Effect of Sucrose on the Rheology and 3D Printability of Pregelatinized Rice Flour Paste
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of α-Rice Flour–Sucrose Paste
2.3. Rheological Measurement
2.4. 3D Printing Process
2.5. Printability Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
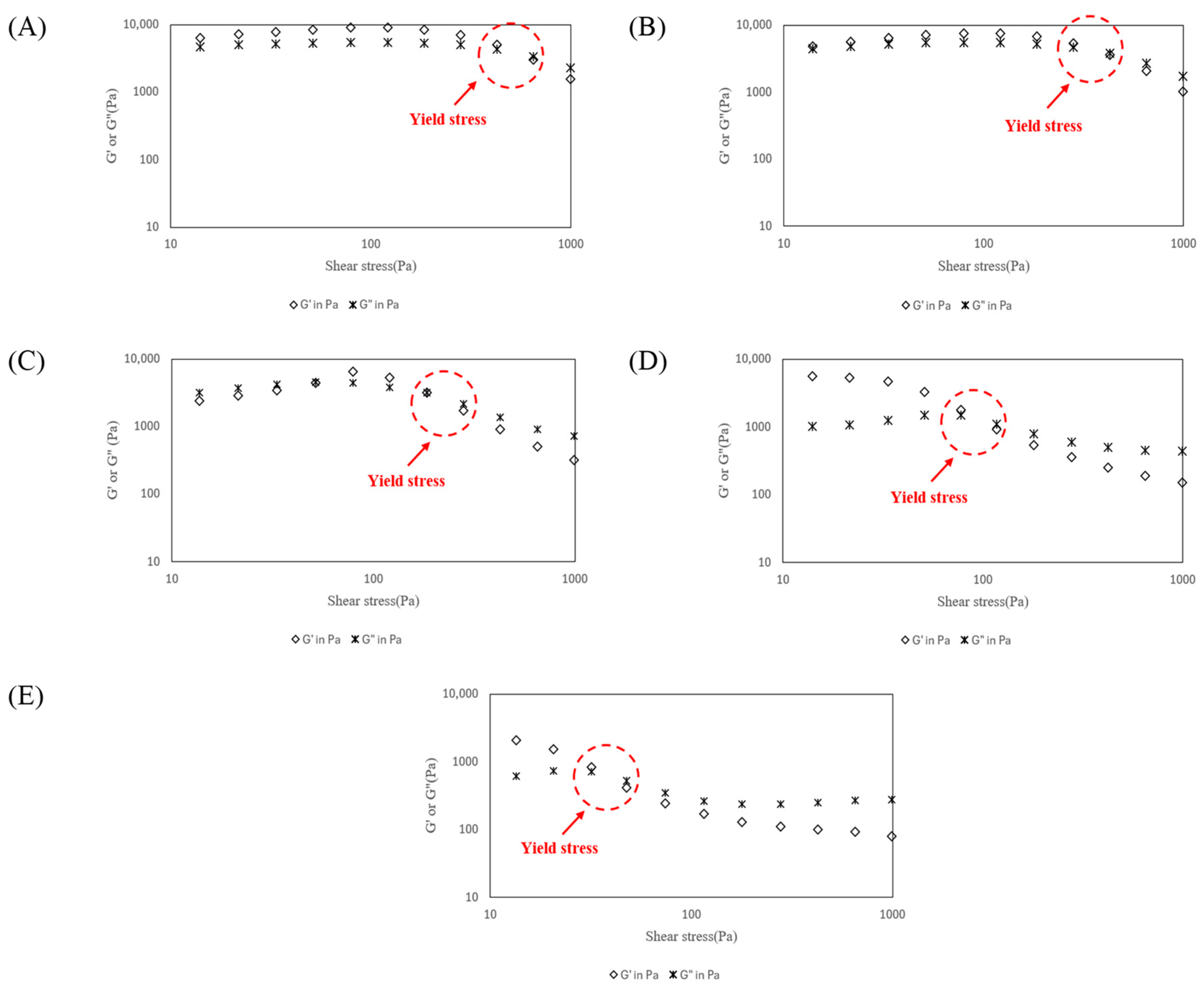
3.1. Rheological Behavior Evaluation
3.2. Evaluation of the Printability
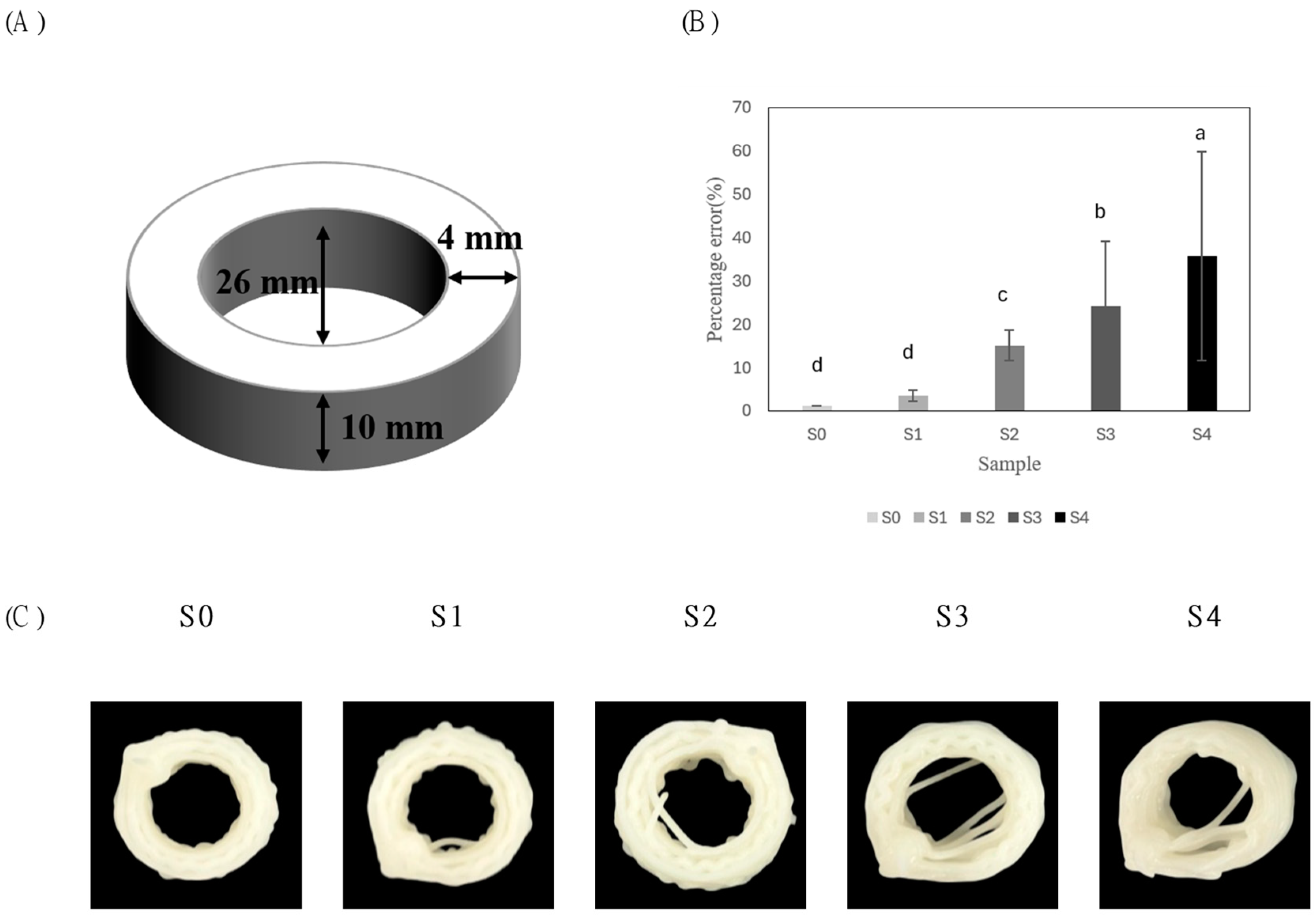
3.2.1. 3D-Printed Hollow Cylinder
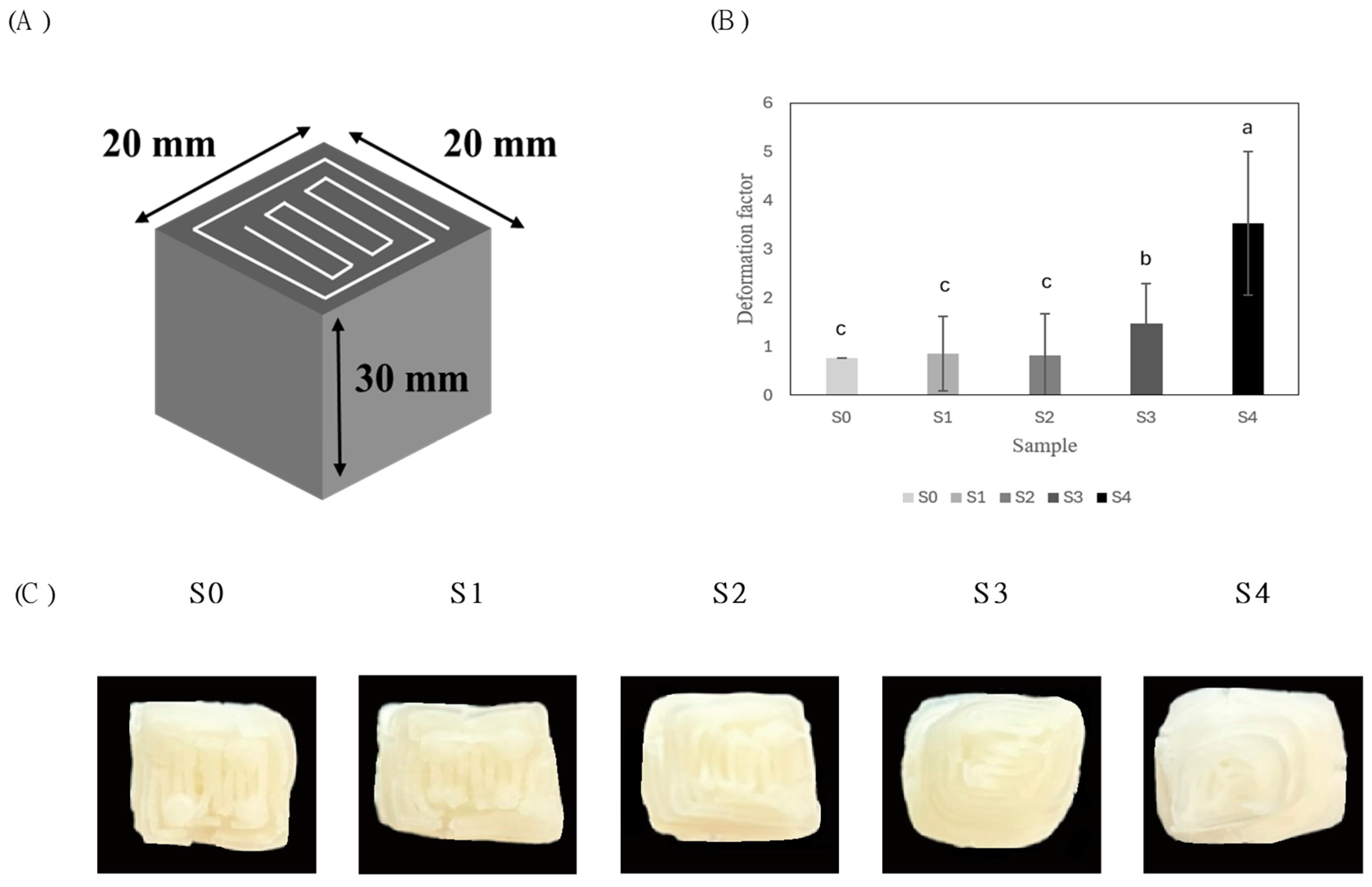
3.2.2. 3D-Printed Cuboid
3.3. Correlations Between Printability and Rheology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, S.; Stieger, M.A.; van der Goot, A.J.; Schutyser, M.A.I. Extrusion-based 3D printing of food pastes: Correlating rheological properties with printing behaviour. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 58, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yuqing, H.; Xiao, L.; Gao, W.; Kang, X.; Sui, J.; Cui, B. Impact of starch amylose and amylopectin on the rheological and 3D printing properties of corn starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado-Rosas, R.; Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Cuan-Urquizo, E.; Mendoza-Cachú, D.; Morales-de la Peña, M.; Alvarado-Orozco, J.M.; Companella, O.H. Evaluation of rheology and printability of 3D printing nutritious food with complex formulations. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 58, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bhandari, B.; Parkash, S.; Mantibal, S.; Zhang, M. Linking rheology and printability of a multicomponent gel system of carrageenan-xanthan-starch in extrusion based additive manufacturing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaesa, A.G.; Villanueva, M.; Vela, A.J.; Ronda, F. Impact of microwave radiation on in vitro starch digestibility, structural and thermal properties of rice flour. From dry to wet treatments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, T.; Duan, S.; Qin, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, A.; Wu, D.; Chen, H.; Han, G.; et al. Effects of sodium alginate and rice variety on the physicochemical characteristics and 3D printing feasibility of rice paste. LWT 2020, 127, 