Ethanolic Extrusion of Indica Rice Flour for Rice Noodle Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of EERF
2.3. Crystalline Structure
2.4. Cold-Paste Viscosity
2.5. Hot-Paste Viscosity
2.6. Hydration Characteristics
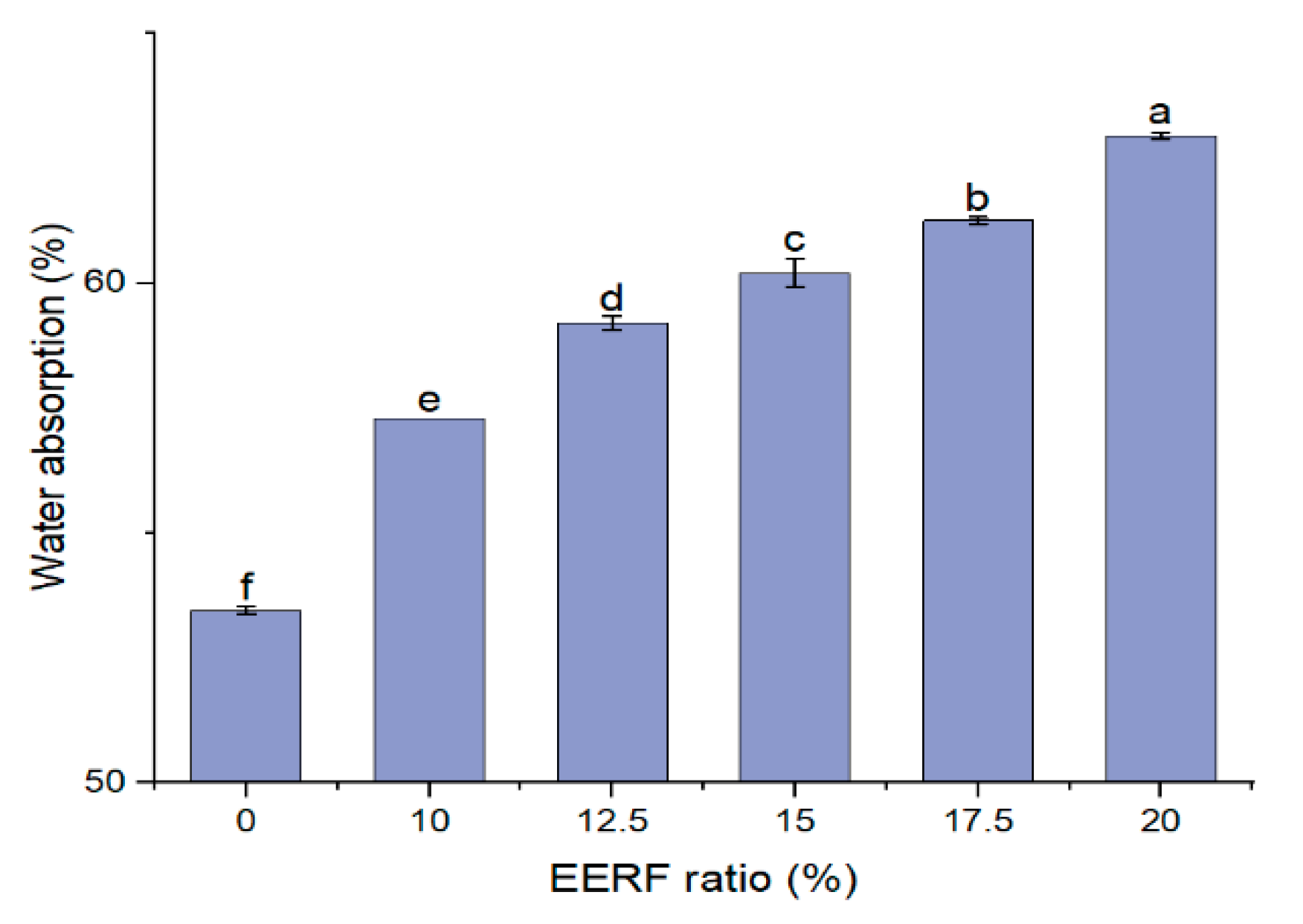
2.7. Water Absorption Properties
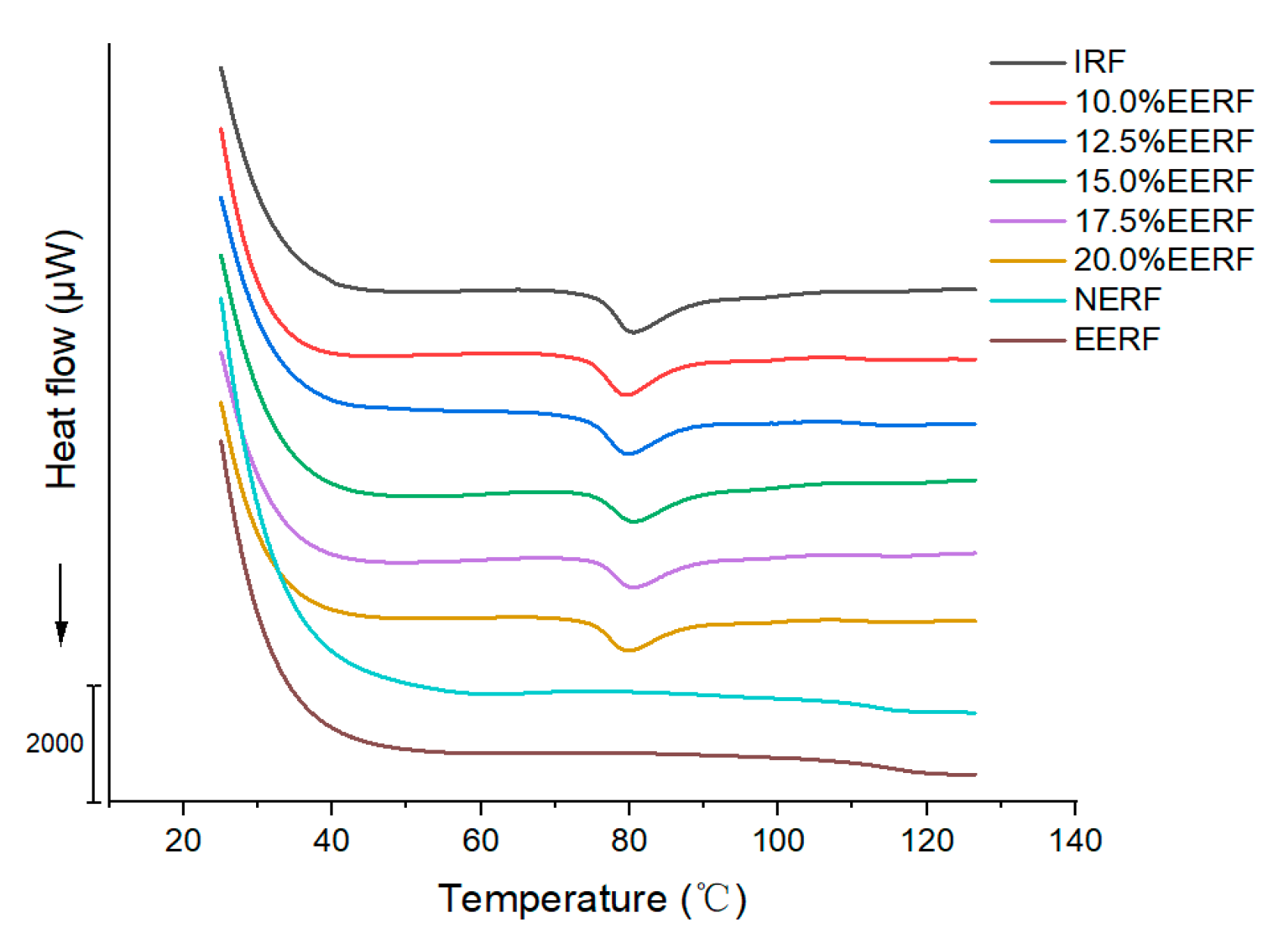
2.8. Thermal Transition Properties
2.9. Preparation of the Rice Noodle Premix
2.10. Preparation of the Rice Noodles
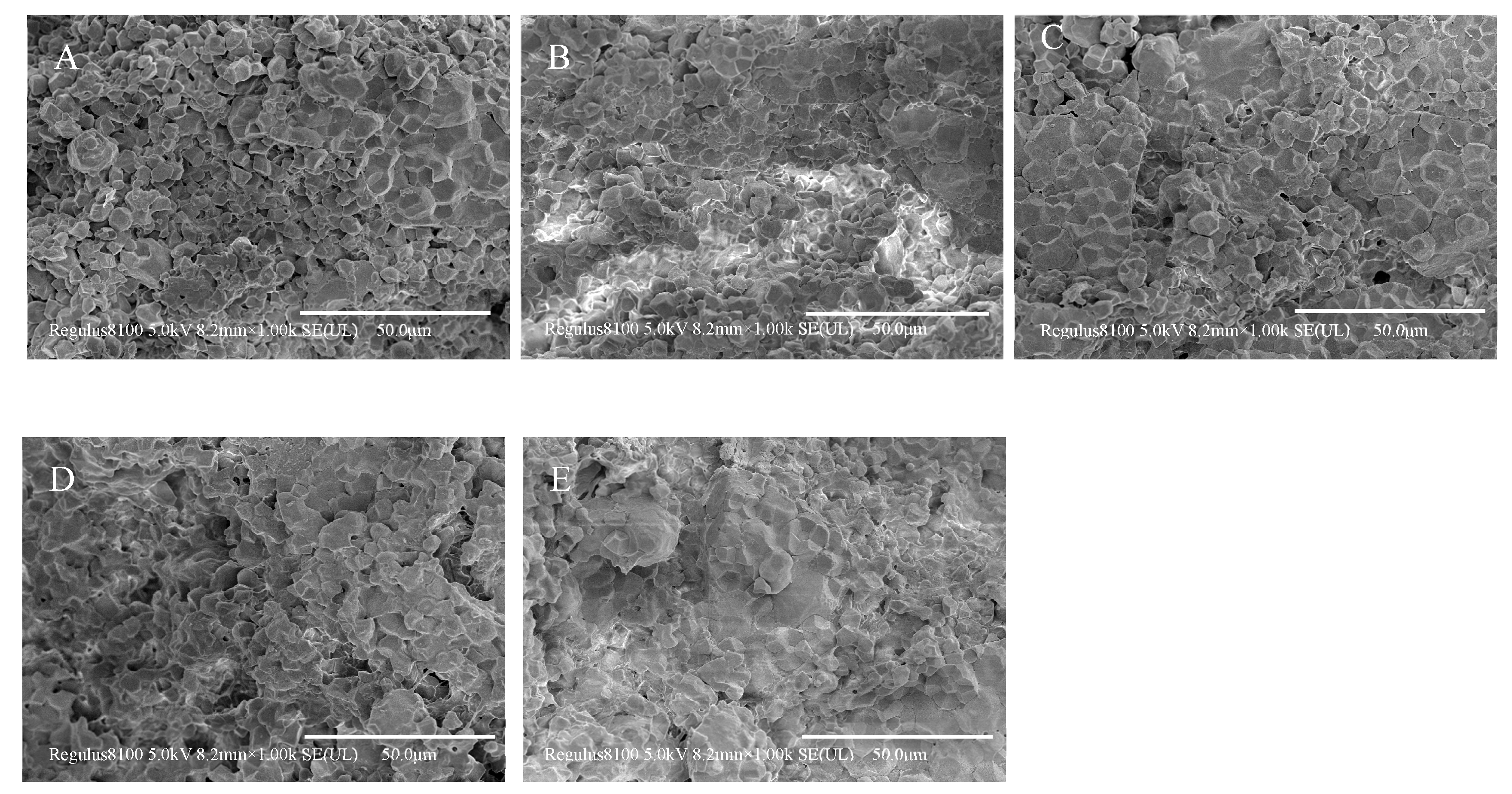
2.11. SEM of the Rice Doughs
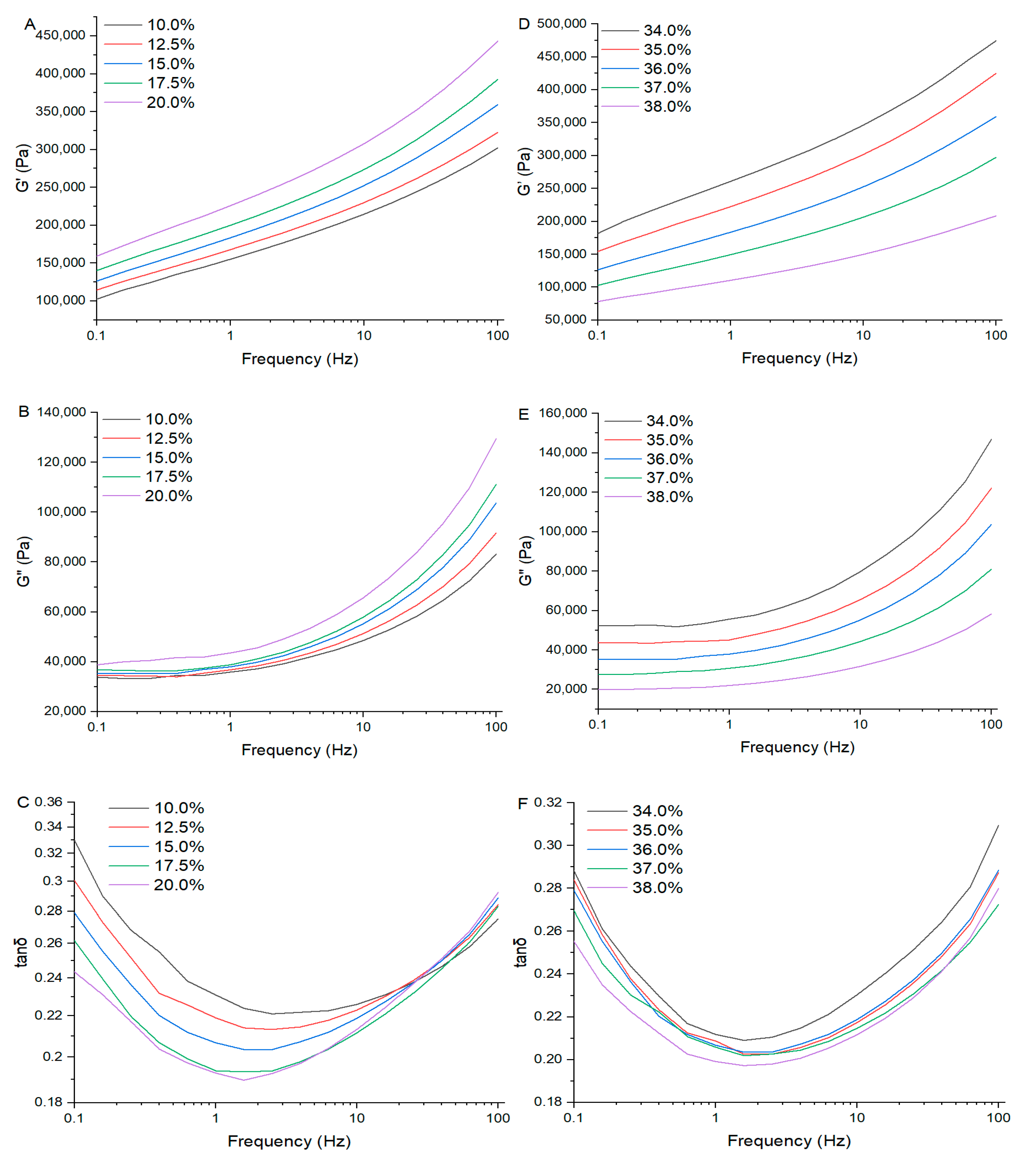
2.12. Rheological Properties of the Rice Doughs
2.13. Texture Properties of the Rice Dough Sheets
2.14. Tensile Strength Properties of the Fresh Rice Noodles
2.15. Properties of the Cooked Rice Noodles
2.15.1. Water Absorption Rate Properties of the Cooked Rice Noodles
2.15.2. Breakage Rate of the Cooked Rice Noodles
2.15.3. Cooking Loss of the Cooked Rice Noodles
2.15.4. Texture Properties of Cooked Rice Noodles
2.15.5. Sensory Qualities of the Cooked Rice Noodles
2.16. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
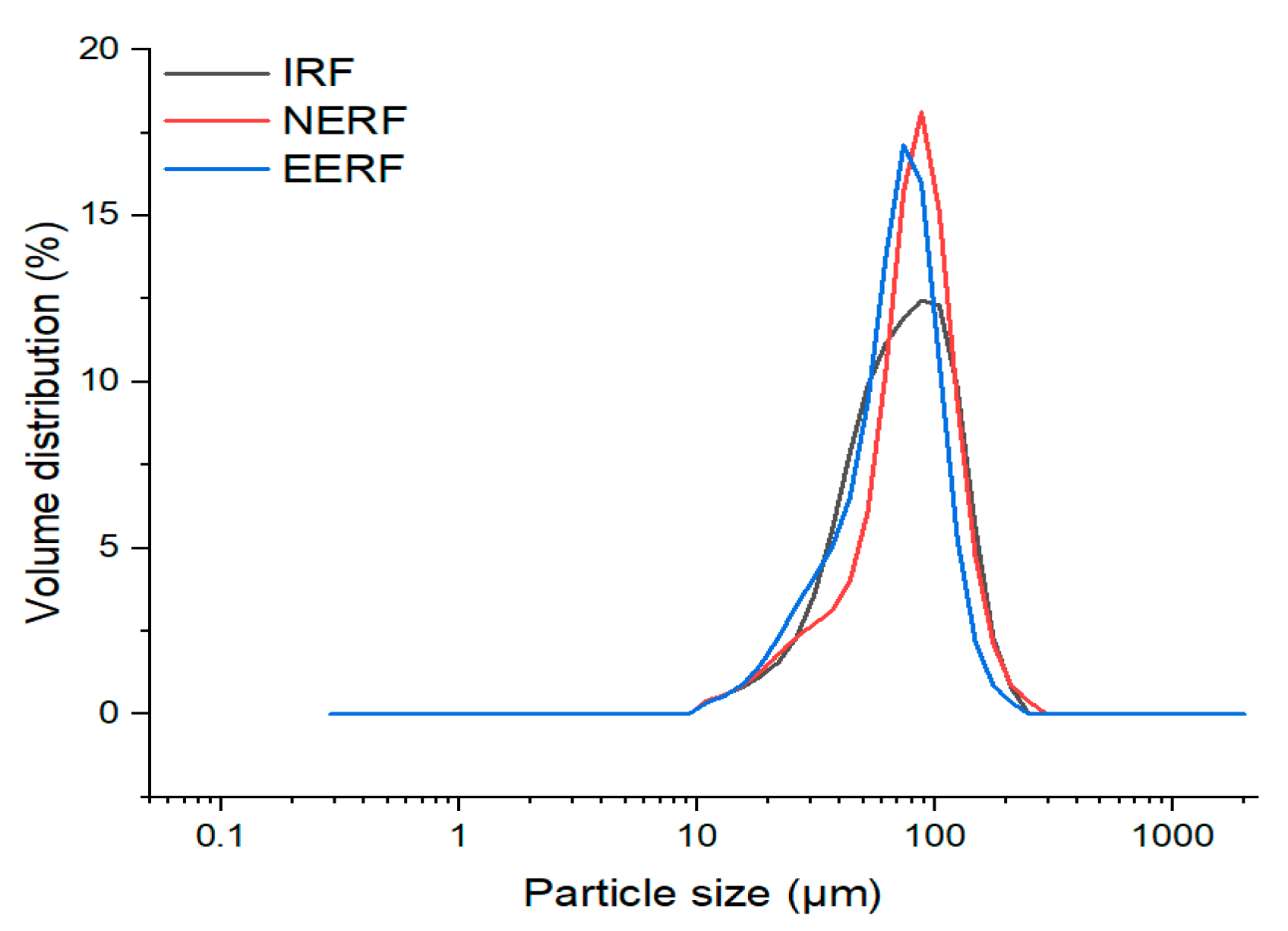
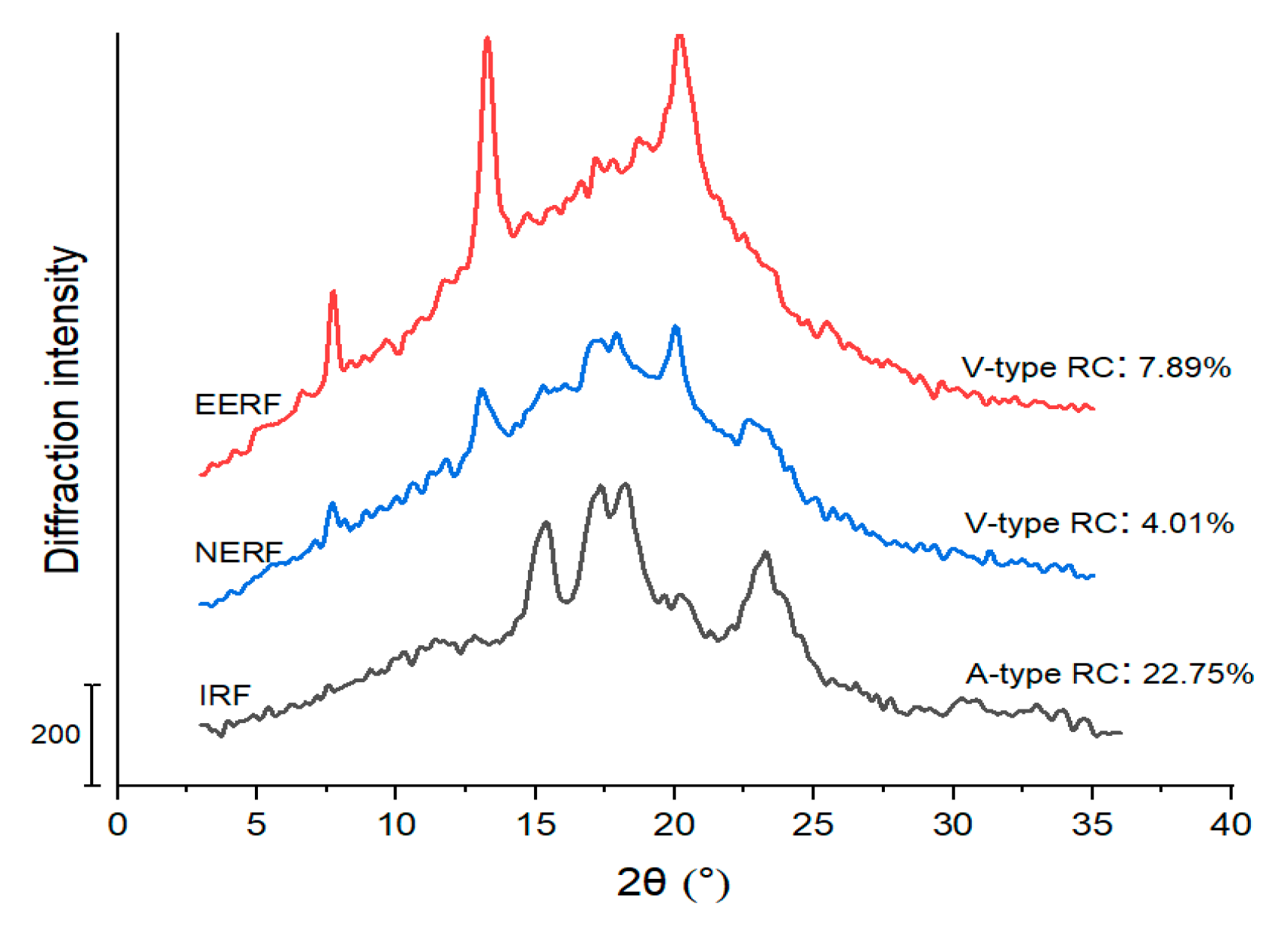
3.1. Crystalline Structure
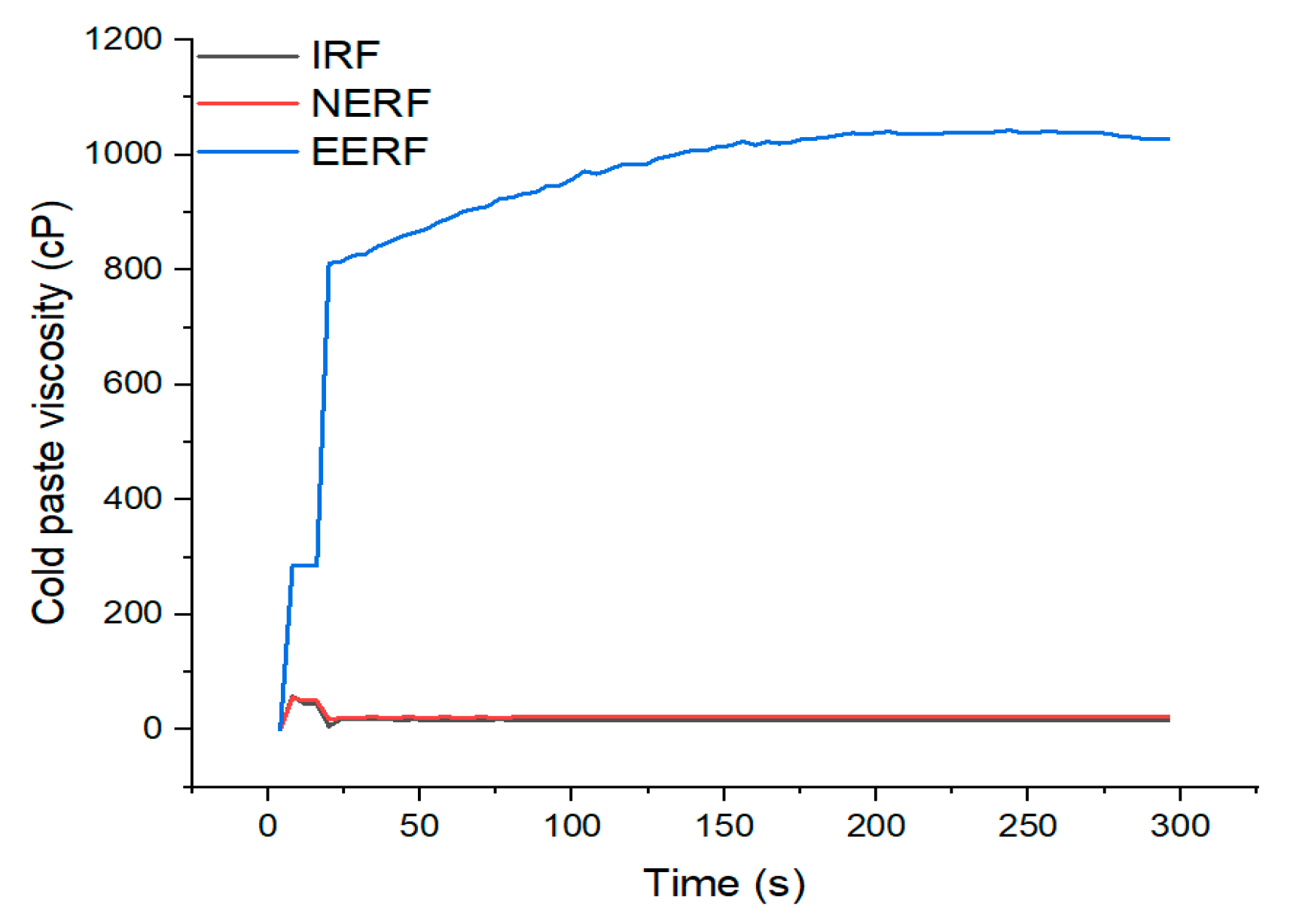
3.2. Cold-Paste Viscosity
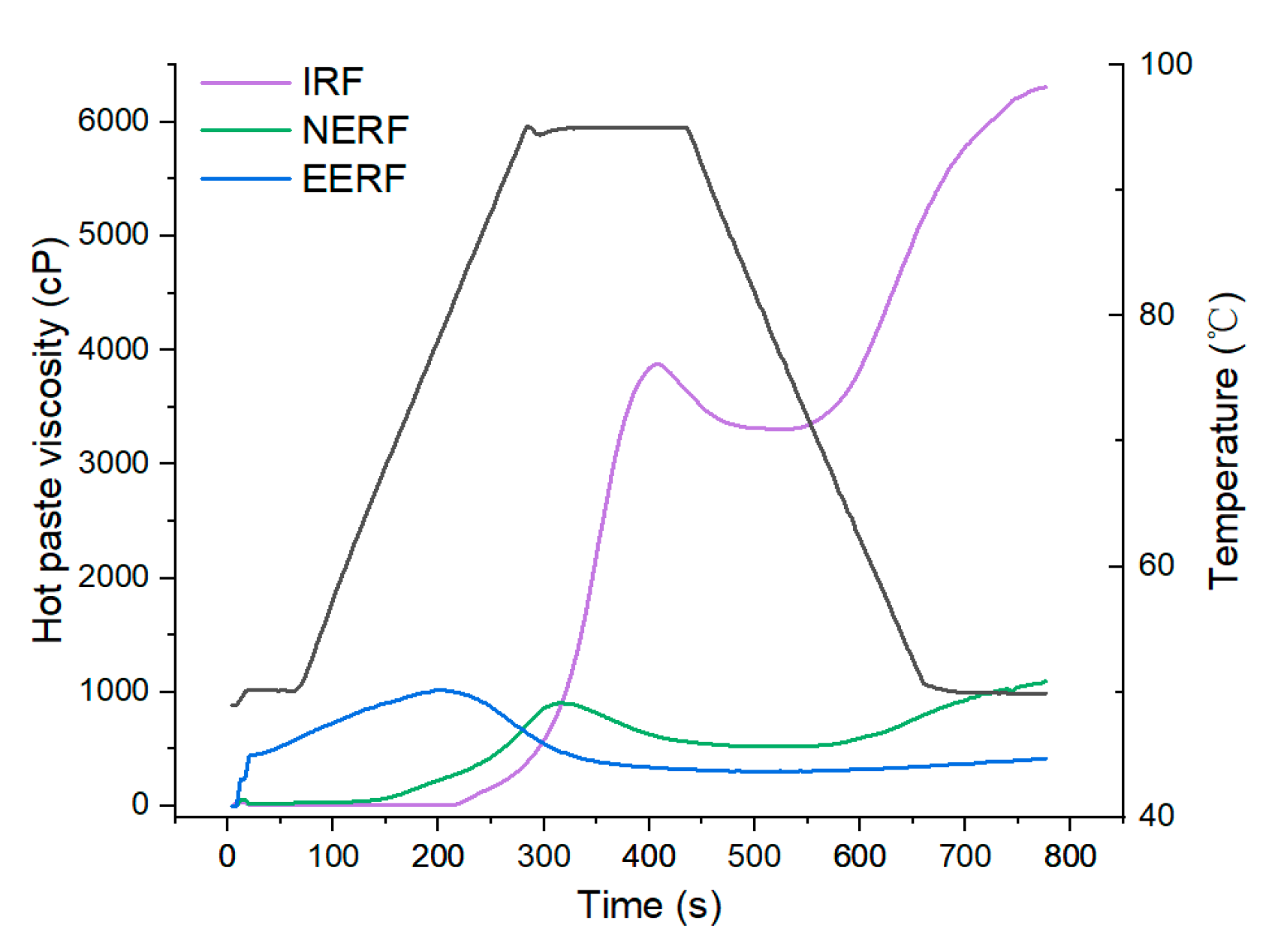
3.3. Hot-Paste Viscosity
3.4. Hydration Characteristics
3.5. Water Absorption of the Rice Noodle Premix
3.6. Thermal Transition Properties of the Rice Noodle Premix
3.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy of Rice Doughs with Different EERF Contents
3.8. Rheological Properties of the Rice Doughs
3.9. Texture Properties of the Rice Dough Sheets
3.10. Tensile Strength Properties of the Fresh Rice Noodles
3.11. Properties of the Cooked Rice Noodles
3.11.1. Cooking Qualities of the Cooked Rice Noodles
3.11.2. Texture Qualities of the Cooked Rice Noodles
3.11.3. Sensory Scores of the Cooked Rice Noodles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EERF | ethanolic-extruded indica rice flour |
| IRF | indica rice flour |
| VCWSS | V-type cold water-soluble starch |
| NERF | no-ethanol extruded indica rice flour |
| RVA | Rapid Visco Analyzer |
| WAI | water absorption index |
| WSI | water solubility index |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| SEM | scanning electron microscope |
| To | onset gelatinization temperature |
| Tp | peak gelatinization temperature |
| Tc | conclusion gelatinization temperature |
| ΔH | enthalpy |
| G′ | storage modulus |
| G″ | loss modulus |
| tanδ | loss tangent |
| V-type RC | V-type relative crystallinity |
| A-type RC | A-type relative crystallinity |
References
