Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences Between Three Different Grades of Hongxin Low-Temperature Daqu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
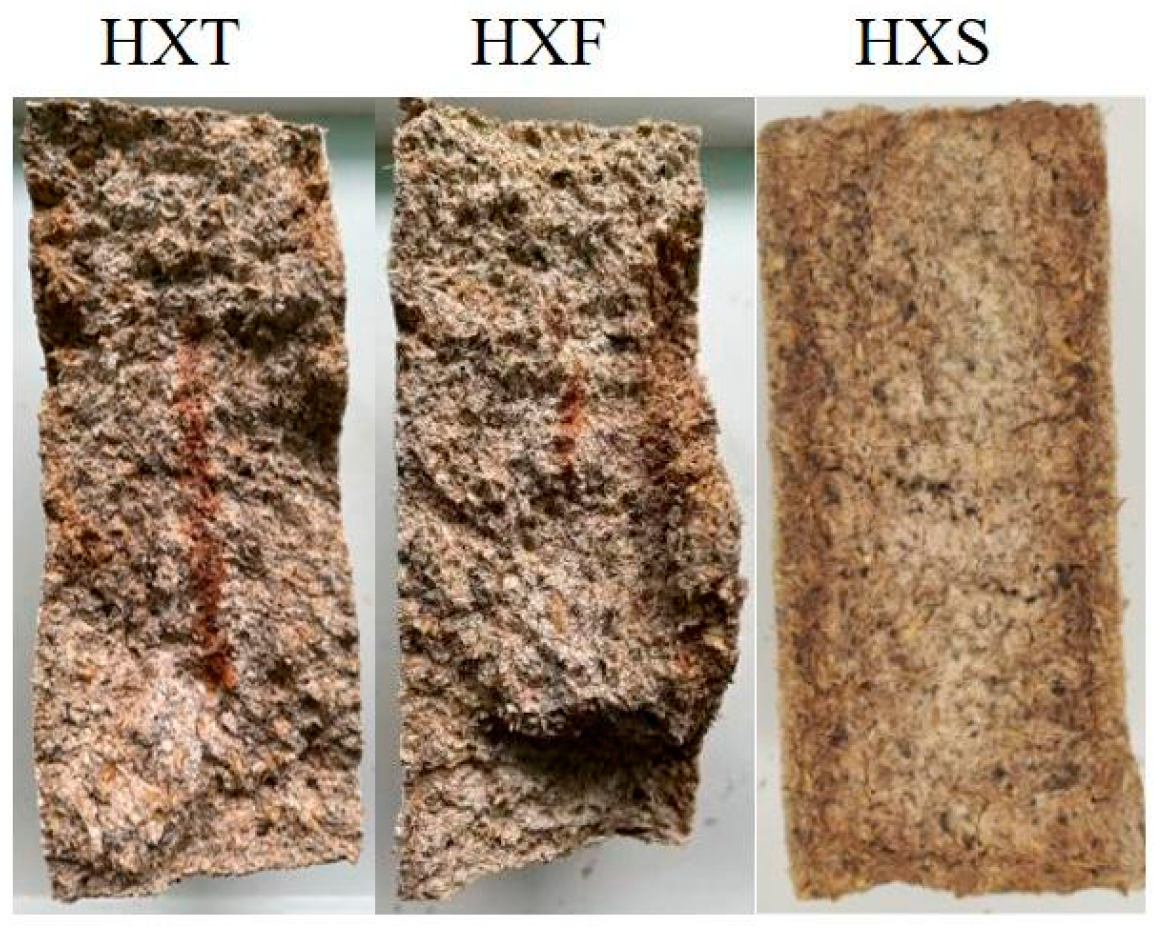
2.1. Sample Collection
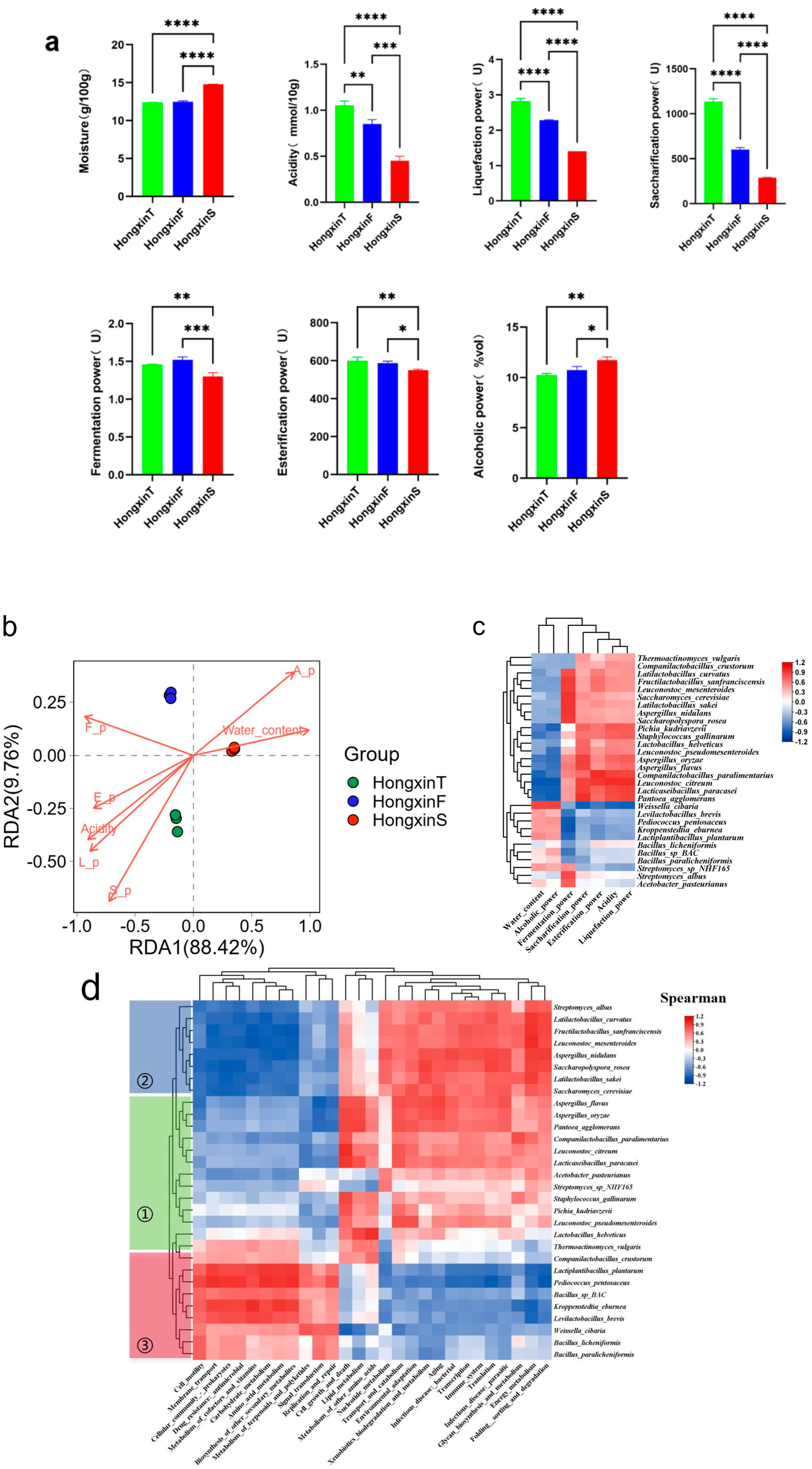
2.2. Determination of Physicochemical and Enzymatic Properties
2.3. Sample DNA Extraction, Library Preparation, and Data Quality Control
2.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
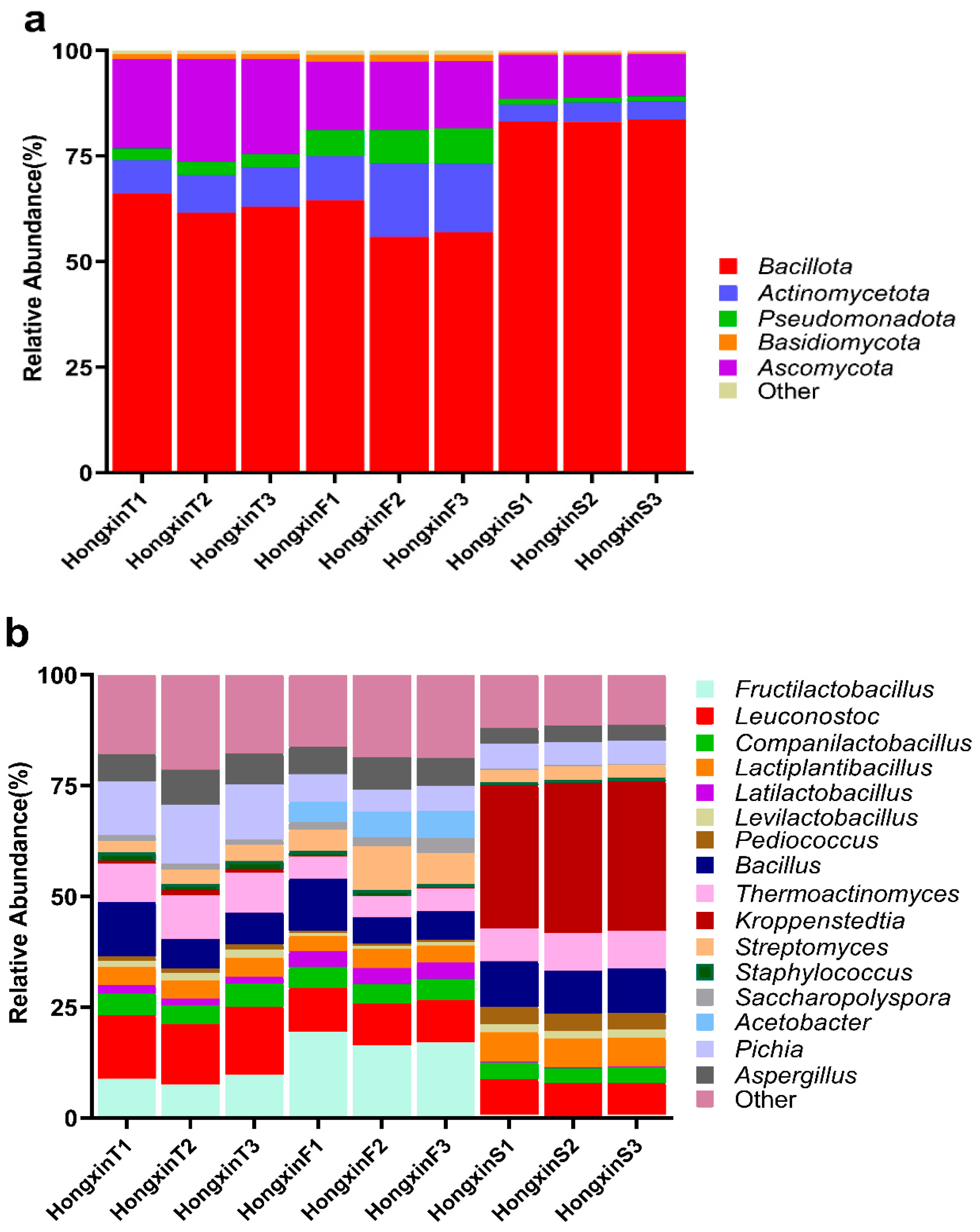
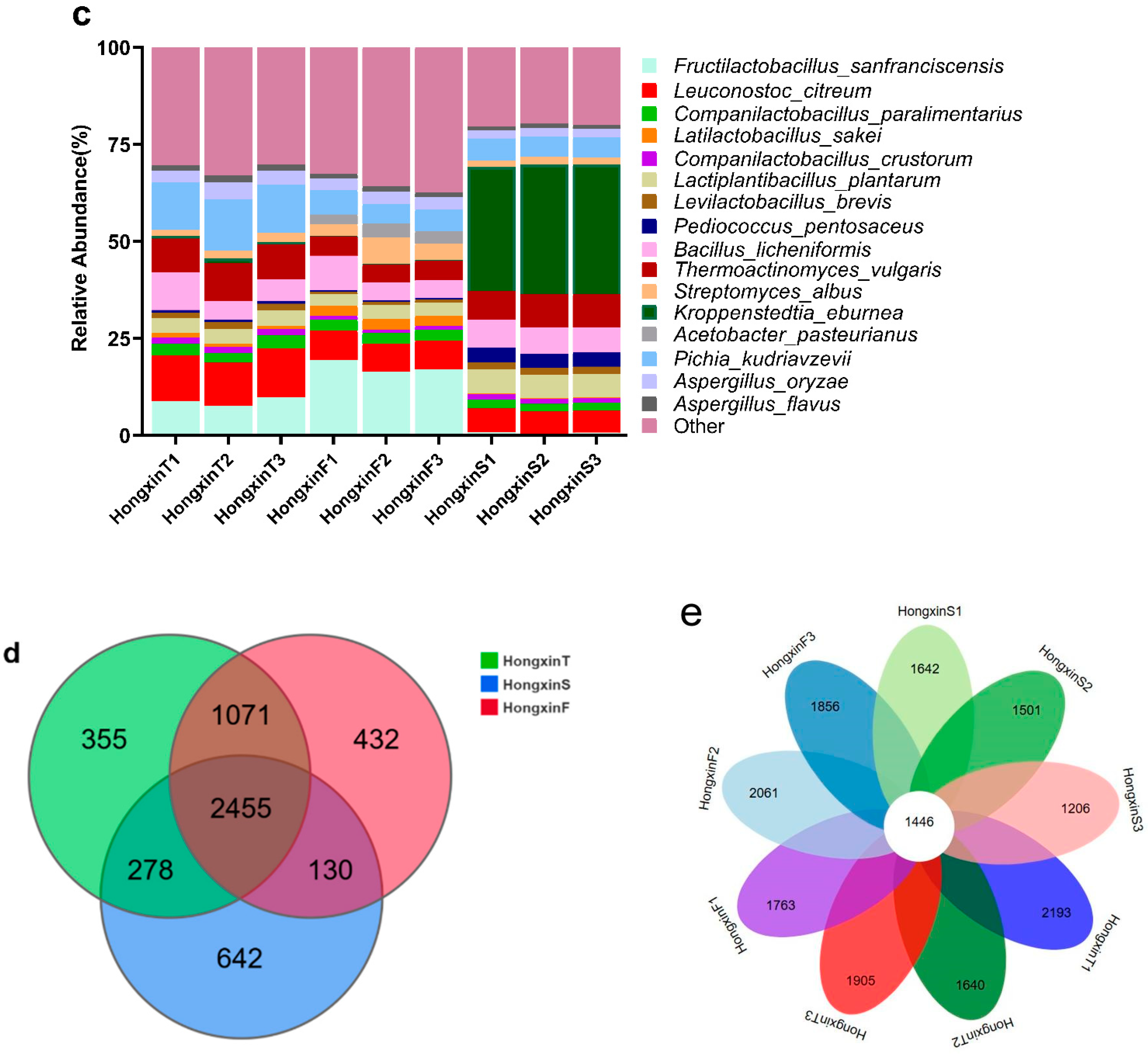
3.1. Microbial Composition Based on Shotgun Metagenomics
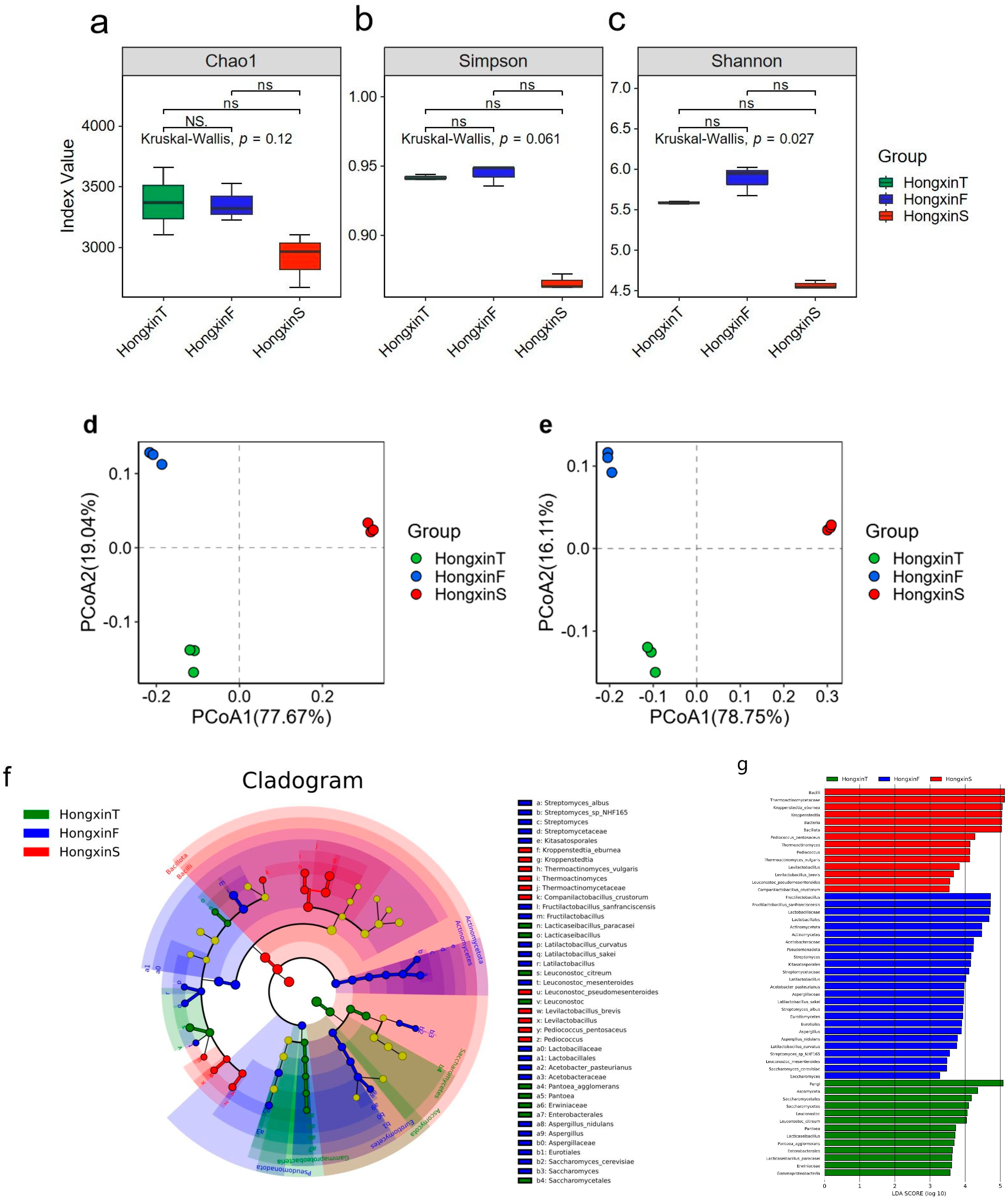
3.2. Differences in the Microbial Community Structure Among the Three Grades of HX
3.3. Metagenomic Functional Characteristics in Three Grades of HX
3.4. Correlation Between the Microbial Group of HX and the Physical and Chemical Properties and the Function of Metagenes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Sun, B. Effect of Fermentation Processing on the Flavor of Baijiu. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, L.; Dai, Z.; Wang, Q. Advances and Opportunities of CRISPR/Cas Technology in Bioengineering Non-conventional Yeasts. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 765396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Zhang, K.; Zou, W.; Hou, Y. Three main flavour types of Chinese Baijiu: Characteristics, research, and perspectives. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Gao, X.; Shi, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, Y.; Tang, K. Comparison of the Aroma-Active Compounds and Sensory Characteristics of Different Grades of Light-Flavor Baijiu. Foods 2023, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.-J.; Luo, L.-J.; Han, Y.; Song, L.; Zhen, P.; Han, D.-Y.; Wei, Y.-H.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Z.; Qiu, J.