetable straw: A combined chemical-bacterial process. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 378, 129010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astafieva, A.A.; Rogozhin, E.A.; Odintsova, T.I.; Khadeeva, N.V.; Grishin, E.V.; Egorov, T.A. Discovery of novel antimicrobial peptides with unusual cysteine motifs in dandelion Taraxacum officinale Wigg. flowers. Peptides 2012, 36, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, J. High-value development and utilization of functional peptides from seafood by-products and discards: A case study of antimicrobial peptides. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Boidin-Wichlacz, C.; Melnyk, O.; Zeppilli, D.; Landon, C.; Thomas, F.; Cambon, M.-A.; Lafond, M.; Mabrouk, K.; Massol, F.; et al. The diversification of the antimicrobial peptides from marine worms is driven by environmental conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 162875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Luan, Y.; Li, Q.; Pang, Y.; Gou, M. Identification of antibacterial activity of liver-expressed antimicrobial peptide 2 (LEAP2) from primitive vertebrate lamprey. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2024, 146, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lu, H.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, X.; Yang, C.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Claesen, J. A Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Derived from Bony Fish IFN1 Exerts Potent Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity in Mammals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02013-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punginelli, D.; Schillaci, D.; Mauro, M.; Deidun, A.; Barone, G.; Arizza, V.; Vazzana, M. The potential of antimicrobial peptides isolated from freshwater crayfish species in new drug development: A review. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2022, 126, 104258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Vega, E.; O’Leary, N.A.; Shockey, J.E.; Robalino, J.; Payne, C.; Browdy, C.L.; Warr, G.W.; Gross, P.S. Anti-lipopolysaccharide factor in Litopenaeus vannamei (LvALF): A broad spectrum antimicrobial peptide essential for shrimp immunity against bacterial and fungal infection. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1916–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, H.M.; dos Santos, C.; Brango-Vanegas, J.; Díaz-Martín, R.D.; Dias, S.C.; Franco, O.L. Unwrapping the structural and functional features of antimicrobial peptides from wasp venoms. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 200, 107069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, P.; Xu, H.; Zheng, W.; Lu, Y.; Fu, Q. Proteomic and antimicrobial peptide analyses of Buffalo colostrum and mature Milk whey: A comparative study. Food Chem. 2024, 448, 139119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Vargas, J.M.; Ramírez-Carreto, S.; Corzo, G.; Possani, L.D.; Becerril, B.; Ortiz, E. Structural and functional characterization of NDBP-4 family antimicrobial peptides from the scorpion Mesomexovis variegatus. Peptides 2021, 141, 170553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanutto-Elgui, M.R.; Vieira, J.C.S.; do Prado, D.Z.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; de Magalhães Padilha, P.; de Oliveira, D.E.; Fleuri, L.F. Production of milk peptides with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties through fungal proteases. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedharan, S.M.; Rishi, N.; Singh, R. Microbial lipopeptides: Properties, mechanics and engineering for novel lipopeptides. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 271, 127363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukagoshi, N.; Tamura, G.; Arima, K. A novel protoplast-bursting factor (surfactin) obtained from Bacillus subtilis IAM 1213: I. The effects of surfactin on Bacillus megaterium KM. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1970, 196, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurko, D.; Łaba, W.; Kancelista, A.; John, Ł.; Gudiña, E.J.; Lazar, Z.; Janek, T. Efficient conversion of black cumin cake from industrial waste into lipopeptide biosurfactant by Pseudomonas fluorescens. Biochem. Eng. J. 2023, 197, 108981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadaikunnan, S.; Vijayaragavan, P.; Rathi, M.A.; Balamuralikrishnan, B.; Alharbi, N.S.; Gopalakrishnan, V.K.; Purushothaman, S.; Sivanesan, R. Antibacterial and biofilm disruptive nonribosomal lipopeptides from Streptomyces parvulus against multidrug-resistant bacterial infections. J. Infect. Public Health 2024, 17, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiyam, D.; Dubey, A.; Malla, M.A.; Kumar, A. Lipopeptides from Bacillus: Unveiling biotechnological prospects—Sources, properties, and diverse applications. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2024, 55, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, F.; Neubauer, P.; Gimpel, M. Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from Bacillus subtilis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2038–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, B.R.; Park, J.S.; Jung, W.-J. Antifungal evaluation of fengycin isoforms isolated from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens PPL against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, P.R.; Torres, M.J.; Petroselli, G.; Erra-Balsells, R.; Audisio, M.C. Antibacterial activity of Bacillus licheniformis B6 against viability and biofilm formation of foodborne pathogens of health importance. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazala, I.; Charfeddine, S.; Charfeddine, M.; Gargouri-Bouzid, R.; Ellouz-Chaabouni, S.; Haddar, A. Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Bacillus mojavensis I4 lipopeptides and their potential application against the potato dry rot causative Fusarium solani. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, P.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Meng, F.; Bie, X. Effect and regulation of fatty acids on bacillomycin D synthesis. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, P. Complete genome sequence of Bacillus velezensis LPL-K103, an antifungal cyclic lipopeptide bacillomycin L producer from the surface of lemon. 3 Biotech 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mageshwaran, V. Rhizospheric Functional Attributes of Paenibacillus polymyxa in Disease and Nutrient Management for Sustainable Crop Production. In Detection, Diagnosis and Management of Soil-Borne Phytopathogens; Singh, U.B., Kumar, R., Singh, H.B., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Hoste, A.C.R.; Görgen, S.; Jacques, P. Chapter 10—Increasing the natural biodiversity of microbial lipopeptides using a synthetic biology approach. In Biosurfactants; Soberón-Chávez, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 203–247. [Google Scholar]
- Kajiyama, S.-I.; Kanzaki, H.; Kawazu, K.; Kobayashi, A. Nostofungicidine, an antifungal lipopeptide from the field-grown terrestrial blue-green alga Nostoc commune. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3737–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendhiran, D.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Marine algae as efficacious bioresources housing antimicrobial compounds for preserving foods—A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 358, 109416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertos, I.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Burón, M.; Rico, D. Development of functional bio-based seaweed (Himanthalia elongata and Palmaria palmata) edible films for extending the shelflife of fresh fish burgers. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 22, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burja, A.M.; Abou-Mansour, E.; Banaigs, B.; Payri, C.; Burgess, J.G.; Wright, P.C. Culture of the marine cyanobacterium, Lyngbya majuscula (Oscillatoriaceae), for bioprocess intensified production of cyclic and linear lipopeptides. J. Microbiol. Methods 2002, 48, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault, D.; Vu, K.D.; Vansach, T.; Horgen, F.D.; Lacroix, M. Antimicrobial effects of marine algal extracts and cyanobacterial pure compounds against five foodborne pathogens. Food Chem. 2016, 199, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.C.X.; Loo, C.T.; Wong, C.Y.; Lee, C.S.; Koh, R.Y.; Lim, C.L.; Kok, Y.Y.; Chye, S.M. Prospecting bioactivity in Antarctic algae: A review of extracts, isolated compounds and their effects. Fitoterapia 2024, 176, 106025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagavathy, S.; Sumathi, P.; Jancy Sherene Bell, I. Green algae Chlorococcum humicola—A new source of bioactive compounds with antimicrobial activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Xue, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.; Quan, C.; Gao, W.; Zu, X.; Bai, X.; Feng, S. Fungi-derived lipopeptide antibiotics developed since 2000. Peptides 2019, 113, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenland, E.; Krishnan, N.; Rönnholm, A.; Kalsum, S.; Puthia, M.; Mörgelin, M.; Davoudi, M.; Otrocka, M.; Alaridah, N.; Glegola-Madejska, I.; et al. A novel derivative of the fungal antimicrobial peptide plectasin is active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2018, 113, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.-H.; Liang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ling, J.; Dong, J.