Exogenous Gibberellin Delays Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Samples
2.2. Measurement of Weight Loss, Leaf Color, and Relative Conductivity
2.3. Determination of Chlorophyll Content
2.4. Measurement of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
2.5. Determination of Soluble Sugar Content
2.6. Chlorophyllase Activity Assay
2.7. RNA Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.8. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
2.9. Metabolite Analysis
2.10. Visualized Analysis of DEGs and DAMs
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
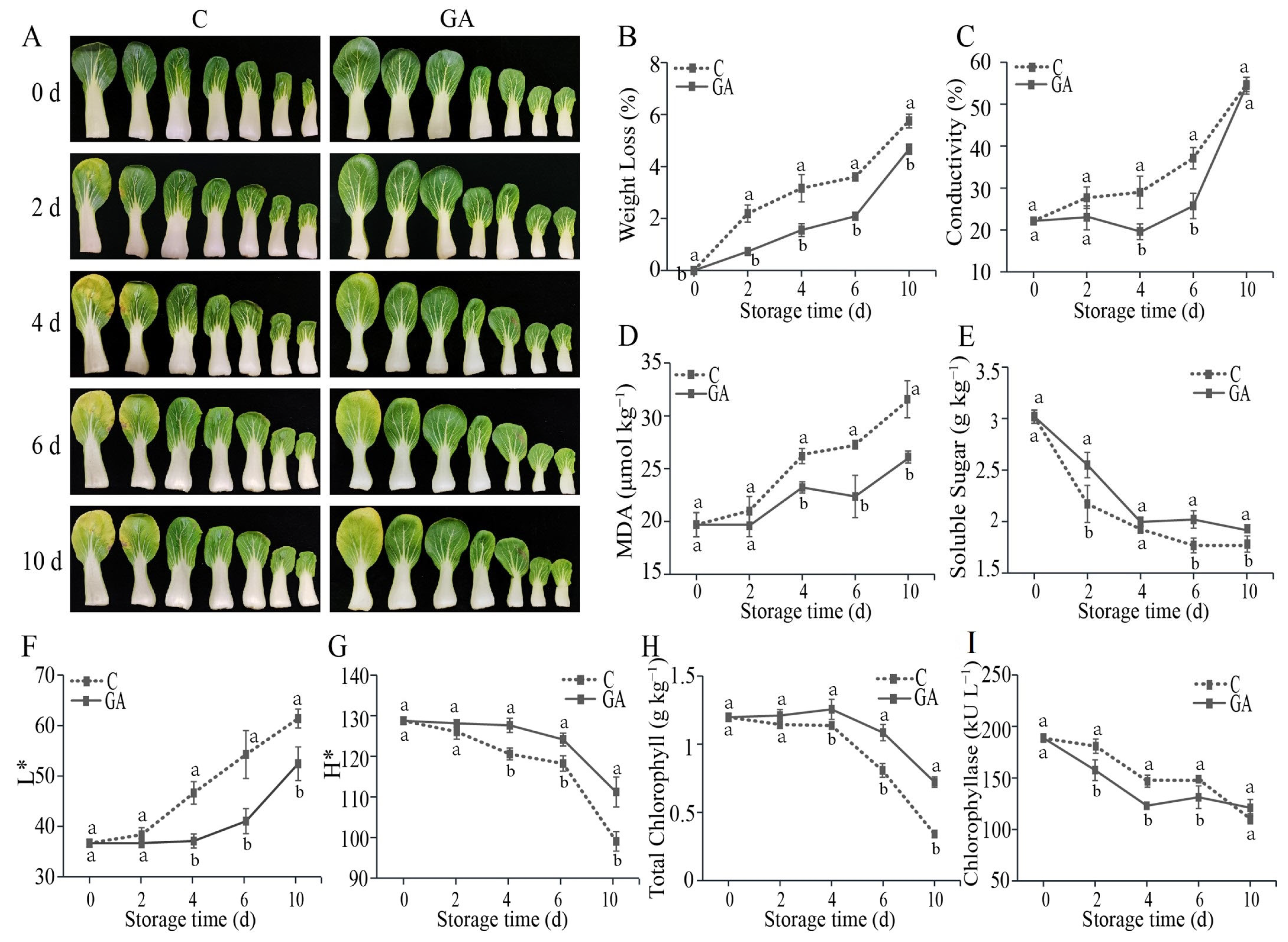
3.1. Effect of GA Treatment on the Quality of Postharvest Pak Choi
3.2. Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
3.3. Regulation of Genes Related to Gibberellin, Chlorophyll, and Leaf Senescence
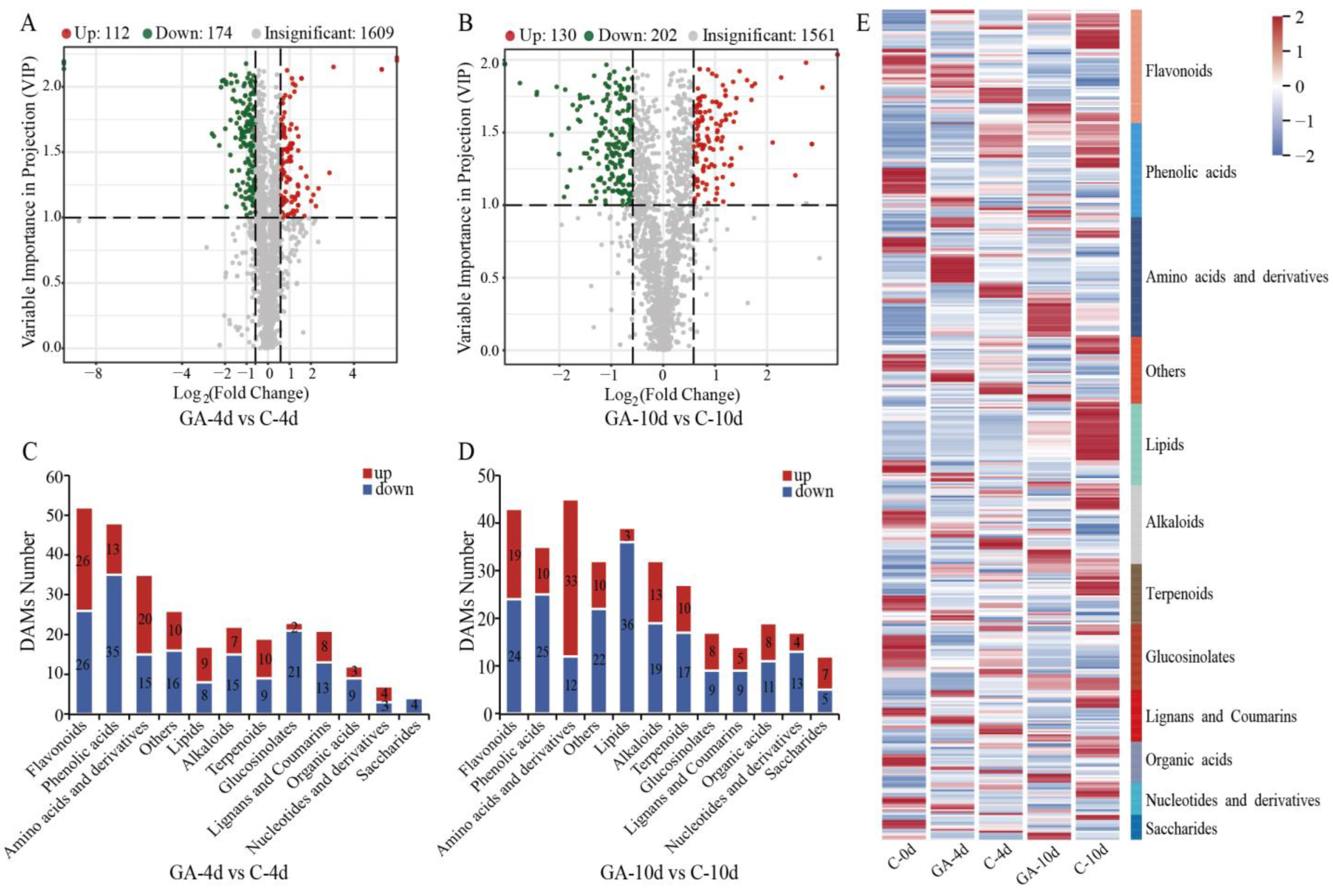
3.4. Differential Accumulated Metabolites (DAMs) Analysis
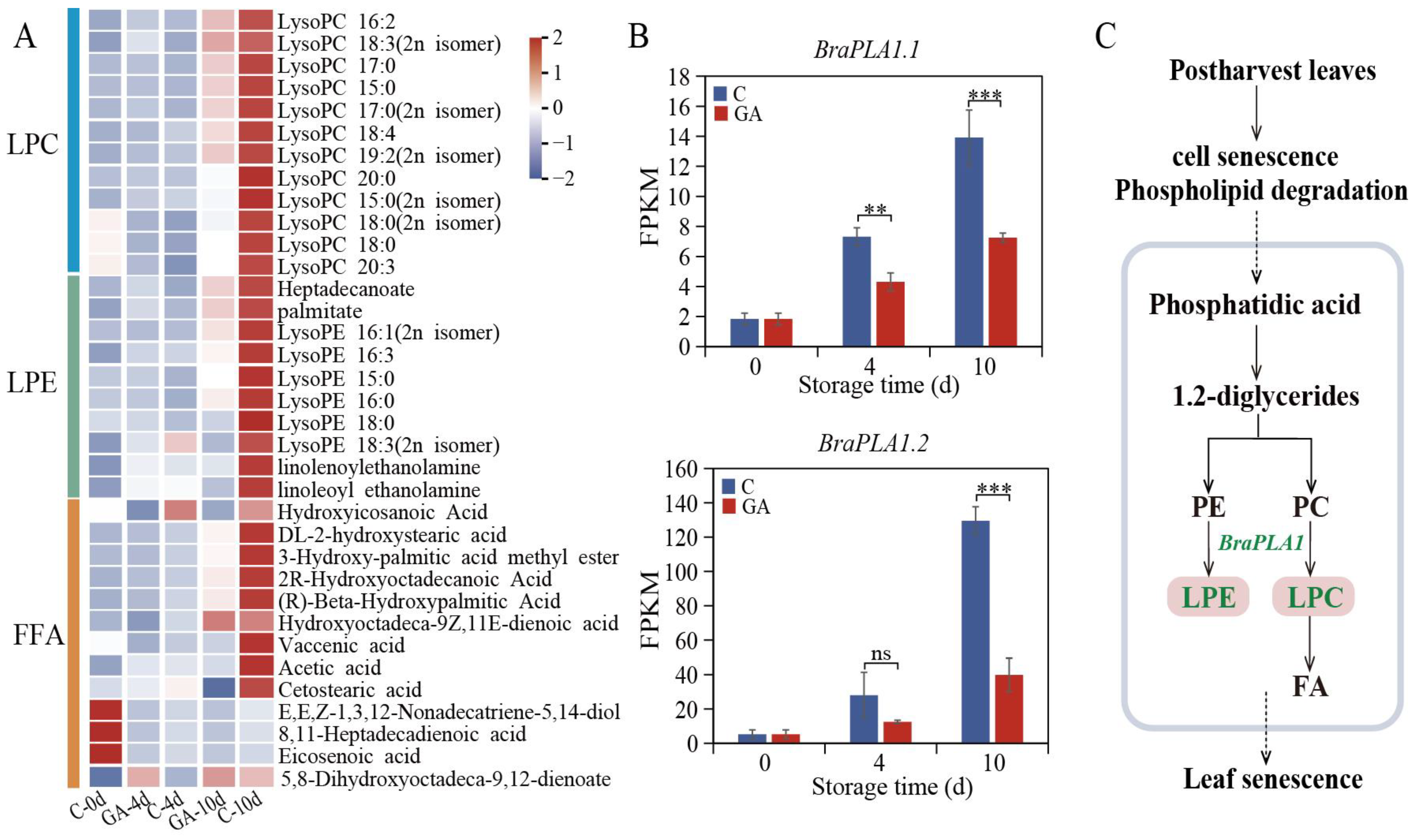
3.5. Regulation of Lipid Metabolism by Exogenous GA During Leaf Senescence
3.6. Regulation of Jasmonic Acid Signal Pathway by Exogenous GA During Leaf Senescence
4. Discussion
4.1. GA Treatment Delays Leaf Senescence in Postharvest Pak Choi
4.2. GA Treatment Inhibits Chlorophyll Degradation Pathways
4.3. GA Treatment Modulates Lipid Metabolism and Stabilizes Membrane Integrity
4.4. GA Interferes with JA-Mediated Senescence Pathways
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, W.; An, R.; Xu, X.; Li, P. 2,4-Epibrassinolide delays leaf senescence in pak choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis) by regulating its chlorophyll metabolic pathway and endogenous hormones content. Gene 2023, 877, 147531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, Z. 1-Methylcyclopropene retards Pak choi (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis) yellowing via BcNAC055-, BcMYB44-, and BcOBF1-mediated regulation of the key chlorophyll degrading gene BcNYC1 during storage at 20 °C. Food Qual. Saf. 2022, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gan, S. Leaf senescence: Signals, execution, and regulation. Curr. Top Dev. Biol. 2005, 71, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, L.M.; Gan, S.; Quirino, B.; Amasino, R.M. A comparison of the expression patterns of several senescence-associated genes in response to stress and hormone treatment. Plant Mol. Biol. 1998, 37, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Hou, H.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, G. 6-Benzyladenine treatment maintains storage quality of Chinese flowering cabbage by inhibiting chlorophyll degradation and enhancing antioxidant capacity. Plants 2023, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Liang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Deng, J. Acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid alleviate postharvest leaf senescence in Chinese flowering cabbage (Brassica rapa var. parachinensis). Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 194, 112070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Kang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Kang, D.; Zhao, P.; Chai, X.; Yang, X. Melatonin delays postharvest senescence through suppressing the Inhibition of BrERF2/BrERF109 on flavonoid biosynthesis in flowering Chinese cabbage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Fan, Z.; Kuang, J.; Lu, W.; Reiter, R.J.; Lakshmanan, P.; Su, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Shan, W. Melatonin delays leaf senescence of Chinese flowering cabbage by suppressing ABFs-mediated abscisic acid biosynthesis and chlorophyll degradation. J. Pineal. Res. 2019, 67, e12570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Wu, R.; Zhang, X.; Fan, X.; Li, G.; Gong, H.; Yin, X.; Zhang, A. The mechanism of gibberellins treatment suppressing kiwifruit postharvest ripening processes by transcriptome analysis. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 198, 112223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, M.; Dong, W.; Zhou, C.; Shi, L.; Chen, W.; Cao, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, S. Gibberellic acid inhibited chlorophyll degradation in post-harvest okras. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 190, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, H.; Qi, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Gai, Y.; et al. Gibberellins play a role in regulating tomato fruit ripening. Plant Cell Physiol. 2019, 60, 1619–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Wei, J.; Ma, Q.; Yu, D.; Li, J. Senescence of aerial parts is impeded by exogenous gibberellic acid in herbaceous perennial Paris polyphylla. J. Plant Physiol. 2009, 166, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keawmanee, N.; Ma, G.; Zhang, L.; Yahata, M.; Murakami, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kojima, N.; Kato, M. Exogenous gibberellin induced regreening through the regulation of chlorophyll and carotenoid metabolism in Valencia oranges. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 173, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Wei, W.; Tan, X.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.; Lu, W.; Su, X.; Lakshmanan, P.; Lin, H.; Chen, J. A NAC transcription factor BrNAC087 is involved in gibberellin-delayed leaf senescence in Chinese flowering cabbage. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 181, 111673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Onik, J.C.; Hu, X.; Duan, Y.; Lin, Q. Effects of (S)-Carvone and Gibberellin on sugar accumulation in potatoes during low temperature storage. Molecules 2018, 23, 3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lande, N.V.; Subba, P.; Barua, P.; Gayen, D.; Keshava Prasad, T.S.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Dissecting the chloroplast proteome of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) provides new insights into classical and non-classical functions. J. Proteom. 2017, 165, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, T.; Chen, H.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ohore, O.E.; Zhang, S. Bacterial succession in epiphytic biofilms and deciduous layer sediments during Hydrilla verticillata decay: A field investigation. J. Environ. Sci 2020, 93, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, J.; Huang, R. 6-BA delays the senescence of postharvest Cabbage leaves by Inhibiting respiratory metabolism. Foods 2024, 13, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.; Liu, K.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of the tomato GASA family identifies SlGASA1 as a repressor of fruit ripening. Hortic. Res. 2022, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, C.; Zhang, J.; Guo, W.; Ding, P.; Lan, F.; Sun, J.; Lyu, Y. A gibberellin-responsive transcription factor from Phalaenopsis ‘Big Chili’ (PIF4) promotes flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 101, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, M.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, S.; Ke, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zou, H.; Zhang, Z. Functional analysis of maize GRAS transcription factor gene ZmGRAS72 in response to drought and salt stresses. Agric. Commun. 2024, 2, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstone, A.L.; Ciampaglio, C.N.; Sun, T. The Arabidopsis RGA gene encodes a transcriptional regulator repressing the gibberellin signal transduction pathway. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Zhu, W.; Chen, C.; Yan, B.; Zhu, L.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. The mechanisms of lysophosphatidylcholine in the development of diseases. Life Sci. 2020, 247, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Hause, B. Jasmonates: Biosynthesis, perception, signal transduction and action in plant stress response, growth and development. An update to the 2007 review in Annals of Botany. Ann. Bot. 2013, 111, 1021–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppu, U.; Puputti, S.; Sandell, M. Factors related to sensory properties and consumer acceptance of vegetables. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qurashi, A.D.; Awad, M.A. Postharvest gibberellic acid, 6-benzylaminopurine and calcium chloride dipping affect quality, antioxidant compounds, radical scavenging capacity and enzymes activities of ‘Grand Nain’ bananas during shelf life. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 253, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yuan, D.; Jiang, Y. Exogenous procyanidin treatment delays senescence of harvested banana fruit by enhancing antioxidant responses and in vivo procyanidin content. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 158, 110999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luan, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y. Prediction and utilization of malondialdehyde in exotic pine under drought stress using near-Infrared spectroscopy. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 735275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favre, N.; Bárcena, A.; Bahima, J.V.; Martínez, G.; Costa, L. Pulses of low intensity light as promising technology to delay postharvest senescence of broccoli. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 142, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guan, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Q. Transcriptome and metabolome integrated analysis revealed the effects and potential mechanism of hydrogen peroxide on antioxidant system in postharvest broccoli. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 206, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shan, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, G.; Ding, X.; Liang, H.; Wang, C.; Kong, X.; Xie, L.; Jiang, Y. A NAC transcriptional factor BrNAC029 is involved in cytokinin-delayed leaf senescence in postharvest Chinese flowering cabbage. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY transcription factors and plant defense responses: Latest discoveries and future prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, T. A truncated ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-like protein, GhLYI, regulates senescence in cotton. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 1177–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, B.; Hörtensteiner, S. Mechanism and significance of chlorophyll breakdown. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2014, 33, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoda, Y.; Ito, H.; Tanaka, A. Arabidopsis STAY-GREEN, Mendel’s green cotyledon gene, encodes Magnesium-dechelatase. Plant Cell 2016, 28, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Su, T.; Zhao, X.; Wang, W.; Xin, X.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; et al. Exogenous Methylation Inhibitor 5-Azacytidine Accelerates Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles. Food Front. 