-Z.; et al. Microbial Community Affects Daqu Quality and the Production of Ethanol and Flavor Compounds in Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Dong, Y.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R. Alteration of Microbial Community for Improving Flavor Character of Daqu by Inoculation with Bacillus velezensis and Bacillus subtilis. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pei, T.; Du, J.; Yao, Q.; Deng, M.-R.; Zhu, H. Comparative Genomics Reveals Genetic Diversity and Metabolic Potentials of the Genus Qipengyuania and Suggests Fifteen Novel Species. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0126421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Ni, H.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhong, J.a.; Guo, Z. Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences between Three Types of Low-Temperature Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2022, 156, 111167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, J.; Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Huang, M.; Sun, B. Identification of Regionalmarkers Based on the Flavor Molecular Matrix Analysis of Sauce-Aroma Style Baijiu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7434–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Fan, Y.; Lu, T.; Kang, J.; Pang, X.; Han, B.; Chen, J. Composition and Metabolic Functions of the Microbiome in Fermented Grain during Light-Flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.-N.; Han, B.-Z.; Huang, X.-N.; Zhang, X.; Hou, L.-F.; Cao, M.; Gao, L.-J.; Hu, G.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Effect of the Environment Microbiota on the Flavour of Light-Flavour Baijiu during Spontaneous Fermentation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Fu, Z.; Teng, C.; Wu, Q.; Liu, P.; Yang, R.; Minhazul, K.A.H.M.; Li, X. Comprehensive Analysis of Different Grades of Roasted-Sesame-Like Flavored Daqu. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Yan, Z.; Nout, M.J.R.; Smid, E.J.; Zwietering, M.H.; Boekhout, T.; Han, J.-S.; Han, B.-Z. Microbiota Dynamics Related to Environmental Conditions during the Fermentative Production of Fen-Daqu, a Chinese Industrial Fermentation Starter. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 182, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberhardt, M.A.; Zarecki, R.; Gronow, S.; Lang, E.; Klenk, H.-P.; Gophna, U.; Ruppin, E. Harnessing the Landscape Of Microbial Culture Media to Predict New Organism-Media Pairings. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Environmental Microbiota Drives Microbial Succession and Metabolic Profiles during Chinese Liquor Fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e02369-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Yan, Z.; Han, B.-Z.; Zwietering, M.H.; Samson, R.A.; Boekhout, T.; Nout, M.J.R. Complex Microbiota of a Chinese “Fen“ Liquor Fermentation Starter (Fen-Daqu), Revealed by Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Methods. Food Microbiol. 2012, 31, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Translating Omics to Food Microbiology. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, A.M.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Finnegan, L.; Claesson, M.J.; Cotter, P.D. Species Classifier Choice is a Key Consideration When Analysing Low-Complexity Food Microbiome Data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-X.; Qin, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, M.; Qian, X.; Guo, X.; Bai, Y. A Practical Guide to Amplicon and Metagenomic Analysis of Microbiome Data. Protein Cell 2021, 12, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quince, C.; Walker, A.W.; Simpson, J.T.; Loman, N.J.; Segata, N. Shotgun Metagenomics, from Sampling to Analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, J.; Guillen, D.; Farres, A.; Diaz-Ruiz, G.; Sanchez, S.; Wacher, C.; Rodriguez-Sanoja, R. Omics in Traditional Vegetable Fermented Foods and Beverages. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlida, Y.; Susalam, M.K.; Harnentis, H.; Jamsari, J.; Huda, N.; Noordin, W.N.M.; Anggraini, L.; Ardani, L.R. Metagenomic Analysis and Biodiversity of Bacteria in Traditional Fermented Fish or Budu from West Sumatera, Indonesia. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2023, 10, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, L.; Yang, C.; Jin, H.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Lv, R.; Ma, T.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z. Shotgun Metagenomic Analysis of Microbiota Dynamics during Long-Term Backslopping Fermentation of Traditional Fermented Milk in a Controlled Laboratory Environment. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 7619–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, P.; Bian, Y.; Ju, N. Relationship between Microorganisms and Milk Metabolites during Quality Changes in Refrigerated Raw Milk: A Metagenomic and Metabolomic Exploration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 425, 110891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurong, W.; Qiangchuan, H.; Hui, N.; Longxin, T.; Juzhen, L.; Jiaping, Z.; Zhuang, G. Multi-Method Joint Analysis Reveals Differences in the Quality and Microbial Composition of High-Temperature and Medium-High-Temperature Daqu. Lwt—Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 209, 116804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Yu, C.; Li, Z.; et al. SOAPnuke: A MapReduce Acceleration-Supported Software for Integrated Quality Control and Preprocessing of High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Gigascience 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chen, L.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Yang, F.; Du, G.