- Han, X.-M.; Xing, J.-J.; Han, C.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. The effects of extruded endogenous starch on the processing properties of gluten-free Tartary buckwheat noodles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, M.; Vicente, A.; Náthia-Neves, G.; Ronda, F. Microwave-treated rice flour halves the need of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose in the formulation of gluten-free bread. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qiao, W.; Bian, N.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, S. The interaction between starch and gluten and related wheat-based noodles quality, a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 307, 142001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; You, Y.; Chen, D.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Holler, T.P.; Ban, X.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z. A systematic review of rice noodles: Raw material, processing method and quality improvement. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wen, W.; Li, M.; Luo, S.; Ye, J.; Liu, C. Effect of chemically modified starch on retrogradation and quality characteristics of semi-dry rice noodles. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2025, 8, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, A.; Sadiq, M.B.; Anal, A.K. Improvement of quality of corn and proso millet-based gluten-free noodles with the application of hydrocolloids. J. Food Process Preserv. 2021, 45, e15165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetapan, N.; Limparyoon, N.; Yooberg, R.; Leelawat, B.; Charunuch, C. Influence of addition of extruded rice flour on preparation and quality of fresh gluten-free yellow alkaline noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2019, 90, 102828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, M.; Ziobro, R.; Juszczak, L.; Korus, J. Starch and starch derivatives in gluten-free systems—A review. J. Cereal Sci. 2016, 67, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, S. Rheological and secondary structural characterization of rice flour-zein composites for noodles slit from gluten-free sheeted dough. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Kierulf, A.; Abbaspourrad, A. Application of granular cold-water-swelling starch as a clean-label oil structurant. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.-J.; Wang, B.-J.; Weng, Y.-M. Preparation of white salted noodles using rice flour as the principal ingredient and the effects of transglutaminase on noodle qualities. Food Biosci. 2020, 33, 100501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raungrusmee, S.; Shrestha, S.; Sadiq, M.B.; Anal, A.K. Influence of resistant starch, xanthan gum, inulin and defatted rice bran on the physicochemical, functional and sensory properties of low glycemic gluten-free noodles. LWT 2020, 126, 109279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kee, J.I.; Lee, S.; Yoo, S.