2024, e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Tan, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Su, X.; Chen, J. Activation of the transcription of BrGA20ox3 by a BrTCP21 transcription factor is associated with gibberellin-delayed leaf senescence in Chinese flowering cabbage during storage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, R. Membrane phospholipids, lipoxidative damage and molecular integrity: A causal role in aging and longevity. BBA-BIioenergetics 2008, 1777, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, R.; Kanno, K.; Sugiyama, A.; Ohata, H.; Araki, A.; Kishikawa, N.; Kimura, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Kodama, M.; Kihira, K.; et al. Cholangiocyte senescence caused by lysophosphatidylcholine as a potential implication in carcinogenesis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pan. Sci. 2015, 22, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibran, R.; Hunter, D.A.; Dijkwel, P.P. Hormonal regulation of leaf senescence through integration of developmental and stress signals. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 82, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Rozhon, W.; Poppenberger, B. The role of hormones in the aging of plants—A mini-review. Gerontology 2014, 60, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zeng, Z.; Ji, S.; Shan, W.; Kuang, J.; Lu, W.; Su, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Physiological and transcription analyses reveal regulatory pathways of 6-benzylaminopurine delaying leaf senescence and maintaining quality in postharvest Chinese flowering cabbage. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Lyou, S.; Yeu, S.; Kim, M.; Rhee, S.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, Y.D.; Cheong, J. Microarray-based screening of jasmonate-responsive genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breeze, E.; Harrison, E.; McHattie, S.; Hughes, L.; Hickman, R.; Hill, C.; Kiddle, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Penfold, C.A.; Jenkins, D.; et al. High-resolution temporal profiling of transcripts during Arabidopsis leaf senescence reveals a distinct chronology of processes and regulation. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 873–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graaff, E.; Schwacke, R.; Schneider, A.; Desimone, M.; Flügge, U.; Kunze, R. Transcription Analysis of Arabidopsis Membrane Transporters and Hormone Pathways during Developmental and Induced Leaf Senescence. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 776–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, S.; Xu, X.; Shi, J.; Zuo, J.; Yue, X.; Su, T.; Wang, Q. Transcriptomic, metabolomic, and physiological analysis of two varieties of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) that differ in their storability. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 210, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Gu, M.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Qi, T.; Cheng, Z.; Peng, W.; Luo, H.; Nan, F.; et al. The Arabidopsis CORONATINE INSENSITIVE1 protein is a jasmonate receptor. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2220–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zeng, H.; Cai, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yin, C. Exogenous Jasmonic Acid and Cytokinin Antagonistically Regulate Rice Flag Leaf Senescence by Mediating Chlorophyll Degradation, Membrane Deterioration, and Senescence-Associated Genes Expression. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 35, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Xu, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; You, C.; Han, Y. MdbHLH162 connects the gibberellin and jasmonic acid signals to regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in apple. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2024, 66, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. The F-box protein RhSAF destabilizes the gibberellic acid receptor RhGID1 to mediate ethylene-induced petal senescence in rose. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 1736–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, G.; Xiong, X.; Dong, D.; Li, G. Transcriptome analysis reveals that exogenous ethylene activates immune and defense responses in a high late blight resistant potato genotype. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Su, T.; Wang, W.; Xin, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; et al. Exogenous Gibberellin Delays Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles. Foods 2025, 14, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060981
Wang D, Zhao X, Su T, Wang W, Xin X, Zhang B, Zhang D, Yu Y, Wang Z, Zhang F, et al. Exogenous Gibberellin Delays Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles. Foods. 2025; 14(6):981. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060981
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dan, Xiuyun Zhao, Tongbing Su, Weihong Wang, Xiaoyun Xin, Bin Zhang, Deshuang Zhang, Yangjun Yu, Zhongjiang Wang, Fenglan Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Exogenous Gibberellin Delays Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles" Foods 14, no. 6: 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060981
APA StyleWang, D., Zhao, X., Su, T., Wang, W., Xin, X., Zhang, B., Zhang, D., Yu, Y., Wang, Z., Zhang, F., Zhou, L., Li, P., & Yu, S. (2025). Exogenous Gibberellin Delays Postharvest Leaf Senescence in Pak Choi by Modulating Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiles. Foods, 14(6), 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14060981





