Ultrafiltration of Whole Milk: Impact of Homogenization and Ultrafiltration Temperature on Processing Efficiency and Component Retention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
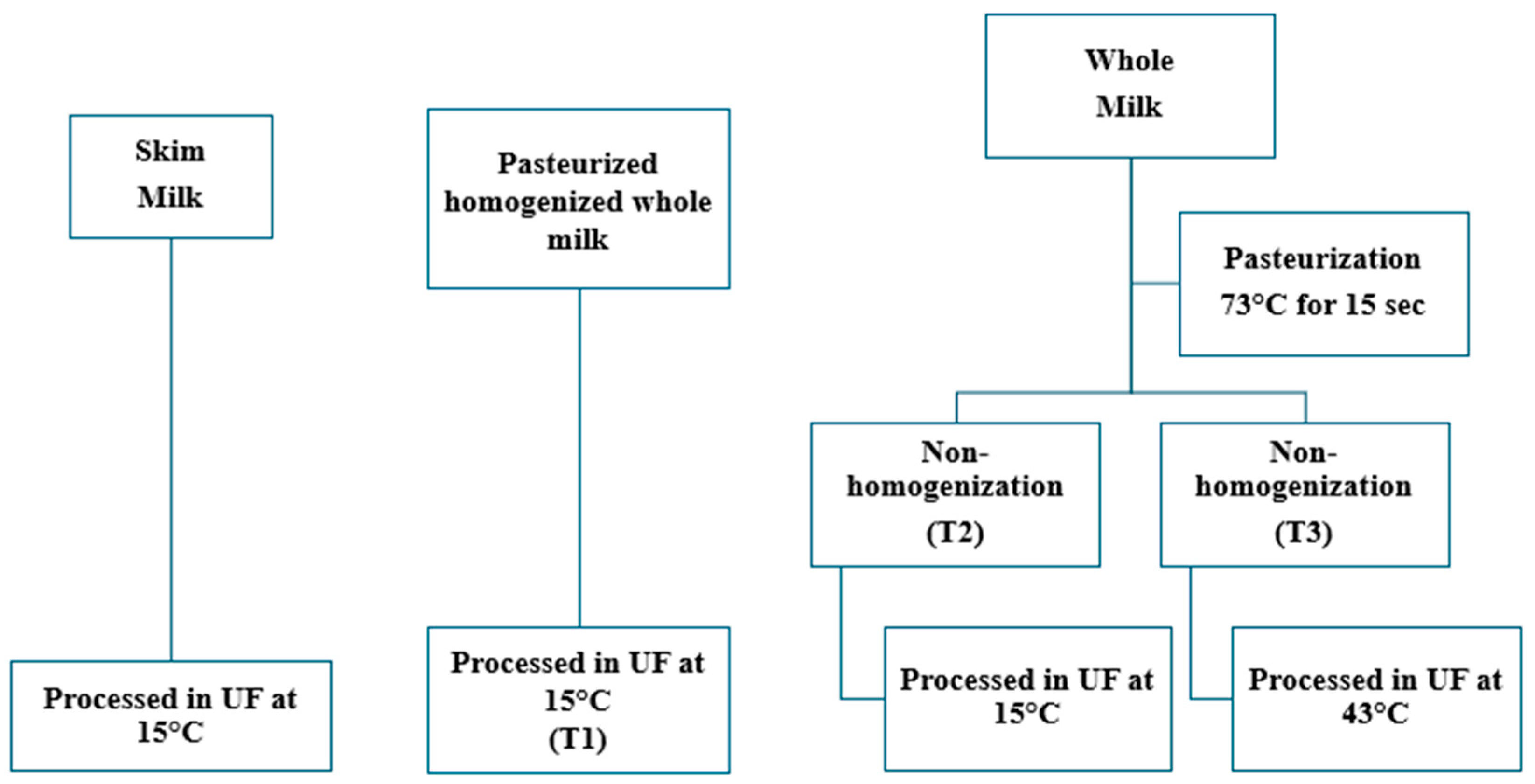
2.1. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
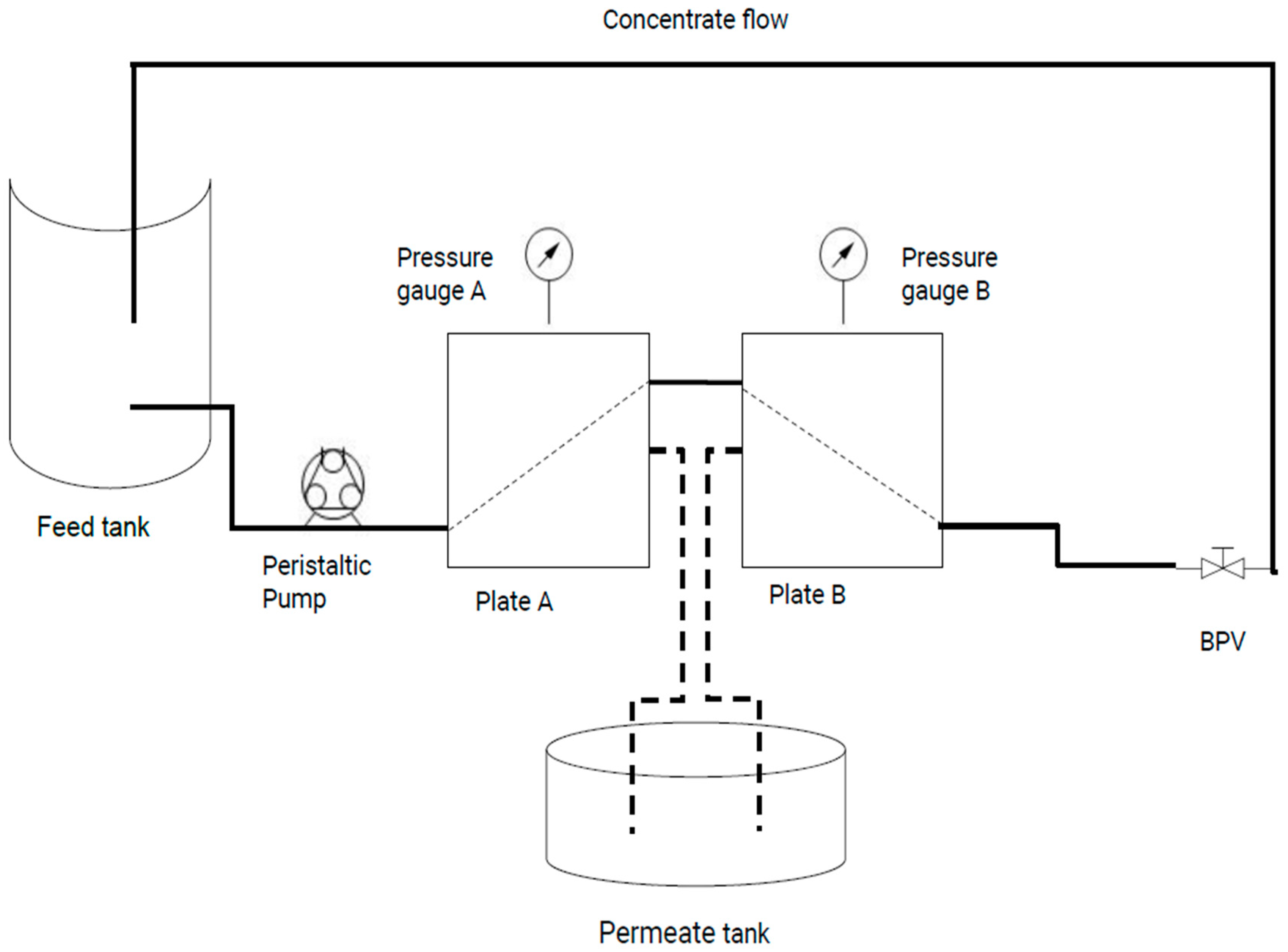
2.2. UF Operation
Processing Performance
2.3. Proximate Chemical Analysis
2.4. Hydrodynamic Diameter
3. Results and Discussions
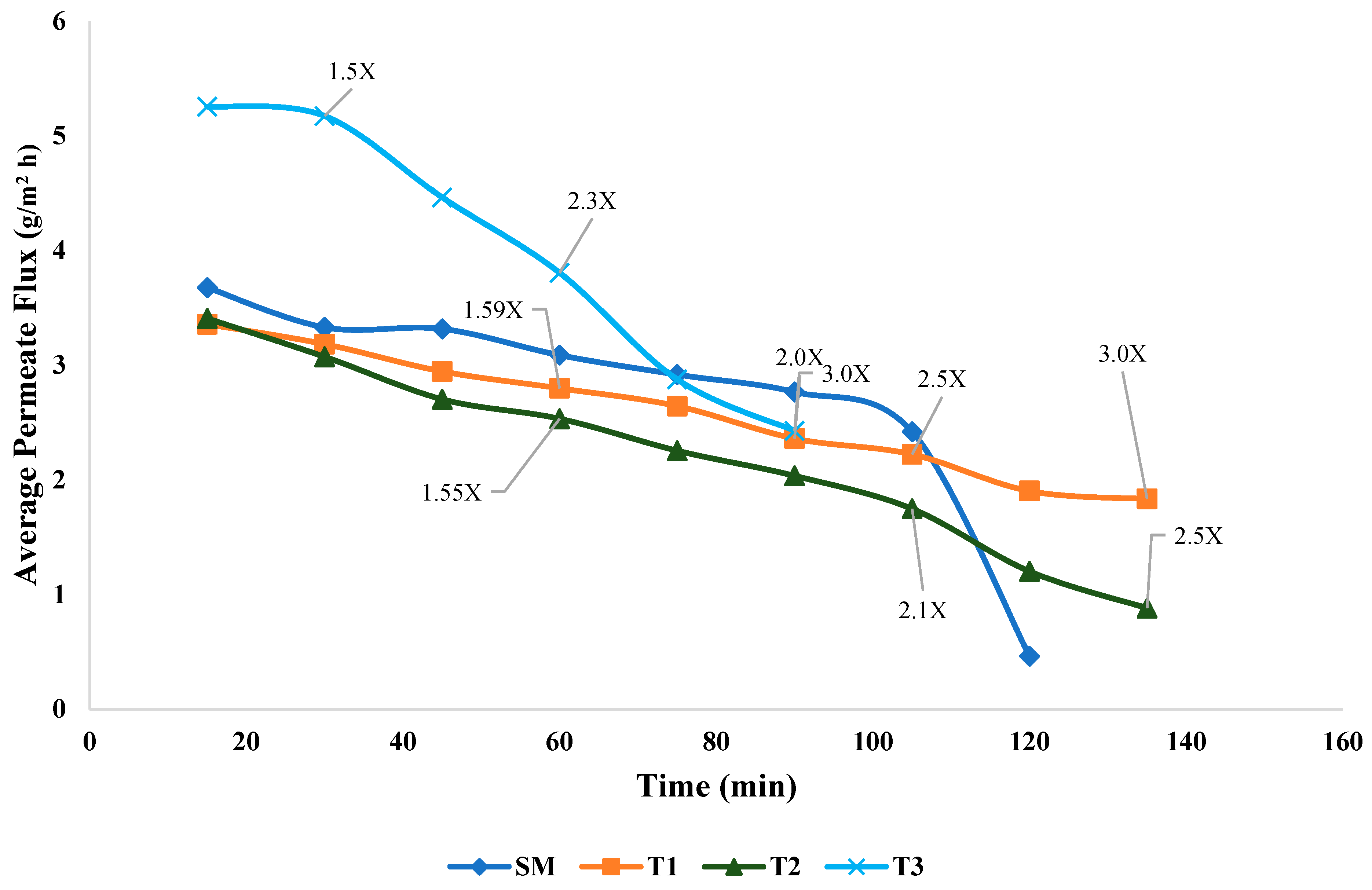
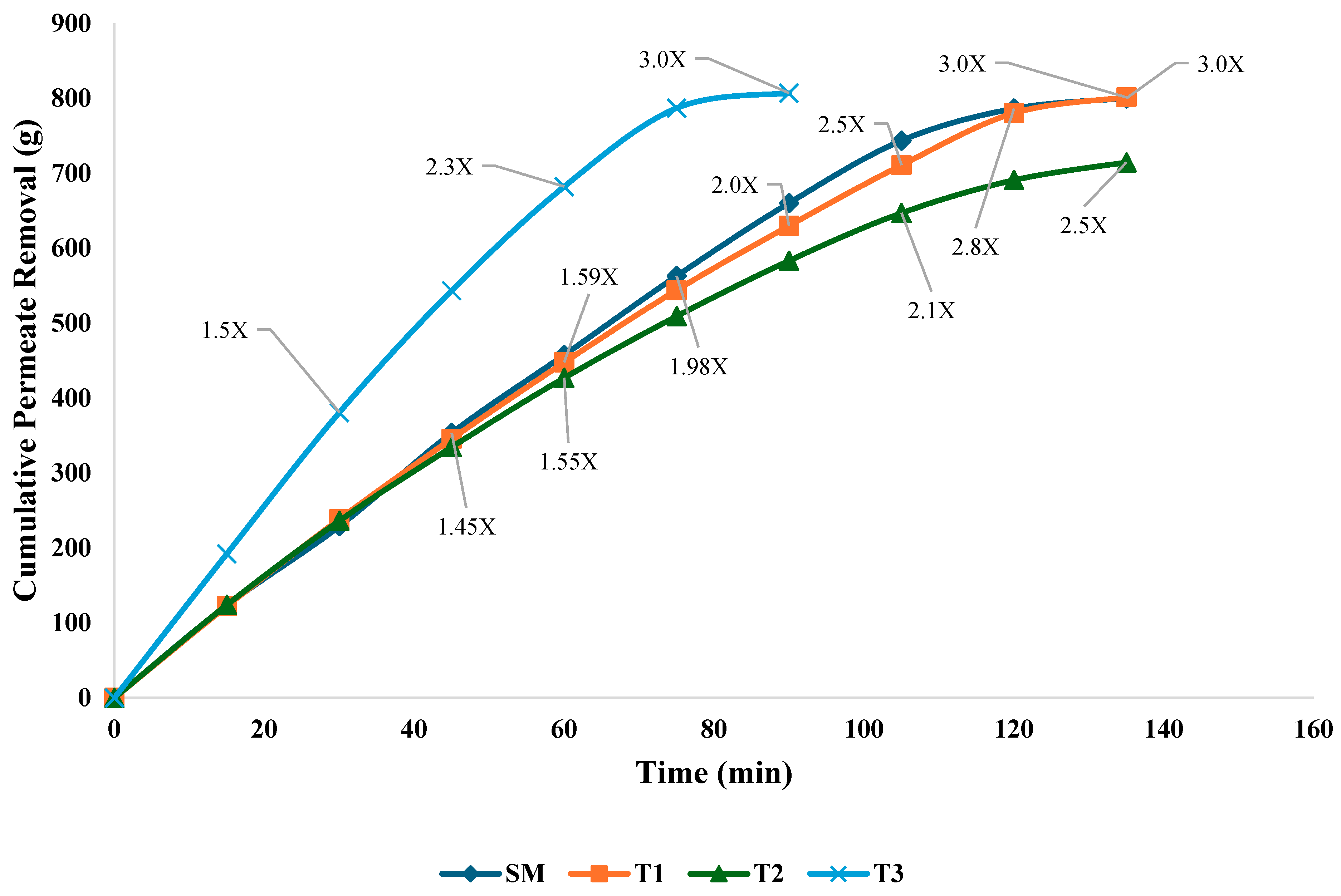
3.1. Flux Rate and Permeate Removal
3.2. Initial Milk Composition
3.3. Retentate Composition at 2X, 3X, and Final Concentration Levels
3.4. Permeate Composition Analysis
3.5. Retentate and Permeate Mineral Analysis
3.6. Hydrodynamic Diameter
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheryan, M. Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Brans, G.; Schroën, C.; Van der Sman, R.; Boom, R. Membrane fractionation of milk: State of the art and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubois, J.-L. Recent developments of membrane ultrafiltration in the dairy industry. In Ultrafiltration Membranes and Applications; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Pouliot, Y. Membrane processes in dairy technology—From a simple idea to worldwide panacea. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. Interactions of milk proteins during the manufacture of milk powders. Le Lait 2007, 87, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, A.; Fane, A.G.; Waite, T. Fouling effects on rejection in the membrane filtration of natural waters. Desalination 2000, 131, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, R.W.; Wu, J.J. Permeate flux in ultrafiltration processes—Understandings and misunderstandings. Membranes 2022, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salunke, P.; Marella, C.; Metzger, L.E. Microfiltration and ultrafiltration process to produce micellar casein and milk protein concentrates with 80% crude protein content: Partitioning of various protein fractions and constituents. Dairy 2021, 2, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Tripathi, B.P.; Kumar, M.; Shahi, V.K. Membrane-based techniques for the separation and purification of proteins: An overview. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srilaorkul, S.; Ozimek, L.; Ooraikul, B.; Hadziyev, D.; Wolfe, F. Effect of ultrafiltration of skim milk on casein micelle size distribution in retentate. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. The effect of ultrafiltration on the acid gelation properties of protein-standardised skim milk systems. Food Res. Int. 2021, 146, 110432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, Y.K. Effect of ultrafiltration, fat reduction and salting on textural properties of white brined cheese. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oommen, B.S.; Mistry, V.V.; Nair, M.G. Effect of homogenization of cream on composition, yield, and functionality of Cheddar cheese made from milk supplemented with ultrafiltered milk. Le Lait 2000, 80, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy-Lucey, S.; Jaeggi, J.; Bostley, A.; Johnson, M.; Lucey, J. Standardization of milk using cold ultrafiltration retentates for the manufacture of Parmesan cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 2789–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindasamy-Lucey, S.; Jaeggi, J.; Martinelli, C.; Johnson, M.; Lucey, J. Standardization of milk using cold ultrafiltration retentates for the manufacture of Swiss cheese: Effect of altering coagulation conditions on yield and cheese quality. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 2719–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, D. Membrane fouling: A challenge during dairy ultrafiltration. Membr. Process. Dairy Ingred. Sep. 2015, 3, 67–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, K.S.; Haribabu, M.; Harvie, D.J.; Dunstan, D.E.; Martin, G.J. Mechanisms of flux decline in skim milk ultrafiltration: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Hill, C., Jr.; Amundson, C. Ultrafiltration of whole milk. J. Dairy Sci. 1979, 62, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.; Hernandez, A.J.; Barbano, D.M.; Drake, M.A. Ultrafiltration: Effect of Process Temperature (7 °C and 50 °C) on Process Performance and Protein Beverage Physical, Chemical, and Sensory Properties. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 8919–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.L.; Glover, F.A.; Scurlock, E.M.; Marshall, R.J.; Hatfield, D.S. Effect of use of milk concentrated by ultrafiltration on the manufacture and ripening of Cheddar cheese. J. Dairy Res. 1981, 48, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keogh, M.K.; Murray, C.A.; T O’Kennedy, B. Effects of ultrafiltration of whole milk on some properties of spray-dried milk powders. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbano, D.; Sciancalepore, V.; Rudan, M. Characterization of milk proteins in ultrafiltration permeate. J. Dairy Sci. 1988, 71, 2655–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Tal, G.; Hankins, N.P.; Gitis, V. Fouling and cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes: A review. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 1, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méthot-Hains, S.; Benoit, S.; Bouchard, C.; Doyen, A.; Bazinet, L.; Pouliot, Y. Effect of transmembrane pressure control on energy efficiency during skim milk concentration by ultrafiltration at 10 and 50 C. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 8655–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC INTERNATIONAL; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023.
- Olson, D.; White, C.; Richter, R. Effect of pressure and fat content on particle sizes in microfluidized milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3217–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leu, M.; Marciniak, A.; Chamberland, J.; Pouliot, Y.; Bazinet, L.; Doyen, A. Effect of skim milk treated with high hydrostatic pressure on permeate flux and fouling during ultrafiltration. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7071–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Nakano, T.; Aoki, T.; Tanimoto, M. Temperature dependence of the casein micelle structure in the range of 10–40° C: An in-situ SAXS study. Food Chem. 2022, 393, 133389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.S.; Dunstan, D.E.; Martin, G.J. Influence of processing temperature on flux decline during skim milk ultrafiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walstra, P.; Geurts, T.J.; Noomon, A.; Van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Dairy Technology: Principles of Milk Properties and Processes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; Volume 7, pp. 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Ong, L.; Yao, S.; Kentish, S.E.; Gras, S.L. Effect of ultrafiltered milk on the rheological and microstructure properties of cream cheese acid gels. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2023, 16, 1728–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurt, E.; Zulewska, J.; Newbold, M.; Barbano, D. Micellar casein concentrate production with a 3X, 3-stage, uniform transmembrane pressure ceramic membrane process at 50 C. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5588–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulewska, J.; Newbold, M.; Barbano, D. Efficiency of serum protein removal from skim milk with ceramic and polymeric membranes at 50 °C. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1361–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermanová, I.; Hanuš, O.; Roubal, P.; Vyletělová, M.; Genčurová, V.; Jedelská, R.; Kopecký, J.; Dolínková, A. Effect of organic farming on selected raw cow milk components and properties. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendelianae Brun. 2011, 59, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, G.S.; Singh, A.K.; Borad, S.; Panjagari, N.R. Effect of concentration, homogenization and stabilizing salts on heat stability and rheological properties of cow skim milk ultrafiltered retentate. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3960–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastian, E.; Collinge, S.; Ernstrom, C. Ultrafiltration: Partitioning of milk constituents into permeate and retentate. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 2423–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, J.W. Effects of Filtration Temperature and Heat Treatment on Composition and Rheological Properties of Whole Milk Ultrafiltration Retentates; California Polytechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, C. The milk salts and their interaction with casein. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry Volume 3: Lactose, Water, Salts and Vitamins; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 233–256. [Google Scholar]
- Walstra, P.; Wouters, J.; Geurts, T. Homogenization. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2006, 2, 279–296. [Google Scholar]
- Huppertz, T.; Kelly, A.L.; Fox, P.F. Effects of high pressure on constituents and properties of milk. Int. Dairy J. 2002, 12, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.; Singh, H. Formation and physical properties of acid milk gels: A review. Food Res. Int. 1997, 30, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, R.; Menne, D.; Riest, J.; Buzatu, P.; Zholkovskiy, E.K.; Dhont, J.K.; Wessling, M.; Nägele, G. Ultrafiltration of charge-stabilized dispersions at low salinity. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 4638–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Ismail, A. Fouling control on microfiltration/ultrafiltration membranes: Effects of morphology, hydrophilicity, and charge. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, J.; Horne, D. Milk salts: Technological significance. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry: Volume 3: Lactose, Water, Salts and Minor Constituents; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 351–389. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.F.; McSweeney, P.L. Dairy Chemistry and Biochemistry; Blackie Academic & Professional (An imprint of Chapman & Hall): London, UK, 1998; pp. 241–296. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Woo, M.W.; Patel, H.; Metzger, L.; Selomulya, C. Improvement of rheological and functional properties of milk protein concentrate by hydrodynamic cavitation. J. Food Eng. 2018, 221, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhanwar, A.; Ward, R. Particle size distribution and lipid composition of skim milk lipid material. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 36, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercan, E.; Sert, D.; Akın, N. Effect of high-pressure homogenisation on viscosity, particle size and microbiological characteristics of skim and whole milk concentrates. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 87, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Muñoz, M.; Chevalier-Lucia, D.; Dumay, E. Characteristics of submicron emulsions prepared by ultra-high pressure homogenisation: Effect of chilled or frozen storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, A.; Ferragut, V.; Jaramillo, P.; Guamis, B.; Trujillo, A. Effects of ultra-high pressure homogenization on the cheese-making properties of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, K.M.; Ho, Q.T.; Drapala, K.P.; Keena, G.M.; Fenelon, M.A.; O’Mahony, J.A.; McCarthy, N.A. Influence of protein standardisation media and heat treatment on viscosity and related physicochemical properties of skim milk concentrate. Int. Dairy J. 2018, 81, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
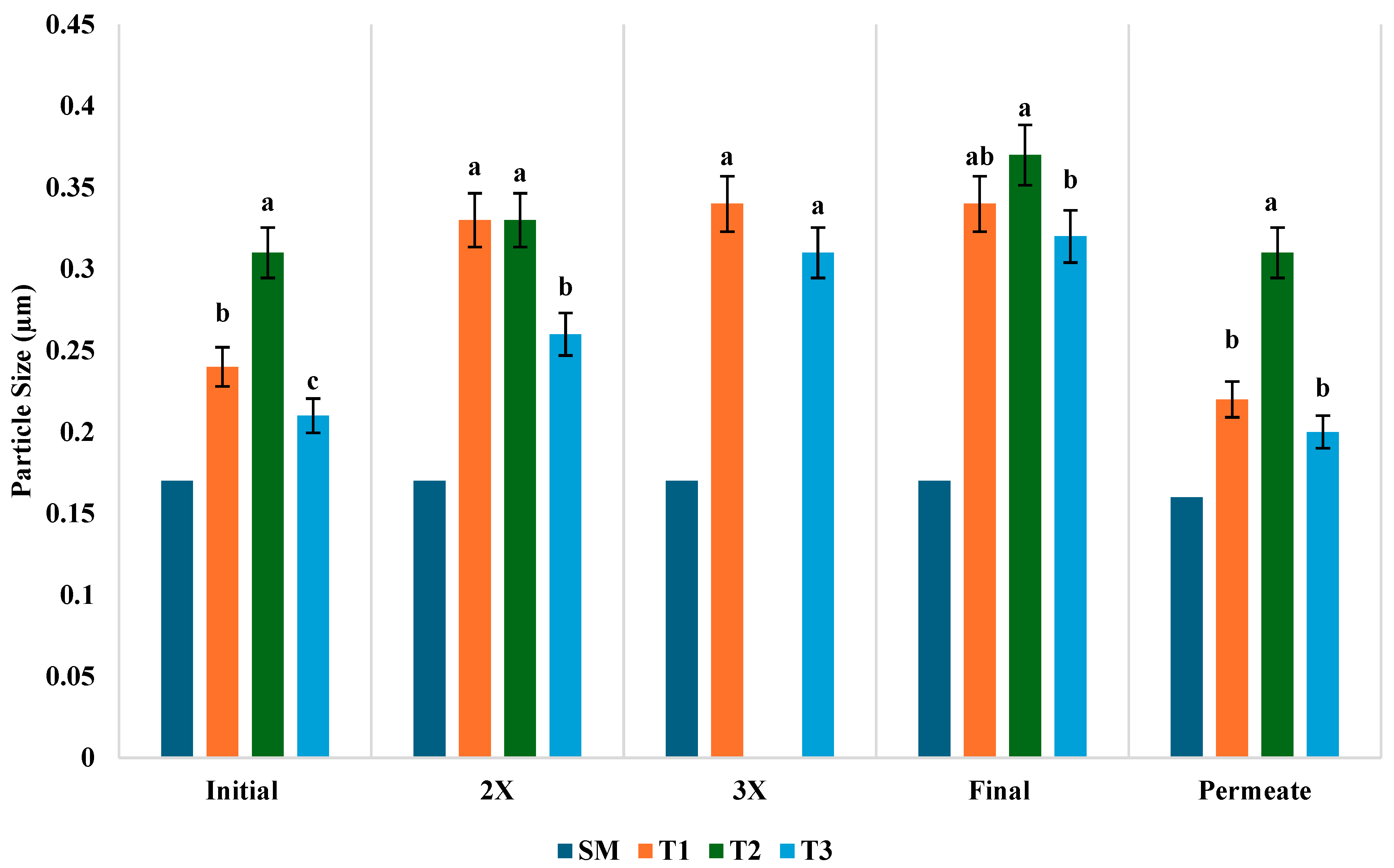
| Treatment | TS | Fat | Ash | CP | NCN | NPN | TP | CN | SP | CN/CP | SP/CP | NPN/CP | CN/TP | SP/TP | NPN/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SD | 9.64 0.12 | 0.33 0.03 | 0.68 0.01 | 3.45 0.04 | 0.82 0.03 | 0.19 0.01 | 3.27 0.03 | 2.63 0.06 | 0.63 0.03 | 76.24 1.03 | 18.31 1.00 | 5.44 0.03 | 80.63 1.07 | 19.37 1.07 | 5.76 0.03 |
| T1 SD | 12.68 0.05 | 3.38 0.02 | 0.66 a 0.01 | 3.41 b 0.01 | 0.67 0.02 | 0.22 0.03 | 3.20 b 0.03 | 2.74 b 0.01 | 0.46 0.02 | 80.32 0.42 | 13.38 0.54 | 6.30 a 0.95 | 85.73 0.43 | 14.27 0.43 | 6.73 a 1.10 |
| T2 SD | 12.35 0.72 | 2.65 0.77 | 0.67 a 0.04 | 3.41 b 0.05 | 0.65 0.02 | 0.18 0.01 | 3.23 b 0.04 | 2.76 b 0.05 | 0.47 0.02 | 80.99 0.53 | 13.68 0.64 | 5.33 ab 0.15 | 85.55 0.66 | 14.45 0.66 | 5.63 ab 0.17 |
| T3 SD | 12.36 0.74 | 2.70 0.78 | 0.52 b 0.06 | 3.54 a 0.06 | 0.65 0.07 | 0.17 0.02 | 3.37 a 0.05 | 2.89 a 0.04 | 0.48 0.07 | 81.58 1.82 | 13.67 1.76 | 4.74 b 0.37 | 85.64 1.85 | 14.36 1.85 | 4.98 b 0.41 |
| Treatment | TS | Fat | Ash | CP | NCN | NPN | TP | CN | SP | CN/CP | SP/CP | NPN/CP | CN/TP | SP/TP | NPN/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SD | 14.35 0.12 | 0.60 0.08 | 1.08 0.01 | 8.18 0.15 | 1.56 0.08 | 0.20 0.01 | 7.97 0.15 | 6.62 0.21 | 1.35 0.08 | 80.94 1.21 | 16.56 1.15 | 2.49 0.07 | 83.02 1.19 | 16.98 1.19 | 2.56 0.07 |
| T1 SD | 20.94 0.32 | 6.27 0.16 | 1.06 a 0.05 | 7.99 a 0.19 | 1.43 a 0.20 | 0.27 0.07 | 7.72 a 0.12 | 6.56 0.17 | 1.17 a 0.17 | 82.11 2.31 | 14.59 2.10 | 3.30 0.80 | 84.91 2.18 | 15.09 2.18 | 3.42 0.86 |
