Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Storage
2.3. Fatty Acid Value
2.4. Malondialdehyde Content
2.5. Amylose Content
2.6. Rice Color Measurement
2.7. Pasting Properties of Rice
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.9. UHPLC-TOF-MS Conditions for Metabolomics Analysis
2.9.1. Metabolite Extraction
2.9.2. UHPLC-TOF-MS Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Changes in Rice Quality
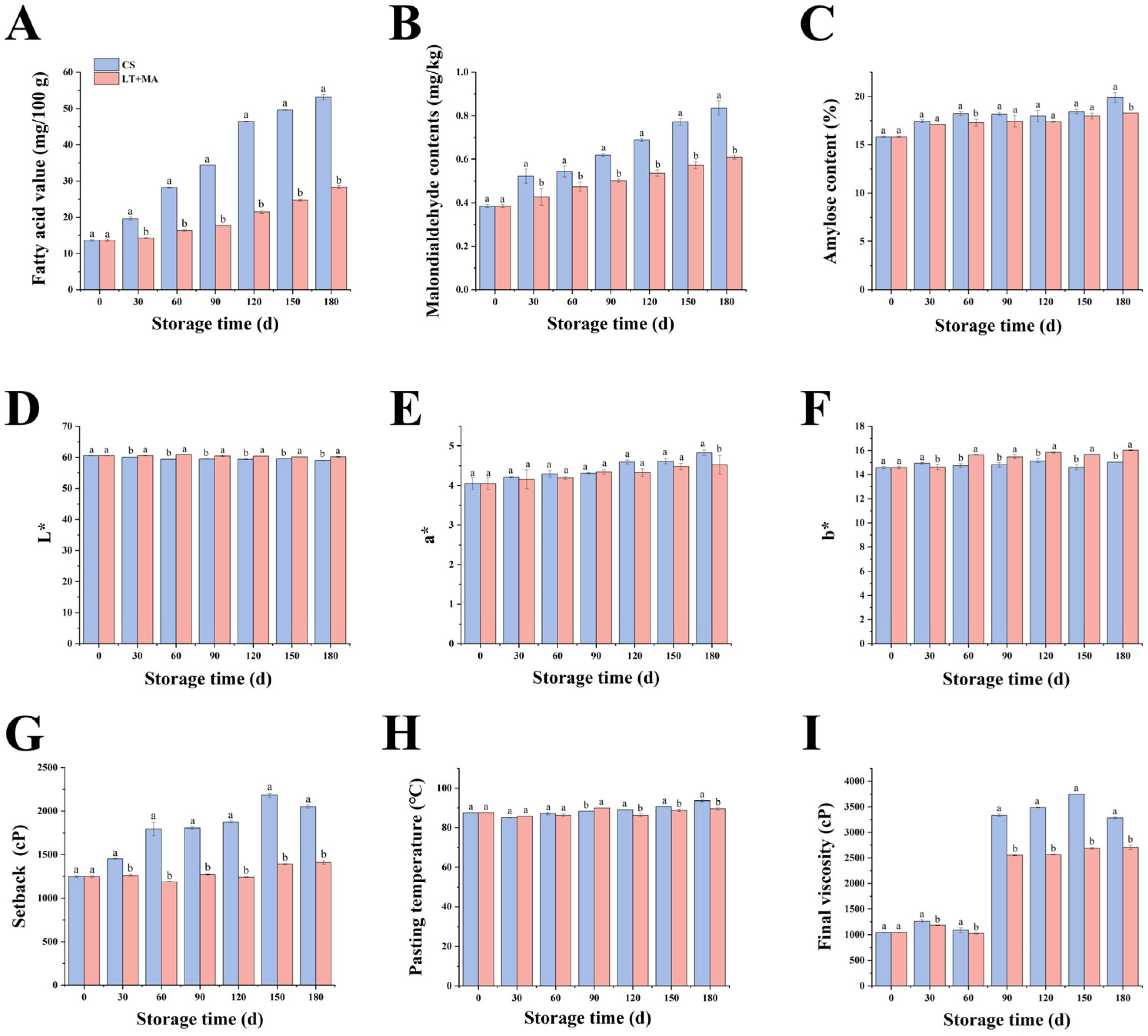
3.1.1. Fatty Acid Values
3.1.2. Malondialdehyde Content
3.1.3. Amylose Content
3.1.4. Color
3.1.5. Pasting Properties
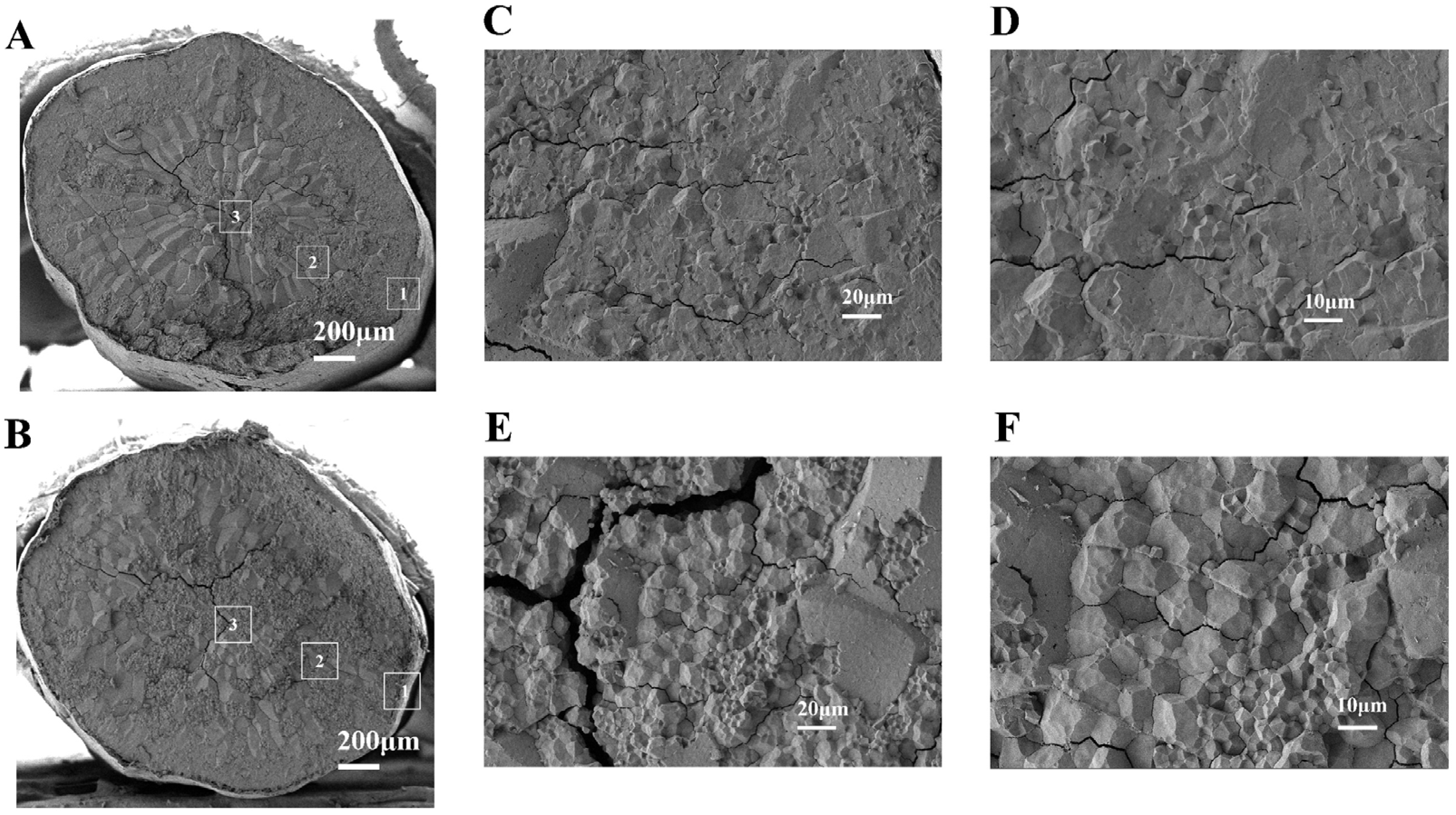
3.1.6. SEM
3.2. Metabolome Profiling of LT + MA vs. CS
3.2.1. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3.2.2. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
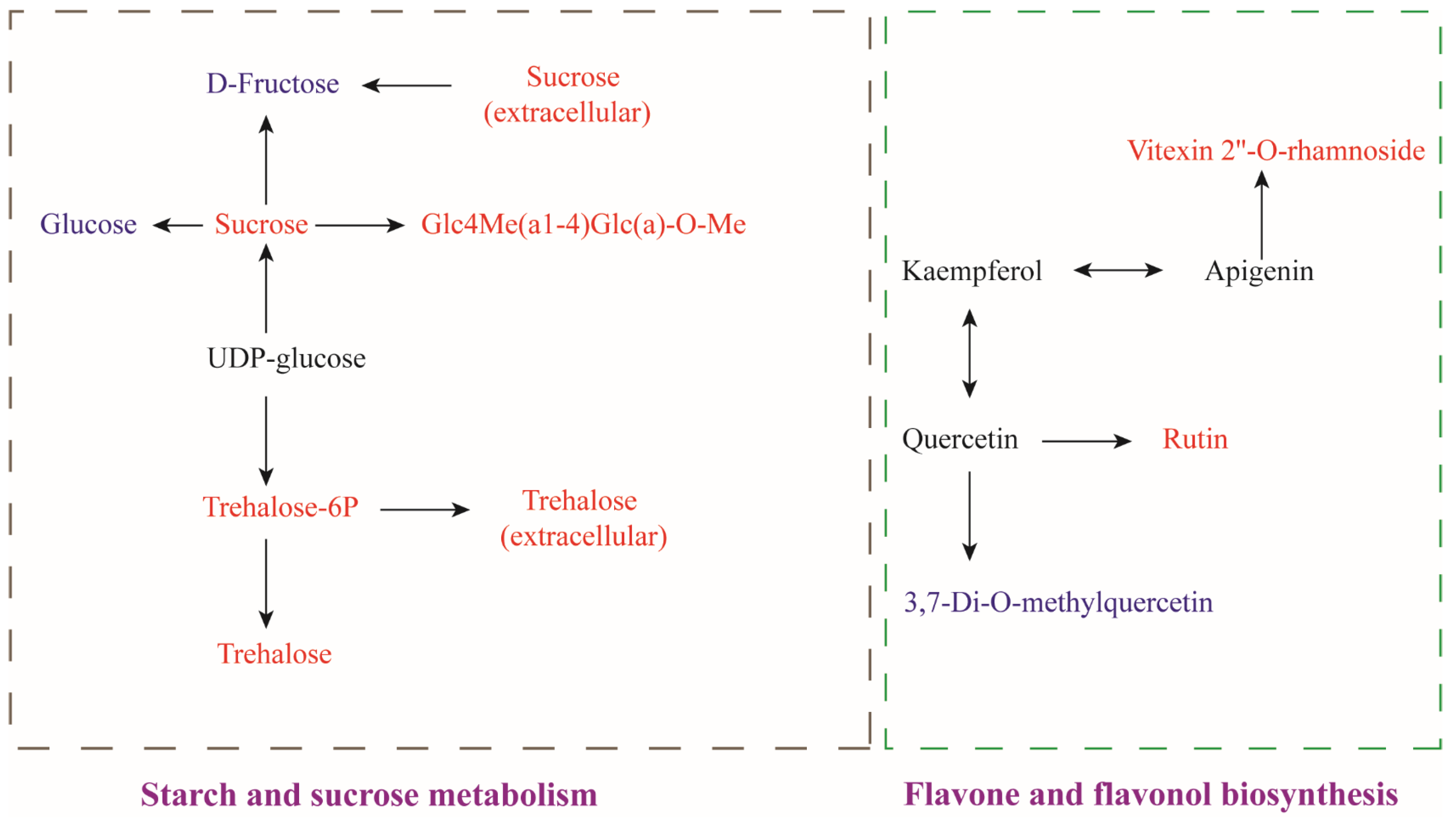
3.2.3. Differential Metabolites Analysis
Starch and Sucrose Metabolism
Flavone and Flavonol Biosynthesis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Müller, A.; Nunes, M.T.; Maldaner, V.; Coradi, P.C.; de Moraes, R.S.; Martens, S.; Leal, A.F.; Pereira, V.F.; Marin, C.K. Rice drying, storage and processing: Effects of post-harvest operations on grain quality. Rice Sci. 2022, 29, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.M.; Proctor, A.; Eason, R.L.; Jain, V. Effects of rice harvest moisture on kernel damage and milled rice surface free fatty acid levels. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C010–C015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.A.; Salazar, R.; Palacios-Ponce, A.; Cornejo, F.; Corradini, M.G. Rice storage under controlled conditions: Changes in its physicochemical and functional properties. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2024, 105, 102236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Guo, J.; Ye, C.; Chen, K.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Xiao, X.; Liu, C. Low temperature storage alleviates aging of paddy by reducing lipid degradation and peroxidation. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, L.; Yang, L.; Lu, Q. Oxidative stress with the damage of scavenging system: A mechanism for the nutrients loss in rice seeds during post-harvest storage. CyTA-J. Food 2019, 17, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhao, C.; Yan, M.; Huang, D.; McClements, D.J.; Huang, Z.; Cao, C. Influence of gene regulation on rice quality: Impact of storage temperature and humidity on flavor profile. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Ahmed, F.; Jabeen, S.; Bhurgri, M.U.; Asif, H.; Hussain, K. Effects of climatic conditions and hermetic storage on the growth of Aspergillus parasiticus and aflatoxin B1 contamination in basmati rice. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2022, 96, 101944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Abadias, M.; Usall, J.; Torres, R.; Teixidó, N.; Viñas, I. Application of modified atmosphere packaging as a safety approach to fresh-cut fruits and vegetables—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 46, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moirangthem, T.T.; Baik, O.-D. Disinfestation of stored grains using non-chemical technologies—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisuttu, C.; Risoli, S.; Moncini, L.; Nali, C.; Pellegrini, E.; Sarrocco, S. Sustainable Strategies to Counteract Mycotoxins Contamination and Cowpea Weevil in Chickpea Seeds during Post-Harvest. Toxins 2023, 15, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.B.S.; Fernández-García, T.; Romero, A.; López, A. Effect of modified atmosphere storage on fazelnut quality. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2001, 25, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Li, W.; Yang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Lu, P.; Hu, M. Metabolic mechanism of nitrogen modified atmosphere storage on delaying quality deterioration of rice. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, D.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, H. Effect of catalase on lipid oxidation and flavor substances of α- instant rice during storage. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e46822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Du, Y.