-H. Quality improvement of rice noodle restructured with rice protein isolate and transglutaminase. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Chiang, J.H.; Tan, M.Y.P.; Saw, L.K.; Xu, Y.; Ngan-Loong, M.N. Physicochemical properties of hydrothermally treated glutinous rice flour and xanthan gum mixture and its application in gluten-free noodles. J. Food Eng. 2016, 186, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xing, Y.; Meng, T.; Li, J.; Chang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Z. Preparation of V-type cold water-swelling starch by ethanolic extrusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 271, 118400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velazquez, G.; Ramirez-Gutierrez, C.F.; Mendez-Montealvo, G.; Velazquez-Castillo, R.; Morelos-Medina, L.F.; Morales-Sánchez, E.; Gaytán-Martínez, M.; Rodríguez-García, M.E.; Contreras-Jiménez, B. Effect of long-term retrogradation on the crystallinity, vibrational and rheological properties of potato, corn, and rice starches. Food Chem. 2025, 477, 143455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Obadi, M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, S.; Xu, B. The impact of starch degradation induced by pre-gelatinization treatment on the quality of noodles. Food Chem. 2020, 302, 125267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhu, H.; Yi, C. Soybean protein isolate affects in vitro digestion properties of fermented indica rice starch by regulating its gel characteristics. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 145, 109165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dou, J.; Shu, Z.; Li, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, X. Preparation of high V-type relative crystallinity dextrin from V-type granular starch via high-temperature acid-ethanol hydrolysis. Food Biosci. 2024, 61, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Q.; Wu, S. Effects of wheat cultivar, oligosaccharide, inulin, arabinoxylan and endoxylanase on the large- and small-strain rheological properties and microstructure of dietary fibre enriched dough. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 308, 142443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-T.; Xie, Z.-J.; Qiu, Y.-Y.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Obadi, M.; Xu, B. Structure changes of ethanol–water modified oat flour and the influence on the processing qualities of oat noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 114, 103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, W.; Liang, C.; Huang, X.; Hu, H.; Huang, Z.; Gan, T.; Zhang, Y. Effects of the addition of cassava starch and the size of water clusters on physicochemical and cooking properties of rice noodles. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Yuan, H.; Jia, R.; Huang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Q.; Liu, X.; Pan, Z. Effects of different enzymatic hydrolysis times on the structures and properties of corn microporous starch particles and their applications in frozen dough. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 164, 111178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dries, D.M.; Gomand, S.V.; Delcour, J.A.; Goderis, B. V-type crystal formation in starch by aqueous ethanol treatment: The effect of amylose degree of polymerization. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, M.; Sun, D.; Wei, W.; Yu, H.; Zhang, T. Twin-Screw Extrusion of Oat: Evolutions of Rheological Behavior, Thermal Properties and Structures of Extruded Oat in Different Extrusion Zones. FOODS 2022, 11, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Cui, K.; Gu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, X.; Jiang, H. Thermal and textural properties of extruded rice affect its cooking performances and the texture of the steamed extruded rice. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2024, 7, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, J.; Lu, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. Effect of ferulic acid incorporation on structural, rheological, and digestive properties of hot-extrusion 3D-printed rice starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xiao, C.; Lu, H.; Deng, X. Effects of extrusion temperature on structure and physicochemical properties of proso millet starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 299, 140011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, N.A.; Ali, T.M.; Moin, A.; Hasnain, A. Comparative study on morphological, rheological and functional characteristics of extruded rice starch citrates and lactates. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xuan, Y.; Lyu, F.; Ding, Y. Microstructural, physicochemical properties and starch digestibility of brown rice flour treated with extrusion and heat moisture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.; Koocheki, A.; Milani, E. Effect of extrusion cooking on chemical structure, morphology, crystallinity and thermal properties of sorghum flour extrudates. J. Cereal Sci. 2017, 75, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Otsubo, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Katsuno, N. Unraveling the changes of physical properties and nanostructures of rice starch incorporated with pregelatinized rice starch paste during gelatinization. Food Hydrocoll. 