| T2 SD | 21.28 0.72 | 8.19 0.72 | 0.93 b 0.01 | 7.00 b 0.48 | 0.94 b 0.21 | 0.23 0.01 | 6.76 b 0.48 | 6.06 0.54 | 0.70 b 0.22 | 86.56 3.37 | 10.12 1.12 | 3.32 0.24 | 89.53 3.50 | 10.47 3.50 | 3.43 0.25 |
| T3 SD | 20.57 0.75 | 7.70 1.68 | 0.99 ab 0.04 | 7.01 b 0.19 | 1.24 a 0.08 | 0.29 0.10 | 6.72 b 0.13 | 5.76 0.22 | 0.96 ab 0.10 | 82.24 1.33 | 13.73 1.80 | 4.03 0.77 | 85.70 1.79 | 14.30 1.79 | 4.20 0.83 |
| Treatment | TS | Fat | Ash | CP | NCN | NPN | TP | CN | SP | CN/CP | SP/CP | NPN/CP | CN/TP | SP/TP | NPN/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SD | 18.08 0.28 | 0.91 0.03 | 1.29 0.03 | 11.45 0.05 | 2.04 0.04 | 0.22 0.01 | 11.24 0.06 | 9.41 0.02 | 1.82 0.04 | 82.20 0.24 | 15.91 0.28 | 1.89 0.06 | 83.78 0.28 | 16.22 0.28 | 1.92 0.05 |
| T1 SD | 29.21 2.35 | 8.15 b 0.29 | 1.45 a 0.02 | 11.29 a 0.32 | 2.39 0.69 | 0.32 0.08 | 10.97 a 0.69 | 8.90 a 0.43 | 2.07 0.61 | 78.92 3.50 | 18.27 2.87 | 2.81 0.64 | 81.18 3.14 | 18.82 3.01 | 2.89 0.68 |
| T3 SD | 27.77 1.26 | 12.13 a 1.22 | 1.27 b 0.11 | 9.51 b 0.55 | 1.69 0.29 | 0.38 0.08 | 9.13 b 0.59 | 7.82 b 0.28 | 1.31 0.31 | 82.3 2.09 | 13.72 2.53 | 3.98 0.98 | 85.72 2.55 | 14.28 2.55 | 4.16 1.10 |
| Treatment | TS | Fat | Ash | CP | NCN | NPN | TP | CN | SP | CN/CP | SP/CP | NPN/CP | CN/TP | SP/TP | NPN/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SD | 18.93 0.35 | 0.96 0.03 | 1.46 0.01 | 12.60 0.15 | 2.23 0.02 | 0.25 0.01 | 12.35 0.15 | 10.36 0.14 | 1.98 0.02 | 82.28 0.17 | 15.72 0.11 | 2.00 0.08 | 83.96 0.12 | 16.04 0.12 | 2.04 0.08 |
| T1 SD | 29.91 1.64 | 10.90 0.48 | 1.54 a 0.03 | 12.47 a 0.17 | 2.56 a 0.42 | 0.36 0.11 | 12.11 a 0.08 | 9.92 a 0.26 | 2.19 a 0.32 | 79.53 3.10 | 17.57 2.31 | 2.89 0.89 | 81.89 2.52 | 18.11 2.52 | 2.98 0.90 |
| T2 SD | 28.41 1.37 | 12.35 1.58 | 1.18 b 0.09 | 8.70 b 0.94 | 1.35 b 0.15 | 0.32 0.04 | 8.39 c 0.92 | 7.36 b 1.10 | 1.03 b 0.17 | 84.27 3.56 | 12.08 3.38 | 3.65 0.39 | 87.46 3.54 | 12.54 3.54 | 3.79 0.42 |
| T3 SD | 28.15 0.94 | 12.76 1.29 | 1.47 a 0.07 | 10.91 a 0.55 | 2.07 a 0.09 | 0.44 0.10 | 10.47 b 0.50 | 8.84 ab 0.52 | 1.63 a 0.16 | 81.04 0.95 | 14.97 1.78 | 3.99 0.85 | 84.41 1.71 | 15.59 1.71 | 4.16 0.92 |
| Treatment | TS | Fat | Ash | CP | NCN | NPN | TP | CN | SP | CN/CP | SP/CP | NPN/CP | CN/TP | SP/TP | NPN/TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM SD | 3.44 0.60 | 0.05 0.03 | 0.09 0.01 | 0.13 0.01 | 0.12 0.01 | 0.11 0.01 | 0.03 0.01 | 0.02 0.01 | 0.01 0.01 | 14.16 0.58 | 6.69 1.23 | 79.15 1.59 | 68.21 2.91 | 31.79 2.91 | 384.32 35.50 |
| T1 SD | 3.32 0.59 | 0.33 0.10 | 0.17 b 0.03 | 0.17 b 0.01 | 0.14 b 0.01 | 0.12 b 0.01 | 0.04 0.01 | 0.02 0.01 | 0.01 0.01 | 18.17 3.52 | 8.66 1.24 | 73.17 3.69 | 66.63 1.84 | 33.37 1.84 | 291.54 8.20 |