-D.; Qi, S.-H. Antifungal peptides from the marine gorgonian-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO41501. Phytochemistry 2021, 192, 112967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiquee, S. Chapter 11—Recent Advancements on the Role and Analysis of Volatile Compounds (VOCs) from Trichoderma. In Biotechnology and Biology of Trichoderma; Gupta, V.K., Schmoll, M., Herrera-Estrella, A., Upadhyay, R.S., Druzhinina, I., Tuohy, M.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 139–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sani, A.; Qin, W.-Q.; Li, J.-Y.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhou, L.; Yang, S.-Z.; Mu, B.-Z. Structural diversity and applications of lipopeptide biosurfactants as biocontrol agents against phytopathogens: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 278, 127518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Liu, X.; Fan, X.; Huang, R.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.; Yang, C. Enhanced production of antifungal lipopeptide iturin A by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LL3 through metabolic engineering and culture conditions optimization. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Niu, M.; Ji, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, X.; Luo, J.; Wei, G.; Yan, M. Development of KLA-RGD integrated lipopeptide with the effect of penetrating membrane which target the αvβ3 receptor and the application of combined antitumor. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 223, 113186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascou, R.; Flick, A.; Guénin, E.; Nesterenko, A. Development of lipopeptide surfactants from silk sericin and evaluation of their surface active properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 678, 132460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Metal coordinating-induced self-assembly of cyclic lipopeptides into high-performance antimicrobial supramolecules. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W. Biosynthesis of isonitrile lipopeptides. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 81, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-Z.; Chen, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Qiao, B.; Xu, Q.-M.; Cheng, J.-S.; Yuan, Y.-J. Construction of multi-strain microbial consortia producing amylase, serine and proline for enhanced bioconversion of food waste into lipopeptides. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 188, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Deng, Y.; Shang, T.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Q. Antibacterial effect of synthetic ultra-short lipopeptide on Streptococcus agalactiae and its active on bacterial mastitis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 601, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Burgard, C.; Popoff, A.; Zaburannyi, N.; Zipf, G.; Maier, J.; Bernauer, H.S.; Wenzel, S.C.; Müller, R. Synthetic biology approaches and combinatorial biosynthesis towards heterologous lipopeptide production. Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental procedures, design of artificial gene cluster, genetic manipulation, LC-MS analysis and structure elucidation. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7510–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espuelas, S.; Roth, A.; Thumann, C.; Frisch, B.; Schuber, F. Effect of synthetic lipopeptides formulated in liposomes on the maturation of human dendritic cells. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 42, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuyan, T.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Patowary, K.; Maity, S.; Nayak, D.; Deka, K.; Meenakshi Sundaram, K.; Muthupandian, S.; Sarma, H. Therapeutic potential of lipopeptide biosurfactant-fabricated copper oxide nanoparticles: Mechanistic insight into their biocompatibility using zebra fish. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2024, 7, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, F.; Pothuvattil, N.S.; Tounsi, S.; Saadaoui, I.; Trigui, M. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Bacillus velezensis M3-7 lipopeptides: Enhanced antifungal activity and potential use as a biocontrol agent against Fusarium crown rot disease of wheat seedlings. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 407, 110420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, V.V.; Kavianinia, I.; Cameron, A.J.; Harris, P.W.R.; Brimble, M.A. Direct synthesis of cyclic lipopeptides using intramolecular native chemical ligation and thiol–ene CLipPA chemistry. Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 2838–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, J.; Gänzle, M.G. Bacillus species in food fermentations: An underappreciated group of organisms for safe use in food fermentations. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2023, 50, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Huang, K.; Ye, C.; Zou, D.; Liu, D.; Wei, X. Enhancing biological control of apple rot: Unveiling the antifungal potential and mechanism of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HZ-12’s lipopeptide. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 325, 112704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Wu, S.; Tang, S.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Ren, Z.; Liu, E. Isolation, identification and characterization of biopotential cyclic lipopeptides from Bacillus subtilis strain JN005 and its antifungal activity against rice pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Biol. Control 2023, 182, 105241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, C.; Ye, X.; Lian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X. Antifungal activity of lipopeptides from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MG3 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in loquat fruits. Biol. Control 2020, 146, 104281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yánez-Mendizábal, V.; Falconí, C.E. Efficacy of Bacillus spp. to biocontrol of anthracnose and enhance plant growth on Andean lupin seeds by lipopeptide production. Biol. Control 2018, 122, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Khan, M.R.; Mukherjee, A.K. Recent advances in the application of microbial biosurfactants in food industries: Opportunities and challenges. Food Control 2024, 163, 110465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Ning, S.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J. Peptides derived from tryptic hydrolysate of Bacillus subtilis culture suppress fungal spoilage of table grapes. Food Chem. 2018, 239, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Moosa, A.; Zulfiqar, F.; Aslam, M.N.; Albalawi, M.A.; Almowallad, S.; Mahmood, T.; Alasmari, A.; Yong, J.W.H. Biocontrol potential of lipopeptides produced by the novel Bacillus altitudinis strain TM22A against postharvest Alternaria rot of tomato. LWT 2024, 191, 115541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, H.; He, J.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, X.; Fan, J. High-cell-density culture enhances the antimicrobial and freshness effects of Bacillus subtilis S1702 on table grapes (Vitis vinifera cv. Kyoho). Food Chem. 2019, 286, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Lu, L.; Liu, D.; Ning, Y.; Wang, Z. Purification, structure and characterization of the novel antimicrobial lipopeptides produced by Paenibacillus ehimensis HD. LWT 2023, 177, 114603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welke, J.E. Fungal and mycotoxin problems in grape juice and wine industries. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 29, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wangjiang, T.; Sun, Z.; Shi, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Wu, W.; Xiong, G.; Wang, L. Inhibition mechanism of crude lipopeptide from Bacillus subtilis against Aeromonas veronii growth, biofilm formation, and spoilage of channel catfish flesh. Food Microbiol. 2024, 120, 104489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathiviraj, R.; Rajeev, R.; Fernandes, H.; Rathna, K.; Lipton, A.N.; Selvin, J.; Kiran, G.S. A gelatinized lipopeptide diet effectively modulates immune response, disease resistance and gut microbiome in Penaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 112, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, M.L.; Cladera-Olivera, F.; dos Santos, J.; Brandelli, A. Purification and characterization of a peptide from Bacillus licheniformis showing dual antimicrobial and emulsifying activities. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Ai, C.; Yan, L.; Jiang, C.; Shi, J. Improvement of antifungal and antibacterial activities of food packages using silver nanoparticles synthesized by iturin A. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 28, 100669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Radoor, S.; Nair, I.C.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Lipopeptide and zinc oxide nanoparticles blended polyvinyl alcohol-based nanocomposite films as antimicrobial coating for biomedical applications. Process Biochem. 2021, 102, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemil, N.; Ouerfelli, M.; Almajano, M.P.; Elloumi-Mseddi, J.; Nasri, M.; Hmidet, N. The conservative effects of lipopeptides from Bacillus methylotrophicus DCS1 on sunflower oil-in-water emulsion and raw beef patties quality. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binmad, S.; Kaewtatip, K.; Kantachote, D.; Sukhoom, A.; Nookongbut, P. Exopolymeric substance from Bacillus velezensis P1 as an antifungal additive in chitosan coating to prolong the shelf life of mangoes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Peng, Y.; Qin, Z.; Tang, W.; Duns, G.J.; Dessie, W.; He, N.; Tan, Y. Chitosan-based packaging films with an integrated antimicrobial peptide: Characterization, in vitro release and application to fresh pork preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 231, 123209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, I.J.; Rivera-Monroy, Z.J.; García-Castañeda, J.E.; Clavijo-Grimaldo, D.; Fuenmayor, C.A.; Zuluaga-Domínguez, C.M. Multilayer polycaprolactone—Pullulan nanofiber mats incorporated with the antimicrobial palindromic peptide LfcinB (21–25)Pal as a potential application in active packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez Espitia, P.J.; de Fátima Ferreira Soares, N.; Dos Reis Coimbra, J.S.; de Andrade, N.J.; Souza Cruz, R.; Alves Medeiros, E.A. Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications in the Packaging and Preservation of Food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2012, 11, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neetoo, H.; Ye, M.; Chen, H.; Joerger, R.D.; Hicks, D.T.; Hoover, D.G. Use of nisin-coated plastic films to control Listeria monocytogenes on vacuum-packaged cold-smoked salmon. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inès, M.; Dhouha, G. Lipopeptide surfactants: Production, recovery and pore forming capacity. Peptides 2015, 71, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanakou, A.E.; Skandamis, P.N. Applications of active packaging for increasing microbial stability in foods: Natural volatile antimicrobial compounds. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin C, F.; Kumar, P.S.; Ngueagni, P.T. A review on new aspects of lipopeptide biosurfactant: Types, production, properties and its application in the bioremediation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, M.; Costa, S.G.V.A.O. Biosurfactants in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lai, Z.; Tan, P.; Shan, A. Antimicrobial peptides with protease stability: Progress and perspective. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmidet, N.; Jemil, N.; Ouerfelli, M.; Pilar Almajano, M.; Nasri, M. Antioxidant properties of Enterobacter cloacae C3 lipopeptides in vitro and in model food emulsion. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 44, e14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoso, S.P.; Angkawijaya, A.E.; Kurniawan, A.; Cheng, K.-C.; Hsieh, C.W. Chapter 8—The role of biosurfactants in the improvement of texture and shelf life of starch-containing products. In Applications of Next Generation Biosurfactants in the Food Sector; Inamuddin, Adetunji, C.O., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Sondhi, S. Chapter 3—Application of biosurfactant as an emulsifying agent. In Applications of Next Generation Biosurfactants in the Food Sector; Inamuddin, Adetunji, C.O., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Robles Hernandez, M.G.; Gerlinsky, M.; Zhang, J.S.; Gänzle, M.G. Use of Bacillus spp. as beneficial fermentation microbes in baking. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 416, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaqat, A.; Chughtai, M.F.J.; Khaliq, A.; Farooq, U.; Shahbaz, M.; Ali, A.; Saeed, K.; Sameed, N.; Kanwal, M.; Wattoo, A.G.; et al. Chapter 24—Applications of biosurfactants in dairy industry. In Applications of Next Generation Biosurfactants in the Food Sector; Inamuddin, Adetunji, C.O., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 509–526. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, B.G.; de Veras, B.O.; dos Santos Aguiar, J.; Medeiros Campos Guerra, J.; Sarubbo, L.A. Biosurfactant produced by Candida utilis UFPEDA1009 with potential application in cookie formulation. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 46, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, R.; Besbes, S.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi-Aydi, D. Cookies from composite wheat–sesame peels flours: Dough quality and effect of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant addition. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, R.; Moalla-Rekik, D.; Sahnoun, Z.; Rebai, T.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi-Aydi, D. Evaluation of dermal wound healing and in vitro antioxidant efficiency of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 biosurfactant. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, H.; Li, J.; Miao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of a novel Bacillus subtilis GXYX crude lipopeptide against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium infection in mice. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ning, Y.; Chen, Z.; Han, P.; Zhi, T.; Li, S.; Ma, A.; Jia, Y. Transcriptomics reveals substance biosynthesis and transport on membranes of Listeria monocytogenes affected by antimicrobial lipopeptide brevilaterin B. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.; Radivojevic, J.; O’Connor, K.; Blagojevic, S.; Begovic, B.; Lukic, V.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Savic, V. Rhamnolipid inspired lipopeptides effective in preventing adhesion and biofilm formation of Candida albicans. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalili, D.; Amini, M.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Fazeli, M.R.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Samadi, N. Isolation and structural characterization of Coryxin, a novel cyclic lipopeptide from Corynebacterium xerosis NS5 having emulsifying and anti-biofilm activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Huang, E.; Yousef, A.E. Brevibacillin, a cationic lipopeptide that binds to lipoteichoic acid and subsequently disrupts cytoplasmic membrane of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 195, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, A.; De, D.; Chaudhuri, S. Anti-biofilm and disinfectant-like activity of pumilacidin, a lipopeptide biosurfactant produced by Bacillus pumilus NITDID1. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 56, 103024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.-H.; Huang, R.; Wu, K.-Y.; Han, X.-L.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Liu, W.-L.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Qin, S.-Y. Infection-activated lipopeptide nanotherapeutics with adaptable geometrical morphology for in vivo bacterial ablation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 154, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ábrahám, Á.; Gyulai, G.; Mihály, J.; Horváth, A.; Dobay, O.; Varga, Z.; Kiss, É.; Horváti, K. Optimizing lipopeptide bioactivity: The impact of non-ionic surfactant dressing. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Chandra Sekhar Jaggarapu, M.M.; Rachamalla, H.K.; Nimmu, N.V.; Banerjee, R. NGRKC16-lipopeptide assisted liposomal-withaferin delivery for efficient killing of CD13 receptor-expressing pancreatic cancer and angiogenic endothelial cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-Y.; Cao, R.-G.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Liu, W.-L.; Huang, R.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Qin, S.-Y. Programming lipopeptide nanotherapeutics for tandem treatment of postsurgical infection and melanoma recurrence. J. Control. Release 2023, 362, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajare, S.N.; Subramanian, M.; Gautam, S.; Sharma, A. Induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells by a Bacillus lipopeptide bacillomycin D. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routhu, S.R.; Nagarjuna Chary, R.; Shaik, A.B.; Prabhakar, S.; Ganesh Kumar, C.; Kamal, A. Induction of apoptosis in lung carcinoma cells by antiproliferative cyclic lipopeptides from marine algicolous isolate Bacillus atrophaeus strain AKLSR1. Process Biochem. 2019, 79, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhao, W.; Cheng, W.; Deng, C.; Ying, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Tu, J.; Jiang, L. Lipopeptide liposomes-loaded hydrogel for multistage transdermal chemotherapy of melanoma. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamley, I.W. Lipopeptides for Vaccine Development. Bioconj. Chem. 2021, 32, 1472–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidel, I.G.; Curti, C.C.; Dorémus, L.; Béré, E.; Delwail, A.; Russi, R.C.; Lecron, J.-C.; Morel, F.; García, M.I.; Müller, D.M.; et al. Liposomal co-encapsulation of a novel gemini lipopeptide and a CpG-ODN induces a strong Th1 response with the co-activation of a Th2/Th17 profile and high antibody levels. Vaccine 2024, 42, 1953–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, M.; Baier, W.; Bessler, W.G.; Heinevetter, L. Modulation of the Th1/Th2 Bias by Lipopeptide and Saponin Adjuvants in Orally Immunized Mice. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffar, K.A.; Marasini, N.; Giddam, A.K.; Batzloff, M.R.; Good, M.F.; Skwarczynski, M.; Toth, I. Liposome-based intranasal delivery of lipopeptide vaccine candidates against group A streptococcus. Acta Biomater. 