2025, 162, 110931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Teng, F.; Li, Y. Effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on physicochemical, thermal, and rheological properties of chemically modified corn starch. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, C.; Miao, D.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, H.; Ding, X.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; et al. Effect of improved extrusion cooking technology (IECT) on structure, physical properties and in vitro digestibility of starch. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-L.; Han, N.; Chen, H.-Q. Physicochemical and structural properties of wheat gluten/rice starch dough-like model. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 98, 103181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gong, W.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; An, X.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J. Insights into the enhancement mechanism of rheological properties of dough induced by wheat flour maturation: The view from gluten proteins aggregation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridou, A.; Duta, D.; Papageorgiou, M.; Belc, N.; Biliaderis, C.G. Effects of hydrocolloids on dough rheology and bread quality parameters in gluten-free formulations. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastromatteo, M.; Guida, M.; Danza, A.; Laverse, J.; Frisullo, P.; Lampignano, V.; Del Nobile, M.A. Rheological, microstructural and sensorial properties of durum wheat bread as affected by dough water content. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peressini, D.; Sensidoni, A. Effect of soluble dietary fibre addition on rheological and breadmaking properties of wheat doughs. J. Cereal Sci. 2009, 49, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Ou, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, H.; Zheng, B. Dietary fiber-rich Lentinula edodes stems influence the structure and in vitro digestibility of low-moisture extruded maize starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Cheng, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Ban, X.; Gu, Z. Study on the gelatinization and digestive characteristics of wheat starch and potato starch under low moisture conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Type of Additive | Additive | Mechanism of Action | Pros and Cons | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein | The ratio of zein and rice flour is 5:95 | The zein can form a viscoelastic network structure above the glass transition temperature | Good mixing stability; high cost, poor color sensory, and low extensibility, taking 6 min to form network structure above 40 °C | [9] |