109360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cano, A.; Mendoza-Báez, R.; Zenteno-Mateo, B.; Rodríguez-Mora, J.S.; Agustín-Serrano, R.; Morales, M.A. Study by DFT of the functionalization of amylose/amylopectin with glycerin monoacetate: Characterization by FTIR, electronic and adsorption properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1269, 133761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Huang, Y.; Chen, P. Effects of sucrose on pasting, thermal, rheological and textural properties of native and alcohol-alkali-treated waxy rice starch treatments. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 166, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, M.; Liang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Sun, L.; Dang, W.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Liu, C. Research progress on properties of pre-gelatinized starch and its application in wheat flour products. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, Y.R. Clean label starch: Production, physicochemical characteristics, and industrial applications. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Obadi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, S.; Xu, B. The impact of starch degradation induced by pre-gelatinization treatment on the quality of noodles. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, N.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of pregelatinized starch on the characteristics, microstructures, and quality attributes of glutinous rice flour and dumplings. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.H.; Xia, W.; Chen, R.Y.; Dai, T.T.; Luo, S.J.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.M. A new pre-gelatinized starch preparing by gelatinization and spray drying of rice starch with hydrocolloids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, D.; Pinho, L.; Patel, B.; Desam, P.; Campanella, O.H. Characterization of starch–water interactions and their effects on two key functional properties: Starch gelatinization and retrogradation. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, J.; Yoo, B. Rheological characteristics of concentrated ternary gum mixtures with xanthan gum, guar gum, and carboxymethyl cellulose: Effect of NaCl, sucrose, pH, and temperature. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.J. Formulation and evaluation of thermoreversible sugar-paste for hot-melt 3D printing. J. Food Eng. 2022, 321, 110944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B. Effect of stearic acid on the microstructural, rheological and 3D printing characteristics of rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Rodríguez, Y.F.; Igual, M.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P. Exploration of changes in rheological and spectral properties of rice protein inks before and after 3D printing. LWT 2024, 210, 116808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liang, K.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W.; Kang, X.; Li, T.; Cui, B. Effect of molecular structure changes during starch gelatinization on its rheological and 3D printing properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Ren, A.; Liu, R.; Xing, Y.; Yu, X.; Jiang, H. Effect of sodium chloride solution on quality of 3D-printed samples molded using wheat starch gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 107197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, T.; Grush, E.; Allan, M.C.; Mauer, L.J. The effects of sugars and sugar alcohols on the pasting and granular swelling of wheat starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 126, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Chao, C.; Cai, J.; Yan, Y.; Copeland, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S. The effect of NaCl on the formation of starch-lipid complexes. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Bao, X.; Li, P.; Zhan, L.; Wu, H.; Chen, P. Effect of NaCl addition on alcohol-alkali-treated waxy rice starch: Structural and physicochemical functionality. Food Chem. 2022, 389, 133021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, O.B. Effects of processing and additives on starch physicochemical and digestibility properties. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamipour-Shirazi, A.; Norton, I.T.; Mills, T. Designing hydrocolloid based food-ink formulations for extrusion 3D printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 95, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S. Effects of NaCl on the Physical Properties of Cornstarch–Methyl Cellulose Blend and on Its Gel Prepared with Rice Flour in a Model System. Foods 2023, 12, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Cervantes, I.; Morales, M.A.; Agustín-Serrano, R.; Cardenas-García, M.; Pérez-Luna, P.V.; Arroyo-Reyes, B.L.; Maldonado-García, A. Polylactic acid/sodium alginate/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds with trabecular tissue morphology designed by a bone remodeling model using 3D printing. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9478–9496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geffrault, A.; Bessaies-Bey, H.; Roussel, N.; Coussot, P. Printing by yield stress fluid shaping. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 75, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijdam, J.J.; LeCorre-Bordes, D.; Delvart, A.; Schon, B.S. A rheological test to assess the ability of food inks to form dimensionally stable 3D food structures. J. Food Eng. 2021, 291, 110235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Meng, X. Effect of glycerol incorporation on the liquid crystal structure of sucrose fatty acid ester in aqueous solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 684, 133213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Qian, X.; Cui, G.; Ma, S.; Wang, X. Synergistic effect of combined sucrose substitutes and partially gelatinized oat flour on gluten-free steamed oat cakes produced only by oat flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 110, 103648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outrequin, T.C.R.; Gamonpilas, C.; Siriwatwechakul, W.; Sreearunothai, P. Extrusion-based 3D printing of food biopolymers: A highlight on the important rheological parameters to reach printability. J. Food Eng. 2023, 342, 111371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Yu, J.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Ge, X.; Li, W.; Zheng, J. A new pre-gelatinized starch preparing by spray drying and electron beam irradiation of oat starch. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainis, W.N.; Feng, R.; van den Berg, F.W.J.; Ahrné, L. Comparing the rheological and 3D printing behavior of pea and soy protein isolate pastes. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 84, 103307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xie, F.; Chen, L.; Zheng, B. Effect of rheological properties of potato, rice and corn starches on their hot-extrusion 3D printing behaviors. J. Food Eng. 2019, 244, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Cuan-Urquizo, E. Towards the development of 3D-printed food: A rheological and mechanical approach. Foods 2022, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Phuhongunge, P. 4D printing induced by microwave and ultrasound for mushroom mixtures: Efficient conversion of ergosterol into vitamin D2. Food Chem. 2022, 387, 132840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Taylor, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning: With Applications in Python; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 69–134. [Google Scholar]

| Ingredients | Mass (g/50 g) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | |
| α-Rice flour | 17.5 | 17 | 16.5 | 16 | 15.5 |
| Sucrose | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 1.5 | 2 |
| Distilled water | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 |
| Total | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Formulation | Storage Modulus G′Max (Pa) | Loss Modulus G″Max (Pa) | Yield Stress τy (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S0 | 9032.0 ± 352.0 a (1) (2) | 5448.1 ± 360.3 a | 3845.3 ± 284.2 a |
| S1 | 7574.0 ± 145.6 b | 5517.9 ± 383.6 a | 3986.0 ± 435.3 a |
| S2 | 6468 ± 291.4 c | 4580.1 ± 175.5 b | 3104.7 ± 43.7 b |
| S3 | 5529.5 ± 403.9 d | 1533.2 ± 148.1 c | 1364.7 ± 142.5 c |
| S4 | 2212.1 ± 397.6 e | 739.1 ± 103.1 d | 658.8 ± 94.7 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, D.; Saleh, M.I.; Lee, Y. Effect of Sucrose on the Rheology and 3D Printability of Pregelatinized Rice Flour Paste. Foods 2025, 14, 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071107
Lee D, Saleh MI, Lee Y. Effect of Sucrose on the Rheology and 3D Printability of Pregelatinized Rice Flour Paste. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071107
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Dongju, Mohammed I. Saleh, and Youngseung Lee. 2025. "Effect of Sucrose on the Rheology and 3D Printability of Pregelatinized Rice Flour Paste" Foods 14, no. 7: 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071107
APA StyleLee, D., Saleh, M. I., & Lee, Y. (2025). Effect of Sucrose on the Rheology and 3D Printability of Pregelatinized Rice Flour Paste. Foods, 14(7), 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071107