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. The Differences in Carbohydrate Utilization Ability between Six Rounds of Sauce-flavor Daqu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, R. Revealing the Synergistic Effects of Qupi-Shaping Pattern and Spatial Variation on High-Temperature Daqu Attributes. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 215, 117194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Hu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Q.; Guo, Z. Understanding the Factors Influencing High-Temperature Daqu from Different Geographical Regions. Food Biosci. 2024, 62, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yang, L.; Mingjuan, Z.; Xin, Z.; Hong, L.; Ting, Z.; Chunhui, X.; Ling, X.; Bolin, Z.; Chi, C. Thermoactinomyces daqus sp. nov., a Thermophilic Bacterium Isolated from High-Temperature Daqu. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 206–210. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wen, Z.; Yake, D.; Yan, W.; Min, Z.; Yajiao, Z.; Zhengyun, W.; Wenxue, Z. Difference of Microbial Community and Gene Composition with Saccharification Function between Chinese Nongxiangxing Daqu and Jiangxiangxing Daqu. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cai, W.; Wang, W.; Shu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Shan, C.; Guo, Z. Analysis of Microbial Diversity and Functional Differences in Different Types Of High-Temperature Daqu. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Li, M.; Jin, J.; Dong, X.; Xu, K.; Jin, L.; Qiao, Y.; Ji, H. Advances in the Application of the Non-Conventional Yeast Pichia kudriavzevii in Food and Biotechnology Industries. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yu, Y.; Kemperman, R.; Jimenez, L.; Ahmed Sadiq, F.; Zhang, G. Comparative Genomics Reveals Genetic Diversity and Variation in Metabolic Traits in Fructilactobacillus sanfranciscensis Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambetta, J.M.; Cozzolino, D.; Bastian, S.E.P.; Jeffery, D.W. Exploring the Effects of Geographical Origin on the Chemical Composition and Quality Grading of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Chardonnay Grapes. Molecules 2017, 22, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mao, J.