| Enzyme | 1.5% transglutaminase (TGase) of total weight of rice flour, wheat flour, and vital gluten; the ratio of rice flour, wheat flour, vital gluten, table salt, and guar gum is set at 80:10:10:2:1 | TGase can catalyze the formation of covalent cross-linked bonds between protein molecules | Good sensory quality; takes more than 1 h to prepare; high gluten content | [11] |
| Hydrocolloid | 2.5% xanthan gum of resistant rice starch; the ratio of resistant rice starch, salt, NaHCO3, and full egg is 100:3:3:30 | Xanthan gum can form viscous solution, and the hydrogen bonds and starch of xanthan gum form a stable gluten-like structure | Gluten-free; fast preparation; high xanthan gum addition | [12] |
| Pregelatinized starch | The ratio of extrude pregelatinized starch, rice flour, NaCO3, and NaCl is 60:40:0.3:1 | It has cold-paste viscosity | Gluten-free; high pregelatinized rice flour addition | [7] |
| Composite | The ratio of rice flour, rice protein isolate, and NaCl is 90:10:1 and 1% TGase | The rice protein isolate can catalyze the formation of covalent cross-linked bonds between protein molecules | Nutritious and gluten-free but expensive and takes more than 2 h to prepare | [13] |
| The ratio of heat-treated glutinous rice flour and xanthan gum (95:5) and rice flour is 10:90 | Xanthan gum polymers form cross-links between starch granules during heat treatment | Gluten-free, with low xanthan gum addition | [14] |
| Grading Criteria | |
|---|---|
| Color (15 points) | whiter, uniform color (10–15) |
| white, uniform color (5–10) | |
| yellow and uneven color distribution (0–5) | |
| Flavor (10 points) | rich rice flavor with no peculiar smell (7–10) |
| rice aroma and a slight peculiar smell (3–7) | |
| faint rice flavor and a peculiar smell (0–3) | |
| Organizational morphology (15 points) | smooth surface, compact structure (10–15) |
| less smooth surface, less compact structure (5–10) | |
| adhesive surface, loose structure (0–5) | |
| Hardness (20 points) | moderate (14–20) |
| harder or softer (7–14) | |
| too hard or too soft (0–7) | |
| Slippery (20 points) | smoother, non-sticky (14–20) |
| smooth, moderate viscosity (7–14) | |
| not slippery, sticky (0–7) | |
| Elasticity (20 points) | good elasticity, chewiness (14–20) |
| medium elasticity, slight dente (7–14) | |
| poor elasticity, poor chewiness (0–7) |
| IRF | NERF | EERF | |
|---|---|---|---|
| WAI (g/g) | 1.985 ± 0.054 c | 4.088 ± 0.018 b | 7.546 ± 0.069 a |
| WSI (%) | 0.465 ± 0.262 c | 3.230 ± 0.311 b | 4.495 ± 0.191 a |
| EERF Content | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0% | 77.45 ± 0.21 a | 80.35 ± 0.07 ab | 86.25 ± 0.21 a | 7.96 ± 0.20 a |
| 10.0% | 77.60 ± 0.28 a | 80.30 ± 0.00 ab | 85.20 ± 0.57 b | 7.08 ± 0.38 b |
| 12.5% | 77.45 ± 0.21 a | 80.20 ± 0.14 ab | 85.65 ± 0.21 ab | 6.76 ± 0.10 b |
