Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate on Quality and Shelf-Life of Depurated Asian Green Mussel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Microbiological Media, and Preparation of Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate (CEC)
2.2. Collection and Extraction of Edible Portion of Asian Green Mussel
2.3. CEC and CAP Treatment of Asian Green Mussel
2.4. Microbiological and Chemical Analyses
2.4.1. Microbial Counts
2.4.2. Total Volatile Base Nitrogen (TVB-N) and Trimethylamine Nitrogen (TMA-N), Pexoide Value (PV), and Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substance (TBARS) Content
2.4.3. Texture Analysis
2.4.4. Cooking Loss
2.4.5. Fatty Acids Profile
2.4.6. Sensory Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
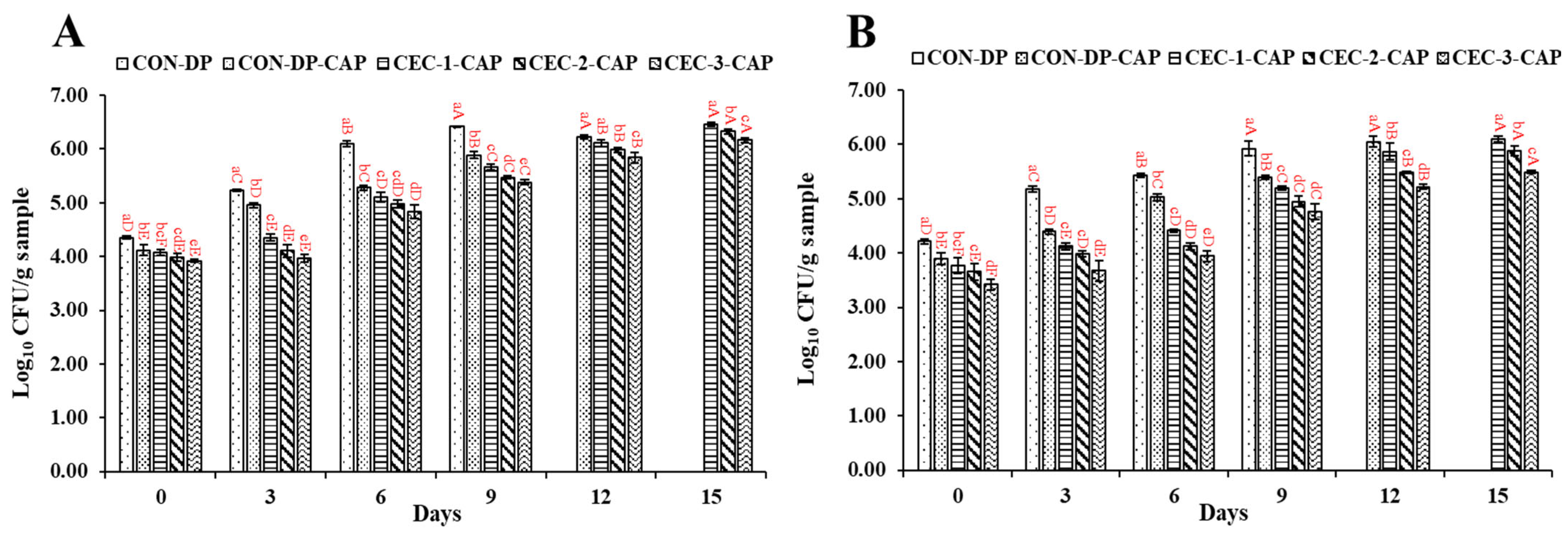
3.1. Changes in the Microbial Counts
3.2. Changes in TVB-N and TMA-N Contents
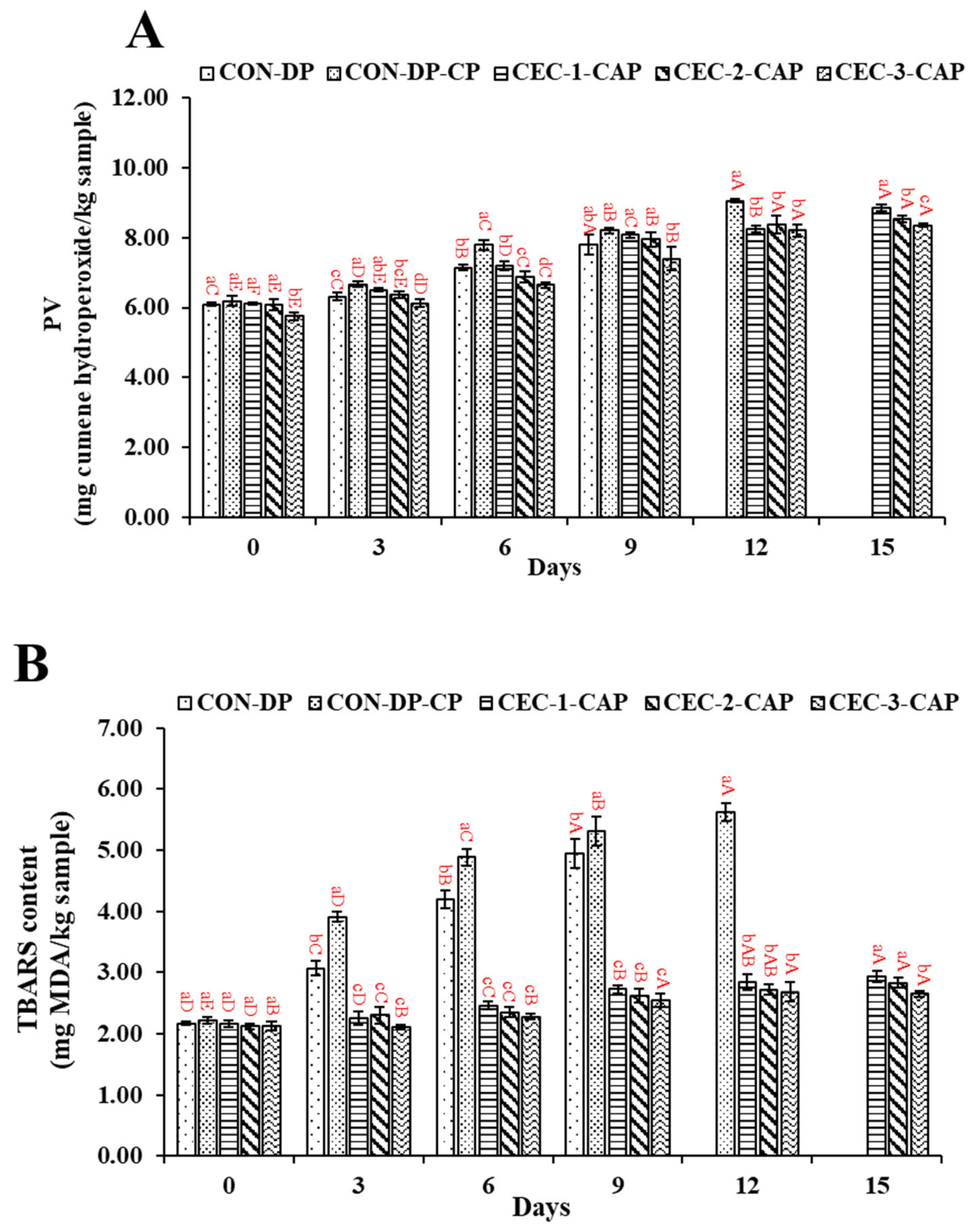
3.3. Changes in PV and TBARS Value
3.4. Changes in Fatty Acid Profiles
3.5. Changes in Textural Properties, Cooking Loss, and Sensory Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- SEAFDEC. Fishery Statistical Bulletin of Southeast Asia 2021; SEAFDEC: Bangkok, Thailand, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty, K.; Chakkalakal, S.J.; Joseph, D.; Asokan, P.; Vijayan, K. Nutritional and antioxidative attributes of green mussel (Perna viridis L.) from the southwestern coast of India. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2016, 25, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, M.; Neacșu, S.M.; Oprea, E.; Dumitrescu, D.-E.; Nedelescu, M.; Drăgănescu, D.; Nicolescu, T.O.; Roșca, A.C.; Ghica, M. Black Sea mussels qualitative and quantitative chemical analysis: Nutritional benefits and possible risks through consumption. Nutrients 2022, 14, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorio, J.C.; Inolino, R.I. Microbial, chemical and sensorial quality of chilled marinated green mussel Perna viridis, (Linnaeus, 1758). Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2018, 6, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buatong, J.; Bahem, N.; Benjakul, S.; Patil, U.; Singh, A. Depuration of Asian green mussels using chitooligosaccharide-epigallocatechin gallate conjugate: Shelf-life extension, microbial diversity, and quality changes during refrigerated storage. Foods 2024, 13, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.H.; Palamae, S.; Yingkajorn, M.; Benjakul, S.; Singh, A.; Buatong, J. Multidrug-resistance of Vibrio species in bivalve mollusks from Southern Thailand: Isolation, identification, pathogenicity, and their sensitivity toward chitooligosaccharide-epigallocatechin-3-gallate conjugate. Foods 2024, 13, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Mittal, A.; Yingkajorn, M.; Saetang, J.; Buatong, J.; Tyagi, A.; Singh, P.; Benjakul, S. Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from Asian green mussel: Molecular characteristics, virulence and their inhibition by chitooligosaccharide-tea polyphenol conjugates. Foods 2022, 11, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, Z.F.; Islam, M.S.; Sabuj, A.A.M.; Pondit, A.; Sarkar, A.K.; Hossain, M.G.; Saha, S. Molecular detection and antibiotic resistance of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Vibrio alginolyticus from shrimp (Penaeus monodon) and shrimp environments in Bangladesh. Aquac. Res. 2023, 2023, 5436552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, V.M.; Chouljenko, A.; Hall, S.G. Depuration of live oysters to reduce Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus: A review of ecology and processing parameters. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3480–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, S.; Elavarasan, K.; Geethalakshmi, V.; Kripa, V.; Mohamed, K. Evaluation of static and flow-through depuration system on depuration of naturally contaminated farmed edible oyster Crassostrea madrasensis (Preston, 1916). Aquaculture 2021, 545, 737141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnadurai, S.; Elavarasan, K.; Geethalakshmi, V.; Kripa, V.; Mohamed, K. Development of a depuration protocol for commercially important edible bivalve molluscs of India: Ensuring microbiological safety. Food Microbiol. 2023, 110, 104172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnot, N.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Gupta, K.; Saikia, S. Cold Plasma Processing Methods: Impact of Decontamination on Food Quality. In Advances in Food Process Engineering; Apple Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 255–275. [Google Scholar]
- Chiozzi, V.; Agriopoulou, S.; Varzakas, T. Advances, applications, and comparison of thermal (pasteurization, sterilization, and aseptic packaging) against non-thermal (ultrasounds, UV radiation, ozonation, high hydrostatic pressure) technologies in food processing. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopuk, B.; Gunes, R.; Palabiyik, I. Cold plasma modification of food macromolecules and effects on related products. Food Chem. 2022, 382, 132356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaguthevar, R.; Packialakshmi, J.S.; Murugesan, B.; Rhim, J.W.; Thiyagamoorthy, U. In-package cold plasma treatment to extend the shelf life of food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Ha, S.-D. Application of cold oxygen plasma for the reduction of Cladosporium cladosporioides and Penicillium citrinum on the surface of dried filefish (Stephanolepis cirrhifer) fillets. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertos, I.; Martín-Diana, A.; Cullen, P.; Tiwari, B.K.; Ojha, S.; Bourke, P.; Álvarez, C.; Rico, D. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) generated plasma on microbial reduction and quality parameters of fresh mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 44, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K. Shelf-life of refrigerated Asian sea bass slices treated with cold plasma as affected by gas composition in packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 324, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sang, X.; Cai, Z.; Zeng, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, J. Optimization of cold plasma combined treatment process and its effect on the quality of Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) during refrigerated storage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 2750–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Andrés, J.M. Chemical Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Food Nutrients; Technological University Dublin: Dublin, Ireland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Albertos, I.; Martin-Diana, A.; Cullen, P.J.; Tiwari, B.K.; Ojha, K.S.; Bourke, P.; Rico, D. Shelf-life extension of herring (Clupea harengus) using in-package atmospheric plasma technology. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 53, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Luan, A.; Yi, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Moderate protein degradation and lipid oxidation induced by cold plasma and its effect on the quality of dried fish products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of high-voltage atmospheric cold plasma treatment on microbiological and quality characters of tilapia fillets. Foods 2022, 11, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Chitooligosaccharides from shrimp shell chitosan prepared using H2O2 or ascorbic acid/H2O2 redox pair hydrolysis: Characteristics, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 58, 2645–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Buatong, J.; Saetang, J.; Benjakul, S. Chitooligosaccharide and Its Derivatives: Potential Candidates as Food Additives and Bioactive Components. Foods 2023, 12, 3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. The combined effect of squid pen chitooligosaccharides and high voltage cold atmospheric plasma on the shelf-life extension of Asian sea bass slices stored at 4 °C. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 64, 102339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Zhang, B.; Visessanguan, W.; Benjakul, S. Chitooligosaccharide conjugates prepared using several phenolic compounds via ascorbic acid/H2O2 free radical grafting: Characteristics, antioxidant, antidiabetic, and antimicrobial activities. Foods 2022, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonphu, K.; Mueangaun, S.; Lerkdumnernkit, N.; Sengking, J.; Tocharus, J.; Benjakul, S.; Mittal, A.; Tocharus, C. Chitooligosaccharide-epigallocatechin gallate conjugate ameliorates lipid accumulation and promotes browning of white adipose tissue in high fat diet fed rats. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2025, 406, 111316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. α-amylase inhibitory activity of chitooligosaccharide from shrimp shell chitosan and its epigallocatechin gallate conjugate: Kinetics, fluorescence quenching and structure–activity relationship. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, K.E.; Niem, V.H. (Eds.) The Living Marine Resources of the Western Central Pacific. Seaweeds, Corals, Bivalves and Gastropods; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998; Volume 1, p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Olatunde, O.O.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K. High voltage cold atmospheric plasma: Antibacterial properties and its effect on quality of Asian sea bass slices. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 52, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturin, L.; Peeler, J. BAM: Aerobic Plate Count; US Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 17410; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Psychrotrophic Microorganisms, in ISO Norm. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 13720; Meat and Meat Products—Enumeration of Presumptive Pseudomonas spp. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization, in ISO Norm. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. Kinetics of total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine formation in stored rohu (Labeo rohita) fish. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2019, 28, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.P.; Hultin, H.O. Contributions of blood and blood components to lipid oxidation in fish muscle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Patil, U.; Saetang, J.; Detcharoen, M.; Suyapoh, W.; Ma, L.K.; Zhang, B.; Benjakul, S. Asian green mussel treated with sous vide and chitooligosaccharide-catechin conjugate: Chemical, physical, microbiological, histological properties and quality changes during refrigerated storage. Food Control 2025, 173, 111206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammed, M.; Domendra, D.; Muthukumar, S.; Sakhare, P.; Bhaskar, N. Effects of fermentatively recovered fish waste lipids on the growth and composition of broiler meat. Br. Poult. Sci. 2015, 56, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meilgaard, M.; Civille, G.V.; Carr, B.T. Selection and training of panel members. Sens. Eval. Tech. 1999, 3, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.-M.; Jeong, Y.-I.; Lim, Y.K.; Kook, J.-K.; Yang, S.-W.; Kook, M.-S.; Kim, B.-H. The effect of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on the formation of reactive oxygen species and treatment of Porphyromonas gingivalis biofilm in vitro for application in treatment of peri-implantitis. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, K.; Heyndrickx, M.; Herman, L.; Devlieghere, F.; Vlaemynck, G. Seafood quality analysis: Molecular identification of dominant microbiota after ice storage on several general growth media. Food Microbiol. 2011, 28, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Valente, C.; Wan, A.H. Vibrio and major commercially important vibriosis diseases in decapod crustaceans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 181, 107527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, A.; Pérez, E.; de Faria, C.T.; Ferrús, M.A.; Carrascosa, C. Food spoilage by Pseudomonas spp.—An overview. In Foodborne Pathogens and Antibiotic Resistance; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 41–71. [Google Scholar]
- Pellissery, A.J.; Vinayamohan, P.G.; Amalaradjou, M.A.R.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Spoilage bacteria and meat quality. In Meat Quality Analysis: Advanced Evaluation Methods, Techniques, and Technologies; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 307–334. [Google Scholar]
- Palevich, N.; Palevich, F.P.; Gardner, A.; Brightwell, G.; Mills, J. Genome collection of Shewanella spp. isolated from spoiled lamb. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 976152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palamae, S.; Temdee, W.; Buatong, J.; Suyapoh, W.; Sornying, P.; Tsai, Y.-H.; Benjakul, S. Use of high pressure processing in combination with acidic electrolyzed water depuration for the shelf-life extension of blood clam (Tegillarca granosa). Food Control 2024, 156, 110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamae, S.; Temdee, W.; Buatong, J.; Zhang, B.; Hong, H.; Benjakul, S. Enhancement of safety and quality of ready-to-cook Asian green mussel using acidic electrolyzed water depuration in combination with sous vide cooking. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2023, 87, 103391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A comprehensive review on freshness of fish and assessment: Analytical methods and recent innovations. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhit, A.E.A.; Giteru, S.G.; Holman, B.W.B.; Hopkins, D.L. Total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine in muscle foods: Potential formation pathways and effects on human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3620–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, G.; Badalucco, C. Combining ozone and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to maximize shelf-life and quality of striped red mullet (Mullus surmuletus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, M.; Xu, X. Research progress of fishy odor in aquatic products: From substance identification, formation mechanism, to elimination pathway. Food Res. Int. 2024, 178, 113914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boziaris, I.S.; Parlapani, F.F. Specific spoilage organisms (SSOs) in fish. In The Microbiological Quality of Food; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 61–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Z.K.; Xie, J. Comparative proteomics reveals the spoilage-related factors of under refrigerated condition. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 740482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parlapani, F.F.; Boziaris, I.S.; Drosinos, E.H. Detection of Fish Spoilage. In Handbook of Seafood and Seafood Products Analysis; Toldrá, F., Nollet, L., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 560–585. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, H.B.; Annapure, U. Consequences of non-thermal cold plasma treatment on meat and dairy lipids-A review. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Riccioli, C.; Sun, D.W. An overview on nondestructive spectroscopic techniques for lipid and lipid oxidation analysis in fish and fish products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.D.; Matos, G.; Casal, S.; Delgadillo, I.; Saraiva, J.A. Quality evolution of raw meat under hyperbaric storage-Fatty acids, volatile organic compounds and lipid oxidation profiles. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. Use of nanoliposome loaded with chitosan-epigallocatechin gallate conjugate for shelf-life extension of refrigerated Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) slices. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3795–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Parrish, C.C.; Shahidi, F. Effects of mechanical handling, storage on ice and ascorbic acid treatment on lipid oxidation in cultured Newfoundland blue mussel (Mytilus edulis). Food Chem. 2006, 99, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Fatty Acids (mg/g) | Day 0 | Day 12 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON-DP | CON-DP-CAP | CEC-3-CAP | CEC-3-CAP | |
| C14:0 (Myristic Acid) | 7.90 ± 1.05 b | 7.73 ± 0.09 bc | 10.62 ± 0.58 aA | 6.43 ± 0.07 B |
| C14:1 (Myristoleic Acid) | 1.14 ± 0.29 a | 0.91 ± 0.01 a | 1.08 ± 0.03 aA | 0.85 ± 0.16 B |
| C15:1 (cis-10-Pentadecanoic Acid) | 33.24 ± 2.15 b | 32.19 ± 0.17 a | 33.10 ± 1.00 bA | 32.61 ± 0.49 A |
| C16:1 (Palmitoleic Acid) | 1.09 ± 0.15 c | 0.94 ± 0.01 c | 1.13 ± 0.04 cA | 1.29 ± 0.14 A |
| C17:0 (Heptadecanoic Acid) | 2.66 ± 0.01 b | 1.57 ± 0.52 c | 2.06 ± 0.31 bcA | ND B |