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H. Changes in Flavour Characteristics and Bacterial Diversity during Traditional Fermentation of Chinese Rice Wines from Shaoxing Region. Food Control 2014, 44, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Mao, J.; Qian, B.; Wang, L.; Mao, J. Metagenomics-based insights into the microbial community profiling and flavor development potentiality of baijiu Daqu and huangjiu wheat Qu”. Food Res. Int. 2022, 157, 110707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Xu, Y. Bacillus licheniformis Affects the Microbial Community and Metabolic Profile in the Spontaneous Fermentation of Daqu Starter for Chinese Liquor Making. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 250, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Zou, S.; Ji, C.; Dong, L.; Zhang, S.; Liang, H.; Lin, X. Analysis of Fungal Diversity, Physicochemical Properties and Volatile Organic Compounds of Strong-Flavor Daqu from Seven Different Areas. Foods 2024, 13, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Revealing the Key Microorganisms Producing Higher Alcohols and Their Assembly Processes during Jiang-flavor Baijiu Fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhou, S.; Duan, C.; Li, Q.; Wei, J.; Liu, G. Exploring the Role of Active Functional Microbiota in Flavor Generation by Integrated Metatranscriptomics and Metabolomics during Niulanshan Baijiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Deng, L.; Li, Z.; Fei, Y.; Bai, W.; Zhao, W.; He, S.; Cao, R. Metagenomic Analysis of Core Differential Microbes between Traditional Starter and Round-Koji-Mechanical Starter of Chi-Flavor Baijiu. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1390899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, D.; Mu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Qi, Q.; Mu, Y.; Su, W. Exploring the Heterogeneity of Community and Function and Correspondence of “Species-Enzymes” among Three Types of Daqu with Different Fermentation Peak-Temperature via High-throughput Sequencing and Metagenomics. Food Res. Int. 2024, 176, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, G.-Y.; Chai, L.-J.; Zhong, X.-Z.; Lu, Z.-M.; Zhang, X.-J.; Wu, L.-H.; Wang, S.-T.; Shen, C.-H.; Shi, J.-S.; Xu, Z.-H. Comparative Genomics Unveils the Habitat Adaptation and Metabolic Profiles of Clostridium in an Artificial Ecosystem for Liquor Production. Msystems 2022, 7, e0029722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, K.; Ye, G.; Luo, H.; Zou, W. Revealing Microbiota Characteristics and Predicting Flavor-Producing Sub-Communities in Nongxiangxing Baijiu Pit Mud through Metagenomic Analysis and Metabolic Modeling. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, P.; Da Costa, A.; Courtois, B.; Courtois, J. Polysaccharide Lyases: Recent Developments as Biotechnological Tools. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2003, 23, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, B.L.; Polikarpov, I. Family 1 Carbohydrate Binding-Modules Enhance Saccharification Rates. Amb Express 2014, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshareef, S.A. Metabolic Analysis of the CAZy Class Glycosyltransferases in Rhizospheric Soil Fungiome of the Plant Species Moringa Oleifera. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 31, 103956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecek, F.; Janecek, S. A Novel Subfamily GH13_46 of the α-Amylase Family GH13 Represented by the Cyclomaltodextrinase from Flavobacterium sp. No. 92. Molecules 2022, 27, 