| 15.0% | 77.70 ± 0.14 a | 80.35 ± 0.35 ab | 85.65 ± 0.07 ab | 5.75 ± 0.04 c |
| 17.5% | 77.70 ± 0.28 a | 80.55 ± 0.07 a | 85.75 ± 0.24 ab | 5.46 ± 0.14 cd |
| 20.0% | 77.45 ± 0.23 a | 80.10 ± 0.14 b | 85.20 ± 0.57 b | 5.12 ± 0.04 d |
| Hardness (N) | Adhesiveness (N.s) | Tensile Strength (N) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EERF con-tent in the premix | 10.0% | 96.176 ± 3.912 a | −0.461 ± 0.080 a | 0.129 ± 0.010 d |
| 12.5% | 85.443 ± 3.248 b | −0.636 ± 0.061 ab | 0.150 ± 0.009 cd | |
| 15.0% | 71.215 ± 1.827 c | −0.743 ± 0.089 b | 0.168 ± 0.009 bc | |
| 17.5% | 62.750 ± 1.924 d | −0.978 ± 0.101 c | 0.185 ± 0.005 ab | |
| 20.0% | 51.842 ± 2.908 d | −1.106 ± 0.094 c | 0.205 ± 0.013 a | |
| Water ratio for making the dough | 34.0% | 101.734 ± 5.212 a | −0.425 ± 0.074 a | 0.216 ± 0.007 a |
| 35.0% | 89.560 ± 5.543 b | −0.597 ± 0.070 ab | 0.193 ± 0.006 a | |
| 36.0% | 71.215 ± 1.827 c | −0.743 ± 0.089 b | 0.168 ± 0.009 b | |
| 37.0% | 57.239 ± 3.486 d | −1.492 ± 0.188 c | 0.142 ± 0.014 c | |
| 38.0% | 44.758 ± 1.003 e | −1.825 ± 0.091 d | 0.111 ± 0.009 d |
| Cooking Time (min) | Water Absorption (%) | Breakage Rate (%) | Cooking Loss (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EERF con-tent in the premix | 10.0% | 5.83 | 98.58 ± 2.24 a | 16.67 ± 3.34 a | 6.48 ± 0.23 a |
| 12.5% | 5.75 | 91.32 ± 1.05 b | 13.33 ± 3.34 ab | 5.60 ± 0.27 b | |
| 15.0% | 5.58 | 86.74 ± 0.93 c | 12.22 ± 1.92 ab | 4.63 ± 0.28 c | |
| 17.5% | 5.75 | 83.18 ± 0.40 cd | 10.00 ± 3.33 b | 5.35 ± 0.12 b | |
| 20.0% | 5.83 | 79.17 ± 2.55 d | 7.78 ± 1.92 b | 5.79 ± 0.19 b | |
| Water ratio for making the dough | 34.0% | 6.17 | 95.18 ± 1.51 a | 6.67 ± 3.34 a | 3.64 ± 0.18 d |
| 35.0% | 5.92 | 91.05 ± 2.06 b | 8.89 ± 1.92 ab | 4.08 ± 0.22 d | |
| 36.0% | 5.58 | 86.74 ± 0.93 c | 12.22 ± 1.92 bc | 4.63 ± 0.28 c | |
| 37.0% | 5.33 | 83.03 ± 1.09 c | 14.44 ± 1.93 cd | 5.57 ± 0.16 b | |
| 38.0% | 5.08 | 77.70 ± 1.37 d | 17.78 ± 1.92 d | 6.40 ± 0.16 a |
| Hardness (g) | Adhesiveness (g.s) | Springiness | Chewiness (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EERF content in the premix | 10.0% | 973.804 ± 17.588 a | −35.020 ± 1.607 a | 0.917 ± 0.008 a | 605.529 ± 21.509 a |
| 12.5% | 927.769 ± 12.180 b | −29.527 ± 2.098 b | 0.904 ± 0.002 b | 579.382 ± 13.310 ab | |
| 15.0% | 884.966 ± 21.978 c | −25.303 ± 1.276 b | 0.896 ± 0.004 b | 545.595 ± 20.842 bc | |
| 17.5% | 850.564 ± 9.518 c | −25.391 ± 2.261 b | 0.874 ± 0.005 c | 506.547 ± 8.589 c | |
| 20.0% | 808.914 ± 11.921 d | −26.707 ± 1.248 b | 0.860 ± 0.011 d | 460.475 ± 16.351 d | |
| Water ratio for making the dough | 34.0% | 1008.997 ± 25.340 a | −29.541 ± 1.416 b | 0.863 ± 0.004 d | 636.378 ± 14.344 a |