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Cao, C. Grain starch, fatty acids, and amino acids determine the pasting properties in dry cultivation plus rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2022, 373, 131472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Hou, D.; Zhu, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Du, X. Effect of heterogeneous protein distribution on in situ pasting properties of black rice starch. LWT 2022, 153, 112388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Yong, F. Lipid oxidation of brown rice stored at different temperatures. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 52, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.-H.; Huang, B.; Ding, C.-B.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Chen, Y.-E.; Hu, C.; Zhou, L.-J.; Huang, Y.; Liao, J.-Q.; Yuan, S.; et al. Effects of Melatonin on Anti-oxidative Systems and Photosystem II in Cold-Stressed Rice Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.-P.; Lv, Y.-Y.; Yuan, W.-J.; Zhang, S.-B.; Hu, Y.-S. Effect of artificial aging on wheat quality deterioration during storage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 80, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-K.; Chang, Y.H. Structure and digestibility properties of resistant rice starch cross-linked with citric acid. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 2166–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Takeda, T.; Yoshida, S. Comparison of Volatiles in Cooked Rice with Various Amylose Contents. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2014, 20, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, L.; Cao, F.; Chen, J.; Huang, M. Relationships between texture properties of cooked rice with grain amylose and protein content in high eating quality indica rice. Cereal Chem. 2024, 101, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.H.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, S.S. Effect of storage temperature for paddy on consumer perception of cooked rice. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, D.; He, L.; Wang, T.; Lu, H.; Yang, F.; Deng, F.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Correlation of taste values with chemical compositions and Rapid Visco Analyser profiles of 36 indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, N.