8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Vinuesa, L.; Hernandez-Hernandez, O.; Javier Moreno, F.; de las Rivas, B.; Munoz, R. Unravelling the Diversity of Glycoside Hydrolase Family 13 α-Amylases from Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Liu, F.; Shao, W.; Chu, J.; Wu, B.; He, B. Efficient Synthesis of Crocins from Crocetin by a Microbial Glycosyltransferase from Bacillus subtilis 168. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11701–11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janickova, Z.; Janecek, S. In Silico Analysis of Fungal and Chloride-Dependent α-Amylases within the Family GH13 with Identification of Possible Secondary Surface-Binding Sites. Molecules 2021, 26, 5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, C.; Zhao, M.; Xue, T.; Geng, T.; Nie, X.; Han, C.; Wen, Y.; Jia, L. Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences Between Three Different Grades of Hongxin Low-Temperature Daqu. Foods 2025, 14, 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071104
Ren C, Zhao M, Xue T, Geng T, Nie X, Han C, Wen Y, Jia L. Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences Between Three Different Grades of Hongxin Low-Temperature Daqu. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071104
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Chao, Mengke Zhao, Tinghui Xue, Tianpei Geng, Xiao Nie, Chaoyue Han, Yuge Wen, and Liyan Jia. 2025. "Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences Between Three Different Grades of Hongxin Low-Temperature Daqu" Foods 14, no. 7: 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071104
APA StyleRen, C., Zhao, M., Xue, T., Geng, T., Nie, X., Han, C., Wen, Y., & Jia, L. (2025). Metagenomic and Physicochemical Analyses Reveal Microbial Community and Functional Differences Between Three Different Grades of Hongxin Low-Temperature Daqu. Foods, 14(7), 1104. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071104