| 35.0% | 955.732 ± 29.138 a | −26.750 ± 1.016 ab | 0.880 ± 0.009 c | 582.063 ± 11.356 b | |
| 36.0% | 884.966 ± 21.978 b | −25.303 ± 1.276 a | 0.896 ± 0.004 b | 545.595 ± 20.842 b | |
| 37.0% | 825.090 ± 10.734 c | −26.002 ± 0.659 ab | 0.905 ± 0.006 ab | 487.473 ± 11.729 c | |
| 38.0% | 744.368 ± 17.857 d | −30.042 ± 2.648 b | 0.912 ± 0.003 a | 453.126 ± 22.639 c |
| Color | Flavor | Organizational Morphology | Hardness | Slippery | Elasticity | Total Score | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EERF con-tent in the premix | 10.0% | 13.75 ± 0.89 a | 9.50 ± 0.76 a | 10.13 ± 1.13 b | 12.50 ± 0.93 c | 13.25 ± 0.71 b | 14.50 ± 1.19 a | 73.63 ± 1.06 c |
| 12.5% | 13.00 ± 1.07 ab | 9.13 ± 0.64 ab | 11.38 ± 1.30 a | 13.25 ± 1.04 c | 14.13 ± 0.83 ab | 13.88 ± 0.83 a | 74.75 ± 1.16 b | |
| 15.0% | 12.63 ± 0.74 b | 8.88 ± 0.83 ab | 12.38 ± 0.92 a | 15.25 ± 0.89 ab | 14.75 ± 1.04 a | 12.50 ± 0.76 b | 76.38 ± 0.74 a | |
| 17.5% | 12.25 ± 1.04 b | 8.75 ± 0.71 ab | 12.13 ± 1.36 a | 15.75 ± 0.89 a | 13.75 ± 1.28 ab | 11.63 ± 1.30 b | 74.25 ± 0.89 ab | |
| 20.0% | 12.00 ± 1.07 b | 8.63 ± 0.74 b | 11.50 ± 1.20 a | 14.50 ± 1.41 b | 13.88 ± 0.83 ab | 12.25 ± 1.16 b | 72.75 ± 1.83 ab | |
| Water ratio for making the dough | 34.0% | 12.50 ± 1.20 a | 9.25 ± 0.71 a | 12.13 ± 0.83 ab | 13.25 ± 0.71 b | 13.75 ± 1.89 b | 10.88 ± 1.73 c | 72.25 ± 0.89 d |
| 35.0% | 12.25 ± 0.71 a | 8.75 ± 0.89 a | 12.88 ± 1.13 a | 14.38 ± 1.30 ab | 14.24 ± 1.16 b | 11.38 ± 1.06 c | 73.88 ± 1.13 c | |
| 36.0% | 12.63 ± 0.74 a | 8.88 ± 0.83 a | 12.38 ± 0.92 a | 15.25 ± 0.89 a | 14.75 ± 1.04 ab | 12.50 ± 0.76 b | 76.38 ± 0.74 b | |
| 37.0% | 13.25 ± 0.71 a | 9.38 ± 0.74 a | 11.13 ± 0.83 bc | 14.88 ± 1.36 ab | 15.38 ± 1.06 a | 14.13 ± 0.99 a | 78.13 ± 1.55 a | |
| 38.0% | 12.88 ± 0.64 a | 9.00 ± 1.25 a | 10.63 ± 1.60 c | 13.75 ± 1.28 b | 14.38 ± 1.06 ab | 14.75 ± 1.04 a | 75.38 ± 1.77 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, M.; Zhou, X.; Tian, H.; Chen, Y.; Jin, Z. Ethanolic Extrusion of Indica Rice Flour for Rice Noodle Production. Foods 2025, 14, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091453
Fu M, Zhou X, Tian H, Chen Y, Jin Z. Ethanolic Extrusion of Indica Rice Flour for Rice Noodle Production. Foods. 2025; 14(9):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091453
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Miaomiao, Xing Zhou, Hong (Sabrina) Tian, Yanxin Chen, and Zhengyu Jin. 2025. "Ethanolic Extrusion of Indica Rice Flour for Rice Noodle Production" Foods 14, no. 9: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091453
APA StyleFu, M., Zhou, X., Tian, H., Chen, Y., & Jin, Z. (2025). Ethanolic Extrusion of Indica Rice Flour for Rice Noodle Production. Foods, 14(9), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091453