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Effect of germination temperature on hierarchical structures of starch from brown rice and their relation to pasting properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, P.; Wang, M. Effects of konjac glucomannan on pasting and rheological properties of corn starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, A.F.; Fibrianto, K.; Torley, P.J.; Bhandari, B. Physical properties of cryomilled rice starch. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Zhu, P.; Sui, Z.; Bao, J. Physicochemical properties of starches from diverse rice cultivars varying in apparent amylose content and gelatinisation temperature combinations. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Morris, C.F.; Murphy, K.M. Evaluation of Texture Differences among Varieties of Cooked Quinoa. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, S2337–S2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Jane, J. Gelatinization and rheological properties of starch. Starch—Stärke 2015, 67, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, R.; Ma, M. Kinetic studies on soluble sugar profile in rice during storage: Derivation using the Laplace transform. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 76, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, J.; Dai, C.; Liu, T.; Cheng, D.; Luo, C. Whole-Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals the Global Molecular Responses and CeRNA Regulatory Network of mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs and circRNAs in Response to Salt Stress in Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Lin, M.; Qi, X.; Chen, J.; Gu, H.; Zhong, Y.; Sun, L.; Muhammad, A.; Bai, D.; Hu, C.; et al. Full-length transcriptome profiling reveals insight into the cold response of two kiwifruit genotypes (A. arguta) with contrasting freezing tolerances. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragoza, S.; González - Párraga, P.; Pedreño, Y.; Alvarez-Peral, F.J.; Argüelles, J.-C. Trehalose accumulation induced during the oxidative stress response is independent of TPS1 mRNA levels in Candida albicans. Int. Microbiol. 2003, 6, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleutherio, E.; Panek, A.; De Mesquita, J.F.; Trevisol, E.; Magalhaes, R. Revisiting yeast trehalose metabolism. Curr. Genet. 