| C17:1 (cis-10-Heptadecanoic Acid) | 1.87 ± 0.20 c | 1.55 ± 0.08 c | 1.14 ± 0.09 dA | 1.19 ± 0.09 A |
| C18:0 (Stearic Acid) | 6.85 ± 0.95 ab | 6.30 ± 0.05 b | 7.82 ± 0.06 aA | 1.27 ± 0.21 B |
| C18:1 (Oleic Acid) | 2.93 ± 0.40 b | 2.96 ± 0.04 b | 4.60 ± 0.63 aA | 2.99 ± 0.74 B |
| C18:2 (Linoleic Acid) | 1.48 ± 0.20 a | 1.39 ± 0.02 a | 1.76 ± 0.29 aA | ND B |
| C18:3 (gamma-Linolenic Acid) | 5.34 ± 0.75 a | 5.22 ± 0.07 a | 7.12 ± 0.68 aA | 4.61 ± 0.05 B |
| C20:1 (cis-11-Eicosenoic Acid) | 2.06 ± 0.30 b | 1.80 ± 0.03 b | 2.81 ± 0.52 aA | 1.94 ± 0.03 B |
| C20:4 (cis-5,8,11,14-Eicosatetraenoic) | 5.07 ± 0.75 ab | 4.67 ± 0.07 ab | 3.66 ± 0.03 cA | 4.41 ± 0.06 B |
| C20:5 (cis-5,8,11,14,17-Eicosapentaenoic Acid) | 12.42 ± 1.42 bc | 12.15 ± 0.17 ab | 12.02 ± 0.80 c | 12.07 ± 0.08 |
| C22:6 (cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-Docosahexaenoic Acid) | 13.58 ± 0.06 a | 12.08 ± 0.16 c | 12.90 ± 0.49 bA | 12.59 ± 0.17 A |
| C23:0 (Tricosanoic) | 2.37 ± 0.56 a | 1.54 ± 0.06 b | 2.02 ± 0.09 abA | 1.74 ± 0.06 B |
| Saturated Fatty Acids | 19.78 ± 1.46 b | 17.13 ± 0.31 c | 22.52 ± 1.04 aA | 9.44 ± 0.20 B |
| Monounsaturated Fatty Acids | 42.33 ± 1.80 b | 40.36 ± 0.17 c | 43.85 ± 0.02 aA | 40.87 ± 0.16 B |
| Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids | 37.90 ± 0.34 a | 35.51 ± 0.14 c | 37.45 ± 0.04 bA | 33.68 ± 0.37 B |
| Day 0 | Day 12 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON-DP | CON-DP-CAP | CEC-3-CAP | CEC-3-CAP | ||
| Cooking loss (%) | 42.28 ± 1.03 a | 43.50 ± 1.08 a | 41.36 ± 0.96 a | 31.52 ± 2.71 b | |
| Textural properties | Firmness (g) | 1881.67 ± 16.64 a | 1898.97 ± 6.65 a | 1744.52 ± 17.69 b | 622.19 ± 56.21 c |
| Toughness (g) | 9149.20 ± 43.69 a | 8404.34 ± 92.84 b | 7819.12 ± 79.36 c | 818.24 ± 23.06 d | |
| Sensory analysis | Appearance | 7.37 ± 0.71 a | 7.33 ± 0.70 a | 6.83 ± 0.91 aA | 5.50 ± 1.21 B |
| Color | 7.17 ± 1.05 a | 7.08 ± 0.83 ab | 6.45 ± 0.97 bA | 5.75 ± 0.90 B | |
| Odor | 7.25 ± 0.99 a | 6.91 ± 0.82 ab | 6.79 ± 0.83 bA | 5.37 ± 1.13 B | |
| Texture | 7.04 ± 0.91 a | 6.92 ± 0.83 a | 6.67 ± 1.09 aA | 5.08 ± 0.97 B | |
| Taste | 7.04 ± 0.81 a | 6.87 ± 0.61 ab | 6.54 ± 0.78 bA | 5.00 ± 0.88 B | |
| Overall likeness | 7.25 ± 0.53 a | 7.17 ± 0.70 a | 6.96 ± 0.81 aA | 5.21 ± 0.77 B | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mittal, A.; Benjakul, S.; Brunton, N.; Kadam, D.; Singh, A. Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate on Quality and Shelf-Life of Depurated Asian Green Mussel. Foods 2025, 14, 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081399
Mittal A, Benjakul S, Brunton N, Kadam D, Singh A. Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate on Quality and Shelf-Life of Depurated Asian Green Mussel. Foods. 2025; 14(8):1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081399
Chicago/Turabian StyleMittal, Ajay, Soottawat Benjakul, Nigel Brunton, Deepak Kadam, and Avtar Singh. 2025. "Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate on Quality and Shelf-Life of Depurated Asian Green Mussel" Foods 14, no. 8: 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081399
APA StyleMittal, A., Benjakul, S., Brunton, N., Kadam, D., & Singh, A. (2025). Combined Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Chitooligosaccharide–EGCG Conjugate on Quality and Shelf-Life of Depurated Asian Green Mussel. Foods, 14(8), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14081399