| T2 SD | 4.10 1.10 | 0.33 0.32 | 0.36 a 0.03 | 0.16 b 0.01 | 0.13 b 0.01 | 0.12 b 0.01 | 0.04 0.01 | 0.03 0.01 | 0.02 0.01 | 16.67 4.95 | 9.25 0.99 | 74.08 3.96 | 63.16 3.36 | 36.84 2.36 | 294.34 5.80 |
| T3 SD | 4.37 1.04 | 0.24 0.14 | 0.18 b 0.01 | 0.24 a 0.01 | 0.22 a 0.01 | 0.19 a 0.01 | 0.05 0.01 | 0.02 0.01 | 0.02 0.01 | 10.82 3.36 | 8.92 0.82 | 80.25 3.61 | 54.06 2.58 | 42.94 2.58 | 418.47 8.60 |
| Minerals | Initial | 2× | 3× | Final | Permeate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ca SD | 137.52 1.08 | 250.29 1.53 | 336.10 9.19 | 380.16 4.70 | 23.07 4.10 |
| K SD | 105.10 8.02 | 135.86 0.85 | 147.25 2.34 | 170.08 3.12 | 35.62 4.44 |
| P SD | 92.78 6.41 | 171.84 3.07 | 233.00 9.13 | 256.60 5.83 | 25.40 6.13 |
| Na SD | 44.61 1.73 | 52.80 2.19 | 59.92 2.94 | 76.73 0.52 | 26.80 1.99 |
| Mg SD | 11.99 0.07 | 18.92 0.89 | 23.70 1.52 | 21.72 3.90 | 6.84 2.84 |
| Zn SD | 0.56 0.06 | 1.34 0.16 | 1.73 0.03 | 1.83 0.13 | 0.24 0.04 |
| Initial | 2X | 3X | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Ca SD | 121.61 10.03 | 126.03 9.50 | 116.05 8.20 | 234.28 a 20.86 | 203.12 b 1.93 | 213.60 ab 4.00 | 353.20 a 19.10 | - | 281.70 b 28.34 |
| K SD | 87.32 b 5.36 | 120.98 a 4.55 | 106.14 a 9.96 | 94.87 b 2.67 | 101.99 ab 6.94 | 110.50 a 3.93 | 113.01 9.60 | - | 112.60 4.90 |
| P SD | 88.53 12.99 | 96.95 5.25 | 83.03 2.43 | 152.73 a 6.90 | 117.60 b 7.96 | 135.27 ab 8.60 | 223.90 8.66 | - | 206.01 9.74 |
| Na SD | 45.80 2.44 | 45.77 1.40 | 47.13 1.12 | 54.91 a 5.76 | 39.41 b 2.70 | 48.73 ab 3.81 | 65.25 a 4.19 | - | 46.87 b 4.43 |
| Mg SD | 12.49 1.23 | 11.10 0.52 | 9.94 1.33 | 17.96 1.61 | 15.67 0.21 | 16.20 0.57 | 23.32 a 1.41 | - | 19.40 b 0.86 |
| Zn SD | 0.45 b 0.04 | 0.55 a 0.03 | 0.40 b 0.03 | 0.92 0.05 | 1.01 0.02 | 1.01 0.05 | 1.60 a 0.11 | - | 1.32 b 0.05 |
| Final | Permeate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| Ca SD | 373.13 a 13.35 | 271.70 c 5.22 | 328.08 b 1.22 | 15.63 1.30 | 25.76 1.80 | 22.04 8.00 |
| K SD | 127.72 a 4.23 | 111.53 b 7.10 | 124.28 a 1.83 | 23.69 c 2.31 | 87.70 a 11.65 | 47.30 b 7.01 |
| P SD | 238.57 a 3.87 | 163.75 b 11.44 | 230.74 a 8.43 | 16.26 b 1.90 | 27.51 a 4.64 | 20.50 ab 2.51 |
| Na SD | 77.86 a 1.74 | 43.71 c 2.42 | 55.96 b 6.24 | 23.85 b 2.15 | 29.35 a 2.55 | 22.89 b 0.52 |
| Mg SD | 24.21 a 1.13 | 18.94 b 0.70 | 21.11 ab 1.94 | 1.31 b 0.40 | 4.65 a 0.94 | 3.50 a 0.70 |
| Zn SD | 1.66 a 0.09 | 1.40 b 0.09 | 1.60 ab 0.06 | 0.16 b 0.01 | 0.40 a 0.10 | 0.23 b 0.03 |
| SM | |||||
| Initial | 2× | 3× | Final | Permeate | |
| Cu | 0.013 ± 0.005 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 0.031 ± 0.004 | 0.036 ± 0.005 | 0.011 ± 0.004 |