2015, 61, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollastri, S.; Tattini, M. Flavonols: Old compounds for old roles. Ann. Bot. 2011, 108, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-S.; Park, H.-R.; Lee, K.-A. A comparative study of rutin and rutin glycoside: Antioxidant activity, anti-Inflammatory effect, effect on platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enogieru, A.B.; Haylett, W.; Hiss, D.C.; Bardien, S.; Ekpo, O.E.; Szymanska, R. Rutin as a potent antioxidant: Implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6241017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, B.; Lú-Chau, T.A.; Moreira, M.T.; Lema, J.M.; Eibes, G. Rutin: A review on extraction, identification and purification methods, biological activities and approaches to enhance its bioavailability. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, M.-F.; Yang, Y.-S.; Li, R.; Tan, J.; Tang, S.-H.; Jiang, Z.-T. Composition, cytotoxicity and antioxidant activities of polyphenols in the leaves of star anise (Illicium verum Hook. f.). ScienceAsia 2019, 45, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Joseph, J.A. Structure-activity relationships of quercetin in antagonizing hydrogen peroxide-induced calcium dysregulation in PC12 cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 27, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y. Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics. Foods 2025, 14, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071262
Zhao Y, Li L, Li Y, Zhao Y. Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics. Foods. 2025; 14(7):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071262
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanan, Lulu Li, Yanfei Li, and Yan Zhao. 2025. "Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics" Foods 14, no. 7: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071262
APA StyleZhao, Y., Li, L., Li, Y., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Effect of Low Temperature and Nitrogen Modified Atmosphere Treatments on the Storage of High Moisture Indica Rice: Quality, Microstructure, and Metabolome Characteristics. Foods, 14(7), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14071262