2016, 41, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brar, D.S.; Kaur, A.; Patil, M.T.; Honda-Okubo, Y.; Petrovsky, N.; Salunke, D.B. Simplified scalable synthesis of a water-soluble toll-like receptor 2 agonistic lipopeptide adjuvant for use with protein-based viral vaccines. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 153, 107835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flagler, M.J.; Tamura, M.; Laughlin, T.; Hartman, S.; Ashe, J.; Adams, R.; Kozak, K.; Cresswell, K.; Mullins, L.; Jarrold, B.B.; et al. Combinations of peptides synergistically activate the regenerative capacity of skin cells in vitro. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.T.; Campos, C.; Milani, M.; Foyaca, M.; Lamy, A.; Kurdian, K.; Trullas, C. Biorevitalizing effect of a novel facial serum containing apple stem cell extract, pro-collagen lipopeptide, creatine, and urea on skin aging signs. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, B.N.; Pessôa, M.G.; Mano, M.C.; Molina, G.; Neri-Numa, I.A.; Pastore, G.M. Current status in biotechnological production and applications of glycolipid biosurfactants. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 10265–10293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seweryn, A.; Wasilewski, T.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z.; Bochynek, M.; Pannert, D.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Lewińska, A. Implementation of sustainable development goals in the cosmetics industry based on the example of cleansing cosmetics containing a surfactin-rich digestate extract. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 3111–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adu, S.A.; Naughton, P.J.; Marchant, R.; Banat, I.M. Microbial Biosurfactants in Cosmetic and Personal Skincare Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, C.; Dumka, S.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S.; Pandey, L.M. Natural lipopeptide surfactin inhibits insulin aggregation and prevents amyloid-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 404, 124917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, L.J.C.; de Oliveira, F.A.; Christoffolete, M.A.; Nascimento-Sales, M.; Berger, S.; Wagner, E.; Lächelt, U.; Giacomelli, F.C. Nucleic acid delivery to retinal cells using lipopeptides as a potential tool towards ocular gene therapies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 655, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Yu, T.; Yan, F. Probiotic role and application of thermophilic Bacillus as novel food materials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rzeszutek, E.; van der Voort, M.; Wu, C.H.; Thoen, E.; Skaar, I.; Bulone, V.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; de Bruijn, I. Diversity of Aquatic Pseudomonas Species and Their Activity against the Fish Pathogenic Oomycete Saprolegnia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbut, R.; Skjolding, L.M.; Mathiessen, H.; Jaafar, R.; Li, X.; Jørgensen, L.v.G.; Kania, P.W.; Wu, B.; Buchmann, K. Toxicity of the antiparasitic lipopeptide biosurfactant SPH6 to green algae, cyanobacteria, crustaceans and zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 243, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ayed, H.; Nasri, R.; Jemil, N.; Ben Amor, I.; Gargouri, J.; Hmidet, N.; Nasri, M. Acute and sub-chronic oral toxicity profiles of lipopeptides from Bacillus mojavensis A21 and evaluation of their in vitro anticoagulant activity. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 236, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahnoun, R.; Mnif, I.; Fetoui, H.; Gdoura, R.; Chaabouni, K.; Makni-Ayadi, F.; Kallel, C.; Ellouze-Chaabouni, S.; Ghribi, D. Evaluation of Bacillus subtilis SPB1 Lipopeptide Biosurfactant Toxicity Towards Mice. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2014, 20, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdille, A.A.; Kitimu, S.R.; Ndubi, M.M.; Kimani, J.; Maina, E.N.; Bulimo, W.; Gavamukulya, Y.; Wamunyokoli, F. Sub-acute and sub-chronic toxicity assessment of the antimicrobial peptide Dermaseptin B2 on biochemical, haematological and histopathological parameters in BALB/c mice and Albino Wistar rats. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida Vaucher, R.; de Campos Velho Gewehr, C.; Folmer Correa, A.P.; Sant‘Anna, V.; Ferreira, J.; Brandelli, A. Evaluation of the immunogenicity and in vivo toxicity of the antimicrobial peptide P34. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Deng, X.; Wu, P.; Shen, Z.; Xu, H. Subacute toxicity of antimicrobial peptide S-thanatin in ICR mice. Peptides 2012, 36, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ren, B.; Li, B.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Phosphorylation as an Effective Tool to Improve Stability and Reduce Toxicity of Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 18807–18827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