| S | 7.358 ± 0.295 | 8.658 ± 0.263 | 10.36 ± 0.534 | 14.93 ± 0.730 | 5.461 ± 0.931 |
| Fe | 0.038 ± 0.011 | 0.080 ± 0.006 | 0.108 ± 0.007 | 0.123 ± 0.005 | 0.021 ± 0.004 |
| Mn | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.033 ± 0.051 | 0.008 ± 0.004 | 0.00 ± 0.000 |
| T1 | |||||
| Initial | 2× | 3× | Final | Permeate | |
| Cu | 0.013 ± 0.005 | 0.021 ± 0.007 | 0.020 ± 0.008 | 0.031 ± 0.007 | 0.016 ± 0.005 |
| S | 8.176 ± 0.182 | 9.520 ± 0.332 | 10.56 ± 0.624 | 11.626 ± 0.286 | 5.133 ± 0.757 |
| Fe | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 0.053 ± 0.005 | 0.083 ± 0.005 | 0.110 ± 0.006 | 0.021 ± 0.004 |
| Mn | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.016 ± 0.040 | 0.050 ± 0.054 | 0.010 ± 0.000 | 0.001 ± 0.004 |
| T2 | |||||
| Initial | 2× | 3× | Final | Permeate | |
| Cu | 0.013 ± 0.005 | 0.021 ± 0.004 | - | 0.031 ± 0.004 | 0.008 ± 0.004 |
| S | 7.281 ± 0.441 | 8.393 ± 0.264 | - | 10.48 ± 0.548 | 5.133 ± 0.757 |
| Fe | 0.026 ± 0.008 | 0.058 ± 0.004 | - | 0.081 ± 0.007 | 0.026 ± 0.008 |
| Mn | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.000 ± 0.000 | - | 0.005 ± 0.005 | 0.001 ± 0.004 |
| T3 | |||||
| Initial | 2× | 3× | Final | Permeate | |
| Cu | 0.011 ± 0.004 | 0.015 ± 0.005 | 0.025 ± 0.005 | 0.030 ± 0.008 | 0.013 ± 0.005 |
| S | 6.088 ± 0.272 | 8.420 ± 0.155 | 9.533 ± 0.295 | 11.45 ± 0.279 | 5.133 ± 0.757 |
| Fe | 0.023 ± 0.005 | 0.055 ± 0.005 | 0.088 ± 0.004 | 0.120 ± 0.008 | 0.011 ± 0.004 |
| Mn | 0.000 ± 0.000 | 0.016 ± 0.040 | 0.033 ± 0.051 | 0.010 ± 0.000 | 0.016 ± 0.040 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Don, P.U.; Modi, Z.; Shah, K.; Salunke, P. Ultrafiltration of Whole Milk: Impact of Homogenization and Ultrafiltration Temperature on Processing Efficiency and Component Retention. Foods 2025, 14, 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081370
Don PU, Modi Z, Shah K, Salunke P. Ultrafiltration of Whole Milk: Impact of Homogenization and Ultrafiltration Temperature on Processing Efficiency and Component Retention. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081370
Chicago/Turabian StyleDon, Pramith U., Zeel Modi, Kartik Shah, and Prafulla Salunke. 2025. "Ultrafiltration of Whole Milk: Impact of Homogenization and Ultrafiltration Temperature on Processing Efficiency and Component Retention" Foods 14, no. 8: 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081370
APA StyleDon, P. U., Modi, Z., Shah, K., & Salunke, P. (2025). Ultrafiltration of Whole Milk: Impact of Homogenization and Ultrafiltration Temperature on Processing Efficiency and Component Retention. Foods, 14(8), 1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081370