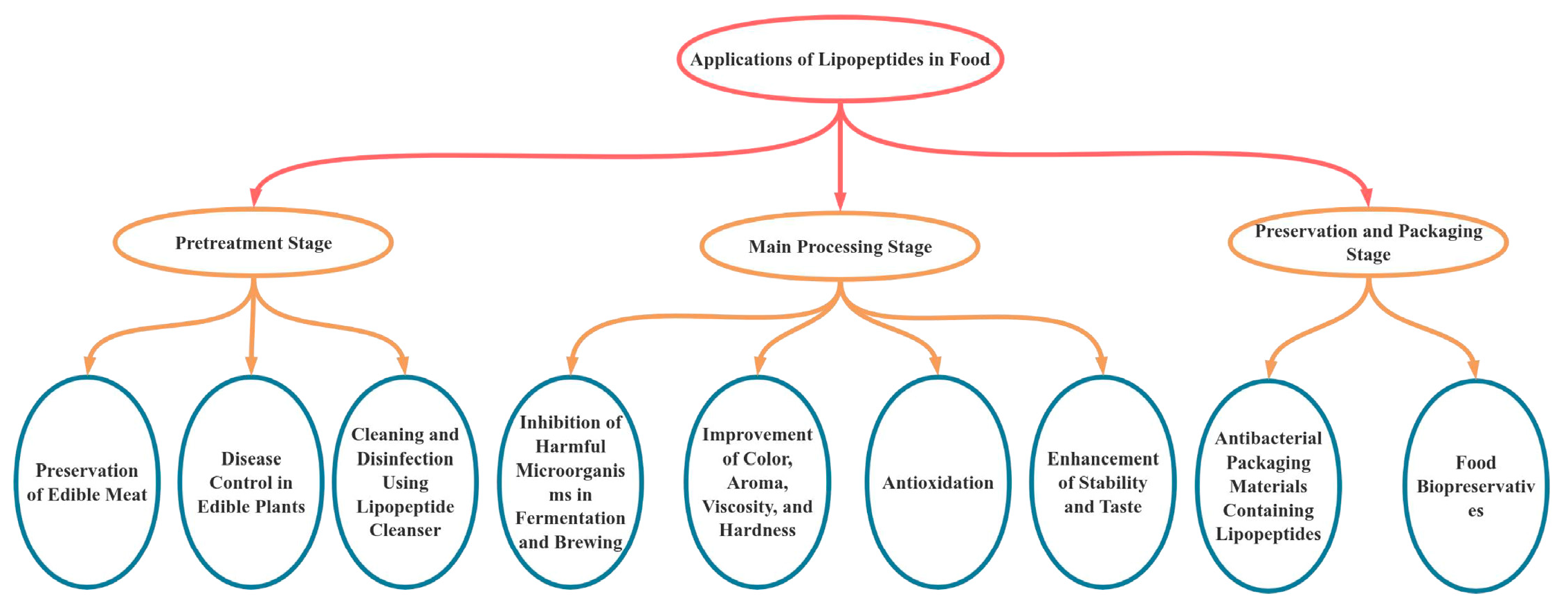
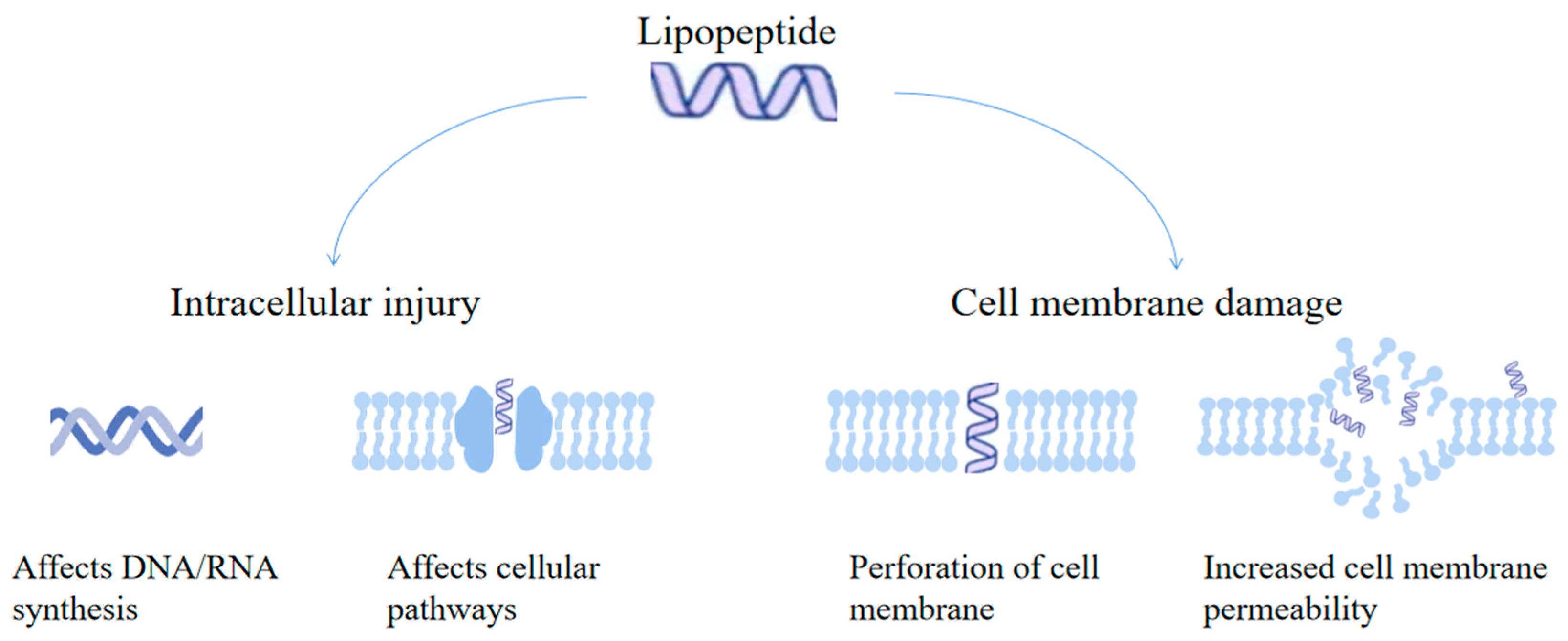
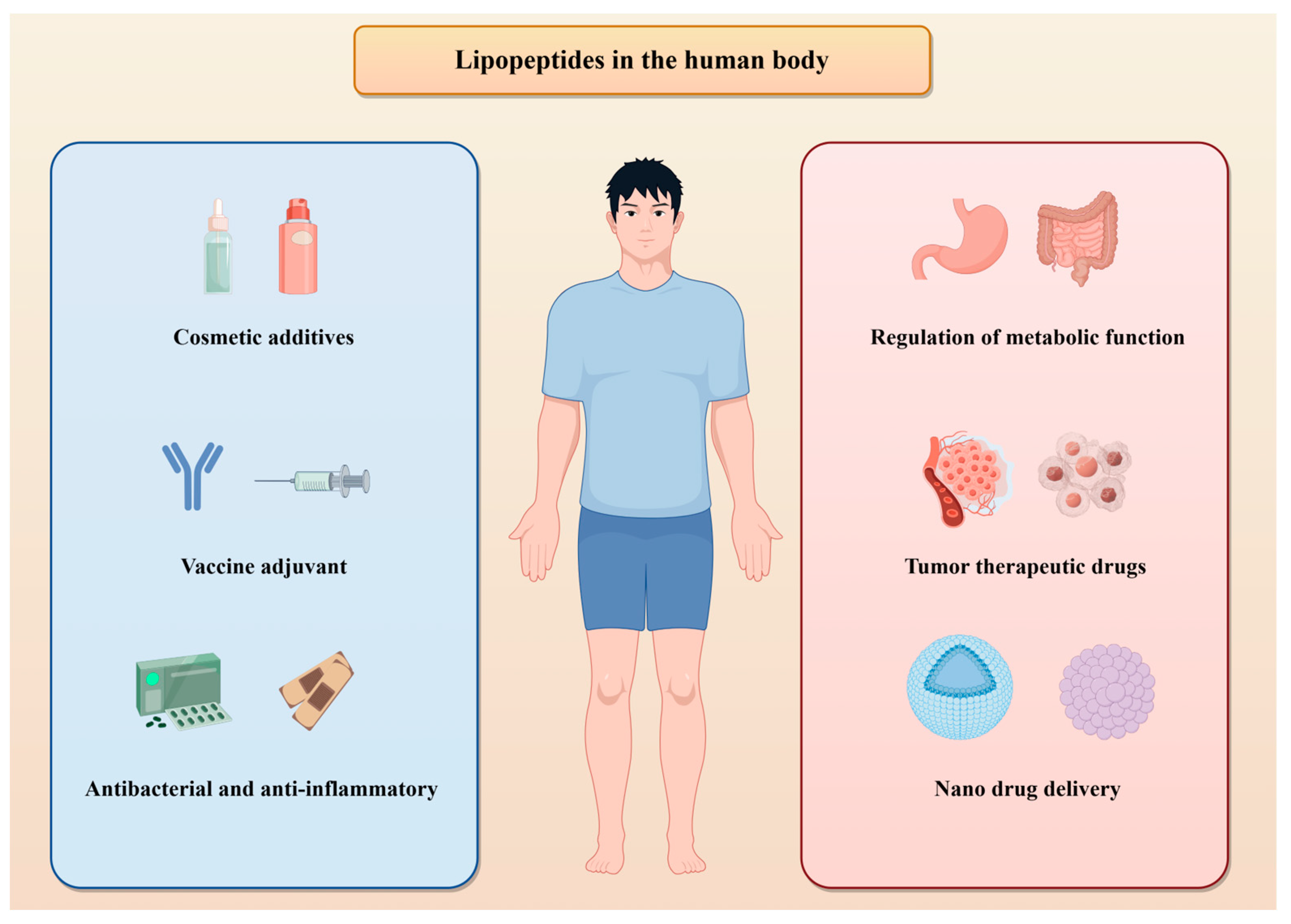
| Type | Source | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surfactin | B. subtilis, B. amyloquefaciens, B. velezensis, B. brevis | It can reduce surface tension and form micelles and is used in the detergent and emulsifier industries. It has an effective antibacterial effect on various microorganisms. | [35] |
| Iturin | B. subtilis B.velezensis, B. amyloquefaciens | Destroys cell membranes by interacting with the lipid components of fungi and bacteria, resulting in cell lysis. It also stimulates plant growth by improving nutrient uptake, protecting plants from pathogens, and promoting root system development. | [36] |
| Fengycin | B. subtilis, B. amyloliquefaciens, B. thuringiensis | It has effective antifungal activity against plant pathogens and filamentous fungi. | [37] |
| Kurstakins | B. licheniformis, B. mojavensis | It has an antibacterial effect against foodborne pathogens. | [38,39] |
| Bacillomycin | B. amyloliquefaciens, B. velezensis | It has an inhibitory effect on a variety of plant pathogens. | [40,41] |
| Polymyxins | Paenibacillus polymyxa | Inhibits most Gram-negative bacteria. | [42] |
| Licheniformin | B. licheniformis | It has antagonistic effects against Staphylococcus and yeast-like bacteria. | [43] |
| Substrate | Methods | Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silk peptide | Grafting of fatty acid hydrophobic chains onto silk peptides for N-acylation. | Endows the lipopeptide with improved emulsification performance. | [58] |
| Cyclolipeptide | Metal ion-induced cyclolipopeptide self-assembly and reconstruction into amphipathic particles. | Complex LPs are prone to coming into contact with and destroying microbial membranes. | [59] |
| IsocyanoLPs (INLPs) | “Isocyanosynthase” or nonheme iron(II) and α-ketoglutarate (KG)-dependent dioxygenase synthesis. | As potential drug targets for TB treatment. | [60] |
| Starch | Amylase is produced by Pichia pastoris to decompose starch in food waste. | Significantly increased bioconversion was observed from food waste to the production of LPs. | [61] |
| Short peptide | Two identical hydrophilic amino acids, X, and several kinds of glycine form 2–4 peptides. Palmitic acid is modified at the N-terminus and amino modification at the C-terminus. | Enhancement of the antibacterial effect of LPs and their activity against bacterial mastitis in mice. | [62] |
| Myxococcus xanthus | Type IIS endonucleases and synthetic DNA platforms. | For the production of various heterologous LPs. | [63] |
| Lipopeptide | The peptide moiety is functionalized with thiol-responsive groups, incorporated into liposomes, and reacts with the thiol-bearing peptide epitopes. | Used in the preparation of liposomal vaccines. | [64] |
| Surfactant | The CuSO4-5H2O solution was mixed with a biosurfactant solution and hydrazine hydrate was added. | As potential candidates for antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer and antidiabetic activities. | [65] |
| Iturin | Synthesis of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) using nanotechnology. | For the control of Fusarium crown rot in wheat seedlings. | [66] |
| KLA and RGD peptides | Solid-phase synthesis. | As an excellent drug carrier, it has a combined anticancer effect. | [57] |
| Iturin | Natural chemical ligation (NCL) was used to achieve the synthesis of the parent peptide macrocycle, and the lipid moieties were then linked via the CLipPA technique using regenerated free thiols. | Altered biological and physical properties. | [67] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Yu, X.; Wan, C.; Wang, Y.; Peng, L.; Li, Q. Sources of Lipopeptides and Their Applications in Food and Human Health: A Review. Foods 2025, 14, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020207
Chen S, Chen S, Yu X, Wan C, Wang Y, Peng L, Li Q. Sources of Lipopeptides and Their Applications in Food and Human Health: A Review. Foods. 2025; 14(2):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020207
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuyi, Sumin Chen, Xin Yu, Caijing Wan, Ying Wang, Lianxin Peng, and Qiang Li. 2025. "Sources of Lipopeptides and Their Applications in Food and Human Health: A Review" Foods 14, no. 2: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020207
APA StyleChen, S., Chen, S., Yu, X., Wan, C., Wang, Y., Peng, L., & Li, Q. (2025). Sources of Lipopeptides and Their Applications in Food and Human Health: A Review. Foods, 14(2), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14020207







